
Acoustic Anomaly Detection for Machine Sounds based on Image
Transfer Learning
Robert M
¨
uller
a
, Fabian Ritz
b
, Steffen Illium
c
and Claudia Linnhoff-Popien
d
Mobile and Distributed Systems Group, LMU Munich, Germany
Keywords:
Acoustic Anomaly Detection, Transfer Learning, Machine Health Monitoring.
Abstract:
In industrial applications, the early detection of malfunctioning factory machinery is crucial. In this paper, we
consider acoustic malfunction detection via transfer learning. Contrary to the majority of current approaches
which are based on deep autoencoders, we propose to extract features using neural networks that were pre-
trained on the task of image classification. We then use these features to train a variety of anomaly detection
models and show that this improves results compared to convolutional autoencoders in recordings of four
different factory machines in noisy environments. Moreover, we find that features extracted from ResNet
based networks yield better results than those from AlexNet and Squeezenet. In our setting, Gaussian Mixture
Models and One-Class Support Vector Machines achieve the best anomaly detection performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Anomaly detection is one of the most prominent in-
dustrial applications of machine learning. It is used
for video surveillance, monitoring of critical infras-
tructure or the detection of fraudulent behavior. How-
ever, most of the current approaches are based on de-
tecting anomalies in the visual domain. Issues arise
when the scenery cannot be covered by cameras com-
pletely, leading to blind-spots in which no prediction
can be made. Naturally, this applies to many inter-
nals of industrial production facilities and machines.
In many cases a visual inspection can not capture the
true condition of the surveilled entity. A pump suf-
fering from a small leakage, a slide rail that has no
grease or a fan undergoing voltage changes might ap-
pear intact when inspected visually but when moni-
tored acoustically, reveal its actual condition through
distinct sound patterns. Further, acoustic monitoring
has the advantage of comparably cheap and easily de-
ployable hardware. The early detection of malfunc-
tioning machinery with a reliable acoustic anomaly
detection system can prevent greater damages and re-
duce repair and maintenance costs.
In this work, we focus on the detection of anoma-
lous sounds emitted from factory machinery such as
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3108-713X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7707-1358
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0021-436X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6284-9286
Figure 1: Overview of the proposed workflow. First, the raw
waveform is transformed into a Mel-spectrogram. Small
segments of ≈ 2s are then extracted in sliding window fash-
ion. Subsequently, a pretrained image classification neural
network is used to extract feature vectors. These feature
vectors serve as the input to an anomaly detection model.
A prediction over the whole recording is made by mean-
pooling the scores of the analyzed segments.
fans, pumps, valves and slide rails. Obtaining an ex-
haustive number of recordings from anomalous oper-
ation for training is not suitable as it would require
either deliberately damaging machines or waiting a
Müller, R., Ritz, F., Illium, S. and Linnhoff-Popien, C.
Acoustic Anomaly Detection for Machine Sounds based on Image Transfer Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0010185800490056
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2021) - Volume 2, pages 49-56
ISBN: 978-989-758-484-8
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
49

potentially long time until enough machines suffered
from damages. Consequently, we assume there is no
access to anomalous recordings during the training
of the anomaly detection systems. Hence, training
the system proceeds in a fully unsupervised manner.
Moreover, we assume normal operation recordings to
be highly contaminated with background noises from
real world factory environments.
In the recent years, using CNNs in conjunction
with a signals time-frequency representations has be-
come ubiquitous in acoustic signal processing for a
variety of tasks such as environmental sound classi-
fication (Salamon and Bello, 2017), speech recogni-
tion (Qian et al., 2016) and music audio tagging (Pons
and Serra, 2019). Nevertheless, these approaches
specifically design CNN architectures for the task at
hand and require a labeled dataset. These results
make evident that CNNs are promising candidates for
acoustic anomaly detection. Due to the lack of labels
the predominant approach is to rely on deep autoen-
coders (AEs). An AE is a neural network (NN) that
first compresses its input into a low dimensional rep-
resentation and subsequently reconstructs the input.
The reconstruction error is taken as the anomaly score
since it is assumed that input differing from the train-
ing data cannot be reconstructed precisely. These is
different to the more traditional approach where one
extracts a set of handcrafted features (requires domain
knowledge) from the signal and use these features as
input to a dedicated anomaly detection (AD) model
e.g. a density estimator. However, these AD models
collapse with high dimensional input (e.g. images or
spetrograms) due to the curse of deminsionality.
In this work we aim to combine the best of both
worlds and ask the question whether it is possible to
use a NN to automatically extract features and use
these features in conjunction with more traditional
anomaly detection models while achieving compara-
ble or even superior performance. By observing that
patterns of anomalous operation can often be spot-
ted visually in the time-frequency representation (e.g.
Mel-spectrogram) of a recording, we claim that pre-
trained image classification convolutional neural net-
works (CNNs) can extract useful features even though
the task at hand is vastly different. This is because
in order to correctly classify images the CNN has to
learn a generic filters such as edge, texture and ob-
ject detectors (Olah et al., 2017; Olah et al., 2020)
that can extract valuable and semantically meaning-
ful features that also transfer to various downstream
tasks. Moreover, this reduces the burden of finding a
suitable neural network architecture.
