
A Secure Integrated Fog Cloud-IoT Architecture based on Multi-Agents
System and Blockchain
Chaima Gharbi
1
, Lobna Hsairi
2
and Ezzeddine Zagrouba
1
1
University of Tunis El Manar, Laboratory of Informatics, Modeling and Information and Knowledge Processing (LIMTIC),
Higher Institute of Computer Science, Ariana, Tunisia
2
University of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Kingdom
Keywords:
Cloud-IoT, Fog Computing, Multi-Agents System, Blockchain.
Abstract:
Nowadays, the integration of Cloud Computing and the Internet of Things (Cloud-IoT) has drawn attention
as new technologies in the Future Internet. Cloud-IoT accommodates good solutions to address real-world
problems by offering new services in real-life scenarios. Nonetheless, the traditional Cloud-IoT will be prob-
ably not going to give suitable service to the user as it handles enormous amounts of data at a single server.
Furthermore, the Cloud-IoT shows huge security and privacy problems that must be solved. To address these
issues, we propose an integrated Fog Cloud-IoT architecture based on Multi-Agents System and Blockchain
technology. Multi-Agents System has proven itself in decision-making aspects, distributed execution, and its
effectiveness in acting in the event of an intrusion without user intervention. On the other side, we propose
Blockchain technology as a distributed, public, authentic ledger to record the transactions. The Blockchain
represents a great advantage to the next generation computing to ensures data integrity and to allows low la-
tency access to large amounts of data securely. We evaluated the performance of our proposed architecture
and compared it with the existing models. The result of our evaluation shows that performance is improved by
reducing the response time.
1 INTRODUCTION
The IoT is the internetworking of physical devices,
embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actua-
tors, and network connectivity, that enable these de-
vices to collect and exchange data (Malik and Om,
2018). Recently, IoT has reached so much devel-
opment and importance that several reports foresee
it as one of the technologies of higher impact until
2025 (J. Molano and R. Crespo, 2017). It permits bil-
lions of connected objects to communicate with each
other to share data that improves the quality of our
everyday lives. So, this will produce a high, unstruc-
tured, and varied volume of data that must be col-
lecting, analyzing, managing, and storing to be in-
terpreted proficiently and simply. However, IoT de-
vices are limited in terms of processing and storage
capacity. So, to solve the shortcomings of IoT, cloud
computing comes into the picture. Cloud Computing
can be defined as a model that allows accessing a set
of shared and configurable computing resources (e.g
networks, servers, storage, and applications) offered
as services (E. Cavalcante, 2016). The Cloud-IoT
offers the possibility of managing IoT resources and
provides a more cost-effective and efficient means to
produce services. However, the transfer of enormous
amounts of data generated by distributed IoT systems
to and from Cloud Computing presents a challenge,
since it is expensive to consume an enormous amount
of bandwidth, time, and energy. Besides, the cen-
tralized clouds will be unlikely to deliver satisfac-
tory services to customers, since cloud servers suffer
from a high processing delay that can affect the over-
all efficiency of real-time applications. Also, it man-
ages huge amounts of data in a single server point,
which can generate a bottleneck in cloud servers. To
solve these problems, the concept of Fog Comput-
ing has been introduced in Cloud-IoT architecture.
Fog Computing is an extension of Cloud Computing
in which the data generated by terminals are not di-
rectly downloaded to the Cloud but is pre-processed
beforehand in a decentralized mini-center (Prakash P,
2017). If the data does not require higher comput-
ing power then their processing is done in the Fog
Nodes which represent a distributed fog computing
entities that allow the deployment of fog services. If
1184
Gharbi, C., Hsairi, L. and Zagrouba, E.
A Secure Integrated Fog Cloud-IoT Architecture based on Multi-Agents System and Blockchain.
DOI: 10.5220/0010345111841191
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2021) - Volume 2, pages 1184-1191
ISBN: 978-989-758-484-8
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

the data requires high computing power, the process-
ing is done partially after which the data is transferred
to cloud computing for the remaining computations.
