
Round-optimal Constant-size Blind Signatures
Olivier Blazy
1
, Brouilhet Laura
1
, C
´
eline Chevalier
2
and Neals Fournaise
1
1
Universit
´
e de Limoges, XLim, Limoges, France
2
Universit
´
e Panth
´
eon-Assas, Paris, France
Keywords:
Blind-signature, Round-optimal, Standard Model, e-Voting.
Abstract:
Blind signatures schemes allow a user to obtain a signature on messages from a signer, ensuring blindness
(the signer should not learn which messages he signed or in which order) and unforgeability (the user should
not be able to produce more signatures than the number of times he interacted with the signer). For practical
purposes, it is important that such schemes are round-optimal (one flow sent by the user and one by the
signer) and constant-size (the amount of data sent during the interaction should not depend on the length of
the message), which are two properties difficult to ensure together. In this paper, we propose the first blind
signature scheme both round-optimal, constant-size, in the standard model (without any random oracle) and
under a classical assumption (SXDH). Our construction follows the classical framework initially presented by
Fischlin. As a side result, we first show how to use a special kind of structure-preserving signatures (where
the signatures also are group elements) in order to construct the first constant-size signatures on randomizable
ciphertexts, a notion presented a few years ago by Blazy et al. Our construction of blind signature then builds
upon this primitive and consists of constant-size two-round communication. It can be instantiated under any
k − MDDH assumption, requires to exchange 9 elements and leads to a final signature with 22 elements when
relying on SXDH. .
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital Signature Schemes are well-known cryp-
tographic primitives analogous to manuscript signa-
tures. They are commonly used to allow a recipient
to strongly believe that a message or document was
created by the supposed sender (authentication) and
that it has not been altered (integrity). Such schemes
are supposed to be unforgeable, in the sense that an
adversary should be unable to output a valid signature
after having had access to a certain number of valid
signatures.
Blind Signature Schemes, introduced in (Chaum,
1982) are a special kind of digital signature schemes,
with an additional property, called blindness, on top
of a variant of the notion of unforgeability. The
blindness property means that in such schemes, the
user does not sign the messages by himself, but
rather interacts with a signer, with the guarantee that
the signer will learn nothing about the signed mes-
sage nor the resulting signature. More precisely, the
view of the signer should be unlinkable to the (mes-
sage/signature) pairs resulting from several execu-
tions of the protocol (he cannot link a pair to a specific
execution).
The second security property for blind signatures
is a notion of unforgeability, which intuitively means
that after n interactions, a user should not obtain more
than n signatures (on different messages). This prop-
erty has been formalized in (Pointcheval and Stern,
2000), motivated by the use of blind signatures for
e-cash: a user should not be able to produce more
(message/signature) pairs (coins) than the number of
signing executions with the bank (withdrawals). The
security model was further revisited in (Schr
¨
oder and
Unruh, 2012) for other contexts.
Blind signature schemes were introduced as a fun-
damental building block for applications that guar-
antee user anonymity, e.g. e-cash (Chaum, 1982;
Chaum et al., 1990; Okamoto and Ohta, 1992; Ca-
menisch et al., 2005; Fuchsbauer et al., 2009), e-
voting solutions (Fujioka et al., 1993; Blazy et al.,
2011; Blazy et al., 2012a), and anonymous credentials
(Brands, 1994; Camenisch and Lysyanskaya, 2001;
Belenkiy et al., 2009; Fuchsbauer, 2011). Due to their
practical interest, it is extremely important that such
schemes offer low complexity both in terms of num-
ber of rounds (not too much interaction between the
user and the signer) and amount of data exchanged
(amount independent of the length of the signed mes-
sage, if possible). Furthermore, for security reasons,
it is better to design schemes in the standard model
(without any random oracle (Bellare and Rogaway,
Blazy, O., Laura, B., Chevalier, C. and Fournaise, N.
Round-optimal Constant-size Blind Signatures.
DOI: 10.5220/0009888702130224
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2020) - SECRYPT, pages 213-224
ISBN: 978-989-758-446-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
213

1993)) and proven secure under a classical and well-
accepted security assumption.
Related Work. The first constructions for blind sig-
nature schemes (such as (Okamoto, 1993; Okamoto,
2006)) were highly interactive, until Fischlin pro-
posed a generic construction of round-optimal blind
signature schemes in (Fischlin, 2006), with only two
flows of communication between the user and the
signer. Several constructions have since then effi-
ciently instantiated this transformation, but at the cost
of exchanging information of size depending on the
message length (Blazy et al., 2011; Blazy et al.,
2012b; Blazy et al., 2012a), or by relying on the
Random Oracle Model (Pointcheval and Stern, 2000;
Abe, 2001; Baldimtsi and Lysyanskaya, 2013; Hauck
et al., 2019).
To the best of our knowledge, the only constant-
size instantiations in the standard model (without
any random oracle) were given in (Abe et al., 2010;
Ghadafi, 2017). The former is given in a pairing-
based setting with a final signature consisting of 18 el-
ements in the first group G
1
and 16 in the second
one G
2
, but relies on a new ad-hoc q-type assump-
tion. In (Ghadafi, 2017), the proposed blind signa-
ture is in the standard model but under a non standard
q-type assumption: The Blind Signature One More,
which basically assumes the security of the scheme
and could likely only be proven in the generic model.
Contributions. In this paper, we answer an open
question mentioned in the presentation of (Hauck
et al., 2019) at Eurocrypt’19 by proposing a new blind
signature scheme, which is round-optimal, constant-
size, in the standard model and with a classical as-
sumption. Our construction follows the framework
presented by Fischlin (Fischlin, 2006), and adapts an
idea from (Blazy et al., 2011) to decrease some cost.
The main tool used in our construction can be
seen as a side contribution: we give the first sig-
nature scheme on randomizable ciphertexts (Blazy
et al., 2011) based on structure-preserving signatures,
which are furthermore constant-size. To this aim, we
prove that we can adapt the structure-preserving sig-
natures proposed in (Kiltz et al., 2015) to sign classes
of elements, in the spirit of (Hanser and Slamanig,
2014). A class of elements is a group of elements
which are ciphertexts of the same message. In other
words, these schemes allow to give a signature on a
ciphertext C, such that one can derive a signature on
any randomization of this ciphertext. Of course, the
unforgeability still guarantees that no adversary can
generate a signature on an unsigned class.
When comparing our schemes with existing ones
(see Figure 1), one can see that we manage to keep
all the communication constant-size with respect to
the message length `, while relying on a standard as-
sumption.
1
.
Organization of the Paper. The paper starts by re-
calling classical definitions and security experiments
in Section 2 and useful building blocks in Section 3.
We then proceed by introducing our constant-size
signature on randomizable ciphertexts (SRC) in Sec-
tion 4 and describing our constant-size blind signature
scheme in Section 5. We finally give another applica-
tion of SRC schemes to e-voting in Section 6.
2 DEFINITIONS
2.1 General Notations and Assumptions
In all the remaining of this paper, we will work in a
pairing-based setting whose notations are recalled be-
low. We will also use the standard security assump-
tions in such a setting: we recall them below for com-
pleteness. Let K be the security parameter.
Pairing Groups. Let GGen be a probabilistic poly-
nomial time (PPT) algorithm that on input 1
K
re-
turns a description G = (p,G
1
,G
2
,G
T
,e,g
1
,g
2
) of
asymmetric pairing groups where G
1
, G
2
, G
T
are
cyclic groups of order p for a K-bit prime p, g
1
and
g
2
are generators of G
1
and G
2
, respectively, and
e : G
1
× G
2
→ G
T
is an efficiently computable (non-
degenerated) bilinear map. Define g
T
:= e(g
1
,g
2
),
which is a generator in G
T
.
Definition 1 (Decisional Diffie-Hellman (DDH)). Let
G be a cyclic group of prime order p. The DDH as-
sumption states that given (g,g
a
,g
b
,g
c
) ∈ G, it is hard
to determine whether c = ab.
Definition 2 (External Diffie-Hellman (XDH (Boneh
et al., 2004))). This variant of DDH, states that while
the DDH is easy in G
2
, DDH is hard in G
1
.
Definition 3 (Symmetric External Diffie-Hellman
(SXDH (Ateniese et al., 2005))). This variant of
DDH, used mostly in bilinear groups in which no
computationally efficient homomorphism exists from
G
2
to G
1
or G
1
to G
2
, states that DDH is hard in
both G
1
and G
2
.
