
SwaNN: Switching among Cryptographic Tools for Privacy-preserving
Neural Network Predictions
Gamze Tillem
1
, Beyza Bozdemir
2
and Melek
¨
Onen
2
1
Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands
2
EURECOM, Sophia Antipolis, France
Keywords:
Privacy, Neural Networks, Secure Two-party Computation, Homomorphic Encryption.
Abstract:
The rise of cloud computing technology led to a paradigm shift in technological services that enabled enter-
prises to delegate their data analytics tasks to cloud servers which have domain-specific expertise and com-
putational resources for the required analytics. Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) is one such service
which provides the enterprises to perform machine learning tasks on the cloud. Despite the advantage of elimi-
nating the need for computational resources and domain expertise, sharing sensitive data with the cloud server
brings a privacy risk to the enterprises. In this paper, we propose SwaNN, a protocol to privately perform
neural network predictions for MLaaS. SwaNN brings together two well-known techniques for secure com-
putation: partially homomorphic encryption and secure two-party computation, and computes neural network
predictions by switching between the two methods. The hybrid nature of SwaNN enables to maintain the ac-
curacy of predictions and to optimize the computation time and bandwidth usage. Our experiments show that
SwaNN achieves a good balance between computation and communication cost in neural network predictions
compared to the state-of-the-art proposals.
1 INTRODUCTION
Neural networks (NN) are a method of supervised ma-
chine learning (ML) which aims to solve a classifi-
cation problem. Although the research on NN dates
back to 1980s (Fukushima et al., 1983), they had not
been commonly used due to their long training times.
With the recent technological advances and the adap-
tation of GPUs in computation systems, the training
time for NN is reduced significantly (Ciresan et al.,
2012) and this improvement triggered the popularity
and outstanding success of NN in certain fields such
as image classification (Ciresan et al., 2012).
The success of NN attracted many companies to
apply it to their businesses. MLaaS enables them to
outsource their ML tasks to a cloud server which has
computational resources and ML expertise (Ribeiro
et al., 2015). A major risk in using MLaaS is the sen-
sitivity of the data sent to the cloud. The concern of
exposing privacy-sensitive data in MLaaS requires the
design of privacy-preserving protocols for ML meth-
ods.
In this paper, we aim to design one such proto-
col for MLaaS to compute NN predictions under pri-
vacy preservation. We assume that the network model
has already been computed during a previous train-
ing phase, and we only focus on the privacy of data
items during the prediction phase. Privacy problem in
MLaaS drew the attention of researchers recently and
several mechanisms have already been proposed. So-
lutions are either based on homomorphic encryption
(HE) (Gilad-Bachrach et al., 2016; Chabanne et al.,
2017; Barni et al., 2006; Orlandi et al., 2007) or
secure two-party computation (2PC) (Mohassel and
Zhang, 2017; Mohassel and Rindal, 2018; Liu et al.,
2017). HE-based solutions usually incur high com-
putation cost and the interactive nature of 2PC-based
solutions leads to a higher bandwidth usage.
Having studied existing solutions, we aim to take
the simple cryptographic tools of both worlds and
optimize the computational and the communication
overhead at the same time. We propose a hybrid pro-
tocol, SwaNN, which switches the computations be-
tween HE and 2PC. We make use of partially HE
(more specifically the additively homomorphic Pail-
lier encryption) to perform linear operations over en-
crypted data. Non-linear operations are supported
thanks to the use of 2PC. We show how to easily
switch from one cryptographic tool to the other. The
combination of these two cryptographic tools helps
Tillem, G., Bozdemir, B. and Önen, M.
SwaNN: Switching among Cryptographic Tools for Privacy-preserving Neural Network Predictions.
DOI: 10.5220/0009890704970504
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2020) - SECRYPT, pages 497-504
ISBN: 978-989-758-446-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
497

maintain the accuracy of predictions.
SwaNN is designed to support two different set-
tings: a client-server setting and a non-colluding two-
server setting. In the client-server setting, the major-
ity of operations are delegated to the server, and the
client helps the server in intermediate steps. In the
two-server setting, the servers perform all operations
simultaneously, with a balanced workload. Our con-
tributions can be summarized as follows:
• We propose a hybrid protocol for NN predictions,
which is based on the additively homomorphic
Paillier encryption scheme and 2PC. We show
how each underlying operation can be supported
easily with the use of these two schemes, only.
• Our protocol is flexible since it is suitable both
for the client-server setting and the non-colluding
two-server setting.
• Compared to existing works, our protocol deploys
several optimizations for the computations in the
linear layers of neural networks which improves
the efficiency in terms of computation cost. These
optimizations consist of some data packing dedi-
cated to the Paillier cryptosystem and the use of
multi-exponentiation algorithm to reduce the cost
of multiplications.