This greatly reduces the delay as the central server
is not overloaded. The integration of Fog Comput-
ing and Cloud-IoT with all its benefits is hindered by
severe privacy and security problems. More specifi-
cally, the major problems in the IoT environment re-
lated to security concern authentication and data in-
tegrity. So, it is necessary to propose a new solution
that provides a satisfactory level of security. Besides,
the development of new IoT application introduces
new challenges such as the ability to monitor, man-
age, and control IoT devices remotely, and to make
new bits of knowledge from huge streams of real-time
data (A. Giordano and A. Vinci, 2016). Hence, to sup-
port these new applications, it is necessary to adopt
new paradigms. To overcome the above problems, we
propose the synergic integration of two paradigms: (i)
Multi-Agents System, which completely bolsters the
development of decentralized, dynamic, cooperative
systems, and (ii) the Blockchain technology, which is
aim at create a distributed ledger to record the transac-
tions and to ensures data integrity. The main compo-
nents of our contribution are summarized as bellow:
• Fog Computing: we have chosen Fog Computing
as the appropriate technology for the Internet of
Things since it offers the lowest-possible latency,
communicates directly with mobile devices, and
allows real-time delivery of data, especially for
delay-sensitive services.
• Multi-Agents System: was adopted since it has
proven itself in decision-making aspects, execu-
tion distribution, communicating objects, and act-
ing in the event of an intrusion without user inter-
vention. (N. Harbi, 2018).
• Blockchain Technology: was integrated into our
proposed architecture as a secure database for
storing data and ensuring data integrity.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows: In Sec-
tion 2, various related works are discussed. Section
3 provides a detailed description of our proposed ap-
proach. Experiment results and analyses are reported
in Section 4. Finally, the conclusion and ongoing
works are presented in Section 5.
2 RELATED WORK
The integration of Cloud Computing and Internet of
Things represents an enormous jump ahead in the Fu-
ture Internet, and many approaches have been pro-
posed in this field. We will discuss some of them
to obtain a comprehensive understanding on the inte-
gration of Coud-IoT and to recognize what has been
investigated in this context.
Many Cloud-IoT architectures have as their main
objective security. In (T. Wang and Q. Jin, 2018) it is
proposed Edge-based Cloud-IoT architecture with a
Trust Evaluation Mechanism. The contribution of this
study is to select trusted devices via an Edge Comput-
ing environment to generate or transfer data. How-
ever, the edge cannot perform processing or decision
without returning to the cloud; hence, the architec-
ture is still centralized in the cloud. Also (P. Sharma,
2017) it is presented new distributed blockchain cloud
architecture with Software-Defined Networking to
efficiently manage the raw data streams produced
by large IoT devices in the distributed cloud and
at the edge of the network. The proposed archi-
tecture is based on three technologies; Fog Nodes,
Blockchain technology, and SDN controller. Al-
though, the experiment result shows that when the
number of requests for services increases the delay
increases which means there is a problem of scalabil-
ity. Besides, this architecture shows its efficiency in
an application with a limited number of IoT devices,
but it must be tested in another big data application
to confirm its effectiveness. In (T. Alam, 2018) the
authors suggested a new integrated model with fog,
IoT, and blockchain technologies to solve the issue
of communication security. The proposed framework
is not dedicated to all IoT applications, it’s specially
dedicated to applications in which data is periodi-
cally transmitted. The main drawback of the proposed
model is that by increasing the number of IoT devices
the transmission delay increases attentively.
On the other hand, some of the research works
were oriented to put in place systems with energy ef-
ficiency. In (T. Ogino, 2018) it is proposed a multi-
agent-based flexible IoT edge computing architecture
to balance global optimization by a cloud and lo-
cal optimization by edges. An application is divided
into multiple subtasks that are assigned to a cloud or
edges according to their characteristics as agents. The
main drawback of the proposed architecture is that it
lacks a security mechanism to protect the data. Also
(T. Baker and Buyya, 2017) it is proposed a high-end
energy-efficient service composition algorithm to ad-
dress the overall amount of energy required by the ap-
propriate composite services. The authors proposed
a novel multi-cloud IoT service composition algo-
rithm named E2C2 to emphasize energy awareness
when searching for optimum composition plans to
meet specified user requirements.
Further, many studies have been proposed to
provide optimal Quality of Service (QoS). In (L.
