
Malware Classification with GMM-HMM Models
Jing Zhao
a
, Samanvitha Basole
b
and Mark Stamp
c
Department of Computer Science, San Jose State University, San Jose, California, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Hidden Markov Model, HMM, Gaussian Mixture Model, GMM-HMM, Malware.
Abstract:
Discrete hidden Markov models (HMM) are often applied to malware detection and classification problems.
However, the continuous analog of discrete HMMs, that is, Gaussian mixture model-HMMs (GMM-HMM),
are rarely considered in the field of cybersecurity. In this paper, we use GMM-HMMs for malware classifi-
cation and we compare our results to those obtained using discrete HMMs. As features, we consider opcode
sequences and entropy-based sequences. For our opcode features, GMM-HMMs produce results that are
comparable to those obtained using discrete HMMs, whereas for our entropy-based features, GMM-HMMs
generally improve significantly on the classification results that we have achieved with discrete HMMs.
1 INTRODUCTION
Due to COVID-19, businesses and schools have
moved their work online and some consider the possi-
bility of going online permanently. This trend makes
cybersecurity more important than ever before.
Malicious software, or malware, is designed to
steal private information, delete sensitive data with-
out consent, or otherwise disrupt computer sys-
tems. The study of malware has been active for
decades (Milosevic, 2013). Malware detection and
classification are fundamental research topics in mal-
ware. Traditionally, signature detection has been the
most prevalent method for detecting malware, but re-
cently, machine learning techniques have proven their
worth, especially for dealing with advanced types of
malware. Many machine learning approaches have
been applied to the malware problem, including hid-
den Markov models (HMM) (Stamp, 2018), k-nearest
neighbors (KNN) (Ben Abdel Ouahab et al., 2020),
support vector machines (SVM) (Kruczkowski and
Szynkiewicz, 2014), and a wide variety of neural net-
working and deep learning techniques (Kalash et al.,
2018).
Each machine learning technique has its own ad-
vantages and disadvantages. It is not the case that one
technique is best for all circumstances, since there are
many different types of malware and many different
features that can be considered. Thus, it is useful to
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3182-4136
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9806-3311
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3803-8368
explore different techniques and algorithms in an ef-
fort to extend our knowledge base for effectively deal-
ing with malware. In this paper, we focus on Gaus-
sian mixture model-hidden Markov models (GMM-
HMMs), which can be viewed as the continuous ana-
log of the ever-popular discrete HMM.
Discrete HMMs are well known for their ability to
learn important statistical properties from a sequence
of observations. For a sequence of discrete observa-
tions, such as the letters that comprise a selection of
English text, we can train a discrete HMM to deter-
mine the parameters of the (discrete) probability dis-
tributions that underlie the training data. However,
some observation sequences are inherently continu-
ous, such as signals extracted from speech. In such
cases, a discrete HMM is not the ideal tool. While
we can discretize a continuous signal, there will be
some loss of information. As an alternative to dis-
cretization, we can attempt to model the continuous
probability density functions that underlie continuous
training data.
Gaussian mixture models (GMM) are probabil-
ity density functions that are represented by weighted
sums of Gaussian distributions (Reynolds, 2015). By
varying the number of Gaussian components and
the weight assigned to each, GMMs can effectively
model a wide variety of continuous probability dis-
tributions. It is possible to train HMMs to learn the
parameters of GMMs, and the resulting GMM-HMM
models are frequently used in speech recognition (Ra-
biner, 1989; Bansal et al., 2008), among many other
applications.
Zhao, J., Basole, S. and Stamp, M.
Malware Classification with GMM-HMM Models.
DOI: 10.5220/0010409907530762
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2021), pages 753-762
ISBN: 978-989-758-491-6
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
753

In the field of cybersecurity, GMMs have been
used, for example, as a clustering method for malware
classification (Interrante-Grant and Kaeli, 2018).
However, to the best of our knowledge, GMM-HMMs
are not frequently considered in the context of mal-
ware detection or classification. In this paper, we ap-
ply GMM-HMMs to the malware classification prob-
lem, and we compare our results to discrete HMMs.
Our results indicate that GMM-HMMs applied to
continuous data can yield strong results in the mal-
ware domain.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows. In Chapter 2, we discuss relevant related work.
Chapter 3 provides background on the various mod-
els considered, namely, GMMs, HMMs, and GMM-
HMMs, with the emphasis on the latter. Malware
classification experiments and results based on dis-
crete features are discussed in Chapter 4. Since
GMM-HMMs are more suitable for continuous ob-
servations, in Chapter 4 we also present a set of mal-
ware classification experiments based on continuous
entropy features. We conclude the paper and provide
possible directions for future work in Chapter 5.
2 RELATED WORK
A Gaussian mixture model (GMM) is a probability
density model (McLachlan and Peel, 2004) consist-
ing of a weighted sum of multiple Gaussian distribu-
tions. The advantage of a Gaussian mixture is that it
can accurately model a variety of probability distribu-
tions (Gao et al., 2020). That is, a GMM enables us to
model a much more general distribution, as compared
to a single Gaussian. Although the underlying distri-
bution may not be similar to a Guassian, the combi-
nation of several Gaussians yields a robust model (Al-
fakih et al., 2020). However, the more Gaussians that
comprise a model, the costly the calculation involving
the model.
One example of the use of GMMs is distribution
estimation of wave elevation in the field of oceanogra-
phy (Gao et al., 2020). GMMs have also been used in
the fields of anomaly detection (Chen and Wu, 2019),
and signal mapping (Raitoharju et al., 2020). As an-
other example, in (Qiao et al., 2019), a GMM is used
as a classification method to segment brain lesions. In
addition to distribution estimation, GMMs form the
basis for a clustering method in (Gallop, 2006).
