
The Importance of Models in Data Analysis with Small Human
Movement Datasets: Inspirations from Neurorobotics Applied to
Posture Control of Humanoids and Humans
Vittorio Lippi
a
, Christoph Maurer
b
and Thomas Mergner
c
Neurological University Clinic, University of Freiburg, Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany
Keywords: Posture Control, Machine Learning, Neurorobotics, Parametric Nonlinear Systems.
Abstract: Machine learning has shown impressive improvements recently, thanks especially to the results shown in
deep learning applications. Besides important advancements in the theory, such improvements have been
associated with an increment in the complexity of the used models (i.e. the numbers of neurons and connec-
tions in neural networks). Bigger models are possible given the amount of data used in the training process is
increased accordingly. In medical applications, however, the size of datasets is often limited by the availability
of human subjects and the effort required to perform human experiments. This position paper proposes the
integration of bioinspired models with machine learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
During the last decade, there have been great im-
provements in machine learning applications, in the
sense that the machine learning systems got more
powerful and accurate. This improvement is associ-
ated with a resurgence of the use of neural networks,
in particular of deep learning. As shown in Fig 1, the
size of the neural networks has increased in the order
of magnitudes during the last 40 years as has the num-
ber of samples used for the training. A massive da-
taset of training samples is not always available, how-
ever. In the case of data from human experiments, the
reason for the difficulty in getting a huge amount of
data lies in the effort required to perform the experi-
ments and in the fact that human data are often de-
scribed by a large number of relevant features; in
some cases, there are more features than samples
(Hastie & Tibshirani, 2004). For this reason, when
working with human data, regularization is of pri-
mary importance. Deep learning systems are finding
application in the analysis of human movements
(Abdu-Aguye & Gomaa, 2019b, 2019a) and, while
the results are promising, the field is still at the begin-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5520-8974
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9050-279X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7231-164X
ning and hence the possibilities are still to be fully ex-
plored. In this position paper, we will present exam-
ples that show the advantage of integrating models in
the analysis of human experiments. The particular
case of human and humanoid posture control is pre-
sented and some examples will be discussed. The ap-
plication of ML to human posture control analysis is
already a research topic, for example to design diag-
nostic tools in a clinical setup (Costa et al., 2016). The
issue will be shown from the point of view of both the
analysis of human data and the control of humanoid
robots’ balance. Modern research on human and hu-
manoid posture control already uses mathematical
models (Alexandrov et al., 2017; Boonstra et al.,
2014; Engelhart et al., 2014; Goodworth & Peterka,
2018; Mergner, 2010; Pasma et al., 2014; van
Asseldonk et al., 2006; H van der Kooij et al., 2007;
Herman van der Kooij et al., 2005). The presented
models are designed to describe, and in some cases
predict, human behavior in specific experiments, and
they incorporate hypotheses about neural movement
control and empirical findings. It comes natural when
applying machine learning to also try to integrate the
knowledge represented by such models with the
adaptability of the learning systems. The examples
Lippi, V., Maurer, C. and Mergner, T.
The Importance of Models in Data Analysis with Small Human Movement Datasets: Inspirations from Neurorobotics Applied to Posture Control of Humanoids and Humans.