1
In this figure, combining (Blazy et al., 2012b) and
(Blazy et al., 2012a) could lead to a scheme with sublinear
communication cost O(log(`)), but at the cost of a slightly
weaker definition of blindness (a-posteriori blindness). Fur-
thermore, the user communication cost would not still be
constant.
SECRYPT 2020 - 17th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
214

Scheme User Server Signature # Rounds Assumptions
(Abe et al., 2010) 2G
1
3G
1
,3G
2
16 G
1
, 14 G
2
2 q−ADH−SDH
(Blazy et al., 2011) O(`)G
1
,O(`)G
2
2G
1
,1G
2
2 G
1
,1G
2
2 SXDH
(Blazy et al., 2012b) O(`/log(`))G
1
2G
1
,1G
2
2 G
1
,1G
2
2 SXDH
Ours 2G
1
6G
1
,1Z
p
12G
1
,8G
2
2 SXDH
Asym (k + 1)G
1
3(k + 1)G
1
,1Z
p
(k + 1)(2k + 4)G
1
,
2 k − MDDH
(k + 1)(3k + 3)G
2
Sym (k + 1)G 3(k + 1)G,1Z
p
(k + 1)(5k + 7)G 2 k − MDDH
Figure 1: Efficiency comparison of our solutions with existing schemes in the standard model.
2.2 Matricial Notations and
Assumptions
Our schemes, that we present under the SXDH as-
sumption for the sake of simplicity, can be proven
under any k − MDDH security assumption. This as-
sumption, presented in (Escala et al., 2013), needs a
few notations to be fully understood: this part can be
omitted at first read but we recall them below for com-
pleteness.
Matricial Notations. If A ∈ Z
(k+1)×n
p
is a matrix,
then A ∈ Z
k×n
p
denotes the upper matrix of A and
A ∈ Z
1×n
p
denotes the last row of A.
We use implicit representation of group elements
as introduced in (Escala et al., 2013). For s ∈ {1,2,T }
and a ∈ Z
p
define [a]
s
= g
a
s
∈ G
s
as the implicit rep-
resentation of a in G
s
(we use [a] = g
a
∈ G if we con-
sider a unique group). More generally, for a matrix
A = (a
i j
) ∈ Z
n×m
p
we define [A]
s
as the implicit rep-
resentation of A in G
s
:
[A]
s
:=
g
a
11
s
... g
a
1m
s
g
a
n1
s
... g
a
nm
s
∈ G
n×m
s
We will always use this implicit notation of el-
ements in G
s
, i.e., we let [a]
s
∈ G
s
be an element
in G
s
. Note that from [a]
s
∈ G
s
it is generally hard
to compute the value a (discrete logarithm problem
in G
s
). Further, from [b]
T
∈ G
T
it is hard to com-
pute the value [b]
1
∈ G
1
and [b]
2
∈ G
2
(pairing in-
version problem). Obviously, given [a]
s
∈ G
s
and
a scalar x ∈ Z
p
, one can efficiently compute [ax]
s
∈
G
s
. Further, given [a]
1
,[b]
2
one can efficiently com-
pute [ab]
T
using the pairing e. For a,b ∈ Z
k
p
define
e([a]
1
,[b]
2
) := [a
>
b]
T
∈ G
T
.
Assumptions. We recall the definition of the matrix
Diffie-Hellman (MDDH) assumption (Escala et al.,
2013).
Definition 4 (Matrix Distribution). Let k ∈ N. We
call D
k
a matrix distribution if it outputs matrices in
Z
(k+1)×k
p
of full rank k in polynomial time.
Without loss of generality, we assume the first k
rows of A
$
← D
k
form an invertible matrix. The D
k
-
Matrix Diffie-Hellman problem is to distinguish the
two distributions ([A],[Aw]) and ([A],[u]) where A
$
←
D
k
, w
$
← Z
k
p
and u
$
← Z
k+1
p
.
Definition 5 (D
k
-Matrix Diffie-Hellman Assumption
D
k
-MDDH). Let D
k
be a matrix distribution and s ∈
{1,2, T }. We say that the D
k
-Matrix Diffie-Hellman
(D
k
-MDDH) Assumption holds relative to GGen in
group G
s
if for all PPT adversaries D,
Adv
D
k
,GGen
(D)
def
= |Pr[D(G,[A]
s
,[Aw]
s
) = 1]
−Pr[D(G, [A]
s
,[u]
s
) = 1]|
= negl(λ),
where the probability is taken over G
$
← GGen(1
λ
),
A
$
← D
k
,w
$
← Z
k
p
,u
$
← Z
k+1
p
.
Definition 6 (D
k
-Kernel Diffie-Hellman Assumption
D
k
− KerMDDH). Let D
k
be a matrix distribution
and s ∈ {1,2}. We define Adv
kmddh
D
k
,GGen
(D) by
Pr[c
>
A = 0 ∧ c 6= 0 |[c]
3−s
$
← D(G,[A]
s
)]
where the probability is taken over G
$
← GGen(1
λ
),
A
$
← D
k
. We say that the D
k
-Kernel Diffie-Hellman
Assumption (D
k
− KerMDDH) assumption holds rel-
ative to GGen in group G
s
, if for all PPT adver-
saries D,
Adv
kmddh
D
k
,GGen
(D) = negl(λ)
In the following, we write k − MDDH for D
k
−
MDDH. It should be noted that 1 − MDDH is the
SXDH assumption used in this paper.
2.3 Cryptographic Primitives
We now present the classical cryptographic primi-
tives used in this paper: (randomizable) encryption
schemes and (blind) signature schemes.
Definition 7 (Encryption scheme). An encryp-
tion scheme E is described by four algorithms
(Setup
E
,KeyGen
E
,Enc, Decrypt):
• Setup
E
(K), where K is the security parameter,
generates the global parameters param of the
scheme;
Round-optimal Constant-size Blind Signatures
215

• KeyGen
E
(param) outputs the encryption and de-
cryption key (ek, dk);
• Enc(ek,m;ρ) outputs a ciphertext c, on the mes-
sage m, under ek, with the randomness ρ;
• Decrypt(dk,c) outputs the plaintext m or ⊥.
Such encryption scheme is required to have the
following security properties:
• Correctness: For every (ek,dk) generated by
KeyGen
E
, every messages m, every random ρ, we
have
Decrypt(dk,Enc(ek,m;ρ)) = m.
• Indistinguishability under Chosen Plaintext At-
tack (Goldwasser and Micali, 1984): This notion
(IND-CPA), states that an adversary should not
be able to efficiently guess which message has
been encrypted even if he chooses the two orig-
inal plaintexts. The game is described in Figure 2.
The advantages are:
Adv
ind
E,A
(K) = |Pr[Exp
ind−1
E,A
(K) = 1]−
Pr[Exp
ind−0
E,A
(K) = 1]
Adv
ind
E
(K,t) = max
A≤t
Adv
ind
E,A
(K).
Exp
ind−b
E,A
(K)
1.param ← Setup
E
(1
K
)
2.(ek,dk) ← KeyGen
E
(param)
3.(m
0
,m
1
) ← A(FIND : ek)
4.c
∗
← Enc(ek,m
b
)
5.b
0
← A(GUESS : c
∗
)
6.RETURN b
0
Figure 2: IND-CPA Game for an Encryption Scheme.
Sometimes, one may want to be able to publicly
randomize the ciphertext c, using the following algo-
rithm:
• Random(ek,c;r
0
) outputs a new ciphertext c
0
equivalent to the ciphertext c, under the public
key ek, using the additional random coins r
0
$
← R
e
.
An encryption scheme is called randomizable if
a randomized ciphertext is indistinguishable from a
fresh one.
Definition 8 (Signature scheme). A signature scheme
is composed by four polynomial time algorithms
S = (Setup
S
,KeyGen
S
,Sign, Verify).
• Setup
S
(K) outputs the global parameters param
of the scheme.
• KeyGen
S
(param) outputs the signature and veri-
fication keys: (sk,vk).
• Sign(sk,m;s) outputs a signature σ on message m
using randomness s ∈ R .
• Verify(vk,σ) checks if σ is a valid signature. It
outputs 1 if the signature is valid, 0 otherwise.
