
Analyzing Adversarial Attacks against Deep Learning for
Robot Navigation
Mohamed Ibn Khedher and Mehdi Rezzoug
IRT - SystemX, 8 Avenue de la Vauve, 91120 Palaiseau, France
Keywords:
Autonomous System, Robot Navigation, Making-decision, Neural Network Verification, Adversarial Attacks,
Defence Techniques, Adversarial Training, Model Evaluation.
Abstract:
The autonomous system sector continues to experiment and is still progressing every day. Currently, it affects
several applications, namely robots, autonomous vehicles, planes, ships, etc. The design of an autonomous
system remains a challenge despite all the associated technological development. One of such challenges is
the robustness of autonomous system decision in an uncertain environment and their impact on the security
of systems, users and people around. In this work, we deal with the navigation of an autonomous robot in
a labyrinth room. The objective of this paper is to study the efficiency of a decision-making model, based
on Deep Neural Network, for robot navigation. The problem is that, under uncertain environment, robot
sensors may generate disturbed measures affecting the robot decisions. The contribution of this work is the
proposal of a system validation pipeline allowing the study of its behavior faced to adversarial attacks i.e.
attacks consisting in slightly disturbing the input data. In a second step, we investigate the robustness of robot
decision-making by applying a defence technique such as adversarial training. In the experiment stage, our
study uses a on a public robotic dataset.
1 INTRODUCTION
Self-driving for autonomous systems is one of the
hottest areas of research and business for the last
decade. The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
and, more precisely, Deep Learning (DL) techniques
to the development of autonomous driving systems is
currently an active area of research.
In fact, recently, some governments, like Japan,
has set aside funds to make autonomous driving tech-
nology a reality for the 2020 Olympics, because it is
considered safe and efficient mode of transportation
(Okuyama et al., 2018). Moreover, most major au-
tomobile manufacturers worldwide have reached ad-
vanced stages of developing self-driving cars.
It is worth mentioning that the advances in the de-
velopment of autonomous systems are strongly linked
to the rapid progression and application of artificial
intelligence in several fields. Artificial intelligence
and specially Deep Learning has shown great suc-
cess in diverse areas such as robot navigation (Ruiz-
del-Solar et al., 2018), speech recognition (Spille
et al., 2018), image recognition (Khedher et al., 2018;
Khedher et al., 2012; Khedher and El Yacoubi, 2015)
and anomaly detection (Jmila et al., 2017; Jmila et al.,
2019). Moreover, DL shows a great success in re-
inforcement Learning based algorithms widely used
for autonomous systems navigation. In fact, contrary
to supervised learning where there exists an output
(supervisor) for a given input, reinforced learning, is
used when an agent has to learn to take the right action
to affect a change in the environment in which it is
placed. The right action of the agent is reinforced with
a reward. Deep Reinforced Learning (DRL) combines
reinforced learning with deep learning.
Despite the great success of DL in several criti-
cal applications (Jmila et al., 2019), DL faces sev-
eral challenges such as the lack of transparency of
the deep learning model, the explicability of such a
decision, the vulnerability of the deep learning mod-
els to adversarial attacks. For the scope of this study,
we focus on the vulnerability of deep learning models
faced adversarial examples. An adversarial example
is an instance of the input in which a minimal per-
turbation is added with the intention of changing the
model decision, i.e to produce a wrong decision.
In a real application, the adversarial examples are
mostly related to the perturbation of the environment.
The perturbation factors are numerous and differ from
one context to another (image, audio, video, etc.).
1114
Ibn Khedher, M. and Rezzoug, M.
Analyzing Adversarial Attacks against Deep Learning for Robot Navigation.
DOI: 10.5220/0010323611141121
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2021) - Volume 2, pages 1114-1121
ISBN: 978-989-758-484-8
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Taking the example of self-driving system, these fac-
tors can be related to: i) Environmental factors linked
with the external environment such as the weather
conditions, the road infrastructure and the traffic be-
havior. ii) Material factors due to system failure re-
lated to its service life, configuration and interference
with other sensors. and iii) Algorithmic/software fac-
tors associated, for example, with the error of variable
precision.
