
TWIN-GRU: Twin Stream GRU Network for Action Recognition from
RGB Video
Hajer Essefi
1
, Olfa Ben Ahmed
1 a
, Christel Bidet-Ildei
2 b
, Yannick Blandin
2 c
and Christine Fernandez-Maloigne
1 d
1
XLIM Research Institute, UMR CNRS 7252, University of Poitiers, France
2
Centre de Recherches sur la Cognition et l’Apprentissage (UMR CNRS 7295), Universit
´
e de Poitiers, Universit
´
e de Tours,
Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, France
Keywords:
Deep Learning, Computer Vision, Human Action Recognition, Action Perception, RGB Video.
Abstract:
Human Action Recognition (HAR) is an important task for numerous computer vision applications. Recently,
deep learning approaches have shown proficiency in recognizing actions in RGB video. However, existing
models rely mainly on global appearance and could potentially under perform in real world applications, such
as sport events and clinical applications. Refereeing to domain knowledge in how human perceive action, we
hypothesis that observing the dynamic of a 2D human body joints representation extracted from RGB video
frames is sufficient to recognize an action in video. Moreover, body joints contain structural information
with a strong spatial (intra-frame) and temporal (inter-frame) correlation between adjacent joints. In this
paper, we propose a psychology-inspired twin stream Gated Recurrent Unit network for action recognition
based on the dynamic of 2D human body joints in RGB videos. The proposed model achieves a classification
accuracy of 89,97% in a subject-specific experiment and outperforms the baseline method that fuses depth and
inertial sensor data on the UTD-MHAD dataset. The proposed framework is more cost effective and highly
competitive than depth 3D skeleton based solutions and therefore can be used outside capture motion labs for
real world applications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human Action Recognition (HAR) is a hot research
topic over the last decades (Hussain et al., 2019).
HAR has a wide-range of potential applications such
as video surveillance (Han et al., 2018), sports train-
ing (Martin et al., 2018) and reeducation and mon-
itoring of elderly people (Ahmedt-Aristizabal et al.,
2019). Traditionally, the task of HAR consists in rec-
ognizing the current human activity on basis of the
perception of human body information received from
environmental sensors. In the domain of biological
action perception, Johansson et al. (Johansson, 1973)
have shown that humans are able to recognize actions
simply by the motion of some moving points of the
human body. It has been proven that humans have a
high sensitivity to biological motion and this sensitiv-
ity is observed at birth (Bidet-Ildei et al., 2013). These
psychological findings would be helpful for designing
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6942-2493
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4699-179X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1773-4409
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4818-9327
action recognition approaches.
With the development of motion capture systems
(Ye et al., 2013), body joints can be obtained for hu-
man movement representation. However, such sys-
tems are very expensive, and require wearing a mo-
tion capture suit with markers which can hinder nat-
ural movements. In addition, motion capture systems
need to be configured in order to save and correct the
motion data. Moreover, in traditional motion capture
environments, highly equipped labs are necessary for
the procedure. Such procedure can be therefore diffi-
cult and inaccessible in certain case, such as for ath-
letes or hospital patients who are unable to physically
be present at these labs. Recently, more sophisticated
depth sensors, such as Microsoft Kinect and RGB-
Depth cameras are proposed for human motion cap-
ture allowing a relatively easier human skeleton ex-
traction. However, these sensors are high sensitive to
external lighting conditions, making outdoor applica-
tions potentially challenging. Yet, such devices are
expensive and not always available. All these reasons
restrict the applicability of depth sensors in real-world
scenarios. In fact, real world applications need widely
available and economics camera that can be placed in
Essefi, H., Ben Ahmed, O., Bidet-Ildei, C., Blandin, Y. and Fernandez-Maloigne, C.
TWIN-GRU: Twin Stream GRU Network for Action Recognition from RGB Video.
DOI: 10.5220/0010324703510359
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2021) - Volume 2, pages 351-359
ISBN: 978-989-758-484-8
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
351

the environment with minimum effort such as video
surveillance systems, smartphones, personal camera,
etc. Hence, recognizing action from only RGB input
is highly desirable in this context.
Based on domain knowledge in human action per-
ception (Johansson, 1973), we assume that the dy-
namic of a 2D human body joint representation ex-
tracted from RGB video frames can be sufficient to
recognize an action in video. Hence, in this paper
we propose a psychology inspired approach for hu-
man action recognition for real word videos and out-
side the motion capture lab (hospitals, schools, etc).
We investigate the intra-frame structural body joints
information and the inter-frame joints motion to de-
scribe an action. The proposed method is based on
twin stream Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) network
that learns the temporal and the spatial information of
an action. Proposed features in this paper are the pair-
wise relative locations and distances between body
joints. A logistic regression based stacking method
is used to fuse the twin stream decisions in order to
give the final prediction of the action. The rest of the
paper is organized as follows: Section 2 presents a
brief literature review on most common and recent
action recognition approaches. Section 3 details the
proposed action recognition framework. Section 4
presents results and discussion. Finally, Section 5
concludes the work and gives some future directions.
