
Creative Writing Web Site 3.0 for 3rd Year General Education
Students
Daniela Michelle Vilatuña Alomoto
1a
, Paúl Francisco Baldeón Egas
2b
, Norma Molina Prendes
2c
and Ernesto Fernández Rivero
2d
1
Fundación Caminitos de Luz, Escuela María Troncatti, Quito, Ecuador
2
Universidad Tecnológica Israel, Quito, Ecuador
Keywords: Creative Writing, Significant Learning, Web 3.0, Information and Communication Technologies (ICT).
Abstract: This work is the basis of a web 3.0 site to contribute to the process of Teaching and Learning of creative
writing of third year students of Basic General Education of the "María Troncatti" school, Quito, Ecuador;
which allows the student the use of web 2.0 tools, the integration of Google Classroom as a learning manager.
Each academic block in the web 3.0 site develops communication skills for creative writing, in which the
teacher can work processes of expression, communication and creation with students, awakening from the
beginning the intrinsic motivation in the student through questions that generate both curiosity to learn and
innovate. The proposal was evaluated by specialists with good results in a general sense.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of science and information and
communication technologies has marked important
changes in the present; this affects education and, of
course, culture, and at the same time demands a
different view of the teaching-learning process within
educational institutions; where the student must
assume a leading role and develop skills oriented to
the 21st century as demanded by UNESCO, where the
development of the ability to "learn to learn" as its
essence requires, integrating, motivating and flexible
contents (UNESCO, 2017).
The teacher, in turn, becomes a mediator of the
teaching and learning process by supporting student
collaboration and participation, thus promoting
meaningful learning and active assessment.
The 21st century and ICTs have transformed
several concepts in society, so it is important to
develop skills that cover new needs such as creativity
and innovation because both skills have allowed the
human being throughout history to adapt and survive
in the face of new changes.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5288-1992
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8939-8964
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9589-3723
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6954-7042
Multiple studies refer to what to understand by
creativity; even theories about creativity have been
developed; some circumscribe it to the ability to
connect ideas, establish original thoughts or
transgress the known, cross limits, break schemes or
the pre-established (Bellón, 2012). It has also been
linked to art, literature, music, science, and even
education (Chacón, 2005). This term has even been
associated with people with certain skills. The truth is
that creativity is one of the essential qualities to
develop in children and young people through
education and has become one of the main challenges
for teachers.
This research assumes the criteria that value the
importance of developing creativity in students and
how this depends on "creative teaching action driven
by the teacher", where the methods, the classroom
organization take a relevant role (Summo, Voisin, &
Téllez-Méndez, 2016). Following these criteria and
given the technological development and the
educational aspirations described above, in the
present research, technological and educational
strategies are designed to promote the development of
creative writing in children in the third year of
192
Vilatuña Alomoto, D., Baldeón Egas, P., Molina Prendes, N. and Fernández Rivero, E.
Creative Writing Web Site 3.0 for 3rd Year General Education Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0010407901920199
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2021) - Volume 2, pages 192-199
ISBN: 978-989-758-502-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

General Basic Education, through the use of a 3.0
JIMDO website, emphasizing the Significant
Learning Process (SLP).
UNESCO in 2013 considers the use of ICTs as a
gateway to a process of quality teaching and learning,
allowing the professional development of teachers
through the acquisition of knowledge and
information, management, direction and
administration of an education system.
On the other hand, the Ministry of Education in
Ecuador, has recognized the great development of
new information technologies and education (ICT) in
the country and has encouraged the development of
new teaching strategies, as these enrich the learning
processes and facilitate the exchange between
students in virtual contexts and of course, allows the
development of oral and written communication
skills, as well as the ability to make decisions, work
collaboratively and self-learning in the exploration
and search for information on the Internet for
educational purposes (MinEduc, 2019).
The prominent researcher, precursor of Soviet
neuropsychology Lev Semionovich Vygotsky,
addressed the close link between thought and
language, since: "thought is not simply expressed in
words, but exists through them". (Rodriguez, 2018)
and argued that writing was the main vehicle for
communication and information exchange, as it went
beyond simple motor skills.
In this way, learning to read and write allows the
human being to develop a series of skills and abilities
that are indispensable in the social, academic and
work development of the human being, defining
writing as a social fact par excellence.
