
Information-theoretic Cost of Decision-making in Joint Action
Dari Trendafilov
1
, Daniel Polani
2
and Alois Ferscha
1
1
Institute of Pervasive Computing, Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria
2
Adaptive Systems Research Group, University of Hertfordshire, Hatfield, U.K.
Keywords:
Collective Behavior, Information Dynamics, Complex Systems, Information Theory.
Abstract:
We investigate the information processing cost relative to utility, associated with joint action in dyadic
decision-making. Our approach, built on the Relevant Information formalism, combines Shannon’s Infor-
mation Theory and Markov Decision Processes for modelling dyadic interaction, where two agents with in-
dependent controllers move an object together with fully redundant control in a grid world. Results show
that increasing collaboration relaxes the pressure on required information intake and vice versa, antagonistic
behavior takes a higher toll on information bandwidth. In this trade-off the particular embodiment of the envi-
ronment plays a key role, demonstrated in simulations with informationally parsimonious optimal controllers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Individual agents with limited information-
processing capabilities can successfully coordinate
their behavior and make well-informed collective
decisions. Examples include collective behaviors,
such as coordinated motion of birds and fishes
(Couzin et al., 2005), bees and ants (Franks et al.,
2002), or coordination of individual cells (Pezzulo
and Levin, 2015), which are complex collective
phenomena studied from various perspectives, e.g.,
population models (Couzin et al., 2005; Marshall
et al., 2009), game-theoretic (Challet and Zhang,
1997), or multi-agent simulations (Goldstone and
Janssen, 2005).
When agents interact socially, sometimes they act
in a complete agreement towards a shared goal, and
other times their goals may diverge or be completely
incompatible with each other. Over time, the inter-
action dynamics could alternate between cooperative
and antagonistic behavior and the flow of informa-
tion could reveal a given player’s contribution for the
emergence of a particular strategy. In certain cases,
limitations in the perception–action loop or in the
decision-making capabilities of agents could make
them behave irrationally while coordinating their joint
activities (e.g. autistic behavior).
In our study, we explore the information-
processing burden imposed on a completely ratio-
nal agent by its irrational (or adverse) partner. We
examine the trade-off between the level of compli-
ance (i.e. cooperative coordination) within a dyad
and the information processing cost incurred by the
cooperative agent while aiming to achieve a pre-
defined goal (i.e. utility level). Our framework, built
on Shannon’s information theory (Shannon, 1949),
imposes certain information processing constraints,
while not assuming any intrinsic dynamics nor a par-
ticular metabolism in providing necessary and suffi-
cient environmental conditions and invariants. This
approach allows to characterize causal relationships
in Bayesian networks. For this purpose, information
theory provides a universal language for quantifying
conditions and invariants for a large class of models in
a generic and principled way. Furthermore, it allows
comparison of models that are otherwise not directly
comparable.
To study agent coordination from an information-
theoretic perspective towards a predictive and quan-
titative theory of agent interactions, we look at em-
bodied agent dyads interacting in a grid-world. The
agents have independent controllers and a fully re-
dundant set of actions for controlling the same ob-
ject in the grid. Using information-theoretic tools, we
explore the information processing constraints of an
agent in achieving a specific goal, depending on the
level of cooperation by its partner.
2 BACKGROUND
Initially, social interaction and coordination have
been studied by (Walter, 1950) in natural and artifi-
cial agents, and more recently by (Ikegami and Iizuka,
2007; Paolo et al., 2008; Goldstone and Janssen,
2005). The study of coordination has applications
304
Trendafilov, D., Polani, D. and Ferscha, A.
Information-theoretic Cost of Decision-making in Joint Action.
DOI: 10.5220/0010252303040311
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2021) - Volume 1, pages 304-311
ISBN: 978-989-758-484-8
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

in ethology, where it helps to understand collec-
tive tasks like foraging, flocking or group decision-
making (Couzin et al., 2005; Nabet et al., 2009). Stig-
mergy in coordinated behavior of ant-like agents was
investigated by (Meyer and Wilson, 1991) in a study
based on cellular models of morphogenesis. Stig-
mergy and local observation are common ways for
modelling agent communication and coordinated be-
havior (Castelfranchi, 2006). In both cases, commu-
nication is ‘channeled’ through the environment, in
the case of stigmergy in a very explicit way by alter-
ing the environment. In these models communication
is spatially bound and limited by the amount of infor-
mation that can be ‘stored’ in the environment.