• The empirical results show that our protocol can
compute the prediction within a neural network
with two activation layers in 10 seconds with 1.73
MB bandwidth usage which is 30-fold better in
computation cost than the HE-based solution and
28-fold more efficient in bandwidth usage than the
2PC-based solution.
2 PRELIMINARIES
Convolutional Neural Networks. CNNs are specif-
ically designed for image recognition. They combine
a series of layers to perform classification. The first
layer of NN is the input layer, where the input image
is provided to the network. The last layer is the output
layer, where the result of the classification is returned.
The layers in between are called hidden layers. Each
hidden layer takes an input X, evaluates a function f
on the input optionally along with a weight matrix W,
and returns an output Y to the subsequent layer. More
details on CNNs’ hidden layers can be found in the
full version of this paper (Tillem et al., 2020).
Homomorphic Encryption and Secure Two-party
Computation. The homomorphic property enables a
cryptosystem to perform operations on the encrypted
input without decryption. If a cryptosystem enables
both additions and multiplications under encryption,
it is called fully homomorphic whereas if it supports
a single type of operation, it is called partially ho-
momorphic. Despite their flexibility on performing
both types of operations, fully homomorphic cryp-
tosystems are expensive in computation. Partially ho-
momorphic schemes remain more efficient. In this
paper, we use a partially homomorphic cryptosys-
tem, namely the Paillier cryptosystem (Paillier, 1999)
which supports additive homomorphism.
Secure two-party computation (2PC) enables two
parties to jointly compute a function f on their in-
puts without revealing the inputs to each other. In our
work, we use arithmetic secret sharing (Beaver, 1991)
and Boolean secret sharing (Goldreich et al., 2019).
In arithmetic sharing, additions can be computed lo-
cally without any additional cost. A multiplication
operation requires some additional computation and
communication cost; however, it is less expensive
than the multiplication in Boolean sharing (Demm-
ler et al., 2015). Therefore, in our protocol, we use
arithmetic sharing for addition and multiplication op-
erations. When other types of operations such as com-
parisons are needed, we use Boolean sharing.
We use the following notation throughout the pa-
per: [x] represents a Paillier encryption of plaintext x
and
h
x
i
i
represents party i’s share x for 2PC opera-
tions.
3 PRIOR WORK
We provide a sketch of the analysis of existing
privacy-preserving neural networks (PP-NN). For the
complete analysis, we refer the reader to the full ver-
sion of this paper (Tillem et al., 2020).
Existing PP-NN solutions can be regrouped into
two main categories based on the underlying cryp-
tographic technique. The first category of solu-
tions (Mohassel and Zhang, 2017; Mohassel and
Rindal, 2018; Liu et al., 2017; Rouhani et al., 2018;
Riazi et al., 2018; Dahl et al., 2018; Wagh et al.,
2019; Riazi et al., 2019) consists of solutions based
on secure multi-party computation. The most relevant
work to SwaNN is MiniONN (Liu et al., 2017) which
defines oblivious transformations for each CNN op-
eration and implements these transformations using
ABY (Demmler et al., 2015). The second category
of solutions (Gilad-Bachrach et al., 2016; Chabanne
et al., 2017; Ibarrondo and
¨
Onen, 2018; Hesamifard
et al., 2017; Bourse et al., 2018; Sanyal et al., 2018;
Hesamifard et al., 2018; Jiang et al., 2018; Chou
et al., 2018) correspond to those based on fully homo-
morphic encryption (FHE). To the best of our knowl-
edge, CryptoNets (Gilad-Bachrach et al., 2016) is the
SECRYPT 2020 - 17th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
498

first PP-NN based on FHE and uses the SEAL li-
brary (SEAL, 2018) to compute CNN predictions on
encrypted inputs.
In comparison with existing solutions from these
two categories, we propose to take advantage of both
cryptographic techniques and design a hybrid proto-
col that combines 2PC with partially HE. To reduce
the computational cost, FHE is replaced with the addi-
tively homomorphic Paillier encryption scheme. This
algorithm is used to compute linear operations and
the x
2
function using a dedicated interactive protocol.
Additionally, we obtain better performance results for
computing nonlinear operations thanks to 2PC.
Few early approaches, such as (Barni et al., 2006;
Orlandi et al., 2007), also use Paillier and Yao’s gar-
bled circuits (GCs). Gazelle (Juvekar et al., 2018) is
a secure NN inference scheme implemented under a
dedicated lattice-based HE scheme. This solution also
makes use of Yao’s GCs to perform ReLU and to re-
duce the noise in the ciphertext.
4 SwaNN
In the Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) model,
the client has limited computation capabilities. Thus,
he outsources the computations to the server who has
expertise in performing ML with adequate computa-
tion power. We consider two different scenarios both
of which aim to maintain privacy: In the 1
st
Scenario:
Client - Server, a client shares a private image with a
server. The server, which holds the NN model, com-
putes the prediction result on the private image. The
majority of the computations are performed by the
server. The client helps the server perform decryp-
tions and/or circuit evaluations when it is necessary.
