
Technological Solution to Optimize the Alzheimer’s Disease Monitoring
Process, in Metropolitan Lima, using the Internet of Things
Katherine Jorge-L
´
evano, Victor Cuya-Chumbile and Willy Ugarte
a
Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas (UPC), Lima, Peru
Keywords:
Alzheimer’s, Internet of Things, Wearable, Health Monitoring.
Abstract:
The use of information technologies (IT) in the health sector has allowed to optimize monitoring processes
for diseases such as Diabetes or Parkinson’s. For this reason, the incorporation of IT into the monitoring of
neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, will enable remote monitoring solutions on the patient’s health.
This study will develop a mobile and web application that will monitor, through an IOT device, changes in the
patient’s vital signs (oxygenation and blood pressure), impairment of cognitive functions (memory, calculation
and concentration) and the patient’s sleep status with Alzheimer’s. In addition, with this solution the patient’s
doctor will be able to record recommendations on the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. The study was
validated with 3 physicians and 3 caregivers, who participated in the validation process by comparing the time
before and after using the technology solution. As a result, the optimization of the monitoring process has been
validated, allowing real-time control of the progress of the disease and having the appropriate considerations
of the doctor in case of any incident that may happen with the patient
1 INTRODUCTION
According to the Peruvian College of Physicians
(CMP), it is estimated that approximately 200,000 Pe-
ruvians could currently suffer from Alzheimer’s dis-
ease, and the figure is estimated to be quintupling by
early 2050 (CMP - https://bit.ly/3lmkHEF).
Alzheimer’s is a disease that increases with age,
starting with subtle symptoms such as memory prob-
lems, disorientation in time/space, and difficulty nam-
ing objects. The World Health Organization (WHO)
classifies the signs and symptoms of early-stage,
intermediate- and late-stage dementia. The early
stage; often goes unnoticed, presenting as more com-
mon symptoms the tendency to forgetfulness, the loss
of the notion of time and spatial desubication (WHO
- https://bit.ly/35lG6Z7).
As dementia evolves into the intermediate stage,
signs and symptoms become more apparent. In view
of this, in order to have greater knowledge about the
impact of this disease, it was proceeded to analyze
the information presented by radio program of Peru
(PTR), in which they indicated that in the Ministry of
Health in 2015 alone the number of Peruvians with
Alzheimer’s were 3,207; in 2016, from 3,309 to 2017
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7510-618X
increased to 3,665, among new and old cases of peo-
ple over the age of 60 (RPP - https://bit.ly/2UuZXiB)
from Figure 1.
Figure 1: Indicator of people over the age of 60 diagnosed
with Alzheimer’s according to the Ministry of Health of
Peru.
This information shows the importance of incur-
ing monitoring the progression of Alzheimer’s dis-
Jorge-Lévano, K., Cuya-Chumbile, V. and Ugarte, W.
Technological Solution to Optimize the Alzheimer’s Disease Monitoring Process, in Metropolitan Lima, using the Internet of Things.
DOI: 10.5220/0010422501790186
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2021), pages 179-186
ISBN: 978-989-758-506-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
179

ease, in order to support the monitoring of patients
with the aforementioned disease.
Faced with this need to find some kind of tech-
nological solution, a study conducted in Catania and
Messina, Sicily, developed a telemedicine system that
involves three approaches: nutritional status, biomet-
ric data monitoring and cognitive status; focused on
the care of the elderly in order to prevent neurodegen-
erative diseases. This system uses a device with inter-
net access, which contains a web platform on which
consultations are made to a doctor.
In addition, this system allows to provide cogni-
tive training sessions to the patient and all the col-
lected data are sent to the corresponding medical units
to assess the patient’s situation. At the end of the val-
idation of this project, an improvement was observed
regarding the nutritional status of the person, cogni-
tive functions and the execution of daily activities of
the participants (Maresca et al., 2019). By identify-
ing this type of solution, it has been validated what to
know about the health status and impairment of a pa-
tient’s cognitive functions makes it easier for the doc-
tor to generate accurate recommendations regarding
the advancement of the patient’s disease.
