
Government Digital Service Co-design: Concepts to Collaboration
Tools
Muneer Nusir
College of Computer Engineering and Sciences, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University,
Sa'ad Ibn Mu'adh Street, 11942 Al-kharj, Saudi Arabia
Keywords: Co-design, Design Business Process, e-Government Services, e-Service Design, Key Stakeholders.
Abstract: The inception of digital services is succeeded with the myriad advancements in ICT that aim to support the
growing needs of users and internet-enabled devices. The diversities of these functionalities and digital
services are motivated by the presence of dynamic technologies, delivery channels, and diverse user needs in
an internet-enabled environment. What appropriate instruments could help to support the collaborative design
and create an environment characterized by active knowledge between providers of service and end-users of
the service? The co-design is a well-known approach within the design community that utilizes advanced
ideas and varied instruments of co-design. This study aimed is how to identify unmet requirements for
Government to Citizen (G2C) e-service design and significant ways of achieving the requisite design needs
using a suitable design process? Detailed interviews were undertaken with three groups of stakeholders in
regards to the service design. This study analyses the data collected using an inductive thematic analysis to
analyze qualitative data collected from study participants. This study also explores the patterns resulting from
the G2C e-service design process and further establishes the interconnection between the processes in regards
to fostering the effectiveness and efficiency of the services.
1 INTRODUCTION
e-Government service suppliers should ideally
emphasize on what makes service users gratified in
their daily life and work, reducing centralization
procedures in government agencies and organizations
(Cordella and Tempini, 2015). In contrast to
commercial services, government digital services are
typically developed by internal service providers and
often neglect the service end-user (Axelsson and
Melin, 2007; Bridge, 2012). Therefore, the delivery
of services might be endangered without due concern
of the service users, deficient consideration of their
needs and prospects in the design process (Wu et al.,
2013; Zhao et al., 2008). The consequence of this
challenge is a failure of e-Government projects and a
lack of trust in e-Government services; particularly in
developing countries (Kim et al., 2019; Choudrie et
al., 2009). Limited user involvement throughout the
design process of e-Government services is typical
practice (Anthopoulos et al., 2007; Olphert and
Damodaran, 2007).
Nevertheless, Heeks (2003) acknowledges the
existence of a high failure rate of e-Government
particularly among nations categorized as unindus-
trialized or undeveloped. Further findings reported by
Heeks indicates that at least 35% of the governmental
projects have failed completely, which is coupled with
an estimated 50% failing partially. The figures eclipse
the success of the proposed projects that is only 15%.
The challenge of failing projects has attracted scrutiny
and opposition due to missing trust and credibility
among service providers and consumers of the e-
Government services (Twizeyimana and Andersson,
2019). Besides, among the developing nations, the
mandate of providing eGovernment services is offered
by service providers internally who have a tendency of
neglecting the concerns of those consuming those
services. Most importantly, Wu et al. (2013), and Zhao
et al. (2008) note that service delivery is threatened as
the users are not taken into consideration in terms of
their diverse needs and expectations form the service
framework process.
The challenge of disregarding the users of e-
Government services indicates that providers are
cushioned by the marginal of the services provided
that limits them from meeting the needs of the service
users. Thus, this study aimed to identify unmet
requirements for Government to Citizen (G2C) e-
service design and significant ways of achieving the
Nusir, M.
Government Digital Service Co-design: Concepts to Collaboration Tools.
DOI: 10.5220/0009956900610070
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2020) - Volume 3: ICE-B, pages 61-70
ISBN: 978-989-758-447-3
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
61

requisite design needs using a suitable design process.
This marks the need to bridge the gap differentiating
these two key stakeholders. Therefore, this study
adopted a relatively known ‘co-design approach’ to
enable the government to align a collaborative
relationship between users of services and providers
for the benefit of the citizens (Bridge, 2012). As a
provider of services, the application of this approach
aims to improve the involvement of services in terms
of participating and collaborating activities with
providers of service.
This paper presents a theoretical “design-led”
contribution from a digital service design study (see
figure 4). Co-design is well realized in the design
environment with some innovative and wide-ranging
co-design tools and methods (Zheng et al., 2019). The
paper starts with theoretical government background
literature, service design methodologies and
subsequently leads to the solution space
encompassing co-design techniques.
The main aim of this paper is to identify unmet
requirements for Government to Citizen (G2C) e-
service design and significant ways of achieving the
requisite design needs using a suitable design process.
Accordingly, Sanders and Stappers (2008) expound
on the implications that result from incongruences
between service design requirements and the service
design activities. Some of the mismatches include the
threat of recording decreased benefits from the entire
design process.