2 RELATED WORK
With the development of sensor technology and the
great success of deep learning approaches in com-
puter vision applications, action can be recognized
by learning the pattern of the collected data. In this
section, we present and discuss recent works in deep
learning-based action recognition methods for skele-
ton and RGB data.
Skeleton-based Approaches. Actions are under-
stood as episodic examples of human dynamics that
have starting and ending temporal points. The dy-
namic of human skeleton can be naturally represented
by a time series of human joint locations in the form
of 2D or 3D coordinates. Recently, a group of works
have sought to encode this skeletal coordinates into
2D images and then fed them to a pre-trained Con-
volutional Neural Networks (CNN) for action classi-
fication. For instance, in (Aubry et al., 2019; Laraba
et al., 2017), the authors convert the extracted skele-
ton motion into an RGB image before going into the
neural network which classifies the action. In the
same idea, Ke et al. (Ke et al., 2017) suggest a new
representation of skeleton data by encoding the 3D
coordinates (x, y, z) into a clip of grey images contain-
ing spatio-temporal information. Liu et al. (Liu et al.,
2019) propose to present 3D skeleton into a clip in-
corporating multiple frames with different spatial re-
lationships. Wang et al. (Wang et al., 2016) encode
joint trajectories into texture images and utilized HSV
space to represent the temporal information. Hou et
al. (Hou et al., 2016) adopt Skeleton Optical Spec-
tra (SOS) to encode dynamic spatial-temporal infor-
mation. Later, Ding et al. (Zewei Ding et al., 2017)
propose an approach for encoding five spatial skeleton
features into images with different encoding methods.
However, this group of skeleton encoding approaches
do not take into account the different ways in which
skeleton joints can be arranged to form an image. In
addition, it is inevitable to lose temporal information
during the encoding and hence it would be hard for
a CNN to effectively capture the dynamic informa-
tion of a skeleton sequence using image-based rep-
resentation. In order to represent such motion-based
dynamics of the skeleton data and the temporal evo-
lution of the joints, an other group of skeleton-based
method used Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)s to
model the long-term context information across the
temporal dimension. RNNs model the contextual de-
pendency in the temporal domain, and have been suc-
cessfully applied to processing sequential data with
variable length such as language modeling and video
analysis (Mandic and Chambers, 2001). For exam-
ple, Zhao et al. (Zhao et al., 2017) combine RNN
with CNN in a voting approach in order to learn the
dynamics of visual features for action detection. Du
et al. (Du et al., 2015) propose an hierarchical RNN,
which is fed with manually divided five groups of the
human skeleton, such as two hands, two legs, and one
torso. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), modified
RNNs that attempts to solve the vanishing gradient
problem, have beed mainly used for action recog-
nition using 2D/3D skeleton data. Liu et al. (Liu
et al., 2017) propose a global context-aware attention
LSTM, for skeleton-based action recognition, which
is capable of selectively focusing on the informative
joints in each frame. Zhu et al. (Zhu et al., 2016) pro-
pose an end-to-end fully connected LSTM network
that learns feature co-occurrences from the skeleton
joints through a designed regularization. Shahroudy
et al. (Shahroudy et al., 2016) develop a part-aware
LSTM model, which is fed with separated five parts of
skeleton for action recognition. However, LSTMs are
mostly suffering from complexity of the networks and
high number of parameters exploding gradient prob-
lem. Recently, Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) has been
introduced (Zhou et al., 2016) and it has proved to
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
352
be be less prone to overfitting on some small datasets
since it only has two gates while LSTM has three.
In our work we use GRU to model the dynamics
of action. Most the aforementioned approaches use
data coming from depth camera which present sev-
eral drawbacks as mentioned in section 1 and there-
fore they are not practical for real-world applications.
RGB-based Approaches. Convolution Neural Net-
works are used to extract and learn visual features
from RGB data for recognizing human actions in
videos. Ji et al. (Ji et al., 2012) have been pri-
marily applied CNN on two-dimensional data (2D-
CNN) in which these models compute features from
the spatial dimensions only. Later, several approaches
have been proposed in order to incorporate the tem-
poral information into CNNs. For instance, in (Si-
monyan and Zisserman, 2014), the authors develop
a two-stream ConvNet architecture that captures the
complementary information on appearance from still
frames and motion between frames. In order, to
add the temporal information for action description,
the 2D convolution has been extended to the spatio-
temporal domain for better analysis of human activ-
ities in videos. For example, (Ji et al., 2012; Arun-
nehru et al., 2018) use 3D CNN for action recogni-
tion. However, the 3D CNN involves many more pa-
rameters than the 2D CNN. Thus, it is much more
expensive on computation, costly on storage, and dif-
ficult to learn. An other set of approaches use RNN
and LSTM to capture the temporal information by
learning the temporal dependencies of the CNN ex-
tracted features from pre-trained networks (Li et al.,
2017b; Ullah et al., 2017; Zhao et al., 2017; Ouyang
et al., 2019). The issue with the RGB-based visual
approach is that it is difficult to extract useful infor-
mation from dense and high dimensional data such
as videos/images. Existing models are generally very
deep, requiring large amounts of data to train effec-
tively. Moreover, they rely mainly on global appear-
ance and could potentially under perform in single-
environment applications, such as a sports events.