For this reason, this study answers the following
question What technology is available, what techno-
logical devices should be taken into account to de-
velop a mobile and web application that optimizes
the monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease, in the city of
Lima, Peru? In response, it is proposed to develop a
technological solution that allows to optimize the pro-
cess of monitoring Alzheimer’s disease, in Metropoli-
tan Lima, using the Internet of Things.
The main contributions in this solution:
• it allows to generate a constant communication
between doctor and caregiver,
• establish a medical control without moving the
patient to the medical center,
• provide real-time information of blood pressure,
oxygenation, the generation of alerts to the doctor
about the signs of health of the patient.
Finally, this research is structured as follows: in
Section 2, brief definitions of the concepts used in
the development of the project will be indicated, Sec-
tion 3 will include the analysis, design and construc-
tion of the project, in Section 4 the comparison will
be made between technological solutions developed
against our proposed proposal, Section 5 will explain
what has been done at the programming level, vali-
dation and results, finally Section 6 will present the
conclusions and recommendations.
2 RELATED WORKS
During the development of our proposal, various con-
tributions from studies were considered as references
such as (Rostill et al., 2018), in which authors indi-
cated that including IoT devices for home monitor-
ing and vital signs, allow to lead to important inter-
ventions in which serious complications could occur
without the use of technology.
Furthermore, in (Alexandru and Ianculescu,
2017), the authors present another assisted technol-
ogy that helps people affected by dementia, such as
the MSI-MDD digital platform.
Nevertheless, it is also evidenced that the authors
of (Jain et al., 2018), through a mobile application
evaluate and improve the emotional state of care-
givers, allowing to optimize the stimulation process
for the caregiver, applying medical metrics.
Finally, in (Gilson et al., 2019), the authors
showed that web-based video services can be used
on tablets, allowing to improve mood in people living
with dementia and improve perceptions of caregivers
about the daily interaction that older adults may have
with their caregivers.
It should be noted the works aforementioned fo-
cus on improving the mood of patients and caregivers,
however, the solutions presented do not allow to es-
tablish a medical control to monitor the disease of the
patient with Alzheimer’s, through the capture of sleep
state data and vital signs, which will allow to gener-
ate constant communication between the doctor and
the caregiver that empowers them to make decisions
about the patient’s health.
3 METHOD
The development of the project was divided into 2 of
the main dimensions of design thinking: desirability,
which will be explained in the analysis and feasibility
section, which will be explained in the design section.
3.1 Analysis
In this phase, an initial survey of the problem was car-
ried out, focusing it on the first dimension of design
thinking: desirability.
• The first step consisted of sharing surveys with
three doctors and ten caregivers of patients with
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), in order to obtain the
relevant data during the AD monitoring process.
