
Experiments with Auto-generated Socratic Dialogue for Source Code
Understanding
Zeyad Alshaikh, Lasang Tamang and Vasile Rus
University of Memphis, Memphis, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Intelligent Tutoring System, Computer Science Education, Socratic Method of Teaching, Dialogue
Generation, Programming Comprehension.
Abstract:
Intelligent Tutoring Systems have been proven to generate excellent learning outcomes in many domains such
as physics, mathematics and computer programming. However, they have seen relatively little use in training
and school classrooms due to the time and cost of designing and authoring. We developed an authoring tool
for dialogue-based intelligent tutoring system for programming called Auto-author to reduce the time and
cost. The tool allows teachers to create fully functional Socratic tutoring dialogue for learning programming
from Java code. First, we conducted a controlled experiment on 45 introductory to programming students to
assess auto-authored tutoring dialogues’ learning outcomes. The result shows that the auto-authored dialogues
improved students’ programming knowledge by 43% in terms of learning gain. Secondly, we conducted
a survey of auto-authored tutoring dialogues by introductory to programming course instructors to evaluate
the dialogues’ quality. The result shows that the instructors rated the questions as agree or strongly agree.
However, the instructors suggested that more improvement is required to help students develop a robust under-
standing of programming concepts.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tutoring is one of the most effective forms of in-
struction. Students in human tutoring conditions
show mean learning gains of 0.4–0.9 (non-expert) to
0.8–2.3 standard deviations (expert tutors) compared
to students in traditional classroom instruction and
other suitable controls (Bloom, 1984; Cohen et al.,
1982; Graesser et al., 2009; Person et al., 2007; Van-
Lehn et al., 2007). Therefore, Intelligent Tutoring
Systems (ITS) that mimic human tutors have been
built, hoping that a computer tutor could be pro-
vided to every student with access to a computer.
As a result, the ITSs have been shown to be effec-
tive for one-to-one tutoring in many domains such as
mathematics, physics and programming (Pillay, 2003;
Freedman et al., 2000; Corbett et al., 1999; Alshaikh
et al., 2020) and can generate impressive learning out-
comes.
Despite many successful ITSs examples, they
have seen relatively little use in training and school
classrooms. In examining the barriers to ITS’s
widespread use, the time and cost for designing and
authoring ITS have been widely cited as the primary
obstacles (Sottilare and Holden, 2013). The costs are
high because authoring content and other needed el-
ements for ITSs is tedious, error-prone (Heffernan
et al., 2006), and time-consuming (Blessing, 1997).
Furthermore, the authoring process usually involves
domain experts, pedagogical experts, cognitive scien-
tists, linguistic experts in the case of dialogue-based
ITSs, and software development expertise (Blessing,
1997). It is estimated that creating one hour of ITS
instruction can take up to 200 hours (Woolf & Cun-
ningham, 1987; Murray, 1999)
To overcome the challenge of authoring high-
quality tutors is to automate the entire authoring
process or as many parts of the process as possi-
ble (Aroyo et al., 2004). Therefore, authoring tools
can reduce time, effort, cost and enable reuse and
customization of content and lower the skill barrier
(Ainsworth et al., 2003; Halff et al., 2003). Conse-
quently, authoring systems were developed in many
domains such as physics, mathematics, and public
policy to increase both the accessibility and the af-
fordability of ITSs (Heffernan et al., 2006). For in-
stance, a successful example of an ITS authoring sys-
tem was developed by Jordan and his colleagues (Jor-
dan et al., 2001) in which they were able to build
knowledge sources for their dialogue system in only
Alshaikh, Z., Tamang, L. and Rus, V.
Experiments with Auto-generated Socratic Dialogue for Source Code Understanding.
DOI: 10.5220/0010398100350044
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2021) - Volume 2, pages 35-44
ISBN: 978-989-758-502-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
35

3 man-months. The system uses a graphical inter-
face for teachers to construct tutoring dialogues for
physics. Another example of such a system was in-
troduced by Aleven and his colleagues (Aleven et al.,
2009) where they developed a graphical user interface
to speed up the development of instructional compo-
nents such as hints and just-in-time messages.
Intelligent tutoring systems with conversational
dialogue form is a special category of educational
technologies. These conversational ITSs are based on
explanation-based constructivist theories of learning
and the collaborative constructive activities that oc-
cur during human tutoring. They have been proven
to promote student learning gains up to an impressive
effect of 1.64 sigma when compared to students learn-
ing the same content in a canned text remediation con-
dition that focuses on the desired content (VanLehn
et al., 2007).
We focus on conversational ITSs that implement a
Socratic tutoring style that relies on prompting stu-
dents to think and provide information in the form
of answers. The questions are designed to follow
a directed, predefined line of reasoning (Ros
´
e et al.,
2001). Based on static analysis and dynamic simula-
tions of code examples that learners are prompted to
understand, we propose an automated method to gen-
erate a Socratic line of reasoning and corresponding
questions necessary to implement a Socratic tutorial
dialogue for code comprehension.