In this paper, we contribute to the study of the ef-
fects of adversarial samples on DL model. In other
words, we investigate the ability of DL model to resist
adversarial attacks. As use case, we take the example
of a Deep Learning model learned to control the nav-
igation of a robot in a smart home. In our second
contribution, we demonstrate that applying a defence
technique is important to hardness the decision model
faced adversarial attacks. Moreover, In this study, we
investigate the impact of attack strength on the robust-
ness of the Deep Learning model. The robustness is
defined as the ability of the model to maintain its ac-
curacy against adversarial attacks.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In
the section 2, a state of the art is presented. It con-
cerns the adversarial attacks proposed to fool Deep
Neural Network and defence techniques proposed to
improve its robustness. The structure of our approach
is described in section 3. Section 4 includes the ex-
perimental results and section 5 concludes the paper.
2 STATE OF THE ART
In this section, two states of the art are presented:
i)the first is about Neural Network Attacks (NNA)
and ii) the second concerns Neural Network Defence
(NND) techniques proposed to robustify neural net-
work face to attacks.
2.1 Robustness Terminology
An adversarial example is defined as an instance with
a small perturbation to make a false prediction. There
are many ways to define adversarial attacks, most of
them rely on minimizing the distance between the ad-
verse example and the original one while making sure
that the prediction is wrong. Some methods require
access to the model gradient while others only need
access to the prediction function. According to the
degree of access to the classifier, type of attacks can
be classified into two categories: white-box attacks
and black-box attacks.
• White-box Attack: It refers to the scenario in
which the attacker has full access to the architec-
ture and parameters of the classifier. To generate
attacks, algorithms have access to the model pa-
rameters including gradient and loss function.
• Black-box Attack: It refers to the scenario in
which the attacker does not have complete access
to the policy network. In other words, in black-
box setting, the model parameters are unknown.
For classification models, the attacker has only ac-
cess to the output for a given input, in one of the
following forms: i) the classifier decision; ii) the
loss of the correct label; iii) the full response for
all classes.
As definitions, we define X the set of classifier inputs
and Y the set of classifier outputs which corresponds
to the possible labels of inputs along K classes: Y =
{
1, . .. , K
}
. Finally, we note C(x) the label of x by
the neural network F(·).
Regardless of the attack type, it is important to dis-
tinct between targeted and non-targeted attack.
• Untargeted Attack: an untargeted attack aims
to misclassify the input by adding an adversar-
ial perturbation. The predicted class of the in-
put is changed to another class in Y without a
specific target class. Mathematically, an untar-
geted attack is defined as a function ρ: X → X
such that the adverse input x
0
= x + ρ(x) verify:
C(x + ρ(x)) 6= C(x)
• Targeted Attack: a targeted attack aims to mis-
classify the input to a targeted class y ∈ Y by
adding an adversarial perturbation. The predicted
class of the input x is changed from the origi-
nal class to a specific target class. Mathemat-
ically, a targeted attack is defined as a func-
tion ψ: X × Y −→ X such that the adverse in-
put x
0
= x + ψ(x, y) verify: C(x + ψ(x, y)) = y,
while keeping this perturbation as small as pos-
sible: kψ(x, y)k
p
≤ ε.
2.2 Neural Network Attacks
There are several attacks proposed in the state of the
art. In this section, we detail the most popular attacks.
2.2.1 Fast Gradient Sign Method (FGSM)
Goodfellow et al. ((Dong et al., 2018; Goodfellow
et al., 2015b)) have developed a method for gener-
ating adverse example based on the gradient descent
technique. Given an original sample x , each compo-
nent is modified by adding or subtracting a small per-
turbation ε.
The method consists in considering the sign of the
loss function gradient ∇
x
L(x, y):
Analyzing Adversarial Attacks against Deep Learning for Robot Navigation
1115

• if ∇
x
L(x, y) is positive then it means that the in-
crease of x increases the loss function L.
• if ∇
x
L(x, y) is negative then it means that the de-
crease of x decreases the loss function L.
FGSM can be targeted or untargeted. For the targeted
version, the adverse function ψ is expressed as fol-
lowing:
ψ : X × Y −→ X
(x, y) 7 −→ −ε . sign(∇
x
L(x, y))
The adverse sample x
0
is is then generated as follow-
ing:
x
0
= x − ε . sign(∇
x
L(x, y))
Regarding the untargeted version, the adverse func-
tion ρ is expressed as following:
ρ : X × Y −→ X
(x, y) 7 −→ ε . sign(∇
x
L(x, y))
The adverse sample x
0
is is then generated as follow-
ing:
x
0
= x + ε . sign(∇
x
L(x, y))
FGSM requires the computation of the loss function
gradient, which makes it a simple method. On the
other hand, the only hyper parameter of FGSM is ε
that affect the class of x
0
.
