
SMSNet: A Novel Multi-scale Siamese Model for Person
Re-Identification
Nirbhay Kumar Tagore
a
and Pratik Chattopadhyay
b
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Banaras Hindu University,
Varanasi, 221005, India
Keywords:
Person Re-Identification, SMSNet, Deep Learning.
Abstract:
We propose a novel multi-scale Siamese architecture to perform person re-identification using deep learning.
The scenario considered in this work is similar to that found in movie/concert halls, where persons enter in
a queue one-by-one through the entry gates and leave in a similar way through the exit gates. Effectiveness
of Siamese network based re-identification is evident from the recent research work in this domain. Here,
we focus on improving the accuracy of the existing re-identification techniques by introducing different di-
lation rates in the convolution layers of the Siamese network, thereby enabling capturing of detailed visual
features. We also introduce a silhouette part-based analysis to preserve the spatial relationships among the
different silhouette segments at a high resolution. The proposed Siamese network model has been fine-tuned
through cross-validation and the pre-trained network has been made available for further comparison. Rigor-
ous evaluation of our approach against varying training parameters, as well as comparison with state-of-the-art
methods over four popularly used data sets, namely, CUHK 01, CUHK 03, Market1501, and VIPeR, verify
its effectiveness.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tracking persons in videos or sequence of image
frames is very important in terms of surveillance, se-
curity and multimedia applications. The continuous
recording of videos from a camera network yields a
large amount of data, and monitoring of this high vol-
ume of data by trained persons is laborious and prone
to manual-error. Thus, there is an urgent need for the
development of an automated re-identification system
that can track individuals robustly against varying il-
lumination conditions, walking poses, etc. An ef-
fective re-identification system can be potentially de-
ployed in public zones such as movie/concert halls
or some meeting place. Cameras positioned at the
entry and exit gates of such places can be used to
track subjects seamlessly and understand their activ-
ities. The importance of surveillance cameras has
been revealed in a past study (Ashby, 2017) where it
is mentioned that CCTV footage videos have helped
in resolving 65% of all the criminal cases recorded
by British Transport Police between years 2011 and
2015. Since the past two decades, researchers of
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4011-0453
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5805-6563
1
2
3
4
3
1
4
2
Surveillance Zone
Entry
Exit
Figure 1: Re-Identification scenario.
the computer vision community are developing var-
ious techniques to automate the process of tracking
and monitoring activity of persons in videos. Among
these, person re-identification deals with associat-
ing images of the same person across multiple cam-
era views (overlapping/non-overlapping). Before the
commencement of deep learning, researchers used to
derive handcrafted features from images/videos for
small-scale evaluation. However, improved surveil-
lance systems and camera networks, as well as avail-
ability of deep learning tools and techniques in the
recent years have significantly benefited research on
person re-identification.
The re-identification scenario considered in this
work is shown schematically in Figure 1. With ref-
erence to the figure, two cameras are positioned at the
Tagore, N. and Chattopadhyay, P.
SMSNet: A Novel Multi-scale Siamese Model for Person Re-Identification.
DOI: 10.5220/0009885001030112
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2020) - DCNET, OPTICS, SIGMAP and WINSYS, pages 103-112
ISBN: 978-989-758-445-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
103

entry and exit gates of a surveillance zone. Subjects
enter into the zone through the entry gate and assem-
ble inside the hall. As each person enters into the
zone, their video gets recorded by the entry gate cam-
era, and a gallery set is formed from the videos corre-
sponding to all the subjects who enter the zone. Sce-
narios like this are commonly found in movie/concert
halls, or meeting places. On completion of the meet-
ing, subjects leave the surveillance zone one-by-one
through the exit gate, during which their videos get
recorded by the exit gate camera. Since, the order
in which the individuals enter may not be the same
as the order in which they exit the zone, there is a
need for re-identifying a person as he/she approaches
the exit gate camera from among the gallery set al-
ready captured by the entry gate camera. Establishing
correspondence between individuals in the two cam-
era fields-of-view through re-identification can help
in performing a number of other high-level computer
vision tasks such as activity monitoring, gait recogni-
tion, etc. The important contributions to the paper can
be summarized as follows:
• Developing a new architecture for person re-
identification based on Siamese network that
computes multi-scale features to capture intrinsic
details of input images at a higher resolution.
• Carrying out silhouette part-based analysis by
segmenting each of the two input images into
three parts, and performing SMSNet based feature
comparison which helps in preserving the contex-
tual information or spatial relationship among the
different silhouette regions at a higher resolution.
• Carrying out extensive experimental evaluation to
verify the effectiveness and superiority in perfor-
mance of our network over state-of-the-art tech-
niques.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In Sec-
tion 2, we discuss about the research trend in person
re-identification approaches starting from the early
non-deep learning-based to the modern deep learning-
based methods. Next, in Section 3, we discuss about
the overall framework and network configuration of
the proposed SMSNet in detail. Data set description,
experiment protocols and detailed evaluation of the
proposed work are presented in Section 5. Conclu-
sions and future scopes are finally highlighted in Sec-
tion 6.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section, we will discuss the research trend on
person re-identification with a major focus on the re-
cently developed methods.
2.1 Early Approaches for Person
Re-Identification
Most of the early attempts to solve person re-
identification are passive approaches, i.e., approaches
without any supervised or unsupervised feature learn-
ing mechanism. These techniques deal with extrac-
tion of handcrafted features from silhouette images
followed by comparison using standard distance met-
rics ((Bazzani et al., 2010), (Bazzani et al., 2013),
(Forss
´
en, 2007)). Few examples of re-identification
methods based on hand-crafted features include (Li
and Wang, 2013) which computes Gabor features
from images, or the color histogram-based techniques
discussed in (Koestinger et al., 2012) and (Xiong
et al., 2014).