Such signature scheme is required to have the fol-
lowing security property:
• Existential Unforgeability under Chosen Message
Attacks (Goldwasser et al., 1988) (EUF − CMA).
Even after querying n valid signatures on chosen
messages (m
i
), A should not be able to output a
valid signature on a fresh message m. We define a
signing oracle:
OSign(vk,m): outputs a signature on m valid un-
der the verification key vk. The requested mes-
sage is added to the signed messages set SM .
The probability of success against the game given
in Figure 3 is denoted by
Succ
euf
S,A
(K) = Pr[Exp
euf
S,A
(K) = 1],
Succ
euf
S
(K,t) = max
A≤t
Succ
euf
S,A
(K).
Exp
euf
S,A
(K)
1.param ← Setup(1
K
)
2.(vk, sk) ← SKeyGen(param)
3.(m
∗
,σ
∗
) ← A(vk,OSign(vk,·))
4.b ← Verify(vk,m
∗
,σ
∗
)
5.IF m
∗
∈ SM RETURN 0
6.ELSE RETURN b
Figure 3: EUF − CMA Game for a Signature Scheme.
In our work, we use a signature scheme, that
of (Kiltz et al., 2015), which is also Structure-
Preserving. In such a scheme, both the messages to
be signed and the signatures are group elements.
Definition 9 (Blind signature scheme). A blind
signature scheme is defined by three polyno-
mial time algorithms and one interactive poly-
nomial time protocol BS = (BSSetup, BSKeyGen,
BSProtocolhS,Ui,Verify).
• BSSetup(K) outputs the parameters param of the
scheme.
• BSKeyGen(param) outputs the signa-
ture/verification keys: (sk, vk).
• BSProtocolhS(sk),U(vk,m)i is an interactive
protocol between user U and signer/server S. It
issues a signature σ on m valid under vk.
• Verify(vk,m,σ) checks if σ is a valid signature. It
outputs 1 if σ is valid, 0 otherwise.
The two expected security properties are the un-
forgeability, protecting the signer, and the blindness,
protecting the user (see Figure 4 and Figure 5).
• The unforgeability is the EUF − CMA property.
• The blindness property says that a malicious
signer who signed two messages m
0
and m
1
shouldn’t be able to decide which one was signed
first.
SECRYPT 2020 - 17th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
216

Exp
uf
BS ,U
∗
(K)
1.(param) ← BSSetup(1
K
)
2.(vk, sk) ← BSKeyGen(param)
3.For i = 1, . .. , q
s
, BSProto colhS (sk),A(INIT : vk)i
4.
(m
1
,σ
1
),..., (m
q
s
+1
,σ
q
s
+1
)
← A(GUESS : vk);
5.IF ∃i 6= j,m
i
= m
j
OR ∃i,Verify(vk,m
i
,σ
i
) = 0
RETURN 0
6.ELSE RETURN 1
Figure 4: Unforgeability Game for a BS Scheme.
Exp
bl−b
BS ,S
∗
(K)
1.param ← BSSetup(1
K
)
2.(vk, m
0
,m
1
) ← A(FIND : param)
3.σ
b
← BSProtocolhA,U(vk, m
b
)i
4.σ
1−b
← BSProtocolhA,U(vk, m
1−b
)i
5.b
∗
← S
∗
(GUESS : m
0
,m
1
);
6.RETURN b
∗
= b.
Figure 5: Blindness Game for a BS Scheme.
3 BUILDING BLOCKS
In this section, we present the standard instantia-
tions of the cryptographic primitives presented in the
former section that we will use in the remaining
of this paper: ElGamal encryption scheme, Kiltz et
al’s structure-preserving signature scheme and Groth-
Sahai commitments.
3.1 ElGamal Encryption Scheme
The four algorithms of this encryption scheme (ElGa-
mal, 1984) are described as follows:
• Setup
E
(1
K
): outputs param = (G, p,[1]).
• KeyGen
E
(param): outputs (ek,dk) = ([h],h) with
h
$
← Z
p
.
• Enc(ek,[m];r) outputs c = (c
1
,c
2
) = ([r,rh + m])
with r
$
← Z
p
.
• Decrypt(dk,c) computes [c
2
−hc
1
] = [m], outputs
[m].
This scheme is semantically secure against
chosen-plaintext attacks (IND-CPA) under DDH.
3.2 Structure-preserving Signatures
We will recall here the SXDH version of the structure-
preserving signature (SPS) of (Kiltz et al., 2015) in
figure 6. As we need to sign only one message we set
their parameters k = n = 1.
Setup
S
(K):
Return (param)
KeyGen
S
(param):
A,B
$
← D
1
;K
$
← Z
2×2
p
K
0
,K
1
$
← Z
2×2
p
C
def
= KA ∈ Z
2×1
p
(C
0
,C
1
)
def
= (K
0
A,K
1
A) ∈ (Z
2×1
p
)
2
(P
0
,P
1
)
def
= (B
|
K
0
,B
|
K
1
) ∈ (Z
1×2
p
)
2
sk
def
= (K,[P
0
]
1
,[P
1
]
1
,[B]
1
);
vk
def
= ([C
0
]
2
,[C
1
]
2
,[C]
2
,[A]
2
)
Sign(sk,m):
r
$
← Z
p
;τ
$
← Z
p
σ
1
def
= [(1,m)K + r
|
(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
∈ G
1×2
1
,
σ
2
def
= [r
|
B
|
]
1
∈ G
1×2
1
, σ
3
def
= [r
|
B
|
τ]
1
∈ G
1×2
1
,
σ
τ
def
= [τ]
2
∈ G
2
Return (σ
1
,σ
2
,σ
3
,σ
τ
)
Verify(vk,m, σ):
Parse σ = (σ
1
,σ
2
,σ
3
,σ
4
)
Check [σ
1
· A]
T
= [(1,m) · C + σ
2
· C
0
+ σ
3
· C
1
]
T
and [σ
2
· σ
4
]
T
= [σ
3
]
T
Figure 6: the SPS algorithms from (Kiltz et al., 2015).
3.3 Groth-Sahai Commitments
In (Groth and Sahai, 2008), Groth and Sahai proposed
non-interactive zero-knowledge proof systems for
bilinear groups. It allows a prover to convince a
verifier that he possesses group elements or scalars
satisfying equations of a particular form. For our
work, we mainly use the satisfiability of pairing
product equations. Various instantiations were
proposed in this seminal paper based on common
hardness assumptions such as DLin and SXDH.
Initialization. We work in a bilinear group
(p,G
1
,G
2
,G
T
,e,g
1
,g
2
). The commitment keys for
group G
1
is u = (u
1
,u
2
). We initialize it with ran-
dom values α, β
$
← Z
∗
p
as u
1
= [1,α]
1
,u
2
= [β,αβ]
1
.
Hence, u is a Diffie-Hellman tuple in G
1
. This com-
mitment is binding but can be set to hiding if we de-
fine instead u
2
= βu
1
− (1,g
1
). The commitment key
v can be analogously defined for G
2
.
Group Element Commitment. To commit to a
group element X ∈ G
1
, using randomness r
1
,r
2
∈ Z
p
,
C(X ) = [r
1
u
1,1
+ r
2
u
2,1
,X + r
1
u
1,2
+ r
2
u
2,2
]
1
.
Scalar Commitment. To commit to a scalar x ∈ Z
p
,
using randomness r ∈ Z
p
,
C
0
(x) = [ru
1,1
+ xu
2,1
,ru
1,2
+ x(u
2,2
+ 1)]
1
Proofs. Under the SXDH assumption, the two ini-
tializations of the commitment key (perfectly binding
Round-optimal Constant-size Blind Signatures
217

or perfectly hiding) are indistinguishable. A Groth-
Sahai proof is a pair of elements (π,θ) ∈ G
2×2
1
×
G
2×2
2
. These elements are constructed to help veri-
fying pairing relations on committed values. Being
able to produce a valid pair implies knowing plain-
texts verifying the appropriate relations. We will note
hX i
1
for a committed group element in G
1
and hxi
2
for a committed scalar x in G
2
.
Throughout the paper, we are going to encounter
two kinds of relations.
• Linear Pairing Product Equations in G
1
:
[
∑
i
X
i
B
i
]
T
= [t]
T
to prove that the committed
group elements [X
i
]
1
satisfy a pairing product
relation with constants vector [B
i
]
2
equal to a
target group element in G
T
. In this particular
case, the proof is composed only of θ ∈ G
2
2
.