A Secure Integrated Fog Cloud-IoT Architecture based on Multi-Agents System and Blockchain
1185

Carnevale, 2019) the authors proposed Osmotic Com-
puting architecture, based on a Multi-Agents System,
according to a new software abstraction called Mi-
croELement (MEL) that encapsulates resources, ser-
vices, and data necessary to run IoT applications. In
the case of Overloading, the microservices can mi-
grate from an agent to another one. However, addi-
tional details and experimental results about the pro-
posed model are required to evaluate its performance,
especially in complex applications. Also (A. Munir
and S. Khan, 2017) it is presented a novel reconfig-
urable fog cloud IoT (IFCIoT) architectural paradigm.
The new model is applied to intelligent transporta-
tion systems as consumer applications use cases. This
study seeks to reconfigure the architectural resource
to better meet the peak workload requirements of an
application at a given time. However, this architec-
ture is not efficient for high-end-batch processing jobs
which are very frequent in the business and scientific
world. The authors in (Lu Hou and W. Xiang, 2016)
proposed an IoT cloud architecture based on both
the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Mes-
sage Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) protocols
to guarantee high performance. The HTTP servers
can provide services for end-users and devices, while
the MQTT servers ensure a large number of device
connections and real-time communication among de-
vices. The simulation results show that the proposed
model has a significant impact on the perceived qual-
ity of the services of the IoT cloud. However, the
proposed solution cannot support the big data, and
security should be taken into account in designing
the IoT Cloud. Also in (A. Abdelaziz and A. Mah-
moud, 2018), the authors proposed a hybrid intel-
ligent model for predicting chronic kidney diseases
(CKD) based on Cloud-IoT by using two intelligent
techniques, which are linear regression (LR) and neu-
ral network (NN). The contribution of this study is
to predict patients of CKD anywhere and anytime in
smart cities. The simulation results show that the pro-
posed model greatly improves the accuracy of predic-
tion. However, the proposed solution has not been
tested in a big data case which is a very important cri-
terion in the healthcare field. Moreover, it needs to
be tested in different application domains to evaluate
the performance of the proposed method. In (Ju Ren,
2017) presented an Edge-based IoT Cloud architec-
ture that exploits transparent computing to build scal-
able IoT platforms. The transparent offer a scalable
IoT platform that can provide desired services on time
for lightweight IoT devices on-demand to address the
changing needs of users. The main drawback of the
proposed architecture is that it lacks a security mech-
anism to protect the system from different attacks.
Other research works have drawn attention to the field
of Big Data. In (M. Elhoseny, 2018) it is introduced
a new model for Cloud-IoT-based health service ap-
plications in an integrated industry 4.0 environment.
The main contribution of this study is to optimize vir-
tual machine selection VMs in Cloud-IoT health ser-
vice applications to efficiently manage a big amount
of data in integrated industry 4.0.
From the literature reviewed, we can find that a
lot of research works have used either Fog Comput-
ing or Edge Computing to their solutions. Both Fog
Computing and Edge Computing provide reliable and
improved quality of service to IoT applications when
compared with Cloud Computing. However, they
are still different from each other. The key differ-
ence is the data in Fog Computing can be stored for
days while Edge Computing provides temporary stor-
age. On the other hand, Fog Computing has multi-
ple wireless access technologies including WIFI, 4G,
and LTE whereas Edge Computing is accessible via
home/Enterprise networks and wifi hotspot (G. Prem-
sankar and T. Taleb, 2018). Based on that, we choose
to use Fog Computing as the appropriate paradigm
for our architecture. There is still a lot of possibility
for the improvement of Cloud-IoT architectures un-
til now. Therefore, our proposed architecture can be
separated from the above state-of-the-art architectures
by the integration of Fog Computing, Multi-Agents
System, and Blockchain technology to help the real-
ization of secure and efficient IoT applications. We
consider Smart Home as an example of an IoT ap-
plication, to provide a more realistic scenario that is
reader-friendly. It is important to note here, that, the
proposed architecture is not restricted to Smart Home
only, but can also be applied to any other IoT applica-
tions.
3 PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE
3.1 Integrated Fog Cloud-IoT
Architecture based on Multi-Agents
System and Blockchain
Figure 1 presents an overview of our distributed
Cloud-IoT architecture, which is categorized into
three layers and each layer has specific roles and re-
sponsibilities within the architecture.
1. Devices Layer: This layer contains all the de-
vices connected to the internet. It aims to collect
data from these devices and transmit it to the next
layer.