Compared to the RGB data, skeleton data are robust
to illumination changes and background noise. Yet,
existing RGB and skeleton-based methods in the lit-
erature do not exploit the spatial relationships among
the joints, which are crucial for understanding human
actions (Vemulapalli et al., 2014). In this paper, in ad-
dition to the temporal information we investigate the
structural relationship between joints. Recent stud-
ies showed how accurate and reliable 2D skeletons
can be generated even by using a single RGB camera
(Cao et al., 2018), thus overcoming many of the lim-
itations of previously reported methods. Hence, rec-
ognizing action using 2D skeleton data extracted from
only RGB image data will combine the advantages of
both skeleton and RGB based approaches in one ap-
proach. In this paper, we propose to classify human
actions from RGB-only streams to make our approach
most amenable to ordinary cameras and thus to real
word applications.
3 TWIN STREAM GRU MODEL
FOR ACTION RECOGNITION
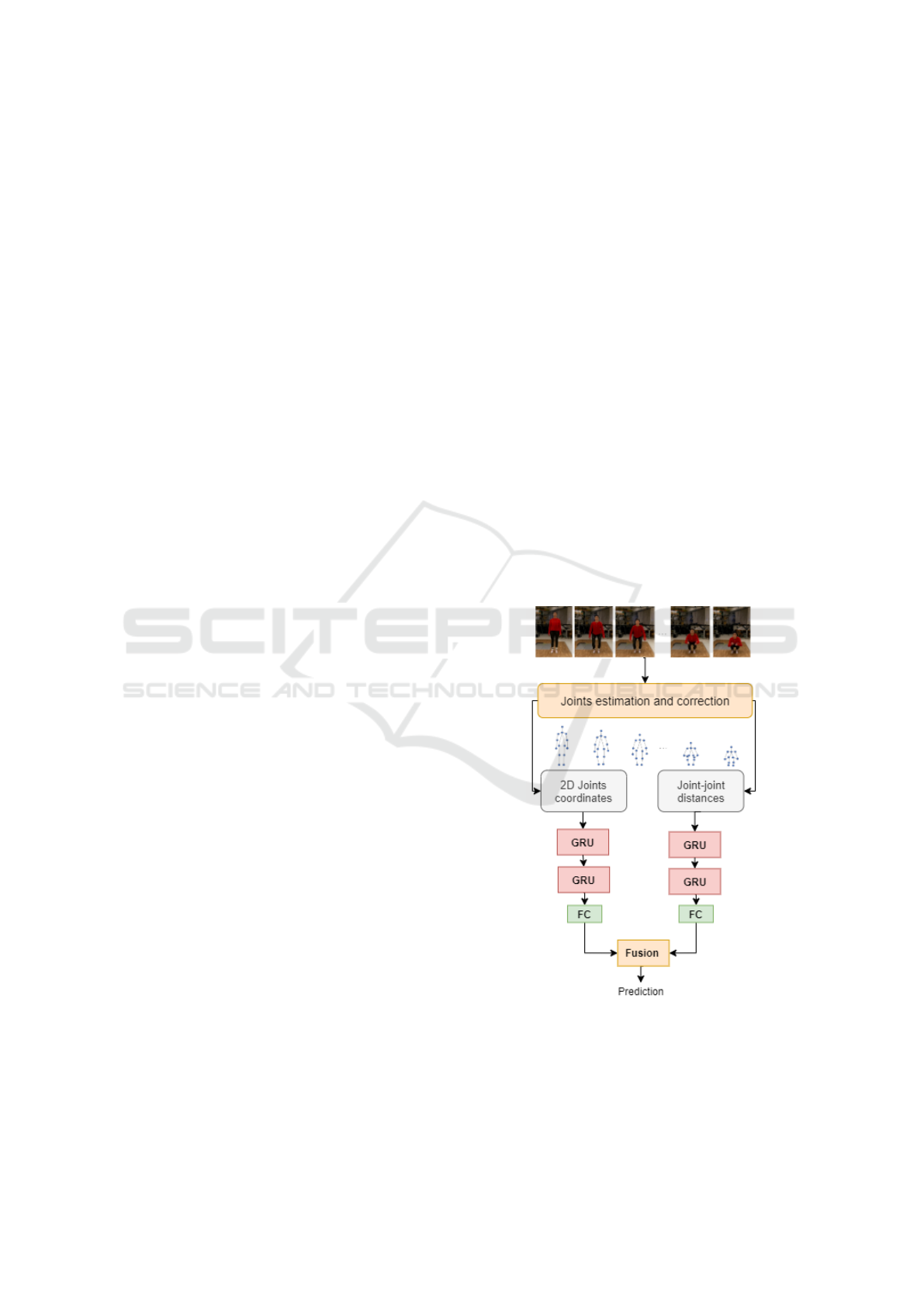
In this section we present the proposed action recog-
nition framework. As illustrated by Figure 1, the gen-
eral framework consists first in estimating the main
joints of the human body in video sequence and then
learning the dynamic pattern of those joints for action
prediction. In order to explore the temporal dynamics
of joints sequences we use twin stream GRU model:
Temporal 2D joints stream and the Spatial dynam-
ics stream. The first one models the temporal dy-
namics of the 2D human body joints coordinates. The
second one captures the motion patterns embedded in
the joint-joint distance evolution over time.
