
ArabiaNer: A System to Extract Named Entities from Arabic Content
Mohammad Hudhud
1
, Hamed Abdelhaq
2,∗
and Fadi Mohsen
3
1
Information & Computer Science Dept., An-Najah National University, Nablus, Palestine
2
Computer Science Apprenticeship Dept., An-Najah National University, Nablus, Palestine
3
Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence, Bernoulli Institute for Mathematics, Groningen, The Netherlands
Keywords:
Natural Language Processing, Named-Entity Recognition, Conditional Random Field.
Abstract:
The extraction of named entities from unstructured text is a crucial component in numerous Natural Language
Processing (NLP) applications such as information retrieval, question answering, machine translation, to name
but a few. Named-entity Recognition (NER) aims at locating proper nouns from unstructured text and clas-
sifying them into a predefined set of types, such as persons, locations, and organizations. There has been
extensive research on improving the accuracy of NER in English text. For other languages such as Arabic,
extracting Named-entities is quite challenging due to its morphological structure. In this paper, we introduce
ArabiaNer, a system employing Conditional Random Field (CRF) learning algorithm with extensive feature
engineering steps to effectively extract Arabic named Entities. ArabiaNer produced state-of-the-art results
with f1-score of 91.31% when applied on the ANERcrop dataset.
1 INTRODUCTION
Named Entity Recognition (NER) is the task of iden-
tifying proper names (named entities) from open-
domain text. NER has applications in a broad range of
fields such as education, health, economics, and poli-
tics. This is because NER is considered a vital infor-
mation extraction step needed in other NLP (Natural
Language Processing) tasks such as information re-
trieval (IR), question answering, and machine transla-
tion. For instance, to build a question answering sys-
tem that gives definitions to concepts people asking
about, we need first to locate the text segments con-
taining these concepts (entities), a task achieved us-
ing NER. In addition to the identification of entities,
NER also classifies these entities into pre-defined cat-
egories such as person name, organization, locations,
and temporal expressions (Grishman and Sundheim,
1996). For example, the sentence “The student went
to his university in Amman“ contains one named en-
tity, namely, “Amman” as a location.
Supervised machine learning has been effectively
used in the Named-entity Recognition field to extract
entities based on the concept of sequence labeling.
One of the most important algorithms applied in this
context is Conditional Random Field (CRF), which is
a probabilistic framework for labeling and segment-
∗
Corresponding Author.
ing structured data, such as sequences, trees and lat-
tices (Sutton and McCallum, 2012). To achieve bet-
ter results in NER, some hybrid techniques have been
proposed towards combining machine learning with
features extracted using rule-base modules, e.g., en-
riching the ML process by features extracted from ex-
ternal lexicons (Villena-Rom
´
an et al., 2011).
The majority of the approaches employed in ex-
tracting entities from text, i.e., NER, are tailored to
English text (Windsor et al., 2019); and hence, ap-
plying these approaches directly on other languages
will not produce the intended results. Arabic, the of-
ficial language in the Arab world, is one of the top-10
popular languages used on the Internet
1
. It is the main
language for about 26 countries and is spoken by hun-
dreds of millions of people around the world; both
native and non-native Arabic speakers. The process
of analyzing Arabic content is challenging because of
the unique nature of its lexical structure, ambiguity,
and spelling variants.
In this paper, we propose a new system
(ArabiaNer) to detect named entities from Arabic
text using CRF after extracting several features from
words. More than 80 features are extracted and cate-
gorized into six groups: Part Of Speech Tags (POS),
Linguistic and Morphological Features (LMF), Ex-
1
https://speakt.com/top-10-languages-used-internet/
Hudhud, M., Abdelhaq, H. and Mohsen, F.
ArabiaNer: A System to Extract Named Entities from Arabic Content.
DOI: 10.5220/0010382404890497
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2021) - Volume 1, pages 489-497
ISBN: 978-989-758-484-8
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
489

ternal Resources Features (ERF), Start/End of state-
ment and Nouns words (BEN), English translation
(ENF), and Lexical Features (LXF). Our System
ArabiaNer is trained and tested using the “ANER-
crop” dataset (Benajiba et al., 2007).
The main steps we follow in this work to accom-
plish this NER task for Arabic content is depicted
in Figure 1. The annotated dataset “ANERcrop” is
split into raw training and testing parts that are then
passed to a feature extraction module to enrich the
samples with more informative features. After that,
the training part is passed on to the machine learn-
ing process to generate the NER model using CRF
algorithm, which is evaluated using predictions from
the test dataset. The experimental evaluation reveals
that the proposed system outperforms the state-of-the-
art approaches (Abdallah et al., 2012; Benajiba and
Rosso, 2007a; Benajiba and Rosso, 2008b; Oudah
and Shaalan, 2012) by achieving an f1-score of 0.91,
detailed as follows: 0.95 for Location names, 0.86 for
organization names, and 0.92 for person names.
The remainder of the paper is organized as fol-
lows. In Section 2, we discuss the main challenges
facing the process of extracting entities from Ara-
bic content. Then, similar research efforts accom-
plished in this domain are presented in Section 3.
In Section 4, the process of extracting entities by
ArabiaNer is described in detail. The dateset and
the conducted experimental evaluation are discussed
in Section 5. Finally, we conclude the paper in Sec-
tion 6.
2 CHALLENGES IN ARABIC NER
SYSTEMS
Arabic is a widely-used language spoken by hundred
millions of users all over the world. Recently, a rapid
increase in the volume of published Arabic content is
witnessed. Extracting actionable knowledge from this
content is challenging due to the following reasons.
Lexical Structure of Words. In some languages, the
lexical structure of words plays an important role in
identifying named entities and specifying their types.