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1186
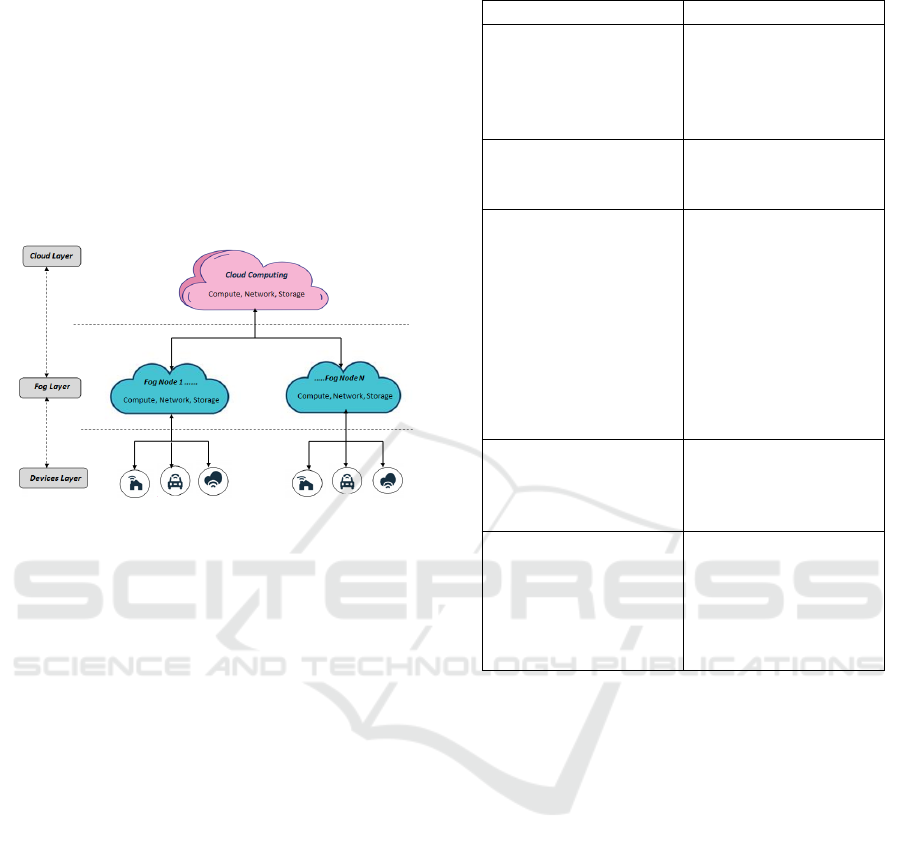
2. Fog Layer: It is composed of several fog nodes
and each fog node is responsible for the small as-
sociated community. The main objective of this
layer is to execute the most time-sensitive requests
and the geographically closest.
3. Cloud Layer: it is the layer that contains more ef-
ficient storage and processing resources than the
fog layer. The Cloud Layer stores a lot of histor-
ical data to be used for deeper data mining and
analysis.
Figure 1: Overview of the proposed architecture.
In this paper, inspired by the approach presented
in (M. Ghazouani and L. ErRajy, 2019), we proposed
a distributed Cloud-IoT architecture that relies on the
combination of three paradigms that are Fog Com-
puting, Multi-Agents System, and Blockchain tech-
nology (Figure 2). Given that, in (M. Ghazouani and
L. ErRajy, 2019) the authors propose the synergic in-
tegration of Multi-Agents System and Blockchain to
solve the problem of managing data deduplication in
Cloud Computing. We integrate into our proposed ar-
chitecture a Multi-Agents System where seven intelli-
gent agents are working in cooperation to manage and
execute the user’s request (Table 1).
When a client sends a request (for service or data),
the Interface Agent is responsible to monitor, filter,
and send the filtered data to the Fog Layer. At the Fog
layer, we first check user authentication, and then the
different agents cooperate with each other to execute
the user’s request. Once the request is executed, the
result is stored in the Local Storage which represents
the local database of the Fog Layer. Local Storage
aims to stock the data locally. Then, a new block is
created in Local BC which represents a secure and
private Blockchain that keeps track of transactions. A
local and private BC is used to provide secure access
control to the IoT devices and their data. If the fog
layer cannot perform this request, then it can offload
their computing workloads to the distributed cloud
when they do not have sufficient computing resources
Table 1: Roles of each agent.