DOI: 10.5220/0010297005790585
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2021), pages 579-585
ISBN: 978-989-758-486-2
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
579
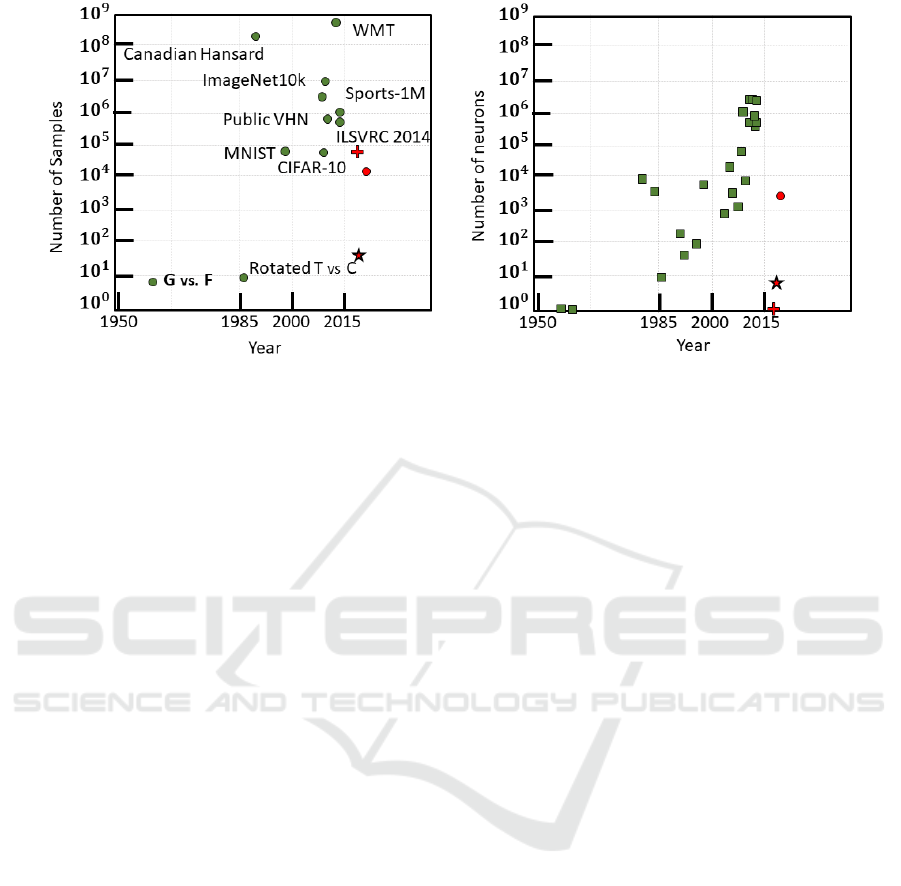
Figure 1: Increase of dataset sizes and numbers of neurons of the neural network through the last 70 years in comparison with
recent posture control and balance applications. On the left (green dots) the number of samples in several datasets used in
machine learning applications, on the right (green squares) the number of neurons in neural networks developed during the
years (from the Perceptron to GoogleNet). The graphs are adapted from (Goodfellow et al., 2016) where the complete list of
NN architectures presented in the figure is available. The red marks represent the number of samples or subjects used in recent
applications (on the left plot) and the size of the neural network in the respective solution (right plot). Specifically, the star
represents (Jafari et al., 2019), the cross Lippi (2018), and the dot (Lippi et al., 2020). It is evident how the three posture
control examples rely on smaller datasets and smaller architectures compared to the possibilities of deep learning at the state
of the art.
presented in the following will try to cover different
applications (i.e. classification, control, and system
identification) and show the advantages of the inte-
gration of modelling and learning. The methods used
in the two examples are on-line linear regression and
deep learning (convolutional neural network); they
are presented not with the intention to compare dif-
ferent ML methods but to show how posture control
models can be integrated in different set-ups.
2 EXAMPLES
2.1 The Disturbance Identification and
Compensation (DEC) Model for
Posture Control
The examples presented in this section will make use
of a bio-inspired posture control model, the DEC
(Mergner et al., 2003). A brief description of the
model is provided as an introduction to the following
examples for a more in-depth description see Lippi &
Mergner (2017), where the DEC is implemented as a
modular control system for humanoid robots. The
DEC control is designed to a describe how human
postural control mechanisms interact with movement
execution control. A schema of the DEC control is
shown in Fig. 2 (top), The components of the control
are: (A) A servo control loop for each degree of free-
dom. The controller is a PD controller, or PID in some
implementations (the block "C" in Fig 2.). The con-
trolled variable consists either of the joint angle, the
orientation in space of the above joint, or the orienta-
tion in space of the centre of mass of the whole body
above the controlled joint. The control is imple-
mented in a modular way, and each module performs
sensor fusion and control. (B) Multisensory estima-
tion of external disturbances, i.e. rotation and transla-
tion of the supporting link or support, contact forces,
and field forces such as gravity. The disturbance esti-
mates are fed into the servo so that the joint torque
compensates on-line for the disturbances while exe-
cuting the desired movements.