Figure 1: Flowchart of the proposed twin stream GRU
model for action recognition in videos using extracted 2D
coordinates from RGB videos.
TWIN-GRU: Twin Stream GRU Network for Action Recognition from RGB Video
353

Figure 2: Illustration of the proposed features : (a) joints
detection (b) 2D joints locations (c) joint-joint distances
(joints connections).
3.1 Features Extraction
The feature extraction step consists in extracting 2D
positions of the human body key points (joints) from
video frames. As illustrated by Figure 2, two types
of features are computed: the”2D joints locations”
(b) and the ”joint-joint distances” (c). The first one
presents the inter-frame joints temporal information
(between consecutive frames) and the second one
presents the intra-frame structural joints information
(between adjacent joints in the same frame)
3.1.1 2D Joints Locations
The action of a person can be described by a series of
articulated human poses represented by the 2D coor-
dinates of joints over time. In order to extract the body
joints, we used a deep-learning based method for hu-
man pose estimation (Cao et al., 2018). The latter is
based on a bottom-up approach, where the body parts
are first detected, then assembled to form a skeleton.
This method is easy to apply in indoor and outdoor
environment and thus suitable for real world applica-
tions. Using the COCO pre-trained model, we extract
18 joints from the RGB video frames. We note the
obtained 2D joints locations features JL of an action
a as follows :
JL
a
= [P
a
(t)]
t∈T
a
, P
a
(t) =
(x
j
(t), y
j
(t))
a
, j ∈ J
.
P
a
(t) represents the a
th
sample pose at time
(frame) t and T
a
represents the time length of sample
a. In particular, P
a
(t) consists of a list of 2D coor-
dinates, namely: P
a
(t) =
(x
j
(t), y
j
(t))
a
. Where j
denotes the landmark index and J is the landmarks set
defined by the pose detector mapping. In our case,
J = 1, ..., 18. P
a
(t) are arranged in a chronological or-
der to present the joint coordinate evolution over time
forming an action.
Since the joints estimation is done frame per frame
and the extracted 2D information can be noisy and
present some jitter in the data which can bias the ac-
tion recognition process. Additional post-processing
is applied to fill missing joints using linear interpo-
lation of neighboring frames. Then, for data clean-
ing, the missing values are substituted with previous
non-missing values, and a 13-point quadratic (order
2) polynomial low pass Savitzky-Golay (S-G) filter
(Savitzky and Golay, 1964) is applied for denoising.
Applying the S-G filter on raw skeletal data helps re-
duce the level of noise while maintaining the 2D geo-
metric characteristics of the input sequences.
3.1.2 Joint-joint Distance
Human action is accomplished in coordination with
each part of the body. Indeed, human body can be
considered as an articulated system of rigid segments
connected by joints (See Figure 2 (c)). When an ac-
tion takes place, this segment length illustrated by the
distance between joints vary. Structural relation be-
tween joints of the same body over time modulates
the articulations evolution and thus build a signatures
for the dynamic.
In order to improve the dynamic of moving points
over time, we propose to add the evolution of dis-
tances between body joints. Hence, we consider that
an action is defined as an evolution of the joint-joint
distances and thus actions are represented by a set of
distances. Intuitively, the temporal dependency that
we are looking at is the variation of the distance be-
tween different parts of the body. For instance, the
evolution of the distance between the elbow and hip,
wrist and head, wrist and shoulder etc. When we
perform an action, these distances change throughout
time in a distinguishable manner from one action to
another. Moreover, the magnitude of displacement
(the computed distance) of joint over frame can in-
form us about the speed of the motion. This distance
is computed between two joints in the same frame.
Hence, each pose is described by a Joint-Joint dis-
tance features computed as follows:
D
a
= [D
a
(t)]
t∈T
a
with:
D
a
(t) =
{
Dist(Jo
1
, Jo
2
), Jo
1
, Jo
2
∈ J, Jo
1
6= Jo
2
}
.
Dist is the Euclidean distance between 2D joints
Jo
1
and Jo
2
. D
a
(t) can be seen as the amount of
displacement of a set of joints between time t − 1
and t. We note that t > 0. To reduce the redundancy,
we remove duplicated features from D
a
(t) due to
symmetry (Dist(Jo
2
, Jo
1
) and Dist(Jo
1
, Jo
2
) are
symmetric)
3.2 Learning Action in a Twin Stream
GRU Network
In this work, human action is described by a series of
time sequences of joint coordinate positions and joint-
joint distances illustrated respectively by the D
a
and
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
354

JL
a
features. In order to learn the temporal context
of those sequences and model their temporal dynam-
ics we use a twin stream GRU architecture. The first
stream tracks and learns the variation of each joint
throughout both the X and Y axis over time. The
second one learns the joint-joint distances variation
between consecutive frames over time.