The approach described in (Kang et al., 2004)
used color Gaussian model to count the edge pix-
els in an image and polar bins have been used to
generate the feature descriptor from the same im-
age. Later these polar bins are used to find the best
match by comparing the most similar feature descrip-
tors. A color histogram clustering based person re-
identification approach is described in (Sivic et al.,
2006) in which the color information is quantized into
a 16-bit histogram, and next clustering of these quan-
tized features is carried out. A part-based model us-
ing HS color histograms was explored in (Bedagkar-
Gala and Shah, 2011), in which HS color histograms
of stable body parts such as torso, left arm, right
arm and legs. A HOG (Histogram Oriented Gradi-
ent) based body part detector is used to detect these
body parts. The reported results from most passive
re-identification approaches are not accurate enough
due to use of simple features and distance metrics. In-
troduction to deep learning has paved the way for the
development of more effective techniques for person
re-identification, which are discussed in the following
sub-section.
2.2 Deep Learning-based Approaches
In this sub-section we will discuss about the two
broad categories of deep learning approaches for per-
son re-identification in the literature, namely (a) Clas-
sification models ((Wu et al., 2016), (Ma et al., 2012),
(Wu et al., 2017), (Xiao et al., 2016), (Su et al., 2017),
(Li et al., 2017)) in which a probe subject is compared
against a large gallery of subjects, and (b) Siamese
models ((Yi et al., 2014), (Ahmed et al., 2015), (Ding
et al., 2015), (Zhang et al., 2015), (Cheng et al.,
2016),(Su et al., 2016)) in which at a time two silhou-
SIGMAP 2020 - 17th International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
104

ettes are compared to test whether they belong to the
same class or not. A generalized model for person re-
identification has been proposed in (Song et al., 2019)
in which the model is trained on a particular domain,
but the trained model can be conveniently used to per-
form re-identification on a different data set without
any model update.
Classification Models. Since labeling across multi-
ple non-overlapping views in surveillance videos con-
sumes up a considerable amount of time, in (Meng
et al., 2019), a weakly supervised learning scheme
has been developed to match a target person with
an untrimmed gallery video without the requirement
of annotating individuals in the video frames dur-
ing the training phase. A feature fusion-based re-
identification technique has been proposed in (Ma
et al., 2012) in which deep features computed from
a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) are fused
with hand-crafted features extracted by ELF descrip-
tor (Tian et al., 2014) at the penultimate layer, fol-
lowing which a soft-max layer does the classifica-
tion by minimizing the cross-entropy loss. In an-
other work (Xiao et al., 2016), Xiao et al. proposed
a CNN model, in which network pruning is done by
observing the contribution of each neuron towards op-
timizing the loss function. Also, the standard dropout
mechanism is replaced by a deterministic domain-
guided dropout in which least important neurons are
discarded to reduce the computational complexity. In
(Li et al., 2017), a multi-scale context aware network
is employed which is trained on full body as well as
smaller body parts. This network also uses convolu-
tions at different scales to enable capturing of large
spatial information without incorporating redundant
information in an efficient manner.
Siamese Architecture-based Models. The shallow
Siamese architecture was proposed for the first time
in (Bromley et al., 1994) for signature matching way
back in 1994. In a basic sense, a Siamese network
consists of two or more similar sub-networks, that
takes as input individual feature vectors at the in-
put layer of each sub-network and compare the fea-
tures generated at the final layer to obtain a similarity
score. Post 2014, several re-identification approaches
were developed that extend the Siamese network to
a deeper architecture. Some of these are highlighted
next. The re-identification approach proposed in (Yi
et al., 2014) jointly handles both feature learning as
well as metric learning, and has been seen to perform
robustly against high variations in illumination and
other factors. A pair-wise Siamese deep learning ar-
chitecture has been proposed in (Ahmed et al., 2015)
in which the final layer is used to calculate cross-
input neighborhood differences to capture intrinsic re-
lations from the mid-layer features. Finally, a patch
summary layer is used to extract the high-level sum-
mary features from the output layer.
The architecture proposed in (Ding et al., 2015)
is a triplet Siamese network that generates a large
number of triplet pairs from a given data set. It
uses L2 distance metric to train a model that learns
a hyperspace to maximize the separation between the
matched pairs and mismatched pairs present in the
gallery set. A multi-channel part-based convolutional
neural network (CNN) model is introduced in (Cheng
et al., 2016) that learns features from both full-body
and local body parts. The model proposed is trained
upon an improved triplet loss function that pushes fea-
tures from different identities further while simultane-
ously pulling features from similar identities closer.
In (Varior et al., 2016), a Siamese long short term
memory (LSTM) architecture has been proposed to
develop a relationship between features of sequen-
tial images. In (Subramaniam et al., 2016), another
Siamese architecture based model (X-Corr) is intro-
duced to learn the similarity features between two in-
put images by applying normalized correlation. Re-
cently, in (Guo and Cheung, 2018) authors fused
two different networks called Convolution Similarity
Network (CSN) and Spatial Transformer Networks
(STN) to learn and combine the visual similarities
at the different levels of the network. Human track-
ing for identity retrieval have got significant atten-
tion in recent years. In (Munjal et al., 2019) a query
based person re-identification approach has been in-
troduced where person detection and re-identification
works jointly. A query-guided Siamese squeeze-and-
excitation network (QSSE-Net) introduced that uses
query and gallery images as a global context.
Existing Siamese based person re-identification
approaches have shown significant effectiveness in
learning features from a rigid body. However, none of
these focus on learning the multi-scale features from
input images. It may be noted that multi-scale fea-
tures are important for establishing higher-order rela-
tionship between the input pairs. To address this prob-
lem of multi-scale feature extraction using Siamese
network, we propose a novel architecture namely the
Siamese Multi-scale Network (SMSNet) to learn and
compare between multi-scaled features correspond-
ing to a pair of inputs, and evaluate its effectiveness
for different large scale person re-identification data
sets.