2.2.2 Basic Iterative Method (BIM)
Kurabin et al. (Kurabin et al., 2017) proposed an ex-
tension of the FGSM attack. It consists on applying
FGSM several times iteratively. At each iteration i,
the adverse sample is generated by applying FGSM
on the generated sample in the iteration i − 1. The
BIM attack is generated as following:
(
x
0
0
= x
x
0
i+1
= x
0
i
+ ψ(x
0
i
,y)
where y represents, in the case of a targeted attack,
the class of the adverse example and y = C(x
0
i
) in the
case of an untargeted attack. Moreover, ψ is the same
function defined in the case of FGSM attack.
2.2.3 Projected Gradient Descent (PGD)
The PGD (Madry et al., 2017) attack is also an ex-
tension of the FGSM and similar to BIM. Indeed, it
is also an iterative method which consists in apply-
ing FGSM several times. The major difference from
BIM is that at each iteration, the generated attack is
projected on the ball B(x, ε) =
{
z ∈ X : kx − zk
p
≤ ε
}
.
The adverse example x
0
is then constructed as follow-
ing:
(
x
0
0
= x
x
0
i+1
= Π
ε
(x
0
i
+ ψ(x
0
i
,y))
where Π
ε
is the projection on the ball B(x, ε) and ψ is
the perturbation function as defined in FGSM.
2.2.4 Jacobian Saliency Map Attack (JSMA)
This attack JSMA differs from the previous ones,
since Parpernot et al. (Papernot et al., 2015) did not
rely on a gradient descent to generate an adverse ex-
ample. The idea of authors is to disturb a minimal
number of pixels according to a criterion.
JSMA is proposed initially for a targeted version. It
consists in controlling the number of pixels of an in-
put image x (or the number of components of an input
vector) that should be modified in order to obtain an
adverse image associated with a target class y. Iter-
atively, JSMA consists in modifying pixels until the
target class is obtained.
The idea behind is to, on one hand, increase F
y
(x)
the probability of the target class y and on the other
hand, decrease the probabilities of the other classes,
until obtaining : y = arg max
j ∈Y
F
j
(x).
To do this, authors introduced the Saliency Map ma-
trix as following:
S(x, y)
+
[i] =
0 si
∂F
y
(x)
∂x
i
< 0 ou
∑
k6=y
∂F
k
(x)
∂x
i
> 0
∂F
y
(x)
∂x
i
·
∑
k6=y
∂F
k
(x)
∂x
i
sinon
The Saliency Map is used as criterion to select pixels
that should be modified. In fact, the way that Saliency
Map is computed, allows to reject pixels that will not
increase the probability of the target class y or will
not decrease the probabilities of the other classes; for
these pixels, the criterion is set to 0.
2.2.5 DeepFool
DeepFool is a non-targeted attack proposed by
Moosavi-Dezfooli et al. (Moosavi-Dezfooli et al.,
2015). The main idea of DeepFool is to find the
closest distance from the original input to the deci-
sion boundary. Authors assumed the used neural net-
work is completely linear using hyperplanes separat-
ing each class from others. To overcome the non-