The purpose of this paper is to establish the
advantages of co-design approaches present in design
environments that are molded to facilitate the wide-
range activities undertaken by stakeholders. The
activities are hinged on a pledge to be delivered
alongside practical benefits linked to an e-service
design. The next section expounds on numerous
theoretical background literature on e-Government
service. The subsequent section will provide a
discussion on the research methods including the
research phases employed in this paper. The last
section will detail a case study on fieldwork testing.
In terms of the conclusion, this paper will provide a
summative discussion on the significant sections
tackled on the subject of e-Government services.
2 E-GOVERNMENT
BACKGROUND
2.1 e-Government Services
Citizens are entitled to access and enjoy e-Government
services with ease. Moreover, the citizenry has the
right to have reliable e-Government services to foster
their interactions with varied e-Government
engagements, such as Government to Government
(G2G), Government to business (G2B), and lastly,
government to employee (G2E) services (Choudrie,
et al., 2009). However, it is vital to note the
experiences of the populace due to the failure of e-
Government services that are marred with problems
evidenced by unmet desires. The challenge of these
aspects that cause the e-Government failure is present
among the emerging nations. The course of reviewing
the significance of the e-Government and exploration
of aspects that dictate the creation of e-Government
has received growing support among communities
that tend to analyze e-Government (Scholl, 2014).
This paper focuses on G2S services and the ways
the government employs to provide services to the
populace. Examples of these services include tax
collection, the execution of welfare payments,
conducting the process of renewing licenses and
passports, and facilitating government agencies as
well as taking a lead role in the provision of social and
healthcare services (Fogli and Provenza, 2012).
Concisely, the provision of G2C e-services is a task
assumed by service suppliers, which have been
creating the challenge of overlooking the requisite
needs of the service's users. (Heeks, 2003).
The implications of these unmet needs have
elicited numerous socio-technical challenges coupled
with the absence of programming skills. The role of
e-Government is to reduce the gap in the
requirements between the government and citizens
through an interactive process exemplified with the
provision of effective and superb online services. The
presence of these expectations is key in encouraging
citizens to use the services (Fogli and Provenza, 2012;
Scholl, 2014). The question that is often directed to
the G2C services is: “Which is the essential
requirement needed to foster the understanding
during the formulation and creation of the appropriate
process of e-services?” The resultant outcome is that
service delivery is often negative without the
consideration of the service users. Nevertheless, in
terms of addressing the requisite needs of the G2C e-
services, it is vital to note that limited staff working
for the service providers, such as consultants
recruited for the e-services design demonstrate the
right knowledge for this task.
2.2 e-Government Services in Pakistan
In the context of Pakistan, the e-Government service
was championed in 2002. The inception and
ICE-B 2020 - 17th International Conference on e-Business
62
execution of the e-Government service was
commenced as a department within the Science and
Technology Ministry. The department had been
tasked with the role of monitoring diverse e-
Government projects and ensured that they adhered to
the established practical guidelines (Warriach and
Tahira, 2015). The main role of the e-Government
was centered on the provision of support to
organizations tied to the public sector. The roles were
modeled and expected to enhance productivity,
efficacy, and transparency using ICT and ensure that
the end-users access the services with ease (Ovais
Ahmad et al., 2013). As an integral sector in the
Pakistan context, ICT helped in the development of e-
Government services. The government was
concerned with providing varied activities that were
focused on improving the lives of people. The
feasible strategy adopted by the ICT was key in
reinforcing the achievement of the reformed social
and economic aspects. Therefore, the development of
robust ICT helped to highlight the improvement of
the e-Government services accessed by the citizenry
(Ali et al., 2018).
Pakistan is categorized under emerging nations.
Correspondingly, Pakistan has its share of e-service
problems that involve the acquisition of moderate
ICT infrastructure, the presence of low levels of
literacy, demographic factors, and relative dwarfed
development of e-Government services, and
technological challenges (Ovais Ahmad et al., 2013;
Chandio et al., 2018). Additional challenges notable
in the Pakistan context are issues with the privacy of
data and the dissatisfaction of the services rendered e-
government that is demonstrated between providers
and end-users. Similarly, Almakki (2009)
acknowledges the challenges and difficulties of e-
Government services that are experienced among
emerging nations that are often experienced at the
developmental of the services. Qaiser and Khan
(2010) echo the findings reported by Almakki (2009)
by outlining numerous restrictions that include:
inadequate ICT facilities and poor implementation
process that limits the significance and advancement
of e-Government services (Ali et al., 2018).