The disturbance compensation mechanism al-
lows the system to use a low loop gain and thus stable
control in face of neural time delays, or, in case of
humanoid control, of delays due to signal transmis-
sion or low sample rate (Ott et al., 2016). The refer-
ence input to each module determines its postural
function, e.g. maintaining a given orientation of the
supported link (either in space or with respect to the
supporting link), or maintaining the COM above its
supporting joint. Modules exchange information with
neighbouring modules, i.e. those mechanically inter-
connected.
ICPRAM 2021 - 10th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
580
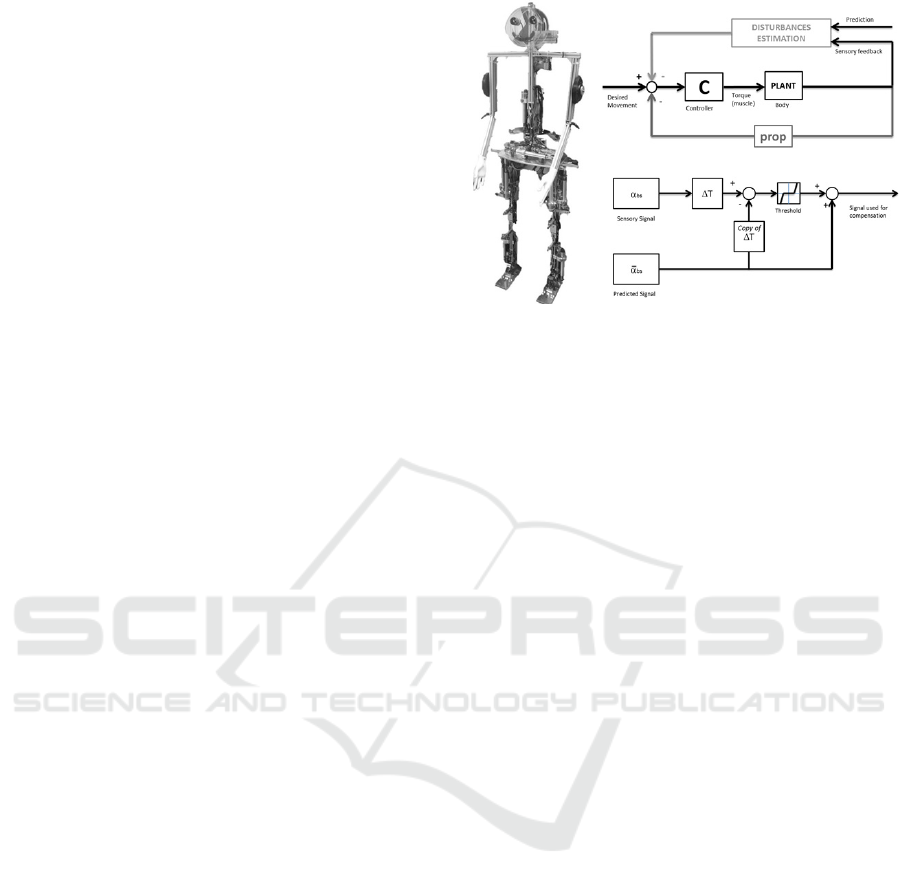
2.2 Online Learning for the Posture
Control of the Lucy Robot
Small human/humanoid datasets may suffice to use
linear learning systems. As an example, our previous
work (Lippi, 2018) shows how the nonlinear DEC
model can be integrated with a linear learning system
to make it capable of controlling human posture con-
trol. The challenge here was represented by the
closed-loop nature of the posture control, i.e. by the
fact that the body is intrinsically unstable and the con-
trol is always active. The machine learning process is
then based on data that are influenced by the use of
the learned predictor itself. Therefore, an on-line
training approach was proposed. It improved the con-
trol of the body sway without endangering control
stability. In Fig. 2 the structure of the bioinspired pre-
dictor is shown. The ML model was a rather simple
linear model, implemented in a way so that it could
learn incrementally as the robot was balancing.