In this survey, the relevance and frequency of tak-
ing vital signs of Alzheimer’s patients was evalu-
ated. The final result made it possible to identify
ICT4AWE 2021 - 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
180
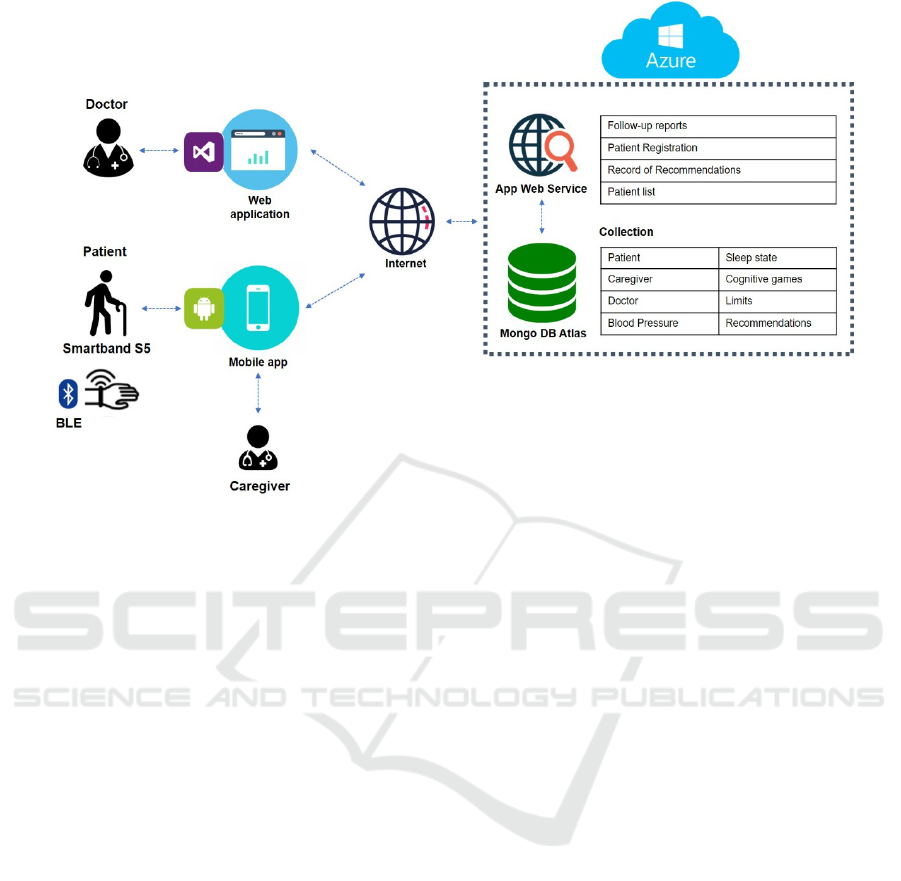
Figure 2: Architecture of integration of the proposed technological solution.
that blood pressure, oxygenation level, sleep sta-
tus and cognitive functions are the relevant data.
• As a second step, through the testimonies ob-
tained, we proceeded to develop the customer
journey of the patient with Alzheimer’s in its
three phases of the disease, in which the moments
through which the patient passes in their day to
day were obtained as a result, identifying eight
moments, which are: grooming, dressing, eating,
cognitive entertainment, relaxation, rest, medica-
tion and physical activity. The development of the
Customer Journey also made it possible to iden-
tify the actors in the monitoring process, which
are: doctor and caregiver, while, on the other
hand, the costs and times associated with the mon-
itoring process were identified.
• In the third step, the wearables available for data
collection were evaluated. Therefore, the evalua-
tion was carried out based on the information col-
lected in the previous steps and on the device char-
acteristics such as water resistance, cost, battery
life, built-in sensors and weight.
• The fourth step is the value proposition canvas
was developed which allowed to reaffirm the ini-
tial approach of the project, through the identifica-
tion of gain creators, pain relievers, gains, pains.
Finally, the wearable Smartband S5 was selected
(S5 Bluetooth Heart Rate Fitness Smart Bracelet -
https://bit.ly/36nQfEc). This device allows the cap-
ture of data such as heart rate, oxygenation level,
blood pressure, step counter, calories and sleep status.
The wearable’s margin of error is 10% in case the per-
son or patient who uses it is in constant motion . This
value was indicated to the physicians who carried out
the initial survey and they said that the margin would
not significantly affect the values obtained from the
patient, since they don’t usually perform high physi-
cal activity
3.2 Design
For the design phase, a logical and physical architec-
ture was developed in order to identify the relation-
ships between the project components. Furthermore,
the development of a mobile application that would
interact with the wearable and a web application was
established.
In addition, the interface design was developed
based on the requirements defined in the analysis
phase (see Figure 2). Likewise, an integration archi-
tecture was developed to identify the relationships be-
tween the participants (doctor, caregiver and patient),
processes (patient monitoring) and information (pa-
tient health report) that compose the technological so-
lution.