2.3 Design Methodologies
User-centered design (UCD) methodologies were
established in 1970 and ultimately became accepted
widely and adopted in 1990 (Sanders and Stappers,
2008). Handler outlooks and concepts are merged
into the software improvement progression regularly
to ensure a better system or service deployment
(Wever, et al., 2008). UCD emerged as being greatly
suitable in designing and developing products for
end-user (van Velsen and van der Geest, 2012; Jacobs
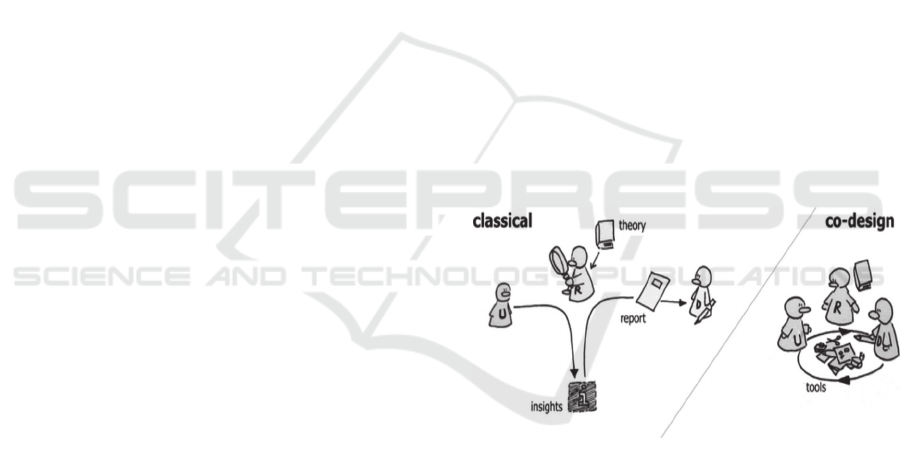
et al., 2019). Figure 1 explains a caricature displaying
the deficiency within the classical user-centered
process of design compared to the co-design
approach, and the rationale for transforming to co-
design approach. Sanders and Stappers (2008, p.11)
stated “the user is a passive object of study, and the
researcher brings knowledge from theories and
develops more knowledge through observation and
interviews”. Moreover, “The designer then passively
receives this knowledge in the form of a report, and
adds an understanding of technology and the creative
thinking needed to generate ideas, concepts, etc.”
(Sanders and Stappers, 2008, p.12). Nevertheless, an
analysis is critical to mentor participants at the
‘performing’ level of creativity, supporting at the
‘adaptive’ level, supporting platforms for resourceful
manifestation at the ‘innovative’ level, and suggest a
delicate account at the ‘designing’ level (Sanders and
Stappers, 2008). Nevertheless, an analysis is critical
to mentor participants at the ‘performing’ level of
creativity, supporting at the ‘adaptive’ level,
supporting platforms for resourceful manifestation at
the ‘innovative’ level, and suggest a delicate account
at the ‘designing’ level (Sanders and Stappers, 2008;
Simonofski et al., 2019).
Figure 1: Classical UCD VS Co-Design (Sanders and
Stappers, 2008).
2.4 Double Diamond Model (DDM)
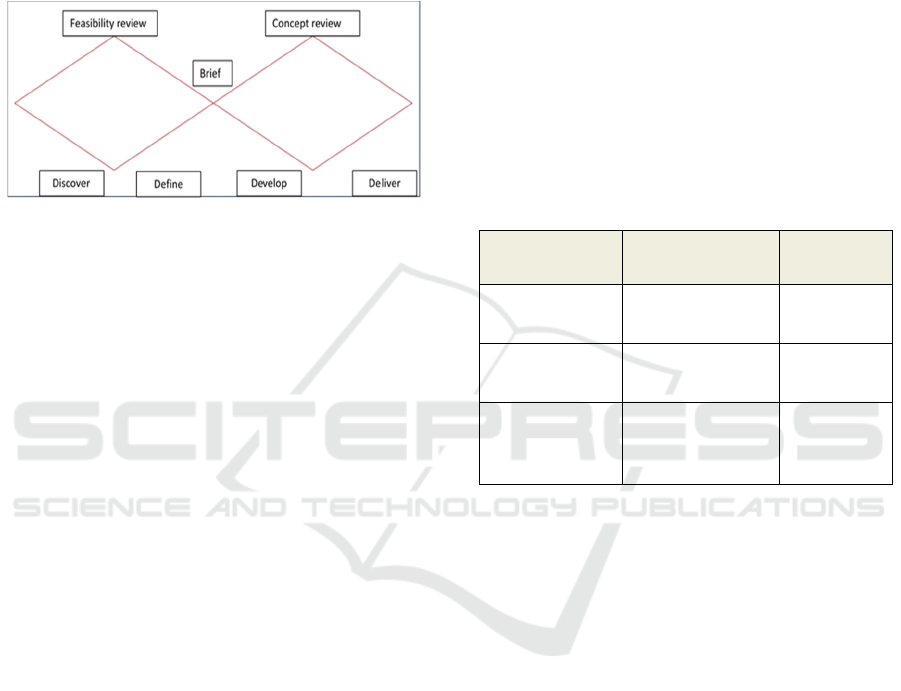
The Double Diamond model (DDM) can be defined
as an basic graphic plan of the process of design as a
creative process (See figure 3) distributed into four
separate stages (Discover, Define, Develop, and
Deliver) representing a typical design process phase
(British Design Council, 2005). These creative
processes reflect various potential ideologies before
refining (i.e. divergent ideas) and narrowing down
ideas to the most suitable ones (i.e. convergent ideas).
