
Distributed Serverless Chat Bot Networks using Mobile Agents:
A Distributed Data Base Model for Social
Networking and Data Analytics
Stefan Bosse
a
University of Bremen, Dept. Mathematics & Computer Science, 28359 Bremen, Germany
Keywords: Chat Bots, Natural Language Processing, Human-machine Interface, Self-organising MAS, Agent-based
Computing, Crowd Sensing.
Abstract: Today human-machine dialogues performed and moderated by chat bots are ubiquitous. Commonly,
centralised and server-based chat bot software is used to implement rule-based and intelligent dialogue robots.
Furthermore, human networking is not supported. Rule-based chat bots typically implement an interface to a
knowledge data base in a more natural way. The dialogue topics are narrowed and static. Intelligent chat bots
aim to improve dialogues and conversational quality over time and user experience. In this work, mobile
agents are used to implement a distributed, decentralised, serverless dialogue robot network that enables ad-
hoc communication between humans and machines (networks) and between human groups via the chat bot
network (supporting personalized and mass communication). I.e., the chat bot networks aims to extend the
communication and social interaction range of humans, especially in mobile environments, by a distributed
knowledge and data base approach. Additionally, the chat bot network is a sensor data acquisition and data
aggregator system enabling large-scale crowd-based analytics. A first proof-of-concept demonstrator is shown
identifying the challenges arising with self-organising distributed chat bot networks in resource-constrained
mobile networks. The novelty of this work is a hybrid chat bot multi-agent architecture enabling scalable
distributed and adaptive communicating chat bot networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
Chat bots are a synonym of the more general class of
dialogue robots. The deployment of dialogue robots
in mobile environments and the WEB requires
extensibility, scalability, and maintenance capability
(Lokman, 2019). A chat bot can be used for specific
tasks like knowledge base interfaces (e.g., business
chat bots answering questions related to products) or
more generally as a conversational bot (e.g.,
cleverbot) with broader topics posing adaptivity (by
learning capabilities) and some kind of social and
emotional capabilities. The majority of work in the
field of dialogue robots addresses 1:1 interaction and
facing text understanding and response challenges.
Modern chatbots pose similar single-instance
architectural design and implementation features
(Lokman, 2019).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8774-6141
Commonly a chat bot is bound either to a user (a
personalized bot) or to a specific service (e.g., a
company or domestic bot). Service related bots are
usually not personalized and are executed on a server.
Distributed chat bot networks can provide extended
social networking and group interaction.
Additionally, hierarchical bot architectures with
specialization of lower levels can be implemented,
too.
Specific distributed tasks like chat bot guided
public or private navigation and crowd flow control
require a binding to the service, to the user, and in
mobile applications and environments to the host
device (i.e., a smartphone or a wearable embedded
device). Distributed chat bot networks require a
powerful but easy distributed communication and
processing model. Swarm intelligence approaches
were proposed for general botnet systems
(Castiglione, 2014).
398
Bosse, S.
Distributed Serverless Chat Bot Networks using Mobile Agents: A Distributed Data Base Model for Social Networking and Data Analytics.
DOI: 10.5220/0010319503980405
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2021) - Volume 1, pages 398-405
ISBN: 978-989-758-484-8
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
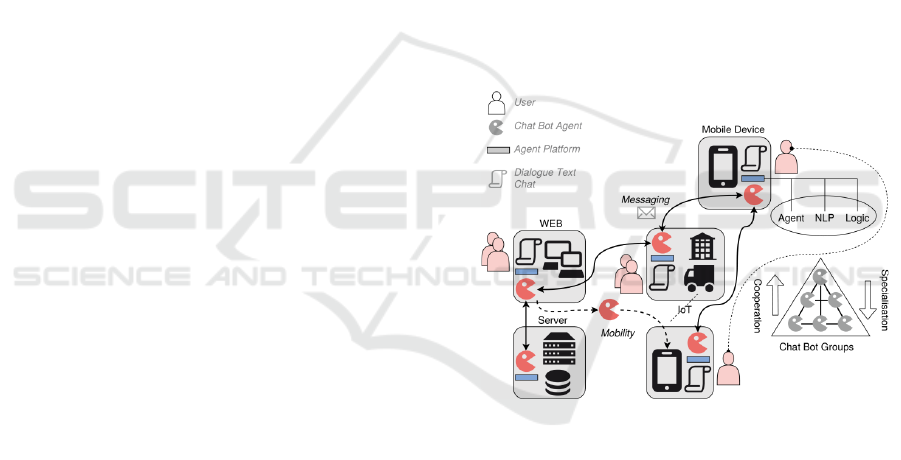
Distributed chat bot networks can provide a
networking platform to achieve enhanced
information distribution (Angelov, 2019), crowd
interaction, and improved dialogue flows. The main
problem to be solved is the interaction and
organisation of the chat bots with an appropriate and
scalable communication and processing model
supporting ad-hoc networking and self-organisation.