In particular, previously and here the learning sys-
tems are trained to predict the COM sway 𝛼
, with
an anticipation of 𝑇
70 ms. The inputs taken
into account are the previous sensory-based values for
the body sway angle 𝛼
and the reference value 𝑦
𝛼
(sampled at previous steps). Every 10 ms an input
vector is constructed using delayed versions of the in-
put signals:
𝑥
𝛼
𝜏 𝛼
𝜏 ∆𝑡 𝛼
𝜏 2∆𝑡 𝛼
𝜏 ∆𝑡 𝛼
𝜏 ∆𝑡 𝛼
𝜏
2∆𝑡
where 𝜏𝑡
𝑇
and ∆t is set to 64 ms. The
predictor has the structure of an affine application,
where the parameter to be learned are the elements of
the transformation matrix. Specifically, the disturb-
ance to be predicted at the time i, 𝑦
can be arranged
in a vector of target values 𝑌𝑦
𝑦
⋯ 𝑦
, and the
observed input is integrated into the matrix
𝑋
𝑥
𝑥
…𝑥
11 1
(1)
The weight matrix is computed as 𝑊𝑌𝑋
, us-
ing the pseudoinverse operation that can be imple-
mented on-line. The values used to build X and Y are
affected by the prediction, as shown in Fig. 2.
The use of the real robotic platform Lucy, with
real noisy sensors, helped to evaluate the hypothesis
about predictions in a real-world setup. The robust-
ness of the system was tested including an additional
delay in the loop. The prediction system allows the
system to stand with a delay of 60 ms, while the sys-
tem without prediction becomes unstable at 10 ms.
The prediction system was compared with a Smith
Figure 2: Integration of the prediction system based on a
linear learning model. On the left the Lucy robot, a human-
oid with 14 DoF, where the system was tested. The schema
above shows how the DEC control integrates disturbances
estimation. In this specific case, the predicted effect is the
gravity torque. The “prop” block represents the propriocep-
tive feedback, based on joint angles, while “disturbances
estimation” is implemented through a sensor fusion inte-
grating proprioception and vestibular (IMU) input. The pre-
diction is compared with the measured value as shown in
the schema below: The threshold function has the effect
that, when the prediction and the sensor value are similar,
the prediction is used, while the sensed value is used when
the difference between the two is large. This approach re-
sembles a Smith predictor and the way the efference copy
mechanism is used in modeling human behavior.
predictor (that is based just on the model of the sys-
tem) and, as result, proved to produce a better perfor-
mance.
2.3 How Models Can Benefit from
Machine Learning (ML): System
Identification with CNN
A previous work (Lippi et al., 2020) presented a
method for posture control parameter identification
based on CNN. It represents an example of how ML
can provide a tool for modelling, exploiting the
knowledge of the posture control system in the form
of a parametric model; the CNN identifies the param-
eters of such a model.
Human posture control exhibits nonlinearities
such as deadbands and gain non-linearities. Nonlinear
models are more complex to be fitted on human data
than linear models and, in the general case, expensive
iterative procedures need to be used. This issue
brought us to the idea to identify the parameters of a
nonlinear bio-inspired posture control system, the
DEC model using ML. The advantage lies here in the
The Importance of Models in Data Analysis with Small Human Movement Datasets: Inspirations from Neurorobotics Applied to Posture
Control of Humanoids and Humans
581

fact that using the trained network is almost
immediate, whereas training the CNN would be more
computationally expensive.
The training set was produced with parameters
from uniform distributions, filtered with the con-
straint that they would produce a stable simulation.