We propose to use features from images of seg-
ments gathered from the Mel-spectrograms of normal
operation data. We then standardize the obtained fea-
tures and use them to train various anomaly detection
models. A sliding window in combination with mean-
pooling is used to make a decision over a longer time
horizon at test time. A visualization of the proposed
system can be seen in Figure 1.
The remaining paper is structured as follows:
In Section 2, we survey related approaches to acous-
tic anomaly detection in an unsupervised learning
learning setting. Section 3 introduces the proposed
approach with more mathematical rigor. Then we
briefly introduce the dataset we used to evaluate our
method in Section 4, followed by a description of the
experimental setup in Section 5. Results are discussed
in Section 6. We close by summarizing our findings
and outlining future work in Section 7.
2 RELATED WORK
While various approaches on classification (Mesaros
et al., 2018; Abeßer, 2020) and tagging (Fonseca
et al., 2019) of acoustic scenes have been proposed in
the last years, acoustic anomaly detection is still un-
derrepresented. Due to the release of publicly avail-
able datasets (Jiang et al., 2018; Purohit et al., 2019;
Koizumi et al., 2019; Grollmisch et al., 2019), the sit-
uation is gradually improving.
As previously mentioned, the majority of ap-
proaches to acoustic anomaly detection relies upon
deep autoencoders. For example, (Marchi et al.,
2015) use a bidirectional recurrent denoising AE to
reconstruct auditory spectral features to detect novel
events. (Duman et al., 2019) propose to use a con-
volutional AE on Mel-spectrograms to detect anoma-
lies in the context of industrial plants and processes.
In (Meire and Karsmakers, 2019), the authors com-
pare various AE architectures with special focus on
the applicability of these methods on the edge. They
conclude that a convolutional architecture operating
on the Mel-Frequency Cesptral coefficients is well
suited for the task while a One-Class Support Vec-
tor Machine represents a strong and more parame-
ter efficient baseline. (Kawaguchi et al., 2019) ex-
plicitly address the issue of background noise. An
ensemble method of front-end modules and back-
end modules followed by an ensemble-based detector
combines the strengths of various algorithms. Front-
ends consist of blind-dereverberation and anomalous-
sound-extraction algorithms, back-ends are AEs. The
final anomaly score is computed by score-averaging.
Finally, in (Koizumi et al., 2017) anomalous sound
detection is interpreted as statistical hypothesis test-
ing where they propose a loss function based on the
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
50

Neyman-Pearson lemma. However this approach re-
lies on the simulation of anomalous sounds using ex-
pensive rejection sampling.
In contrast to these architecture-driven ap-
proaches, (Koizumi et al., 2019) introduced Batch-
Uniformization, a modification to the AE’s training-
procedure where the reciprocal of the probabilistic
density of each sample is used to up-weigh rare
sounds.
Another line of work investigates upon methods
that operate directly on the raw waveform (Hayashi
et al., 2018; Rushe and Namee, 2019). These
methods use generative, WaveNet-like (Oord et al.,
2016) architectures to predict the next sample and
take the prediction error as a measure of abnormal-
ity. Their results indicate a slight advantage over
AE based approaches at the cost of higher compu-
tational demands. In this work, we propose a dif-
ferent approach to acoustic anomaly detection. We
use features extracted from NNs pretrained with im-
age classification to train anomaly detection mod-
els, which is inspired by the success of these fea-
tures in other areas, such as snore sound classifica-
tion (Amiriparian et al., 2017), emotion recognition
in speech (Cummins et al., 2017), music information
retrieval (Gwardys and Grzywczak, 2014) and medi-
cal applications (Amiriparian et al., rint).
3 PROPOSED APPROACH
Let X ∈ R
F×T
be the time-frequency representation of
some acoustic recording where T is the time dimen-
sion and F the number of frequency bins. In the con-
text of acoustic anomaly detection, we want to find
a function F : X → R such that F (X) is higher for
anomalous recordings than for recordings from nor-
mal operation without having access to anomalous
recordings during training. To reduce computational
demands and to increase the number of datapoints, it
is common to extract smaller patches x
1
,... x
i
,. .. x
n
of
the underlying spectrogram X across the time dimen-
sion in a sliding window fashion where x
i
∈ R
t×F
,t <
T . Here we propose to extract a d-dimensional fea-
ture vector using a feature extractor f : R
t×F
→ R
d
for each x
i
. Then we can set F to be some anomaly
detection algorithm and train F on all features of ex-
tracted patches in the dataset D = {X
j
∈ R
F×T
}
N
j=1
.
The anomaly score for the entire spectrogram X can
be computed by averaging (mean-pooling) the predic-
tions from the smaller patches:
F (X) =
1
n
n
∑
i=1
F ◦ f (x
i
) (1)
Since we observed that acoustic anomalies of factory
machinery can often be spotted visually (see Figure
2), we claim that a NN pretrained on the task of image
recognition can extract meaningful features that help
to distinguish between normal and anomalous opera-
tion. The filters of these networks were shown (Olah
et al., 2017; Olah et al., 2020) to having learned to
recognize colors, contrast, shapes (e.g. lines, edges),
objects and textures. Leveraging pretrained NNs is
commonly referred to as transfer learning.