The study of collective behavior has traditionally
relied on a variety of different methodological tools,
ranging from more theoretical methods such as popu-
lation or game-theoretic models to empirical ones like
Monte Carlo or multi-agent simulations. More recent
approaches use information theory as a methodolog-
ical framework to study the flow of information and
the statistical properties of collectives of interacting
agents. Several general purpose tools provide effi-
cient information-theoretic analysis, including classi-
cal information-theoretic measures, measures of in-
formation dynamics and information-based methods
to study the statistical behavior of collective systems
(Moore et al., 2018; Lizier et al., 2014; Lindner et al.,
2011). A study by (Valentini et al., 2018), using
simulated agents, applies transfer entropy (Schreiber,
2000) to measure the flow of information generated in
collective decision-making mechanisms. The appli-
cation of complexity measures, and information the-
ory metrics in general, to support the automatic design
and analysis of collaborative dynamics, have recently
attracted the interest of multi-agent and robotics com-
munities, owing to their capability to capture relevant
features of robot behaviors while abstracting from im-
plementation details (Roli et al., 2019). In a study of a
homeokinetic dyad (Martius et al., 2008) suggest the
fundamental role of the maximal integration of the en-
vironment into the sensorimotor loop. Building on the
free energy principle of the brain (Friston, 2010), in
conjunction with the theory of sense-making, (Davis
et al., 2017) proposed a method to quantify interac-
tion dynamics of creative collaboration, e.g. rhythm
of interaction or turn-taking style, in order to charac-
terize collaborations over time. Multi-objective rein-
forcement learning has been applied with respect to
fairness (Matsui, 2019) and dyadic trust models have
been investigated by (Callebert et al., 2016).
Information theory has been successfully em-
ployed to models of embodied agents in a grow-
ing body of scientific literature starting from (Ashby,
1956). It provides a quantitative framework for as-
sessing how information is exchanged and processed
in collectives and has been explored in studies of nat-
ural (Zenil et al., 2015; Meyer, 2017; Butail et al.,
2016; Mwaffo et al., 2017) and artificial systems
(Sperati et al., 2011; Boedecker et al., 2011; Walker
et al., 2012; Kim et al., 2015). The premise is that
information is a key resource for organisms, which
is costly to process and affects the way information-
theoretic models of agents are investigated (Polani
et al., 2007). This idea has received an increased
attention due to new techniques by (Touchette and
Lloyd, 2000; Klyubin et al., 2007), and there are now
broad applications of information theory (Shalizi and
Crutchfield, 2002). The concept of relevant informa-
tion, introduced by (Polani et al., 2001; Polani et al.,
2006), builds on the Information Bottleneck princi-
ple (Tishby et al., 1999), extended to the perception–
action loop. Building on the relevant information for-
malism, (Harder et al., 2010) introduced a measure
of individuality (or autonomy) in a collaborative task
under information processing constraints.
3 INFORMATION THEORY
Shannon’s Information Theory defines entropy by
H(X) = −
∑
x
p(x)log p(x)
where X denotes a discrete random variable taking
values from X , and p(x) the probability of X taking
on the value x ∈ X . Entropy can be interpreted as the
average amount of information gained when a vari-
able’s value is revealed. When multiple random vari-
ables are correlated, then knowing the value of one
reduces the uncertainty about the other. The average
uncertainty about Y left after revealing the value of X
is quantified by the conditional entropy
H(Y |X) = −
∑
x,y
p(x, y)log p(y|x).
The average reduction in uncertainty, interpreted as
the amount of information that knowing X gives about
Y , is defined as the mutual information between the
two variables
I(X;Y ) = H(Y ) − H(Y |X).
In this study we apply and adapt the Relevant Infor-
mation method originally introduced in (Polani et al.,
2006), to joint action. It provides a measure depend-
ing only on the stochastic model and independent of
the topology of the environment. The measure quan-
tifies the minimal amount of information an agent
needs to process in order to achieve a certain level
Information-theoretic Cost of Decision-making in Joint Action
305

of utility as specified by a reward function. It reflects
an information parsimony principle, suggesting that
processing information has a metabolic cost (Polani
et al., 2007) and complies with findings that certain
neurons work at informational limits, minimising the
bandwidth to just maintain their function (Laughlin,
2001). In theory, the relevant information can be
much lower than the bandwidth of the sensor, that is,
different sensory inputs lead to the same distribution
of actions. An algorithm, proposed in (Polani et al.,
2006), computes the information-utility trade-off us-
ing a utility in terms of a reward structure.
4 SCENARIO
In our experimental scenario two agents perform the
task of achieving a particular goal configuration to-
gether (under information processing constraints) us-
ing controls from the same set of actions and alternat-
ing their moves on even (agent A) and odd (agent B)
steps. We can compute the optimal policy for each
agent using the Relevant Information method, assum-
ing we have a prediction for the policy of the other
agent. Our goal is to investigate how the behavior of
agent B influences the optimal policy and the infor-
mation constraints of agent A, and how that affects
the joint action.
The experimental setup consists of two agents
jointly moving an object in a 2-D grid-world by us-
ing four actions (up, down, left, right). The goal is
to move the object from one corner of the grid to the
opposite corner along the diagonal. The state of the
environment is denoted with the random variable S.
The scenario uses deterministic state transition model
p(s
t+1
|a
t
, s
t
) ∈ {0, 1}, which reflects the movement of
the object in the grid-world constrained by the walls.