The number of samples can be as large as needed, be-
ing here produced through a simulation. In order to
obtain more human-like examples, the data-set was
enriched with samples of larger body sways. In the
future, the CNN can also be tested a posteriori by
comparing the distribution of the parameters it pro-
duces for the validation set with the expected distri-
bution for the real data. This can help in choosing hy-
perparameters as shown in previous works (Sforza et
al., 2011; Sforza & Lippi, 2013). Fig. 3 schematically
summarizes the pipeline of the work. The input of the
network is a 2-channel picture, representing the mod-
ulus and the phase of the fft of the body sway com-
puted on time windows (in Fig.3 the two channels are
visualized as “green” and “blue”). Because of its ar-
chitecture, i.e. training the same weights on different
parts of the image, the CNN is able to recognize pat-
terns translated in time and in frequency. While the
invariance in time has the obvious advantage of mak-
ing the recognition of a specific motion feature inde-
pendent from its onset in the input signal, the invari-
ance in frequency has no obvious physical interpreta-
tion. The SIP model proved to be suitable to describe
the analysed posture control scenario, this even in the
sub-optimal case of identifying the control parameter
of the ankle joint in a DIP model.
3 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This position paper gives two examples of the use of
posture control models in learning. The examples
suggest that the modeling can be useful in reducing
the number of features used with the ML algorithm,
simplifying the complexity of the ML system re-
quired to perform the task, or increasing the number
of training samples using simulations to produce arti-
ficial data.
The identification of posture control model pa-
rameters can be applied to the benchmarking of hu-
manoid robots (Lippi et al., 2019; Torricelli et al.,
2020) and to the analysis of clinical data (Exarchos et
al., 2015).
From the point of view of control applications,
synergies between machine learning and posture con-
trol can find applications in the control of wearable
Figure 3: The pipeline of the learning problem is presented
in Lippi et al.( 2020). The simulated scenario represents a
subject standing on a tilting support surface. The tilt profile
is a pseudo-random ternary sequence (PRTS) function for
all the simulations. The parameters of the simulations are
generated randomly and the output of the simulation is the
profile of the body COM sway. The training process, aim-
ing to identify the parameters, "reverses" the relationship
between the data: body sway, here transformed into a pic-
ture, is the input, and the parameters, centred around the
mean and divided by the variance of the training set ('Nor-
malization' block) are the target output. The identification
is formally a regression problem.
robots. Fig. 4. shows an example presenting the hy-
pothetical structure of the control system for a full-
body exoskeleton. The actuated ankle joint and the
fact that the robot’s geometry prevents the user from
having direct contact with the support surface implies
that the robot has to balance by itself. The balance and
posture control issues specific to legged humanoids
apply also to wearable robots. This implies the com-
plication of physical interactions between the robot
and the human. The figure provides a map of possible
applications of the ML approaches presented in the
examples (Section 2) for the components of the exo-
skeleton control.
Besides posture control and balance, a wearable
robot poses issues that have not been covered by the
presented examples and can still be solved with
proper integration of models and ML. Specifically, a
transparent transfer of voluntary movements between
the user and the robot requires the mapping of
trajectories between different kinematic structures,
even if the user’s joints are not necessarily coincident
with those of the robot (Godoy et al., 2018; Lee et al.,
2018). Machine learning techniques provide means to
also solve such problems (see for example (Makondo
et al., 2015). Learning trajectories and libraries of
trajectories associated with tasks, e.g. gait, can be
achieved by exploiting models for movement
representation such as movement primitives
(Paraschos et al., 2013; Schaal et al., 2005; Schaal,
2006) and the algorithms to generalize and transfer
ICPRAM 2021 - 10th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
582

them. For tasks
Figure 4: Hypothetical configuration of a user wearing a full-body exoskeleton. The block diagram shows the two mechanical
components of the system (robot and user) as two separate blocks to highlight how their interaction is mediated by control
systems that can be tuned using machine learning and thereby can benefit from the integration of modeling. The robot model
"exos model” can integrate a learning process like the one presented in (Lippi, 2018). The control system parameters can be
tuned accordingly. The haptic feedback that the robot here produces, "physical interaction" block, could be designed on the
basis of human sensor fusion in order to map the behavior of the robot to match the perception of the user (for example, the
robot should be in equilibrium when the user perceives himself as being in equilibrium). For this purpose, using a model of
the user's posture control, the "user model", can be beneficial. On the other hand, such a model can also be used to anticipate
the user's movements in the block "intention recognition", which is used to provide commands to the control system of the
robot. Both the "Exos model” and the “User model” can be identified by means of machine learning (Lippi et al., 2020).