GRU (Cho et al., 2014) is a recent generation of
RNN designed to overcome the vanishing gradient
problem from which RNNs suffer. In fact, the gradi-
ent being the value used to update a neural network’s
weight shrinks as it back propagates through time,
making it insignificant to the training. In addition,
GRU uses fewer parameters and so it is faster to train.
It ensures long-term dependencies using its two gates.
Features from a human action video of length
T
a
can be seen as an input sequence f = ( f
1
, ..., f
T
)
where for each f
t
we aim to provide action activation
h
t
, forming the output h = (h
1
, ..., h
T
). We consider
f
t
is the action feature at time frame t. f
t
can be the
set of 2D joints coordinates P
a
(t)
t∈T
a
or the joint-joint
distances D
a
(t). The GRU cell takes as input features
f
t
at time step t together with the output h
t−1
at the
previous time step t − 1. To generate such output, we
investigate GRU as defined below:
z
t
= σ(W
z
f
t
+U
z
h
t−1
+ b
z
)
r
t
= σ(W
z
f
t
+U
r
h
t−1
+ b
r
)
h
t
= z
t
h
t−1
+ (1 − z
t
)
tanh(W
h
f
t
+U
h
(r
t
h
t−1
) + b
h
)
(1)
Here, z
t
and r
t
are respectively the update and the re-
set gates respectively. The update gate decides what
information to forget from previous state, and what
information to keep from the current input. The Reset
gate decides which information to ’forget’. The twin
stream GRU model is trained using the cross entropy
loss.
The decisions of the two streams are fused using a
stacking approach (Sewell, 2008). The predictions of
the twin stream are given as inputs to a second stage
learning model. Indeed, this different model is used
to train these predictions. Here we use logistic re-
gression to train the predictions from the twin stream.
Final action prediction is given by the trained logistic
regression model.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
In this section we present the dataset used for evalua-
tion as well as the results presentation and discussion.
4.1 UTD-MHAD Dataset
The dataset used to test our proposed framework, is
the UTD MHAD dataset (Chen et al., 2015). The
dataset was created for use in algorithms for action
classification using different modality sensors. Four
temporally synchronized modalities are available to
download: Depth videos, skeleton positions and in-
ertial data collected using a kinect device along with
a wearable sensor. The kinect camera was used for
the capturing of color images (video) with a resolu-
tion of 640x480 pixels and a 16-bit depth image with
a resolution of 320x240 pixels. The frame rate is 30
frames per second. The wearable inertial sensor was
used to record the inertial sensor signals of the move-
ments. The dataset is made of 27 different actions,
8 different subjects performing the actions, 4 females
and 4 males with 4 repetitions of each action. The
27 actions are: right arm swipe to the left, right arm
swipe to the right, right hand wave, two hand front
clap, right arm throw, cross arms in the chest, bas-
ketball shoot, right hand draw X, right hand draw
circle (clockwise), right hand draw circle (counter-
clockwise), draw triangle, bowling (right hand), front
boxing, baseball swing from right, tennis right hand
forehand swing, arm curl (two arms), tennis serve,
two hand push, right hand knock on door, right hand
catch an object, right hand pick up and throw, jog-
ging in place, walking in place, sit to stand, stand to
sit, forward lunge (left foot forward), squat (two arms
stretch out). Figure 3 presents examples of actions
from this dataset.
Figure 3: Example of videos from UTD MHAD dataset.
4.2 Model Setting and Training
In the proposed Twin stream network, each stream is
composed of two GRU layers. We found out exper-
imentally that adding more layers does not improve
our network results. Each GRU layer is followed by
a ReLU activation function. In order to ovoid overfit-
TWIN-GRU: Twin Stream GRU Network for Action Recognition from RGB Video
355

ting, a dropout layer is added between the two GRU
layers, with a probability of 0.3. Network weights
were initialized with an Xavier initialization. Classi-
fication is done using a Fully-Connected (FC) layer
followed by a softmax activation function and trained
with cross-entropy loss. In the GRU, we fix the time
step to 32. Training is done using the Adam Opti-
mizer with an initial learning rate of 0.001. We use
mini batches of size 32, and we train our model up
to 1000 epochs. For the training/testing data split we
followed the original paper’s cross-subject protocol.
The data we have is split on training and test data ac-
cording in the following manner: Subjects 1,3,5 and
7 are used, for training while subjects 2,4,6 and 8 are
used for testing.
4.3 Results and Discussion
Table 1: Accuracy results on the test set of the UTD MHAD
dataset with the cross-subject splitting protocol.
Model Accuracy
Temporal 2D joints stream 85,3 %
Spatial dynamics stream 81,56 %
Twin stream 89,97%
Table 1 presents the obtained classification accura-
cies for the two streams (Temporal 2D joints and Spa-
tial dynamics) as well as for the Twin stream model.
We’ve obtained respectively an accuracy of 85, 3%,
81, 56% and 89, 97% on the test data. The model
stacking improves the classification results by 4, 6%.