For example, in English, when a word starts with a
capital letter in the middle of a sentence, we then have
a strong evidence that this word refers to a named en-
tity. Figure 2 illustrates the importance of capital let-
ters appearing in a sentence in English. However, it is
not the case in Arabic, making identifying such nouns
more difficult.
Ambiguity. There are a relatively large number of
homonyms in Arabic where the same word might
have a number of senses according to the context.
For example, the word “ÉJ
Ô
g
.
” that means “beautiful”
might sometimes appears as an adjective and it can
also be used as a proper noun. Another example is
the word “
á
¢Ê
¯” (Palestine) that might come as a
country or as person. In addition, omitting diacritics
in Arabic makes the problem of disambiguation more
difficult.
Spelling Variants. Some words are spelled differ-
ently because the process of transliterating characters
from a certain language to Arabic is usually not stan-
dardized. For example, The word “google” can be
written in Arabic as Ég
.
ñk
.
, É¿ñ»and É
«ñ
«, keep-
ing the same meaning.
Lack of Resources. NER tasks need specialized re-
sources such as lexicons that contain entities of sev-
eral types. The data in these resources can be used
to engineer additional features in order to improve
the learning process. Since there are few and inade-
quate lexicons for Arabic language, researchers have
to build up their own resources to be used in their Ara-
bic NER systems.
3 RELATED WORK
This section surveys previous works on named entity
recognition in Arabic text. These works can be clas-
sified into three categories based on the employed ap-
proach (Shaalan, 2014): (1) machine-learning based,
(2) rule-based, and (3) hybrid approaches.
3.1 ML-based NER
In this line of efforts, linguistic resources with ade-
quate amount of annotated Arabic content are used to
train a supervised machine learning classifier. This
classifier can detect and tag named entities from Ara-
bic content. For example, Benajiba et al. (Benajiba
et al., 2007) introduced the ANERsys 1.0 system to
recognize four types of named entity tags from Arabic
text based on Maximum Entropy (ME). In (Benajiba
and Rosso, 2007b), they improved the approach by
adding features related to Part-of-speech (POS) tags.
Finally, more features, such as “base phrase chunks”
are added besides using Conditional Random Field
(CRF) instead of maximum entropy model, which led
to a significant improvement (Benajiba and Rosso,
2008a).
In (Ali et al., 2018), the authors employed a Bidi-
rectional LSTM recurrent network along with pre-
trained word embedding to include the sequence of
words in learning process towards achieving better
NER performance. The obtained F-score on the
NLPinAI 2021 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
490
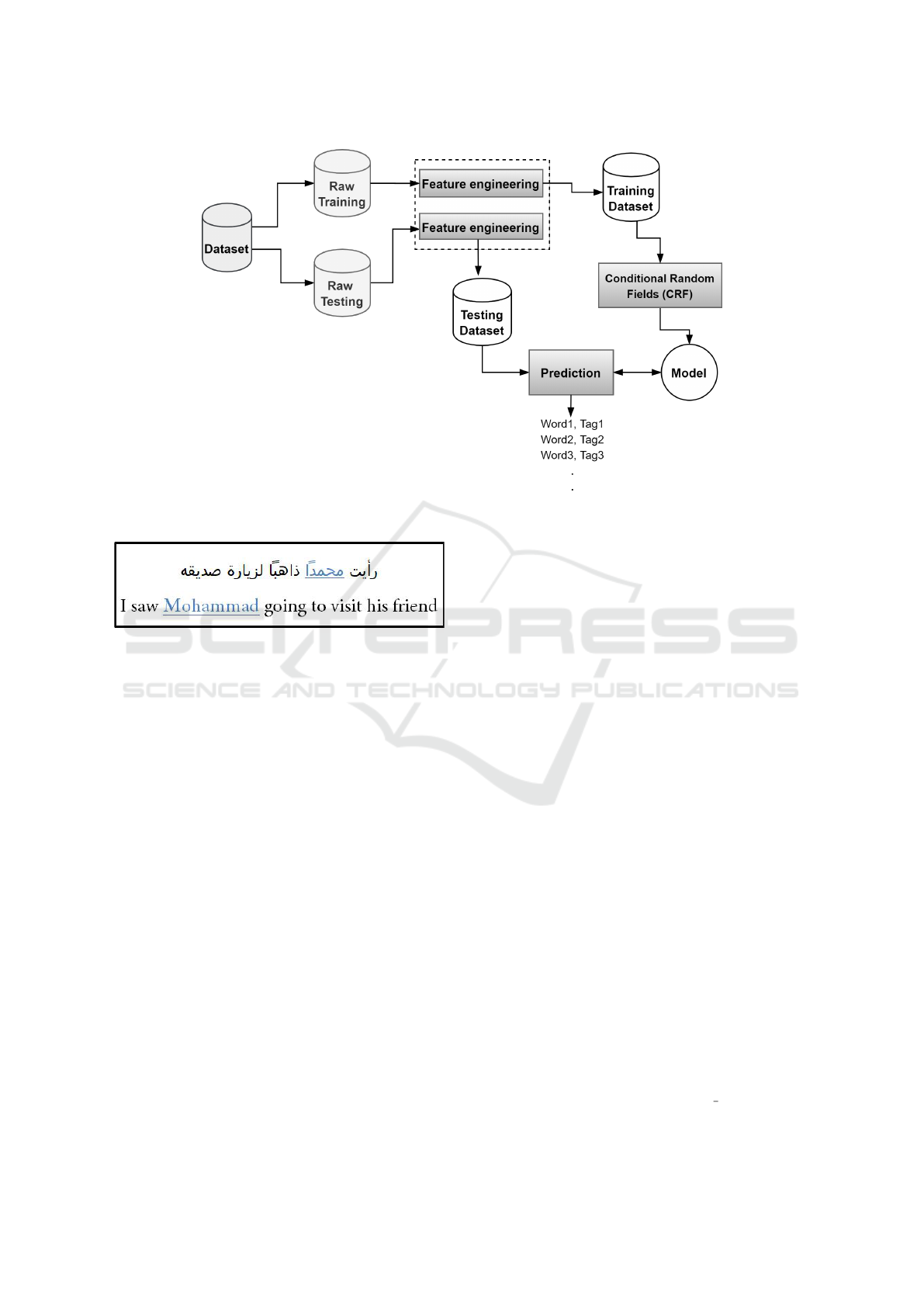
Figure 1: System overview of ArabiaNer.