Additionally, the interface design was developed
based on the requirements identified in the analysis
phase.
Technological Solution to Optimize the Alzheimer’s Disease Monitoring Process, in Metropolitan Lima, using the Internet of Things
181

3.3 Elaboration
During this stage, the applications that compose part
of the technological solution were developed: mobile
and web.
On the one hand, the coding of the mobile appli-
cation included the libraries android-smartband-sdk-
sxrblejy2aidl-release.aar and android-smartband-sdk-
sxrblejy2library-release.aar to establish the connec-
tion with the wearable Smartband S5. Likewise, this
library allowed obtaining data related to vital signs
(arterial pressure and blood oxygenation) and sleep
status. Additionally, stimulation games aimed at the
following cognitive functions were included: mem-
ory, concentration and calculation. The data related
to vital signs, sleep status and scores in the cognitive
stimulation games were stored in the MongoDB At-
las database and the visualization functionality was
integrated through reports with the support of the
AAChartCore-Kotlin library.
On the other hand, the code of the web applica-
tion includes the development of functionalities for
displaying reports related to the patient’s health sta-
tus with support of the Chart JS library. Likewise, the
functionality of recording recommendations for each
patient was incorporated (see more details in the demo
video).
4 EXPERIMENTS
For validating the system for patients with AD, sur-
veys were conducted focused on evaluating the im-
pact on time and costs in the monitoring process.
4.1 Experimental Protocol
A virtual meeting was held with a doctor and two
caregivers to consult on the functionalities of the
web and mobile solution, it should be noted that be-
fore starting the meeting a pre-validation survey was
shared, which allowed obtaining the indicators related
to costs and time that involves monitoring the disease.
After presenting the solution, insights were ob-
tained about the system and with a post-validation
survey the information was collected to identify the
variation in the initial indicators. Likewise, the same