Note that the simple summation in Equation 1 ne-
glects the temporal dependency between the patches.
In our case the signals we study are considerably less
complex than e.g. speech or music and, to some ex-
tend, exhibit stationary patterns. Thus, we argue that
introducing recurrence has only minor benefits at the
cost of increased complexity.
4 DATASET
In our experiments, we use the recently introduced
MIMII dataset (Purohit et al., 2019). It consists of
recordings from four industrial machine types (fans,
pumps, slide rails and valves) under normal and
anomalous operation. For each machine type, four
datasets exist, each representing a different prod-
uct model. Note that anomalous recordings exhibit
various scenarios such as leakage, clogging, voltage
change, a loose belt or no grease. In addition, back-
ground noise recorded in real-world factories was
added to each recording according to a certain Signal-
to-Noise-Ratio (SNR). In our analysis, we use sounds
with a SNR of −6dB. We argue that this is very
close to the practical use as it is unpreventable that
microphones monitoring machines will also capture
background noises in a factory environment. Each
single-channel recording is 10 seconds long and has
a sampling rate of 16kHz. Figure 2 depicts Mel-
spectrograms of normal and anomalous sounds for all
machine types.
5 EXPERIMENTS
To study the efficacy of image transfer learning for
acoustic anomaly detection, we first compute the Mel-
Spectrograms for all recordings in the dataset us-
ing 64 Mel-bands, a hanning window of 1024 and a
hop length of 256. Afterwards, we extract 64 × 64
Mel-spectrogram patches (≈ 2s) in a sliding win-
dow fashion with an offset of 32 (≈ 1s) across the
Acoustic Anomaly Detection for Machine Sounds based on Image Transfer Learning
51
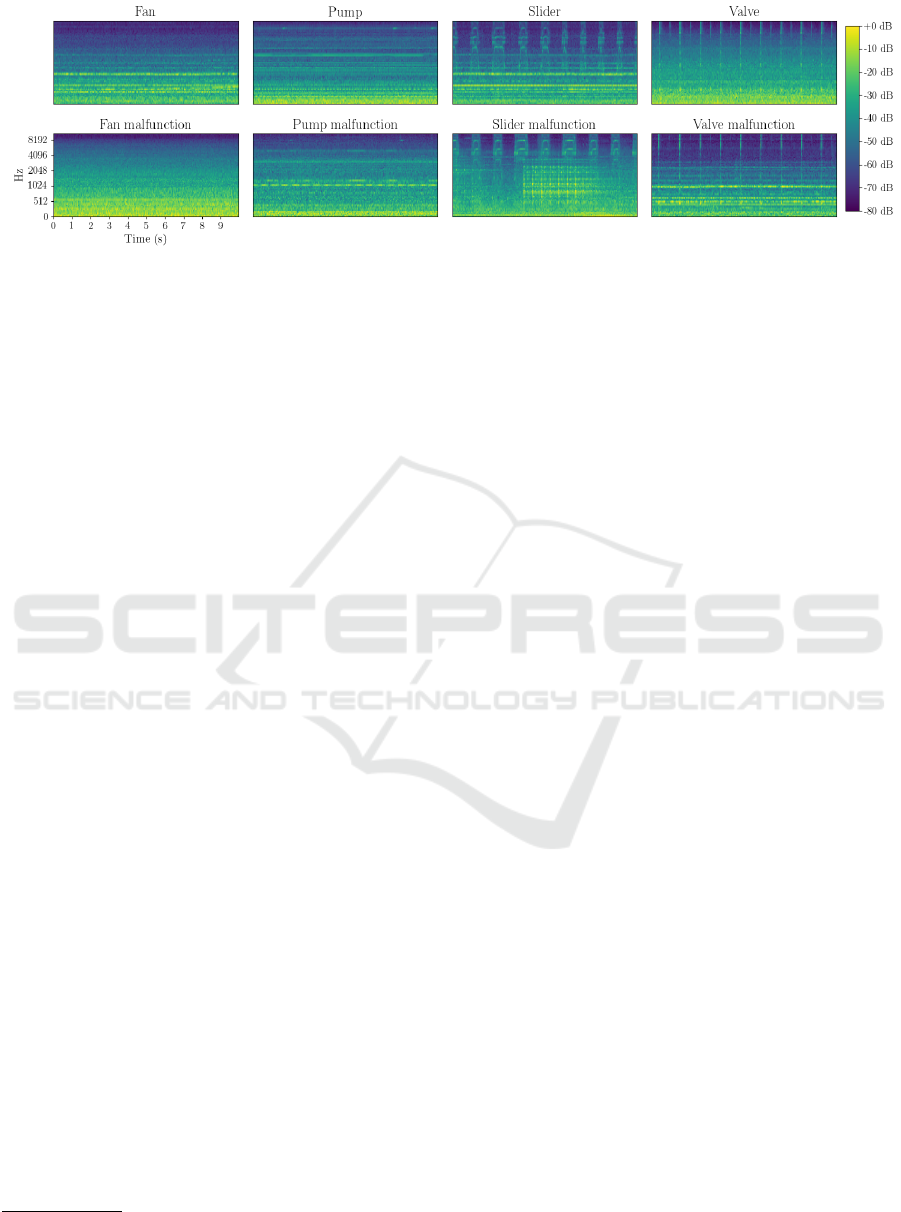
Figure 2: Mel-spectrograms of recordings from normal (top row) and anomalous operation (bottom row) across all machine
types in the MIMII dataset. Since anomalies can often be spotted visually in this representation, using image classification
models is reasonable.