To reduce the workload on the client side further, we
design a 2
nd
Scenario: Two - Server whereby two
semi-honest non-colluding servers perform the com-
putations together. The client provides the servers
their shares on the input and private keys. Thus, the
computations on the client side are completely dele-
gated to the servers. In such a setting, to fully utilize
the capabilities of both servers, one image can be pro-
vided to each server such that at one execution two
images are evaluated simultaneously.
In both scenarios, we assume a semi-honest secu-
rity model, where the parties do not collude: Parties
exactly follow the protocol steps but they are curious
to obtain some information from the output and in-
termediary messages. The client’s goal is to hide the
image content and the result of classification from the
server(s). On the other hand, the server(s) does not
want to reveal the model parameters used during com-
putations to the client.
4.1 Scenario 1: Client - Server
Figure 1 illustrates our first scenario. The client en-
crypts an image with his public key and sends it to
the server. Depending on the NN operation the client
may be involved in the computations or not.
Client
Server
Figure 1: Client-Server scenario in SwaNN.
The protocol mainly consists of two phases: The non-
interactive phase during which the operations are per-
formed by the server without the client’s involvement;
and, the interactive phase which requires the collabo-
ration of both parties. Below, we explain how each
NN layer is executed in the client-server scenario
1
.
4.1.1 Non-interactive Phase
In this phase, the server, who has received the en-
crypted image, computes the linear NN layers as fol-
lows.
Convolutional Layer (Conv). The main operation in
the convolutional layer is the dot product. Given an
input image X and a weight matrix W, their dot prod-
uct is computed as Y =
∑
x
i, j
× w
i, j
. When the input
image is encrypted with Paillier and the weight ma-
trix is in plaintext, using the homomorphic property
of encryption, the dot product is computed as
[Y] =
∑
x
i, j
× w
i, j
=
∏
[x
i, j
]
w
i, j
. (1)
Fully Connected Layer (FC). The fully connected
layer requires to compute a matrix multiplication.
The underlying operation for matrix multiplication is
the dot product (1) which has to be performed for each
column and row pair.
Mean Pool Layer (Pool). Similar to (Gilad-Bachrach
et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2017) we use a linear approx-
imation of the mean pooling operation: We compute
the scaled mean pool instead of the mean pool, where
the division is omitted. Hence, the scaled mean pool
can be computed when using Paillier without interac-
tion.
1
For more detail on CNNs’ architecture, we refer the
reader to the full version of this paper (Tillem et al., 2020)
SwaNN: Switching among Cryptographic Tools for Privacy-preserving Neural Network Predictions
499

4.1.2 Interactive Phase
In this phase, the server computes the nonlinear NN
layers in collaboration with the client.
Activation Layer (Act). Computing the nonlinear
activation function in NN is a challenging task when
data is encrypted. In the existing literature, there are
two approaches to compute the activation function:
The first approach (Gilad-Bachrach et al., 2016; Liu
et al., 2017) is to compute a polynomial approxima-
tion, namely x
2
. In SwaNN, since Paillier does not
support multiplications, we design a dedicated, inter-
active secure square function. Our solution mainly
adapts the secure multiplication protocol in (Toft,
2011) (see Protocol 1). Alternatively, we also propose
to compute x
2
with arithmetic sharing. The multipli-
cation requires to switch the computations from HE
to arithmetic sharing which is explained later in this
section.
Protocol 1: Secure Square Computation.
Client (pk, sk) Server (pk)
[x],r ∈
R
{0,1}
`+κ
x
r
← decr([x
r
])
[x
r
]
←−−− [x
r
] ← [x] · [r]
x
2
r
← x
r
· x
r
[x
2
r
] ← enc(x
2
r
)
[x
2
r
]
−−−→ [x
2
] ← [x
2
r
] ·
[r
2
] · [x]
2r
−1
The second approach (Liu et al., 2017; Mohassel and
Zhang, 2017) is the computation of the ReLU func-
tion using 2PC techniques. In SwaNN, we compute
ReLU using a comparison gate under Boolean shar-
ing.
Max Pool Layer. We implement the maximum pool-
ing using the comparison gates under Boolean shar-
ing. We perform the max pool layer right after the
activation to reduce the number of switching opera-
tions between 2PC and PHE.
Switching between HE and 2PC. Since linear and
nonlinear operations follow each other repetitively,
we design secure switching mechanisms between
PHE and 2PC (see Protocols 2 and 3) which is sim-
ilar to the secure decryption mechanism in (Henecka
et al., 2010).