• Multi-scalar multiplications equations: [yA]
1
=
[X ]
1
to prove that the committed scalar in G
2
is
the discrete log of the committed element X com-
mitted in G
1
.
4 SIGNATURE ON
RANDOMIZABLE
CIPHERTEXT
A signature on randomizable ciphertexts, introduced
in (Blazy et al., 2011), is a primitive which allows
to sign a ciphertext, as well as all its randomiza-
tions (including the plaintext). It has been further
generalized in (Hanser and Slamanig, 2014; Fuchs-
bauer et al., 2019) to structure-preserving signature
on equivalence classes.
4.1 Definition and Security Properties
Definition 10. A Signature on Randomizable Cipher-
texts (SRC) scheme is composed by the seven follow-
ing algorithms:
• Setup(1
K
): generates the global parameters
param.
• KeyGen
E
(param) generates encryp-
tion/decryption keys (ek,dk).
• KeyGen
S
(param) generates verification/signing
keys (vk, sk).
• Enc(ek,vk,m; r) outputs a ciphertext c on mes-
sage m ∈ M with ek, using the random coins
r ∈ R .
• Sign(sk,ek,c; s), with random coins s ∈ R , out-
puts a signature σ, or ⊥ if c is not valid (w.r.t. ek,
and possibly vk).
• Decrypt(dk,vk,c) decrypts c using dk. It outputs
the plaintext, or ⊥ if c is invalid (w.r.t. ek, and
possibly vk).
• Verify(vk,ek,c,σ) checks whether σ is a valid sig-
nature on c, w.r.t. the public key vk. It outputs 1
if σ is valid, and 0 otherwise (possibly because
of an invalid ciphertext c, with respect to ek, and
possibly vk).
• Random(vk,ek,c, σ;r
0
) outputs a ciphertext c
0
that encrypts the same message as c under ek, and
a signature σ
0
on c
0
.
A signature on ciphertexts is called ciphertext ran-
domizable if a randomized signature on a random-
ized ciphertext is statistically indistinguishable from
a fresh one.
We will denote by 0
e
the neutral element in R that
keeps the ciphertexts unchanged after randomization.
4.1.1 Extractable Signatures on Randomizable
Ciphertexts
For SRC scheme,we define the following algorithm:
• SEDecrypt(dk,vk,σ), which is given a decryption
key, a verification key and a signature, outputs a
signature σ
0
.
Let us assume that there is a signature scheme S
where Setup
S
, Setup
E
are the respective projec-
tions of Setup on the signature and ciphertext
components, and that KeyGen
S
and KeyGen
E
are
the associated keygen projections. For (vk, sk) ←
KeyGen
S
(param),m ∈ M , random coins r ∈ R ,s ∈
R , c = Enc(ek, vk,m; r) and σ = Sign(sk,ek,c;s), the
output σ
0
= SEDecrypt(dk,vk,σ) is a valid signature
on m under vk, that is, Verify
S
(vk,m,σ
0
) is true.
An extractable SRC scheme SC allows the follow-
ing. First, a user can encrypt a message m and obtain a
signature σ on the ciphertext c. From (c,σ), the owner
of the decryption key can now not only recover the
encrypted message m, but also a signature σ
0
on the
message m, using the functionality SEDecrypt. The
signature σ on the ciphertext c could thus be seen as
an encryption of a signature on the message m: for
extractable signatures on ciphertexts, encryption and
signing can thus be seen as commutative (see Fig-
ure 7).
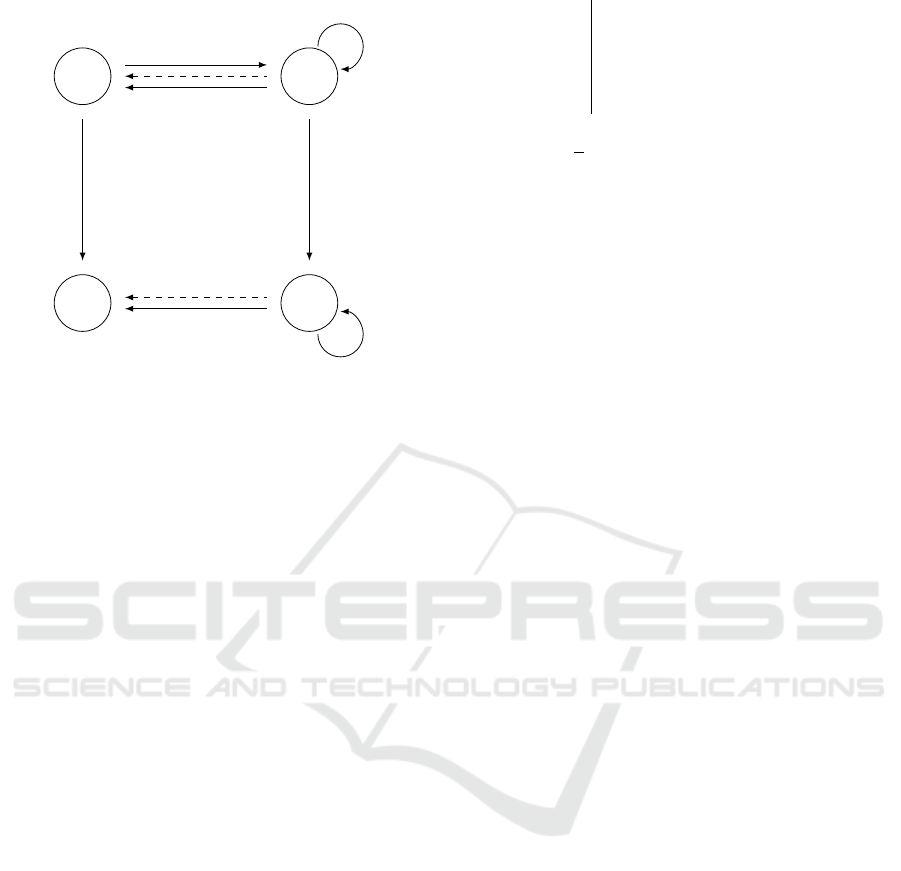
On this figure, one can easily see that SEDecrypt◦
Sign ◦ Enc = Sign
S
, guarantying therefore some kind
of commutativity between the signature and the en-
cryption:
• A message m can be encrypted using random
coins r (Enc);
• The signer can sign this ciphertext (Sign) and any-
one can randomize the inner cipher (Random);
• A signature on the plaintext can be obtained using
either dk (for SEDecrypt) or the coins r (if σ(c)
has not been randomized); the result is the same
SECRYPT 2020 - 17th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
218
σ(m) σ(c)
m c
dk
r
SEDecrypt
sk;s
Sign
S
sk,ek, c;s
Sign
dk
r
Decrypt
E
ek,r
Encrypt
r
0
Random
r
0
Random
Figure 7: Extractable signatures on randomizable cipher-
texts.
as a signature of m by the signer (Sign
S
).
Practical Aspect of Signature on Randomizable
Ciphertext. In practice, when running Random, one
wants to obtain a signature on a ciphertext unlink-
able to the execution (besides the tag), the final form
may not have to be identical to a fresh signature, nor
to be randomizable again. We call this algorithm
WRandom, and the natural verification algorithm for
the associated output is named WVerify.
• WRandom(vk,ek,c, σ;r
0
) outputs a ciphertext c
0
that encrypts the same message as c under the
public encryption key ek, and a signature σ
0
on
c
0
valid under vk, with the same tag.
4.2 Instantiation with SXDH
Our construction is presented in Figure 8 and a gen-
eralization from any k − MDDH assumption is pre-
sented in Appendix 7. It should be noted, that in this
case the WRandom algorithm drops the σ
ek
compo-
nent, while this may prevent a further randomization
of the signature, this is enough for the user to get a
fresh c
0
,σ
0
under the same tag.
Proof Idea. In order to prove the notion of unforge-
ability for this instantiation, we need the following
lemma from (Kiltz et al., 2015). Compared to the
original signature, we add a game in order to ran-
domize σ
ek
. The complete proof is presented in Ap-
pendix 7.