time axis and convert them to RGB-images utilizing
the viridis color-map
1
. Subsequently, images are up-
scaled (224 × 224) and standardized using the values
obtained from ImageNet to match the domain of the
feature extractor f . Note that due to our choice of the
size of Mel-spectrogram patches, the original aspect-
ratio remains unaltered, countering potential informa-
tion loss. Then, we extract a feature vector for each
patch by using various NNs that were pretrained on
ImageNet and apply standardization. Finally, we train
multiple anomaly detection models on these features.
During training, we randomly exclude 150 samples,
each with a length of 10s, from the normal data for
testing. The same amount of anomalous operation
data is randomly added to the test set. A decision
for each sample is made using mean pooling, as dis-
cussed in Section 3. The whole process is repeated
5 times with 5 different seeds and the average Area
Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve
(AUC) is used to report performance.
5.1 Pretrained Feature Extractors
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are known
to perform well on two dimensional data input with
spatial relations. Hence, we repurpose the following
classifiers, pretrained on ImageNet (Deng et al., 2009)
for feature extraction:
Alexnetv3 (Krizhevsky et al., 2012) is a two stream
network architecture involving convolutions (kernels:
11 × 11, 5 × 5 and 3 × 3) and max pooling followed
by two fully connected layers. We use the activations
from the penultimate layer, resulting in a 4096 dimen-
sional vector.
ResNet18 (He et al., 2016) was designed to
counter the problem of diminishing returns when net-
work depth increases. The architecture consists of
1
We have found the choice of colormap to be neglectable
in terms of performance.
multiple residual blocks. 16 + 2 layers (initial convo-
lution and max-pooling, followed by 8 convolutional
residual blocks) with increasing convolutional filter
sizes lead to a single average pooling operation. We
use the 512 activations thereafter for training.
ResNet34 (He et al., 2016) adheres to the same
principles as ResNet18 at an increased depth of 32 +
2 layers.
SqueezeNet (Iandola et al., 2016) was designed
to use as few parameters as possible (50 times fewer
than AlexNet) while still providing comparable clas-
sification accuracy. This is achieved with the help of
Fire layers equipped with squeeze (1 × 1) and expand
(3 × 3) modules. We apply 2 × 2 average pooling to
the final feature-map before the classifier to extract a
2048-dimensional feature vector.
5.2 Anomaly Detection Models
We compare six well established anomaly detection
algorithms:
The Isolation Forest (IF) (Liu et al., 2008) is based
upon the assumption that anomalies lie in sparse re-
gion in feature space and are therefore easier to iso-
late. Features are randomly partitioned and the av-
erage path length across multiple trees is used as the
normality score. The number of trees in the forest is
set to 128.
A Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) fits a mixture
of Gaussians on to the observed features. The log-
probability of a feature vector under the trained GMM
is used as the normality score. Parameters are esti-
mated via expectation-maximization. We use 80 mix-
ture components with diagonal covariance matrix ini-
tialized using k-means. The iteration limit is set to
150.
The Bayesian Gaussian Mixture Model (B-GMM)
is trained via variational inference and places prior
distributions over the parameters. In many cases, it
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
52

is less dependent on the specified number of mix-
tures. In our setting, this might be advantageous as
this quantity is hard to determine due to the lack of
anomalous data for validation. We use the same pa-
rameters as for the GMM.
A One-Class Support Vector Machine (OC-
SVM) (Sch
¨
olkopf et al., 2000) aims to find the max-
imum margin hyperplane that best separates the data
from the center. As ν (approximate ratio of outliers)
must be > 0, we set ν = 10
−4
since the training data
consists of normal data only.
Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) is a non-
parametric density estimation algorithm that centers a
predefined kernel with some bandwidth over each dat-
apoint and increases the density around this point. Ar-
eas with many datapoints will therefore have a higher
density than those with only a few. We use a gaus-
sian kernel with a bandwidth of 0.1. The density at a
datapoint is used as normality score.
A Deep Convolutional Autoencoder (DCAE) re-
constructs its own input, in this case the Mel-
spectrogram images. We use a LeNet style, three
layer convolutional encoder architecture with 32,64
and 128 output channels, a kernel size of 5, Ex-
ponential Linear Unit (ELU) (Clevert et al., 2016)
activation functions, batch normalization (Ioffe and
Szegedy, 2015) and a 128-dimensional bottleneck
(LeNet-AE). Moreover, we also consider a simpler
encoder architecture with 12,24 and 48 output chan-
nels, ReLU (Nair and Hinton, 2010) activation func-
tions and a kernel size of 4 (Small-DCAE). The de-
coders mirror the encoders using de-convolutional
layers. For optimization, we use Adam with learn-
ing rate = 10
−4
, batch size = 128 and train for 80
epochs. The mean squared error between the origi-
nal image and the reconstruction is used as the loss
function and anomaly score.