Switching from PHE to 2PC (Protocol 2) requires
a secure decryption of the encrypted value masked
with a random r. Once the client securely decrypts the
masked value x + r, he creates the secret shares of it
for himself and for the server as
h
x + r
i
c
and
h
x + r
i
s
.
In the mean time, the server creates the secret shares
of r as
h
r
i
c
and
h
r
i
s
to remove the mask from the orig-
inal value x. Finally, both parties perform a local sub-
traction on their shares
h
x + r
i
and
h
r
i
to compute the
secret shared value
h
x
i
which is going to be used in
2PC operations. Switching from 2PC to PHE (Pro-
Protocol 2: Switching from PHE to 2PC.
Client (pk, sk) Server (pk)
[x], r ∈
R
{0,1}
`+κ
x + r ← decr([x + r])
[x+r]
←−−− [x + r] ← [x] · [r]
x + r →
h
x + r
i
c
+
h
x + r
i
s
h
x+r
i
s
−−−−→
h
r
i
c
←−− r →
h
r
i
c
+
h
r
i
s
h
x
i
c
←
h
x + r
i
c
−
h
r
i
c
h
x
i
s
←
h
x + r
i
s
−
h
r
i
s
tocol 3) reverses the former procedure. It starts with
a secret shared value
h
x
i
. Similar to the previous pro-
tocol, to prevent the leakage of the original value the
parties reveal it after masking. Thus, the server gen-
erates a random mask r
0
and sends a secret share of
it
h
r
0
i
c
to the client. Both parties perform an addition
operation to mask
h
x
i
, and then the server sends the
masked value
h
x + r
0
i
s
to the client. The client reveals
x + r
0
by adding the two shares and encrypts it with
his public key. In the final step, the server removes
the random mask from [x + r
0
] with a homomorphic
subtraction.
Protocol 3: Switching from 2PC to PHE.
Client (pk, sk) Server (pk)
h
x
i
c
h
x
i
s
, r
0
∈
R
{0,1}
`+κ
h
x + r
0
i
c
←
h
x
i
c
+
h
r
0
i
c
h
r
0
i
c
←−− r
0
→
h
r
0
i
c
+
h
r
0
i
s
x + r
0
←
h
x + r
0
i
c
+
h
x + r
0
i
s
h
x+r
0
i
s
←−−−−
h
x + r
0
i
s
←
h
x
i
s
+
h
r
0
i
s
[x + r
0
] ← enc(x + r
0
)
[x+r
0
]
−−−→ [x] ← [x + r
0
] · [r
0
]
−1
4.2 Scenario 2: Two - Server
To reduce the workload at the client side, we con-
sider a second scenario which introduces two non-
colluding servers: The client provides the input to
both servers and delegates all operations. Further-
more, if only a single image is provided to the servers,
one of the servers is going to be idle during the non-
interactive phase. Thus, we propose to provide one
different image to each server to fully utilize the com-
putation capabilities of the servers and classify two
images at once.
SECRYPT 2020 - 17th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
500
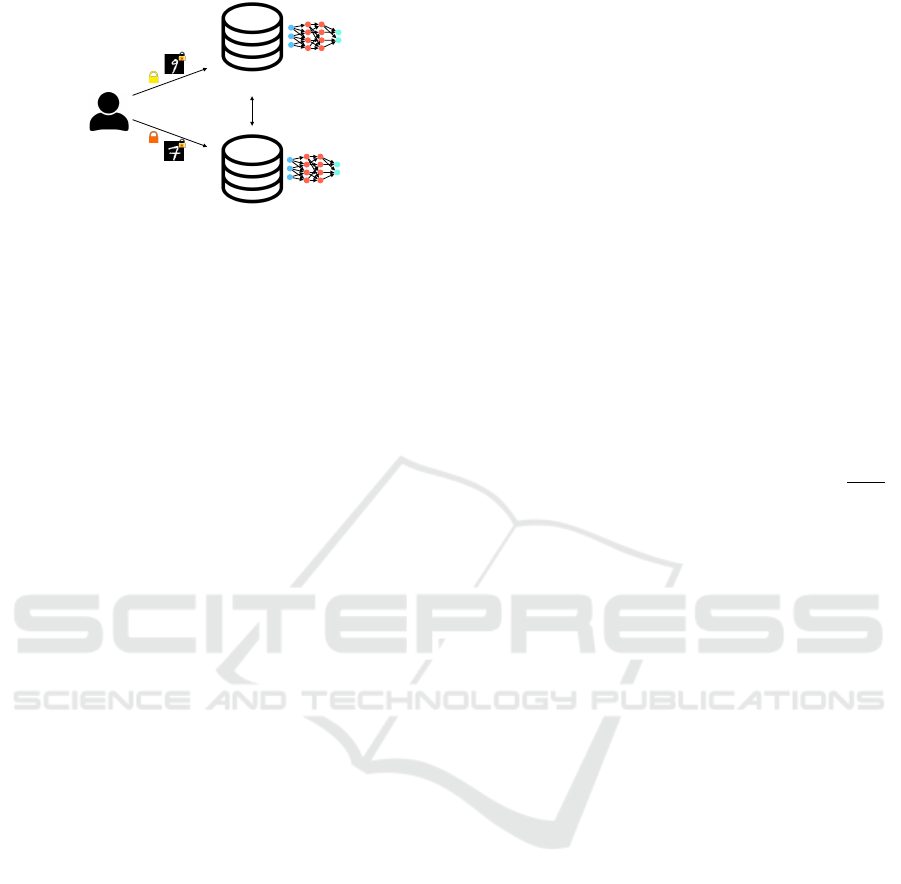
Client
Server 2
Server 1
Figure 2: Two-Server scenario in SwaNN.