Lemma 1 (Computational core lemma for unbounded
CMA-security). For all adversaries A, there exists a
challenger B with T (A) ≈ T (B) and
Pr
A,B
$
← D
k
;
K
0
,K
1
$
← Z
k+1×k+1
p
τ
∗
/∈ Q
tag
(P
0
,P
1
)
def
= (B
|
K
0
,B
|
K
1
) ∈ (Z
k×k+1
p
)
2
∧b
0
= b vk
def
= ([P
0
]
1
,[P
1
]
1
,[B]
1
,K
0
A,K
1
A,A)
b
$
← {0,1}; b
0
$
← A
O
b
(.),O
∗
(.)
(vk)
≤
1
2
+ 2Q · Adv
mddh
D
k
,Setup
(B) + Q/q
where :
• O(τ) returns ([bµa
⊥
+ r
>
(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
,[r
>
B]
1
) ∈
(G
1×(k+1)
1
)
2
with µ
$
← Z
p
, r
$
← Z
k
q
and adds τ to
Q
msg
. Here, a
>
is a non-zero vector in Z
1×(k+1)
p
that satisfies a
⊥
A = 0.
• O
∗
([τ
∗
]
2
) returns [K
0
+τ
∗
K
1
]
2
. A only gets a sin-
gle call τ
∗
to O
∗
.
• Q is the number of queries A makes to O
b
.
5 BLIND SIGNATURE
5.1 High-level Idea
Following (Blazy et al., 2011), we can now provide a
blind signature scheme using our freshly made signa-
ture scheme on randomizable ciphertexts.
The intuition is that after recovering the signa-
ture σ
SRC
= Sign(sk, ek,c = Enc(ek, vk,m; r)); s), a
user can compute σ = WRandom(vk, ek,c,σ
SRC
,−r),
which is a valid signature on (1,m). This gives him a
signature on m.
The tricky part is now to achieve blindness. While
fully randomizing the signature (as in (Blazy et al.,
2011)) would be the best solution, this is not possi-
ble with the signature from (Kiltz et al., 2015) that
we consider in this paper. Instead, following Fis-
chlin’s idea in (Fischlin, 2006), we add a complete
zero-knowledge proof of the knowledge of σ. More-
over, due to the fact that we cannot extract a scalar τ
from a commitment, we need to commit to τ in G
2
,
and to the original σ
3
= [τσ
2
]
1
.
A high-level idea of the process (pre-blinding) is
explained in the figure 9.
5.2 Overview of the Construction
In this section, we instantiate algorithms from
the definition 9 of a blind signature BS =
(BSSetup,BSKeyGen,hS,Ui,Verify).
• BSSetup(K) calls the setup algorithm of the SRC
scheme. It outputs param.
• BSKeyGen(param) calls the KeyGen
S
algorithm
of the SRC scheme. It is run by the server S.
Round-optimal Constant-size Blind Signatures
219
Setup(1
K
):
Return param
KeyGen
E
(param):
dk = h
$
← Z
p
,ek = [1,h]
1
∈ G
2
1
Return ek,dk
KeyGen
S
(param):
A,B
$
← D
2
,X
$
← Z
2×2
p
K
0
,K
1
$
← Z
2×2
p
,
C = KA ∈ Z
k+1
p
(C
0
,C
1
) = (K
0
A,K
1
A) ∈
Z
2
p
× Z
2
p
(P
0
,P
1
) = (B
>
K
0
,
B
>
K
1
) ∈ Z
1×2
p
× Z
1×2
p
sk = (K, [P
0
]
1
,[P
1
]
1
,[B]
1
)
vk = ([C
0
]
2
,[C
1
]
2
,[C
2
]
2
,[A]
2
)
Return vk,sk
Enc(ek,⊥, m):
r
$
← Z
p
, c = [r, rh + m]
1
Return c
Sign(sk,ek, c; s) :
s
$
← Z
p
,τ
$
← Z
p
σ
1
= [(1, c
>
)K + s(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
∈ G
1×2
1
σ
ek
= [(0, ek
>
)K + s(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
∈ G
1×2
1
σ
2
= [sB
>
]
1
∈ G
1×2
1
, σ
τ
= τ ∈ Z
p
Return σ = (σ
1
,σ
ek
,σ
2
,σ
τ
)
Verify(vk,ek,c,σ)
Check whether:
[σ
1
A
>
]
T
= [(1, c
>
)C
>
+σ
2
(C
>
0
+σ
τ
C
>
1
)]
T
[σ
ek
A
>
]
T
= [(0,ek
>
)C
>
+ σ
2
(C
>
0
+
σ
τ
C
>
1
)]
T
Decrypt(dk,c) :
Return [m]
1
= c
2
/c
dk
1
= [rh + m − rh]
1
WRandom(vk,ek, c, σ) :
r
0
$
← Z
p
Compute c
0
= c + [r
0
,r
0
h]
1
and update:
σ
0
1
= σ
1
+ r
0>
σ
ek
, σ
0
2
= (1 + r
0
)σ
2
Return c
0
and σ
0
= (σ
0
1
,σ
0
2
,σ
τ
)
WVerify(vk,ek,c
0
,σ
0
)
Check whether:
[σ
1
A
>
]
T
= [(1,c
>
)C
>
+ σ
2
(C
>
0
+
σ
τ
C
>
1
)]
T
Figure 8: SXDH Instantiation of Constant Size SRC.
σ(m) σ(c)
m c
r
sk,ek, c;s
Sign
SE
dk
r
Decrypt
E
ek,r
Encrypt
SE
User
Signer
Figure 9: High level Blind Signature.
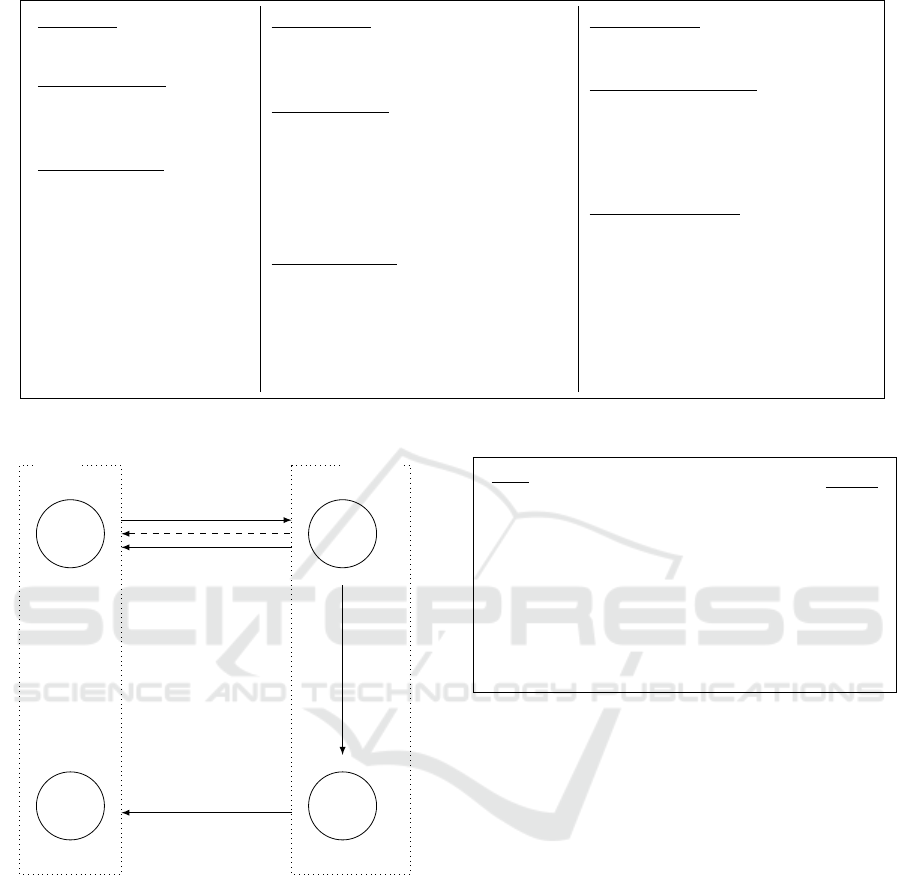
• Signature Issuing is described by Figure 10. It is
an interactive protocol in which the user U has
to encrypt its message and send it to the signer S
which in return computes a SRC signature σ
SRC
.
Having received σ
SRC
, U checks its validity using
vk. If it is valid, he extracts a signature on m by
using the WRandom algorithm.