As the name suggests, a discrete hidden Markov
model (HMM) includes a “hidden” Markov process
and a series of observations that are probabilistically
related to the hidden states. An HMM can be trained
based on an observation sequence, and the result-
ing model can be used to score other observation se-
quences. HMMs have found widespread use in signal
processing, and HMMs are particularly popular in the
area of speech recognition (Guoning Hu and DeLiang
Wang, 2004). Due to their robustness and the effi-
ciency, HMMs are also widely used in medical ar-
eas, such as sepsis detection (Stanculescu et al., 2014)
and human brain studies based on functional mag-
netic resonance imaging (Dang et al., 2017). Motion
recognition is another area where HMMs play a vi-
tal role; specific examples include recognizing danc-
ing moves (Laraba and Tilmanne, 2016) and 3D ges-
tures (Truong and Zaharia, 2017).
Gaussian mixture model-HMMs (GMM-HMM)
are also widely used in classification problems. Given
the flexibility of GMMs, GMM-HMMs are pop-
ular for dealing with complex patterns underlying
sequences of observations. For example, Yao et
al. (Yao et al., 2020) use GMM-HMMs to clas-
sify network traffic from different protocols. GMM-
HMMs have also been used in motion detection—
for complex poses, GMM-HMMs outperform dis-
crete HMMs (Zhang et al., 2020).
3 BACKGROUND
In this section, we first introduce the learning tech-
niques used in this paper—specifically, we dis-
cuss Gaussian mixture models, HMMs, and GMM-
HMMs. We then discuss GMM-HMMs in somewhat
more detail, including various training and parameter
selection issues, and we provide an illustrative exam-
ple of GMM-HMM training.
3.1 Gaussian Mixture Models
As mentioned above, a GMM is a probabilistic model
that combines multiple Gaussian distributions. Math-
ematically, the probability density function of a GMM
is a weighted sum of M Gaussian probability density
functions. The formulation of a GMM can be written
as (Fraley and Raftery, 2002)
P(x |λ) =
M
∑
x=i
ω
i
g(x |µ
i
, Σ
i
),
where x is a D-dimensional vector and ω
i
is the weight
assigned to the i
th
Gaussian component, with the mix-
ture weights summing to one. Here, µ
i
and Σ
i
are
the mean and the covariance matrix of the i
th
com-
ponent of the GMM, respectively. Each component
of a GMM is a multivariate Gaussian distribution of
ForSE 2021 - 5th International Workshop on FORmal methods for Security Engineering
754

the form
g(x |µ
i
, Σ
i
) =
1
(2π)
D
2
|Σ
i
|
1
2
e
−
1
2
(x−µ
i
)
0
Σ
−1
i
(x−µ
i
)
.
3.2 Discrete HMM
In this paper, we use the notation in Table 1 to de-
scribe a discrete HMM. This notation is essentially
the same as that given in (Stamp, 2018). An HMM,
which we denote as λ, is defined by the matrices A, B,
and π, and hence we have λ = (A, B, π).
Table 1: Discrete HMM notation.
Notation Explanation
T Length of the observation sequence
O Observation sequence, O
0
, O
1
, . . . , O
T −1
N Number of states in the model
K Number of distinct observation symbols
Q Distinct states of the Markov process, q
0
, q
1
, . . . , q
N−1
V Observable symbols, assumed to be 0, 1, . . . , K − 1
π Initial state distribution, 1 × N
A State transition probabilities, N × N
B Observation probability matrix, N × K
We denote the elements in row i and column j of A
as a
i j
. The element a
i j
of the A matrix is given by
a
i j
= P(state q
j
at t +1 | state q
i
at t).
The (i, j) element of B is denoted in a slightly un-
usual form as b
i
( j). In a discrete HMM, row i of B
represents the (discrete) probability distribution of the
observation symbols when underlying Markov pro-
cess is in (hidden) state i. Specifically, each element
of B = {b
i
( j)} matrix is given by
b
i
( j) = P(observation j at t | state q
i
at t).
The HMM formulation can be used to is solve the
following three problems (Stamp, 2018).
1. Given an observation sequence O and a model λ
of the form λ = (π, A, B), calculate the probability
of the observation sequence. That is, we can score
an observation sequence against a given model.
2. Given a model λ = (π, A, B) and an observation
sequence O, find the “best” state sequence, where
best is defined to be the sequence that maximizes
the expected number of correct states. That is, we
can uncover the hidden state sequence.
3. Given an observation sequence O, determine a
model λ = (A, B, π) that maximizes P(O |λ). That
is, we can train a model for a given observation
sequence.
In this research, we are interested in problems 1 and 3.
Specifically, we train models, then we test the result-
ing models by scoring observation sequences. The
solution to problem 2 is of interest in various NLP
applications, for example. For the sake of brevity,
we omit the details of training and scoring with dis-
crete HMMs; see (Stamp, 2018) or (Rabiner, 1989)
for more information.
3.3 GMM-HMM
The structure of a GMM-HMM is similar to that of
a discrete HMM. However, in a GMM-HMM, the B
matrix is much different, since we are dealing with a
mixture of (continuous) Gaussian distributions, rather
than the discrete probability distributions a discrete
HMM. In a GMM-HMM, the probability of an ob-
servation at a given state is determined by a prob-
ability density function that is defined by a GMM.
Specifically, the probability density function of obser-
vation O
t
when the model is in state i is given by
P
i
(O
t
) =
M
∑
m=1
c
im
g(O
t
|µ
im
, Σ
im
), (1)
for i ∈ {1, 2, . . . , N} and t ∈ {0, 1, . . . , T − 1, where
M
∑
m=1
c
im
= 1 for i ∈ {1, 2, . . . , N}.
Here, M is the number of Gaussian mixtures com-
ponents, c
im
is the mixture coefficient or the weight
of m
th
Gaussian mixture at state i, while µ
im
and Σ
im
are the mean vector and covariance matrix for the m
th
Gaussian mixture at state i. We can rewrite g in equa-
tion (1) as
g(O
t
|µ
im
, Σ
im
) =
1
(2π)
D
2
|Σ
im
|
1
2
e
−
1
2
(O
t
−µ
im
)
0
Σ
−1
im
(O
t
−µ
im
)
,
where D is the dimension of each observation. In a
GMM-HMM, the A and π matrices are the same as in
a discrete HMM.