As illustrated in Figure 2, the client encrypts two im-
ages with his public key and provides one image to
each server. Furthermore, he creates and sends shares
of the private key for each server as in (Damg
˚
ard and
Jurik, 2001). Similar to the first scenario, during the
non-interactive phase, the servers compute the lin-
ear operations on their inputs in the same way as de-
scribed in Section 4.1.1. The interactive phase and the
switching phase also perform similarly to the descrip-
tion in Section 4.1.2 except at the decryption proce-
dure. In the two-server scenario, the decryption task
is also delegated to the two servers along with their
shares on the secret key. Therefore, the decryption
function decr([·]) in Protocols 1 and 2 is performed by
both servers. In the full version of our paper (Tillem
et al., 2020), Protocol 4 defines the secure square pro-
tocol using this new decryption procedure.
4.3 Security Analysis
SwaNN aims to compute private NN predictions in
the semi-honest adversarial model. We assume that
the semi-honest adversary is non-adaptive and com-
putationally bounded. For both scenarios, the two
communicating parties should not be able to retrieve
any additional information from the protocol execu-
tion apart from their inputs, outputs, and intermediary
messages. SwaNN’s security is ensured thanks to the
security of the underlying cryptographic tools. De-
tails of the security analysis can be found in the full
version of the paper (Tillem et al., 2020).
5 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
We implemented SwaNN in C++ using the GMP 6.1.2
library for big integer operations and the ABY frame-
work (Demmler et al., 2015) for 2PC operations. For
the homomorphic operations, we used the Paillier im-
plementation of ABY due to its efficiency. We se-
lected 2048 bits modulus size in Paillier operations
to meet the current security standards. For the ABY
operations, we selected 32-bit shares. The experi-
ments are run in a machine with Intel Core i5-3470
CPU@3.20GHz and Ubuntu 16.04.
5.1 Optimizing Computations
In our implementation, we use several optimization
techniques which help reduce the computation and
communication cost by enabling simultaneous exe-
cution. To optimize 2PC operations, we use single
instruction multiple data (SIMD) techniques (Smart
and Vercauteren, 2014). SIMD techniques cannot be
fully utilized for the computations with the Paillier
cryptosystem. Therefore, to improve the efficiency in
HE, we adapt two techniques to Paillier which enables
simultaneous computation. We first use data pack-
ing (Bianchi et al., 2010): It packs multiple data items
into a single ciphertext. Accordingly, we create slots
of t + κ bits for each data item where κ is the security
parameter and t is the length of the data item. Given
the plaintext modulus N, we can pack ρ =
j
log
2
N
t+κ
k
items in a single ciphertext as in (2).
[ ˆx] =
ρ−1
∑
m=0
[x
i, j
] · (2
t+κ
)
m
(2)
With data packing, we can use the full plaintext do-
main in the Paillier cryptosystem and perform addi-
tions on the packed ciphertext simultaneously. Fur-
thermore, in interactive protocols, using data packing
helps reduce the bandwidth usage and the cost of de-
cryption operations.
The second technique we use to improve effi-
ciency is using a multi-exponentiation algorithm to
simultaneously perform the operations in the form of
w
∏
i=1
a
b
i
i
= a
b
1
1
· a
b
2
2
...a
b
w
w
. (3)
Lim-Lee’s multi-exponentiation algorithm (Lim and
Lee, 1994; Lim, 2000) enables to perform (3) si-
multaneously by modifying the binary exponentiation
algorithm using several precomputation techniques.
In our work, we can apply multi-exponentiation for
the computation of dot product (in (1)) over en-
crypted data thanks to Paillier. To summarize, the per-
layer optimizations are the following: (i) For Conv,
multi-exponentiation reduces the cost of dot prod-
ucts; (ii) Data packing is used before Act and SIMD
is used if Act is performed with 2PC; (iii) Pool
does not require any optimization; (iv) For FC, multi-
exponentiation reduces the cost of matrix multiplica-
tions.