For instance, for each target concept in the abstract
syntax tree (AST), we generate a question that the cor-
rect answer is the target information. For example,
the static analysis of the statement “int num = 10;”
results in the following benchmark answer declar-
ing an integer variable num and initializing it to 10
. When students are prompted to answer the ques-
tion, what does the statement at line 1 do?, the stu-
dent response is automatically compared to the corre-
sponding benchmark answer using semantic similar-
ity. If the two match, positive feedback is provided
to the students, e.g., Great job! Otherwise, the stu-
dents receive negative feedback followed by an asser-
tion indicating the correct answer. The students may
also receive neutral feedback depending on how se-
mantically close their answer is to the benchmark an-
swer. In sum, we adopt the following Socratic Tutor-
ing Framework for our automatically generated So-
cratic ITSs (see Figure 1).
The Socratic ITS Framework just presented can
be implemented adaptively. In other words, not all
students will receive all the prompts/questions. Some
students, e.g., students who show mastery of certain
concepts, e.g., conditions, will be asked fewer ques-
tions about it than students who have yet to master the
conditions. Thus, this adaptive Socratic ITS uses in-
struction tailored to each learner should result in bet-
ter learning outcomes for all learners.
It should be noted that the above framework cov-
ers the inner loop or within-task interaction of an ITS.
We assume an instructional task has been selected for
the learner to work on, e.g., a particular Java code ex-
ample has been chosen for the learner to read to com-
prehend. Therefore, our task is to automate the inter-
action with the learner within such a task. The outer
loop responsible for selecting an appropriate instruc-
tional task for a given learner is not described here
(see VanLehn’s two-loop ITS framework (Vanlehn,
2006)). How to automatically select the appropriate
next instructional tasks in adaptive ITSs is a topic we
plan to explore in the future.
It is important to add that our Socratic line of
reasoning for a target code example only targets the
program level or program model aspects of compre-
hension. Indeed, comprehension theories distinguish
between the program model, the domain model, and
the situation model (Pennington, 1987; Schulte et al.,
2010).
This paper investigates and proposes an approach
to generate Socratic dialogue for programming com-
prehension automatically. This work’s research hy-
pothesis is that auto-generated dialogues will help in-
troductory to programming students learn program-
ming and produce learning gain. The proposed ap-
proach was implemented and evaluated throughout a
controlled experiment and survey.
2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Socratic Author was designed and developed as a
stand-alone tool that can be used by ITS developers.
The authoring tool requires only source code exam-
ples as input to produce a full dialogue framework
that can simply be played. The current implemen-
tation was developed for the Java language to help
students understand Java code examples. The tool
was developed in Python and the output dialogue is
a JSON object (JavaScript Object Notation, or JSON,
is a lightweight data-interchange format that is easy
for machines to parse and generate). When porting
to a new target language, e.g., Python, the only com-
ponents that need to be changed are the static code
analyzer and the underlying dynamic simulator of the
code, which are typically available as off-the-shelf
components.
The architecture of the authoring tool consists of
five major components: question generation, bench-
mark answer generation, feedback generation, run
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
36

WHILE t h e r e a r e i t e m s t o ask a b o u t i n t h e AST {
Prom pt t h e s t u d e n t t o a n swer a q u e s t i o n f o r a t a r g e t i n f o r m a t i o n
i n t h e AST o r fro m t h e dynamic c ode s i m u l a t i o n
A u t o m a t i c a l l y a s s e s s t h e c o r r e c t n e s s o f t h e s t u d e n t an s w e r .
P r o v i d e s h o r t f e e d b a c k f o l l o w e d by t h e a s s e r t i o n o f t h e c o r r e c t
an swer , i f ne e d ed
}
Figure 1: The Socratic ITS Framework.
Figure 2: Architecture of Socratic Author.
time information, and dialogue generation (see Fig-
ure 2). The dialogue generation module takes as in-
put the output of the other four components or mod-
ules (question generation, answer generation, feed-
back generation, run time information) to generate a
complete segment of dialogue. As already noted, the
generated dialogue can be adaptively played by con-
versational ITSs. That is, all learners need not be
asked all questions; questions can be chosen adap-
tively depending on learners’ knowledge and other
characteristics, such as their emotional state.
2.1 The Question Generation Module
The question generation module uses a Java parser
to identify programming concepts and sub-concepts
in an abstract syntax tree as well as program run
time information from the dynamic program simula-
tion model to generate two types of questions. The
first question type is based on the dynamic behavior
of the code, e.g., how many times a loop is executed
and what are the values of the counter i during the
execution of the loop. The second type of questions
are generated based on the static code analysis of the
code, such as What is the name of the integer variable
declared in line 1? These questions were generated
from the code shown in Figure 3.