We plot the confusion matrix in Figure 4. The
UTD-MHAD dataset is much challenging compared
with other state of the art datasets. Nevertheless, we
can see that 7 out of 27 actions in the dataset are clas-
sified with 100% accuracy and 9 other actions are
classified with an accuracy more than 90%. In par-
ticular, the model success in distinguishing between
jog and walk actions which are the most challeng-
ing classes. Indeed, the magnitude of displacement of
joint over frame illustrated by the joint-joint distance
features can inform us about the speed of the motion
and thus help distinguishing similar action such as jog
and walk. We can see also that the model struggles to
distinguish between certain actions more than others.
For example, the actions draw circle and draw trian-
gle are missclassified this can be explained by the fact
that one body part is moving and hence no joint-joint
distance information was used by the model to learn
those actions.
Moreover, we conduct a preliminary psychologi-
cal experiment on 15 participants (mean age 19 years
old). Participants are asked to recognize visually 19
actions (walk, jog, crouch, turn, stand up, sweep,
hand draw, etc.) presented as an animated sequences
of 3D joints obtained using a motion capture (mocap)
system and second as 2D joints extracted from the
corresponding RGB videos using our method. Ob-
tained statistic results show that participants success
to recognize 19 actions from the 2D data and the 3D
data with accuracies respectively of 62.9 ± 9% and
62.5 ± 9.9%. Therefore, perceiving 2D human joints
movement from only RGB frames is sufficient to rec-
ognize an action.
4.4 Comparison with State-of-the-Art
Table 2 presents the results obtained on the UTD-
MHAD for action recognition, and its comparison
with some other methods in the literature. We com-
pare our method to depth and 3D-skeleton-based state
of the art methods. As we can see, our method
surpasses the baseline results on the UTD-MHAD
dataset (Chen et al., 2015). The latter used multi-
modal data, including depth and inertia where our
model only uses 2D skeleton data extracted from
RGB videos. We improve the UTD-MHAD kinekt
baseline by 23.87% and the UTD-MHAD inertial
baseline by 22.77% and even the fusion by 10, 8%. To
the best of our knowledge, there is only one work that
use the RGB data to recognize action on the MHAD
dataset (McNally et al., 2018). The authors of this
work focus on transforming the positions or trajec-
tories of skeleton joints into images and then adapt-
ing CNN for classification. They reported an accu-
racy of 76, 1% which is lower by 13, 87% that ours.
We can conclude from Table 2 that our method sur-
pass most of the state-of-art 3D-based skeleton ap-
proaches. In addition, dealing with the extracted
3D points requires significant time and memory con-
sumption where in our work training takes 2, 6 min-
utes on a simple CPU computer and prediction takes
4, 8 seconds which makes it suitable even for real-
time applications. Hence, the proposed RGB-only
scheme is more cost effective and highly competitive
than depth and 3D-skeleton based solutions and there-
fore can be used outside capture motion labs for real
world applications. The used 2D skeletons extracted
from RGB video allows the use of the proposed ap-
proach in both indoor and outdoor environment.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we propose an action recognition frame-
work that uses only 2D body joints extracted from
RGB videos. The proposed framework learns the
intra-frame structural body joints information and the
inter-frame joints motion in a twin stream GRU net-
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
356
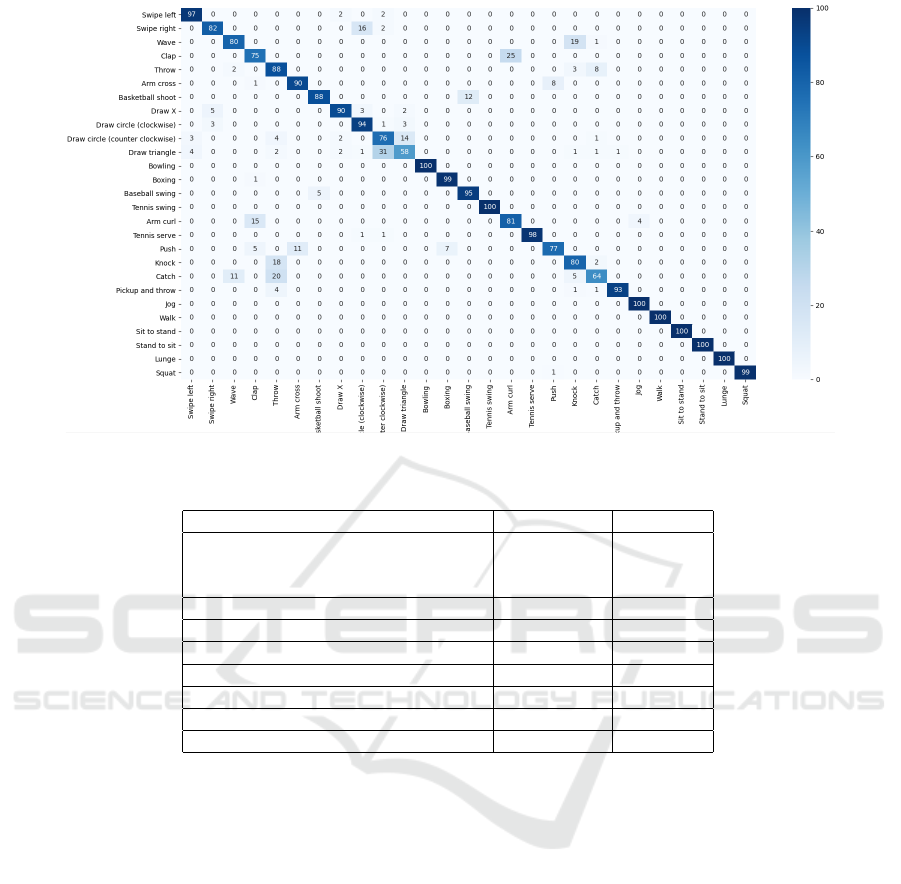
Figure 4: Confusion matrix of the twin models.