SwaNN: Switching among Cryptographic Tools for Privacy-preserving Neural Network Predictions
501

Table 1: Computation time per layer in both scenarios (in ms). * shows the simultaneous run time of SwaNN for two images.
Non-optimized - PHE only Optimized - PHE only Optimized - Hybrid
Layer Client Server Server-1 Server-2 Client Server Server-1 Server-2 Client Server Server-1 Server-2
Conv – 1831 1883 1883 – 892 917 911 – 917 919 900
Act 12651 15805 33442 33319 2487 19253 23973 23941 2292 566 2947 2984
Pool – 35 34 34 – 34 34 33 – 33 33 34
Conv – 2799 2911 2948 – 1329 1347 1344 – 1386 1378 1364
Pool – 37 37 37 – 38 38 37 – 37 37 39
FC – 6420 6579 6536 – 3809 3802 3818 – 3989 3973 3977
Act 1504 1879 3993 4009 314 2231 2795 2797 273 266 607 573
FC – 10 10 10 – 11 11 10 – 11 11 11
Total 42972 48892* 30399 32902* 9841 9904*
5.2 Experiments
We design three experiments with respect to Act used
in NN. In the first experiment, we used x
2
and re-
trained the NN structure in (Gilad-Bachrach et al.,
2016). In the second and third experiments, we used
ReLU and re-trained the NN structure for MNIST and
Cifar-10 in (Liu et al., 2017). It is worth to note that in
these experiments, we have achieved the same accu-
racy stated in (Gilad-Bachrach et al., 2016; Liu et al.,
2017).
Experiment 1. We measured the performance of
SwaNN with the x
2
activation function in the client-
server and the two-server scenario. We designed two
different cryptographic settings. The first setting is an
only-PHE setting which is totally based on Paillier.
x
2
is implemented as described in Protocol 1. The
second setting is a Hybrid Setting where we imple-
mented the secure switching protocols in Protocols 2
and 3 and x
2
is implemented using ABY.
Table 1 shows the performance of SwaNN for both
scenarios in the only-PHE and the hybrid setting and
when optimizations are integrated. For the only-PHE
setting, we also provide results without using any op-
timization. In the client-server scenario, when no op-
timizations are used, the prediction of one image ap-
proximately takes 43 seconds. This computation time
is reduced to 30 seconds with optimizations. In the
hybrid setting, the prediction takes 10 seconds. In the
two-server scenario, there is a slight increase in com-
putation time. Nevertheless, two images can be pro-
cessed simultaneously (for example, 10 seconds are
needed to classify two images in the hybrid setting).
In Table 2, we provide the details of the computa-
tion time for Act in the hybrid setting. The packing,
decryption, and unpacking operations are performed
during the switching from PHE to 2PC. The encryp-
tions are computed by both parties when switching
from 2PC to PHE. In the client-server scenario, the
client spends 2.3 seconds for the computations while
the server spends 581 milliseconds, approximately. In
the two-server scenario, both servers spend around 6
seconds for two simultaneous instances.
Table 2: Computation time for the activation layer for the
hybrid setting (in ms).
Operation Client Server Server-1 Server-2
Packing – 409 413 406
Decryption 72 – 147 146
Unpacking 0.1 – 0.1 0.1
ABY 11 14 28 28
Encryption 2220 158 2373 2685
Total 2884 3265*
We have also analyzed the bandwidth usage of
SwaNN. Table 3 shows the communication cost in
both scenarios for the only-PHE and the hybrid set-
tings. The packing technique used in the activation
layers helps reduce the bandwidth usage by half. Due
to the interactive nature of 2PC, the bandwidth usage
in the hybrid setting is higher than in the only-PHE
setting.
Table 3: Bandwidth usage for the two settings in SwaNN
(in MB).
Client-Server Two-Server
PHE only (w/o opt.) 0.97 0.96
PHE only (w/ opt.) 0.51 0.51
Hybrid (w/ opt.) 1.69 1.69
Finally, in Table 4 we compare SwaNN with Cryp-
toNets (Gilad-Bachrach et al., 2016) and Min-
iONN (Liu et al., 2017). The performance results
of CryptoNets and MiniONN are taken from the re-
spective papers. According to (Gilad-Bachrach et al.,
2016), which uses FHE for computations, one pre-
diction requires 297.5 seconds. The protocol enables
simultaneous computation by packing 4096 images
SECRYPT 2020 - 17th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
502

into a single ciphertext. This is an advantage when
the same client has a very large number of prediction
requests. With the same NN, MiniONN ((Liu et al.,
2017)) takes 1.28 seconds. This computation requires
47.6 MB of bandwidth usage. SwaNN computes the
same prediction in 10 seconds. Although the com-
putation time of SwaNN is higher than MiniONN,
SwaNN achieves a 28-fold less bandwidth usage.