dynamic was carried out with two additional care-
givers, but in this case, the virtual meeting was re-
placed with a demonstration video (see more detail in
this meeting).
4.2 Experimental Results
The focus of the validation is analyzing the results ob-
tained in the pre-validation and post-validation survey
that was carried out as a final step of the desirability
dimension. The results of the aforementioned surveys
allowed to verify the reduction of costs and time re-
lated to the monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease (see
more detail of these surveys).
The following is what has been identified with re-
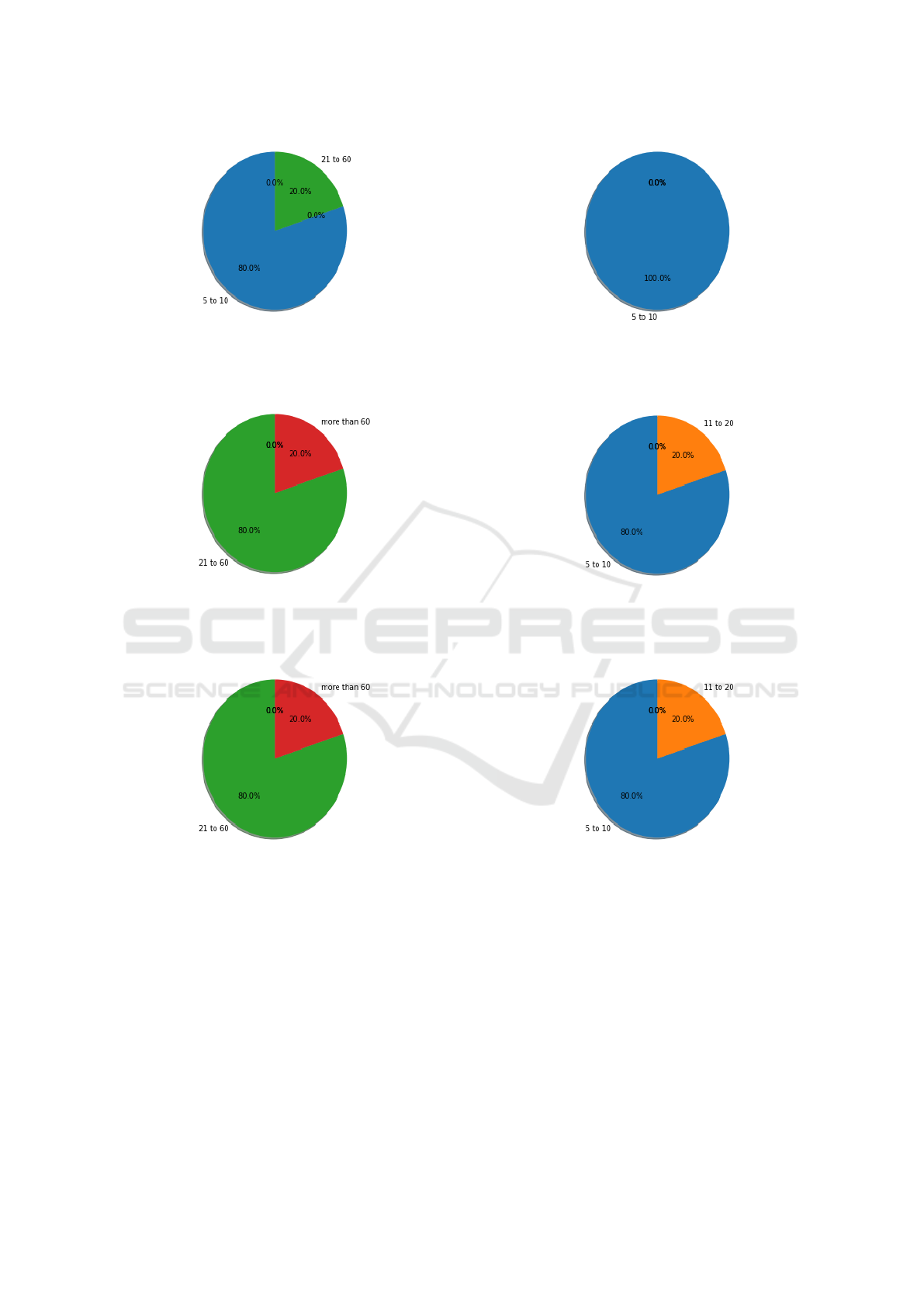
spect to cost reduction (see Figure ??):
• Initial Phase: it was identified that 50% of
the people surveyed in the pre-validation, indi-
cated as costs related to the monitoring process
of Alzheimer’s disease, the transfer to the med-
ical center. However, in the post-validation this
percentage was reduced to zero, leaving only the
costs related to the care service (see Figures 3a
and 3b). The reduction in the mentioned cost
was achieved by the use of telemedicine, which
doesn’t require a constant physical transfer by the
patient to the medical center.
• Moderate Phase and Severe Phase: it was iden-
tified that, on average, 38% of the people sur-
veyed in the pre-validation indicated as costs re-
lated to the monitoring process of Alzheimer’s
disease two main sources: a) emergency services
and b) transportation costs to the medical Center.
However, in post-validation, this percentage was
reduced to 29% (see Figures 3c, 3d, 3e and 3f).
The reduction of the cost of the emergency service
was achieved due to the fact that there is constant
monitoring of the patient’s health by the doctor,
who gets daily information about the variation of
the patient’s vital signs. This allows the doctor to
make immediate decisions about the medications
that the patient may require.
Nevertheless, the reduction in the cost of trans-
portation to the medical center, as in the
mild phase, was achieved due to the use of
telemedicine, since the doctor has the information
required for the evaluation of the patient.