DDM designates these four stages to work together as
a map design providing guidelines for the
Government Digital Service Co-design: Concepts to Collaboration Tools
63
organization of thoughts in order to improve the
creative process (JustInMind, 2018). The creative
process is an iterative process (not a linear process),
which implies that the specific ideas are developed,
tested, refined several times to match diverse
thoughts and perspectives of stakeholders; weak ideas
are omitted in the design process (British Design
Council, 2005).
Figure 2: The presentation of the Double Diamond model
(UK Design Council, 2005).
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data Collection and Sampling
In-depth interviews were used to collect the views,
ideas, and thoughts from the research subjects, which
helped to categorize G2C e-service design
requirements. Evidence from studies conducted has
reported that the use of a small sample population, such
as between 5 and 50 respondents was sufficient enough
to record a wide range of requirements (Dworkin,
2012). Study participants recruited for this study were
selected purposively. As demonstrated in Table 1, the
purposive sampling approach was employed to recruit
the study participant by reaching out to the potential
respondents. Siau et al. (2010) emphasize on the need
to utilize an appropriate sampling approach to ensure
that different respondents with diverse experiences are
recruited in a study.
This study focused on recruiting stakeholders
identified as users of service, and frontline staff along
with service providers. The author chose to use
interviews since they offer a chance to delve deeper
into the subject being researched, compared to using
surveys (Bell and Nusir, 2017). Cumulatively, the
author carried out 24 in-depth interviews that last
from 45 minutes to one hour. Nonetheless, the author
guaranteed that the experience and familiarity of all
the respondents with the area of investigation (i.e.
G2C e-service design process) was sufficient. All the
interviews began with a brief summary of the
questions in the interview (open-ended), to ensure the
respondents understood the areas being investigated.
Subsequently, the interviewing protocol and
guidelines including additional questions were
explained to participants as an introduction as a way
of facilitating the interviewing process. After a brief
introduction about interview protocol, service users
were supposed to answer questions about their
experiences -What/how do you wish to contribute
and/or enhance your experience with services and
service outcomes? Service providers and frontline-
staff were interviewed on prevailing processes of
design - Which steps are followed by e-Government
projects in Pakistan when creating government to
citizen (G2C) services? This study presents data
analysis and results findings from the comprehensive
interviews in sub-sequent section.
Table 1: The sample population for the in-depth interviews.
Stakeholders Participants
Category
#
participants
Service
Provider
*NITB 6
Service
Frontline-staff
**PITB 6
Service User varied & diverse
Background &
Experience
12
3.2 Data Analysis
The translations of the interview transcripts were
exported to Spreadsheets for data cleaning and
management. This study used the inductive thematic
analysis method to analyze the grouped transcripts
of the research subjects. This process was followed
with the compilation of all the transcripts in a single
file and the analysis of the data executed conducted
using the inductive thematic analysis, which is one
of the popular methods used in qualitative data
analysis. The rationale for selecting this method was
due to its accessibility and flexibility. Additionally,
there are no major limitations that are tied to any
specific theory as the method works with diverse
and changing occurrences. Accordingly, the
description of the study’s dataset was rich with a
throughout interpretation procedure (Braun and
Clarke, 2006).
The procedure for the thematic analysis method
was undertaken in six key phases as elaborated by
Braun and Clarke (2006). The first step involved
familiarization with the data, which involved going
through the data numerous times to achieve a
ICE-B 2020 - 17th International Conference on e-Business
64

comprehensive understanding. The second step
involved the development of the initial analysis from
the transcripts. This step involved the consideration
of the key points that tended to be significant in the
examination of the study interviews (Allan, 2003).
The third phase involved sorting the initial relevant
transcript codes in a bid to identify potential
categories resulting from the interviews. Potential
themes were reviewed in the fourth phase. This phase
involved the process of reviewing and refining
potential categories to ensure that high levels of
consistency are maintained. The fifth step involved
the definition and classification of the categories
derived from the fourth phase using appropriate titles.
The last phase involved the identification of the
satisfied categories and using them to discuss the
study findings in a clear and convincing way.
This study derived 30 requirement labels. The four
categories identified involved the service conception,
explanation and organization of service, development,
and deployment of the service, and service unveiling
and implementation. The categorization of the labels
into four groups was undertaken for all the 24
stakeholders involved in the study.