Based on the static analysis of the code, this sys-
tem generated three types of questions. Definition
questions check students’ knowledge of basic pro-
gramming concepts (e.g., What is a variable? or What
is an assignment statement about?). Second are ques-
tions targeting syntactic knowledge of the target pro-
gramming language (e.g., Can you indicate the con-
dition of the for loop in line 2?). Third are complex
questions or sequences of related questions targeting
all aspects of statements. For instance, for a line of
code declaring an integer variable and initializing it
to 0, a generic question is generated (e.g., What does
the statement in line 1 do?) and a sequence of two re-
lated questions (e.g., What is the main purpose of the
statement in line 1? and What value, if any, are the
variables in the declaration statement in line 1 initial-
ized to?). That is, the sequence of questions targets
the declaration and initialization aspects of a declara-
tion statement. For more complex statements, e.g., for
loops, a sequence of questions promoting deep under-
standing of this more complex statement is generated.
Each question in the sequence targets an important as-
pect of the loop concept, such as the loop variable
i, the initialization of the loop variable, the terminal
condition, and the increment of the loop variable. For
instance, the following questions are generated for the
for loop, as shown in Figure 3: (1) What is the initial-
ization statement of the for loop? (2) What is the stop
condition of the loop? (3) What is the inc/decrement
statement?
Finally, the question generation module generates
questions for a block of statements as well. For a
block, i.e., a group of statements between balanced
braces, questions are generated to ask the learner
to summarize the goal of the block, e.g., functions,
loops, and if-else. For instance, a block question gen-
erated for the code in Figure 3 is What does the code
on the block from line 24 do?
Figure 3: Java for loop.
There is one challenge with these block-level ques-
tions. Generating a higher level benchmark response
summarizing the function of the block in order to au-
tomatically assess student responses was beyond the
scope of the current method, which focused on the
program model as opposed to the domain model. Fur-
thermore, automatically generating functional bench-
mark responses for a given block of code is a chal-
Experiments with Auto-generated Socratic Dialogue for Source Code Understanding
37

lenging task the researcher plans to tackle in the fu-
ture. For this reason, the current solution to gener-
ate the benchmark responses for a given block is to
concatenate the benchmark responses of the individ-
ual statements in the block, as detailed later.
Figure 4: Auto-generated questions from Figure 2 program.
2.2 The Benchmark Answer Generation
Module
To generate a meaningful answer, the answer genera-
tion model starts with the abstract syntax tree of the
input Java program obtained from Java parser. The
model generates block- and statement-level answers
by traversing the syntax tree. A complete pass of
the tree statement nodes generates a complete sen-
tence, where each type of node is associated with
a predefined template. That is, this study followed
a template-based text generation approach, which is
Figure 5: Abstract syntax tree for static final int x = 10.
widely used in natural language generation (Jurafsky
and Martin, 2008). For instance, a complete pass over
the tree of the statement final static int = 10 produces
the following benchmark answer Declare a final static
integer x and initialize it to 10. For block-level an-
swers, the answer generation module first identifies
the block by matching the node type with a prede-
fined list of types, e.g., function, loop, and if-else,
then analyzes the sub-tree to generate an answer for
each statement in the block. Next, the module com-
bines the answers for each individual statement in the
block into a single paragraph. For example, the block-
level answer for the for loop presented in Figure 3 is
“The for loop in line 2 iterates over the counter i from
0 to 9, increasing the counter by 1 in each iteration.
In each iteration, the value of sum is incremented to
its current value plus the value of i.”
2.3 The Code Simulation Module
Generating answers from abstract syntax trees is not
enough because the trees do not represent any run-
time information. This is critical for code examples
that require user input, in which case the behavior
of the code will change depending on the user input.
Therefore, a Java Debugger Interface (JDI) was used
to simulate the execution of Java programs and record
variable values. This information answers questions
such as what the value of the variable sum is in line
3 when i is 4 or what the values of the counter i are
during the execution of the for loop. Therefore, the
simulation module offers the ability to trace the exe-
cution of Java code and generate questions based on
the results of this dynamic execution of the code.