Regarding the reduction in the time of the tasks
associated with the monitoring of Alzheimer’s (see
Figures 4,5,6,7 and 8), it was identified that various
tasks are usually performed in a range greater than 20
minutes, it should be noted that, when using mobile
app, web app, and wearable, task time is reduced by a
maximum of approximately 19 minutes in total.
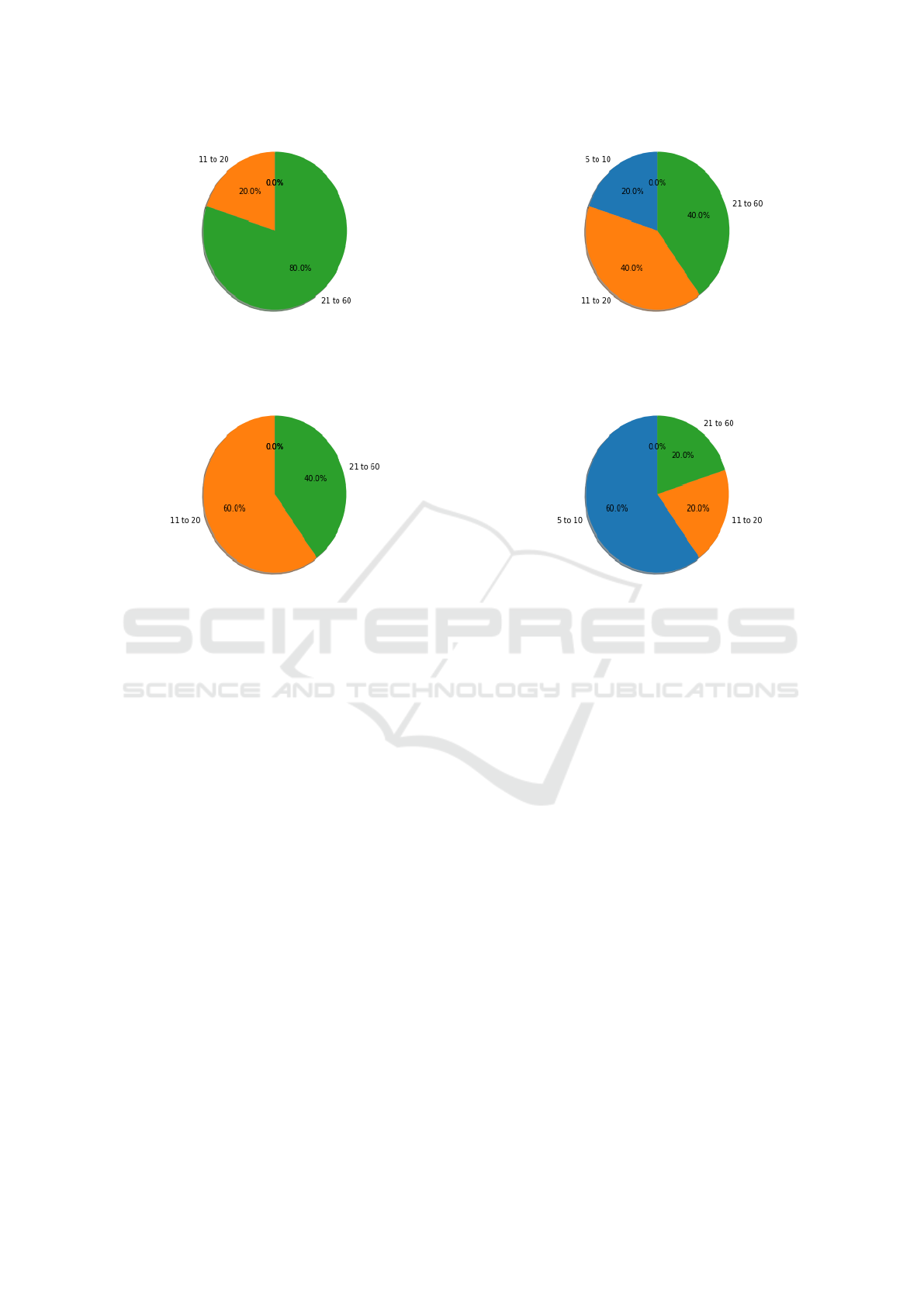
• Measurement of Blood Pressure and Oxygena-
tion: we identified that this task (see Figure 4)
was previously performed between 5 to 10 min-
utes (80% of the time) and between 21 to 60 min-
ICT4AWE 2021 - 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
182

(a) Pre-validation (Initial) (b) Post-validation (Initial)
(c) Pre-validation (Moderate) (d) Post-validation (Moderate)
(e) Pre-validation (Severe) (f) Post-validation (Severe)
Figure 3: Pre- and post-25cm.