linearity in high dimension, they performed an iter-
ative attack with a linear approximation. For an affine
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1116
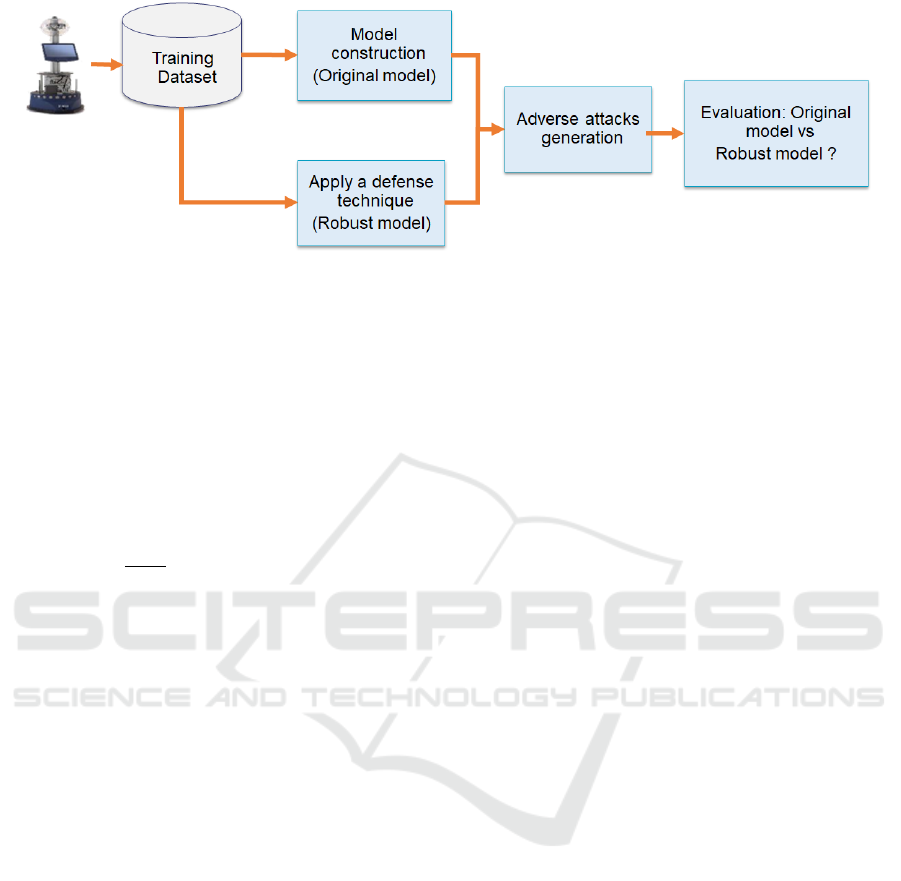
Figure 1: Proposed approach.
classifier f (x) = wT x + b, where w is the weight of
the affine classifier and b is the bias, the minimal per-
turbation of an affine classifier is the distance to the
separating affine hyperplane F = x:wT x + b = 0,.
Given the example of a linear binary classifier,
the robustness of the classifier f for an input x
0
is
equal to the distance of x
0
to the hyperplane separat-
ing the two classes. In fact, the minimal perturbation
to change the classifier’s decision corresponds to the
orthogonal projection of x
0
onto the hyperplane, given
by: η
∗
(x) = −
f (x)
kwk
2
2
∗ w.
For a general differentiable classifier, DeepFool
assumes that f is linear around x
i
at each iteration.
The minimal perturbation is expressed as following:
argmin
η
i
kη
i
k
2
subject to f (x
i
) + ∇ f (x
i
)
T
η
i
= 0.
This process runs until f (x
i
) 6= f (x), and the mini-
mum perturbation is eventually approximated by the
sum of η
i
.
This technique can also be extended to the multi-
class classifier by finding the closest hyperplanes. It
can also be extended to a more general `
p
norm,
p ∈ [0, ∞). As mentioned in (Yuan et al., 2019), Deep-
Fool provided less perturbation compared to FGSM
and JSMA. Compared to JSMA, DeepFool also re-
duced the intensity of perturbation instead of the num-
ber of selected features (Yuan et al., 2019).
2.3 Neural Network Defences
There are several defence techniques proposed in the
state of the art to improve neural network robustness
face adversarial attacks. In this section, we detail the
most popular defence techniques.
2.3.1 Adversarial Training
The adversarial training (Goodfellow et al., 2015a)
consists in improving the robustness of the classifier
C(x) by integrating adversarial samples in the training
set.
Given an attack ρ, a classifier C and the original train-
ing set (x
1
, y
1
),. . . ,(x
n
, y
n
), the approach consists in
generating the adversarial samples (ρ(x
i
), C(ρ(x
i
)))
for i = 1, . . . , n. After applying the attack to all origi-
nal training samples, the resulting augmented training
set will have a size of 2 × n. The augmented data is
then used to retrain the classifier C(x). Mostly, adver-
sarial training is used to hardness the classifier faces
multiple-attacks (a set of m attacks ρ
1
,. . . , ρ
m
. After
applying the m attacks to all training set, the latter is
augmented by n ∗ m samples.
It is worth mentioning that in most cases, adver-
sarial samples are generated only for a subset from
the training dataset, and then the training dataset is
augmented only by a predefined rate. The data aug-
mentation rate is a hyper parameter of the technique.