In every step the agents get a reward determined by a
reward function r(s
t+1
;a
t
;s
t
), which depends on the
current state, the action taken and the state of the
world after the action is executed. The reward func-
tion of agent A is −1 for all states except the goal
state where it is 0. Thus, a policy that maximises the
expected utility of agent A is one that takes the short-
est path to the goal configuration. Note that due to the
particular action set there are many different shortest
paths to the goal, which however differ in informa-
tional cost as will be demonstrated later.
The underlying Markov Decision Process (MDP)
defines a reinforcement learning problem in which a
state value function V
π
(s) specifies the expected fu-
ture reward at some state s following the policy π, and
a utility function U
π
(s, a) that gives the expected re-
ward incorporating the action chosen at state s and
following the policy π, defined as
U
π
(s, a) =
∑
s
0
p(s
0
|s, a)[r(s, a, s
0
) + γV
π
(s
0
)]. (1)
The discount factor γ ∈ [0, 1] controls the trade-off be-
tween long-term and short-term rewards – if γ is large,
future rewards weigh more in the expected sum, and
if it is small immediate rewards have higher relative
weight.
Finding an expected future reward maximising
policy is equivalent to solving the following optimiza-
tion problem:
π
∗
= argmax
π
V
π
(s),
where the optimal policy π
∗
is not necessarily unique.
Moreover, any convex combination απ
∗
1
+ (1 − α)π
∗
2
(α ∈ (0, 1)) of two optimal policies π
∗
1
and π
∗
2
results
in a new optimal policy. Having multiple optimal
policies poses the question of whether one is preferred
over the others. One natural criterion is the cognitive
processing associated with executing a specific pol-
icy, i.e. the cost of making a decision. The standard
value iteration algorithm finds an optimal policy by
computing first the optimal value function V
∗
:
V
∗
(s) = max
a
p(s
0
|s, a)[r(s, a, s
0
) + γV
∗
(s
0
)] (2)
starting from an arbitrary V and iterating Equation 2
until convergence (Bellman, 1957). From dynamic
programming this iteration is known to converge
to a global optimal solution, providing a numerical
method for its computation (Sutton et al., 1999).
If the agents have independent controllers and
their actions are interleaving, that is, if agent A makes
a move on even and agent B on odd steps, the prob-
lem boils down to optimizing one agent’s policy with
respect to the other agent’s policy. In the optimisation
we use a static prediction for agent B’s policy, which
we scale in different trials from fully cooperative to
completely antagonistic. Assuming a particular strat-
egy of agent B, agent A optimizes its own action pol-
icy in order to achieve the goal under informational
constraints.
The scenario involves two dependent MDPs that
are not deterministic anymore and whose transition
probabilities depend on a prediction of the other
agent’s action. In every iteration we use as a predic-
tor the policy of the other agent. In a scenario where
agents do not know anything about each other it is rea-
sonable to set the predictor to a uniform distribution.
In this study, we investigate how the behavior of one
agent adapts to various strategies of the other agent.
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
306

5 OPTIMAL POLICIES
The relevant information represents the minimal level
of information (mutual information between states
and actions over all optimal policies) required for
achieving a certain level of performance as charac-
terised by the expected utility E[U (S, A)], which is
defined as:
E
π
[U (S, A)] =
∑
s,a
π(a|s)p(s)U (s, a).
The problem of informational parsimony can be
formulated as search for a value-optimal strategy
π
∗
(a|s), which at the same time minimises the re-
quired relevant information I(S;A), i.e. is also
information-optimal. This double optimisation is
transformed into an unconstrained minimisation prob-
lem via Lagrange multipliers:
min
π(a|s)
(I(S; A) − βE[U(S, A)]).
The β multiplier implicitly enforces the maximisation
of U (S; A). For β → ∞ the optimisation restricts the
policy to a value-optimal one. A reduction of β, how-
ever, makes the minimisation less sensitive to a drop
in utility. This minimax optimisation problem corre-
sponds to trading in utility for a reduction of relevant
information.
To compute the policies corresponding to com-
pletely rational and completely irrational behavior we
executed the Relevant Information algorithm with a
single agent and two extreme β multipliers, β → −∞
and β → ∞, as suggested in (Ortega and Braun, 2013),
the former providing the antagonistic policy and the
latter the cooperative one. In both cases the reward
function was the same: 0 for the goal state and -1 else-
where. The task is episodic and the agents act only
until they reach the goal configuration.
To obtain a policy that is optimal and informa-
tionally parsimonious (Polani et al., 2006) extended
the standard value iteration method to accommodate
for the double optimisation by adding an interleaved
Blahut-Arimoto iteration (Blahut, 1972) with the util-
ity as a distortion measure for computing the strategy
π
0
as follows:
p
k
(a) =
∑
s
p(s)π
k
(a|s)
π
k+1
(a|s) =
1
ζ
p
k
(a)exp[βU
π
(s, a)] (3)
where k denotes the iteration step, ζ is a normalis-
ing partitioning function and β a parameter trading
off utility and relevant information.