Figure 2: Letter case in English and its role in NER.
benchmark dataset in this field ANERcrop is 0.88.
Helwe and Elbassuoni (Helwe and Elbassuoni, 2019)
adopted deep co-learning approach to detect and clas-
sify named entities in Arabic text. Although there
are a number of recent efforts started exploiting deep
learning in this context (Mohammed and Omar, 2012;
Ali and Tan, 2019), still hybrid approaches that com-
bine rule-based and classical machine learning tech-
niques supported by feature engineering achieve bet-
ter results on ANERcrop (Oudah and Shaalan, 2012).
3.2 Rule-based NER
In rule-based NER systems, handcrafted rules are
built and used to search for entities within text. These
works rely heavily on defining patterns and creating
lexicons of entities to find matching tokens. Mal-
oney and Niv (Maloney and Niv, 1998) introduced
TAGARAB, as one of the earliest systems for extract-
ing Arabic named entities, namely, Person, Organiza-
tion, Location, Number and Time entities. This sys-
tem is designed as a 2-module pipeline to tokenize
words and then to find names using a pattern matching
engine. The obtained results reveal that the accuracy
of the system is much better when both modules are
jointly used than applying each module separately.
In (Khalil et al., 2020), the authors used linguis-
tic grammar-based techniques to extract composite
names from Arabic content, in particular the geni-
tive Arabic grammar rules that are used to distinguish
between definite and indefinite nouns. Based on do-
main knowledge and Arabic Genitive rules, a number
of syntactical rules are used to identify definiteness
within phrases and then to extract composite names.
Elsherif et al. (Elsherif et al., 2019) used GATE to
build rules for the extraction of entities. Although
there are many approaches have been implemented in
this rule-based NER track (Elsebai et al., 2009; Al-
faries et al., 2013), a considerable amount of time and
effort should be spent in order to keep such systems
perform well with high recall by continuously adding
more rules, lexical resources, grammars etc.
3.3 Hybrid NER Approaches
In order to benefit from the advantages of both
rule-based and ML-based NER systems, hybrid ap-
proaches have come into existence. Benajiba and
Rosso. (Benajiba and Rosso, 2007a) developed a new
version of ANERsys 1.0, ANERsys 2.0, which com-
bines ME with POS tag information for the purpose of
improving the recognition of long proper noun. Be-
najiba and Rosso. (Benajiba and Rosso, 2008b) fur-
ther introduced a new system, which uses the same
features used in ANERsys 2.0 in addition to the con-
ditional random fields (CRF). Abdallah et al (Abdal-
lah et al., 2012) presented a Hybrid
NERA system
based on integrating rule-based system with classifi-
ArabiaNer: A System to Extract Named Entities from Arabic Content
491

cation. Another hyprid approach was developed by
Oudah and Shaalan (Oudah and Shaalan, 2012) in
which rule-based and Machine Learning were inte-
grated to detect 11 types of named entities. Shaalan
and Raza (Shaalan and Raza, 2007) developed Person
Name Entity Recognition for Arabic (PERA), using a
rule-based approach employed with linguistic exper-
tise.
In this work, we follow hybrid NER paradigm and
conduct extensive feature engineering on the word
and character levels. The incorporation of rule-based
entities is done by adding many lexicon features used
in fitting the ML model.
4 ENTITY EXTRACTION
APPROACH
In this section, we give a detailed description on the
process of entity extraction using our proposed sys-
tem. The system is based on Conditional Random
Field (CRF) Algorithm applied on a training dataset
after engineering various features. In Section 4.1, we
describe the sets of features used in the system. Then,
we detail the important aspect of CRF and how to in-
tegrate the new features in Section 4.2.
4.1 Feature Engineering
In this section, the set of features that we extracted
and used in building our NER model are thoroughly
explained. A total of 81 features (see Table 2) are
classified into the following groups:
Part Of Speech Tags (POS): Since entities normally
come as proper nouns and not as adjectives nor verbs,
it is essential to find out the types of words and feed
them as new features to CRF. In this group, we use
part of speech tagging (POS) to determine the linguis-
tic category of a word. In addition, this set includes
other features indicating whether the word and its ad-
jacent words are nouns or not. See Features (1-12)
and (36-40) in Table 2. To achieve the POS task, two
types of taggers are utilized: (1) Madamira and (2)
Aratools.
Madamira (Pasha et al., 2014): is an efficient Java-
based toolkit for Morphological Analysis with partic-
ular focus on the Arabic language. In ArabiaNer,
we used Madamira to extract POS, stem, aspect, case,
gender, mood, number, person, state, and voice for
each word in the dataset. Madamira receives XML
files as illustrated in Listing 1.