2.3.2 Gaussian Data Augmentation
Gaussian data augmentation (Zantedeschi et al.,
2017) is a popular technique that has been proposed
to improve the robustness of Neural Network faced
adversarial attacks. It is a standard technique mostly
used in computer visions tasks. Its usage is mostly in-
tended for the augmentation of the training set. It con-
sists in augmenting the original dataset with copies of
the original samples to which Gaussian noise has been
added. Notice that the labels y are not required, as the
method does not apply any preprocessing to them. it
is worth mentioning that this technique can be applied
only by adding Gaussian noise to an existing sample
without augmentation.
Analyzing Adversarial Attacks against Deep Learning for Robot Navigation
1117

3 EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH
Figure 1 shows the flowchart of our approach. The
input is a pre-trained model. The output is a robust
model face adversarial attacks. Our approach consists
basically of four stages:
• Construct an original decision-making model
• Generate adverse attacks allowing disruption of
model decisions
• Apply a defence technique to improve model ro-
bustness
• Evaluate a decision-making model
3.1 Original Model Construction
The first step of our approach is to construct a deci-
sion model based on DNN. As architecture, our DNN
composed of N fully-connected layers, each of them
are followed by an activation function and a dropout
layer, and a final softmax layer indicating robot de-
cision. The decision model takes as input a vectors
of 24 components and outputs a probability vector 4
components (the number of decisions in the dataset).
Each layer, in the DNN architecture, contains a set of
neurons where each one is connected to neurons of the
previous layer. Each neuron is a simple processing el-
ement that responds to the weighted inputs it received
from other neurons (Shrestha and Mahmood, 2019).
The action of a neuron depends on its activation func-
tion, which is described as:
y
i
= f
n
∑
j=1
w
i j
∗ x
j
+ θ
i
!
(1)
where x
j
is the j
th
input of the i
th
neuron, w
i j
is the
weight from the j
th
input to the i
th
neuron, θ
i
is the
bias of the i
th
neuron, y
i
is the output of the i
th
neuron
and f (.) is the activation function.
3.2 Attacks Generation
After the construction of the decision model, we test
the resilience of the model to adversarial examples.
To demonstrate this, we generate our own adversarial
samples from the robotic dataset. To generate adver-
sarial samples, we used three techniques proposed in
the state of the art. These techniques are: i) the Fast
Gradient Sign Method (FGSM) , ii) the Basic Itera-
tion Method (BIM), and iii) the Deep Fool attack. In
our study, we assume that attacks are:
• Evasion-based: the attacks are injected during
the prediction phase of the decision model.
• White-box: the attacker has a complete knowl-
edge of the decision model.
• Untargeted: we do not target any specific pre-
diction out-come, rather we seek to confuse the
decision model to take a bad decision.
3.3 Robustness Model Construction
To improve resilience to adversaries, we test the im-
pact of defence techniques to detect attacks. What-
ever the defence strategy, it aims to enforce the se-
curity of machine learning based systems against ad-
versarial attacks. In this study, we investigate the ad-
versarial training based technique. Its principle con-
sists in including adversarial examples in the training
set, and then retrain the model using the augmented
dataset. The adversarial training technique has sev-
eral advantages:
• It is not data dependant; it can be applicable to any
type of data outside images.
• It is easy to implement.
• It is effective when attacks during deployment are
similar to ones in training.
3.4 Model Evaluation
To evaluate decision models, whether it was the orig-
inal model or after adversarial training, performance
metric is used. Performance is defined as the rate of
correct decisions predicted by the neural network.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Our analyze of Deep Neural Network against adver-
sarial attacks is done on a robot navigation dataset.
4.1 Dataset
To evaluate our experimental approach, a public
Robotic dataset is used. It is a sensor dataset proposed
in (Freire et al., 2009) for wall-following robot navi-
gation. The dataset is a collection of 24 ultrasound
sensors arranged around a mobile robot «SCITOS
G5» during its navigation inside a room. The pos-
sible decisions of the robot are: 1) Move-Forward, 2)
Slight-Right-Turn, 3) Slight-Left-Turn and 4) Sharp-
Right-Turn. The dataset is composed of 5456 sam-
ples: 70% of the available data is used for training
and the remaining 30% for evaluation. Notice that
the training stage is not considered in this work. Our
analysis takes as input a pre-trained model whose vul-
nerability to adversarial attacks we investigate.
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1118

Figure 2: Original model performance according to attack’s
strength.