The agent model and technology can extend the
behavioural capabilities of chat bots providing
decoupling and raising the autonomy level
significantly, i.e., a chat bot can be considered as a
semi-autonomous agent (Karunananda, 2015),
especially concerning chat bots to pursue specific
goals to collect information or to control the
environment. In (Bosse, 2019) agent-based chat bots
processed on a slim JavaScript Agent processing
Platform (APP) were used to perform crowd sensing
surveys in mobile networks by using questionnaire
dialogues. The dialogue consists of a questionnaire
graph with nodes describing a specific question and
edges describing the dialogue flow. Edges can be
conditional using context or domain specific data
(e.g., from previously answered questions) and
creating some kind of conversational dynamic.
Answers are stored in the questionnaire graph as well
as additional environmental sensors like position or
user identifications.
Chat bots are now integrated in popular
messaging programs and also appear as stand-alone
services like Amazon Alexa, Microsoft’s Cortana,
and Apples Siri. Central part of dialogue robots is
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Natural
Language Synthesis (NLS), both are non-trivial tasks.
Scale is a critical factor that influences the
effectiveness of dialogue robot nets in accomplishing
their tasks. Recruitment of new nodes makes the
network complexity grow (Castiglione, 2014).
It is still difficult to build chat bots. Developers
have to choose the conversational topics carefully, the
coordination of the cognitive services to build the
chat bot interface, and the integration of the chat bot
with external services like knowledge bases. Finally,
extensibility, scalability, maintenance, and resource
costs to run the chat bot has to be addressed. Server-
based and centralised chat bot services do not scale
linearely on a large scale.
Serverless computing (Baldini, 2017) has recently
emerged as an alternative way of creating back-end
applications. Serverless computing does not require a
dedicated infrastructure, although distributed service
points are required, too. Serverless architectures pose
a better scaling and are inherently distributed.
Serverless chat bots are basically integrated software
encapsulating code and data. The serverless concept
of dialogue robots is still emerging (Lehvä, 2018), but
due to the requirement of big knowledge data bases a
challenge. City management (Teslya, 2018) is one
prominent field of application, emerging rapidly, too.
But, for instance, (Teslya, 2018) use still a server-
centred approach with SQL data bases. The clients are
basically information requester, but cannot create
information processing actively and lack of adaptivity
and specialisation at run-time (personalisation,
localisation).
The principle agent-based chat bot architecture
and methodology is illustrated in Fig. 1. Distributed
serverless chat bots are able to interact with users and
to interact with each other. A chat bot group can
provide a personalized and localized services with
global networking. A chat bot group can service
different conversational tasks and goals (a group of
specialized chat bots). The agent-based approach
provides necessary decoupling from users and
locations and enables temporal personalized and
context-based services.
Figure 1: The proposed unified agent-based dialogue robot
network architecture providing distributed serverless and
communicating chat bot groups.
The novelty of this work is the composition of a
distributed dialogue robot network with a hybrid
approach of agents, NLP, and predicate logic data
bases and inference engines addressing resource-
constrained processing (e.g., mobile networks) and
nearly linear scaling with respect to the number chat
bots. Networks of dialogue robots can interact via
high-level Agent-0 messaging primitives (Shoham,
1991) using the APP communication API. Messaging
enables remote modification of agent data bases, i.e..,
creating a distributed data base, and dialogue
interaction. E.g., an agent A can request an agent B to
ask his current user a question to extend its
information base. This way, conversations of
Distributed Serverless Chat Bot Networks using Mobile Agents: A Distributed Data Base Model for Social Networking and Data Analytics
399

different humans can be coupled by bot agents, too.