Aratools (Aratools, 2020): is a freely available
system including a dictionary for the Arabic lan-
guage and providing the following functionalities: (1)
1 < mad am i r a _i n pu t xm lns =" ur n :e du . c ol um bi a
. c cls . ma da mi ra . c on f ig u r a ti o n: 0 .1 " >
2 < m a da m ir a _ c o n fi g ur a ti o n > ... </
ma d am i ra _ c o n f ig u ra t io n >
3 < in _d oc id = " Ex am p l e Do c um e nt " >
4 < in _s eg id = " S ENT 1 " > The se nt en ce
here </ in _s e g > </ i n_d oc >
5 < / ma d am i ra _i n pu t >
Listing 1: Input file for Madamira.
translating Arabic into English, (2) Part Of Speech
(POS) tagging and (3) stemming (see Figure 3). In
ArabiaNer, we used Aratools to generate POS tags
and stems for each word in the dataset.
Figure 3: A screenshot of Aratools on Windows OS (Ara-
tools, 2020).
Linguistic and Morphological Features (LMF). For
the purpose of enhancing the prediction power of our
CRF model, we incorporated the morphological char-
acteristics of words, which link the words, their stems
and types, as new features. Therefore, we have pre-
pared several look-up tables that contain prepositions,
adverbs, adverbs of place and stop words. These ta-
bles are used to check whether a word (or a stem) and
its adjacent words exist or not. If yes, a respective fea-
ture with value of “true” is included, and “false” oth-
erwise. In addition, we create features from this cat-
egory for neighboring words. For example, location
names are usually preceded by prepositions. In this
sentence,
á
¢Ê
¯ ú
¯ AªJ
Ô
g
.
àðYg
.
@ñ
JK
(they are all lo-
cated in Palestine) the place name
á
¢Ê
¯ (Pales-
tine) is preceded by the preposition ú
¯ (in). This in-
creases the likelihood that the word
á
¢Ê
¯ is a lo-
cation name. The features from 13 to 29 in Table 2
correspond to this category.
External Resources Features (ERF). This set of fea-
tures encodes the existence of entities in pre-built dic-
tionaries (lexicons or gazetteers). Such features sup-
port the detection of emerging entities that were not
seen in the training dataset, and hence boost recall.
To measure the impact of using external lexicons in
ArabiaNer, three gazetteers are utilized: a gazetteer
with location names, person names and a third one
containing organization names. In Addition, we built
three lists of words that usually precede organiza-
tions names, location names and nationality indica-
tors. The first list contains words that normally pre-
NLPinAI 2021 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
492

cede organizations names, e.g., (
éÒ
¢
JÓ ,
éªÓAg
.
,Êm
.
×
)
for example, ...
éªÓAg
.
úÍ@ H
.
A
Ë@ I
.
ë
X. In this case,
the phrase is detected as “oraganisation”. The sec-
ond list contains words that usually precede loca-
tion names like (
éK
PñêÔ
g
.
,
éËðX). For example, in
the sentence,
á
¢Ê
¯
éËðX úÍ@ H
.
A
Ë@ I
.
ë
X, the word
á
¢Ê
¯ corresponds to a location name. The third
list contains nationality words that precedes person
names. For example, the word ú
æJ
¢Ê
®Ë@ in the sen-
tence
èQ
KA£ ¨@
Q
gAK
.
YÒm
×
ú
æJ
¢Ê
®Ë@ ÐA
¯ is a national-
ity indicating that the next YÒm
×
word will most prob-
ably be a person name. The features in this category
are listed in Table 2 from 30 to 35.
Beginning/End of Statements (BES). This set con-
tains binary flags to check if a word lies at the begin-
ning or at the end of a sentence. See Features (36-42)
in Table 2.:
English Features (ENF). Here, we employ a num-
ber of successful feature engineering practises that
are usually applied on English content. For example,
Arabic letters do not have different cases, i.e., whether
a letter has a lower or upper case, and hence, we
translate Arabic content to English in order to make
use of letter case by building several related features.
In addition, we prepare gazetteers for English names.
To translate words from Arabic to English we used
Googletrans which is a free python library that uti-
lizes Google Translate API (Google, 2020). See Fea-
tures (43-56) in Table 2.
Lexical Features (LXF). Many words in Arabic
share the same meaning but have slightly different
forms. Stemming is a very important preprocess-
ing step used to reduce words to their morphemes
(stems), mainly by eliminating derivational suffixes
and/or prefixes. In addition, word shingles with dif-
ferent lengths are built and used as features (See Ta-
ble 1). The remaining features from 57 to 81 in Ta-
ble 2 belong to this category.
4.2 Conditional Random Fields
Conditional Random Field (CRF), which is a general-
ization of Hidden Markov Models, has been shown to
outperform many machine learning algorithms in la-
beling a sequence of words. In other words, the infor-
mation of adjacent words affects the label prediction
of the current word. For example, the type of word
“went” will be affected by the features extracted from
its neighbors, which are ”Mohammad” and ”to” in the
sentence ”Mohammad went to Amman”.
CRF is a discriminative machine learning classi-
Table 1: Leading and trailing of the word Aî
EñÒºm
'
.
Aî
EñÒºm
'
Characters
@ [-1:]
H [:1]
Aë [-2:]
l
'
[:2]
Aî
E [-3:]
½m
'
[:3]
Aî
Eð [-4:]
Õºm
'
[:4]
Aî
EñÓ [-5:]
ñÒºm
'
[:5]
½g [1:3]
Aî
EñÒºm
'
Characters
Õ» [2:4]
é
K [-3:-1]
àð [-4:-2]
Õºk [1:4]
ñÒ» [2:5]
é
Kð [-4:-1]
àñÓ [-5:-2]
ñÒºk [1:5]
àñÒ» [2:6]
é
KñÓ [-5:-1]
àñÒ» [-6:-2]
fier, which learns the conditional probability by con-
verting sentences into feature functions. Each func-
tion receives a sentence s, the position i of a word in
the sentence, the label l
i
of the current word and the
label l
i−1
of the previous word. Each feature function
outputs a real-valued number, which is normally just
0 or 1. An example of these functions:
f
j
(s, i, l
i
, l
i−1
) =
1 l
i
= ADV. and w
i
ends with ly
0 otherwise
To assign a score score(l|s) for each sentence s and its
corresponding labeling l, each feature function f
j
is
multiplied by a respective weight λ
j
and then summed
up over the sentence words and features as follows:
score(l|s) =
m
∑
j=1
n
∑
i=1
λ
j
f
j
(s, i, l
i
, l
i−1
), (1)
where m is the number of features and n is the num-
ber of words in a sentence. The weights associated
with feature functions are learned using gradient de-
cent (Ruder, 2016).