Agents Roles
Interface Agent Interact with users for
receiving requests,
filtring data, and
transmitting them to
mediator agent.
Mediator Agent Manage the
communication
between agents.
Analysis-F
Agent/Analysis-C
Agent
Analysis-F Agent is
devoted to Fog Layer
and Analysis-C
Agent is devoted to
Cloud Layer.It aim to
check the necessary
resources and has
access to all the
devices in order to
resolve the request.
Control Agent Checks the
authentication and
access control of
users and devices.
Data-Fog Agent /
Data-Cloud Agent
Create a new block
for each transaction
in the Blockchain and
store the data to the
Storage Server or
Local Storage.
to process their local data streams with the sacrifice
of increased latency in communications and resource
consumption.
The following algorithm presents the pseudo-code of
the proposed approach.
INPUT: SRequest, FogN, Cloud
OUTPUT:SRequest_Result
Begin
1.Filter the data.
2.Send the filtred data to Mediator Agent.
3.Check the access control.
4.If user or device has the right to access
FogN Then
5. Allow the request to be processing at FogN.
6. If (SRequest.Resource <= FogN.Resource)
Then
7. FogN can perfect final result processing.
8. Store the final result in Local Storage.
9. Store the final result in Local BC.
10. Return the result to user or device.
11. Else
12. Select the cloud as the platform
for final result processing.
13. Sotre the final result in Storage Server.
14. Store the final result in BLockchain.
A Secure Integrated Fog Cloud-IoT Architecture based on Multi-Agents System and Blockchain
1187

15. Return the final result to user or device.
16. EndIf
17.EndIf
18.End
Figure 2: The Distributed Cloud-IoT Architecture based on
Multi-Agents System and Blockchain.
To exemplify our ideas, we use an illustrative ex-
ample of a smart home in the next section. However,
our proposed architecture is well suited for diverse
IoT applications.
3.2 Case Study: Smart Home
A smart home creates a future home network, where
embedded sensors and intelligent devices are self-
configured and can be controlled remotely through
the Internet to provide a comfortable environment for
humans (A. Dorri and P. Gauravaramz, 2017). The
smart home is very important especially to the elderly
and people with disabilities who will find the house
capable of taking charge of activities that today may
require excessive effort or manual assistance. Based
on the case study presented in (A. Dorri and P. Gau-
ravaramz, 2017), we consider a typical smart home
setting where a user has equipped his home with a
number of IoT devices including a smart thermostat,
an IP camera and several other sensors. The proposed
architecture for the Smart Home case is presented by
Figure 3.
The smart home architecture is comprised of the
following components:
• User: the final users of the system can be the per-
son that lives in the house, his family, or the tech-
nicians.
Figure 3: Smart Home Architecture.
• Devices: all the smart devices located in the
home.
• Fog Node: is a device that processes incoming
and outgoing transactions to and from the smart
home and is responsible for data analysis and ser-
vice delivery in a timely manner.
• Local Storage: is a storing device that is used by
devices to store data locally.
• Local BC: is a secure and private BC specified to
one smart home. Each block in the local BC con-
tains two headers that are block header and policy
header. The block header has the hash of the pre-
vious block to keep the BC immutable. The policy
header is used for authorizing devices and enforc-
ing the owner’s control policy over his home.
The communication between different devices and
the user are known as transaction. The different trans-
actions we can found in this smart home are:
• Access to data from different devices in smart
home.
• Modify the status of a device.
• Store data.
In the following, we will detail the different transac-
tions in our case study.
3.2.1 Transaction: Access to Data
The home owner or the user can access/check certain
information from their smart home devices in real-
time. For example, he can check the current temper-
ature of his smart thermostat. The execution of the
monitor transaction is illustrated in the sequence dia-
gram (Figure 4).
1. The user sends a request for the current status of
the thermostat.
2. The Interface Agent receives this request and trans-
mits it to the Mediator Agent.
3. The Mediator Agent sends the request of the user
to the Control Agent.
4. The Control Agent checks the policy in the Lo-
cal BC to verify if the user has permission to access
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1188

data, which should have been granted previously by
the home owner.
5. If so, the Control Agent sends the request to the
Analysis-Fog Agent.