The policy update iteration is alternated with a
value iteration to get a consistent utility. This leads
to the following iteration:
π
(2)
−→ V
π
(1)
−→ U
π
(3)
−→ π
0
,
which generates a sequence of consistent policy–
utility (π–U) pairs for a specific β, by interlacing
the updates corresponding to Equations 1 and 3, and
performing these iterations until convergence of both
policy and utility.
This approach allows the computation of optimal
strategies while trading off utility and relevant infor-
mation. However, it does not address the cost in-
volved with obtaining information, but focuses only
on how much (relevant) information needs to be ac-
quired (and processed) in order to achieve a certain
level of utility, ignoring the possible acquisition cost.
It specifies the amount of information an agent takes
in and processes on average per time-step in the action
selection process. This amount depends on the pol-
icy – different policies require different informational
bandwidth, i.e. processing capacity. It is hypothe-
sised that the required capacity is correlated to the
metabolic cost of information processing and consti-
tutes a quantitative measure of cognitive burden. The
parsimony pressure tries to minimise this quantity
while the efficiency pressure drives towards higher
performance. Therefore for β → ∞ the resulting opti-
mal policy maximizes the expected utility and at the
same time minimizes the mutual information I(S; A).
Two extensions of relevant information to multi-
ple steps provide similar algorithms unifying Value
Iteration with Blahut-Arimoto for minimizing infor-
mation quantities in Bayesian graphs under optimality
constraints (Tishby and Polani, 2011).
To adapt the relevant information algorithm for the
scenario involving two agents with independent con-
trollers we introduce the following modification. As
the agents alternate in taking actions, the policy op-
timization of agent A needs to take into account the
policy of agent B, which we replace by a static pre-
diction. On every iteration we combine the static pre-
diction of agent B’s policy with the current policy of
agent A:
˜
π ∼ π
A
+ π
B
and use the resulting policy
˜
π in the utility update,
which provides the following modified iteration:
π
A
−→ V
˜
π
−→ U
˜
π
−→ π
0
A
.
This iteration optimizes the policy of agent A while
taking into consideration the implications of the co-
operative or antagonistic behavior of agent B in the
shared environment.
Information-theoretic Cost of Decision-making in Joint Action
307
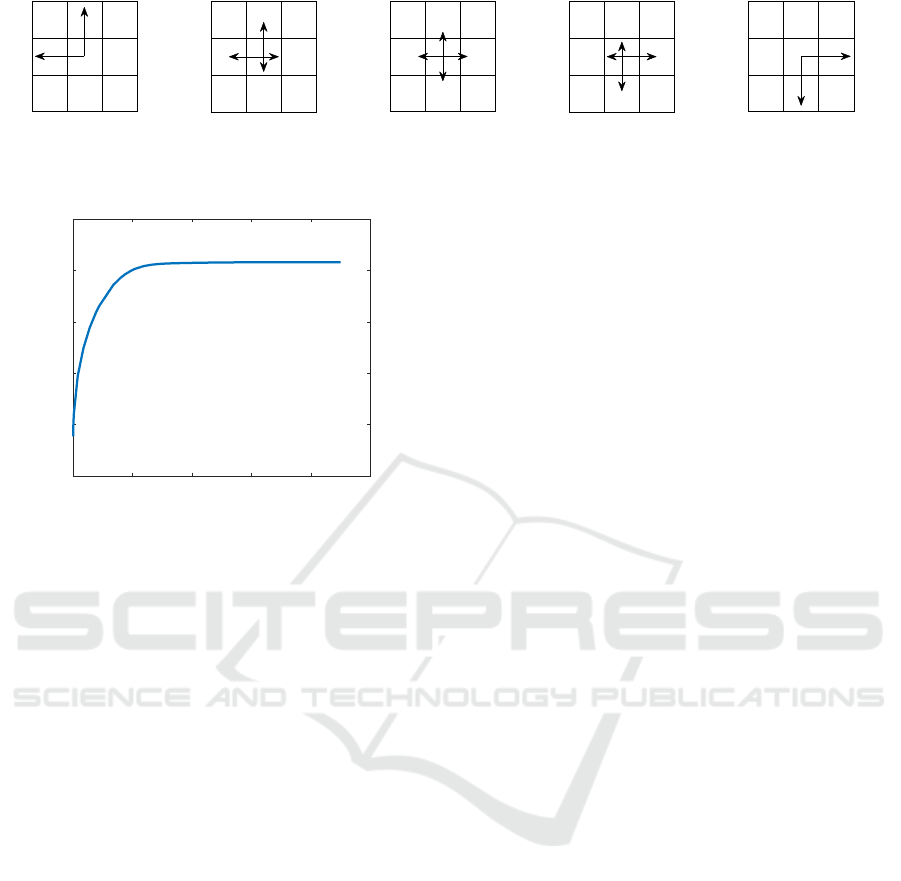
G
G
G
G
G
Figure 1: Various uniform strategies of agent B ranging from completely antagonistic to fully cooperative (left to right). G
denotes the goal state and the arrow length represents the action probability, which is 0.5 at the extremes (left/right) and 0.25
in the middle.