The labeling score of a sentence is normalized as
follows:
P(l|s) =
exp[
∑
m
j=1
∑
n
i=1
λ
j
f
j
(s, i, l
i
, l
i−1
)]
∑
l
0
exp[
∑
m
j=1
∑
n
i=1
λ
j
f
j
(s, i, l
0
i
, l
0
i−1
)]
(2)
then these functions will then be transformed to prob-
abilities.
5 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
In this section, we evaluate the performance of
ArabiaNer in extracting entities from a dataset de-
ArabiaNer: A System to Extract Named Entities from Arabic Content
493
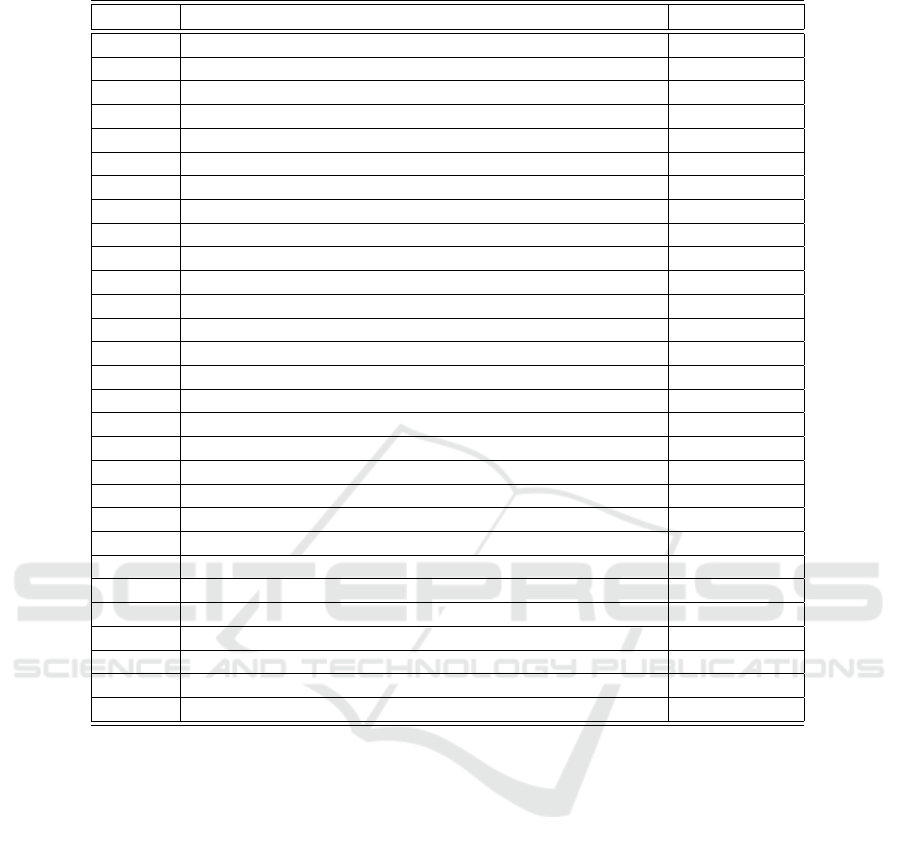
Table 2: List of the entire set of features used in ArabiaNer.
Feature Feature Description Feture value
1 current word Word
2 next word Word
3-12 POS of the current and surrounding words POS tag
13 is stem a stopword? True/False
14 is previous word an adverb? True/False
15 is previous word an adverb of place? True/False
16 is previous word a preposition? True/False
17-29 asp,cas,enc0,gen,mod,num,per,prc0,prc1,prc2,prc3,stt,vox MADAMIRA
30-32 is a (person, location, organization) name? True/False
33 is a nationality? True/False
34 The previous word in List1? True/False
35 The previous word in List2? True/False
36 is noun? True/False
37-40 are surrounding words nouns? True/False
41-42 start/end of sentence? True/False
43 English translation English Word
44 is the first letter capital? True/False
45-46 Last two/three characters characters
47 is the translation a stopword? True/False
48 POS of the translated word POS tag
49 The translation of the previous word English Word
50-51 is the previous/current word “in” ? True/False
52 is the previous word a direction (south, east, . . . )? True/False
53 is the translation of the previous word a stopword? True/False
54 POS of the translation of the previous word POS tag
55 the translation of the next word English Word
56 POS of the translation of the next word POS tag
57-78 leading and trailing as in Table 1. Characters
79-81 stem of the current/previous words Word
tailed in Section 5.1. The benchmark dataset “AN-
ERcorp” is used to compare our approach against
state-of-the-art systems (see Section 5.4), which is
conducted using a number of evaluation metrics de-
scribed in Section 5.2. In addition, the impact of
each feature category on the classification power of
ArabiaNer is discussed in Section 5.3.
5.1 Dataset
The Arabic dataset “ANERcrop” by Benajiba (Bena-
jiba et al., 2007) is available for research purposes
and widely utilized as an Arabic benchmark to evalu-
ate NER systems. ANERcrop consists of 4686 differ-
ent news documents discussing politics, culture, sport
and various other news genres, which are manually
collected from different sources. “ANERcrop” in-
cludes many words borrowed from English language,
such as
Pñk
.