Faced with a time of great technological change, it
is important to generate links that motivate affective
communication, whether oral or written, decision
making, the development of critical thinking and
empowerment, because we face challenges that require
creative solutions. However, it is important to take
advantage of the potential of the use of technological
tools that encourage creativity in students, so that if we
educate in creativity we direct the student to discover
new ways of finding solutions, the ability to choose
between various options and innovation.
This means that the use of ICT within the process
of teaching and learning is increasingly necessary
particularly for reading and writing, as it becomes a
complement to the printed text and therefore can
contribute to the SLP of creative writing.
The research was developed in the third-year
classroom of Basic General Education of the María
Troncatti school in the city of Quito, Ecuador; whose
general objective was to develop a 3.0 website to
contribute to the process of Teaching Learning of
creative writing of students.
2 GENERAL
CONTEXTUALIZATION OF
ART
The present research starts from theoretical
conceptions about the object of study such as: main
concepts, theoretical sources consulted and other
similar research that seeks to support the
investigation.
Nowadays, "the technological era" has been
synonymous with new challenges and innovation in
educational solutions, which has allowed the human
being to develop countless skills of the 21st century,
based also on philosophical, methodological and
pedagogical foundations that allow us to get involved
in a process of teaching and learning. The following
is a summary of the theoretical foundations that serve
as a basis for the development of the project:
2.1 Applied Theoretical Foundations
The website 3.0 is based on the exposition of the
articulation of three components of the Pedagogical
Model mediated by ICT.
2.2 Theoretical Component
The research assumes as a theoretical component to
constructivism and connectivism.
2.2.1 Constructivism
The constructivist approach in the teaching-learning
process proposes to be a path where the teacher stops
being the only channel of knowledge transmission
and becomes a learning mediator. It is based on Jean
Piaget's theory, who talks about the development of
differentiated cognitive learning in different learning
stages where the construction of knowledge is
continuous, focusing in this way on the way a child
learns. Important are the Piagetian conceptions in
terms of conceiving the acquisition of knowledge
through a dynamic and not static relationship between
the individual and the object;
since the active subject interprets the information of
the environment, from previous knowledge and from
what has been acquired, reconstructs, restructures and
transcends it.
Creative Writing Web Site 3.0 for 3rd Year General Education Students
193

In the same way we mention Ausubel's Significant
Learning, which sustains as significant learning the
relationship of previous knowledge with the
acquisition of new concepts (Larios, 2018).
Constructivism as a reaction to traditional
conceptions of learning, where the student passively
receives the knowledge transmitted by the teacher,
supports the need to learn and is linked to the
development of creativity, in this sense Rodriguez
Ramirez et al, refer that "you cannot think of
constructivism without linking it to critical thinking,
since this can be produced through experiences of
students' lives located (Ramirez & Trejo, 2018). The
individual acquires his own learning in an active and not
passive way which allows to propitiate a significant
learning where the previous learning plays an important
role in order to achieve cognitive structures. Add to this
Vygotsky's contributions about the importance of the
"specific socio-cultural and historical context that gives
meaning" (Castellaro, 2012).
2.2.2 Connectivism
Currently one of the main objectives in education is
focused on improving the processes of teaching,
learning, connectivity, innovation and criticality.
On the other hand, UNESCO considers ICTs as a
source of information that allows users to
complement, enrich and transform their teaching and
learning process (UNESCO, undated).
For this reason, the connectivism of George
Siemens as a representative is considered as a
theoretical approach for the present investigation, this
theory generates a representative impact in the
process of learning, discovery and communication.
According to Siemens (2004; 2006) defines
connectivism as a continuous learning process that
occurs in the midst of various changing elements
through ICT. According to Siemens "Learning
(defined as actionable knowledge) can reside outside
of ourselves" (Siemens, 2004); which means that
connectivism is about managing knowledge and
connecting with people.
In view of the mentioned, the technological
advances, the incidence in the use of the ICT to
promote the SAP, the importance of considering the
connectivism as a learning theory in the present
investigation can be identified.
2.3 Methodological Component
The resources and forms that the teacher uses for the
process of teaching and learning, is thus structurally
based on PACIE, pedagogically FONTÁN.
2.3.1 PACIE
PACIE is considered the methodology that is applied
in a virtual learning environment and that contributes
"to achieve the objectives of the teaching-learning
process through the incorporation of ICT in a gradual
and reflexive way" (Basantes & Ojeda, 2018).
2.3.2 FONTÁN
Fontán's relational education is based on the student's
self-learning, respecting his work rhythm, developing
intellectual, personal, social and emotional
competences important for his integral development.