The notation for a GMM-HMM is given in
Table 2. This is inherently more complex than a dis-
crete HMM, due to the presence of the M Gaussian
distributions. Note that a GMM-HMM is defined by
the 5-tuple
λ = (A, π, c, µ, Σ).
Analogous to a discrete HMM, we can solve the same
three problems with a GMM-HMM. However, the
process used for training and scoring with a GMM-
HMM differ significantly as compared to a discrete
HMM.
3.4 GMM-HMM Training and Scoring
To use a GMM-HMM to classify malware samples,
we need to train a model, then use the resulting model
Malware Classification with GMM-HMM Models
755

Table 2: GMM-HMM notation.
Notation Explanation
T Length of the observation sequence
O Observation sequence, O
0
, O
1
, . . . , O
T −1
N Number of states in the model
M Number of Gaussian components
D Dimension of each observation
π Initial state distribution, 1 × N
A State transition matrix, N ×N
c Gaussian mixture weight at each state, N × M
µ Means of Gaussians at each state, N × M × D
Σ Covariance of Gaussian mixtures, N ×M × D × D
to score samples—see the discussion of problems 1
and 3 in Section 3.2, above. In this section, we discuss
scoring and training in the context of a GMM-HMM
in some detail. We begin with the simpler problem,
which is scoring.
3.4.1 GMM-HMM Scoring
Given a GMM-HMM, which is defined by the 5-tuple
of matrices λ = (A, π, c, µ, Σ), and a sequence of ob-
servations O = {O
0
, O
1
, . . . , O
T −1
}, we want to deter-
mine P(O |λ). The forward algorithm, which is also
known as the α-pass, can be used to efficiently com-
pute P(O |λ).
Analogous to a discrete HMM as discussed
in (Stamp, 2018), in the α-pass of a GMM-HMM, we
define
α
t
(i) = P(O
0
, O
1
, . . . , O
t
, x
t
= q
i
|λ),
that is, α
t
(i) is the probability of the partial sequence
of observation up to time t, ending in state q
i
at time t.
The desired probability is given by
P(O |λ) =
N−1
∑
i=0
α
T −1
(i).
The α
t
(i) can be computed recursively as
α
t
(i) =
N−1
∑
j=0
α
t−1
(i)a
ji
b
i
(O
t
). (2)
At time t = 0, from the definition it is clear that we
have α
0
(i) = π
i
b
i
(O
0
).
In a discrete HMM, b
i
(O
t
) gives the probability of
observing O
t
at time t when the underlying Markov
process is in state i. In a GMM-HMM, however,
simply replacing b
i
(O
t
) in (2) by the GMM pdf cor-
responds to a point value of a continuous distribu-
tion. To obtain the desired probability, as discussed
in (Nguyen, 2016), we must integrate over of a small
region around observation O
t
, that is, we compute
b
i
(O
t
) =
Z
O
t
+ε
O
t
−ε
p
i
(O
t
|θ
i
)dO, (3)
where θ
i
consists of the parameters c
i
, µ
i
and Σ
i
of the
GMM, and ε is a (small) range parameter.
3.4.2 GMM-HMM Training
The forward algorithm or α-pass calculates the prob-
ability of observing the sequence from the beginning
up to time t. There is an analogous backwards pass
or β-pass that calculates the probability of the tail of
the sequence, that is, the sequence from t + 1 to the
end. In the β-pass, we define
β
t
(i) = P(O
t+1
, O
t+2
, . . . , O
T −1
|x
i
= q
i
, λ).
The β
t
(i) can be compute recursively via
β
t
(i) =
N−1
∑
j=0
a
i j
b
j
(O
t
)β
t+1
( j)
where we the initialization is β
T −1
(i) = 1, which fol-
lows from the definition.
In a discrete HMM, to re-estimate the state transi-
tions in the A matrix, we first define
γ
t
(i, j) = P(x
t
= q
i
, x
t+1
= q
j
|O, λ)
which is the probability of being in state q
i
at time t
and transiting to state q
j
at time t + 1. Using
the α-pass and the β-pass, we can efficiently com-
pute γ
t
(i, j); see (Stamp, 2018) for the details. The
sum of these “di-gamma” values with respect to the
transiting states gives the probability of the obser-
vation being in state q
i
at time t, which we define
as γ
t
(i). That is,
γ
t
(i) =
N
∑
j=1
γ
t
(i, j).
Thus, we can re-estimate the elements of the A matrix
in a discrete HMM as
a
i j
=
T −2
∑
t=0
γ
t
(i, j)
T −2
∑
t=0
γ
t
(i)
To train a GMM-HMM, we use an analogous strategy
as that used for the discrete HMM. The GMM-HMM
analog of the di-gamma form is
γ
t
( j, k) = P(x
t
= q
j
|k, O, λ),
where t = 0, 1, . . . , T − 2, and j = 1, 2, . . . , N, and we
have k = 1, 2, . . . , M. Here, γ
t
( j, k) represents the
probability of being state q
j
at time t with respect
to the k
th
Gaussian mixture. According to (Rabiner,
1989), these γ
t
( j, k) are computed as
γ
t
( j, k) =
α
t
( j)β
t
( j)
N
∑
j=1
α
t
( j)β
t
( j)
·
c
jk
N(O
t
|µ
jk
, Σ
jk
)
M
∑
m=1
c
jm
N(O
t
|µ
jm
, Σ
jm
)
ForSE 2021 - 5th International Workshop on FORmal methods for Security Engineering
756
where the α
t
( j) and β
t
( j) are defined above, and c
jk
is the weight of the k
th
Gaussian mixture component.