SMSNet: A Novel Multi-scale Siamese Model for Person Re-Identification
105

3 PROPOSED WORK
In this section, we discuss the individual steps of our
proposed approach in detail including the network ar-
chitecture, training algorithm and the final classifica-
tion step in the different sub-sections.
3.1 Multi-Scale Siamese Architecture
An insight view of the proposed Siamese Multi-scale
Network (SMSNet) model is given in Figure 2.
Table 1 presents the detailed network configura-
tion used in the study.
Table 1: Layer specification of each Siamese Multi-scale
Network (SMSNet).
Layer kernel No. of filters
Conv2d 0 5×5 32
Conv2d 1 3×3 32
Conv2d 2 3×3 32
Conv2d 3 3×3 32
Conv2d 4 3×3 32
Layer No. of neurons
Fully Connected 500
With reference to Figure 2 and Table 1, the first layer
of the network consists of two parallel tied convolu-
tion layers (Conv2d
0) that accepts two input images
of size 60×160, and this is followed by four more
convolution layers, each equipped with dilation rates
of 1,2 and 3 (Conv2d 1, Conv2d 2, Conv2d 3, and
Conv2d 4). As already explained before, application
of dilation in the convolution layers helps in obtain-
ing a multi-scale feature representation that encodes
the visual characteristics of an input image at a high
resolution. The size of the filters at every convolu-
tion layer is 3×3, except for the first layer in which
the size is 5×5, and the number of filters used in each
layer is the same (i.e, 32). The feature difference layer
shown after all the convolution layers is used to com-
pute the cross-input neighborhood difference (Ahmed
et al., 2015) between the outputs of the aggregated
features extracted from both the branches of the SM-
SNet. Mathematically, if f
i
and g
i
represent the i
th
feature maps at a particular layer corresponding to the
two images input to the SMSNet, then, the cross-input
neighborhood distance K between f
i
and g
i
at each
pixel location (x,y) is computed as follows:
K(x, y) = f
i
(x, y) ∗ I(n, n) − N [g
i
(x, y)], (1)
where, n is the neighborhood size, f
i
(x, y) is the pixel
value of feature map f
i
at location (x,y), I(n, n) de-
notes a n×n matrix of ones, and N [g
i
(x, y)] denotes a
n×n neighborhood around pixel (x,y) of feature map
g
i
. In the present work, the value of n has been chosen
as 5. Use of the cross-input neighborhood difference
is advantageous in the sense that it helps in obtain-
ing the positional differences between the two input
features.
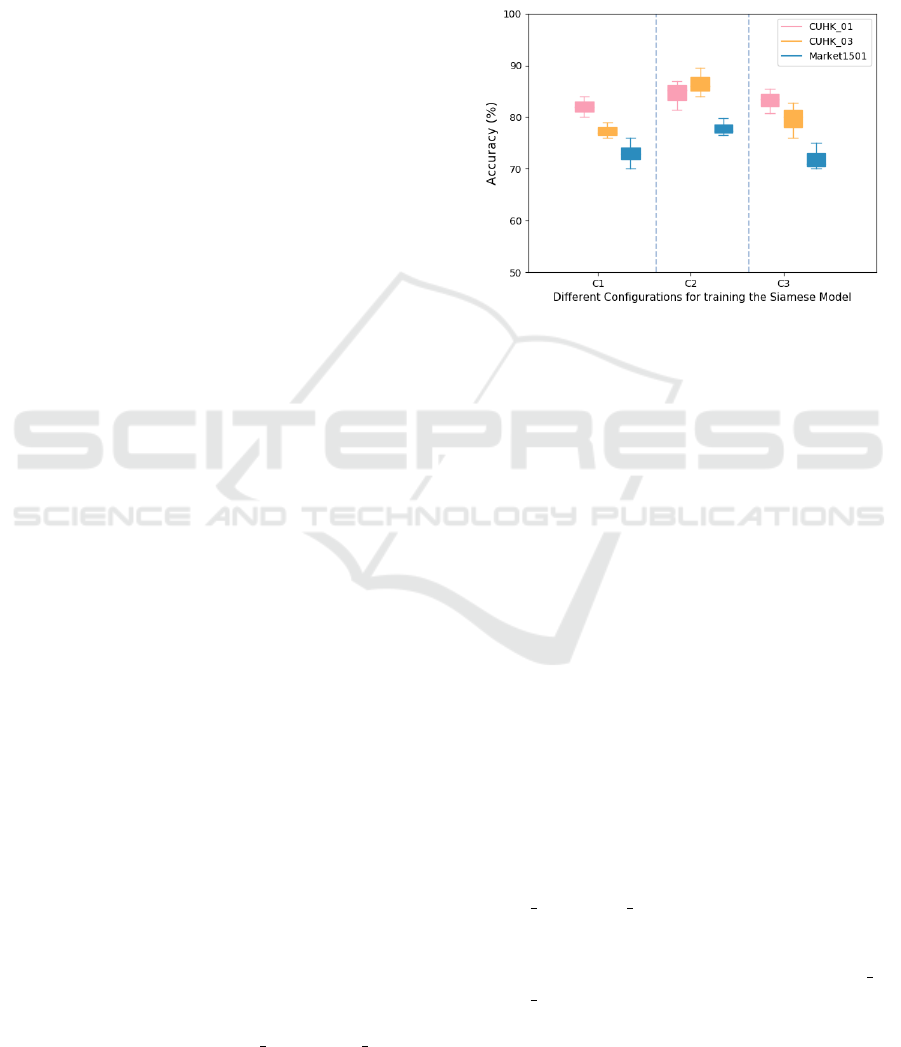
3.2 Network Training
We propose dividing each silhouette into multiple
segments, and pass each of these segments in paral-
lel through different SMSNet channels. This helps
in preserving the spatial relationship among the in-
put features at a high resolution and preserve better
contextual information. The above re-identification
process is explained clearly using Figure 3. It can
be seen from the figure that each of the two input
images is segmented into three equal parts, namely,
Segment1, Segment2, and Segment3. These three im-
age segments from each image pair are provided as
inputs to the three different SMSNets (namely, SM-
SNet1, SMSNet2, SMSNet3) in a manner as shown in
Figure 3. With reference to the figure, SMSMNet1
computes the cross-neighborhood distance between
the first segments of the two images at its final layer
denoted by fc 1, while SMSNet2 and SMSNet3 com-
pute the cross-neighborhood distances between the
second and third segments at their final layers denoted
by fc 2 and fc 3, respectively. Each of the features in
the fc 1, fc 2 and fc 3 layers is 500 dimensional, and
provide useful information regarding the dissimilarity
between the corresponding segments in the two in-
put images. These features are next concatenated into
a single feature vector of dimension 1500, denoted
by FC. The FC layer is now fully connected with
a final classification layer with two nodes represent-
ing Similar Class and Dissimilar Class, respectively.