Finally, the chat bot interaction can extend the
knowledge base and achieve improved speaker
independence by accessing a broader dialogue and
information data base. Often dialogue responses
express a lack of information and knowledge.
Additionally, the chat bot network is a sensor data
acquisition and data aggregator system enabling
large-scale crowd-based analytics.
The next sections introduce the requirements and
principles for the proposed hybrid dialogue
processing architecture and the agent-based dialogue
processor networks. A preliminary case study
addressing city management poses first insights in the
capabilities and limitations of the proposed multi
agent-based architecture and the benefit of loosely
coupled bot groups.
2 HYBRID ARCHITECTURE
Basically there are three different peer-to-peer
dialogue schemas classified by initiator roles and
stimulus types Q:Question, S:Statement:
• Question-Answer (Initiator: Bot/Q, Master:
Bot);
• Topic and context-related knowledge query or
guidance in problem solving (Initiators: Bot:Q
or human:Q, Master: bot);
• Free form (Initiators: Bot and human Q/S,
Master: both)
Statements can be informational with facts ("I am
driving a car") and can be stored in a knowledge data
base using logic rules or can be fuzzy assumptions
presented likely as a thesis that have to be proven by
the conversation partner ("You are mad!") requiring
reactivity (commonly a question).
Implementing human-machine dialogues is a
challenge on a broad variety of levels. A dialogue
robot basically consists of:
1. Natural language parsing, processing, and
understanding (NLP, natural language ⇒ logic);
2. Information query, learning, and logical
solving;
3. Natural language synthesis (NLS).
Levels 1 and 3 are related to speech-to-text (STT)
and text-to-speech (TTS) transformations, too.
Simple dialogue robots just associate facts from a
simple knowledge base (FAQ!) to questions from a
user. Simple text pattern matching is a sufficient
approach. It is basically a conversational search
engine. But expanding conversational topics and
allowing conversation with only partially or not
available knowledge requires advanced techniques.
Questions can be divided in different classes with
respect to the answer type:
• Numerical data (limited by value intervals)
• Categorical data (limited by symbolic choices)
• Logic (facts and knowledge)
• Free text (limited by length)
Universal conversation chat bots (e.g., cleverbot)
are state-based with history and accesses and updates
big data bases to create a meaningful and useful
dialogue consisting of questions, facts, statements,
and answers. The cleverbot machine is online since
more than 10 years with billions of processed user
dialogues and can still not used for goal-directed
dialogues.
In this work, the chat bot is mobile software with
limited storage capabilities that is executed on the
user side. Therefore, a simplified NLP framework
compromise (Kelly, 2020) is used to parse, analyse,
and modify text snippets. Text sentences are
tokenized and mapped on text descriptor objects. This
descriptor object contains the following information
(simplified):
type sentence-descriptor = {
text : string,
verbs: string [],
nouns: string [],
pronouns: string [],
adverbs : string [],
adjectives : string [],
conjunctions: string [],
topics: string [],
keywords : string [],
}
Topics are more general classifications than
keywords. Like any other NLP system, compromise
can only cover a sub-set of (English) language
constructs. Hence, the classification and recognition
of sentence tokens is error prone. A more powerful
feature of compromise is the capability to match
phrases using the has operation and language
patterns, e.g.:
parser=nlp('Where are you?');
locate=parser.has('where * #Pronoun');
person=parser.pronouns().has('I')?
'You':parser.pronouns().has('you')?'I':
parser.nouns().first().text();
Dictionary lookups play an important role in NLP
to classify sentences with keywords quickly. The
minimalistic dialogue processor proposed in this
work uses compressed dictionaries based on tries
(prefix trees).
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
400

Matching of keywords and groups of keywords
are the most relevant features used to determine the
chat bot response to a user sentence and to develop
conversation threads.
Facts of interest can be transformed in logical
rules and stored in the logic data base of the agent. A
PROLOG logic solver (Valverde, 2020) is used to
process and infer on logic rules. The usage of simple
interval temporal logic (time stamps, temporal
validity) ensures revision and garbage collection of
logic rules. Examples for logic rules are spatial and
context rules. Each dynamic fact or rule (an event)
holds a time interval [t0, t1] defining its temporal
validity. Simple interval rules based on Allen's
interval arithmetic (Janhunen, 2019) are used to
evaluate events, e.g., meet, overlaps.