The re-estimates for the weights c
jk
of the Gaus-
sian mixtures are given by
ˆc
jk
=
T −1
∑
t=0
γ
t
( j, k)
T −1
∑
t=0
M
∑
k=1
γ
t
( j, k)
, (4)
for j = 1, 2, . . . , N and k = 1, 2, . . . , M; see (Juang,
1985) and (Rabiner, 1989) for additional details. The
numerator in (4) can be interpreted as the expected
number of transitions from state q
j
as determined by
the k
th
Gaussian mixture while the denominator can
viewed as the expected transitions from state q
j
given
by the M Gaussian mixtures. Accordingly, the re-
estimation for µ
jk
and Σ
jk
are of the form
ˆµ
jk
=
T −1
∑
t=0
γ
t
( j, k)O
t
T −1
∑
t=0
γ
t
( j, k)
and
ˆ
Σ
jk
=
T −1
∑
t=0
γ
t
( j, k)(O
t
− µ
jk
)(O
t
− µ
jk
)
0
T −1
∑
t=0
γ
t
( j, k)
,
for i = 1, 2, . . . , N and k = 1, 2, . . . , M.
3.5 GMM-HMM Example
As an example to illustrate a GMM-HMM, we train
a model on English text, which is a classic exam-
ple for discrete HMMs (Cave and Neuwirth, 1980).
With N = 2 hidden states and M = 27 observation
symbols (corresponding the the 26 letters and word-
space), a discrete HMM trained on English text will
have one hidden state corresponding to consonants,
while the other hidden state corresponds to vowels.
That the model can make this key distinction is a good
example of learning, since a priori no information is
provided regarding the differences between the ob-
servations. We consider this same experiment using
a GMM-HMM to see how this model compares to a
discrete HMM.
The English training data is from the “Brown cor-
pus” (Brown Corpus of standard American English,
1961), and we convert all letters to lowercase and re-
move punctuation, numbers, and other special sym-
bols, leaving only 26 letters and word-spaces. For
our GMM-HMM training, we set N = 2, M = 6 (i.e.,
we have a mixture model consisting of 6 Gaussians)
Table 3: Mean of each Gaussian mixture in each state.
State
Gaussian
1 2 3 4 5 6
0 26.00 14.00 8.00 4.00 20.00 0.00
1 22.60 6.31 15.00 12.08 2.31 18.14
and T = 50000. The A matrix is N × N, π is 1 × N,
both of which are row stochastic, and initialized to ap-
proximately uniform. The parameter c represents the
weights of the mixture components and is initialized
with row stochastic values, also approximately uni-
form. We use the global mean value (i.e., the mean
of all observations) and global variance to initialize µ
and Σ. Note that each Gaussian is initialized with the
same mean and variance.
We train 100 of these GMM-HMM models, each
with different random initializations. As the obser-
vations are discrete symbols, the probability of each
observation in state i at time t is estimated by the prob-
ability density function. The best of the trained mod-
els clearly shows that the GMM-HMM technique is
able to successfully group the vowels into one state.
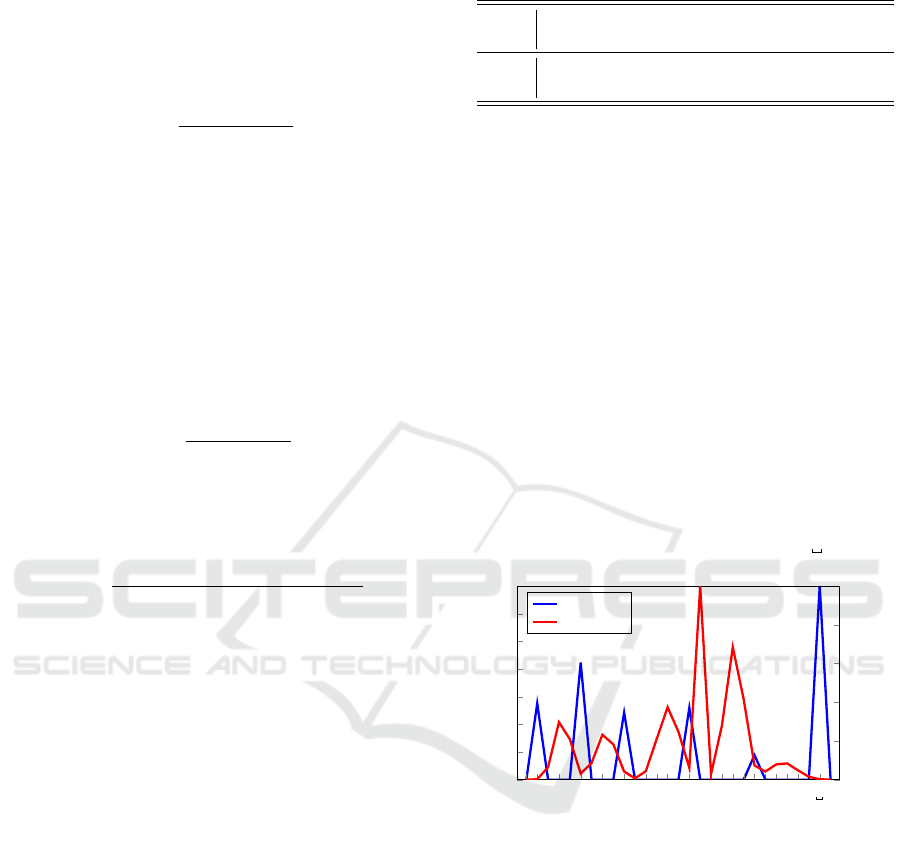
This can be seen from Figure 1. Note that in Figure 1,
word-space is represented by the symbol “ ”.
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
Gaussian 1
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
Gaussian 2
Gaussian 1
Gaussian 2
Figure 1: English letter distributions in each state.
Figure 1 clearly shows that all vowels (and word
space) belong to the first state. Table 3 lists the mean
value for each Gaussian mixture in the trained model.
The mean value of each Gaussian mixture component
corresponds to the encoded value of each observation
symbol.
In this example, since we know the number of
vowels beforehand, we have set the number of Gaus-
sian mixture components to 6 (i.e., 5 vowels and
word-space). In practice, we generally do not know
the true number of hidden states, in which case we
would need to experiment with different numbers of
Gaussians. In general, machine learning and deep
learning requires a significant degree of experimen-
tation, so it is not surprising that we might need to
fine tune our models.
