
Usability Testing of Educational Computer Games on the Topic
“Safe Internet”
Daniela Tuparova
1a
, Krista Mehandzhiyska
2b
and Georgi Tuparov
3c
1
Department of Informatics, South-West University Neofit Rilski, 66 Ivan Mihaylov Str, Blagoevgrad, Bulgaria
2
Department of Mathematics, South-West University Neofit Rilski, 66 Ivan Mihaylov Str, Blagoevgrad, Bulgaria
3
Department of Informatics, New Bulgarian University, 21 Montevideo Bul, Sofia, Bulgaria
Keywords: Usability, Educational Computer Game, Lower Secondary School, Safe Internet, Computer Science
Education.
Abstract: In the paper we present methods and techniques for usability testing and evaluation of educational computer
games. We present a case of application of usability methods in process of development of four educational
computer mini-games “Safe Internet”. The target users groups cover students from 4th till 7th grade,
teachers in school subjects Information technology and Computer modelling. Therefore we apply different
methods and tools to plan and testing of the usability of the games. For the current research we use a
laboratory testing with an interview with limited number of students and user opinion study with
questionnaires for stakeholders – teachers and students. We apply ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development,
Implementation, Evaluation) in a combination with Agile methodologies – Scrum methodology with three
sprints. The usability study and implementation are conducted in all stages of development of the games.
The case study shows that conducted approach based on the agile methodology with combination of
usability study with stakeholders (teachers and students) of the games give good results. The students have
positive perception to the final versions of the developed educational computer games.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0358-0648
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4244-6812
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4162-5106
1 INTRODUCTION
Educational computer games have a positive impact
on the acquisition of knowledge, development of
skills in any school subject area, and motivation of
the students in learning activities at macro and micro
level.
In the same time in the process of planning and
developing of educational computer games its
necessary to provide usability, relevant to
requirements of the stakeholders and mainly to
needs and preferences of the end-users – the
students.
In the paper we present methods and techniques
for usability evaluation of educational computer
games. We present a case of application of usability
methods in process of development of educational
computer mini-games “Safety Internet”. The target
users groups cover students from 4th till 7th grade,
teachers in school subjects Information technology
and Computer modelling.
The theme for safe usage of the Internet from
youngsters is a key topic in the IT curricular in
Bulgarian schools. In the same time, this topic is an
important part of nowadays digital culture. It is
completely important to develop skills for
identifying and protecting from danger in the
Internet. A possible approach for more effective
forming of those skills is usage of educational
computer games through which students get into
simulation situation, solve different types of
problems and situations, connected with safe
usage, behavior etc . (Tuparova & Mehandzhiyska,
2018).
694
Tuparova, D., Mehandzhiyska, K. and Tuparov, G.
Usability Testing of Educational Computer Games on the Topic “Safe Internet”.
DOI: 10.5220/0009817606940701
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2020), pages 694-701
ISBN: 978-989-758-417-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 BASIC CONCEPTS
/LITERATURE REVIEW/
2.1 Serious Game
Variety of definitions about serious game analyse
their characteristics and aspects (Stoyanova ,
Tuparova, & Samardzhiev, 2017). Zyda (Zyda,
2005) defines the serious game as a “mental contest,
played with computer in accordance with specific
rules that uses entertainment to further government
or corporate training, education, health, public
policy, and strategic communication objectives”.
Main characteristics of the serious games are:
computer games, their goal is not entertainment,
mostly the aim of serious games are directed to the
training and education (https://www.igi-global.com/
dictionary/serious-games/26549) to “enhancing
some aspect of educational, political, social, or
workplace interaction” (Oravec, 2019)
Regarding the digital tools for creating and using
serious games in (Terzieva, Golev, & Stavrev, 2017)
the authors point out that “Serious games can be
considered as part of the online education as
separate and independent programs or as modules,
supporting the conservative education.”
2.2 Educational Computer Game
(ECG)/ Didactical Computer Game
Educational computer game is type of serious
computer game, applicable in educational subject-
domain.