Table 2: Comparison with state-of-the-art approaches on the UTD-MHAD dataset using cross-subjects protocol.
Work Data Accuracy
Baseline Kinect (Chen et al., 2015) Depth 66.1%
Baseline Intertial (Chen et al., 2015) Depth 67.2%
Kinect+Inertial (Chen et al., 2015) Depth 79.1%
(Weiyao et al., 2019) Depth 88,7%
(Hussein et al., 2013) 3D Skeleton 85.6 %
(Hou et al., 2016) 3D Skeleton 86.97%
(Wang et al., 2016) 3D Skeleton 85.81 %
(Li et al., 2017a) 3D Skeleton 88.10 %
(McNally et al., 2018) RGB 76.1%
Twin stream (Ours) RGB 89,97 %
work. The effectiveness of our model is demonstrated
through experiments on the UTD-MHAD benchmark
datasets. We achieved a classification accuracy of
89, 97% in a subject-specific experiment. The pro-
posed method outperforms the baseline method that
fuses depth and inertial sensor data. In our future
works we will add more psychology-inspired features
to the framework in order to boost the classification
accuracy and test the approaches on clinical dataset
for patient activities recognition.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Support for this research was provided by a grant
from La R
´
egion Nouvelle Aquitaine (CPER-FEDER
P-2017- BAFE-68), in partnership with the European
Union (FEDER/ ERDF, European Regional Develop-
ment Fund).
REFERENCES
Ahmedt-Aristizabal, D., Denman, S., Nguyen, K., Sridha-
ran, S., Dionisio, S., and Fookes, C. (2019). Under-
standing patients’ behavior: Vision-based analysis of
seizure disorders. IEEE journal of biomedical and
health informatics, 23(6):2583–2591.
Arunnehru, J., Chamundeeswari, G., and Bharathi, S. P.
(2018). Human action recognition using 3d con-
volutional neural networks with 3d motion cuboids
in surveillance videos. Procedia computer science,
133:471–477.
Aubry, S., Laraba, S., Tilmanne, J., and Dutoit, T. (2019).
Action recognition based on 2d skeletons extracted
from rgb videos. In MATEC Web of Conferences, vol-
ume 277, page 02034. EDP Sciences.
Bidet-Ildei, C., Kitromilides, E., Orliaguet, J.-P., Pavlova,
M., and Gentaz, E. (2013). Preference for point-
light human biological motion in newborns: Contri-
bution of translational displacement. Developmental
psychology, 50.
TWIN-GRU: Twin Stream GRU Network for Action Recognition from RGB Video
357

Cao, Z., Hidalgo, G., Simon, T., Wei, S.-E., and Sheikh,
Y. (2018). Openpose: realtime multi-person 2d pose
estimation using part affinity fields. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1812.08008.
Chen, C., Jafari, R., and Kehtarnavaz, N. (2015). Utd-mhad:
A multimodal dataset for human action recognition
utilizing a depth camera and a wearable inertial sen-
sor. In 2015 IEEE International conference on image
processing (ICIP), pages 168–172. IEEE.
Cho, K., Van Merri
¨
enboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D.,
Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., and Bengio, Y. (2014).
Learning phrase representations using rnn encoder-
decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1406.1078.
Du, Y., Wang, W., and Wang, L. (2015). Hierarchical recur-
rent neural network for skeleton based action recog-
nition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 1110–
1118.
Han, Y., Zhang, P., Zhuo, T., Huang, W., and Zhang,
Y. (2018). Going deeper with two-stream convnets
for action recognition in video surveillance. Pattern
Recognition Letters, 107:83–90.
Hou, Y., Li, Z., Wang, P., and Li, W. (2016). Skeleton op-
tical spectra-based action recognition using convolu-
tional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits
and Systems for Video Technology, 28(3):807–811.
Hussain, Z., Sheng, M., and Zhang, W. E. (2019). Different
approaches for human activity recognition: A survey.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.05074.
Hussein, M. E., Torki, M., Gowayyed, M. A., and El-Saban,
M. (2013). Human action recognition using a tem-
poral hierarchy of covariance descriptors on 3d joint
locations. In Twenty-Third International Joint Con-
ference on Artificial Intelligence.
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., and Yu, K. (2012). 3d convolu-
tional neural networks for human action recognition.
IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine
intelligence, 35(1):221–231.
Johansson, G. (1973). Visual perception of biological mo-
tion and a model for its analysis. Perception & psy-
chophysics, 14(2):201–211.