Central part of the dialogue system is the script
data base. It consists of a dynamic set of active
dialogue snippets, basically dialogue rules. These
snippets contain data and functional code executed by
the dialogue processor. The type signature of a
snippet is shown below.
type script database = snippet []
type snippet = {
tag:string,
condition?:function,
evaluate?:function,
stimulus : {
activation?,condition?,
question?,message?,
choices?:[]|function,
mutual?:boolean,
range?:[]|function,
},
action? : {response?},
process?:function,
next?:string []|function,
answer?:[], utility:number,
keywords?:string [],
topics?:string [],
phrases?:string []
}
There are reactive and pro-active dialogue
snippets. E.g., a pro-active bot question has the
format stimulus: {question, choices?,
range?}, condition?, evaluate?, next?,
a reactive message enabled by a stimulus (user input)
has the format stimulus: {activation},
action: {response}.
The script data base is dynamic and can be
extended, updated, and entries can be deleted or
exchanged. Entries and sub sets of the script data base
can be created and passed to other chat bots, for
example.
The script snippets spawn a universal and
dynamic conversational directed cyclic graph
C=<S,E> consisting of snippet nodes and edges
connecting cascades of snippets (consecutive Q/A
mini dialogues). Edges can be conditional, i.e.,
depending on user input, sensor data (location), and
previously given user answers.
The logic programming is implemented with
PROLOG. The logic data base used by each agent
bases on predicate logic with temporal predicate
rules. I.e., dynamic logic facts and rules are
associated with time stamps, time conditions (e.g.,
valid in the past), and time intervals estimating the
validity of facts and rules. Logic and time attributes
are handled separately. The logic rules are stored by
the agent in text format (i.e., a logic program). Logic
inference requires the compilation of the text data
base (deserialisation, only one time on a new platform
for a session). At any time the compiled logic DB can
be modified and serialised to text (DB snapshot).
Script entries get a utility score measure and the
dialogue processes can select appropriate script
snippets based on this utility score. A garbage
collector can remove snippets based on low utility, for
example.
All three principles are seamlessly integrated in an
agent-based execution and perception model
described in the next section.
3 MOBILE REACTIVE CHAT
BOT AGENTS
The main feature of this work is the coupling and
fusion of dialogue robot and mobile reactive agent
architectures. Mobile agents are mobile software that
is executed on an agent platform in a sandbox
environment. In this work the JavaScript Agent
Machine (JAM, details in (Bosse, 2017)) is used to
process mobile agents on a broad range of host
devices, including, but not limited to, smart phones,
WEB browsers, embedded and IoT devices, and
servers. JAM agents are reactive and programmed in
JavaScript, too.
JAM agents are modelled and programmed with a
directed activity-transition graph (ATG)
ATG=<A,T> consisting of activity nodes A and
transitions T. Activities perform actions:
Computation, interaction, messaging, agent control
including replication and modification, and mobility.
Agents carry a private set of body variables. The ATG
is dynamic and can be modified by the agent at run-
time (details in (Bosse, 2017)) providing adaptivity
Distributed Serverless Chat Bot Networks using Mobile Agents: A Distributed Data Base Model for Social Networking and Data Analytics
401

and specialization. Each activity performs actions,
e.g., computation, communication, replication, and
mobility. An activity corresponds to a sub-goal (with
a specific desire) of the agent. Transitions between
activities can be conditional depending on the
evaluation of agent data (body variables).
One major feature of JAM is the separation of data
from code. Although, the agent carries its behavioural
code, it uses a large API set provided by the platform,
see Fig. 2 and (Bosse, 2019). Among the agent core
API the platform provides dedicated module APIs for
Machine Learning (ML), Logic, NLP, and many
more. All module APIs are procedural, i.e., the agent
keeps the (mobile) data, e.g., of a trained ML model,
and passes the data to the API functions. This feature
keeps the entire data and code size of agents small
(typically 10k-100k Bytes for one agent).
Agents can communicate via tuple spaces (bound
to the platform location) or by sending signals. Each
agent can access a set of sensors provided by the
platform via the tuple space (e.g., location).