Malware Classification with GMM-HMM Models
757

Table 4: Number of samples in each malware family.
Family Samples
Winwebsec 4360
Zeroaccess 2136
Zbot 1305
Total 7801
4 MALWARE EXPERIMENTS
In this section, we fist introduce the dataset used in
our experiments, followed by two distinct sets of ex-
periments. In our first set of experiments, we com-
pare the performance of discrete HMMs and GMM-
HMMs using opcode sequences as our features. In
our second set of experiments, we consider entropy
sequences, which serve to illustrate the strength of the
GMM-HMM technique.
4.1 Dataset
In all of our experiments, we consider three malware
families, namely, Winwebsec, Zbot, and Zeroaccess.
Winwebsec: is a type of Trojan horse in the Win-
dows operating system. It attempts to install ma-
licious programs by displaying fake links to bait
users (Winwebsec, 2017).
Zbot: is another type of Trojan that tries to steal user
information by attaching executable files to spam
email messages (Zbot, 2017).
Zeroaccess: also tries steal information, and it can
also cause other malicious actions, such as down-
loading malware or opening a backdoor (Neville
and Gibb, 2013).
Table 4 lists the number of samples of each malware
family in our dataset. These families are part of the
Malicia dataset (Nappa et al., 2015) and have been
used in numerous previous malware studies.
The samples of each malware family are split
into 80% for training and 20% for testing. We train
models on one malware family, and test the resulting
model separately against the other two families. Note
that each of these experiments is a binary classifica-
tion problem.
We use the area under the ROC curve (AUC) as
our measure of success. The AUC can be interpreted
as the probability that a randomly selected positive
sample scores higher than a randomly selected nega-
tive sample (Bradley, 1997). We perform 5-fold cross
validation, and the average AUC from the 5 folds is
the numerical result that we use for comparison.
Table 5: Percentage of top 30 opcodes.
Family Top 30 opcodes
Winwebsec 96.9%
Zeroaccess 95.8%
Zbot 93.4%
4.2 Opcode Features
For our first set of malware experiments, we compare
a discrete HMM and GMM-HMM using mnemonic
opcode sequences as features. To encode the input,
we disassemble each executable, then extract the op-
code sequence. We retain the most frequent 30 op-
codes with all remaining opcodes lumped together
into a single “other” category, giving us a total of 31
distinct observations. The percentage of opcodes that
are among the top 30 most frequent are listed in
Table 5.
For training, we limit the length of the observation
sequence to T = 100000, and for the discrete HMM,
we let N = 2. For the GMM-HMM, we we experi-
ment with the number of Gaussian mixtures ranging
from M = 2 to M = 5.
As mentioned above, we train a model with one
malware family and test with the other two mal-
ware families individually (i.e., in binary classifica-
tion mode). To test each model’s performance, we use
one hundred samples from both families in the binary
classification.
We initialize π and A to be approximately uniform,
as well as making them row stochastic. For each dis-
crete HMM, the B matrix is initialize similarly, while
for each GMM-HMM, the mean values and the co-
variance are initialized with the global mean value
and the global covariance of all training samples.
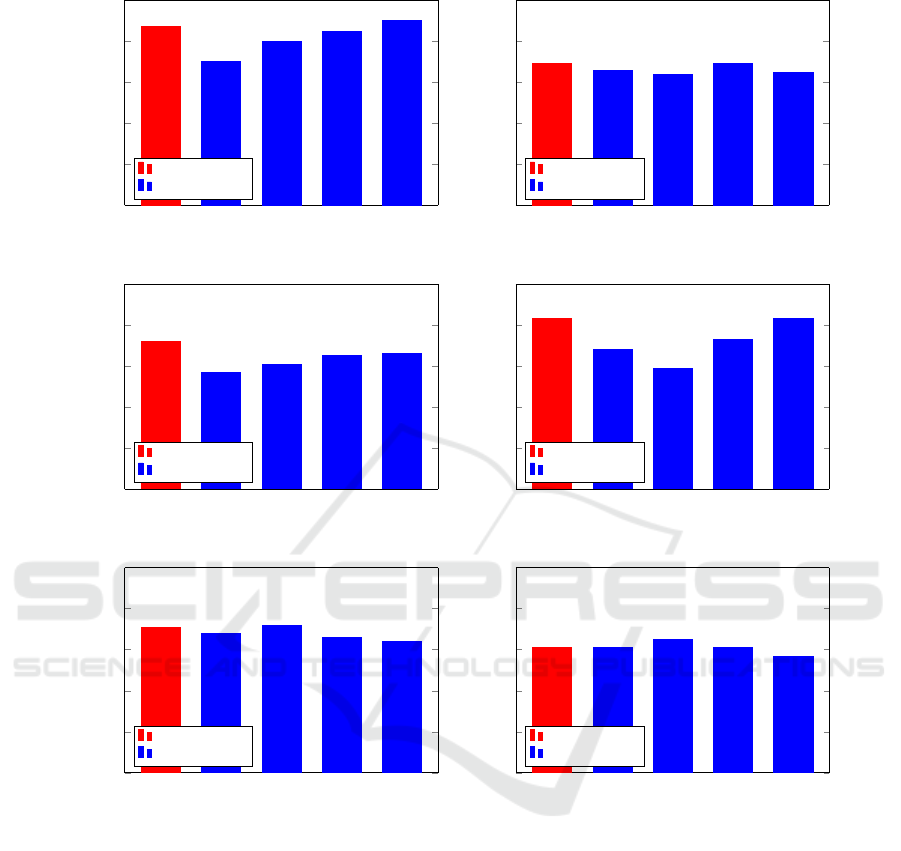
Figure 2 gives the average AUC (over the 5
folds) for models trained with discrete HMMs and the
GMM-HMMs with different values for m, the number
of Gaussians in the mixture. For most of the models,
the GMM-HMM is able to obtain comparable results
to the discrete HMM, and it does slightly outperform
a discrete HMM in some cases. but the improvement
is slight.