2.4 The Scaffolding Module
The scaffolding module uses the information from the
answer generation module and a set of short prede-
fined phrases expressing positive (Good job), neutral
(Good try), or negative (Not quite so) feedback to gen-
erate a more complete feedback utterance, which con-
sists of short feedback (e.g., Good job) followed by
an assertion of the correct answer or a more informa-
tive follow-up hint. The system can generate three
levels of Socratic hints, as shown in Figure 6. At the
first level, the tutor may ask definition questions about
the targeted programming concept, e.g., “What is the
int keyword used for in line 1?” For level 2 ques-
tions, the tutor may ask a concept completion ques-
tion in the form of a fill-in-the-blank question, e.g.,
“The int keyword is used to a that can
hold a 32-bit signed .” The expected keywords
are declare, variable, and integer. Finally, at Level
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
38
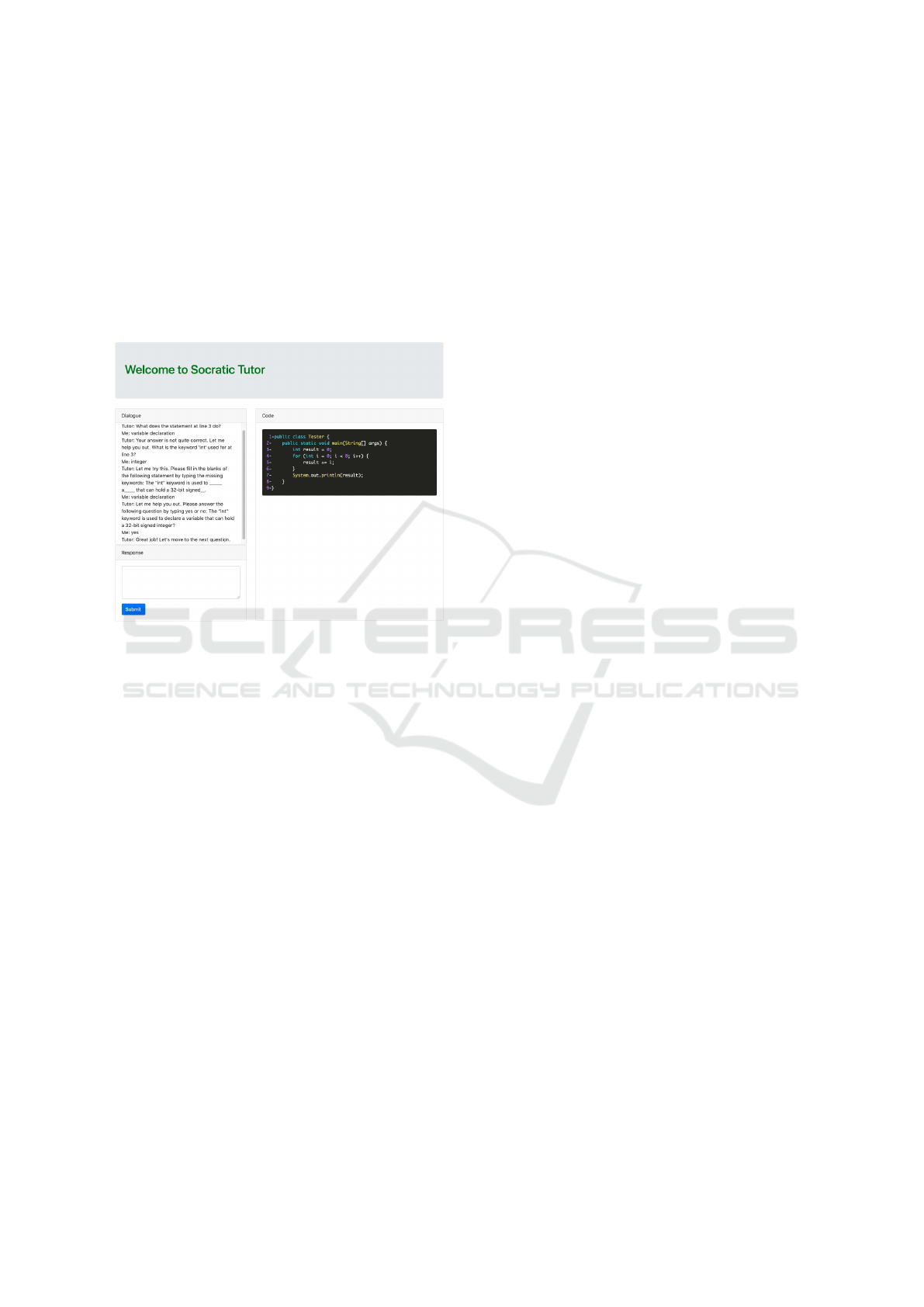
3, the tutor asks a verification question in the form
of a yes/no question, e.g., “The int keyword is used
to declare a variable that can hold a 32-bit signed in-
teger? Please answer the following question by typ-
ing yes or no.” Using yes/no questions allows the sys-
tem to verify common misconceptions students may
have and correct them. However, at this moment, no
misconception information has been incorporated into
the method to account for and correct misconceptions,
but this feature will be added in the future.
Figure 6: Tutoring session.
2.5 The Dialogue Module
Once the questions, answers, feedback, and run-time
simulations are produced, the dialogue module gen-
erates a complete segment dialogue in the form of
a sequence of questions and corresponding expected
benchmark answers, which are used to automatically
assess whether student responses are correct using a
semantic similarity approach (Khayi and Rus, 2019).
Technically speaking, the dialogue is specified as an
JSON object.
2.6 Enacting the Dialogue Model
The dialogue generated for a given code example
needs to be played by a dialogue manager as part of a
dialogue-based ITS. The role of the dialogue manager
is to present the learner with questions in a particular
order. Typically, the dialogue manager presents the
questions in a sequence corresponding to the lines of
code the questions are about. For blocks, the Socratic
dialogue starts with questions about each statement
within the code block. When all the statements in a
block are covered, the ITS asks the students to sum-
marize the block. Other orders of presenting the ques-
tions can be envisioned, such as the execution order of
the lines of code for a given input.