3.3 A Tailored Double Diamond Model
The tailored diamond model (DDM) used in this
study proposed varying weights for the mentioned
stages (Ruhl et al., 2014). Figure 3 is a representation
of the DDM, which is a version redesigned from the
Double Diamond model and the Double Diamond
Model of Product Definition and Design (Hinman,
2012).
The consideration of the varying weights and
stakeholders is documented for the different stages,
which is dependent on the shared interests, tasks, and
requirements among the groups. The stages are
retitled appropriately to ensure that they match with
the expectations of the c-design strategy. As such,
discover was retitled to co-discover. The first two
stages, co-discover and co-define demonstrate a
significant process of definition; whilst the last two
stages consisting of co-develop and deliver indicate
the process of the design.
Figure 3: The Tailored DDM.
The figure above is a representation of the divergent
and though mode that is connected with interview
results. The classification of the G2C’s requirements
and categories are showcased in Figure 4.
The systematic process outlined in Figure 4 spells
out the stakeholder groups that are mapped into
appropriate categories that relate to the DDM phases.
The systematic process further outlines the key
components of defining each stage of design that
matches with the corresponding roles and definitions
purposely to achieve the goal of each design phase
(British Design Council, 2005). It is vital to note that
co-define, co-develop, and co-discover are different
and do not relate to each other due to the fact that they
are found within the stages encompassing the
engaged and the stakeholders.
The Business Process Modelling Notation
(BPMN) denoted in Figure 4 was useful in the
creation of the tailored DDM that ensured that
suitable design tools were utilized in the design
phases. Whereas the BPMN was modeled to operate
internally, it provided a platform for engaging diverse
stakeholders. The three co-design stages are
discussed as follows:
Co-Discover: This is the first stage in the co-
design stage, which is notably identified as the
scoping and service initialization. As such, the design
problem was identified in this stage. Moreover, this
stage was characterized by a wide range of activities,
such as procedures, support activities, and
Figure 4: Co-Design Framework.
Government Digital Service Co-design: Concepts to Collaboration Tools
65

instruments that are used to generate thoughts,
opinions, and views from participants.
Co-Define: This is the second stage where ideas
are filtered from information collected from
participants. The synthesis of ideas at this stage
further involves reviews and eliminations and used to
recommend solutions that are design-led. The
implication of this stage explains the need for
analyzed and synthesized design ideas that are
dependent on the requirements stipulated in the
design brief.
Co-Develop: At this stage, the G2C e-service
participants are first introduced to the solution led by
design (Design Council, 2007, p. 19). The purposes
or resolutions for designing the process of G2C e-
service are expounded in this phase. The development
of the resolutions is key to the demarcating the
requisite objects for the design methodology.
Deliver: This last stage provides the platform for
testing service. This stage which is also known as the
service unveiling and implementation involves the
objects that are a resultant of the previous stage. The
implementation and the delivery process involve the
relationship that required from the inner design staff
only.
4 DATA RESULTS-KEY
CATEGORIES
The main categories identified were based on
frequency as the criterion indicator. Notably, Goffin
et al. (2006) acknowledge that frequency as one of the
vital indicators. The rationale for selecting this
criterion emanated from the reviewed literature that
stipulated how frequency was important such that a
minimum of 25% formed the baseline for the
participants. The overwhelming mention of the
frequency is an indicative factor that this category
was candid as demonstrated in Figure 5.
Nevertheless, it was difficult to determine the
category that was significant given that the results
were not 100%. As such, identified categories are as
follows:
4.1 Service Deployment
The formulation, creation, and deploying services
forms one of the vital categories alongside the
stakeholder groups. Given that the resulting
frequency was 27%, this category is significant when
compared to the group of service providers.
Moreover, this category offers significant attributes to
the users of the service and the group consisting of
front-line service staff. The significance of this
category is characterized by diverse classifications of
the individual stakeholders who are tasked with the
responsibility of making decisions of the
requirements within this category.
4.2 Service Launching and Updating
This category which is 15% comes last in terms of
frequency when compared with other groupings. The
explanation for this significant difference is that the
prospects of launching and updating the service
happen continuously as the services work on
organizing the services with the intention of meeting
the diverse needs of the end-users. The requirements
are elicited from the expectations from stakeholders
using the service and the responses from the service
frontline staff. As an integral component in the
service development, this category demonstrates that
it is only significant to the group of service providers
and not the other groupings.
4.3 Service Delineation and
Organization
This category comprises of the responses, which
estimated at 25% of the frequency when compared
with the other groupings. The responses are derived
from the stakeholder groups, which demonstrates a
high significance towards other groups. However,
this category ranked a low significance in the services
providers groups. Similarly, the categories consisting
of the users of service, as well as the frontline staffs,
are ranked highly as exhibited by the frequency
scores. As such, decision-makers need to take into
consideration vibrant requirements by restructuring
the current service design model.