Training of the complete network is done using Adam
optimizer (Kingma and Ba, 2014) by computing the
binary cross-entropy loss at the final layer nodes in
multiple epochs until convergence.
To train the network, we first prepare a gallery set
in the form of positive and negative pairs of images.
Positive pairs are formed from the image sequences
of the same identity, whereas each negative pair is
formed with two different identities. The procedure
for sampling the data into positive and negative pairs
is explained with an example next. CUHK 03 (Li
et al., 2014), one of the popular re-identification data
sets consists of 13164 images from 1360 subjects.
From this data, we randomly sample 1160 person ids
(i.e., 90% of total number of subjects) for training and
two sets of 100 test ids for testing and validation, re-
spectively. A similar training-test split criterion has
also been considered for each of the other data sets
used in the study.
SIGMAP 2020 - 17th International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
106
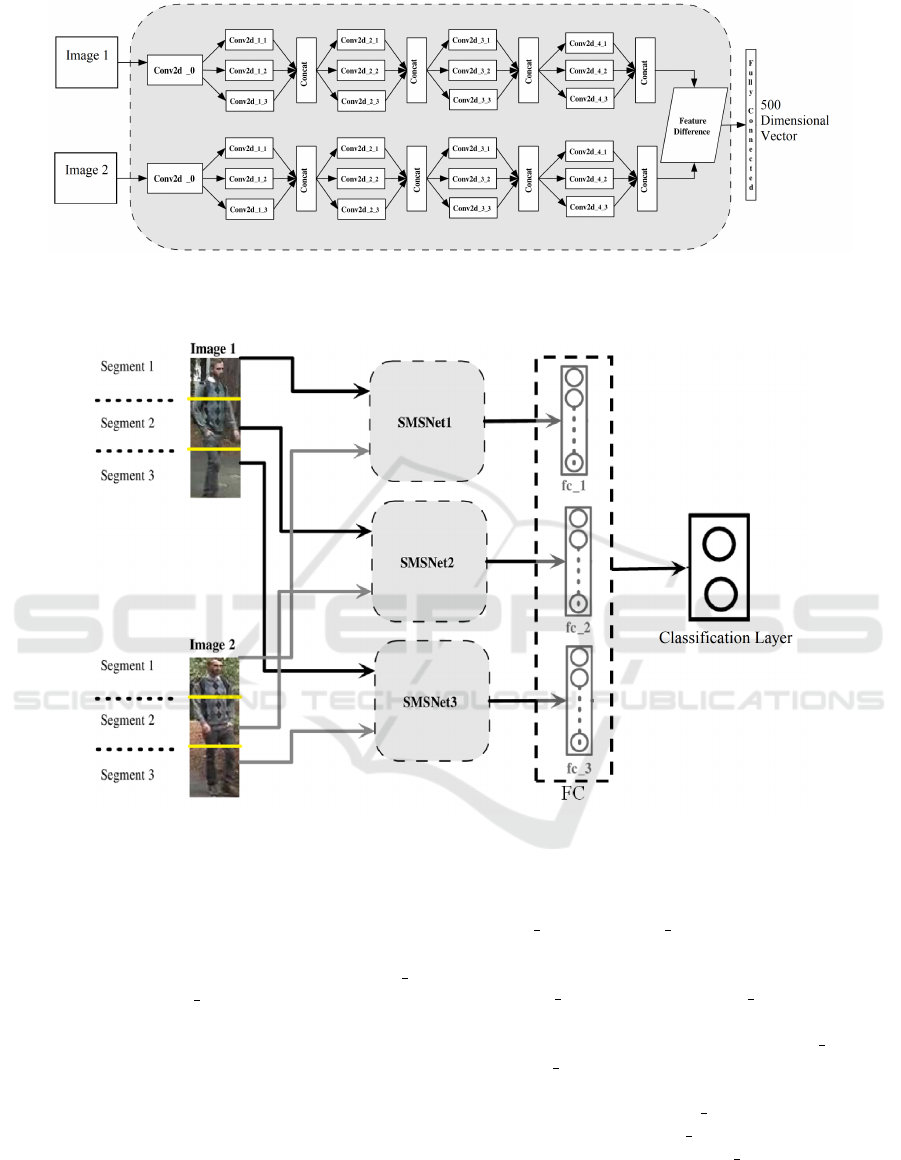
Figure 2: Insight view of the proposed Siamese Multi-scale Network (SMSNet) architecture. First layer of convolution is
unaffected of dilation parameters. All other layers are dilated with rate 1,2,3 and feature aggregation has been done after each
convolution layer in form of concatenation. Feature difference is computed after 4
th
convolution layer.