6 RESULTS
In this section, we discuss the key findings of the re-
sults depicted in Table 1. Note that these findings only
refer to the setting introduced in the prior chapters.
1) Image Transfer Learning is More Effective for
Detecting Anomalous Machine Sounds than Au-
toencoders Trained from Scratch. Autoencoders
outperform the models based on image transfer learn-
ing only in a single setting (Small-DCAE on Pump-
M6). In the majority of the cases, LeNet-DCAE
yields better results than Small-DCAE. Mostly, the
DCAEs do not even come close to their competitors,
which supports our hypothesis that the features ex-
tracted by learned filters from pretrained image clas-
sification models are better suited for detecting sub-
tle anomalies. Further, reconstruction based anomaly
detection is based upon a proxy task rather than mod-
eling the task explicitly.
2) ResNet Architectures are Superior Feature Ex-
tractors. To compare the feature extractors, we
count the scenarios in that a specific feature extrac-
tor combined with different anomaly detection mod-
els yields the highest or the second highest score and
create tuples of the form (1
st
,2
nd
). As depicted in
Table 1, there are 16 distinct evaluation settings in
which either the highest or the second highest score
can be achieved. Ranked from best to worst, we
get the following results: ResNet34 (7,6), ResNet18
(3,5), AlexNet (3,2), SqueezeNet (2,2) and Autoen-
coders (1, 0). A clear superiority of ResNet based
feature feature extractors can be observed. Interest-
ingly, these are also the models with a lower classi-
fication error on ImageNet compared to SqueezeNet
and AlexNet. These results are consistent with a re-
cent finding that there is strong correlation between
ImageNet top-1 accuracy and transfer learning ac-
curacy (Kornblith et al., 2019). Another important
observation is that ResNet34’s good performance al-
most exclusively stems from top performance on slid-
ers and valves. The Mel-spectrogram images from
these machines have more fine granular variations
than those from fans and pumps which show a more
stationary allocation of frequency bands. We assume
that ResNet34 extracts features on a more detailed
level which can explain inferior performance on fan
and pump data. Generally, we have found SqueezeNet
to be the least reliable feature extractor. Note that
these findings also hold when all feature vectors are
reduced to the same dimensionality using Principle
Components Analysis (PCA).
3) GMM and OC-SVM Yield the Best Perfor-
mance. To compare the anomaly detection models,
we count the scenarios in that a specific anomaly de-
tection model combined with different feature extrac-
tors achieves the best or second best result. Employ-
ing the same ranking strategy as above, the results are
as follows: GMM (9,8), OC-SVM (6,2), Autoen-
coders (1,0), B-GMM (0, 3), IF (0,2), KDE (0,0).
Clearly, GMM and OC-SVM outperform all other
models by a large margin. Together, they account
for 15/16 of the best performing models and 10/16
of second best performing models. Although GMM
and B-GMM are both based on the same theoretical
assumptions, B-GMM produces inferior results. We
Acoustic Anomaly Detection for Machine Sounds based on Image Transfer Learning
53
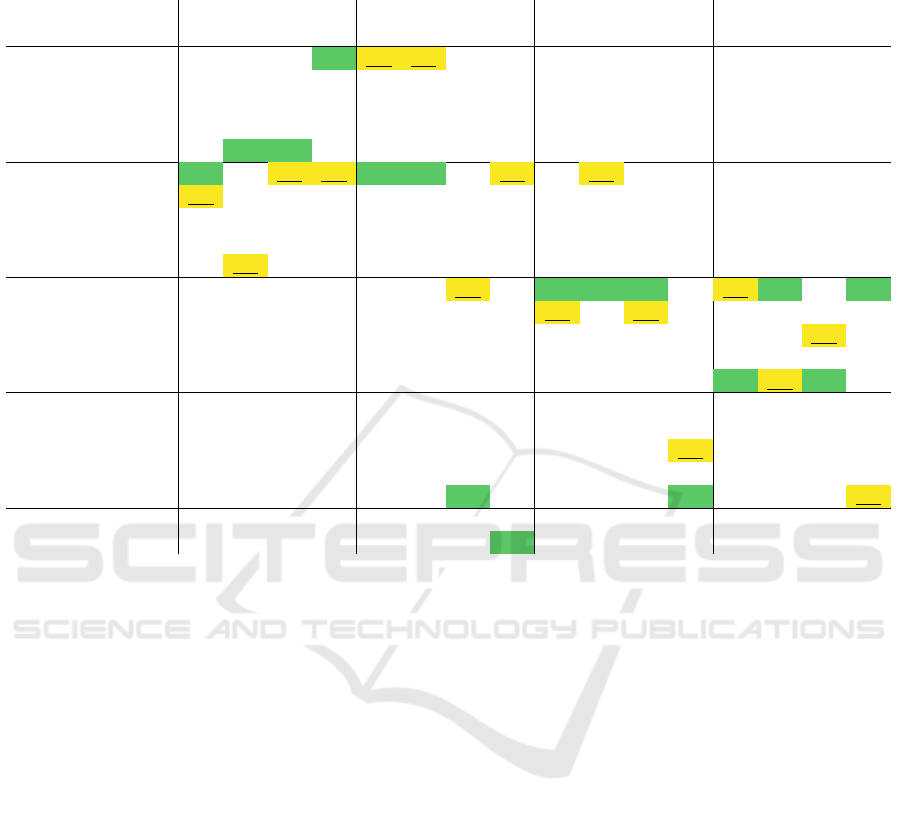
Table 1: Anomaly detection results for all machine types and machine IDs (M0, M2, M4 and M6). The best performing
model (read vertically) is written in bold and colored in green, the second best is underlined and colored in yellow. Each entry
represents the average AUC across five seeds.