FONTÁN education also aims to develop
important skills so that each individual can develop
their maximum potential, improving their quality of
life through the following principles: each person is
an author, an actor and is unique and diverse.
Julio Fontán, in an interview with the media,
mentions that one of the basic principles of the
methodology mentions the student as the main author
of his own life, which allows him to set goals and
achieve them in a natural way, in this way his
educational process is much more significant
(Fontan, 2017).
Students describe the construction of meaning in
what they learn by allowing them to develop
criticality, work discipline in decision making, goal
planning and time management.
FONTÁN Education handles as planning
"Learning Guides", based on 4 moments of learning
as:
Starting Point: It is the initial stage of the
process, the objective is to remember the things that
the student already knows from his daily experience,
considered as a trigger activity that allows to identify
previous knowledge.
Research: In this stage, relationships are
established between previous knowledge and new
knowledge, thus influencing the PAS, giving
meaning to what we want to investigate, considered
as a stage of thought, students usually use thought
maps and graphic organizers.
Skill Development: In this stage the student will
put into practice what he or she learned in the thinking
stage, his or her objective is to test his or her learning
through any type of action.
Relationship: It is the final stage of the process,
its objective is to reflect on what has been learned and
put it into practice in its own context and other topics,
it is important to reflect on what this knowledge is for
and how I can apply it in my daily life and
environment.
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
194
Writing and creativity have helped humans adapt
to change and progress by putting both hemispheres
of the brain to work, learning to recognize and
transform concerns, memories and moments.
It is taken into consideration to carry out the
development of creative writing through the use of
FONTÁN methodology in three areas:
Table 1: Academic blocks.
Development of
creativity
It is proposed to work on
self-identification, to
encourage the habit of
readin
g
.
The writer's work The student has the
opportunity to have
experiences that allow
inspiration and creative
b
locka
g
e to work.
Fiction Genres Allows the student to
understand literary
relationships such as the
story
2.4 Practical Component
It is proposed to use techno-educational strategies that
allow to achieve the desired objective.
The project was based on the very demands of the
world context characterized by great technological
changes that require a different look at the teaching-
learning process; where it is important to generate
links that motivate emotional communication,
whether oral or written, decision-making, the
development of critical thinking, empowerment and
creative solutions. In the María Trocatti educational
unit in the city of Quito, Ecuador, there are great
potentialities for the use of ICT, given the
technological equipment, distributed in three
laboratories that need to be used more in classes. On
the other hand, students are highly motivated by the
use of technology and all have access to ICT outside
the institution, which facilitates the development of
virtual activities that, with the development of virtual
activities due to the Pandemic, as it increased the
relevance of the Project.
Now, on the other hand, it is important to take
advantage of the potential of the use of technological
tools that promote creativity in students, so that if we
educate in creativity we direct the student to discover
new ways of finding solutions, the ability to choose
between several options and innovation.
Said aspirations and potentialities of the
educational context contrast with the reality within
the classrooms, where traditional learning
conceptions are assumed; especially in Language and
Literature classes, making this process monotonous
and not very motivating for the student, specifically
in the writing process.
2.4.1 Techno-educational Strategies
The techno-educational strategies aim to influence
the teaching and learning process through the
integration of ICT, with the objective of improving
the Significant Learning Process (SAP) by generating
motivation and interaction between the teacher and
the student who are the main actors.
It is worth mentioning that the acquisition of
learning changes according to the person, since there
are people who learn with practice, others in a visual,
auditory way, etc. Therefore, the following is a list of
techno-educational strategies that are best adapted to
the Significant Learning Process of creative writing
by third-year students in Basic General Education.
Table 2: Learning strategies.
Learnin
g
strate
gy
Descri
p
tion
Surprising questions consists of elaborating a
series of surprise
questions so that the
student can respond
quickly and
automaticall
y
.
Fantastic Binomial Create a story from two
words.
Description Generate characteristics
of an ob
j
ect
Antidescription From own characteristics
use anton
y
ms.