They have the technological characteristics and
elements of computer games but are connected with
a concrete school subject and define educational
content. They are dedicated to solving various and
diverse pedagogical tasks – learning knew
knowledge, verification and evaluation of
knowledge, development of skills, consolidation of
knowledge and skills (Tuparova, 2019). They can be
used in lessons for assistance the different school
activities during the lesson (micro level) or for self-
learning for a concrete subject (micro and macro
level).
2.3 Usability
It is considered that the first introduction of the term
usability is in 1971 from Miler who examines the
usability of concrete system in the characteristic of
“easy to use” (Shackel, 1991). Shackel defines
usability in operational style and recommends
creating a plan for usability insurance of the system
in the stage of specification. He defines four main
attributes of usability which is needed to be achieved
and in the same time measurable: Effectiveness,
Learnability, Flexibility, Attitude.
Jakob Nielsen determines the term usability of
computer system as quality feature which
determines how easy it is to be used. He defines five
main characteristics of usability: Learnability,
Efficiency, Memorability, Errors, and Satisfaction.
(Nielsen, 1993)
According to (Quesenbery, 2004) usability has
five dimensions, called 5Е: Effective, Efficient,
Engaging, Error tolerant, Easy to learn.
With development of technology the models of
usability regarding the characteristics and attributes
are getting expanded. There are common names but
some of them have different meaning. (Tuparova,
2019). International developed standards for
defining the characteristics of usability of software
are included. The standard ISO/IEC 9126-1:2001
Software engineering - Product quality - Part 1:
Quality model sees usability as characteristic (part)
of software’s quality model. Revised by ISO/IEC
25010:2011 - Systems and software engineering --
Systems and software Quality Requirements and
Evaluation (SQuaRE) -- System and software
quality models standard. The last update is made in
2017. (ISO, 2017). This standard defines usability in
the context of how much “product of system can be
used from concrete users for achieving determined
aims with effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction
in concrete context of usage.”
In standards’ definitions for usability and
its characteristics there is a mandatory connection
with “concrete context for usage.” This suppose
that for the different technologies, software and
domains for software products' application, the
characteristics/attributes of usability need to be
refined.
2.4 Usability of Application Software
and Systems for Education
It is needed to broaden the different models of
usability. For example: starting from the attributes in
the ISO standards, which are connected with the
achievement of concrete aims in the context of
concrete content, in the educational software the
attributes effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction
are conditioned from the achievement of concrete
points and aims, acquirement of educational content,
they are also connected with the cognitive and
Usability Testing of Educational Computer Games on the Topic “Safe Internet”
695

psychological students’ characteristics, who in the
same are part of the software users.
A number of researchers and scientists, dealing
with developing and research the usability of
educational software and systems for the
technological support of the educational process,
suggest expanded and advanced models for research
and evaluation of usability. Apart from the classic
categories of characteristics the researcher add
additional categories. (Tuparova, Usabilty of
educational resources, 2019).
The model MUUX-E (Harpur & de Villiers,
2015) is directed to analyze of mobile education and
consists 5 categories: main interface usability (9
criteria, bases on the Nielsen’s model) and the
specific Educational Usability with 4 included
criteria, Web based learning Usability has 6 criteria,
M-learning features with 5 criteria and User
Experience with 7 criteria.
The model, described in (Ssemugabi & De
Villiers., 2010), for web-based education usability
includes the following categories: General interface
criteria, customised for e-learning; Website-specific
criteria; Educational criteria for learner-centred
instructional design – orientated to educational and
learning goals achieving, efficiency of contemporary
learning, ability of control from student side, support
the individual approach in learning process, setting
up and elimination of cognitive mistakes, reflection
and feedback, importance of the content regarding
the subject and the student, student’s motivation and
implementing active studying.
The model (Sobodić, Balaban, & Kermek, 2018)
for usability of gamification of e-leaning is based on
General usability (Nielsen’s model), Educational
usability and User experience.