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Relevant information I(S,A) (bits)
-600
-550
-500
-450
-400
-350
Utility
Figure 2: Utility vs. Relevant Information trade-off curve
of agent A corresponding to the uniform policy of agent B.
For different policies of agent B the curve has similar shape
with specific offsets in utility levels.
6 INFORMATION-UTILITY
TRADE-OFF
We computed the optimal policies of agent A for a
range of antagonistic and cooperative behaviors of
agent B (see Figure 1) and for multiple levels of the
trade-off factor β. The level of collaboration of agent
B (denoted with δ) varies in the range of (0,1) – where
0 corresponds to fully antagonistic and 1 to fully co-
operative behavior (see Figure 1. Factor of 0.5 corre-
sponds to a uniformly distributed policy over the ac-
tion space (see Figure 1). As expected, the resulting
utility vs. relevant information trade-off curves have
similar shapes, with specific offsets in utility levels,
increasing with the level of cooperation of agent B.
For brevity, Figure 2 presents only the trade-off curve
of agent A corresponding to the uniform policy of
agent B (see Figure 1).
A theoretic upper limit on the amount of relevant
information is given by the cardinality of the action
space, which in this case is log |A | = 2 bits. However,
the required information is below 1 bit on average (see
Figure 2), since partitioning the state space by only
two actions (right and down) provides an optimal so-
lution. As β tends to 0 so is the amount of relevant
information, since in every state of the grid a uniform
action policy over the two actions (right and down)
provides a solution, however with a lower utility.
Figure 5 reveals the change in the optimal policy
of agent A corresponding to a uniform policy of agent
B for two levels of β, low and high. The size of the ar-
rows reflects the probability of dominant actions. For
low β the (soft) policy is close to a uniform distribu-
tion over two actions (right and down), while for high
β most states have deterministic action probabilities.
A characteristic policy transition can be observed in
the upper-left corner of the grid in the form of rectan-
gle.
The simulated trajectories generated when apply-
ing the optimal policies of agent A for two levels of
β – high (see Figure 3) and low (see Figure 4) – are
demonstrated for five levels of collaboration. Figure 3
reveals how increasing cooperation (left to right) in-
fluences the optimal path of agent A. For antagonistic
behaviors of agent B, agent A prefers to stick to the
wall, which protects the object from moving back and
decrease utility. As cooperation of agents increases,
agent A gradually moves away from the wall towards
the diagonal, which represents the optimal informa-
tionally parsimonious policy. In this particular sce-
nario the collaboration rate plays the role of a trade-
off factor between following the wall and the diago-
nal. Initially, the agent feels more confident by the
wall before switching to the diagonal, and this period
of initial uncertainty gets shorter as the agent can in-
creasingly rely on its partner. Figure 4 reveals that the
trends for lower β are similar with the typical blur,
which relaxes the required level of relevant informa-
tion. Interestingly, even with a lower pressure on the
utility level, agent A still tends to stick to the wall,
which shows how the embodiment in this scenario
helps the agent tackle excess uncertainty and stabilize
performance.
Figure 6 demonstrates similar shapes of the utility
as a function of the collaboration rate for two levels
of β (high and low). The normalized distance between
the two utility curves reveals that increased collabora-
tion rates emphasize the utility gap between different
levels of β. This suggests that decreasing the collab-
oration level has a damping effect on the influence β
has on utility, i.e., for antagonistic policies utility lev-
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
308
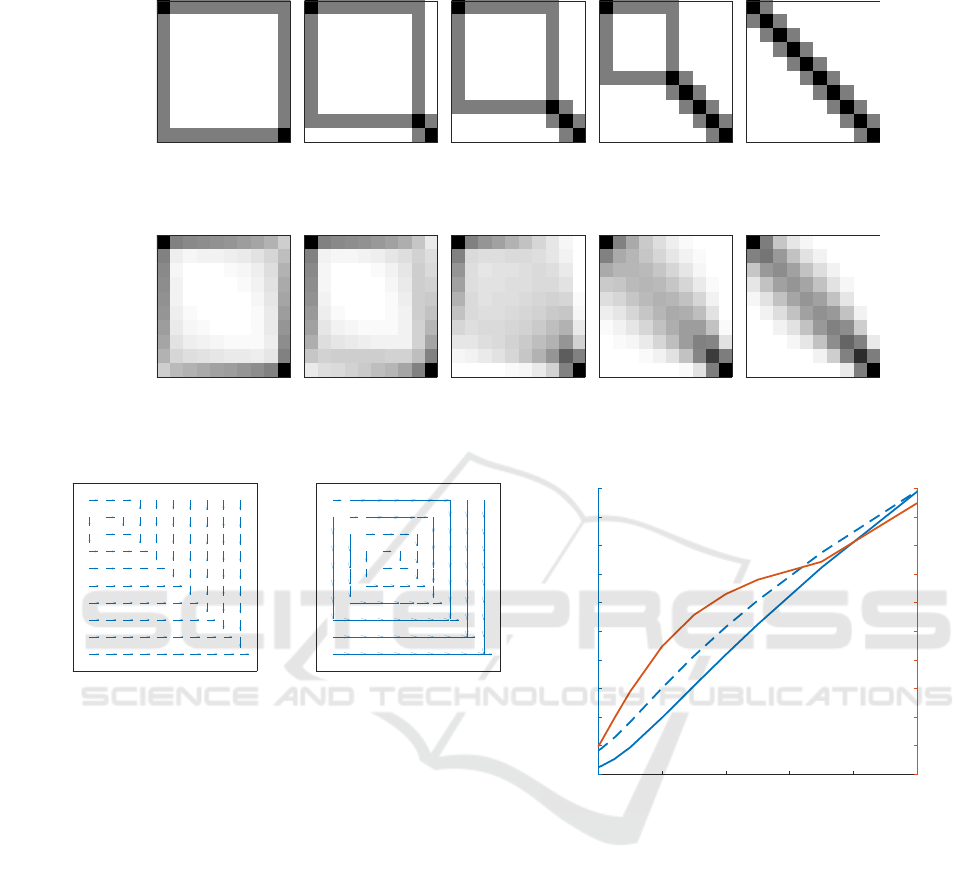