such as manipulations, where reaction forces may
reasonably be more important than the trajectories
themselves, models representing the stiffness of the
robot (e.g. Calinon, 2016; Calinon et al., 2007) or
specifications of the particular mechanical variables
(torques, velocity positions, etc.) involved in the task
can be used (Deimel, 2019b, 2019a). In all these cases
the models have a powerful regularization effect, in
that a model of human motor behavior can be learned
from a few samples, or even just a single sample
(Schaal, 2006).
The topic of reinforcement learning (RL) has not
been considered in specific examples. RL is a popular
way to solve problems where a measure of success
can be formalized (e.g, body sway amplitude, number
of falls of a robot) but the desired output may not be
explicitly available. An example can be the closed-
loop control in section 2.2 and in general the problem
of humanoid balance (e.g. in Phaniteja et al., 2018;
Vuga et al., 2013; Yang et al., 2017). As RL relies on
the exploration of a space of possible control policies
it can benefit substantially from training in
simulations (where making a mistake is not
expensive) and hence it can exploit posture control
models.
Overall, we contend that the proposed examples
suggest that knowledge of human behaviour models
(be they bio-inspired or just descriptive of a given
outcome) as well as models of human sensorimotor
functions are crucial for the analysis of human
behavioural data. The models may provide powerful
tools for the control of humanoid robots. Both the
functionality of the bio-inspired models and the
modern ML techniques will benefit from being
mutually integrated.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the project
COMTEST, a sub-project of
EUROBENCH (European Robotic
Framework for Bipedal Locomotion
Benchmarking,
www.eurobench2020.eu) funded by
the H2020 Topic ICT 27-2017 under
grant agreement number 779963.
REFERENCES
Abdu-Aguye, M. G., & Gomaa, W. (2019a). Robust human
activity recognition based on deep metric learning.
ICINCO 2019 - Proceedings of the 16th International
Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and
Robotics. https://doi.org/10.5220/0007916806560663
Abdu-Aguye, M. G., & Gomaa, W. (2019b). VersaTL:
Versatile transfer learning for IMU-based activity
recognition using convolutional neural networks.
ICINCO 2019 - Proceedings of the 16th International
The Importance of Models in Data Analysis with Small Human Movement Datasets: Inspirations from Neurorobotics Applied to Posture
Control of Humanoids and Humans
583

Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and
Robotics. https://doi.org/10.5220/0007916705070516
Alexandrov, A. V. A. V., Lippi, V., Mergner, T., Frolov, A.
A. A. A., Hettich, G., & Husek, D. (2017). Human-
inspired Eigenmovement concept provides coupling-
free sensorimotor control in humanoid robot. Frontiers
in Neurorobotics, 11(APR). https://doi.org/10.3389/
fnbot.2017.00022
Boonstra, T. A., van Vugt, J. P. P., van der Kooij, H., &
Bloem, B. R. (2014). Balance asymmetry in
Parkinson’s disease and its contribution to freezing of
gait. PLoS One, 9(7), e102493.
Calinon, S. (2016). A tutorial on task-parameterized
movement learning and retrieval. Intelligent Service
Robotics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-015-0187-9
Calinon, S., Guenter, F., & Billard, A. (2007). On learning,
representing, and generalizing a task in a humanoid
robot. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics. https://doi.org/
10.1109/TSMCB.2006.886952
Costa, L., Gago, M. F., Yelshyna, D., Ferreira, J., Silva, H.