6. The Analysis-Fog Agent requests the current status
from the Thermostat.
Afterward, the Analysis-Fog Agent demands to Data-
Fog Agent to store the data in the Local Storage.
7. Data-Fog Agent stores the data in the Local Stor-
age.
8. Then, Data-Fog Agent creates a new block in the
Local BC.
9. Data-Fog Agent sends to the Mediator Agent a
pointer to the block corresponding to that data.
10.The Mediator Agent sends to the Interface Agent
the pointer and data required.
11. The Interface Agent re-transmits the pointer and
the current status of the thermostat to the concerned
user.
Figure 4: Sequence diagram of Access to data transaction.
3.2.2 Transaction: Modify Data
Some users have the right to modify the status of a
device. For example, one of the children in the house
forgot his keys. One of the parents can from a Smart-
phone open the door of the house from his office. The
execution of the monitor transaction is illustrated in
the sequence diagram (Figure 5).
1. The user sends a request to open the door.
2. The Interface Agent receives this request and trans-
mits it to the Mediator Agent.
3. The Mediator Agent sends the demand of the user
to the Control Agent.
4. The Control Agent checks the policy in the Lo-
cal BC to verify if the user has permission to modify
data, which should have been granted previously by
the homeowner.
5. If so, the Control Agent sends the request to the
Analysis-Fog Agent.
6. The Analysis-Fog Agent modifies the current sta-
tus of the door lock from “close” to “open”.
7. Afterward, the Analysis-Fog Agent demands to
Data-Fog Agent to store the data in the Local Stor-
age.
8. Data-Fog Agent stores the Modified data in the Lo-
cal Storage.
9. Then, Data-Fog Agent creates a new block in the
Local BC.
10. Data-Fog Agent sends to the Mediator Agent a
pointer to the block corresponding to that data.
11. The Mediator Agent sends to the Interface Agent
the pointer and data required.
12. The Interface Agent re-transmits the pointer and
the new status of the door to the parent.
Figure 5: Sequence diagram of Modify Data Transaction.
3.2.3 Transaction: Store Data
Each device can store data in local, or in cloud stor-
age. For example, the surveillance camera can store
the recordings locally for a week, and afterward, it
transmits it to the cloud Storage.The execution of the
monitor transaction is illustrated in the sequence dia-
gram (Figure 6).
1. The device sends a request to store the data.
2. The Interface Agent receives this request and trans-
mits it to the Mediator Agent.
3. The Mediator Agent sends the demand of the de-
vice to the Control Agent.
4. The Control Agent checks the policy in the Lo-
cal BC to verify if the device has permission to store
data, which should have been granted previously by
the homeowner.
5. If so, the Control Agent sends the request to the
Data-Cloud Agent.
6. Data- Cloud Agent stores the data in Cloud Stor-
age.
7. Then, the Data-Cloud Agent creates a new block in
the BC.
8. Data-Cloud Agent sends to the Mediator Agent a
pointer to the block corresponding to that data.
9. The Mediator Agent sends to the Interface Agent
the pointer.