Figure 3: Simulated trajectories of agent A’s optimal policies for five collaboration rates increasing from left to right (high β).
Darker color denotes higher recurrence. For antagonistic behaviors of agent B agent A initially sticks to the wall to mitigate
risk, before gradually moving towards the diagonal as cooperation increases.
Figure 4: Simulated trajectories of agent A’s optimal policies for five collaboration rates increasing from left to right (low β).
Darker color denotes higher recurrence. Regardless of lower pressure on utility level agent A sticks to the wall to gain control
over uncertainty, revealing the role of embodiment in this scenario.
Figure 5: Optimal policies of agent A corresponding to a
uniform policy of agent B for low (a) and high (b) β. Arrow
size reflects dominant action probability. A policy transition
propagates from the upper-left corner along the diagonal.
els are relatively close to each other across different β.
This trend can also be observed in Figures 3/a and 4/a,
which reveal similar trajectory paths.
7 DISCUSSION
We explored a dyadic collaborative scenario in a 2-
D grid-world, where two memoryless agents with in-
dependent controllers interact using fully redundant
control. We applied a variation of the relevant in-
formation method to compute the optimal policies of
one of the agents under information processing con-
straints. Our study investigated how the behavior of
one agent influences the optimal strategy of the other
in a range of different configurations. The results
demonstrate that when the agents cooperate towards a
common goal they achieve a higher utility at a lower
informational cost. However, when their behavior is
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Collaboration rate
-1000
-900
-800
-700
-600
-500
-400
-300
-200
-100
0
Utility
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.1
0.12
0.14
0.16
0.18
0.2
0.22
0.24
Normalized distance
Figure 6: Utility as a function of collaboration rate for high
(dashed) and low (solid) levels of β (blue). The normal-
ized distance between these utility curves (red) reveals how
higher collaboration emphasize the utility gap in β levels.
antagonistic to each other, the utility level drops sig-
nificantly and the informational cost increases. One
could think of various situations where this scenario
could arise, for example, if the controllers are stochas-
tic, or the precise knowledge of the other agent’s
model is unavailable or compromised, or the other
agent is adverse or autistic.
The results reveal that when facing an antagonis-
tic partner, the cooperative agent exploits the partic-
ular embodiment of its environment in order to max-
imize its control abilities. This suggests that the ap-
plied method of relevant information is able to iden-
tify salient features of the state space and benefit from
them in order to provide an optimal informationally
Information-theoretic Cost of Decision-making in Joint Action
309

parsimonious strategy in various environmental con-
ditions. This initial study did not reveal further in-
terplay between the informational cost and the rate
of collaboration, however, future work could explore
this trade-off with more elaborate and focused scenar-
ios. The optimal policies derived in our study operate
with relevant information intake in the range of [0,1]
bits on average per step, which is considerably lower
than the theoretical limit of 2 bits, suggesting that a
different embodiment could result in a higher infor-
mation burden and provide deeper insights.
In this particular scenario, our approach highlights
two types of optimal trajectories, one following the
walls and another one traversing the diagonal, and
trades off these two paths on the base of cooperation
level. Furthermore, the results demonstrate that high
cooperation rates (δ) emphasize the role of β in re-
inforcing high performance levels, which suggests a
specific trade-off between δ and β and is an interest-
ing topic for future research.