2.5 Usability Methods and Techniques
A lot of methods exist for planning and testing of
usability. For the need of current research is used a
laboratory testing with an interview with limited
number of students and user opinion study with
questionnaires for stakeholders – teachers and
students.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Methodology for Development of
Educational Computer Games
“Safety Internet”
The topic of safe use of the internet by middle age
school students is key topic in Bulgarian IT
curricula. It is part of the modern digital culture. "It
is necessary to reach children's perceptions and
awareness of the importance of the subject. Children
should be aware of the dangers they encounter by
using various services on the Internet, including e-
mail and social networks. It is important to develop
skills to identify and prevent online hazards."
(Kaseva , Tuparova, & Stoyanov, 2018).
The educational computer game “Safe in the
Internet” is consisted by 4 mini games (Situations,
Let’s Save Polly, Who wants to be a millionaire,
Let’s make the puzzle) in field of Safe Internet.
Main aim of the games is to check how the students
will react in different type of dangerous realistic
situations in the Internet, if they know the rules for
safety in the internet browsing. The games are
suitable to educational curricula of ICT school
subject. The target group of the games is students
between 5-th and 7-th grade. The levels of the
different grades are separated and the games could
be used and played with all the 3 grades in order to
introduce the rules of safe browsing and reminding
them as well. The scenario, the design and the
avatars are fully pursuant with the age of the target
group.
The game is developed by using Adobe
Captivate 10 as SCORM package and distributed
among the students through e-learning environment
Moodle.
3.2 Model for Usability Study of
Educational Computer Game
One of the main aims during the games development
was planning and providing usability of the games.
The used model is presented in (Tuparova, 2019)
which includes 3 stages.
Stage 1. Preliminary research and analysis of the
requirements.
The stage includes activities as: Defining the
target group of students; Research and analysis
users’ needs – trainers and trainees; Research and
GonCPL 2020 - Special Session on Gamification on Computer Programming Learning
696

analysis trainees’ profile; Analysis and selection of
educational content which needs to be added.
Stage 2. Development and current/formative
usability analysis.
The activities during the stage are aimed at:
Choice of methods for usability and utility research;
Selection of estimators according with the chosen
methods and techniques; Formation of directions for
research and heuristics; Results analysis – choice of
statistics methods for analysis of the quantitative
data of the researches.
Stage 3. Testing the usability and utility with the
end-users – trainers and trainee.
The stage is connected with: Selection of
methods for usability testing; Defining the groups of
testing users and the sample volume of each group;
Toolkit creation for users testing; Games and toolkit
provision; Collecting and data analysis from the
conducted research.
The used model during the process of games is
ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development,
Implementation, Evaluation) in a combination with
Agile methodologies – Scrum methodology with
three sprints. The usability study and
implementation ware conducted in all stages of
development of the games. (Fig.1.)
4 PRACTICAL EXAMPLE OF
PLANNING AND
IMPLEMENTATION OF
USABILITY OF ECG “SAFETY
INTERNET”
4.1 Stage 1
During the stage was made an analysis of students’
preferences in that age group for components of
educational computer games, the educational
program and students characteristics was researched.
It was made questionnaire research among the
students for their most preferred devices for playing
games, the importance of the different games’
elements, types of played games and etc.
4.2 Stage 2
During the stage 2 three cycles for games
development and usability testing were conduct.
During the first cycle a common game for 5-7 is
developed. The first version of the design was
discussed with two pre-service teachers. The
characters in the game and the graphic design was
chosen. The game scenario, structure and interface
are discussed. (Figure 2.) Translations in English are
performed in yellow boxes.
The first version of the game was presented in
front of university teachers. Recommendations
regarding interface improvement and structure were
made: dividing the game regarding the age of
student – 5, 6 and 7 gradе according the school
curricular and dividing the game into minigames
which are SCORM compatible.
Figure 1: Process of usability testing of educational computer game.