Following Fischlin’s framework, the blind signa-
ture consists in the NIZK proof π guaranteeing U
has the elements satisfying the signature verifica-
tion equations w.r.t to vk and m.
• Verify(vk,σ) calls the NIZK proof verification
algorithm. If the proof is valid, the signature is
valid and it outputs 1, otherwise 0.
User Signer
c ← Enc(ek,vk, m;r)
c
−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−→
σ
SRC
= Sign(sk,ek,c;s,τ)
σ
SRC
←−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−
If Verify(vk,ek,c,σ
SRC
) outputs 1 then
σ = WRandom(vk,ek, c,σ
SRC
;−r)
NIZK.Prove(σ,Verify(vk,ek,m,σ))
Figure 10: Blind Signature.
5.3 Security Results and Proofs Ideas
Theorem 1. Our construction achieves the blindness
property under the SXDH assumption.
Proof Idea. Every value sent by the user is either
encrypted (committed) or a Zero-Knowledge proof.
The flow in the SRC hides the target message, while
the Zero-Knowledge proof hides both the tag and
the randomness used in the signature. Hence, un-
der the IND-CPA property of the encryption and the
Zero-Knowledge property of the proof, the scheme
achieves blindness.
Theorem 2. Our construction is unforgeable under
the XDH in G
1
and D
1
− KerMDDH in G
2
.
Proof Idea. Following the original proof from (Kiltz
et al., 2015), we proceed via successive games. First,
we guess whether the adversary picks a fresh tag for
the forgery or reuse one of the signature he received,
and we simulate all the other answers. Then, we show
that for a given tag, the signature becomes a valid 1-
time signature.
SECRYPT 2020 - 17th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
220

σ(m) σ(c)
m c
dk
SEDecrypt
sk,ek, c;s
Sign
r
ek,r
Encrypt
r
0
Random
User
Authority
Figure 11: Viewing an SRC as a e-voting solution.
6 APPLICATION TO E-VOTING
WITH RECEIPT FREENESS
In voting schemes, anonymity is a crucial property,
since nobody should be able to learn the content of
someone else’s vote. This can be achieved using ho-
momorphic encryption schemes. Basically, each user
will compute his vote v
i
, commit it into c
i
, and then,
through the homomorphic property of the encryption
scheme, the voting center will compute f (c
1
,. .., c
n
)
and open it to solely obtain the global result of the
election.
However, this does not address the problem of
vote sellers: a voter may sell his vote and then re-
veal/prove the content of his encrypted vote to the
buyer. He could do so by simply revealing the ran-
domness used when encrypting the vote, which al-
lows to verify that a claimed message was encrypted.
To avoid this, we need to be able to randomize en-
cryption, and adapt the signature accordingly. But be-
fore doing so, the voting center randomizes c into c
0
(which cannot be opened by the voter anymore since
he no longer knows the random coins) and then proves
(in a non-transferable way) that c and c
0
contain the
same plaintext. The used proof is thus a designated-
verifier zero-knowledge proof. Finally, after receiving
c
0
and being convinced by the proof, the voter signs c
0
.
Our SRC allows to avoid those extra interactions:
a voter simply encrypts his vote v as c and makes a
signature σ on c. The voting center can now consis-
tently randomize both c and σ as c
0
and σ
0
, so that
the randomness used in c
0
is unknown to the signer,
who is however guaranteed that the vote was not mod-
ified by the voting center because of the unforgeabil-
ity notion for SRC. We have thus constructed a non-
interactive receipt-free voting scheme.
2
Since our SRC candidates use both randomizable
and homomorphic encryption schemes, classical tech-
niques for voting schemes with homomorphic encryp-
tion and threshold decryption can be used (Baudron
et al., 2001): there is no risk for the signature on
the ciphertext to be converted into a signature on the
plaintext if the board of authorities uses the decryp-
tion capability on the encrypted tally only.
The size of the ballot is only 6 group elements and
a scalar in the instantiation with using ElGamal, in-
dependently from the number of check boxes in the
vote.
7 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we answer to an open question raised
during Eurocrypt’19, by providing the first round-
optimal constant-size blind signature in the standard
model based on a classical assumption. Towards this
goal, we give the first constant-size signature on ran-
domized ciphertext as a side contribution. This sig-
nature is based upon a variant of structure-preserving
signature.
Our blind signature scheme offers several advan-
tages: in addition to being constant-size in terms of
interaction (rather than asking the user to send a first
flow linear in the size of the message to be signed)
and to being built under well-studied security assump-
tions, the signature kept on the user side remains very
compact (4 group elements and 1 scalar), which is of
critical importance for constrained systems.
One way to improve the final size of the signature
would be to find a randomizable structure-preserving
signature, in order to get rid of the zero-knowledge
proof. More generally, finding the lower bound for
a blind signature in the standard model remains an
open question. Finally, following the study initiated
in (R
¨
uckert, 2010), future work could include finding
a post-quantum version of our scheme (building on a
lattice- or code-based assumption).
2
We want to stress, that as the secret signing key is se-
cret, users cannot craft fake encrypted ballot in a way that
would allow two of them to be combined in a third one. In
addition, as the signer changes the tag with every signing
query, this combination would be impossible.
Round-optimal Constant-size Blind Signatures
221

ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like thanks the rewievers for detailed com-
ments. This work was supported in part by the
French ANR projects IDFIX (ANR-16-CE39-0004)
and CryptiQ (ANR-18-CE39-0015).
REFERENCES
Abe, M. (2001). A secure three-move blind signature
scheme for polynomially many signatures. In Pfitz-
mann, B., editor, EUROCRYPT 2001, volume 2045 of
LNCS, pages 136–151. Springer, Heidelberg.
Abe, M., Fuchsbauer, G., Groth, J., Haralambiev, K., and
Ohkubo, M. (2010). Structure-preserving signatures
and commitments to group elements. In Rabin, T.,
editor, CRYPTO 2010, volume 6223 of LNCS, pages
209–236. Springer, Heidelberg.
Ateniese, G., Camenisch, J., Hohenberger, S., and
de Medeiros, B. (2005). Practical group signatures
without random oracles. Cryptology ePrint Archive,
Report 2005/385.
Baldimtsi, F. and Lysyanskaya, A. (2013). On the secu-
rity of one-witness blind signature schemes. In Sako,
K. and Sarkar, P., editors, ASIACRYPT 2013, Part II,
volume 8270 of LNCS, pages 82–99. Springer, Hei-
delberg.
Baudron, O., Fouque, P.-A., Pointcheval, D., Stern, J., and
Poupard, G. (2001). Practical multi-candidate elec-
tion system. In Kshemkalyani, A. D. and Shavit, N.,
editors, 20th ACM PODC, pages 274–283. ACM.
Belenkiy, M., Camenisch, J., Chase, M., Kohlweiss, M.,
Lysyanskaya, A., and Shacham, H. (2009). Random-
izable proofs and delegatable anonymous credentials.
In Halevi, S., editor, CRYPTO 2009, volume 5677 of
LNCS, pages 108–125. Springer, Heidelberg.
Bellare, M. and Rogaway, P. (1993). Random oracles are
practical: A paradigm for designing efficient proto-
cols. In Denning, D. E., Pyle, R., Ganesan, R.,
Sandhu, R. S., and Ashby, V., editors, ACM CCS 93,
pages 62–73. ACM Press.
Blazy, O., Fuchsbauer, G., Pointcheval, D., and Vergnaud,
D. (2011). Signatures on randomizable ciphertexts. In
Catalano, D., Fazio, N., Gennaro, R., and Nicolosi,
A., editors, PKC 2011, volume 6571 of LNCS, pages
403–422. Springer, Heidelberg.
Blazy, O., Pointcheval, D., and Vergnaud, D. (2012a). Com-
pact round-optimal partially-blind signatures. In Vis-
conti, I. and Prisco, R. D., editors, SCN 12, volume
7485 of LNCS, pages 95–112. Springer, Heidelberg.
Blazy, O., Pointcheval, D., and Vergnaud, D. (2012b).
Round-optimal privacy-preserving protocols with
smooth projective hash functions. In Cramer, R., edi-
tor, TCC 2012, volume 7194 of LNCS, pages 94–111.
Springer, Heidelberg.
Boneh, D., Boyen, X., and Shacham, H. (2004).