Table 4: Comparison with the state-of-the-art in exp. 1.
Computation
time (s)
Bandwidth
usage (MB)
CryptoNets 297.5 372.2
MiniONN 1.28 47.6
SwaNN 9.9 1.69
Experiment 2. We measured the performance of
SwaNN with the ReLU activation function for the net-
work described in Table IX in the appendix of the full
version (Tillem et al., 2020). We provide the timings
for the max pooling along with ReLU since we im-
plemented them together. Table 5 details the compu-
tation time for each layer.
Table 5: Computation time per layer in the two scenarios
(in ms).
Layer Client Server Server-1 Server-2
Conv – 10192 10196 10195
Act+Pool 6852 2593 11968 10613
Conv – 1148 1150 1153
Act+Pool 778 467 1448 1411
FC – 1325 1332 1360
Act 274 508 801 866
FC – 5 5 6
Total 24242 26099
The prediction takes 24 seconds in the client-server
scenario and 26 seconds in the two-server scenario
(for two images). The first activation layer is the dom-
inant layer in the run time. As expected, this is due to
the decryption operations during the switching from
PHE to 2PC.
Table 6: Comparison with the state-of-the-art in exp. 2.
Computation
time (s)
Bandwidth
usage (MB)
MiniONN 9.32 657.5
SwaNN 26.00 160.9
In Table 6, we compare the performance of SwaNN
with MiniONN. Clearly, MiniONN outperforms
SwaNN almost 3-fold in computation time. However,
in terms of communication, SwaNN is more efficient
with a bandwidth usage of 160 MB (compared to 657
MB in MiniONN).
Experiment 3. We measured the performance of
SwaNN with ReLU for the network described in Ta-
ble X in Appendix in the full version (Tillem et al.,
2020). In Table 7, we compare the performance
of SwaNN with MiniONN and Gazelle. Clearly,
SwaNN outperforms MiniONN in computation time
and bandwidth usage. Nevertheless, Gazelle seems
perform better than SwaNN. It is worth to note that
these results are taken for the reference paper (Ju-
vekar et al., 2018) and were hard to reproduce in our
environment. Furthermore, in SwaNN, compared to
Gazelle, we make use of simple mechanisms such as
Boolean sharings for ReLU and Max Pool instead of
Garbled Circuits.
Table 7: Comparison with the state-of-the-art in exp. 3.
Computation
time (s)
Bandwidth
usage (MB)
MiniONN 544 9272
Gazelle 12.9 1236
SwaNN 394.1 1939
6 CONCLUSION
We have proposed a privacy-preserving neural net-
work prediction protocol that combines the additively
homomorphic Paillier encryption scheme with 2PC.
Thanks to the use of Paillier for linear operations and
x
2
, the solution achieves better computational cost
compared to existing HE-based solutions. Different
computation optimizations based on the use of data
packing and multi-exponentiation have been imple-
mented. Furthermore, the communication cost is also
minimized since 2PC is only used for non-linear op-
erations (max pooling and/or RELU). SwaNN can
be executed in the two-server setting, in case the
client lacks resources. Experimental results show that
SwaNN actually achieves the best of both worlds,
namely, better computational overhead compared to
HE-based solutions and, better communication over-
head compared to 2PC-based solutions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partly supported by the PAPAYA
project funded by the European Union’s Horizon
SwaNN: Switching among Cryptographic Tools for Privacy-preserving Neural Network Predictions
503

2020 Research and Innovation Programme, under
Grant Agreement no. 786767.
REFERENCES
Barni, M., Orlandi, C., and Piva, A. (2006). A privacy-
preserving protocol for neural-network-based compu-
tation. In MM&Sec.
Beaver, D. (1991). Efficient multiparty protocols using cir-
cuit randomization. In CRYPTO.
Bianchi, T., Piva, A., and Barni, M. (2010). Composite
signal representation for fast and storage-efficient pro-
cessing of encrypted signals. IEEE Trans. Information
Forensics and Security.
Bourse, F., Minelli, M., Minihold, M., and Paillier, P.
(2018). Fast homomorphic evaluation of deep dis-
cretized neural networks. In CRYPTO.
Chabanne, H., de Wargny, A., Milgram, J., Morel, C., and
Prouff, E. (2017). Privacy-preserving classification on
deep neural network. IACR.
Chou, E., Beal, J., Levy, D., Yeung, S., Haque, A., and Fei-
Fei, L. (2018). Faster CryptoNets: Leveraging spar-
sity for real-world encrypted inference. CoRR.
Ciresan, D. C., Meier, U., and Schmidhuber, J. (2012).
Multi-column deep neural networks for image classi-
fication. CVPR.