Usability Testing of Educational Computer Games on the Topic “Safe Internet”
697
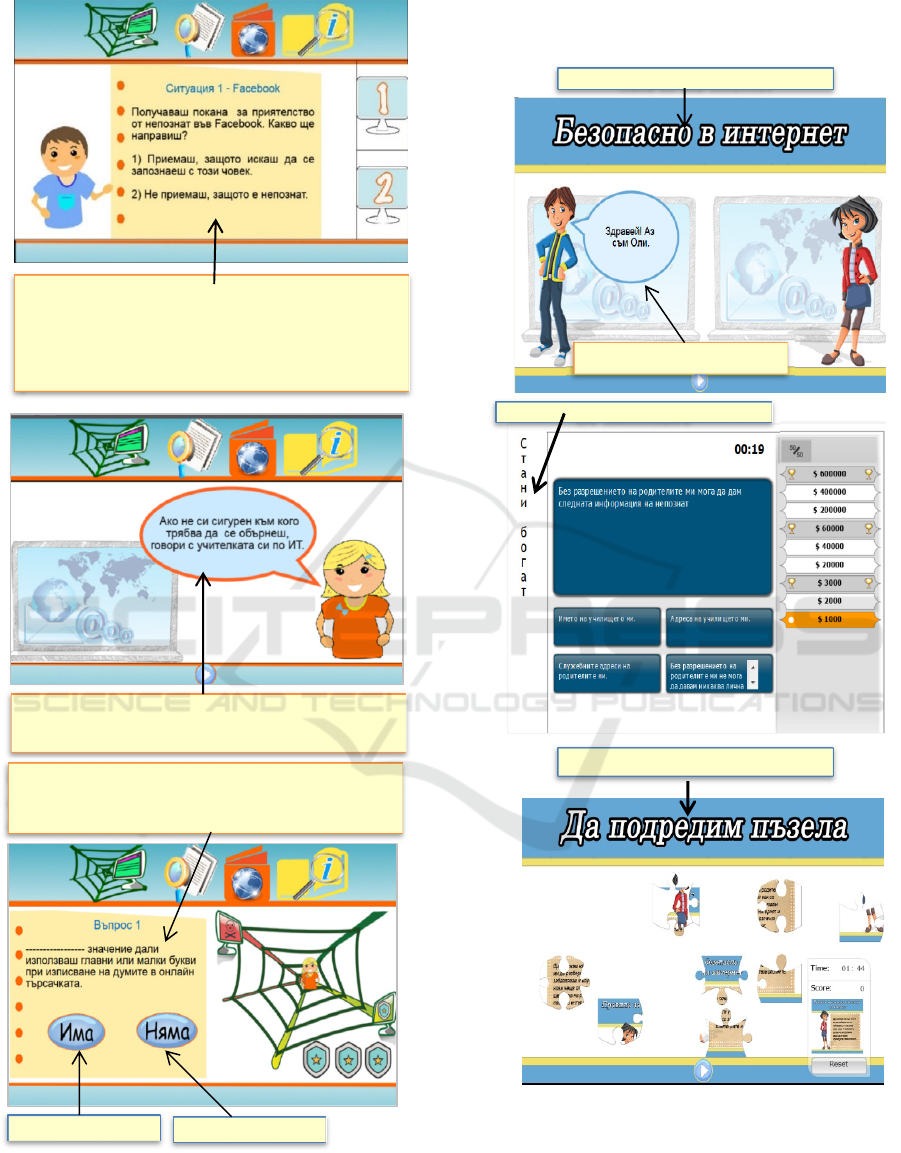
Figure 2: Screenshots from first version.
Characters for each grade according to students’
age were chosen during the second stage of
development, as well as changing the colour
schemes. (Figure 3, Figure 4).
Figure 3: Screenshots from games for 6
th
grade.
Situation 1. Facebook
What would you do if you receive a Facebook
friend request?
1)Accept because you want to know this
p
erson.