Fan Pump Slider Valve
M0 M2 M4 M6 M0 M2 M4 M6 M0 M2 M4 M6 M0 M2 M4 M6
GMM 57.7 61.7 53.9 94.5 84.1 70.8 81.6 66.0 98.3 80.9 61.4 57.5 60.2 69.2 59.9 53.5
B-GMM 50.9 61.4 47.7 82.2 71.8 60.2 73.4 53.3 83.2 65.0 50.0 57.0 55.2 62.7 51.4 48.3
IF 53.1 59.7 48.9 84.6 75.9 62.4 75.0 55.9 89.4 69.0 51.9 56.2 50.1 63.4 53.3 49.8
KDE 55.7 59.1 50.5 90.3 76.4 65.9 74.8 61.0 97.8 79.3 59.7 55.0 54.6 64.4 57.1 51.4
AlexNet
OC-SVM 51.0 73.1 59.7 93.2 77.5 56.4 81.1 60.1 96.2 81.4 53.6 56.5 61.6 73.6 48.3 48.9
GMM 62.6 64.1 59.3 94.4 84.5 71.3 84.0 68.3 99.1 85.8 68.8 65.6 58.3 73.3 60.2 56.9
B-GMM 59.2 60.5 54.8 91.0 79.1 69.7 79.4 59.5 98.3 77.7 61.4 61.2 70.1 71.7 56.1 50.3
IF 58.0 60.5 55.3 86.5 70.8 59.0 77.3 54.6 97.7 72.7 60.6 61.2 56.5 69.8 58.2 47.5
KDE 57.9 59.1 55.6 85.9 76.6 56.5 76.7 62.2 98.1 77.0 61.2 60.9 57.6 62.9 56.8 49.7
ResNet18
OC-SVM 55.0 68.8 57.4 87.7 71.6 55.2 78.6 60.6 96.7 79.6 69.3 66.2 61.1 76.1 56.8 43.1
GMM 58.7 65.6 57.0 90.9 78.4 66.8 87.9 63.2 99.6 90.4 82.5 69.1 73.0 79.1 60.1 61.9
B-GMM 55.7 61.8 52.3 85.8 71.5 61.1 84.5 55.2 99.2 85.4 72.3 63.6 70.8 76.2 59.3 57.9
IF 53.9 62.0 49.9 82.2 52.3 48.3 79.3 49.4 98.6 83.1 69.5 60.2 65.9 71.2 60.3 54.0
KDE 55.0 62.6 52.3 83.1 62.0 51.8 82.8 58.3 99.0 84.0 68.2 62.2 67.5 71.9 53.9 58.2
ResNet34
OC-SVM 50.1 67.4 57.5 83.0 64.9 51.5 81.2 60.2 96.8 85.0 71.4 64.3 75.6 77.8 64.3 53.1
GMM 56.1 60.4 49.4 83.4 72.1 46.4 87.6 60.8 96.7 76.8 52.1 62.9 62.8 75.3 53.3 57.3
B-GMM 54.4 59.8 47.0 84.5 72.3 48.2 86.2 69.0 95.0 78.8 55.8 65.0 63.8 74.0 52.4 56.8
IF 53.2 64.0 44.8 84.6 76.1 45.5 85.3 60.2 98.9 78.2 53.1 70.6 56.6 68.7 51.5 56.6
KDE 54.4 60.5 47.0 84.3 74.5 45.2 86.5 61.4 98.7 80.8 56.4 69.2 65.0 74.5 52.8 57.7
SqueezeNet
OC-SVM 55.6 64.8 46.2 86.7 78.8 49.4 88.4 62.3 99.2 81.5 59.4 71.6 69.0 71.3 53.1 58.2
LeNet-DCAE - 49.1 57.0 53.2 66.9 65.3 54.4 76.0 66.6 95.9 70.4 56.2 50.6 42.3 55.6 51.2 45.5
Small-DCAE - 48.3 54.1 49.3 63.7 69.9 52.9 73.1 69.2 95.3 68.4 55.7 53.3 36.6 57.2 51.2 45.4
suspect the weight priors to potentially be too restric-
tive.
4) Results are Highly Dependent on the Machine
Type and the Machine Model. The model per-
forming best on valves has an average AUC of 79.1.