A Secure Integrated Fog Cloud-IoT Architecture based on Multi-Agents System and Blockchain
1189
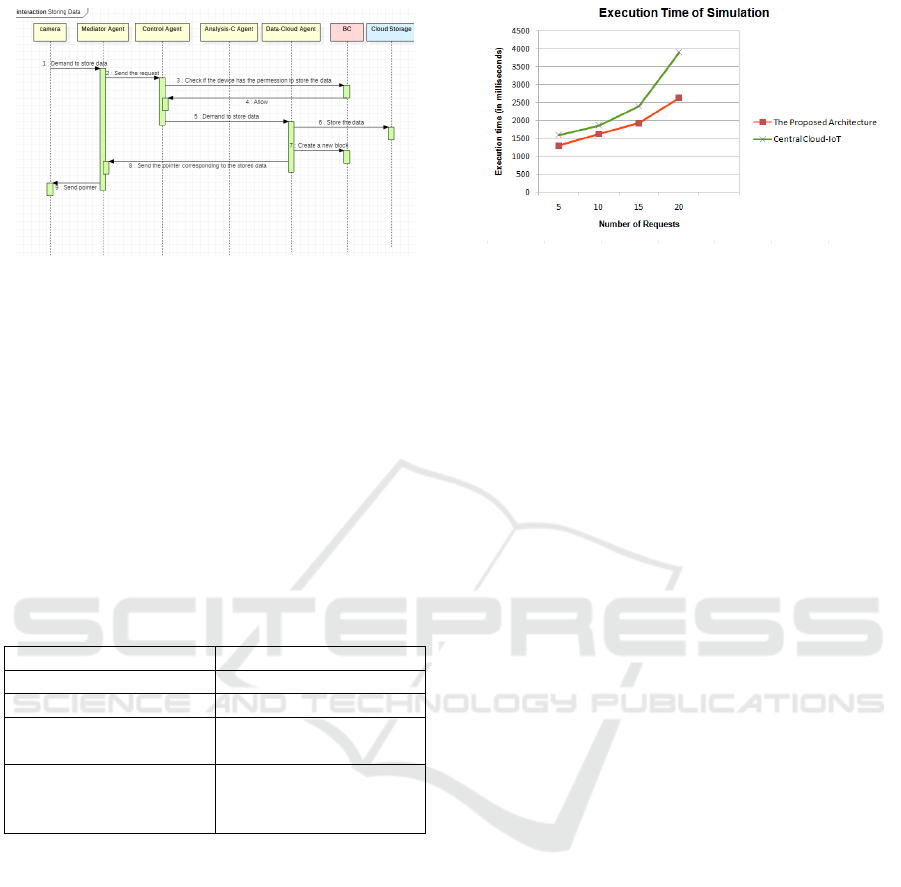
Figure 6: Sequence diagram of Store Data Transaction.
4 EVALUATION
The simulation platform is Eclipse. We carry out sim-
ulation experiments on an Intel Core i5 2.4 GHz CPU
and 4 GB RAM personal computer. We evaluate the
efficiency of the proposed model by measuring the
speed with which it can host the request to the cor-
responding resources (Fog Node or Cloud). The ex-
perimental setting consists of two Fog Nodes and one
cloud, where every Fog Node has different types of
IoT devices. The parameters are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Experimental parameters.
Parameter Value
Number of Cloud 1
Number of Fog Nodes 2
Latency from Fog
Node to Cloud (ms)
100
Latency from IoT
device to Fog Node
(ms)
45
In this experiment, we will focus on the strategy
used by our distributed architecture to host requests.
When a device sends a service request to Fog Node
through Interface Agent; the first step is to decide
where the request should be executed; either in the
Cloud or the Fog Node. So for each request, we first
try to place it on a Fog Node which provides the mini-
mum delay. However, if there is no sufficient resource
in Fog Node, then it can send the request to the cloud.
We use the Response Time metric in our simulation
experiment. This measurement reveals to us what
amount of time needed to receive a response from
the system. In this experiment, we evaluate the per-
formance of the proposed architecture by varying the
number of requests from 5 to 20. Figure 7 shows the
efficiency of our distributed architecture against com-
pared centralized Cloud-IoT architecture. The exe-
cution time is smaller in the proposed model than in
Figure 7: Average Execution time with different number of
requests.
the case using the centralized Cloud-IoT architecture,
which demonstrates the efficiency of our proposed ar-
chitecture. The results of the simulation demonstrate
how placement strategy can impact the execution time
of requests.
5 CONCLUSION AND ONGOING
WORKS
In this paper, we presented a new distributed Cloud-
IoT architecture to support real-time data delivery, se-
curity, and low latency. It is based on three emerging
technologies; Fog Computing, Multi-Agents System,
and Blockchain. Fog Computing can greatly reduces
the delay since it is located near to IoT devices. Multi-
Agents System provides distributed execution and has
very efficient proactive and reactive features which
are very useful in IoT applications. We also integrated
Blockchain technology into our architecture as it is a
great advantage to the next generation computing to
ensures data integrity and to allows low latency access
to large amounts of data securely. A simplified case
study is presented to illustrate that our approach can
be used in any other IoT applications. The results of
our performance evaluation can greatly improve the
response time compared to the traditional cloud-IoT
computing infrastructure. However, there is still a lot
of work to be finished. Future work will seek to im-
prove the architecture. Additional experiments will
be implemented to evaluate the proposed architecture
performance in different environments.