Besides the questions generated from the abstract
syntax trees and the dynamic execution of the code,
there are two general types of questions or statements:
a question or statement to elicit self-explanation (Can
you read the code and explain in your own words what
the code does and what it means to you while you
read the code?) and a prediction question or state-
ment (Please read the code and predict its output).
Each generated question is labeled internally ac-
cording to its type and a list of concepts in order
to track students’ mastery of key programming con-
cepts. Therefore, this labeling mechanism gives the
dialogue manager freedom to choose what questions
to present. Various ITS developers may choose dif-
ferent question sequencing strategies. For instance,
the following is a potential sequencing: the dialogue
manager starts by asking the students to explain the
code in detail and predict its output. The Socratic line
of questioning is only triggered if the student’s expla-
nation and prediction are incorrect or incomplete. For
instance, for incomplete explanations, the sequencing
strategy may be implemented to ask questions only
about the parts of the code that were not explained in
sufficient detail.
2.7 User Interface
The user interface is simple, easy to use, and consists
of a text area to write or paste Java code and three
buttons (see Figure 7). The interface offers authors
two options: (1) generate a Socratic dialogue and save
it as a JSON script or (2) start a tutoring session for
testing purposes. Furthermore, the interface provides
the ability to choose what concepts the author prefers
to generate a dialogue for. For example, if an author
wants to encourage students to practice for loops, they
can select the for loop concept only.
The authoring tool also offers an interface for ITSs
by using REST API technology. This allows ITSs
to easily integrate the tool by requesting a dialogue
script for a given Java code and getting as a response
the corresponding Socratic dialogue as a JSON ob-
ject.
3 EVALUATION
3.1 Method
We carried out two evaluations to assess the qual-
ity of auto-generated dialogue and its effect on pro-
gramming comprehension. The first evaluation was
Experiments with Auto-generated Socratic Dialogue for Source Code Understanding
39

Table 1: Mean and Stander Deviation of pre-test, post-test, and learning gain.
Pre-test Post-test Learning gain
Section n Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD
Group-1 14 58 21 86 13 51% 21
Group-2 15 56 16 70 11 43% 19
Group-3 15 57 35 61.3 33 12% 9.1
Table 2: Mean and Stander Deviation of turns, words, sentences and content-words.
Section Turns Words Sentences Content-words
Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD
Group-1 123 13 402 217 45 8 191 164
Group-2 115 28 334 183 35 18 154 106
Figure 7: Socratic Authoring Tool Interface.
to let a group of programming instructors evaluate the
auto-generated dialogues to explore if this approach
is educationally useful. The second evaluation was
conducted as a control experiment by letting intro-
ductory to programming course’s students use either
auto-authored, expert-authored Socratic dialogue or
output only. The goal of the second evaluation is to
analyze the learning outcomes to see how easy, effi-
cient, and friendly the system is.
3.2 Participants
In the first evaluation, participants (n=13) were in-
structors teaching Java programming courses. More-
over, the second study participants were undergrad-
uate students (n=45) who enrolled in the introduc-
tory to programming course at a major 4-year Asian
university. The participants were divided into three
groups of 15 students. The first group (Group-1) was
assigned to a tutoring session where experts generated
the tutoring dialogues. The second group (Group-2)
was assigned to a condition in which they used auto-
generated tutoring dialogues. And finally, the last
group (Group-3) was assigned to a scaled-down ver-
sion of the system. The scaled-down version presents
Java code examples and asks about the output without
providing any feedback.
3.3 Materials
Materials for the first evaluation study included fifteen
auto-generated dialogues from Java code examples
covering the following concepts: variables, if and if-
else conditionals, for loop, while loop and array. The
dialogues were formatted in a human readable form
and then shown one by one to each rater. At the end
of each dialogue, a survey consists of 10 questions
using a 5-point Likert scale presented (see Table 4)
where 1 is strongly disagree and 5 is strongly agree.
Materials for the controlled experiment included
a pre- and post-test measuring participants’ knowl-
edge on a number of key computer programming con-
cepts and a survey that contains 7 questions to eval-
uate the authored dialogues. The pre- and post-test
have similar difficulty levels and contain 6 Java pro-
grams where each question assessed students’ under-
standing of a particular programming concept. For
each question in the pre- and post-test, the participants
were asked to predict the code example’s output.
3.4 Procedure
For the first evaluation, we emailed the survey link
to introductory to programming courses instructors.
The instructors were given five days to complete the
survey.
On the other hand, the controlled experiment was
conducted in a computer lab under supervision. First,
participants were debriefed about the purpose of the
experiment and were given a consent form. Those
who consented started by taking a pre-test. Once
they have finished the pre-test, an approximately 60-
minute tutoring session started. Finally, participants
took the post-test and an evaluation survey. For
group-3, there was no survey at the end of the experi-
ment since they did not interact with the dialogue ITS.