This is low compared to the other machine types as
these always have at least one scenario with an aver-
age AUC > 80. Moreover, the highest achieved score
varies considerably across all machine types. This
indicates that some machine types are more suited
for our approach (pumps, sliders) than others (fans,
valves). More importantly, a significant variance be-
tween different machine IDs (M0 - M6) can be ob-
served. Results on fans make this problem most evi-
dent. While M0, M2 and M4 have average scores of
62.6,73.1 and 59.7, M6 achieves an average of 94.5.
M6 improves upon M4 at ≈ 30%. This suggests that
anomalous sound patterns are vastly different (more
or less subtle) even for different models of the same
machine type. Future approaches should take this into
account.
7 CONCLUSION
In this work, we thoroughly studied acoustic anomaly
detection for machine sounds. For feature extraction,
we used readily available neural networks that were
pretrained to classify ImageNet images.
We then used these features to train five differ-
ent anomaly detection models. Results indicate that
features extracted with ResNet based architectures in
combination with a GMM or an OC-SVM yield the
best average AUC.
Moreover, we confirmed our hypothesis that the
image based features are general purpose and conse-
quently also yield Competitive acoustic anomaly de-
tection results.
Future work could investigate upon further ensem-
ble approaches and other feature extraction architec-
tures (Kawaguchi et al., 2019; Pons and Serra, 2019;
Howard et al., 2017; Huang et al., 2016). In addi-
tion, our approach might benefit from techniques that
reduce background noise (Zhang et al., 2018) or en-
able decisions over a longer time-horizon (Xie et al.,
2019). One might also try to use pretrained feature
extractors from other, more related domains such as
music or environmental sounds.
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
54

REFERENCES
Abeßer, J. (2020). A review of deep learning based methods
for acoustic scene classification. Applied Sciences,
10(6).
Amiriparian, S., Gerczuk, M., Ottl, S., Cummins, N., Fre-
itag, M., Pugachevskiy, S., Baird, A., and Schuller,
B. W. (2017). Snore sound classification using image-
based deep spectrum features. In INTERSPEECH,
volume 434, pages 3512–3516.
Amiriparian, S., Schmitt, M., Ottl, S., Gerczuk, M., and
Schuller, B. (im Druck / in print). Deep unsupervised
representation learning for audio-based medical appli-
cations. In Nanni, L., Brahnam, S., Ghidoni, S., Brat-
tin, R., and Jain, L., editors, Deep Learners and Deep
Learner Descriptors for Medical Applications.
Clevert, D.-A., Unterthiner, T., and Hochreiter, S. (2016).
Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponen-
tial linear units (elus). arxiv 2015. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1511.07289.
Cummins, N., Amiriparian, S., Hagerer, G., Batliner, A.,
Steidl, S., and Schuller, B. W. (2017). An image-based
deep spectrum feature representation for the recogni-
tion of emotional speech. In Proceedings of the 25th
ACM international conference on Multimedia, pages
478–484.
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., and Fei-
Fei, L. (2009). ImageNet: A Large-Scale Hierarchical
Image Database. In CVPR09.
Duman, T. B., Bayram, B., and
˙
Ince, G. (2019). Acoustic
anomaly detection using convolutional autoencoders
in industrial processes. In International Workshop on
Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmen-
tal Applications, pages 432–442. Springer.
Fonseca, E., Plakal, M., Font, F., Ellis, D. P. W., and Serra,
X. (2019). Audio tagging with noisy labels and min-
imal supervision. In Submitted to DCASE2019 Work-
shop, NY, USA.
Grollmisch, S., Abeβer, J., Liebetrau, J., and Lukashe-
vich, H. (2019). Sounding industry: Challenges and
datasets for industrial sound analysis. In 2019 27th
European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO),
pages 1–5. IEEE.
Gwardys, G. and Grzywczak, D. (2014). Deep image
features in music information retrieval. Interna-
tional Journal of Electronics and Telecommunica-
tions, 60(4):321–326.
Hayashi, T., Komatsu, T., Kondo, R., Toda, T., and Takeda,
K. (2018). Anomalous sound event detection based on
wavenet. In 2018 26th European Signal Processing
Conference (EUSIPCO), pages 2494–2498. IEEE.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2016). Deep resid-
ual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of
the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition, pages 770–778.
Howard, A. G., Zhu, M., Chen, B., Kalenichenko, D.,
Wang, W., Weyand, T., Andreetto, M., and Adam,
H. (2017). Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neu-
ral networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1704.04861.
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Weinberger, K., and van der Maaten, L.
(2016). Densely connected convolutional networks.
arxiv 2017. arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.06993.
Iandola, F. N., Han, S., Moskewicz, M. W., Ashraf, K.,
Dally, W. J., and Keutzer, K. (2016). Squeezenet:
Alexnet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters
and¡ 0.5 mb model size, 2016. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1602.07360, 1(10).
Ioffe, S. and Szegedy, C. (2015). Batch normalization: Ac-
celerating deep network training by reducing internal
covariate shift. In International Conference on Ma-
chine Learning, pages 448–456.
Jiang, Y., Li, C., Li, N., Feng, T., and Liu, M. (2018).