D., Rocha, L., Sousa, N., & Bicho, E. (2016).
Application of Machine Learning in Postural Control
Kinematics for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3891253
Deimel, R. (2019a). A Dynamical System for Governing
Continuous, Sequential and Reactive Behaviors.
Proceedings of the Austrian Robotics Workshop.
Deimel, R. (2019b). Reactive Interaction Through Body
Motion and the Phase-State-Machine. IEEE
International Conference on Intelligent Robots and
Systems.
https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS40897.2019.8968557
Engelhart, D., Pasma, J. H., Schouten, A. C., Meskers, C.
G. M., Maier, A. B., Mergner, T., & van der Kooij, H.
(2014). Impaired standing balance in elderly: a new
engineering method helps to unravel causes and effects.
Journal of the American Medical Directors
Association, 15(3), 227--e1.
Exarchos, T. P., Bellos, C., Bakola, I., Kikidis, D., Bibas,
A., Koutsouris, D., & Fotiadi, D. I. (2015).
Management and modeling of balance disorders using
decision support systems: The EMBALANCE project.
Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09012-2_4
Godoy, J. C., Campos, I. J., Pérez, L. M., & Muñoz, L. R.
(2018). Nonanthropomorphic exoskeleton with legs
based on eight-bar linkages. International Journal of
Advanced Robotic Systems. https://doi.org/10.1177/
1729881418755770
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., & Courville, A. (2016). Deep
Learning. MIT Press.
Goodworth, A. D., & Peterka, R. J. (2018). Identifying
mechanisms of stance control: a single stimulus
multiple output model-fit approach. Journal of
Neuroscience Methods, 296, 44–56.
Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (2004). Efficient quadratic
regularization for expression arrays. Biostatistics.
https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/kxh010
Jafari, H., Nikolakopoulos, G., & Gustafsson, T. (2019).
Stabilization of an inverted pendulum via human brain
inspired controller design. IEEE-RAS International
Conference on Humanoid Robots. https://doi.org/
10.1109/Humanoids43949.2019.9035019
Lee, H., Kim, H. J., & Park, J. (2018). Control of a
nonanthropomorphic exoskeleton for multi-joint
assistance by contact force generation. International
Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems.
https://doi.org/10.1177/1729881418782098
Lippi, V. (2018). Prediction in the context of a human-
inspired posture control model. Robotics and
Autonomous Systems. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.robot.2018.05.012
Lippi, V., & Mergner, T. (2017). Human-derived
disturbance estimation and compensation (DEC)
method lends itself to a modular sensorimotor control
in a humanoid robot. Frontiers in Neurorobotics,
11(SEP). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbot.2017.00049
Lippi, V., Mergner, T., & Maurer, C. (2020). Deep
Learning for Posture Control Nonlinear Model System
and Noise Identification. Proceedings of the 17th
International Conference on Informatics in Control,
Automation and Robotics - Volume 1: ICINCO,.
Lippi, V., Mergner, T., Seel, T., & Maurer, C. (2019).
COMTEST Project: A Complete Modular Test Stand
for Human and Humanoid Posture Control and
Balance. IEEE-RAS International Conference on
Humanoid Robots. https://doi.org/10.1109/Humanoids
43949.2019.9035081
Makondo, N., Rosman, B., & Hasegawa, O. (2015).
Knowledge transfer for learning robot models via Local
Procrustes Analysis. IEEE-RAS International
Conference on Humanoid Robots. https://doi.org/
10.1109/HUMANOIDS.2015.7363502
Mergner, T. (2010). A neurological view on reactive human
stance control. Annual Reviews in Control, 34(2), 177–
198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcontrol.2010.08.001
Mergner, T., Maurer, C., & Peterka, R. J. (2003). A
multisensory posture control model of human upright
stance. Progress in Brain Research, 142, 189–201.