4.4 Service Inauguration and Scoping
This category which accumulated 21% of the
frequency of mention fails to showcase the integral
significance, which other categories can depend on.
Evidently, this category is built on the assertions and
viewpoints collected from the service frontline staff.
This reveals how government staff exhibit the highest
correspondence in the event a service has design
glitches that result from the daily usage of the service
by the end-users of the service. Conversely, this
category signifies a modest standing when compared
with the other groupings based on mention frequency.
ICE-B 2020 - 17th International Conference on e-Business
66
Figure 5: Cognitive Mapping.
5 CO-DESIGN FRAMEWORK -
FIELDWORK TESTING
A qualitative research method was conducted and led
by author (i.e. predetermined interview questions
using the focus group discussions (FGDs) as form of
semi-structured interviews) with total of 24
participants recruited to participate in this study. The
involvement of the participants was hinged upon to
generate intriguing, appropriate, and subjective
information, such as their experiences with the design
G2C e-service. In the Pakistan context, prototype
evaluation and post-test interview questions and tasks
were administered to the participants to validate the
proposed framework. Co-design Wiki is an
innovative workspace-platform (see figure 6). The
innovation workspace was produced by realizing
several features (core functions) as these functions
explain four phases of the typical design process. For
example, generating checklists for possible services,
creating an account, upload media that informs
design, search, a toolbox including options and text
boxes for providing feedback on the service design
process. Furthermore, rating and voting features grant
participants the opportunity to assess the service
design characteristics. The FGDs with the
participants lasted between 45 minutes and 60
minutes. Study participants were encouraged to
collaborate in task-based planning. As such, they
were required to provide answers to the semi-
structured questions, which were formulated to assess
their adequacy.
Figure 6: Online collaborative Co-design Wiki.
The three main themes resulting from this study,
namely, Creativity and collaborative platform,
Situating and tailoring co-design tools; and
limitations and shortcomings of involvement.
Moreover, the six subthemes resulting from the study
can be identified as follows: demonstrating
engagement, communication, originality, design
instruments of a collaborative nature, interaction and
some advantages and disadvantages. The collective
themes demonstrated varying comparisons in terms
of the groups of the service provider and users of the
service among the other groups. However, the groups
showcased diverse viewpoints that included the
opportunities and difficulties of using a proposed
prototype that comprised the end-users in the process
design. The findings were identified using inductive
thematic analysis as an example of theoretical
analysis for the FGD’s answers. The three major
themes and sub-themes from the study were identified
and explained as follows:
5.1 Creativity and Collaborative
Platform
This platform was presented with positive reports
drawn from the experiences of the participants who
had interacted with the proposed prototype. Some of
the participants even identified the proposed
Government Digital Service Co-design: Concepts to Collaboration Tools
67

prototype as intriguing. It is vital to note that the
frontline staff took part in the entire assessment
process. However, there are numerous participants
who revealed the significance of collaboration with
the exception of one participant who reported the
need to improve the prototype’s interface. The
significance of this theme is exhibited as it emerged
from the merger of two themes, namely, user
communication and involvement, and cooperation
co-design platform.
5.2 Situating and Tailoring Co-design
Tools
Participants from the groups dominated by the
frontline staff took part in the assessment aimed
toward the improvement of the diverse stages of the
iterative design process. Accordingly, the
involvement of this group was geared towards
making most of the opportunity to present ideas on
the process of designing e-services. The previous
suggestion sought by the frontline staff groups
received a warm reception among the groups of the
service provider. Nevertheless, the main objective of
the groups was to position the co-design tools in all
the design phases purposely to enable diverse
stakeholders to modify their varying viewpoints.
5.3 Limitations and Shortcomings of
Involvement
The adoption of design instruments differed
throughout the design phases. For instance, the
frontline staff groups demonstrated higher levels of
interest when compared with other groups of the
service provider. However, there were notable
limitations that were evidenced by the service
provider in regard to the participation of users of
services. The challenges were evidenced through the
design process of the services due to the lack of
knowledge and experience. Evidence from groups
like the frontline staff showcased wide-ranging
opportunities through which they could reduce the
fears of supporting the participants in a more effective
and timely manner. Moreover, the frontline staff
groups did not originate from the service providers.
6 CONCLUSION
This study has provided a significant co-design
activities emerge from a diverse set of service design
stakeholders (see figure 4). Identified themes and
related sub-themes (see figure 5).
Underpin our blueprinting process construction
and subsequent technique selection. Author describes
a design study where co-design is utilized in a
participant (stakeholder group) specific e-
Government service co-design process. Working with
several e-Government stakeholders in Jordan.