If you are not sure whom to contact, get in
touch with your ICT teacher..
Safe in the Interne
t
Hi, I am Olly
Be millionaire
Let's make the puzzle
Question 1: ……… importance if you are using
capital or lowercase letters while using in an
online search en
g
ine.
There is
There isn’t
GonCPL 2020 - Special Session on Gamification on Computer Programming Learning
698

Figure 4: Interface of mini games for 7
th
grade.
The minigames in tat stage were presented to 11
ICT teachers and 7 students for testing. In order to
evaluate the usability, we used questionnaires, for
the teachers we used questionnaires which are
consisted of questions referring to each of the mini
games and interviews for the students.
The recommendations were mainly connected
with the minigame “Let’s make the Puzzles” –
diversification of the puzzles and reducing their
number. There was a difference in teachers and
students’ opinion regarding adding sound. While the
teachers consider it is good to be added sound, the
students have the opposite opinion and consider it is
not appropriate and sound will disturb them.
In the third sprint cycle we took into
consideration the recommendations for
diversification of the puzzles and control of the
dialog between to two characters – there was the
opportunity for controlling the conversation between
the characters with a button for moving forward,
which gives the chance to the trainees to follow their
own reading tempo.
Figure 5: Pictures of the renewed puzzles.
4.3 Stage 3. Final Evaluation
During the third stage we made a final evaluation of
the minigames with students from 5, 6 and 7 grade.
For that, for each minigame was developed a
questionnaires.
Safe in the interne
t
Hey, I am Polly!
Let's save Polly
Unfortunately, you did not make it to save Polly
from the danger depth of Internet because yo
u
made tree mistakes.
I would immediately tell my parents if I find an
information which I feel is impropriate for me. I can
also report it here: htttps://www.safenet.bg/bg/
A
m
ong my parents we will make rules for safe
Internet usage.
I would never agree to meet someone whom "I
know" from Internet without talking with m
y
parents in advance.
Usability Testing of Educational Computer Games on the Topic “Safe Internet”
699
The questionnaires for the games “Let’s Safe
Poly” and “Situations – What would you do if …”
consist of 25 items. The items are grouped as
follows: one item is related to the gender of the
students; four items related to educational usefulness
(utility) of the game; five items in group “easy to
use”; seven items in group “design” including,
colors, avatars, navigation; five items in group
“general perception”; one item is open answer and
related to suggestions for game improving.
The questionnaire for the minigame “Let’s make
the Puzzles” consists of 16 items. The items are
grouped as follows: one item is related to the gender
of the students; one item related to educational
usefulness (utility) of the game; five items in group
“easy to use”; four items in group “design
satisfaction” including, colors and navigation; four
items in group “general satisfaction”; one item is
open answer and related to suggestions for game
improving.
The questionnaires for the mini games “Who
wants to be millionaire” consists of 17 Items. The
items are grouped as follows: one item related to the
gender of the students; two items related to
educational usefulness (utility) of the game; five
items in group “easy to use”; nine items in group
“design satisfaction” including, colors, avatars,
navigation; five items in group “general
satisfaction”; one item is open answer and related to
suggestions for game improving. (Appendix1.)
At the end of February 2020, we collected data
of 91 students from 7
th
grade – 44 girls and 47 boys.
All items, except Gender, are 5 level Likert type
questions - 5-Definitely Yes , 1 – Definitely No.