4.2 Evaluation Protocol
In the rest of the paper, the Original Model (OM) is
defined as the pre-trained decision model without any
defence technique; however the Robust Model (RM)
is defined as the new model after applying a defence
technique (adversarial training for example) and re-
training the decision model.
In the evaluation step, to evaluate models against
adversarial attacks, three attacks are investigated: Fast
Gradient Sign Method, Basic Iterative Method and
DeepFool. On the other hand, to improve robustness,
two defence techniques are studied: Adversarial train-
ing and Gaussian Data Augmentation. As evaluation
metrics, the accuracy metric is used. In fact, given a
N test samples {s
i
,∀i ∈ [1, N]}, each sample is asso-
ciated with a ground truth label GT
i
and a predicted
label Pred
i
. The accuracy is defined as the fraction of
samples that verify (GT
i
= Pred
i
).
4.3 Attacks Evaluation
The evaluation of the original model is performed
by varying the attack strength from 0 to 1. Figure
2 presents the comparison of the model’s accuracy
against three attacks: FGSM, BIM and DeepFool. In
Fig.2, the Y-axis represents the accuracy, and the X-
axis portrays the strength of the attack.
4.4 Defence Evaluation
After the evaluation of the original model against ad-
versarial attacks, two defence techniques are inves-
tigated to improve its accuracy: 1) Gaussian Aug-
mentation and 2) Adversarial Training. For both
techniques, an augmentation rate of 100% is used.
Moreover, for the Gaussian Augmentation technique,
a Gaussian distribution with variance equal to 1 is
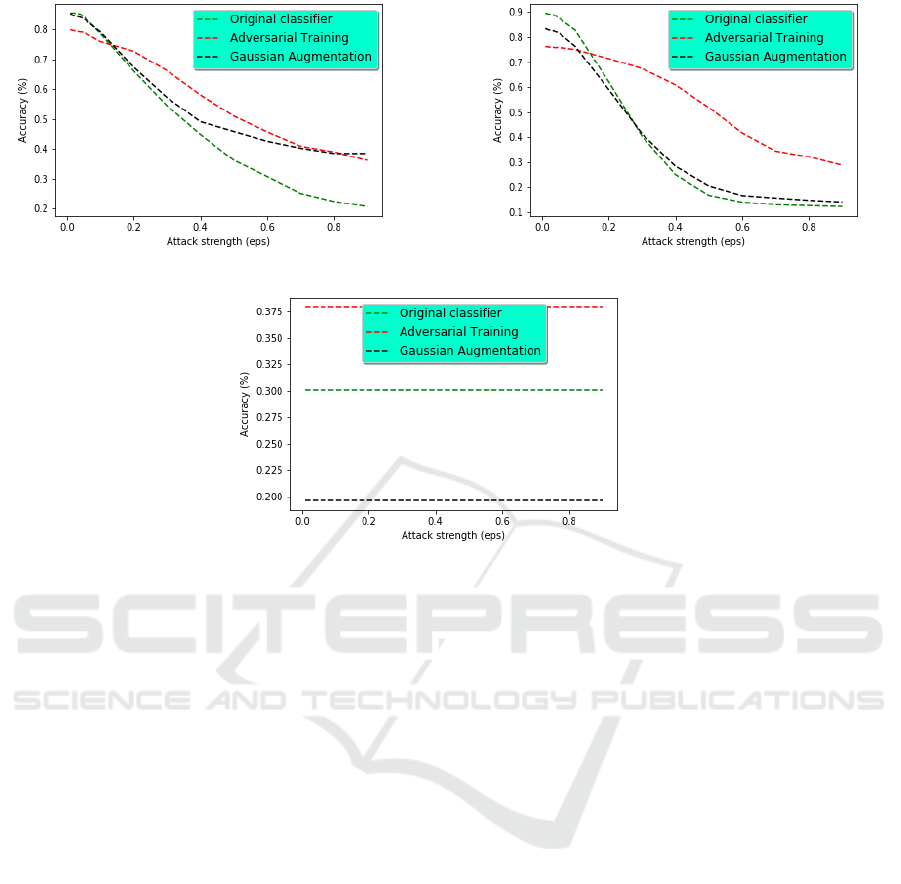
used. Figure 3 depicts the performance of the original
model and the robust model. Each sub-figure shows
the impact of defence techniques against one from the
three investigated attacks. For each sub-figure, the Y-
axis shows the accuracy, and the X-axis represents the
strength of the attack.