Elements of participant and stakeholder group
cognitive models were then synthesized into a
context-specific co-design blueprint, itself based on
the UK Design Council’s DDM. The ‘co-develop’
and ‘co-define’ stages demand convergent thinking to
stimulate diverse stakeholder groups to identify the
concrete strategies for managing and planning
alternative practices by synthesizing the problem. In
contrast, the co-discover stage needs more divergent
thinking, covering different stakeholders for more
robust exploration in the problem phase. The
blueprint was then operationalized (as a practical
process model) to elaborate on the specific service
design steps.
Moreover, it is supporting the designate tools
needed for effective service co-design usage. The
operationalized design process offers an executive
approach that can be utilized to develop e-services in
a governmental domain-context. Remarkably, the
discursive nature of our collaborative process and the
rating tools employed were particularly popular
amongst stakeholders.
This study had a number of limitations primarily
linked to a focus on a single context. Participant
numbers are small and issues are likely to have a
context specific nature. Consequently, the findings
may not be generalizable, but design oriented
qualitative research provides depth, effectiveness and
transferability rather than generalizability. Future
research could determine the extent to which different
stakeholder groups are influenced by the size of task
ahead. It may also be the case that this is linked to the
historical experience of each stakeholder.
Based on the findings from this study, the
recommended approach is the co-design framework
for the G2C e-service for its effectiveness in mapping
out the tailored requirements. Additionally, co-design
deems appropriate as it is integral in the selection
process mechanism as well as matching e-Service
design categories with relevant design methodologies
throughout the phases of the process design.
Therefore, the implementation of this approach will
foster communication among key stakeholders
involved in the design process for the G2C e-service.
ICE-B 2020 - 17th International Conference on e-Business
68

ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The author would like to acknowledge of the
appreciation of the Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz
University
REFERENCES
Alam, I.: An exploratory investigation of user involvement
in new service development. Journal of the Academy of
Marketing Science 30(3), 250 (2002).
Ali, M.A., Hoque, M.R. and Alam, K.: “An empirical in-
vestigation of the relationship between e-government
development and the digital economy: the case of Asian
countries”, Journal of Knowledge Management Vol. 22
No. 5, pp. 1176-1200. (2018).
Allan, G.: A critique of using grounded theory as a research
method. Electronic Journal of Business Research Meth-
ods 2, 1-10 (2003).
Almakki, R.: Communities of Practice and Knowledge
Sharing in E-government Initiatives, The University of
Manchester, Manchester (2009).
Anthopoulos, L. G., Siozos, P., & Tsoukalas, I. A.: Apply-
ing participatory design and collaboration in digital
public services for discovering and re-designing e-Gov-
ernment services. Government Information Quarterly
24(2), 353-376 (2007).
Axelsson, K., & Melin, U.: Talking to, not about, citizens–
Experiences of focus groups in public e-service devel-
opment. In International Conference on Electronic
Government 2007 (pp. 179-190). Springer, Berlin, Hei-
delberg (2007).
Braun, V., & Clarke, V.: Using thematic analysis in psy-
chology. Qualitative research in psychology 3(2), 77-
101 (2006).
Bridge, C.: Citizen Centric Service in the Australian De-
partment of Human Services: The Department's Expe-
rience in Engaging the Community in Co‐design of
Government Service Delivery and Developments in E‐
Government Services (澳大利
亚人类服务部以公民
为中心的服务
:
该部门在促进群体参与协同设计政
府服务提供和发展在电子政府的经验
). Australian
Journal of Public Administration 71(2), 167-177
(2012).
British Design Council, 2005. The double diamond design
process model, [Online]. Available at :<http://www.
designcouncil.org.uk/designprocess/>, last accessed
2020/01/19.
Chandio, A. R., Haider, Z., Ahmed, S., Ali, M., & Ameen,
I. (2018). E–Government In Pakistan: Framework of
Opportunities and challenges. GSJ, 6(12).
Choudrie, J., Wisal, J., & Ghinea, G.: Evaluating the usa-
bility of developing countries’e-government sites: a
user perspective. Electronic Government, an Interna-
tional Journal 6(3), 265–281 (2009).
Cordella, A., & Tempini, N. E-government and organiza-
tional change: Reappraising the role of ICT and bureau-
cracy in public service delivery. Government Infor-
mation Quarterly, 32(3), 279–286 (2015).
Bell, D., & Nusir, M. (2017, January). Co-design for gov-
ernment service stakeholders. In Proceedings of the
50th Hawaii International Conference on System Sci-
ences.
Design Council. 2007. The design process: Eleven lessons:
managing design in eleven global companies, [Online].
Available at :<http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.
uk/20080821115409/ designcouncil.org.uk/en/about-
design/managingdesign/the-study-of-the-design-pro-
cess>, last accessed 2020/01/30.
Dworkin, S. L.: Sample size policy for qualitative studies
using in-depth interviews. Electronic Government (pp.