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
40

Table 3: Mean and Stander Deviation of scaffolding questions and success rate.
Section Feedback First Second Third
Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD
Group-1 28 4 55% 16 70% 23 61% 37
Group-2 31 7.5 41% 21 47% 13 73% 24
Table 4: Mean and Stander Deviation of survey questions for evaluating tutoring dialogues by students.
Question Group-1 Group-2
Mean SD Mean SD
I think the questions were clear and easy to understand. 3.6 0.9 3.4 0.8
I think the system was able to understand my answers and response accordingly 4.6 1.2 4.3 0.9
I think the scaffolding questions from the system helped me produce the correct
answer.
4.4 0.5 4.2 0.4
I think the system was effective at helping me understand the code examples. 4.6 0.5 4.4 0.7
I think the system was effective at helping me understand core programming
concepts.
3.6 1.1 3.7 1.2
I think the system helped me to understand Java programming. 4 0.8 4.3 1.2
I think the system provides a useful learning experience. 4.5 0.5 3.4 1.3
3.5 Assessment
The pre and post-test questions were scored 1 when
the student answer was correct and 0 otherwise. The
learning gain score (LG) was calculated for each par-
ticipant as follows (Marx and Cummings, 2007).
Learning gain =
post-test−pre-test
100−pre-test
post-test > pre-test
post-test−pre-test
pre-test
post-test < pre-test
drop pretest = posttest = 100 or 0
0 post-test = pretest
(1)
4 RESULT
To understand each type of tutoring method’s over-
all effectiveness on students’ knowledge, we report
the knowledge change in terms of learning for each
group. Table 1 shows the average scores of the pre-
test for each group 1, 2, and 3 are 58%, 56% and 57%,
respectively, in which they are in the range of 2% dif-
ference. Thus, the pre-test scores indicate that par-
ticipants in both groups have, to some extent, similar
knowledge—however, the post-test scores improved
by 28% in group-1, 14% in group-2 and 4% in group-
1. Therefore, the difference between pre- and post-
test scores result in learning gain of 51%, 34% and
12% for group 1,2 and 3, respectively. Thus, the result
indicates that the auto-authoring dialogues improved
students’ knowledge by 34% and outperformed the
output only group by 22%.
Despite the difference in learning gain between
group-1 and 2, the result from a two-tailed t-test
showed that there is no statistically significant differ-
ence (t=0.83, df=19, p>0.05). Furthermore, the re-
sults from the two-tailed t-test also showed that there
is a statistically significant difference between group-
3 and other groups (t=3.1, df=52, p<0.05) in terms of
learning gain.
To evaluate dialogue efficiency, we analyzed the
students’ responses from dialogue logs in terms of
turns, word, sentence and content-word for each
group (see Table 2). For group-1, the results show
that, on average, each tutoring session consist of 123
turns and participants produced 402 words, 45 sen-
tences, and 191 content-words. On the other hand,
group-2 students produced 334 words, 35 sentences,
and 154 content-words within 115 turns. Therefore,
students assigned to expert-written dialogues interact
more with the tutor and produce more words, sen-
tences, and content-words. However, the result from
a two-tailed t-test showed that there is only a statisti-
cally significant difference (t=6.13, df=19, p<0.05)
in terms of sentences.
We further analyzed the scaffolding questions to
understand the difference between expert- and auto-
generated help. Table 3 shows the average number
of help received by students and the success rate.
The question would be considered a success if the
student was able to provide the correct answer. Ta-
ble 3 shows that students in group-1 received more
questions and have a higher success rate in the first
and second levels. Furthermore, the result shows that
the auto-generated third level has a 12% higher suc-
cess rate. However, the result from a two-tailed t-
test showed only a statistically significant difference
in first (t=3.6, df=25, p>0.05) and second (t=-4.1,
Experiments with Auto-generated Socratic Dialogue for Source Code Understanding
41

df=25, p<0.05) level.
To understand how efficient and user-friendly the
system was to the students, we analyzed the result
from after session survey, as shown in Table 4. The
survey contains 7 questions using a 5-point Likert
scale where 5 is strongly agree and 1 is strongly dis-
agree. Students in group-1 gave a higher rate in all
questions except the answer to the question “the sys-
tem was effective at helping me understand core pro-
gramming concepts” and “the system helped me to
understand Java programming.” We further calculated
Fleiss’ kappa for inter-rater reliability, and the result
shows that (Fleiss’ Kappa = 0.52) for group-1 and
(Fleiss’ kappa = 0.43) for group-2. Therefore, the
Fleiss’ kappa score suggests that the agreement be-
tween subjects in group-1 is higher than the subjects
in group-2.
Table 5 shows the result in terms of average and
standard deviation for 10 questions using a 5-point
Likert scale where 5 is strongly agree and 1 is strongly
disagree. Questions 1 and 2 target the quality of the
auto-generated questions, feedback, and model an-
swers regarding their syntactic and semantic quality.