The key benefits of the applied information-
theoretic treatment are that it is universal, general and
could enable the direct comparison of scenarios with
different computational models. The proposed ap-
proach reframes the problem into a trade-off between
the reward achieved and the informational cost of per-
forming a task by incorporating limits on the informa-
tion processing capacity, which are fundamental prop-
erties of agent–environment systems. The framework
can be further extended to tackle issues of time shifts
and turn-taking in the decision process.
8 CONCLUSION
This paper presents an application of an information-
theoretic framework to a reward driven decision
process in the perception–action cycle of a dyad.
We demonstrate interesting behaviors generated in
robotic agents based on self-organization following
the principle of homeokinesis. Driven by this prin-
ciple through the interaction with its environment, the
agent shows preferences for states where its control
actions are most effective in avoiding unpredictable
and undesired situations. We believe that theories and
tools from complex systems and information theory
may successfully be applied in the future for facili-
tating the automated design of robot collectives and
for the analysis of their dynamics. The proposed ap-
proach could provide a framework supporting the cre-
ation of artificial agents, which not only act optimally,
but optimize also their computational resources in the
decision-making process. Further work is required to
evolve this methodology into the continuous action
domain and showcase its application in more realis-
tic practical scenarios.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge support by
H2020-641321 socSMCs FET Proactive and FFG-
6112792 Pro
2
Future projects.
REFERENCES
Ashby, W. R. (1956). An Introduction to Cybernetics. Chap-
man & Hall Ltd.
Bellman, R. E. (1957). Dynamic Programming. Princeton
University Press.
Blahut, R. (1972). Computation of channel capacity and
rate distortion functions. IEEE Transactions on Infor-
mation Theory, 18(4):460–473.
Boedecker, J., Obst, O., Lizier, J., Mayer, N., and Asada, M.
(2011). Information processing in echo state networks
at the edge of chaos. Theory in biosciences, 131:205–
13.
Butail, S., Mwaffo, V., and Porfiri, M. (2016). Model-free
information-theoretic approach to infer leadership in
pairs of zebrafish. Physical Review E, 93.
Callebert, L., Lourdeaux, D., and Barth
`
es, J.-P. (2016).
A trust-based decision-making approach applied to
agents in collaborative environments. In Proceedings
of the 8th International Conference on Agents and Ar-
tificial Intelligence, pages 287–295.
Castelfranchi, C. (2006). Silent agents: From observation
to tacit communication. Advances in Artificial Intelli-
gence - IBERAMIA-SBIA, (4140):98–107.
Challet, D. and Zhang, Y.-C. (1997). Emergence of co-
operation and organization in an evolutionary game.
Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications,
246(3):407 – 418.
Couzin, I., Krause, J., Franks, N., and Levin, S. (2005).
Effective leadership and decision-making in animal
groups on the move. Nature, 433 (7025):513–516.
Davis, N., Hsiao, C., Singh, K. Y., Lin, B., and Magerko, B.
(2017). Quantifying collaboration with a co-creative
drawing agent. ACM Transactions on Interactive In-
telligent Systems (TiiS), 7:1–25.
Franks, N., Pratt, S., Mallon, E., Britton, N., and Sumpter,
D. (2002). Information flow, opinion-polling and col-
lective intelligence in house-hunting social insects.
Philosophical Transactions B: Biological Sciences,
357 (1427):1567–1583.
Friston, K. (2010). The free-energy principle: a unified
brain theory? Nature reviews. Neuroscience, 11:127–
38.
Goldstone, R. and Janssen, M. (2005). Computational mod-
els of collective behavior. Trends in Cognitive Sci-
ences, 9(9):424–430.
Harder, M., Polani, D., and Nehaniv, C. L. (2010). Two
agents acting as one. In Artificial Life, pages 599–606.
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
310

Ikegami, T. and Iizuka, H. (2007). Turn-taking interaction
as a cooperative and co-creative process. Infant Be-
havior and Development, (30):278–288.
Kim, H., Davies, P., and Walker, S. (2015). New scal-
ing relation for information transfer in biological
networks. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface,
12(113):20150944.
Klyubin, A. S., Polani, D., and Nehaniv, C. L. (2007). Rep-
resentations of space and time in the maximization of
information flow in the perception-action loop. Neural
Computation, 19(9):2387–2432.
Laughlin, S. B. (2001). Energy as a constraint on the cod-
ing and processing of sensory information. Current
Opinion in Neurobiology, 11:475–480.
Lindner, M., Vicente, R., Priesemann, V., and Wibral, M.
(2011). Trentool: A matlab open source toolbox
to analyse information flow in time series data with
transfer entropy. BMC neuroscience, 12:119.
Lizier, J. T., Prokopenko, M., and Zomaya, A. Y. (2014).
A Framework for the Local Information Dynamics of
Distributed Computation in Complex Systems, pages
115–158.
Marshall, J. A. R., Bogacz, R., Dornhaus, A., Planqu
´
e,
R., Kovacs, T., and Franks, N. R. (2009). On
optimal decision-making in brains and social insect
colonies. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface,
6(40):1065—1074.