The results in Figure 2 indicate that for opcodes
sequences, GMM-HMMs perform comparably to dis-
crete HMMs. However, GMM-HMMs are more com-
plex and more challenging to train, and the additional
complexity does not appear to be warranted in this
case. But, this is not surprising, as opcode sequences
are inherently discrete features. To obtain a more
useful comparison, we next consider GMM-HMMs
trained on continuous features.
ForSE 2021 - 5th International Workshop on FORmal methods for Security Engineering
758
Test on Zeroaccess Test on Winwebsec
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.87
0.70
0.80
0.85
0.90
AUC
Discrete HMM
GMM-HMM
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.69
0.66
0.64
0.69
0.65
AUC
Discrete HMM
GMM-HMM
(a) Zbot models
Test on Zbot Test on Zeroaccess
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.72
0.57
0.61
0.65
0.66
AUC
Discrete HMM
GMM-HMM
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.83
0.68
0.59
0.73
0.83
AUC
Discrete HMM
GMM-HMM
(b) Winwebsec models
Test on Zbot Test on Winwebsec
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.71
0.68
0.72
0.66
0.64
AUC
Discrete HMM
GMM-HMM
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.61 0.61
0.65
0.61
0.57
AUC
Discrete HMM
GMM-HMM
(c) Zeroaccess models
Figure 2: Average AUC.
4.3 Entropy Features
GMM-HMMs are designed for continuous data, as
opposed to discrete features, such as opcodes. Thus
to take full advantage of the GMM-HMM technique,
we consider continuous entropy based features.
We use a similar feature-extraction method as
in (Baysa et al., 2013). Specifically, we consider the
raw bytes of an executable file, and we define a win-
dow size over which we compute the entropy. Then
we slide the window by a fixed amount and repeat the
entropy calculation. Both the window size and the
slide amount are parameters that need to be tuned to
obtain optimal performance. In general, the slide will
be smaller than the window size to ensure no infor-
mation is lost.
Entropy is computed using Shannon’s well known
formula (Togneri and DeSilva, 2003)
E = −
∑
x∈W
i
p(x)log
2
p(x),
where W
i
is the i
th
window, and p(x) is the relative
frequency of the occurrence of the byte x within the
window W
i
.
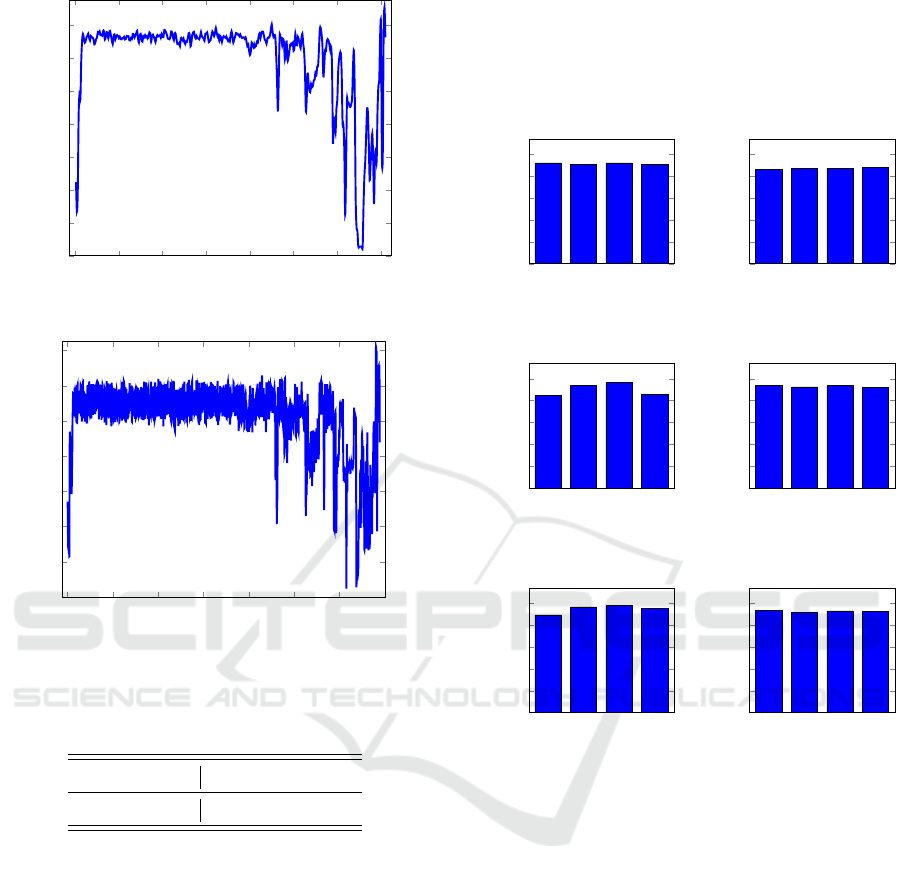
The entropy tends to be smoothed out with larger
window sizes. We want to select a window size suffi-
ciently large so that we reduce noise, but not so large
as to lose useful information. Examples of entropy
plots for different parameters are given in Figure 3.
Malware Classification with GMM-HMM Models
759
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Window number
Entropy
(a) Window size = 512
0 200 400
600
800 1000 1200 1400
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Window number
Entropy
(b) Window size = 128
Figure 3: Entropy plots.
Table 6: Window size and slide amount.
Window size 512 256 128
Slide 256 128 64
Based on the results in (Baysa et al., 2013), we use
half of the window size as the slide amount. To se-
lect the best values for the parameters, we conduct
experiments with the window and slide combinations
listed in Table 6. Also, as part of the parameter tuning
process, we selected ε in (3) to be 0.000001 for both
Zbot and Zeroaccess, while we find 0.1 is optimal for
Winwebsec.
For models trained on Zbot, the results of our ex-
periments with the different window and slide size
pairings in Table 6 are given in Figure 4. We have
conducted analogous experiments for Winwebsec and
Zeroaccess; however for the sake of brevity, we have
omitted the corresponding bar graphs. Note that we
have experimented with the number of Gaussians in
our mixture ranging from m = 2 to m = 5. We see that
a window size of size 512 performs the worst, while
window sizes of size 256 and 128 give improved re-
sults, with size 128 being slightly better than 256. The
optimal number of Gaussians depends on the families
we are classifying.