(George),
Q
Ö
ß
XC
¯ (Vladimir),
ñK
.
(Bush) which makes NER on Arabic language a chal-
lenging task. ANERcrop contains a total of 150,287
lines, each of which consists of a single word a long
with its named entity tag. A sample example of this
dataset is shown in Table 4.
The majority of those words have no tags, and
hence are labeled as ”O” (Others), whereas the re-
maining words (about 10%, namely 14875 words) are
tagged with named entities (see Table 5 for further
statistics). The entity types used in this dataset are:
1) location, 2) organization, and 3) person.
5.2 Evaluation Metrics
For evaluation purposes, we use the F1-score, which
is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, where
the relative contribution of precision and recall to
the F1-score are equal. F1-score takes on values in
the range [0,1] where 0 refers to the poorest perfor-
mance and 1 to the best. Formally, F1-score is defined
as: (Pedregosa et al., 2011)
NLPinAI 2021 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
494

Table 3: The precision, recall, and F1-score of each feature set and entity type.
F.
Set
LOCATION ORGANIZATION PERSON OVERALL
Prec. Rec. F1 Prec. Rec. F1 Prec. Rec. F1 Prec. Rec. F1
POS 0.918 0.835 0.875 0.852 0.639 0.731 0.888 0.758 0.818 0.886 0.744 0.808
LMF 0.954 0.787 0.863 0.844 0.662 0.742 0.849 0.751 0.797 0.883 0.733 0.801
ERF 0.958 0.806 0.876 0.911 0.614 0.733 0.924 0.63 0.749 0.931 0.683 0.786
BES 0.961 0.737 0.834 0.939 0.568 0.708 0.930 0.488 0.640 0.943 0.598 0.727
ENF 0.959 0.886 0.921 0.913 0.713 0.801 0.897 0.768 0.827 0.923 0.789 0.85
LXF 0.94 0.889 0.914 0.859 0.710 0.778 0.906 0.818 0.860 0.902 0.806 0.850
Table 4: A sample from ANERcrop dataset a long with respective tags.
é
¯A¢Ë@
é
JJ
ë
KP ©Ó ñºñÓ ú
¯ ú
æ
AÖ
Ï
@ ¨ñJ
.
B@ ù
®
JË@
–
KA
®K
@
àA¿ð Word
I-ORG B-ORG O O B-LOC O O O O B-BERS O Tag
Table 5: Number of tokens for each entity type.
Number of words Named entity tag
5034 Location
3407 Organization
6434 Person
F1-score =
2 ∗ precision ∗ recall
precision + recall
Precision (also called positive predictive value) is the
fraction of relevant instances (TP) retrieved by the
system among all relevant (TP) and non-relevant (FP)
instances.
Precision =
T P
T P + FP
while recall (also known as sensitivity) is the frac-
tion of relevant instances (TP) that have been retrieved
among the entire set of relevant instances (TP + FN).
Formally, the recall is defined as (Powers, 2011):
Recall =
T P
T P + FN
The F1-score measure is calculated for each entity
type, considering the one-versus-rest tag identifica-
tion. Then, the macro-average of all F1-scores is es-
timated as one score for the entire system. The F1-
score is computed on a test dataset that was not in-
volved in the training process. From the ANERcrop
dataset, 10% of the dataset is taken as a test dataset.
5.3 Impact of Features
In this section, we discuss the impact of different fea-
ture sets on the overall performance of the system,
where such feature sets are studied both individually
and jointly.
In Table 3, we list the precision, recall, and F1-score
for each feature set and entity type. In general, all
feature sets have positive impact on precision, which
indicates that the system tries to avoid making mis-
takes while assigning labels to identified entities. Re-
garding recall, it is obvious that the system performs
pretty well in identifying location entities, in particu-
lar, when using English (ENF) and lexical (LXF) fea-
tures.
Translating Arabic into English and producing an
English feature set (ENF) leads to incorporating the
feature of “uppercase letters” that is crucial in identi-
fying named entities. In addition, ENF features al-
leviate the adverse impact of ”spelling variants” in
Arabic. It turns out that Arabic words with different
forms are usually translated into a single English word
that have compatible senses across different contexts.
Lexical features (LXF) that include the stem of a
word and a number of word shingles (as described in
Section 4.1) give better results than ENF. This is be-
cause such features deal with the “highly inflectual”
nature of Arabic in a better way than ENF features
do. LXF features try to normalize the tokens by stem-
ming and extracting parts that lie in the middle of the
words. Such parts will be similar to those words with
the same meaning. For example, the word “
éJ
.
JºÖ
Ï
@”
and the word “
éJ
.
JºÓ” are different in shape but have
the same meaning. Trying to catch the middle part
“I
.
J»” as a feature will certainly improve the NER
task.