REFERENCES
A. Abdelaziz, A. Salama, A. and A. Mahmoud (2018). A
machine learning model for predicting of chronic kid-
ney disease based internet of things and cloud comput-
ing in smart cities. In Security in Smart Cities: Mod-
els, Applications, and Challenges, Pages: 93-114.
ICAART 2021 - 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1190

A. Dorri, S. Kanhere, R. and P. Gauravaramz (2017).
Blockchain for iot security and privacy: The case
study of a smart home. In IEEE PERCOM Work-
shop On Security Privacy And Trust In The Internet
of Things.
A. Giordano, G. and A. Vinci (2016). Smart agents and
fog computing for smart city applications. In Lecture
Notes in Computer Science.
A. Munir, P. and S. Khan (2017). Ifciot: Integrated fog
cloud iot. In Internet of Things,Vol.6, Pages: 74-82.
E. Cavalcante, J. Pereira, M. P. R. T. F. P. (2016). On the
interplay of internet of things and cloud computing: A
systematic mapping study. In Computer Communica-
tions, Vol.89, Pages 17-33.
G. Premsankar, M. and T. Taleb (2018). Edge computing
for the internet of things: A case study. In Internet of
Things Journal, Vol.5, Pages: 1275-1284.
J. Molano, J. Lovelle, C. J. and R. Crespo (2017). Meta-
model for integration of internet of things, social net-
works, the cloud and industry 4.0. In Journal of Am-
bient Intelligence and Humanized Computing.
Ju Ren, Hui Guo, C. Y. (2017). Serving at the edge: A scal-
able iot architecture based on transparent computing.
In IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol.31, Pages:
96 - 105.
L. Carnevale, A. Celesti, A. S. M. (2019). Osmotic com-
puting as a distributed multi-agent system: The body
area network scenario. In Internet of Things, Pages:
130–139.
Lu Hou, S. Zhao, X. K. P. M. and W. Xiang (2016). Internet
of things cloud: Architecture and implementation. In
IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol.54, Pages: 32-
39.
M. Ghazouani, M. K. and L. ErRajy (2019). Blockchain
& multi-agent system: A new promising approach for
cloud data integrity auditing with deduplication. In In-
ternational Journal of Communication Networks and
Information Security (IJCNIS), Vol.11, Pages: 175-
184.
Malik, A. and Om, H. (2018). Cloud computing and inter-
net of things integration: Architecture, applications,
issues, and challenges. In Sustainable Cloud and En-
ergy Services.
M. Elhoseny, A. Abdelaziz, A. A. R. K. A. (2018). A hybrid
model of internet of things and cloud computing to
manage big data in health services applications. In
Future Generation Computer Systems, Vol.86, Pages
1383-1394.
N. Harbi, K. Nadia, B. (2018). Les syst
`
emes multi agents
au service de la s
´
ecurit
´
e des donn
´
ees entrepos
´
ees dans
le cloud. In EDA.
Prakash P, Darshaun K.G, Y. P. M. V. G. V. B. (2017). Fog
computing: Issues, challenges and future directions.
In International Journal of Electrical and Computer
Engineering (IJECE) Vol.7, Pages: 3669-3673.
P. Sharma, M. Chen, J. (2017). A software defined fog node
based distributed blockchain cloud architecture for iot.
In I IEEE Access , Vol.6, Pages: 115-124.
T. Baker, M. Asim, H. T. B. A. and Buyya, R. (2017). An
energy-aware service composition algorithm for mul-
tiple cloud-based iot applications. In Journal of Net-
work and Computer Applications, Vol.89, pages 96-
108.
T. Alam (2018). Iot-fog: A communication framework us-
ing blockchain in the internet of things. In Interna-
tional Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering
(IJRTE), Volume.7.
T. Ogino, T. S. (2018). A multi-agent based flexible iot
edge computing architecture harmonizing its control
with cloud computing. In International Journal of
Networking and Computing,Vol.8, pages 218-239.
T. Wang, G. Zhang, A. M. and Q. Jin (2018). A secure
iot service architecture with an efficient balance dy-
namics based on cloud and edge computing. In IEEE
Internet of Things Journal, Vol.6, Pages: 4831- 4843.
A Secure Integrated Fog Cloud-IoT Architecture based on Multi-Agents System and Blockchain
1191