Figure 3: Overall framework of the re-identification approach.
4 DATA SET DESCRIPTION
For experiments, we consider four large scale data
sets, namely, VIPeR (Gray et al., 2007), CUHK 01
(Li et al., 2012), CUHK 03 (Li et al., 2014) and Mar-
ket1501 (Zheng et al., 2015).
VIPeR: VIPeR stands for Viewpoint Invariant Pedes-
trian Recognition data set. In this data set, the images
of persons are captured from two different camera
viewpoints. The complete data set consists of 1264
images from 632 persons, with exactly two images
per person from different viewpoints. We use this
data for evaluating our network performance only. It
has not been used to train the SMSNet model, since
it consists of only a few number of samples which is
likely to be insufficient to train a deep network accu-
rately.
CUHK 01 and CUHK 03. Both these data sets are
captured by the Chinese University of Hongkong.
There is a total of 3884 images from 971 persons
in CUHK 01 whereas in CUHK 03 13164 images
from 1360 persons. There are exactly four images
from two different camera views for CUHK 01, while
in CUHK 03 images are captured from six different
cameras, and a single person is observed from two dif-
ferent viewpoints. In CUHK 01 there are four images
per person, but in CUHK 03 there are five to eight
images per person. The CUHK 03 data is stored in
two forms one is ’labeled’ and another is ’detected’.
In ’detected’ the bounding box is drawn with a pedes-
trian detector whereas in ’labeled’ it is drawn manu-
ally.
SMSNet: A Novel Multi-scale Siamese Model for Person Re-Identification
107
Market1501. The Market1501 data set is collected
in an open environment at Tsinghua University. This
data is collected with six overlapping camera views:
five with high-resolution and one with low-resolution.
In total, there are 32268 images from 1501 individu-
als captured simultaneously from two different cam-
era views, out of which 12936 images are marked as
training images and 19732 images are marked as test
images. This data set is quite extensive as well as
challenging due to its large size and variability.
It may be noted that, the above-mentioned data
sets already provide the silhouette images extracted
from video frames. However, during working with
video data in real-life scenarios, accurate localization
(i.e., estimating the bounding box) of individuals in
each video frame has to be carried out. Since, the
re-identification scenario considered in this work as-
sumes one person to be present in the camera field-
of-view at a time, localizing the moving person in the
background can be done effectively using recent tech-
niques such as (Jiang et al., 2019). Even if the bound-
ing box detected around the moving person is not very
precise, it would still not affect the re-identification
accuracy much, since the proposed algorithm consid-
ers the RGB information of the entire bounding box,
and does not require segmentation of clean object sil-
houette from the background. Hence, as long as a
major portion of a target subject appears in the esti-
mated bounding box, our approach should be able to
work satisfactorily.
5 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
A detailed evaluation of our algorithm as well as per-
formance comparison with state-of-the-art algorithms
are presented in this section. All experiments have
been performed using Tensorflow (Abadi et al., 2016)
on a system having 64 GB RAM, NVIDIA TITAN Xp
and NVIDIA RTX-1080Ti GPUs with a total capacity
of 34 GB memory capacity.
We train the proposed Siamese Multi-scale Net-
work (SMSNet) model with the l2 regularizer using
a learning rate of 0.001. To avoid over-fitting dur-
ing training the network, a weight decay factor (γ)
of 5e-4 is introduced at each convolution layer. The
optimal values of the hyper-parameters, i.e., learning
rate (η) and weight decay (γ) are determined by carry-
ing out three-fold cross-validation on the training set
for different combination of these hyper-parameters,
and next choosing the configuration that yields the
highest cross-validation accuracy. Corresponding to
each data set, namely CUHK
01, CUHK 03 and
Market1501, we consider three different combina-
tions of η and γ namely, C1 (0.01,2.5e-3), C
2
(0.01,5e-
4), C
3
(0.03,5e-4), and for each of these combinations,
we perform three-fold cross-validation and observe
the effectiveness of learning the training data for five
different initialization of the network weights. Figure
4 presents the results of this experiment by means of
box and whiskers plot.
Figure 4: Range of three-fold cross-validation accuracy for
various combinations of parameters η and γ corresponding
to different the data sets by setting different initial weights
of the network.
In this figure, each box represents the variation of
Rank 1 training accuracy for a particular data set and
network configuration. From the figure, it can be
seen that, the configuration C2 (0.01,5e-4), in general,
works best for all the data sets used in the study. The
accuracy values obtained using C2 is significantly bet-
ter than that obtained from C1 and C3. Hence, these
values of η and γ have been used to report the results
for all the future experiments.
Next, we test the robustness of the proposed net-
work (SMSNet) on unknown test data for different
initialization of the network weights as well as for the
different combinations of training and test sets. Basi-
cally, we train the SMSNet five different times, with
a different training set, and next evaluate its perfor-
mance on the same test set. Figure 5 presents the
results of this experiment in terms of the box and
whiskers plot.
The four boxes in the figure correspond to the
range of accuracy obtained for the following data sets:
CUHK 01, CUHK 03, Market1501, and VIPeR for
the five runs. With reference to the figure it can be ob-
served that, the inter-quartile range (i.e., between 25
th
to 75
th
percentile) corresponding to the CUHK 01,
CUHK 03 and Market 1501 data sets are 1.5%, 1.7%
and 2.6%, respectively which is quite small. The
corresponding number for the VIPeR data set is 5%
which is slightly larger than the others, and this is be-
SIGMAP 2020 - 17th International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
108

Figure 5: Boxplot showing the performance of the proposed
approach after five different times of run on three data set
i.e., CUHK 01, CUHK 03, and Market1501.
cause the network does not get trained properly due
to availability of limited training data as already ex-
plained in Section 4. The small range of the whiskers
in Figure 5 emphasize the robustness of our approach
against a wide variety of data sets.