Short group signatures. In Franklin, M., editor,
CRYPTO 2004, volume 3152 of LNCS, pages 41–55.
Springer, Heidelberg.
Brands, S. (1994). Untraceable off-line cash in wallets with
observers (extended abstract). In Stinson, D. R., ed-
itor, CRYPTO’93, volume 773 of LNCS, pages 302–
318. Springer, Heidelberg.
Camenisch, J., Hohenberger, S., and Lysyanskaya, A.
(2005). Compact e-cash. In Cramer, R., editor, EURO-
CRYPT 2005, volume 3494 of LNCS, pages 302–321.
Springer, Heidelberg.
Camenisch, J. and Lysyanskaya, A. (2001). An efficient
system for non-transferable anonymous credentials
with optional anonymity revocation. In Pfitzmann,
B., editor, EUROCRYPT 2001, volume 2045 of LNCS,
pages 93–118. Springer, Heidelberg.
Chaum, D. (1982). Blind signatures for untraceable pay-
ments. In Chaum, D., Rivest, R. L., and Sherman,
A. T., editors, CRYPTO’82, pages 199–203. Plenum
Press, New York, USA.
Chaum, D., Fiat, A., and Naor, M. (1990). Untraceable elec-
tronic cash. In Goldwasser, S., editor, CRYPTO’88,
volume 403 of LNCS, pages 319–327. Springer, Hei-
delberg.
ElGamal, T. (1984). A public key cryptosystem and a signa-
ture scheme based on discrete logarithms. In Blakley,
G. R. and Chaum, D., editors, CRYPTO’84, volume
196 of LNCS, pages 10–18. Springer, Heidelberg.
Escala, A., Herold, G., Kiltz, E., R
`
afols, C., and Villar, J.
(2013). An algebraic framework for Diffie-Hellman
assumptions. In Canetti, R. and Garay, J. A., editors,
CRYPTO 2013, Part II, volume 8043 of LNCS, pages
129–147. Springer, Heidelberg.
Fischlin, M. (2006). Round-optimal composable blind sig-
natures in the common reference string model. In
Dwork, C., editor, CRYPTO 2006, volume 4117 of
LNCS, pages 60–77. Springer, Heidelberg.
Fuchsbauer, G. (2011). Commuting signatures and verifi-
able encryption. In Paterson, K. G., editor, EURO-
CRYPT 2011, volume 6632 of LNCS, pages 224–245.
Springer, Heidelberg.
Fuchsbauer, G., Hanser, C., and Slamanig, D. (2019).
Structure-preserving signatures on equivalence
classes and constant-size anonymous credentials.
Journal of Cryptology, 32(2):498–546.
Fuchsbauer, G., Pointcheval, D., and Vergnaud, D. (2009).
Transferable constant-size fair e-cash. In Garay, J. A.,
Miyaji, A., and Otsuka, A., editors, CANS 09, volume
5888 of LNCS, pages 226–247. Springer, Heidelberg.
Fujioka, A., Okamoto, T., and Ohta, K. (1993). A practical
secret voting scheme for large scale elections. In Se-
berry, J. and Zheng, Y., editors, Advances in Cryptol-
ogy — AUSCRYPT ’92, pages 244–251, Berlin, Hei-
delberg. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Ghadafi, E. (2017). Efficient round-optimal blind signa-
tures in the standard model. In Kiayias, A., editor,
FC 2017, volume 10322 of LNCS, pages 455–473.
Springer, Heidelberg.
Goldwasser, S. and Micali, S. (1984). Probabilistic en-
cryption. Journal of Computer and System Sciences,
28(2):270–299.
SECRYPT 2020 - 17th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
222

Goldwasser, S., Micali, S., and Rivest, R. L. (1988).
A digital signature scheme secure against adaptive
chosen-message attacks. SIAM Journal on Comput-
ing, 17(2):281–308.
Groth, J. and Sahai, A. (2008). Efficient non-interactive
proof systems for bilinear groups. In Smart, N. P., edi-
tor, EUROCRYPT 2008, volume 4965 of LNCS, pages
415–432. Springer, Heidelberg.
Hanser, C. and Slamanig, D. (2014). Structure-preserving
signatures on equivalence classes and their application
to anonymous credentials. In Sarkar, P. and Iwata,
T., editors, ASIACRYPT 2014, Part I, volume 8873 of
LNCS, pages 491–511. Springer, Heidelberg.
Hauck, E., Kiltz, E., and Loss, J. (2019). A modu-
lar treatment of blind signatures from identification
schemes. In Ishai, Y. and Rijmen, V., editors, EURO-
CRYPT 2019, Part III, volume 11478 of LNCS, pages
345–375. Springer, Heidelberg.
Kiltz, E., Pan, J., and Wee, H. (2015). Structure-
preserving signatures from standard assumptions, re-
visited. In Gennaro, R. and Robshaw, M. J. B., editors,
CRYPTO 2015, Part II, volume 9216 of LNCS, pages
275–295. Springer, Heidelberg.
Okamoto, T. (1993). Provably secure and practical identifi-
cation schemes and corresponding signature schemes.
In Brickell, E. F., editor, CRYPTO’92, volume 740 of
LNCS, pages 31–53. Springer, Heidelberg.
Okamoto, T. (2006). Efficient blind and partially blind sig-
natures without random oracles. In Halevi, S. and
Rabin, T., editors, TCC 2006, volume 3876 of LNCS,
pages 80–99. Springer, Heidelberg.
Okamoto, T. and Ohta, K. (1992). Universal electronic cash.
In Feigenbaum, J., editor, CRYPTO’91, volume 576 of
LNCS, pages 324–337. Springer, Heidelberg.
Pointcheval, D. and Stern, J. (2000). Security arguments
for digital signatures and blind signatures. Journal of
Cryptology, 13(3):361–396.
R
¨
uckert, M. (2010). Lattice-based blind signatures. In Abe,
M., editor, ASIACRYPT 2010, volume 6477 of LNCS,
pages 413–430. Springer, Heidelberg.
Schr
¨
oder, D. and Unruh, D. (2012). Security of blind
signatures revisited. In Fischlin, M., Buchmann, J.,
and Manulis, M., editors, PKC 2012, volume 7293 of
LNCS, pages 662–679. Springer, Heidelberg.
APPENDIX
PROOFS OF OUR SRC
CONSTRUCTIONS
Unforgeability Proof
In this section, we present the proof of unforgeability
for our SRC construction. As we use a SPS of Kiltz
et.al, our proof is an adaptation from their.
Proof. Game 1. In this game, we modify the ver-
ification algorithm. The pairing equation became :
[σ
1
· 1]
T
= [(1,m
>
K) · 1 + σ
2
· (K
0
+ τK
1
)]
T
.
Suppose [σ
2
· σ
4
]
T
= [σ
3
]
T
, we note that:
[σ
1
· A]
T
= [(1,m
>
) · C + σ
2
· C
0
+ σ
3
· C
1
]
T
⇐⇒ [σ
1
· A]
T
= [(1,m
>
) · KA + σ
2
· K
0
A + σ
3
· K
1
A]
T
⇐⇒ [σ
1
· 1]
T
= [(1,m
>
) · K + σ
2
· K
0
+ σ
3
· K
1
]
T
⇐⇒ [σ
1
· 1]
T
= [(1,m
>
) · K + σ
2
· (K
0
+ τK
1
)]
T
The value σ
1
− ([(1,m
>
)K]
1
+ σ
2
K
0
+ σ
3
K
1
) ∈
G
1×(k+1)
1
is a non-zero vector in the kernel of
A, which is hard to be computed under the D
k
-
KerMDDH assumption in G
2
. This means that:
|Adv
0
− Adv
1
| ≤ Adv
k−MDDH
D
k
,Setup
(B
0
).
Game 2. Let τ
1
,...,τ
Q
the randomly chosen tags
in the Q queries made by the adversary A to OSign.
We abort if τ
1
,...,τ
Q
are not all distinct. So, we ob-
tain: Adv
1
≥ Adv
1
− Q
2
/2q.
Game 3. We define τ
Q +1
def
= τ
∗
. Now, pick ı
∗
$
←
[Q +1] and abort if i
∗
is not the smallest index of i
∗
for
which τ
∗
= τ
i
. In the rest of the proof, we focus on the
case we do not abort i.e τ
∗
= τ
i
∗
and τ
1
,...,τ
i
∗
−1
are all
different from τ
∗
. Given τ, OSign can check whether
τ
∗
equals τ. For the rest i
∗
− 1 queries, answer NO,
and starting from the i
∗
’th query, we know τ
∗
.