Deformed Words Create words from your
imagination
Discussion forums Discussions
Incomplete ends create endings from your
ima
g
ination and creativit
y
Storytelling Listening to stories,
imagining them to
recreate the
m
Impossible headlines Create stories from
headlines or fantas
y
tales
What would happen if? Building stories from
fictional questions
3 PROPOSAL
The research aims to develop an interactive website
3.0 for creative writing, for this reason JIMDO was
selected as a website focused on learning, based on
the concept of Web 3.0 (Semantic), where embedded
code is used for insertion into the website and Google
Creative Writing Web Site 3.0 for 3rd Year General Education Students
195
Classroom, based on the concept of bringing together
conceptually in one place, allowing the
implementation of activities and resources of
technological tools 2. 0 (social collaborative web),
where there is bidirectional interactivity between the
student and the teacher; in addition to the articulation
with Google Classroom as a Learning Management
System, where the learning process is complemented
through the monitoring of the student's participatory
evaluation and feedback.
The website is public and can be accessed through
the following link: https://dmvilatuna-
digital.jimdofree.com.
3.1 General Structure
The general structure of this research is based on the
PACIE and FONTAN methodology, in which there
are three blocks: zero block, academic blocks and
closing block. This structure establishes the exchange
of information in a dynamic and interactive way, in
addition to developing students' digital competencies,
autonomy in learning and the fulfillment of
objectives.
Each section has a strategic name that motivates
and empowers students to carry out activities that
allow them to develop their learning process.
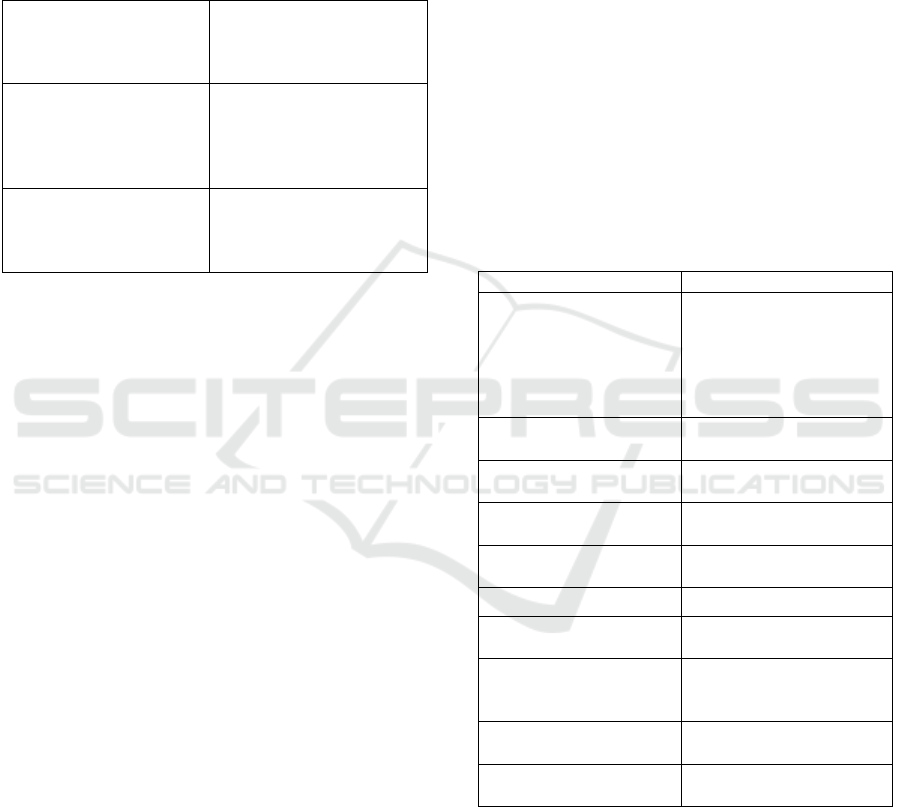
Figure 1: General structure.
3.1.1 Zero Block or PACIE
PACIE is the result of sequential processes such as
Presence: Motivating structure for the student
Scope: Objectives to be achieved
Training: Development of the Teaching and
Learning Process
Interaction: Resource and collaborative work
activities
Elearning: Use of ICT in the SLP
Figure 2: JIMDO and GOOGLE CLASSROOM zero block.
3.1.2 Academic Block
Each academic block will be executed weekly
through the application of FONTÁN methodology.
Figure 3: Academic block 1.
The following is the matrix of the articulation of
the product made with the theoretical,
methodological and technological supports of
academic block 1 - Writing about us. We identify:
● A: resources
● AA: asynchronous activity
● AS: synchronous activity
● Q: presentations
● OG: graphic organizers
● A: resources
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
196
● E: evaluation
● S: simulator
● I: interaction
● Or: others
Figure 4: Academic Block Articulation Matrix 1.