utes (20% of the time) (see Figure 4a), however,
it can now be all performed in a maximum of 10
minutes (see Figure 4b). The reduction in time to
perform this activity was achieved due to the use
of the wearable, which generates the measurement
of blood pressure and oxygenation automatically,
without the need to prepare the patient with the
devices that were used to control the mentioned
vital signs.
• Transfer the Patient to a Medical Center: we
identified that this task (see Figure 5) was previ-
ously performed between 21 to 60 minutes (80%
of the time) and more than 60 minutes (20% of
the time) (see Figure 5a), however, it can now be
all performed in a maximum of 20 minutes (see
Figure 5b). The reduction to carry out this activ-
ity was achieved due to the use of telemedicine,
which reduces the need to travel to a medical cen-
ter periodically.
Technological Solution to Optimize the Alzheimer’s Disease Monitoring Process, in Metropolitan Lima, using the Internet of Things
183
(a) Pre-validation (b) Post-validation
Figure 4: Measuring Blood Pressure and Oxygenation (in minutes).
(a) Pre-validation (b) Post-validation
Figure 5: Transferring the Patient to a Medical Center (in minutes).
(a) Pre-validation (b) Post-validation
Figure 6: Supporting Cognitive Stimulation Activities (in minutes).
• Activities to Support Cognitive Stimulation:
we identified that this task (see Figure 6) was
previously performed between 21 to 60 minutes
(80% of the time) and more than 60 minutes (20%
of the time) (see Figure 6a), however, it can now
be all performed in a maximum of 20 minutes (see
Figure 6b). The reduction to carry out this activ-
ity was achieved by the use of the mobile applica-
tion, which includes games aimed at the follow-
ing cognitive functions: memory, calculation and
concentration. For this reason, the search time for
activities related to cognitive functions decrease,
according to the values indicated above.
• Supporting Physical Exercise Activities: we
identified that this task (see Figure 7) was previ-
ously performed between 11 to 20 minutes (20%
of the time) and around 21 to 60 minutes (80% of
the time) (see Figure 7a), however, it can now be
all performed in 30 minutes in average (see Fig-
ure 7b). The reduction to perform this activity,
ICT4AWE 2021 - 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
184
(a) Pre-validation (b) Post-validation
Figure 7: Supporting Physical Exercise Activities (in minutes).
(a) Pre-validation (b) Post-validation
Figure 8: Communication with an Specialist in case of complication (in minutes).
like the previous activity, was achieved by the use
of the mobile application, which includes recom-
mendations for physical exercises, which is sug-
gested by the patient’s doctor. For this reason, the
search time for physical exercises decreases, ac-
cording to the values indicated above.
• Communication with an Specialist in Case of
Complication: we identified that this task (see
Figure 8) was previously performed between 11 to
20 minutes (60% of the time) and around 21 to 60
minutes (40% of the time) (see Figure 8a), how-
ever, it can now be all performed in 22 minutes in
average (see Figure 8b). The reduction to perform
this activity, like the last two mentioned before,
was achieved by the use of the mobile applica-
tion, which includes a section on ”Generate alert”
for the doctor, in case the ranges of the variation
of the patient’s vital signs are outside the limits es-
tablished by the doctor and by the information that
the he maintains on the website of the patient’s re-
sults. For this reason, the time taken to explain to
the doctor how the patient’s health behavior has
been in a given period is reduced because the doc-
tor has all the variation generated day by day.