Next, we compare the effectiveness of the pro-
posed approach with respect to other state-of-the-art
techniques, namely ((Varior et al., 2016),(Guo and
Cheung, 2018),(Ahmed et al., 2015),(Subramaniam
et al., 2016)) along with two non-Siamese Network
based techniques: Deep-Reid (Li et al., 2014), and
MuDeep (Qian et al., 2017). Results are shown in Ta-
ble 2 in terms of Rank 1 accuracy percentage. For
this experiment also we use a similar training-test set
combination as already discussed in Section 3.2. The
first two rows in Table 2 correspond to the two Non-
Siamese Network-based approaches while the rest of
the rows show the performance of Siamese Network-
based approaches developed in the recent past.
With reference to the table, it has been observed
that the proposed SMSNet model for person re-
identification usually performs better than the state-
of-the-art approaches in terms of accuracy. Only in
the case of the CUHK 01 data, our approach falls
short of the accuracy obtained from (Guo and Che-
ung, 2018) by a very small percentage of 0.8. How-
ever, in all other situations our approach stands out to
be the winner. The superior performance of the pro-
pose SMSNet on the VIPeR data set is due to the fact
that our model is first trained on an extensive data,
namely, CUHK 03 data, and next fine-tuned using the
VIPeR data. This prevents the network from getting
under-fitted thereby improving its accuracy.
Often instead of finding the best match only, we
are interested in observing if the correct class falls
within the top few predictions of the model. Cu-
mulative Matching Characteristic (CMC) curves are
Table 2: Comparison of Rank 1 accuracy (in %) for 100
test ids of our proposed approach with state-of-the-art tech-
niques.
Methods
Rank 1 Accuracy (%)
VIPeR CUHK 01 CUHK 03 Market
1501
Non-Siamese based
Li et al. 56.1 27.9 20.6 44.4
Qian et al. 44.7 79.6 82.4 71.2
Siamese based
Ahmed et al. 35.2 64.2 55.0 56.7
Subramaniam et al. 68.7 81.2 72.3 76.7
Varior et al. 68.7 - 57.3 61.6
Guo et al. 50.9 88.1 88.3 -
SCap Net 76.2 83.0 79.0 67.4
Proposed SMSNet 91.5 87.3 89.6 79.2
usually used to study the rank-wise performance im-
provement of a model with increase in rank. In
this curve, the rank value (plotted along horizon-
tal axis) indicates the number of top predictions to
be considered for computing the accuracy (plotted
along vertical axis). The CMC curves corresponding
to the different data sets used in the study, namely
CUHK 01, CUHK 03, Market1501 and VIPeR data
are presented in Figures 6(a)-(d) respectively up to
Rank 10. Once again, it is observed from the CMC
curves that our proposed model provides a high accu-
racy for most rank values for the different data sets.
Although the Rank 1 accuracy of our approach on
CUHK 01 data was lower than that of (Guo and Che-
ung, 2018) (as seen in Table 2), from Rank 2 on-
wards, our approach performs better than (Guo and
Cheung, 2018) throughout. In general, the rank-wise
accuracy of each of the other competing techniques is
considerably lower than our approach for the differ-
ent rank values. Also, it is observed that our method
achieves the 90% accuracy mark at Rank 1 for the
VIPeR data, and within Rank 2 for both the CUHK 01
and CUHK 03 data, and within Rank 7 for the Mar-
ket1501 data. We also observe that the average Rank
5 accuracy of our work is 96.02%, which is better than
that of (Guo and Cheung, 2018) (i.e., the approach
with the second best performance (85.65%)) by about
10%, which is remarkable. From the above experi-
ments, we can conclude that the proposed SMSNet-
based person re-identification performs robustly and
more accurately than the state-of-the art techniques.
SMSNet: A Novel Multi-scale Siamese Model for Person Re-Identification
109
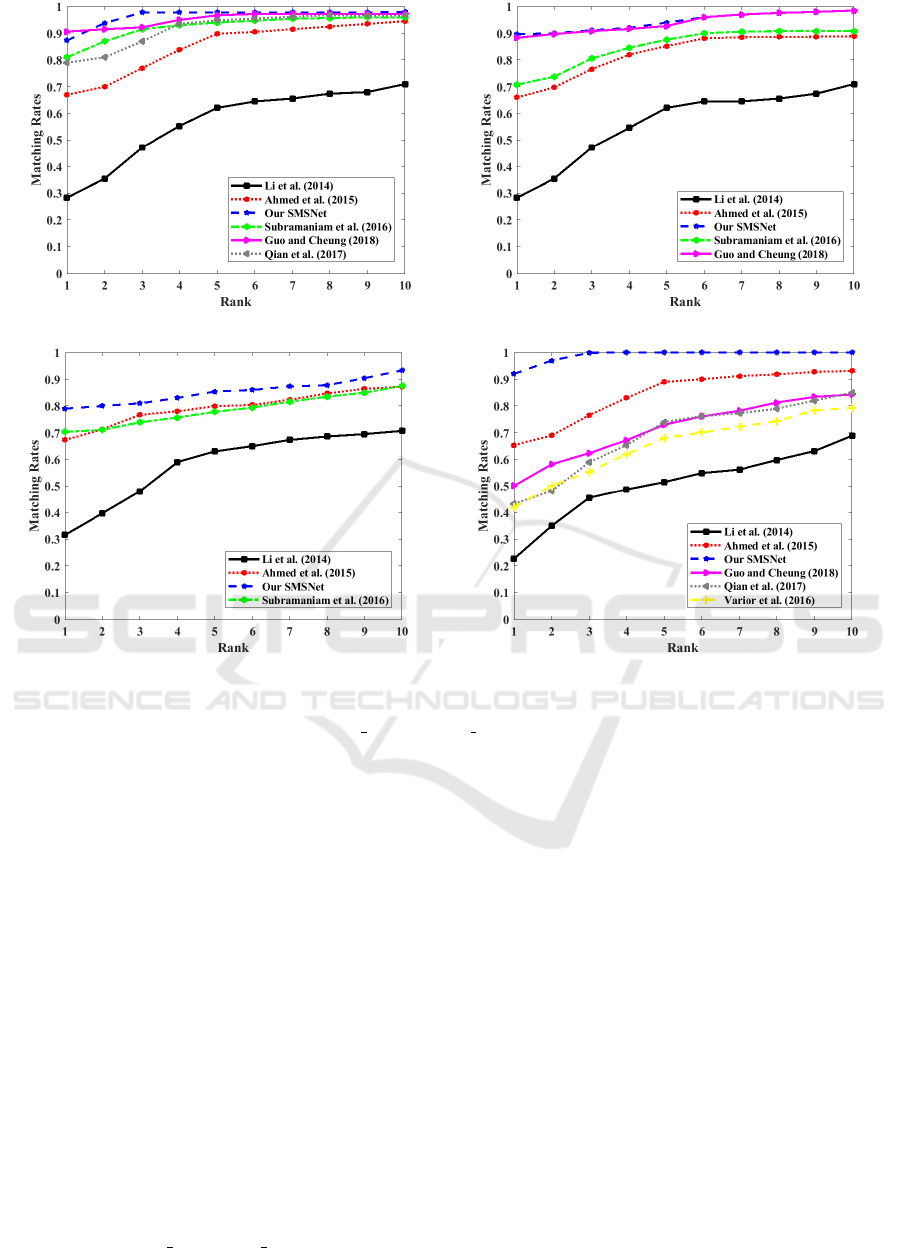
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 6: Cumulative matching characteristic curves showing improvement in re-identification accuracy with rank for the