As an example, the figure of an academic block of
the topic Development of Creativity is presented.
Figure 5: Example of an academic block.
3.1.3 Integrator Project
In the last block, according to the methodologies
applied, an integrative project was developed in
which the Web site developed in JIMDO is
articulated with the learning management system
Google Classroom, where the learning process is
complemented with evaluation and feedback, based
on interactive and dynamic activities.
In general terms, if we exemplify a class in three
phases: introduction, where the motivation is made
and the objectives set for the class are presented;
development, the activities according to the techno-
educational strategies; and, the closing, where the
evaluation or verification of knowledge and its
respective feedback is made. Phases one and two are
developed with the support of the web site and phase
three in the learning management system.
The link to Google Classroom for the last phase is
available on the website in each academic block.
Figure 6: The Integrator Project.
4 EVALUATION BY
SPECIALISTS
The proposal was submitted for consideration by
specialists with a scale of values: Excellent, Very
Good, Good, Fair and Deficient; the indicators for
evaluation were the following: level of operation,
communication, educational impact, thematic
coherence and design.
To determine the specialists, the following
indicators were established:
● Be a graduate of the specialty of Language and
Literature.
● Have a master's or doctorate.
● Have at least 5 years of experience in the
exercise of the profession.
● Have carried out research related to
educational ICT.
Creative Writing Web Site 3.0 for 3rd Year General Education Students
197
The proposal was evaluated by 15 specialists, to
whom the proposal was given, as well as a guide for
its evaluation.
The assessment made by specialists using the
Delphi method and the results obtained in table 4
which are the indicators by category. This is how the
cut-off points obtained confirm that the indicators are
in the range of "Excellent".
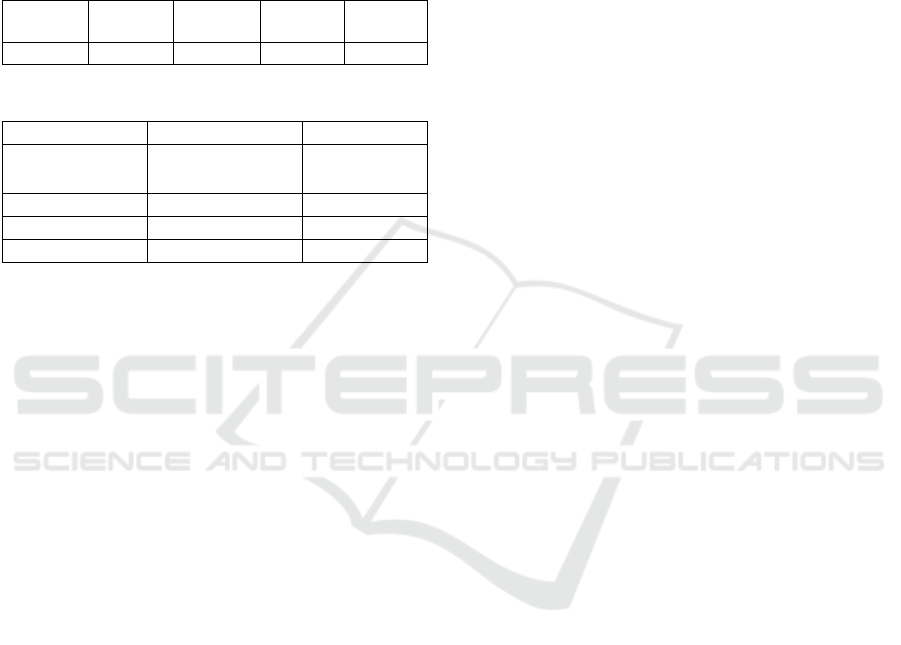
Table 3: Cutting point table.
Excellent Very
Ade
q
uate
Adequate Regular Deficien
t
1,61948 2,69692 3,49 3,49
Table 4: Results of the assessment.
Indicators N-P Category
1 -0,86214037
Very suitable
2 -0,86214037 Very suitable
3 -0,45178944 Very suitable
4 -0,45178944 Very suitable
Therefore, it can be said that the virtual
environment design in Jimdo for the creative reading
process is possible to implement it in the educational
context.