For all questionnaires we calculated Cronbach’s
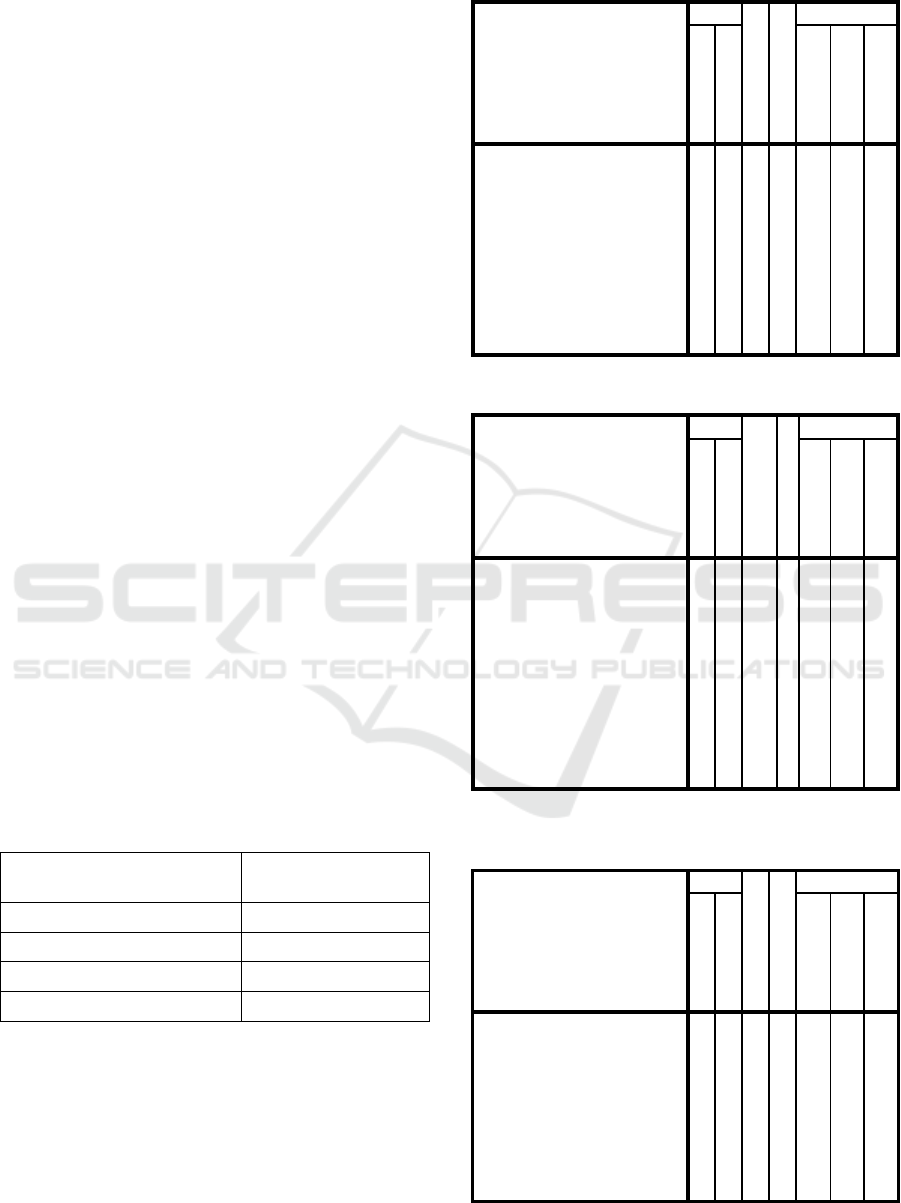
alfa coefficient of reliability (Table 1.)
Table 1: Reliability of the questionnaires.
Game Cronbach’s alfa
coefficient
Let’s safe Poly 0,861
Situations 0,915
Who wants to be millionaire 0,775
Puzzles 0,805
Due to ordinal data we applied descriptive
statistics – mode, median and percentiles. The
students show positive perception of the games.
(Table 2, 3, 4, 5). For all items related to the general
perception/satisfaction of the games median and
mode are 5 – Definitely yes and 4-Yes.
Table 2: General perception of the game “Let’s safe Poly”.
Game Let’s safe Poly
N
Median
Mode
Percentiles
Vali
d
Missing
25 50 75
The game's pace is suitable
for
y
ou
89 2 5,0 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
Generally you like the
g
ame
89 2 5,0 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
You will recommend the
game to your friends are
classmates
88 3 5,0 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
You like
p
la
y
in
g
the
g
ame 88 3 4,0 5 4,0 4,0 5,0
15. You like the scenarios
of the
g
ame
90 1 5,0 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
Table 3: General perception of the game Situations.