By combining all feature sets together in one
CRF model, our system ArabiaNer produced the best
results in identifying named entities. The macro-
average score of precision, recall, and f1-score for
all entity types are 94.67%, 88.28%, 91.31%, respec-
ArabiaNer: A System to Extract Named Entities from Arabic Content
495
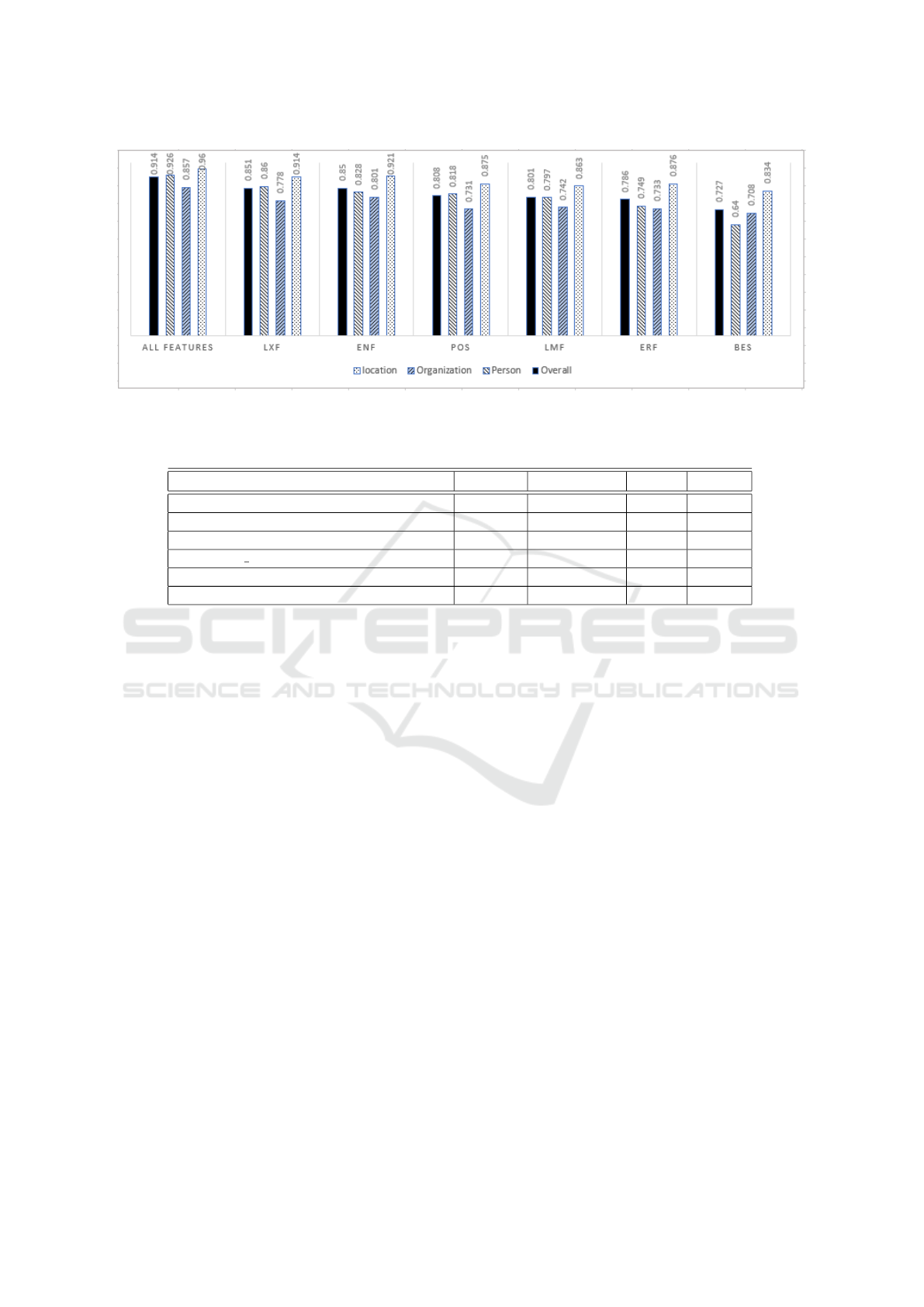
Figure 4: This figure illustrates the impact of each entity type (location, person, and organization) on the performance of
ArabiaNer in terms of f1-score.
Table 6: Performance comparison summary.
System Location Organization Person Overall
ANERsys 1.0 (Benajiba et al., 2007) 80.25 36.79 46.69 54.58
ANERsys 2.0 (Benajiba and Rosso, 2007a) 86.71 46.43 52.13 61.76
CRF (Benajiba and Rosso, 2008b) 89.74 65.76 73.35 76.28
Hyprid Nera (Abdallah et al., 2012) 87.39 86.12 92.80 88.78
Pipeline (Oudah and Shaalan, 2012) 90.10 88.20 94.40 90.90
ArabiaNer 95.60 85.71 92.61 91.31
tively.
5.4 Performance Comparison
Table 6 presents a summary that compares the
named entity detection performance of our approach
ArabiaNer and the previous work using the bench-
mark “ANERcrop” dataset. ArabiaNer outperforms
the state-of-the-art approaches with respect to the
overall F1-score. It is clear that hybrid systems,
e.g., (Abdallah et al., 2012) and (Oudah and Shaalan,
2012), give in general better f1-scores than traditional
approaches.
The “Pipeline” system described in (Oudah and
Shaalan, 2012) achieves the second best f1-score after
ArabiaNer. Although the f1-scores of PERSON and
ORGANIZATION types were a little better than what
ArabiaNer achieved, ArabiaNer has led to a 5.5%
gain over “Pipeline” with respect to LOCATION en-
tity types.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we have proposed “ArabiaNer”, a sys-
tem to detect and classify named entities from Arabic
text. This system is hybrid in the sense that extensive
rule-based steps are followed to extract features to fit
the machine learning model that is based on condi-
tional random field (CRF).
NER is a challenging task when applied on Arabic
content due to its morphological structure. Therefore,
extensive feature engineering is conducted, produc-
ing a set of 81 featured to come up with a robust NER
model in this context. The experimental results show
that ArabiaNer outperforms the state-of-the-art ap-
proaches in detecting named entities, achieving a pre-
cision , recall, and f1-score of 94.67%, 88.28% and
91.31%, respectively.