5 COPYRIGHT FORM
The copyright of this project is held by the authors
and the companies Jimdo and Google through two
types of license, which the Jimdo website belongs to
the same company and the content being a public
space is through Creative Commons, where it can be
used freely for non-commercial purposes. The access
to the content of the virtual classroom of the learning
management system Google Classroom is under
approval of the authors and was made privately for
the group of students who are part of the project, and
being part of the Google company, the copyright
belongs to them.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The proposal is theoretically based on constructivism
and connectivism, which allows the student to
participate in his/her learning through the use of
technological tools, improving his/her level of
understanding and communication of verbal and
written language, allowing the development of a
creative language through the use of ICT.
The adequate use and participation of ICT within
the teaching-learning process is evident, as well as the
access to technological resources of both students and
language and literature teachers, which allows
determining the necessary conditions for the use of a
3.0 website that contributes to the teaching-learning
process of creative writing.
The design of the JIMDO virtual environment
facilitates the process of teaching and learning
creative writing, developing cognitive skills such as
memory and perception, as well as affective and
social skills that allow students to relate to the
environment and provide creative and innovative
solutions.
The evaluation by specialists through the Delphi
method was able to determine that the use of the
interactive website 3.0 is feasible for its execution.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
If any, should be placed before the references section
without numbering.
REFERENCES
Basantes, A., & Ojeda, M. E. (2018). PACIE Methodology
in Virtual Education: an experience at the Universidad
Técnica del Norte. Formación universitaria, 11(2), 35-
44. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0718-
50062018000200035
Bellón, F. M. (2012). DARE TO BE CREATIVE: STEPS
TO BE CREATIVE. Iberoamerican Journal on
Quality, Effectiveness and Change in Education, 10(2),
248-263. Retrieved November 6, 2020, from
https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/551/55124596017.pd
Castellaro, M. A. (2012). Theoretical definitions and areas
of research proposed from constructivism, in Latin
American publications of psychology and education
present in the REDALYC database. Liberabit, 18(2),
131-146. Retrieved from
http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext
&pid=S1729-48272012000200004&lng=es&tlng=es.
Chacón, Y. (2005). A critical review of the concept of
creativity. Actualidades Investigativas en Educación,
5(1). Retrieved November 6, 2020, from
https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/447/44750106.pdf.
Fontán, J. (21 of 01 of 2017). Education FONTÁN. (R.
Roldan, Interviewer)
Larios, B. (2018). Significant Learning. Reista
Internacional del Magisterio , 18- 22.
MinEducation (2019). Program of Continuous Training of
the Fiscal Teaching Profession Information and
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
198

Communication Technologies applied to education.
Quito: MinEDuc. Retrieved from
https://educacion.gob.ec/wp-content/uploads/
downloads/2013/03/SiProfe-TIC-aplicadas.pdf
Ramirez, N. E., & Trejo, M. D. (2018). Constructivist
learning environments as an alternative to generate
innovation in the university. International Journal of
Information Systems and Software Engineering for Big
Companies (IJISEBC), 41-52. Retrieved from
http://uajournals.com/ojs/index.php/ijisebc/article/vie
w/397/293
Rodríguez, C. (2018). Contemporary problems in
educational psychology. Colombia: La Sabana
University. Retrieved from
https://elibro.net/es/ereader/uisrael/116742?page=34.
Siemens, G. (2004). Connectivism: a learning theory for the
digital age. International Journal of Instructional
Technology & Distance Learning, 2(1), 1-8. Obtenido
de http://www.itdl.org/Journal/Jan_05/article01.htm
Summo, V., Voisin, S., & Téllez-Méndez, B.-A. (2016).
Creativity: axis of education in the 21st century. Revista
iberoamericana de educación superior, 7(18), 83-98.
Retrieved November 6, 2020, from
http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext
&pid=S2007-28722016000100083&lng=es&tlng=es.
UNESCO. (2017). E2030: Education and Skills for the 21st
Century. Retrieved from http://www.unesco.org/new/
fileadmin/MULTIMEDIA/FIELD/Santiago/pdf/Habili
ties-SXXI-Buenos-Aires-Spa.pdf
UNESCO. (undated). ICT in Education. Retrieved from
unesco.org: https://es.unesco.org/themes/tic-educacion
Vilatuña, D. (09 de 2020). Web site 3.0 of creative writing
for third year students of General Education. Obtained
from Digital Repository University Israel:
http://repositorio.uisrael.edu.ec/bitstream/47000/2661/
1/UISRAEL-EC-MASTER-EDUC-378.242-2020-
134.pdf
Creative Writing Web Site 3.0 for 3rd Year General Education Students
199