Game Situations
N
Median
Mode
Percentiles
Vali
d
Missing
25 50 75
22. The game's pace is
suitable for
y
ou
85 9 5,00 5 5,0 5,0 5,0
23. Generally you like the
g
ame
86 8 5,00 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
24. You will recommend
the game to your friends
are classmates
85 9 5,00 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
16. You like playing the
game
86 8 5,00 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
15. You like the scanario
of the game
85 9 4,00 5 4,0 4,0 5,0
Table 4: General perception of the game “Who wants to be
millionaire”.
Game Who wants to be
millionaire
N
Median
Mode
Percentiles
Vali
d
Missing
25 50 75
14. The game's pace is
suitable for
y
ou
87 9 5,0 5 5,0 5,0 5,0
15. Generally you like the
g
ame
86 10 5,0 5 5,0 5,0 5,0
16. You will recommend
the game to your friends
are classmates
87 9 5,0 5 5,0 5,0 5,0
11. You like playing the
g
ame
86 10 5,0 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
GonCPL 2020 - Special Session on Gamification on Computer Programming Learning
700
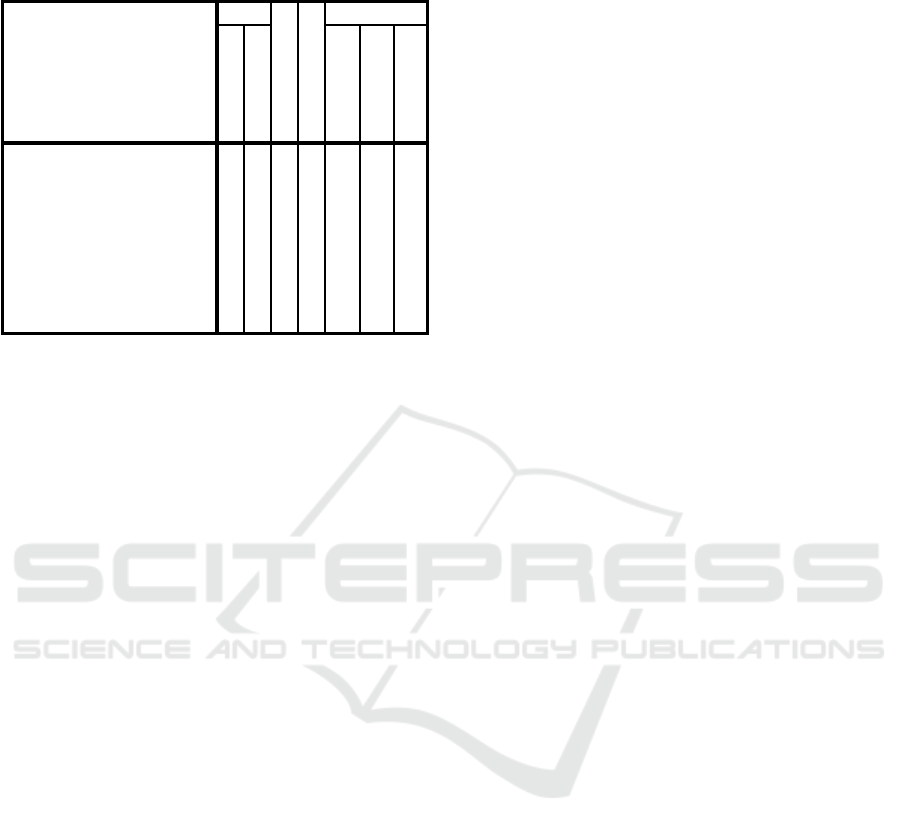
Table 5: General perception of the game “Let’s play with
puzzles”.