1–9). Springer (2012).
Fogli, D., & Provenza, L. P.: A meta-design approach to the
development of e-government services. Journal of Vis-
ual Languages & Computing 23(2), 47-62 (2012).
Jacobs, C., Rivett, U., & Chemisto, M. (2019). Developing
capacity through co-design: the case of two municipal-
ities in rural South Africa. Information Technology for
Development, 25(2), 204-226, DOI:
10.1080/02681102.2018.1470488.
JustInMind. 2018. The Double Diamond model: what is it
and should you use it?, [Online]. Available at :<
https://www.justinmind.com/blog/double-diamond-
model-what-is-should-you-use/>,last-accessed
2020/03/21.
Goffin, K., Lemke, F. & Szwejczewski, M.: An exploratory
study of ‘close’supplier–manufacturer relationships.
Journal of operations management 24, 189- 209.
(2006).
Heeks, R.: Most egovernment-for-development projects
fail: how can risks be reduced? (Vol. 14). Institute for
Development Policy and Management, University of
Manchester Manchester (2003).
Hinman, R.: The mobile frontier. “O’Reilly Media, Inc”
(2012).
Kim, Suk Kyoung, Min Jae Park, and Jae Jeung Rho. "Does
public service delivery through new channels promote
citizen trust in government? The case of smart devices."
Information Technology for Development 25, no. 3
604-624 (2019).
Ovais Ahmad, M., Markkula, J., & Oivo, M.: Factors af-
fecting e-government adoption in Pakistan: a citizen's
perspective. Transforming Government: People, Pro-
cess and Policy 7(2), 225-239 (2013).
Qaiser, N. and Khan, H.G.A.: “E-government challenges in
public sector”, International Journal of Computer Sci-
ence, Vol. 7 No. 5, pp. 310-317 (2010).
Ruhl, E., Richter, C., Lembke, J., & Allert, H.: Beyond
methods: Co-creation from a practice-oriented perspec-
tive. In Proceedings of Design Research Society Bien-
nial International Conference, Umeå, Sweden (Vol. 1,
No. 1, pp. 967-979 (2014).
Sanders, E. B.-N., & Stappers, P. J.: Co-creation and the
new landscapes of design. Co-Design 4(1), 5–18
(2008).
Government Digital Service Co-design: Concepts to Collaboration Tools
69

Simonofski, A., Snoeck, M., & Vanderose, B. (2019). Co-
creating e-Government Services: An Empirical Analy-
sis of Participation Methods in Belgium. In Setting
Foundations for the Creation of Public Value in Smart
Cities (pp. 225-245). Springer, Cham.
Scholl, H. J.: The EGOV research community: An update
on where we stand. In Electronic Government (pp. 1–
16). Springer (2014).
Siau, K., Tan, X., & Sheng, H.: Important characteristics of
software development team members: an empirical in-
vestigation using Repertory Grid. Information Systems
Journal 20(6), 563-580 (2010).
Stegaru, G., Danila, C., Sacala, I. S., Moisescu, M., &
Stanescu, A. M.: E-Services quality assessment frame-
work for collaborative networks. Enterprise Infor-
mation Systems 9(5-6), 583-606 (2015).
Twizeyimana, J. D., & Andersson, A.: The public value of
E-Government–A literature review. Government infor-
mation quarterly (2019).
van Velsen, L., van der Geest, T., ter Hedde, M., & Derks,
W.: Requirements engineering for e-Government ser-
vices: A citizen-centric approach and case study. Gov-
ernment Information Quarterly 26(3), 477-486 (2009).
Warriach, N.F. and Tahira, M.: “Impact of information and
communication technologies on research and develop-
ment: a case of university of the Punjab-Pakistan”, Pa-
kistan Journal of Library and Information Management,
Vol. 15 (2015).
Wu, A.: Convertino, G., Ganoe, C., Carroll, J. M., & Zhang,
X. L. Supporting collaborative sense-making in emer-
gency management through geo-visualization. Interna-
tional Journal of Human-Computer Studies 71(1), 4-23
(2013).
Wever, R., Van Kuijk, J., & Boks, C. User-centred design
for sustainable behaviour. International Journal of Sus-
tainable Engineering, 1(1), 9–20 (2008).
Zhao, Y., Tang, L. C., Darlington, M. J., Austin, S. A., &
Culley, S. J.: High value information in engineering or-
ganizations. International Journal of Information Man-
agement 28(4), 246-25 (2008).
Zheng, P., Wang, Z., Chen, C. H., & Khoo, L. P. (2019). A
survey of smart product-service systems: Key aspects,
challenges and future perspectives. Advanced Engi-
neering Informatics, 42, 100973.
ICE-B 2020 - 17th International Conference on e-Business
70