3.1 Bot Architecture
The central part of the dialogue robot agent (chat bot)
is the script data base, the predicate logic data base
containing facts and rules, and the central dialogue
processor, shown in Fig. 2. The data bases as well as
the processor code is part of the agent. The NLP,
optional ML, and logic modules are part of the agent
processing platform.
Bot agents can interact with each other by
exchanging messages. There are high-level messages
to deliver or request logic facts/rules and dialogue
snippets based on logical queries or search patterns.
Dialogue snippets are active units that can be
exchanged by agents.
Figure 2: The dialogue robot script, data base, and
dictionary architecture accessed by the dialogue processor
(parts of the chat bot agent).
3.2 Dialogue Processor
The dialogue processor and manager has to infer the
next action to be executed based on current text input
(parsed and analysed by the NLP module block) and
sensor input data (e.g., the spatial position). There are
different actions resulting from the perception
(environmental sensors of the agent) and textual input
stimulus:
• The next output sentence is selected and
synthesized (e.g., an answer to a user question, a
thesis based on facts or assumptions, bridges, or
new question directed to the user);
• The dialogue and logic data base is updated
(adding new dialogue rules, revision and removal
of rules and logic facts, invalidating rules);
• Sending of information and query messages to
other chat bots (pending user question);
• Query of external knowledge data bases (e.g.,
Wikipedia, also pending user question);
• Replication (spiders, extending the interaction
range, distributing knowledge and script rules);
• Migration (to another user or device).
The inference of relevant information (feature
selection) from the current textual user input uses
primarily phrase, keyword, and topics matching,
finally using token classification analysis.
Furthermore, the dialogue memory can be used to
derive a contextual situation.
The dialogue processor is implemented with
different agent activities processed by the agent
processing platform, shown in Fig. 3.
Figure 3: The dialogue and action processor as a sub-graph
of the agent ATG behaviour model with access to agent
body variables/data bases (right) and interface to modules
of the APP (left).
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
402

3.3 Networks and Multi-Bot Groups
The bots implemented by mobile reactive agents are
created on a specific host node (e.g., on a server or by
accessing a WEB page in the client WEB browser).
They can interact in different ways with other agents
(related to communication in a more general point of
view):
• Replication by forking of child agents
(inheriting the script and logic data base);
• Sending messages (inform, ..) updating script
and logic data bases;
• Exchanging information and knowledge by
anonymous tuple exchange;
• Migration between nodes (i.e., mobile devices,
servers, WEB platforms, etc.).
Agent forking creates parent-child groups and
family trees. This is useful for the concept of
hierarchical chat bots, i.e., there are different chat bot
able to perform conversations on specific topics
(location service, small talk, social, ...).
A single dialogue robot agent can perform One-
to-One (1:1) conversation. With respect to mobility,
it can perform One-to-Many (1:m) conversation
sequentially. Groups of connected agents can perform
additionally Many-to-Many (m:m) and Many-to-One
(m:1) conversations.
3.4 Messaging
Chat bot agents can interact via exchanging addressed
messages (agent signals, including multi-cast) or by
using tuple spaces for synchronised data exchange.
Messages can be used to access the script and logic
data bases of other agents and to request remote
dialogue actions. There are different message types
based on Agent-0 messaging (Shoham, 1991) with
remote procedure call semantics:
• inform delivers new dialogue snippets or logic
rules to other agents (the receiving agent can
deny the suggestion)
• ask is used to get information (dialogue snippets
based on patterns, logical inference, sensors)
from remote agents
• request is used to execute a dialogue snippet by
the remote chat bot agent
• unrequest cancels a pending request
4 CHAT BOT INTERACTION
Human-Bot Communication. The chat bot can
interact with humans primarily via text messages.
Speech-to-Text technologies can be added, but are
not considered in this work. Because the chat bot is
an agent, it will interact with other agents to get in
touch with humans. Mobile device apps or textual
interaction embedded in WEB pages provide a chat
manager agent that provides a filtered and gated
bridge between humans and the chat bot.
Bot-Service Communication. Although, serverless
chat bots carry their own data bases. they have still to
interact with a set of diverse commodity services
publicly available on the Internet like navigation
(location) or weather services. The dialogue
processor can request information from such services
via a HTTP/JSON API that is provided by most
public Internet services.