Ke, Q., Bennamoun, M., An, S., Sohel, F., and Boussaid, F.
(2017). A new representation of skeleton sequences
for 3d action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE
conference on computer vision and pattern recogni-
tion, pages 3288–3297.
Laraba, S., Brahimi, M., Tilmanne, J., and Dutoit, T. (2017).
3d skeleton-based action recognition by representing
motion capture sequences as 2d-rgb images. Com-
puter Animation and Virtual Worlds, 28(3-4):e1782.
Li, C., Hou, Y., Wang, P., and Li, W. (2017a). Joint dis-
tance maps based action recognition with convolu-
tional neural networks. IEEE Signal Processing Let-
ters, 24(5):624–628.
Li, C., Wang, P., Wang, S., Hou, Y., and Li, W. (2017b).
Skeleton-based action recognition using lstm and cnn.
In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multime-
dia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), pages 585–590.
IEEE.
Liu, J., Akhtar, N., and Mian, A. (2019). Skepxels:
Spatio-temporal image representation of human skele-
ton joints for action recognition. In CVPR Workshops.
Liu, J., Wang, G., Duan, L.-Y., Abdiyeva, K., and Kot,
A. C. (2017). Skeleton-based human action recog-
nition with global context-aware attention lstm net-
works. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
27(4):1586–1599.
Mandic, D. and Chambers, J. (2001). Recurrent neural net-
works for prediction: learning algorithms, architec-
tures and stability. Wiley.
Martin, P.-E., Benois-Pineau, J., P
´
eteri, R., and Morlier, J.
(2018). Sport action recognition with siamese spatio-
temporal cnns: Application to table tennis. In 2018
International Conference on Content-Based Multime-
dia Indexing (CBMI), pages 1–6. IEEE.
McNally, W., Wong, A., and McPhee, J. (2018). Ac-
tion recognition using deep convolutional neural net-
works and compressed spatio-temporal pose encod-
ings. Journal of Computational Vision and Imaging
Systems, 4(1):3–3.
Ouyang, X., Xu, S., Zhang, C., Zhou, P., Yang, Y., Liu,
G., and Li, X. (2019). A 3d-cnn and lstm based multi-
task learning architecture for action recognition. IEEE
Access, 7:40757–40770.
Savitzky, A. and Golay, M. J. (1964). Smoothing and dif-
ferentiation of data by simplified least squares proce-
dures. Analytical chemistry, 36(8):1627–1639.
Sewell, M. (2008). Ensemble learning. RN, 11(02).
Shahroudy, A., Liu, J., Ng, T.-T., and Wang, G. (2016). Ntu
rgb+ d: A large scale dataset for 3d human activity
analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 1010–
1019.
Simonyan, K. and Zisserman, A. (2014). Two-stream con-
volutional networks for action recognition in videos.
In Advances in neural information processing sys-
tems, pages 568–576.
Ullah, A., Ahmad, J., Muhammad, K., Sajjad, M., and Baik,
S. W. (2017). Action recognition in video sequences
using deep bi-directional lstm with cnn features. IEEE
Access, 6:1155–1166.
Vemulapalli, R., Arrate, F., and Chellappa, R. (2014). Hu-
man action recognition by representing 3d skeletons
as points in a lie group. In Proceedings of the IEEE
conference on computer vision and pattern recogni-
tion, pages 588–595.
Wang, P., Li, Z., Hou, Y., and Li, W. (2016). Action recog-
nition based on joint trajectory maps using convolu-
tional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 24th
ACM international conference on Multimedia, pages
102–106.
Weiyao, X., Muqing, W., Min, Z., Yifeng, L., Bo, L., and
Ting, X. (2019). Human action recognition using mul-
tilevel depth motion maps. IEEE Access, 7:41811–
41822.
Ye, M., Zhang, Q., Wang, L., Zhu, J., Yang, R., and Gall,
J. (2013). A survey on human motion analysis from
depth data. In Time-of-flight and depth imaging. sen-
sors, algorithms, and applications, pages 149–187.
Springer.
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
358

Zewei Ding, Pichao Wang, Ogunbona, P. O., and Wanqing
Li (2017). Investigation of different skeleton features
for cnn-based 3d action recognition. In 2017 IEEE
International Conference on Multimedia Expo Work-
shops (ICMEW), pages 617–622.
Zhao, R., Ali, H., and Van der Smagt, P. (2017). Two-
stream rnn/cnn for action recognition in 3d videos. In
2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelli-
gent Robots and Systems (IROS), pages 4260–4267.
IEEE.
Zhou, G.-B., Wu, J., Zhang, C.-L., and Zhou, Z.-H. (2016).
Minimal gated unit for recurrent neural networks. In-
ternational Journal of Automation and Computing,
13(3):226–234.
Zhu, W., Lan, C., Xing, J., Zeng, W., Li, Y., Shen,
L., and Xie, X. (2016). Co-occurrence feature
learning for skeleton based action recognition us-
ing regularized deep lstm networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1603.07772.
TWIN-GRU: Twin Stream GRU Network for Action Recognition from RGB Video
359