Game Puzzles
N
Median
Mode
Percentiles
Vali
d
Missing
25 50 75
13. The game's pace is
suitable for
y
ou
86 5 5,0 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
14. Generally you like the
g
ame
85 6 5,0 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
15. You will recommend
the game to your friends
are classmates
86 5 5,0 5 4,0 5,0 5,0
10. You like playing the
game
86 5 4,0 5 3,0 4,0 5,0
5 CONCLUSIONS
In the paper we presented a case study for usability
planning and evaluation of educational computer
games. The case study shows that conducted
approach based on the agile methodology with
combination of usability study with stakeholders
(teachers and students) of the games give good
results. The students have positive perception to the
final versions of the developed educational computer
games.
The next steps in our studies will be directed to
data analysis regarding the gender perception of the
proposed mini games and their usability
characteristics – “easy to use”, design,
usefulness/utility, and general satisfaction.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The study is supported by Bulgarian National
Scientific Fund under contract DN 05/10, 2016
REFERENCES
Harpur , P., & de Villiers, M. R. (2015). MUUX-E, a
framework of criteria for evaluating the usability, user
experience and educational features of m-learning
environments. South African Computer Journal, 1-21.
ISO. (2017). Retrieved from https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/
#iso:std:iso-iec:25010:ed-1:v1:en
Kaseva , M., Tuparova, D., & Stoyanov, M. (2018).
Pedagogical Issues for Design and Development of
Educational Computer Games for Primary School.
National Conference on "Education and Research in
the Information Society" (pp. 047-056). Plovdiv:
Institute of Mathematics and Informatics Bulgarian
Academy of Sciences, Association for the
Development of the Information Society.
Nielsen, J. (1993). Usability Engineering. SanDiego, CA,
USA: Academic Press.
Oravec, J. A. (2019). Cyberloating and Constructive
Recreation. In Advanced Methodologies and
Technologies in Business Operations and Management.
doi:DOI 10.4018/978-1-5225-7362-3.ch063
Quesenbery, W. (2004). Balancing the 5Es: Usability.
Cutter IT Journal, 17(2), 4-11.
Shackel, B. (1991). Usability - Context, framework,
definition, design and evaluation. In Human Factors
for Informatics Usability (pp. 21-38). Cambridge
University Press.
Sobodić, A., Balaban, I., & Kermek, D. (2018). Usability
Metrics for Gamified E-learning Course: A Multilevel
Approach. International Journal of Emerging
Technologies in Learning (iJET), 13(05), 41-55.
Ssemugabi , S., & De Villiers., M. R. (2010).
Effectiveness of heuristic evaluation in usability
evaluation of e-learning applications in higher
education. South African computer journal, 45, 26-39.
Stoyanova , M., Tuparova, D., & Samardzhiev, K. (2017).
Gamification in 11th Grade Mathematics Lessons –
One Possible Interactive Approach. In M. Auer , D.
Guralnick , & J. Uhomoibhi (Eds.), Interactive
Collaborative Learning. ICL 2016. Advances in
Intelligent System.
Terzieva, T., Golev, A., & Stavrev, C. (2017). Serious
games – innovative tool for education. Innovative
software tools and technologies with application in
matematics, informatics, and education (pp. 104-107).
University of Plovdiv “Paisii Hilendarski".
Tuparova, D. (2019). Usabilty of educational resources.
Sofia: Obrazovanie i Poznanie.
Tuparova, D., & Mehandzhiyska, K. (2018). Online
Educational Computer Games Related to Topic
“Internet Safety” – Analysis of Case Studies.
Proceedings of the National Conference on
"Education and Research in the Information Society"
(pp. 057-066). Plovdiv: Institute of Mathematics and
Informatics Bulgarian Academy of Sciences,
Association for the Development of the Information
Society.
Zyda, M. (2005). From visual simulation to virtual reality
to games. IEEE Computer, 38(9), 25–32.
Usability Testing of Educational Computer Games on the Topic “Safe Internet”
701