different approaches corresponding to: (a) CUHK 01, (b) CUHK 03, (c) Market1501 and (d) VIPeR data sets.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this work, we have presented a part-based Siamese
Multi-scale Network (SMSNet) that is capable of
learning multi-scale visual context information due to
its dilation architecture which increases the receptive
view of the network. It helps in detecting the fine
details at higher resolution and also makes the net-
work response more efficient with few parameter tun-
ing. Fusion of features from three parallel SMSNets
corresponding to three different body parts has been
done for capturing contextual information of the im-
ages at a higher resolution. The proposed approach
is view-invariant, cost-effective, and can be conve-
niently integrated with existing surveillance setup in
public places such as movie/theater halls, conference
venues, and similar places. Extensive evaluation of
our algorithm on three large publicly available data
sets, namely, CUHK 01, CUHK 03, and Market1501
verify its effectiveness. However, similar to most ex-
isting appearance-based re-identification approaches,
our approach will work well in situations where per-
sons are expected to wear different colored clothes.
Application of the proposed method in school, col-
leges, or other similar application sites where every-
one wears a standard uniform, is not expected to pro-
vide reliable results. In such situations, biometric in-
formation may be fused with the re-identification al-
gorithm to achieve a better performance. This can be
considered as a part of the future work. Other scopes
for future work include extending the proposed ap-
proach to perform open-set re-identification, multi-
person tracking, and straining the network with a dif-
ferent distractor set during training, which is likely to
improve the robustness of the model further.
SIGMAP 2020 - 17th International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
110

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge NVIDIA for
supporting their research with the TITAN Xp Graph-
ics processing unit.
REFERENCES
Abadi, M., Barham, P., Chen, J., Chen, Z., Davis, A.,
Dean, J., Devin, M., Ghemawat, S., Irving, G., Isard,
M., et al. (2016). Tensorflow: A system for large-
scale machine learning. In 12th {USENIX} Sympo-
sium on Operating Systems Design and Implementa-
tion ({OSDI} 16), pages 265–283.
Ahmed, E., Jones, M., and Marks, T. K. (2015). An
improved deep learning architecture for person re-
identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages
3908–3916.
Ashby, M. P. J. (2017). The value of cctv surveillance cam-
eras as an investigative tool: An empirical analysis.
European Journal on Criminal Policy and Research,
23(3):441–459.
Bazzani, L., Cristani, M., and Murino, V. (2013).
Symmetry-driven accumulation of local features for
human characterization and re-identification. Com-
puter Vision and Image Understanding, 117(2):130–
144.
Bazzani, L., Cristani, M., Perina, A., Farenzena, M.,
and Murino, V. (2010). Multiple-shot person re-
identification by hpe signature. In Proceedings of the
20
th
International Conference on Pattern Recognition,
pages 1413–1416. IEEE.
Bedagkar-Gala, A. and Shah, S. K. (2011). Multiple per-
son re-identification using part based spatio-temporal
color appearance model. In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision Work-
shops (ICCV Workshops), pages 1721–1728. IEEE.
Bromley, J., Guyon, I., LeCun, Y., S
¨
ackinger, E., and Shah,
R. (1994). Signature verification using a” siamese”
time delay neural network. In Proceedings of the
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
pages 737–744.
Cheng, D., Gong, Y., Zhou, S., Wang, J., and Zheng,
N. (2016). Person re-identification by multi-channel
parts-based cnn with improved triplet loss function.
In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1335–1344.
Ding, S., Lin, L., Wang, G., and Chao, H. (2015). Deep
feature learning with relative distance comparison
for person re-identification. Pattern Recognition,
48(10):2993–3003.