Dahl, M., Mancuso, J., Dupis, Y., Decoste, B., Giraud, M.,
Livingstone, I., Patriquin, J., and Uhma, G. (2018).
Private machine learning in tensorflow using secure
computation. CoRR.
Damg
˚
ard, I. and Jurik, M. (2001). A generalisation, a sim-
plification and some applications of paillier’s proba-
bilistic public-key system. In Public Key Cryptogra-
phy.
Demmler, D., Schneider, T., and Zohner, M. (2015). ABY -
A framework for efficient mixed-protocol secure two-
party computation. In NDSS.
Fukushima, K., Miyake, S., and Ito, T. (1983). Neocogni-
tron: A neural network model for a mechanism of vi-
sual pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Systems, Man,
and Cybernetics.
Gilad-Bachrach, R., Dowlin, N., Laine, K., Lauter, K. E.,
Naehrig, M., and Wernsing, J. (2016). CryptoNets:
Applying neural networks to encrypted data with high
throughput and accuracy. In ICML.
Goldreich, O., Micali, S., and Wigderson, A. (2019). How
to play any mental game, or a completeness theo-
rem for protocols with honest majority. In Providing
Sound Foundations for Cryptography.
Henecka, W., K
¨
ogl, S., Sadeghi, A., Schneider, T., and
Wehrenberg, I. (2010). TASTY: tool for automating
secure two-party computations. In ACM CCS.
Hesamifard, E., Takabi, H., and Ghasemi, M. (2017). Cryp-
toDL: Deep neural networks over encrypted data.
CoRR.
Hesamifard, E., Takabi, H., Ghasemi, M., and Wright, R. N.
(2018). Privacy-preserving machine learning as a ser-
vice. PETS.
Ibarrondo, A. and
¨
Onen, M. (2018). Fhe-compatible batch
normalization for privacy preserving deep learning. In
DPM.
Jiang, X., Kim, M., Lauter, K. E., and Song, Y. (2018). Se-
cure outsourced matrix computation and application
to neural networks. In ACM CCS.
Juvekar, C., Vaikuntanathan, V., and Chandrakasan, A.
(2018). GAZELLE: A low latency framework for se-
cure neural network inference. In USENIX.
Lim, C. H. (2000). Efficient multi-exponentiation and appli-
cation to batch verification of digital signatures. Un-
published manuscript.
Lim, C. H. and Lee, P. J. (1994). More flexible exponentia-
tion with precomputation. In CRYPTO.
Liu, J., Juuti, M., Lu, Y., and Asokan, N. (2017). Oblivi-
ous neural network predictions via minionn transfor-
mations. In ACM CCS.
Mohassel, P. and Rindal, P. (2018). ABY
3
: A mixed proto-
col framework for machine learning. In ACM Confer-
ence on Computer and Communications Security.
Mohassel, P. and Zhang, Y. (2017). SecureML: A system
for scalable privacy-preserving machine learning. In
IEEE S&P.
Orlandi, C., Piva, A., and Barni, M. (2007). Oblivious neu-
ral network computing via homomorphic encryption.
EURASIP.
Paillier, P. (1999). Public-key cryptosystems based on com-
posite degree residuosity classes. In EUROCRYPT.
Riazi, M. S., Samragh, M., Chen, H., Laine, K., Lauter,
K. E., and Koushanfar, F. (2019). XONN: xnor-based
oblivious deep neural network inference. CoRR.
Riazi, M. S., Weinert, C., Tkachenko, O., Songhori, E. M.,
Schneider, T., and Koushanfar, F. (2018). Chameleon:
A hybrid secure computation framework for machine
learning applications. In AsiaCCS.
Ribeiro, M., Grolinger, K., and Capretz, M. A. M. (2015).
MLaaS: Machine learning as a service. In ICMLA.
Rouhani, B. D., Riazi, M. S., and Koushanfar, F. (2018).
DeepSecure: scalable provably-secure deep learning.
In DAC.
Sanyal, A., Kusner, M. J., Gasc
´
on, A., and Kanade, V.
(2018). TAPAS: tricks to accelerate (encrypted) pre-
diction as a service. In ICML.
SEAL (2018). Simple Encrypted Arithmetic Library (re-
lease 3.1.0).
Smart, N. P. and Vercauteren, F. (2014). Fully homomor-
phic SIMD operations. Des. Codes Cryptogr.
Tillem, G., Bozdemir, B., and
¨
Onen, M. (2020). SwaNN:
Switching among cryptographic tools for privacy-
preserving neural network predictions. https://www.
eurecom.fr/
∼
bozdemir/SwaNNfull.pdf.
Toft, T. (2011). Sub-linear, secure comparison with two
non-colluding parties. In PKC.
Wagh, S., Gupta, D., and Chandran, N. (2019). SecureNN:
Efficient and private neural network training. In PETS.
SECRYPT 2020 - 17th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
504