Test on Winwebsec Test on Zeroaccess
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.92
0.91
0.92
0.91
Number of mixture components
AUC
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.86
0.87 0.87
0.88
Number of mixture components
AUC
(a) Window size = 512
Test on Winwebsec Test on Zeroaccess
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.85
0.94
0.97
0.86
Number of mixture components
AUC
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.94
0.92
0.94
0.92
Number of mixture components
AUC
(b) Window size = 256
Test on Winwebsec Test on Zeroaccess
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.89
0.97
0.98
0.95
Number of mixture components
AUC
m = 2 m = 3 m = 4
m = 5
0.00
0.20
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
0.94
0.92
0.93
0.92
Number of mixture components
AUC
(c) Window size = 128
Figure 4: Entropy vs window size for Zbot models.
In Table 7, we provide a direct comparison of discrete
HMMs trained on opcodes to GMM-HMM trained
on opcodes, as well as the best GMM-HMM mod-
els trained on (continuous) entropy sequences. In
every case, the entropy-trained GMM-HMM outper-
forms the corresponding opcode based models. It is
also worth noting that computing an entropy sequence
is more efficient than extracting mnemonic opcodes.
While it is costlier to train a GMM-HMM, the scoring
cost is similar to that of a discrete HMM. Since train-
ing is one-time work, efficiency considerations also
favor the entropy-based GMM-HMM technique over
opcode-based HMMs.
From Table 7 we see that GMM-HMMs trained
on entropy perform dramatically better than discrete
HMMs, except in the two cases where models where
Zbot and Zeroaccess are involved. To gain fur-
ther insight into these anomalous case, we use the
ForSE 2021 - 5th International Workshop on FORmal methods for Security Engineering
760

Table 7: Comparison of discrete HMM and GMM-HMM.
Train Test
Opcode Opcode Entropy
HMM GMM-HMM GMM-HMM
Zbot Zeroaccess 0.87 0.90 0.94
Zbot Winwebsec 0.69 0.69 0.98
Zeroaccess Zbot 0.71 0.72 0.77
Zeroaccess Winwebsec 0.61 0.65 0.99
Winwebsec Zbot 0.72 0.66 1.00
Winwebsec Zeroaccess 0.83 0.83 1.00
Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence (Joyce, 2011) to
compare the probability distributions defined by of
our trained GMM-HMM models. The KL divergence
between two probability distributions is given by
KL(pk q) =
Z
∞
−∞
p(x)log
p(x)
q(x)
, (5)
where p and q are probability density functions. Note
that the KL divergence in (5) is not symmetric, and
hence not a true distance measure. We compute a
symmetric version of the divergence for models M
1
and M
2
as
KL(M
1
, M
2
) =
KL(M
1
kM
2
) + KL(M
2
kM
1
)
2
. (6)
Using equation (6) we obtain the (symmetric) diver-
gence results in Table 8. We see that the Zbot and
Zeroaccess models are much closer in terms of KL
divergence, as compared to the other two pairs. Thus
we would expect GMM-HMM models to have more
difficulty distinguishing these two families from each
other, as compared to the models generated for the
other pairs of families.
Table 8: The KL divergence of different models.
Models KL divergence
Zbot, Zeroaccess 611.58
Zbot, Winwebsec 1594.05
Zeroaccess, Winwebsec 1524.39
Curiously, the models trained on Zbot and tested on
Zeroaccess perform well.
1
Hence, a relatively small
KL divergence does not rule out the possibility that
models can be useful, but intuitively, a large diver-
gence would seem to be an indicator of potentially
challenging cases. This issue requires further study.
1
It is worth noting that the opcode based models also
performed well in this case.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we have explored the usage of GMM-
HMMs for malware classification, We compared
GMM-HMMs to discrete HMMs using opcode se-
quences, and we further experimented with entropy
sequences as features for GMM-HMMs. With the op-
code sequence features, we were able to obtained re-
sults with GMM-HMMs that are comparable to those
obtained using discrete HMMs, However, we expect
GMM-HMMs to perform best on features that are nat-
urally continuous, so we also experimented with byte-
based entropy sequences. In this latter set of exper-
iments, the GMM-HMM technique yielded stronger
results than the discrete HMM in all cases—and in
four of the six cases, the improvement was large. We
also directly compared the GMMs of our trained mod-
els using KL divergence, which seems to provide in-
sight into the most challenging cases.
For future work, more extensive experiments over
larger numbers of families with larger numbers of
samples per family would be valuable. True mul-
ticlass experiments based on GMM-HMM scores
would also be of interest. Further analysis of the KL
divergence of GMM-HMMs might provide useful in-
sights into these models.
REFERENCES
Alfakih, M., Keche, M., Benoudnine, H., and Meche, A.
(2020). Improved Gaussian mixture modeling for ac-
curate Wi-Fi based indoor localization systems. Phys-
ical Communication, 43.
Bansal, P., Kant, A., Kumar, S., Sharda, A., and Gupta,
S. (2008). Improved hybrid model of hmm/gmm for
speech recognition. In International Conference on
Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems, IN-
FOS 2008.
Baysa, D., Low, R., and Stamp, M. (2013). Structural en-
tropy and metamorphic malware. Journal of Com-
puter Virology and Hacking Techniques, 9(4):179–
192.
Ben Abdel Ouahab, I., Bouhorma, M., Boudhir, A. A.,
and El Aachak, L. (2020). Classification of grayscale
malware images using the k-nearest neighbor algo-
rithm. In Ben Ahmed, M., Boudhir, A. A., Santos,
D., El Aroussi, M., and Karas,
˙
I. R., editors, Innova-
tions in Smart Cities Applications, pages 1038–1050.
Springer, 3 edition.
Bradley, A. P. (1997). The use of the area under the
ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning al-
gorithms. Pattern Recognition, 30(7):1145–1159.