4.5 Discussion
Several observations could be drawn from the ob-
tained results. The first observation concerns the
result of the Original Model against attacks. The
common remark for all attacks is that the accuracy
decreases with the increase of attack strength. For
FGSM and BIM, the behavior is similar. Indeed,
for a small attack strength (eps < 0.05), the model
maintains its overall accuracy. However, it loses
quickly its performance for a moderate strength attack
(0.1 < eps < 0.6). Taken the example of FGSM, the
accuracy drops from 78.74% (eps = 0.1) to 30.72%
(eps = 0.6). Then, when the attack strength becomes
high (eps > 0.7), the accuracy stabilizes about 22%.
In the case of DeepFool attack, the decision model has
a different behavior: the accuracy drops to 30.05%
even for a small attack strength (eps = 0.01) and
then it remains stable regardless of the attack strength.
DeepFool is therefore the most efficient attack capa-
ble of attacking the model and dropping its perfor-
mance. Our first observation leads us to conclude that
our decision model accepts an ultrasound sensor per-
turbation about 5% (i.e. eps = 0.5) without losing its
initial accuracy.
The second observation concerns the impact of
defence techniques on the model robustness against
adversarial attacks. The expected result is that the
model accuracy against attacks is improved by apply-
ing defence techniques. However, this expectation is
not always guaranteed and the model behaves in dif-
ferent ways depending on the attack type and the de-
fence technique. Regarding FGSM and BIM, Fig.3a
and Fig.3b shows that defence techniques improve
model robustness. Indeed, this improvement is sig-
nificant for a moderate attack strength (eps). For an
eps = 0.3, the adversarial training improved robust-
ness by 20% against BIM and 30% against FGSM.
On the other hand, the accuracy of the model is not
affected (or is decreased) against attacks of small
strength (eps < 0.1). Compared the two defence tech-
niques, the contribution of adversarial training tech-
nique is more significant than Gaussian augmentation
in most cases. Indeed, for an eps = 0.3, adversarial
training improves accuracy by 30%, while the Gaus-
sian augmentation has practically no impact on the
model, in the case of BIM. However, in the case, of
Analyzing Adversarial Attacks against Deep Learning for Robot Navigation
1119
(a) FGSM attack performance (b) BIM attack performance
(c) DeepFool attack performance
Figure 3: Original model and defence techniques performances.
FGSM, both defence techniques improve significantly
accuracy starting from eps = 0.5.
The behavior of DeepFool is completely different
from FSGM and BIM. Whatever the defence tech-
nique, the model accuracy does not depend on the at-
tack strength. Moreover, the accuracy is improved by
8% using adversarial training while it drops by 10%
applying a Gaussian augmentation.
Our main conclusion is that defence techniques
are important to improve the robustness of the deci-
sion model against adversarial attacks. On the other
hand, the effectiveness of these approaches depends
strongly on the strength of the attack. In a practical
case, having a decision model, the expert has to set
the strength of the attack against which we would like
our model to be effective.
5 CONCLUSION AND
PERSPECTIVES
In this paper, we examined the robustness of deci-
sion model against adversarial attacks. In our studied
use case, the decision model is based on Deep Neu-
ral Network and allows the navigation of a robot in
a smart room. In this paper, we proposed an exper-
imental pipeline to investigate the behaviour of our
decision model against adversarial attacks of neural
network. Moreover, we investigated the impact of de-
fence techniques to improve model robustness against
attacks. In the experiment stage, our study is achieved
on a public robotic dataset. Our results show that
model maintains its overall accuracy for a small attack
strength and loses quickly its performance for a mod-
erate strength attack. Regarding defence techniques,
its contribution depends on attack strength. It is more
effective for attacks of moderate strength than small
strength.
In future work, we plan to study the behavior of
our decision model against more complex attacks.
The goal is to imagine any possible attacks that may
put the decision model in difficulty. Moreover, we
plan to investigate more defence techniques. The se-
lected defence technique should be effective against
the most likely attacks.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research work has been carried out in the frame-
work of IRT SystemX, Paris-Saclay, France, and
therefore granted with public funds within the scope
of the French Program Investissements d’Avenir. This
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1120

work is a part of the project EPI project (EPI for “AI-
based Decision Making Systems’ Performance Eval-
uation”).