Bot-Bot Communication. Two cases have to be
distinguished:
• Coupled bot families (Parent-children groups):
This bots relationship can directly communicate
via messages propagated in the communication
network (Internet) using signals (provided by the
APP), i.e., on a private level.
• Uncoupled bots: This bots relationship can only
use tuple spaces (provided by the APP) to
exchange information and data anonymously
(public level). Bots initiate a dialogue request on
remote devices if they try to extend their
knowledge base or if they want to establish
human-human communication.
Human-Human Communication. Due to the
networking capabilities of chat bots as proposed in
this work, chat bots can be used to connect two or
more humans. Chat bot agents can forward messages
to other agents either unmodified or by applying
filters, modificators, and gates (i.e., performed by
require messages between coupled agent groups).
Alternatively, explorer agents can interact with chat
bots ad-hoc via tuple space communication.
5 USE-CASE SCENARIO: CITY
EVENT AND LOCATION
GUIDE NETWORK
5.1 Setup
A preliminary demonstrator deploys a simple
distributed and loosely coupled ad-hoc multi chat bot
system for a simple distributed city event
management and tourism (business)guidance, i.e., a
goal-oriented dialogue system. It is used primarily to
get performance and utility metrics. Users are
conversational partners (communication endpoints)
Distributed Serverless Chat Bot Networks using Mobile Agents: A Distributed Data Base Model for Social Networking and Data Analytics
403

as well as provider of spatial context-related
information (communication sources), shown
basically in Fig. 4. Although the conversational
context is limited, more general question can be
answered (e.g., about weather).
The goal of the bots is navigation and guidance of
culture events (in tourism context) and places/points
of interest (restaurants, meeting points, domestic
services, etc.). This includes well known planned
static events (e.g., theatre, cinema) and dynamic ad-
hoc events (e.g., visit and recognition of interesting
places by other people).
The logic data base is related to general and
domain specific ontologies. Facts and rules represent
information about events in PROLOG clauses, e.g.,
event(music). event(ev001, music,
bremen, start, end. containing a temporal
constraint.
The chat bots agents are processed by the JAM
App available stand alone for mobile devices and
integrated in WEB browsers, too (details in (Bosse,
2019)).
Figure 4: The smart city use-case connecting people in
streets, buildings, and vehicles via distributed chat bot
agents performing city event management and navigation.
The chat bot are data sensors and aggregators, too (for
further data analytics, e.g., parking management).
Communication takes place via mobile Internet,
WLAN, and Bluetooth (P2P). The chat bot agents
have the capability to create children with a sub set of
behaviour and data (logic, script). Theses child
explorer agent can leave the platform and migrate to
another platform, e.g., a Bluetooth beacon. The
explorer agent can exchange information with other
chat bot agents via tuple spaces. People can scan a QR
code either using a WEB browser opening a new page
with the embedded APP and the chat bot agent or by
a dedicated App with integrated APP loading the
agent only.
The script data base contained initially a set of
about 40 questions, statements, and phrases with
respect to the limited conversational topic city event
and location service. The logic data base started with
about 100 facts and rules. Users are asked for
interesting places and events, too, extending
knowledge and script data bases.
5.2 Resources and Performance
The performance of the agent platform is given by the
code-text serialization and deserialization capability
with about 10kB/ms (1GHz CPU) with respect to the
text size (JavaScript). Agents up to a size of 1MB
(serialized text size) can migrate between agent
platforms with low latency (< 1s). Agent sizes
(code+data, serialized) ranges typically between
10kB-100kB without data bases. Logic data base
deserialisation (compilation at start-up) requires
about 0.5-1.0 ms/rule, i.e., up to 1000 facts and rules
can be handled without a significant boot time of the
agent. New rules can be added at run-time with low
overhead. Dictionary sizes depend on application
scenarios. Keyword data bases (hash tables) are
populated typically with 100 rows requiring about
4kB, dialogue script data bases require averaged 300
Bytes/rule (data + code). A large script data base with
1000 entries requires only 300kB storage.
Typical response times of agent-agent interaction
was below 500ms, i.e., a running conversation flow is
not delayed significantly. Each chat bot agent
occupies less than 4MB memory (average) on the
host device (e.g., a smart phone). The entire JAM APP
requires less than 5MB static data space (serialised
text) and less than 50MB dynamic memory space.