Forss
´
en, P.-E. (2007). Maximally stable colour regions for
recognition and matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Gray, D., Brennan, S., and Tao, H. (2007). Evaluating ap-
pearance models for recognition, reacquisition, and
tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International
Workshop on Performance Evaluation for Tracking
and Surveillance (PETS), volume 3, pages 1–7. Cite-
seer.
Guo, Y. and Cheung, N.-M. (2018). Efficient and deep per-
son re-identification using multi-level similarity. In
Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vi-
sion and Pattern Recognition, pages 2335–2344.
Jiang, Y., Wang, J., Liang, Y., and Xia, J. (2019). Combin-
ing static and dynamic features for real-time moving
pedestrian detection. Multimedia Tools and Applica-
tions, 78(3):3781–3795.
Kang, J., Cohen, I., and Medioni, G. (2004). Object reac-
quisition using invariant appearance model. In Pro-
ceedings of the 17
th
International Conference on Pat-
tern Recognition, 2004. ICPR 2004., volume 4, pages
759–762. IEEE.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A
method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1412.6980.
Koestinger, M., Hirzer, M., Wohlhart, P., Roth, P. M., and
Bischof, H. (2012). Large scale metric learning from
equivalence constraints. In Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, pages 2288–2295. IEEE.
Li, D., Chen, X., Zhang, Z., and Huang, K. (2017). Learn-
ing deep context-aware features over body and latent
parts for person re-identification. In Proceedings of
the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, pages 384–393.
Li, W. and Wang, X. (2013). Locally aligned feature trans-
forms across views. In Proceedings of the IEEE Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
pages 3594–3601.
Li, W., Zhao, R., and Wang, X. (2012). Human reidentifica-
tion with transferred metric learning. In Proceedings
of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pages
31–44. Springer.
Li, W., Zhao, R., Xiao, T., and Wang, X. (2014). Deep-
reid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-
identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages
152–159.
Ma, B., Su, Y., and Jurie, F. (2012). Local descriptors en-
coded by fisher vectors for person re-identification.
In Proceedings of the European Conference on Com-
puter Vision, pages 413–422. Springer.
Meng, J., Wu, S., and Zheng, W.-S. (2019). Weakly su-
pervised person re-identification. In Proceedings of
the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, pages 760–769.
Munjal, B., Amin, S., Tombari, F., and Galasso, F. (2019).
Query-guided end-to-end person search. In Proceed-
ings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pages 811–820.
Qian, X., Fu, Y., Jiang, Y.-G., Xiang, T., and Xue, X.
(2017). Multi-scale deep learning architectures for
person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pages
5399–5408.
SMSNet: A Novel Multi-scale Siamese Model for Person Re-Identification
111

Sivic, J., Zitnick, C. L., and Szeliski, R. (2006). Finding
people in repeated shots of the same scene. In Pro-
ceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference,
volume 2, page 3.
Song, J., Yang, Y., Song, Y.-Z., Xiang, T., and Hospedales,
T. M. (2019). Generalizable person re-identification
by domain-invariant mapping network. In Proceed-
ings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pages 719–728.
Su, C., Li, J., Zhang, S., Xing, J., Gao, W., and Tian, Q.
(2017). Pose-driven deep convolutional model for
person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pages
3960–3969.
Su, C., Zhang, S., Xing, J., Gao, W., and Tian, Q.
(2016). Deep attributes driven multi-camera per-
son re-identification. In Proceedings of the Euro-
pean Conference on Computer Vision, pages 475–491.
Springer.
Subramaniam, A., Chatterjee, M., and Mittal, A. (2016).
Deep neural networks with inexact matching for per-
son re-identification. In Proceedings of the Ad-
vances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
pages 2667–2675.
Tian, C., Zeng, M., and Wu, Z. (2014). Person re-
identification based on spatiogram descriptor and col-
laborative representation. IEEE Signal Processing
Letters, 22(10):1595–1599.
Varior, R. R., Shuai, B., Lu, J., Xu, D., and Wang, G. (2016).
A siamese long short-term memory architecture for
human re-identification. In Proceedings of the Euro-
pean Conference on Computer Vision, pages 135–153.
Springer.
Wu, L., Shen, C., and Van Den Hengel, A. (2017). Deep
linear discriminant analysis on fisher networks: A hy-
brid architecture for person re-identification. Pattern
Recognition, 65:238–250.
Wu, S., Chen, Y.-C., Li, X., Wu, A.-C., You, J.-J., and
Zheng, W.-S. (2016). An enhanced deep feature rep-
resentation for person re-identification. In Proceed-
ings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications
of Computer Vision (WACV), pages 1–8. IEEE.
Xiao, T., Li, H., Ouyang, W., and Wang, X. (2016). Learn-
ing deep feature representations with domain guided
dropout for person re-identification. In Proceedings
of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition, pages 1249–1258.
Xiong, F., Gou, M., Camps, O., and Sznaier, M. (2014).
Person re-identification using kernel-based metric
learning methods. In Proceedings of the Euro-
pean Conference on Computer Vision, pages 1–16.
Springer.
Yi, D., Lei, Z., Liao, S., and Li, S. Z. (2014). Deep met-
ric learning for person re-identification. In Proceed-
ings of the 22
nd
International Conference on Pattern
Recognition, pages 34–39. IEEE.
Zhang, R., Lin, L., Zhang, R., Zuo, W., and Zhang, L.
(2015). Bit-scalable deep hashing with regularized
similarity learning for image retrieval and person re-
identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Process-
ing, 24(12):4766–4779.
Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., Wang, S., Wang, J., and Tian,
Q. (2015). Scalable person re-identification: A bench-
mark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Con-
ference on Computer Vision, pages 1116–1124.
SIGMAP 2020 - 17th International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
112