Hence, we have: Adv
3
≥
1
Q+1
Adv
2
.
Game 4.1. We switch OSign to OSign
∗
1
:
OSign
∗
1
: OSign
∗
2
r
$
← Z
p
;τ
$
← Z
p
;µ
1
$
← Z
p
σ
1
def
= [(1,C
1
,C
2
)K + µ
1
a
⊥
+ r
>
(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
∈ G
1×2
1
σ
ek
def
= [(0,1, ek)K + r
>
(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
∈ G
1×2
1
σ
ek
def
= [(0,1, ek)K + µ
2
a
⊥
+ r
>
(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
∈ G
1×2
1
σ
2
def
= [r
|
B
|
]
1
∈ G
1×2
1
, σ
τ
def
= τ ∈ Z
p
Return(σ
1
,σ
ek
,σ
2
,σ
τ
)
Here, a
⊥
∈
1×(k+1)
is non-zero vector in the ker-
nel of A such that: a
⊥
A = 0. We will apply
Lemma 1 in order to show: |Adv
3
− Adv
4.1
| ≥
2Q Adv
mddh
D
k
,Setup
(B
1
)+Q /q. We pick K and we use O
b
to simulate either OSign or OSign
∗
1
and O
∗
to simulate
Verify as follow:
• For the i’th signing query where i 6= i
∗
,
we query O
b
at τ
$
← Z
p
to obtain:
(σ
0
1
,σ
2
)
def
= ([bµ
1
a
⊥
+ r
>
(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
,[r
>
B
>
]
2
)
with b
$
← {0,1} and we return:
(σ
1
def
= [(1,m>)K]
1
· σ
0
1
,σ
ek
,σ
2
,σ
3
,σ
4
).
• For the i
∗
’th query, where i
∗
≤ Q , we run Sign
honestly.
• For Verify
∗
, we will query O
∗
on τ
∗
to get [K
0
+
τ
∗
K
1
]
2
. The latter is sufficient to simulate Verify
∗
Round-optimal Constant-size Blind Signatures
223

query by computing [σ · (K
0
+ τ
∗
K
1
)]
T
.
So, we are allowed to build a distinguisher for
Lemma 1.
Game 4.2.
We have to modify σ
ek
in the same way as before:
In order to apply lemma 1, we simulate oracles:
• For i 6= i
∗
, we have:
(σ
0
1
,σ
0
ek
,σ
2
)
def
=([bµ
1
a
⊥
+ r
>
(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
,
[bµ
2
a
⊥
+ r
>
(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
,[r
>
B
>
]
2
).
We return: (σ
1
def
= [(1, m>)K]
1
· σ
0
1
,σ
ek
def
=
[(1,m>)K]
1
· σ
0
ek
,σ
2
,σ
4
).
• For the challenge, we run Sign honestly.
Game 5. In this game we modify the matrix K
in Setup algorithm. We switch K by K = K
0
+ ua
⊥
with K
$
← Z
(n+1)×(k+1)
p
and u
$
← Z
n+1
p
. ua
⊥
is masked
by a uniform matrix K
0
, K is still uniformly random.
Thus, Game 5 and Game 4.2 are identical, so we have:
Adv
5
= Adv
4.2
.
Now, we have to bound Adv
5
.
• C = KA = (K
0
+ ua
⊥
)A = K
0
A. u is completely
hide.
• OSign
∗
2
on (C
1
,C
2
,ek, τ) for τ 6= τ
∗
returns:
(1,C
1
,C
2
)(K
0
+ ua
⊥
) + µ
1
a
⊥
and (0,1, ek) +
(K
0
+ua
⊥
)+µ
2
a
⊥
. u is hide since outputs is iden-
tically distributed as: (1,C
1
,C
2
)K
0
+ µ
1
a
⊥
and
(0,1,ek)K + µ
2
a
⊥
.
• OSign
∗
2
on τ
∗
leaks (1,C
1
,C
2
)K
0
+ µ
1
a
⊥
and
(1,ek)K+µ
2
a
⊥
, which is captured by (1,C
1
,C
2
)u
and by (0,1,ek)u.
The adversary has to compute correctly:
(1,C
∗
1
,C
∗
2
)(K
0
+ ua
⊥
) and (0,1,ek)(K
0
+ ua
⊥
)
to convince Verify
∗
to accept a signature σ
∗
on
(1,C
∗
1
,C
∗
2
) and on (0,1,ek
∗
). As u
$
← Z
k+1
p
,
(1,C
∗
1
,C
∗
2
)u and (0,1,ek
∗
)u are in Z
p
.
Given (1,C
∗
1
,C
2
∗)u and (0, 1,ek
∗
)for any adap-
tively chosen (C
∗
1
,C
∗
2
) 6= (C
1
,C
2
) and ek
∗
6= ek,
(1,C
∗
1
,C
∗
2
)u and (0,1,ek
∗
)u are uniformly random
over Z
p
from the adversary’s view-point.
Proof of Blindness
Proof. We proceed via a series of games.
Game 0. This is the Blindness experiment from fig-
ure 5: Adv
0
= Adv
Blind
BS
.
In this game, we don’t modify existing algorithms.
During the different games, A proposed two messages
m
0
and m
1
to the challenger.
Game 1. Both proofs are replaced by simulated ones
thanks to the Zero-Knowledge property of the Groth-
Sahai proof system. We replace the NIZK algorithm
by a simulated one. Thus, we have:
Adv
0
≤ Adv
1
+ Adv
SXDH
GS
Game 2. Both encryptions of m
0
and m
1
are
replaced by random group elements i.e the chal-
lenger encrypts a random group element noted v
instead of m
b
. By the indistinguishability prop-
erty of the ElGamal encryption scheme, we have:
Adv
1
≤ Adv
2
+ Adv
SXDH
EG
In this game, A is given absolutely no information
on m
0
and m
1
therefore Adv
2
= 0.
GENERIC CONSTRUCTION
We present the generalization of our SXDH constant
size SRC. The construction is derived from (Kiltz
et al., 2015), and proofs have to be tweaked the same
way to achieve unforgeability for equivalence classes.
Setup(1
K
):Return param
KeyGen(param):
ek = [H]
1
$
← G
(k+1)×k
1
, dk = H ∈ Z
(k+1)×k
p
Return ek,dk
KeyGen(param):
A,B
$
← D
k+1
,X
$
← Z
k+1×k+1
p
, K
0
,K
1
$
← Z
k+1×k+1
p
C = KA ∈ Z
k+1
p
(C
0
,C
1
) = (K
0
A,K
1
A) ∈ (Z
k+1
p
)
2
(P
0
,P
1
) = (B
>
K
0
,B
>
K
1
) ∈ (Z
1×(k+1)
p
)
2
sk = (K, [P
0
]
1
,[P
1
]
1
,[B]
1
)
vk = ([C
0
]
2
,[C
1
]
2
,[C
2
]
2
,[a]
2
)
Return vk,sk
Enc(ek,⊥,m):
r
$
← Z
p
, Return c = [r, rh + M]
1
Sign(sk,ek,c;
~
s) :
s
$
← Z
k
p
,τ
$
← Z
p
σ
1
= [(1,c
>
)K + s
>
(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
∈ G
1×k+1
1
σ
ek
= [(0,H
>
)K + s
>
(P
0
+ τP
1
)]
1
∈ G
k×k+1
1
σ
2
= [s
>
B
>
]
1
∈ G
1×k+1
1
, σ
τ
= τ ∈ Z
p
Return σ = (σ
1
,σ
ek
,σ
2
,σ
τ
)
Decrypt(ek,c) :
Return [m]
1
= c
2
/c
dk
1
= [rh + m − rh]
1
Verify(vk,ek, c, σ)
Check whether:
[σ
1
a
>
]
T
= [(1,c
>
)C
>
+ σ
2
(C
>
0
+ σ
τ
C
>
1
)]
T
[σ
ek
a
>
]
T
= [(0,ek
>
)C
>
+ σ
2
(C
>
0
+ σ
τ
C
>
1
)]
T
Figure 12: Generic Construction of Constant Size SRC.
SECRYPT 2020 - 17th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
224