To further improve NER for Arabic content, we
are currently working on enhancing the system to ana-
lyze informal text arriving from social media services,
such as Twitter and facebook. This can be achieved by
enriching the feature engineering process with custom
text normalization steps tailored to social media.
REFERENCES
Abdallah, S., Shaalan, K., and Shoaib, M. (2012). Inte-
grating rule-based system with classification for ara-
bic named entity recognition. volume 7181, pages
311–322.
Alfaries, A., Albahlal, M., Almazrua, M., and Almazrua,
A. (2013). A rule-based annotation system to extract
NLPinAI 2021 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
496

tajweed rules from quran. In 2013 Taibah University
International Conference on Advances in Information
Technology for the Holy Quran and Its Sciences, pages
281–286. IEEE.
Ali, M. and Tan, G. (2019). Bidirectional encoder–decoder
model for arabic named entity recognition. Arabian
Journal for Science and Engineering, 44.
Ali, M., Tan, G., and Hussain, A. (2018). Bidirectional
recurrent neural network approach for arabic named
entity recognition. Future Internet, 10.
Aratools (2020). Aratools Arabic-English dictionary.
http://aratools.com/.
Benajiba, Y. and Rosso, P. (2007a). Anersys 2.0 : Conquer-
ing the ner task for the arabic language by combin-
ing the maximum entropy with pos-tag information.
In Proc. Workshop on Natural Language-Independent
Engineering, 3rd Indian Int. Conf. on Artificial Intel-
ligence, IICAI-2007.
Benajiba, Y. and Rosso, P. (2007b). Anersys 2.0: Conquer-
ing the ner task for the arabic language by combining
the maximum entropy with pos-tag information. pages
1814–1823.
Benajiba, Y. and Rosso, P. (2008a). Arabic named en-
tity recognition using conditional random fields. In
In Arabic Language and local languages processing:
Status Updates and Prospects.
Benajiba, Y. and Rosso, P. (2008b). Named entity recogni-
tion using conditional random fields.
Benajiba, Y., Rosso, P., and Bened
´
ıRuiz, J. M. (2007).
Anersys: An arabic named entity recognition system
based on maximum entropy. In Gelbukh, A., editor,
Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Pro-
cessing, pages 143–153. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Elsebai, A., Meziane, F., Belkredim, F. Z., et al. (2009).
A rule based persons names arabic extraction system.
Communications of the IBIMA, 11(6):53–59.
Elsherif, H. M., Alomari, K., AlHamad, A. Q., and Shaalan,
K. (2019). Arabic rule-based named entity recognition
system using gate. In MLDM.
Google (2020). Google Translate API for Python.
https://pypi.org/project/googletrans/.
Grishman, R. and Sundheim, B. (1996). Message under-
standing conference-6: A brief history. In Proceed-
ings of the 16th Conference on Computational Lin-
guistics - Volume 1, COLING ’96, page 466–471,
USA. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Helwe, C. and Elbassuoni, S. (2019). Arabic named en-
tity recognition via deep co-learning. Artificial Intel-
ligence Review, 52(1):197–215.
Khalil, H., Osman, T., and Miltan, M. (2020). Extract-
ing arabic composite names using genitive principles
of arabic grammar. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour.
Lang. Inf. Process., 19(4).
Maloney, J. and Niv, M. (1998). TAGARAB: A fast, ac-
curate Arabic name recognizer using high-precision
morphological analysis. In Computational Ap-
proaches to Semitic Languages.
Mohammed, N. and Omar, N. (2012). Arabic named entity
recognition using artificial neural network. Journal of
Computer Science, 8(8):1285–1293.
Oudah, M. and Shaalan, K. (2012). A pipeline Arabic
named entity recognition using a hybrid approach.
In Proceedings of COLING 2012, pages 2159–2176,
Mumbai, India. The COLING 2012 Organizing Com-
mittee.
Pasha, A., Al-Badrashiny, M., Diab, M., El Kholy, A., Es-
kander, R., Habash, N., Pooleery, M., Rambow, O.,
and Roth, R. (2014). MADAMIRA: A fast, compre-
hensive tool for morphological analysis and disam-
biguation of Arabic. In Proceedings of the Ninth In-
ternational Conference on Language Resources and
Evaluation (LREC’14), pages 1094–1101.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer,
P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., Vanderplas, J., Passos,
A., Cournapeau, D., Brucher, M., Perrot, M., and
Duchesnay, E. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning
in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
12:2825–2830.
Powers, D. M. W. (2011). Evaluation: From precision, re-
call and f-measure to roc., informedness, markedness
& correlation. Journal of Machine Learning Tech-
nologies, 2(1):37–63.
Ruder, S. (2016). An overview of gradient descent opti-
mization algorithms. CoRR, abs/1609.04747.
Shaalan, K. (2014). A survey of arabic named entity
recognition and classification. Comput. Linguist.,
40(2):469–510.
Shaalan, K. and Raza, H. (2007). Person name entity recog-
nition for arabic. In Proceedings of the 2007 Work-
shop on Computational Approaches to Semitic Lan-
guages: Common Issues and Resources, Semitic ’07,
pages 17–24, Stroudsburg, PA, USA. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Sutton, C. and McCallum, A. (2012). An introduction
to conditional random fields. Found. Trends Mach.
Learn., 4(4):267–373.
Villena-Rom
´
an, J., Collada-P
´
erez, S., Lana-Serrano, S., and
Gonz
´
alez, J. (2011). Hybrid approach combining ma-
chine learning and a rule-based expert system for text
categorization. In FLAIRS Conference.
Windsor, L. C., Cupit, J. G., and Windsor, A. J. (2019). Au-
tomated content analysis across six languages. PLOS
ONE, 14(11):1–14.
ArabiaNer: A System to Extract Named Entities from Arabic Content
497