REFERENCES
Dong, Y., Liao, F., Pang, T., Su, H., Zhu, J., Hu, X., and Li,
J. (2018). Boosting adversarial attacks with momen-
tum. CoRR, 1710.06081v3.
Freire, A. L., Barreto, G. A., Veloso, M., and Varela, A. T.
(2009). Short-term memory mechanisms in neural
network learning of robot navigation tasks: A case
study. In 2009 6th Latin American Robotics Sym-
posium, pages 1–6.
Goodfellow, I., Shlens, J., and Szegedy, C. (2015a). Ex-
plaining and harnessing adversarial examples. In In-
ternational Conference on Learning Representations.
Goodfellow, I. J., Shlens, J., and Szegedy, C. (2015b). Ex-
plaining and harnessing adversarial examples. ICLR,
1412.6572v3.
Jmila, H., Khedher, M. I., Blanc, G., and El-Yacoubi,
M. A. (2019). Siamese network based feature learn-
ing for improved intrusion detection. In Gedeon, T.,
Wong, K. W., and Lee, M., editors, Neural Infor-
mation Processing - 26th International Conference,
ICONIP 2019, Sydney, NSW, Australia, December
12-15, 2019, Proceedings, Part I, volume 11953 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 377–389.
Springer.
Jmila, H., Khedher, M. I., and El-Yacoubi, M. A. (2017).
Estimating VNF resource requirements using machine
learning techniques. In Liu, D., Xie, S., Li, Y., Zhao,
D., and El-Alfy, E. M., editors, Neural Information
Processing - 24th International Conference, ICONIP
2017, Guangzhou, China, November 14-18, 2017,
Proceedings, Part I, volume 10634 of Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 883–892. Springer.
Khedher, M. I. and El Yacoubi, M. A. (2015). Local sparse
representation based interest point matching for per-
son re-identification. In Arik, S., Huang, T., Lai,
W. K., and Liu, Q., editors, Neural Information Pro-
cessing, pages 241–250, Cham. Springer International
Publishing.
Khedher, M. I., El-Yacoubi, M. A., and Dorizzi, B. (2012).
Probabilistic matching pair selection for surf-based
person re-identification. In 2012 BIOSIG - Proceed-
ings of the International Conference of Biometrics
Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), pages 1–6.
Khedher, M. I., Jmila, H., and Yacoubi, M. A. E. (2018).
Fusion of interest point/image based descriptors for
efficient person re-identification. In 2018 Interna-
tional Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN),
pages 1–7.
Kurabin, A., Goodfellow, I. J., and Bengio, S. (2017). Ad-
versarial examples in the physical world. ICLR,
1607.02533v4.
Madry, A., Makelov, A., Schmidt, L., Tsipras, D., and
Vladu, A. (2017). Towards deep learning models re-
sistant to adversarial attacks. 1706.06083v3.
Moosavi-Dezfooli, S.-M., Fawzi, A., and Frossard, P.
(2015). Deepfool : a simple and accurate method to
fool deep neural networks. CoRR, 1511.04599.
Okuyama, T., Gonsalves, T., and Upadhay, J. (2018). Au-
tonomous driving system based on deep q-learning.
In 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Au-
tonomous Systems (ICoIAS), pages 201–205.
Papernot, N., McDaniel, P., Jha, S., Fredrikson, M.,
Berkay Celik, Z., , and Swami, A. (2015). The limi-
tations of deep learning in adversarial settings. IEEE,
1511.07528v1.
Ruiz-del-Solar, J., Loncomilla, P., and Soto, N. (2018).
A survey on deep learning methods for robot vision.
CoRR, abs/1803.10862.
Shrestha, A. and Mahmood, A. (2019). Review of deep
learning algorithms and architectures. IEEE Access,
7:53040–53065.
Spille, C., Ewert, S. D., Kollmeier, B., and Meyer, B. T.
(2018). Predicting speech intelligibility with deep
neural networks. Comput. Speech Lang., 48:51–66.
Yuan, X., He, P., Zhu, Q., and Li, X. (2019). Adversar-
ial examples: Attacks and defenses for deep learning.
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning
Systems, 30(9):2805–2824.
Zantedeschi, V., Nicolae, M., and Rawat, A. (2017). Ef-
ficient defenses against adversarial attacks. CoRR,
abs/1707.06728.
Analyzing Adversarial Attacks against Deep Learning for Robot Navigation
1121