Moreover, the third question asks about the coherence
and consistency of the dialogue. The rest of the ques-
tions focus on educational goals and the raters’ overall
likelihood of using the system in their teaching in the
future.
The result shows an average score above 4 for
all questions except the fifth question that asking
if the generated dialogue would help students de-
velop a robust understanding of programming con-
cepts. Furthermore, the instructors agreed that the
auto-generated dialogues would help students under-
stand Java programs better and learn programming
concepts (Fleiss’ Kappa = 0.51). We also allowed
the raters to provide voluntary feedback at the end of
the survey, and the voluntary feedback was positive.
For instance, one of the raters stated that “the system
looks promising and the dialogue looks coherent to
the point you feel it is not auto-generated.”
5 DISCUSSION
The controlled experiment results show that the auto-
generated Socratic dialogue for programming com-
prehension can improve students’ knowledge. The
average learning gain of group-2 students is 43%
comparing with 12% group-3 students. However,
group-1 students outperform both group-2 and group-
3 in which we expected; however, it was not statisti-
cally significant.
Analyzing tutoring logs shows that group-1 stu-
dents produced more words, sentences and content-
words and were more interactive in terms of turns.
Furthermore, group-1 students received more scaf-
folding questions and have higher success rates in
providing the correct answer to the first and second
levels. However, group-2 students achieved a higher
success rate on the third level; however, the difference
was not statistically significant.
Post tutoring survey shows that on average group-
2 students rated the evaluation questions of auto-
authored dialogues as agree or strongly agree. How-
ever, the rating dropped to neither agree nor disagree
for questions 1, 5 and 7 (see Table 4). On the other
hand, group-1 students rated questions 1 and 5 as nei-
ther agree nor disagree. The overall result suggests
that students preferred to interact with expert-written
dialogues. On the other hand, the evaluation by pro-
gramming instructors shows that they chose to agree
or strongly agree to every question except question
5 (see Table 5) suggesting that more improvement is
required to help students developing a robust under-
standing of programming concepts.
To conclude, expert-written tutoring dialogues
outperformed auto-generated dialogues in many as-
pects. However, auto-generated dialogue can be cre-
ated from java code examples in less than a minute
and requires no technical or educational knowledge.
We believe that considering the cost, skills and time
required to generate expertly written dialogues, the
tool offers a great opportunity to students and teach-
ers.
6 CONCLUSION
Intelligent Tutoring Systems can generate impressive
learning outcomes in many domains such as physics,
mathematics and computer programming. However,
they have seen relatively little use in training and
school classrooms due to the time and cost of de-
signing and authoring ITS. We developed an author-
ing tool for programming dialogue intelligent tutoring
system called Auto-author to reduce the time and cost.
The tool allows instructors to create fully functional
Socratic tutoring dialogue for teaching programming
from Java code examples.
A controlled experiment on 45 introductory to
programming students was carried out to evaluate
auto-authored tutoring dialogues’ learning outcomes.
The result shows that the auto-authored dialogues im-
proved students’ programming knowledge by 43% in
terms of learning gain. Furthermore, we conducted
a survey of auto-authored tutoring dialogues by pro-
gramming instructors to evaluate the dialogues’ qual-
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
42

Table 5: Mean and Stander Deviation of survey questions for evaluating auto-generated tutoring dialogues by instructors.
Question Mean SD
I think the generated questions, feedback, and answers are syntactically correct. 4.2 0.55
I think the generated questions, feedback, and answers are semantically correct. 4.5 0.84
I think the generated dialogue is coherent and consistent. 4.4 0.45
I think the generated dialogue (questions, feedback) would help students understand Java
code.
4.2 0.84
I think the generated dialogue (questions, feedback) would help students develop a robust
understanding of programming concepts.
3.8 0.55
I think the generated scaffolding questions would help students learn and understand the
corresponding Java code.
4.6 0.55
I think the generated dialogue covers all important programming concepts presented in
the code.
4.8 0.45
I think I may use this system in the classroom. 4.2 0.84
I think the system is effective at helping students understand Java code. 4.2 0.45
I think the system is effective at helping students understand programming concepts. 4.2 0.84
ity. The result shows that the teachers believe the di-
alogues as good. However, the instructors believed
that more improvement is required to help students
developing a robust understanding of programming
concepts.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work as partially funded by the National Science
Foundation under the award #1822816 (Collaborative
Research: CSEdPad: Investigating and Scaffolding
Students’ Mental Models during Computer Program-
ming Tasks to Improve Learning, Engagement, and
Retention) to Dr. Vasile Rus. All opinions stated or
implied are solely the authors’ and do not reflect the
opinions of the funding agency.
REFERENCES
Ainsworth, S., Major, N., Grimshaw, S., Hayes, M., Un-
derwood, J., Williams, B., and Wood, D. (2003). Re-
deem: Simple intelligent tutoring systems from usable
tools. In Authoring Tools for Advanced Technology
Learning Environments, pages 205–232. Springer.