Ott, C., Henze, B., Hettich, G., Seyde, T. N., Roa, M. A.,
Lippi, V., & Mergner, T. (2016). Good Posture, Good
Balance: Comparison of Bioinspired and Model-Based
Approaches for Posture Control of Humanoid Robots.
IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 23(1), 22–33.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MRA.2015.2507098
Paraschos, A., Daniel, C., Peters, J., & Neumann, G.
(2013). Probabilistic movement primitives. Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems.
Pasma, J. H., Engelhart, D., Schouten, A. C., der Kooij, H.,
Maier, A. B., & Meskers, C. G. M. (2014). Impaired
standing balance: the clinical need for closing the loop.
Neuroscience, 267, 157–165.
Phaniteja, S., Dewangan, P., Guhan, P., Sarkar, A., &
Krishna, K. M. (2018). A deep reinforcement learning
approach for dynamically stable inverse kinematics of
humanoid robots.
2017 IEEE International Conference
on Robotics and Biomimetics, ROBIO 2017.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBIO.2017.8324682
ICPRAM 2021 - 10th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
584

Schaal, S. (2006). Dynamic Movement Primitives -A
Framework for Motor Control in Humans and
Humanoid Robotics. In Adaptive Motion of Animals
and Machines. https://doi.org/10.1007/4-431-31381-
8_23
Schaal, S., Peters, J., Nakanishi, J., & Ijspeert, A. (2005).
Learning movement primitives. Springer Tracts in
Advanced Robotics. https://doi.org/10.1007/11008
941_60
Sforza, F., & Lippi, V. (2013). Support vector machine
classification on a biased training set: Multi-jet
background rejection at hadron colliders. Nuclear
Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, Section
A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and
Associated Equipment, 722. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.nima.2013.04.046
Sforza, F., Lippi, V., & Chiarelli, G. (2011). Rejection of
multi-jet background in pp
̄
→ eν + jȷ
̄
channel through a
SVM classifier. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
331(PART 3). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-
6596/331/3/032045
Torricelli, D., Mizanoor, R. S. M., Lippi, V., Weckx, M.,
Mathijssen, G., Vanderborght, B., Mergner, T.,
Lefeber, D., & Pons, J. L. (2020). Benchmarking
Human Likeness of Bipedal Robot Locomotion: State
of the Art and Future Trends. In Metrics of Sensory
Motor Coordination and Integration in Robots and
Animals (pp. 147–166). Springer.
van Asseldonk, E. H. F., Buurke, J. H., Bloem, B. R.,
Renzenbrink, G. J., Nene, A. V, van der Helm, F. C. T.,
& van der Kooij, H. (2006). Disentangling the
contribution of the paretic and non-paretic ankle to
balance control in stroke patients. Experimental
Neurology, 201(2), 441–451.
van der Kooij, H, van Asseldonk, E. H. F., Geelen, J., van
Vugt, J. P. P., & Bloem, B. R. (2007). Detecting
asymmetries in balance control with system
identification: first experimental results from Parkinson
patients. Journal of Neural Transmission, 114(10),
1333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-007-0801-x
van der Kooij, Herman, van Asseldonk, E., & van der Helm,
F. C. T. (2005). Comparison of different methods to
identify and quantify balance control. Journal of
Neuroscience Methods, 145(1–2), 175–203.
Vuga, R., Ogrinc, M., Gams, A., Petric, T., Sugimoto, N.,
Ude, A., & Morimoto, J. (2013). Motion capture and
reinforcement learning of dynamically stable humanoid
movement primitives. Proceedings - IEEE
International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2013.6631333
Yang, C., Komura, T., & Li, Z. (2017). Emergence
of human-comparable balancing behaviours by
deep reinforcement learning. IEEE-RAS
International Conference on Humanoid Robots.
https://doi.org/10.1109/HUMANOIDS.2017.8246900
The Importance of Models in Data Analysis with Small Human Movement Datasets: Inspirations from Neurorobotics Applied to Posture
Control of Humanoids and Humans
585