Martius, G., Nolfi, S., and Herrmann, J. (2008). Emergence
of interaction among adaptive agents. In 10th Interna-
tional Conference on Simulation of Adaptive Behav-
ior, pages 457–466.
Matsui, T. (2019). A study of joint policies considering
bottlenecks and fairness. In Proceedings of the 11th
International Conference on Agents and Artificial In-
telligence, pages 80–90.
Meyer, B. (2017). Optimal information transfer and
stochastic resonance in collective decision making.
Swarm Intelligence, 11:1–24.
Meyer, J. A. and Wilson, S. W. (1991). The Dynamics of
Collective Sorting Robot - Like Ants And Ant - Like
Robots, pages 356–363.
Moore, D. G., Valentini, G., Walker, S. I., and Levin, M.
(2018). Inform: Efficient information-theoretic anal-
ysis of collective behaviors. Frontiers in Robotics and
AI, 5:60.
Mwaffo, V., Butail, S., and Porfiri, M. (2017). Analysis of
pairwise interactions in a maximum likelihood sense
to identify leaders in a group. Frontiers in Robotics
and AI, 4:35.
Nabet, B., Leonard, N., Couzin, I., and Levin, S. (2009).
Dynamics of decision making in animal group mo-
tion. journal of nonlinear science. Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of
America, 19(4):399–435.
Ortega, P. and Braun, D. (2013). Thermodynamics as a the-
ory of decision-making with information-processing
costs. Royal Society: Mathematical, Physical and En-
gineering Sciences, 469(2153).
Paolo, E. D., Rohde, M., and Iizuka, H. (2008). Sensitivity
to social contingency or stability of interaction? mod-
elling the dynamics of perceptual crossing. New Ideas
in Psychology, 26(2):278–294.
Pezzulo, G. and Levin, M. (2015). Re-membering the body:
applications of computational neuroscience to the top-
down control of regeneration of limbs and other com-
plex organs. Integr. Biol., 7:1487–1517.
Polani, D., Martinetz, T., and Kim, J. T. (2001). An
information-theoretic approach for the quantification
of relevance. 6th European Conference on Advances
in Artificial Life, pages 704–713.
Polani, D., Nehaniv, C., Martinetz, T., and Kim, J. T.
(2006). Relevant information in optimized persistence
vs. progeny strategies. In 10th International Confer-
ence on the Simulation and Synthesis of Living Sys-
tems, pages 337–343. MIT Press.
Polani, D., Sporns, O., and Lungarella, M. (2007). How in-
formation and embodiment shape intelligent informa-
tion processing. In 50 Years of Artificial Intelligence,
pages 99–111.
Roli, A., Ligot, A., and Birattari, M. (2019). Complex-
ity measures: Open questions and novel opportunities
in the automatic design and analysis of robot swarms.
Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 6:130.
Schreiber, T. (2000). Measuring information transfer. Phys.
Rev. Lett., 85(2):461–464.
Shalizi, C. R. and Crutchfield, J. P. (2002). Information bot-
tlenecks, causal states, and statistical relevance bases:
How to represent relevant information in memoryless
transduction. Advances in Complex Systems, (5):91.
Shannon, C. E. (1949). The mathematical theory of com-
munication. The University of Illinois Press, Urbana.
Sperati, V., Trianni, V., and Nolfi, S. (2011). Self-organised
path formation in a swarm of robots. Swarm Intelli-
gence, 5:97–119.
Sutton, R., Precup, D., and Singh, S. (1999). A frame-
work for temporal abstraction in reinforcement learn-
ing. Artificial intelligence, 112(1-2):181–211.
Tishby, N., Pereira, F. C., and Bialek, W. (1999). The
information bottleneck method. In The 37th annual
Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and
Computing, pages 368–377.
Tishby, N. and Polani, D. (2011). Information theory of de-
cisions and actions. In Cutsuridis, V., Hussain, A., and
Taylor, J., editors, Perception-Action Cycle: Models,
Architecture and Hardware, pages 601–636. Springer.
Touchette, H. and Lloyd, S. (2000). Information-theoretic
limits of control. Phys. Rev. Lett., 84(6):1156–1159.
Valentini, G., Moore, D. G., Hanson, J. R., Pavlic, T. P.,
Pratt, S. C., and Walker, S. I. (2018). Transfer of in-
formation in collective decisions by artificial agents.
Artificial Life Conference Proceedings, (30):641–648.
Walker, S., Cisneros, L., and Davies, P. (2012). Evolution-
ary transitions and top-down causation. 13th Interna-
tional Conference on the Simulation and Synthesis of
Living Systems, pages 283–290.
Walter, W. (1950). An imitation of life. Scientific American,
May:42–45.
Zenil, H., Marshall, J. A. R., and Tegn
´
er, J. (2015). Ap-
proximations of algorithmic and structural complexity
validate cognitive-behavioural experimental results.
CoRR, abs/1509.06338.
Information-theoretic Cost of Decision-making in Joint Action
311