The network under test deployed up to 50
interacting agents (and users) in parallel and up to
1000 agents during a first field test. During the field
test, the chat bots modified about 20% of their script
data base and about 200% of their logic data base due
to new perceptions and chat bot interaction. Local
WLAN/Bluetooth beacons and mobile explorer
agents delivered updates to the chat bot agents. One
challenge is short-time and short-range connectivity
and unlinked communication, especially with
Bluetooth. Agent communication and agent
migration between platforms require at least 1MBs
data volume for successful data exchange.
One main issue of the simplified NLP and script-
snippet data base approach is the quality of dialogues
and teh acceptance of users that must be improved in
future work.
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
404

6 CONCLUSION
The fusion of chat bots technologies with multi-agent
systems enables the orchestration and connection of
dynamic large-scale chat bot networks that are
capable to interact with users dynamically either
directly or indirectly via bot messaging. Both
specialisation by hierarchical bot networks as well as
cooperation is supported (knowledge extension). The
proposed approach already provide chat bot
interaction via the agent communication with high-
level messaging allowing information and dialogue
exchange, eventually connecting spatially separated
users via chat bots. The slim agent processing
platform can be easily integrated in existing software
or WEB pages, especially supporting mobile
networks and devices. The agent bot communication
and interaction enables distributed knowledge and
dialogue data bases.
REFERENCES
Angelov, S., Lazarova, M., E-commerce Distributed
Chatbot System. In Proceedings of the 9th Balkan
Conference on Informatics (BCI'19). Association for
Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article
8, 1–8., 2019
Baldini, I., Castro, P., Chang, K., Cheng, P., Fink, S.,
Ishakian, V., Mitchell, N., Muthusamy, V., Rabbah, R.,
Slominski, A., Suter, P., Serverless Computing:
Current Trends and Open Problems, Research
Advances in Cloud Computing, Springer, 2017
Bosse, S., Engel, U., Real-time Human-in-the-loop
Simulation with Mobile Agents, Chat Bots, and Crowd
Sensing for Smart Cities, Sensors (MDPI), 2019
Bosse, S., Pournaras, E., An Ubiquitous Multi-Agent Mobile
Platform for Distributed Crowd Sensing and Social
Mining, FiCloud 2017: The 5th International
Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud,
2017, Prague, Czech Republic
Castiglione, A., Prisco, R. D., Santis, A. D., Fiore, U., and
F. Palmieri, A botnet-based command and control
approach relying on swarm intelligence, Journal of
Network and Computer Applications 38, vol. 38, pp.
22-23, 2014.
Janhunen, T., Sioutis, M., Allen’s Interval Algebra Makes
the Difference, INAP 2019, WLP 2019, 2019
Karunananda, B. Hettige and A., Octopus: A Multi Agent
Chatbot, in Proceedings of 8th International Research
Conference, KDU, 2015.
Kelly, S., compromise: modest natural-language
processing, https://github.com/spencermountain/
compromise, accessed 14.10.2020, 2020
Lehvä, J., Mäkitalo, N., Mikkonen, T., Case Study:
Building a Serverless Messenger Chatbot, in Current
Trends in Web Engineering. ICWE 2017., Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, vol 10544, 2018
Lokman, A. S., Ameedeen, M. A., Modern Chatbot
Systems: A Technical Review. In: Arai K., Bhatia R.,
Kapoor S. (eds) Proceedings of the Future
Technologies Conference (FTC) 2018. FTC 2018.
Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol
881. Springer, Cham., 2019
Shoham, Y., AGENTO: A simple agent, in AAAI, 1991, pp.
704-709.
Teslya, N. N., Ryabchikov, I. A., Petrov, M. V., Taramov,
A. A., and E. O. Lipkin, Smart City Platform
Architecture for Citizens’ Mobility Support, in 13th
International Symposium “Intelligent Systems”
(INTELS’18), Procedia Computer Science, 2018.
Valverde, J., tau-prolog: An open source Prolog interpreter
in JavaScript, http://tau-prolog.org, accessed
21.10.2020, 2020.
Distributed Serverless Chat Bot Networks using Mobile Agents: A Distributed Data Base Model for Social Networking and Data Analytics
405