Haasd: A dataset of household appliances abnormal
sound detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd In-
ternational Conference on Computer Science and Ar-
tificial Intelligence, CSAI ’18, page 6–10, New York,
NY, USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Kawaguchi, Y., Tanabe, R., Endo, T., Ichige, K., and
Hamada, K. (2019). Anomaly detection based on an
ensemble of dereverberation and anomalous sound ex-
traction. In ICASSP 2019 - 2019 IEEE International
Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Process-
ing (ICASSP), pages 865–869.
Koizumi, Y., Saito, S., Uematsu, H., and Harada, N. (2017).
Optimizing acoustic feature extractor for anomalous
sound detection based on neyman-pearson lemma. In
2017 25th European Signal Processing Conference
(EUSIPCO), pages 698–702. IEEE.
Koizumi, Y., Saito, S., Uematsu, H., Harada, N., and
Imoto, K. (2019). Toyadmos: A dataset of miniature-
machine operating sounds for anomalous sound de-
tection. In 2019 IEEE Workshop on Applications of
Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA),
pages 313–317. IEEE.
Koizumi, Y., Saito, S., Yamaguchi, M., Murata, S., and
Harada, N. (2019). Batch uniformization for minimiz-
ing maximum anomaly score of dnn-based anomaly
detection in sounds. In 2019 IEEE Workshop on Ap-
plications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics
(WASPAA), pages 6–10.
Kornblith, S., Shlens, J., and Le, Q. V. (2019). Do better
imagenet models transfer better? In Proceedings of
the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition, pages 2661–2671.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012). Im-
agenet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. In Advances in neural information process-
ing systems, pages 1097–1105.
Liu, F. T., Ting, K. M., and Zhou, Z. (2008). Isolation for-
est. In 2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on
Data Mining, pages 413–422.
Marchi, E., Vesperini, F., Eyben, F., Squartini, S., and
Schuller, B. (2015). A novel approach for automatic
acoustic novelty detection using a denoising autoen-
coder with bidirectional lstm neural networks. In 2015
IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech
and signal processing (ICASSP), pages 1996–2000.
IEEE.
Meire, M. and Karsmakers, P. (2019). Comparison of deep
autoencoder architectures for real-time acoustic based
Acoustic Anomaly Detection for Machine Sounds based on Image Transfer Learning
55

anomaly detection in assets. In 2019 10th IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition
and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and
Applications (IDAACS), volume 2, pages 786–790.
Mesaros, A., Heittola, T., and Virtanen, T. (2018). A
multi-device dataset for urban acoustic scene classi-
fication. In Proceedings of the Detection and Classifi-
cation of Acoustic Scenes and Events 2018 Workshop
(DCASE2018), pages 9–13.
Nair, V. and Hinton, G. E. (2010). Rectified linear units
improve restricted boltzmann machines. In Proceed-
ings of the 27th international conference on machine
learning (ICML-10), pages 807–814.
Olah, C., Cammarata, N., Schubert, L., Goh, G., Petrov, M.,
and Carter, S. (2020). An overview of early vision in
inceptionv1. Distill, 5(4):e00024–002.
Olah, C., Mordvintsev, A., and Schubert, L. (2017). Feature
visualization. Distill, 2(11):e7.
Oord, A. v. d., Dieleman, S., Zen, H., Simonyan, K.,
Vinyals, O., Graves, A., Kalchbrenner, N., Senior,
A., and Kavukcuoglu, K. (2016). Wavenet: A
generative model for raw audio. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1609.03499.
Pons, J. and Serra, X. (2019). musicnn: Pre-trained con-
volutional neural networks for music audio tagging.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.06654.
Purohit, H., Tanabe, R., Ichige, K., Endo, T., Nikaido,
Y., Suefusa, K., and Kawaguchi, Y. (2019). Mimii
dataset: Sound dataset for malfunctioning industrial
machine investigation and inspection. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1909.09347.
Qian, Y., Bi, M., Tan, T., and Yu, K. (2016). Very
deep convolutional neural networks for noise robust
speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Au-
dio, Speech, and Language Processing, 24(12):2263–
2276.
Rushe, E. and Namee, B. M. (2019). Anomaly detec-
tion in raw audio using deep autoregressive networks.
In ICASSP 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Con-
ference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing
(ICASSP), pages 3597–3601.
Salamon, J. and Bello, J. P. (2017). Deep convolutional neu-
ral networks and data augmentation for environmental
sound classification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters,
24(3):279–283.
Sch
¨
olkopf, B., Williamson, R. C., Smola, A. J., Shawe-
Taylor, J., and Platt, J. C. (2000). Support vector
method for novelty detection. In Advances in neural
information processing systems, pages 582–588.
Xie, W., Nagrani, A., Chung, J. S., and Zisserman,
A. (2019). Utterance-level aggregation for speaker
recognition in the wild. In ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE
International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and
Signal Processing (ICASSP), pages 5791–5795. IEEE.
Zhang, X., Zhou, X., Lin, M., and Sun, J. (2018). Shuf-
flenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural
network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the
IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition, pages 6848–6856.
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
56