Brown Corpus of standard American English (1961). The
Brown corpus of standard American English. http:
//www.cs.toronto.edu/
∼
gpenn/csc401/a1res.html.
Malware Classification with GMM-HMM Models
761

Cave, R. L. and Neuwirth, L. P. (1980). Hidden Markov
models for English. In Ferguson, J. D., editor, Hidden
Markov Models for Speech. IDA-CCR.
Chen, Y. and Wu, W. (2019). Separation of geochemical
anomalies from the sample data of unknown distribu-
tion population using gaussian mixture model. Com-
puters & Geosciences, 125:9–18.
Dang, S., Chaudhury, S., Lall, B., and Roy, P. K. (2017).
Learning effective connectivity from fMRI using au-
toregressive hidden Markov model with missing data.
Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 278:87–100.
Fraley, C. and Raftery, A. E. (2002). Model-based clus-
tering, discriminant analysis, and density estima-
tion. Journal of the American Statistical Association,
97(458):611–631.
Gallop, J. (2006). Facies probability from mixture distribu-
tions with non-stationary impedance errors. In SEG
Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2006, pages
1801–1805. Society of Exploration Geophysicists.
Gao, Z., Sun, Z., and Liang, S. (2020). Probability density
function for wave elevation based on Gaussian mix-
ture models. Ocean Engineering, 213.
Guoning Hu and DeLiang Wang (2004). Monaural speech
segregation based on pitch tracking and amplitude
modulation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks,
15(5):1135–1150.
Interrante-Grant, A. M. and Kaeli, D. (2018). Gaus-
sian mixture models for dynamic malware
clustering. https://coe.northeastern.edu/wp-
content/uploads/pdfs/coe/research/embark/4-
interrante-grant.alex final.pdf.
Joyce, J. M. (2011). Kullback-Leibler divergence. In
Lovric, M., editor, International Encyclopedia of Sta-
tistical Science, pages 720–722. Springer.
Juang, B. (1985). Maximum-likelihood estimation for mix-
ture multivariate stochastic observations of Markov
chains. AT&T Technical Journal, 64(6):1235–1249.
Kalash, M., Rochan, M., Mohammed, N., Bruce, N. D. B.,
Wang, Y., and Iqbal, F. (2018). Malware classification
with deep convolutional neural networks. In 2018 9th
IFIP International Conference on New Technologies,
Mobility and Security, NTMS, pages 1–5.
Kruczkowski, M. and Szynkiewicz, E. N. (2014). Sup-
port vector machine for malware analysis and classi-
fication. In 2014 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Joint
Conferences on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent
Technologies, WI-IAT ’14, pages 415–420.
Laraba, S. and Tilmanne, J. (2016). Dance performance
evaluation using hidden Markov models. Computer
Animation and Virtual Worlds, 27(3-4):321–329.
McLachlan, G. and Peel, D. (2004). Finite Mixture Models.
Wiley.
Milosevic, N. (2013). History of malware. https://arxiv.org/
abs/1302.5392.
Nappa, A., Rafique, M. Z., and Caballero, J. (2015).
The MALICIA dataset: Identification and analysis of
drive-by download operations. International Journal
of Information Security, 14(1):15–33.
Neville, A. and Gibb, R. (2013). ZeroAccess Indepth. https:
//docs.broadcom.com/doc/zeroaccess-indepth-13-en.
Nguyen, L. (2016). Continuous observation hidden Markov
model. Revista Kasmera, 44(6):65–149.
Qiao, J., Cai, X., Xiao, Q., Chen, Z., Kulkarni, P., Ferris,
C., Kamarthi, S., and Sridhar, S. (2019). Data on MRI
brain lesion segmentation using k-means and Gaus-
sian mixture model-expectation maximization. Data
in Brief, 27.
Rabiner, L. R. (1989). A tutorial on hidden Markov models
and selected applications in speech recognition. Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE, 77(2):257–286.
Raitoharju, M., Garc
´
ıa-Fern
´
andez, A., Hostettler, R., Pich
´
e,
R., and S
¨
arkk
¨
a, S. (2020). Gaussian mixture models
for signal mapping and positioning. Signal Process-
ing, 168:107330.
Reynolds, D. (2015). Gaussian mixture models. In Li, S. Z.
and Jain, A. K., editors, Encyclopedia of Biometrics,
pages 827–832. Springer.
Stamp, M. (2018). A revealing introduction to hid-
den Markov models. https://www.cs.sjsu.edu/
∼
stamp/
RUA/HMM.pdf.
Stanculescu, I., Williams, C. K. I., and Freer, Y. (2014).
Autoregressive hidden Markov models for the early
detection of neonatal sepsis. IEEE Journal of Biomed-
ical and Health Informatics, 18(5):1560–1570.
Togneri, R. and DeSilva, C. J. S. (2003). Fundamentals of
Information Theory and Coding Design. CRC Press.
Truong, A. and Zaharia, T. (2017). Laban movement analy-
sis and hidden Markov models for dynamic 3D ges-
ture recognition. EURASIP Journal on Image and
Video Processing, 2017.
Winwebsec (2017). Win32/winwebsec threat descrip-
tion - Microsoft security intelligence. https:
//www.microsoft.com/en-us/wdsi/threats/malware-
encyclopedia-description?Name=Win32/Winwebsec.
Yao, Z., Ge, J., Wu, Y., Lin, X., He, R., and Ma, Y.
(2020). Encrypted traffic classification based on
Gaussian mixture models and hidden Markov models.
Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 166.
Zbot (2017). Pws:win32/zbot threat description - Microsoft
security intelligence. https://www.microsoft.com/en-
us/wdsi/threats/malware-encyclopedia-description?
Name=PWS%3AWin32%2FZbot.
Zhang, F., Han, S., Gao, H., and Wang, T. (2020). A Gaus-
sian mixture based hidden Markov model for motion
recognition with 3D vision device. Computers & Elec-
trical Engineering, 83.
ForSE 2021 - 5th International Workshop on FORmal methods for Security Engineering
762