Aleven, V., Mclaren, B. M., Sewall, J., and Koedinger, K. R.
(2009). A new paradigm for intelligent tutoring sys-
tems: Example-tracing tutors. International Journal
of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 19(2):105–154.
Alshaikh, Z., Tamang, L. J., and Rus, V. (2020). Exper-
iments with a socratic intelligent tutoring system for
source code understanding. In The Thirty-Third Inter-
national Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Soci-
ety Conference (FLAIRS-32).
Aroyo, L., Inaba, A., Soldatova, L., and Mizoguchi, R.
(2004). Ease: Evolutional authoring support environ-
ment. In International Conference on Intelligent Tu-
toring Systems, pages 140–149. Springer.
Blessing, S. B. (1997). A programming by demonstra-
tion authoring tool for model-tracing tutors. Interna-
tional Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education
(IJAIED), 8:233–261.
Bloom, B. S. (1984). The 2 sigma problem: The search
for methods of group instruction as effective as one-
to-one tutoring. Educational researcher, 13(6):4–16.
Cohen, P. A., Kulik, J. A., and Kulik, C.-L. C. (1982).
Educational outcomes of tutoring: A meta-analysis
of findings. American educational research journal,
19(2):237–248.
Corbett, A., Anderson, J., Graesser, A., Koedinger, K., and
VanLehn, K. (1999). Third generation computer tu-
tors: learn from or ignore human tutors? In CHI’99
Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing
Systems, pages 85–86, New York, NY, USA. Associa-
tion for Computing Machinery.
Freedman, R., Ros
´
e, C. P., Ringenberg, M. A., and Van-
Lehn, K. (2000). Its tools for natural language dia-
logue: A domain-independent parser and planner. In
International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Sys-
tems, pages 433–442. Springer.
Graesser, A. C., D’Mello, S., and Person, N. (2009). 19
meta-knowledge in tutoring. Handbook of metacogni-
tion in education, page 361.
Halff, H. M., Hsieh, P. Y., Wenzel, B. M., Chudanov, T. J.,
Dirnberger, M. T., Gibson, E. G., and Redfield, C. L.
(2003). Requiem for a development system: reflec-
tions on knowledge-based, generative instruction. In
Authoring tools for advanced technology learning en-
vironments, pages 33–59. Springer.
Heffernan, N. T., Turner, T. E., Lourenco, A. L., Macasek,
M. A., Nuzzo-Jones, G., and Koedinger, K. R. (2006).
The assistment builder: Towards an analysis of cost
effectiveness of its creation. In Flairs Conference,
pages 515–520.
Jordan, P., Ros
´
e, C. P., and VanLehn, K. (2001). Tools for
authoring tutorial dialogue knowledge. In Proceed-
ings of AI in Education 2001 Conference.
Experiments with Auto-generated Socratic Dialogue for Source Code Understanding
43

Jurafsky, D. and Martin, J. H. (2008). Speech and lan-
guage processing: An introduction to speech recog-
nition, computational linguistics and natural language
processing. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Khayi, N. A. and Rus, V. (2019). Bi-gru capsule networks
for student answers assessment. In 2019 KDD Work-
shop on Deep Learning for Education (DL4Ed).
Marx, J. D. and Cummings, K. (2007). Normalized change.
American Journal of Physics, 75(1):87–91.
Pennington, N. (1987). Stimulus structures and mental
representations in expert comprehension of computer
programs. Cognitive psychology, 19(3):295–341.
Person, N., Lehman, B., and Ozbun, R. (2007). Pedagog-
ical and motivational dialogue moves used by expert
tutors. In 17th Annual Meeting of the Society for Text
and Discourse. Glasgow, Scotland.
Pillay, N. (2003). Developing intelligent programming tu-
tors for novice programmers. ACM SIGCSE Bulletin,
35(2):78–82.
Ros
´
e, C. P., Moore, J. D., VanLehn, K., and Allbritton, D.
(2001). A comparative evaluation of socratic versus
didactic tutoring. In Proceedings of the Annual Meet-
ing of the Cognitive Science Society, volume 23.
Schulte, C., Clear, T., Taherkhani, A., Busjahn, T., and Pa-
terson, J. H. (2010). An introduction to program com-
prehension for computer science educators. In Pro-
ceedings of the 2010 ITiCSE working group reports,
pages 65–86.
Sottilare, R. A. and Holden, H. K. (2013). Motivations for
a generalized intelligent framework for tutoring (gift)
for authoring, instruction and analysis. In AIED 2013
Workshops Proceedings, volume 7, page 1.
Vanlehn, K. (2006). The behavior of tutoring systems. In-
ternational journal of artificial intelligence in educa-
tion, 16(3):227–265.
VanLehn, K., Graesser, A. C., Jackson, G. T., Jordan, P.,
Olney, A., and Ros
´
e, C. P. (2007). When are tutorial
dialogues more effective than reading? Cognitive sci-
ence, 31(1):3–62.
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
44