In addition to the aforementioned results, the med-
ical specialists who participated in the survey indi-
cated opportunities for improvement, such as:
• Add alerts for taking medications for the patient
and caregiver.
• Include the wearable activation functionality from
the caregiver interface.
• Include other measurement variables such as: step
count and heart rate.
Likewise, the general opinions that the respon-
dents commented regarding the project presented
were the following:
• The solution not only improves the quality of life
of the patient, but also of the family member and
caregiver.
• Definitely the doctor’s monitoring is more effi-
cient with the results obtained from the patient.
• It is a good starting point, the solution has a lot of
potential.
Technological Solution to Optimize the Alzheimer’s Disease Monitoring Process, in Metropolitan Lima, using the Internet of Things
185

5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the information indicated in the previous
sections, the reduction of transfer costs, emergency
service costs and time associated with monitoring
Alzheimer’s disease has been demonstrated, the op-
timizing the EA monitoring process.
Likely, as a continuation of this work, we plan
to expand the scope of the solution by incorporating
the elderly, without restriction of having Alzheimer’s
disease. This approach is done because of what this
population should have constant monitoring about its
vital signs, to prevent future diseases to which they
may be vulnerable due to their age. Evenmore, store
all the data using blockchain (Cueva-S
´
anchez et al.,
2020) technology to ensure security and accesibility.
For this reason, adding more variables such as
temperature control, stress management, step count-
ing, will allow you to have accurate control over the
current state of an elderly person, which the doc-
tor will be able to make preventive decisions before
your patient. Taking this platform into cloud (Xu
et al., 2020) could be a interesting topic or with other
kinds of wearables (Roopaei et al., 2018) or using a
chatbot to detect the symptoms (Solis-Quispe et al.,
2021), and therefore extract patterns from the ob-
tained data (Ugarte et al., 2015).
REFERENCES
Alexandru, A. and Ianculescu, M. (2017). Enabling assis-
tive technologies to shape the future of the intensive
senior-centred care: A case study approach. Studies
in Informatics and Control, 26.
Cueva-S
´
anchez, J. J., Coyco-Ordemar, A. J., and Ugarte, W.
(2020). A blockchain-based technological solution to
ensure data transparency of the wood supply chain. In
2020 IEEE ANDESCON, pages 1–6.
Gilson, A., Dodds, D., Kaur, A., Potteiger, M., and II,
J. H. F. (2019). Using computer tablets to improve
moods for older adults with dementia and interactions
with their caregivers: Pilot intervention study. JMIR
Formative Research, 3(3):e14530.
Jain, F., Sikder, A., Yang, F., Schafer, R., Dowling, G., and
Traeger, L. (2018). Mentalizing imagery therapy mo-
bile application to enhance mood of family demen-
tia caregiver: Feasibility and limited efficacy testing
(preprint). JMIR Aging, 2.
Maresca, G., Cola, M. C. D., Caliri, S., Luca, R. D.,
Manuli, A., Scarcella, I., Silvestri, G., Bramanti, P.,
Torrisi, M., Calabr
`
o, R. S., Bramanti, A., and the
Sicilian Teleneurology Group (2019). Moving to-
wards novel multidisciplinary approaches for improv-
ing elderly quality of life: The emerging role of
telemedicine in sicily. Journal of Telemedicine and
Telecare, 25(5):318–324.
Roopaei, M., Rad, P., and Prevost, J. J. (2018). A wearable
iot with complex artificial perception embedding for
alzheimer patients. In WAC, pages 1–6. IEEE.
Rostill, H., Nilforooshan, R., Morgan, A., Barnaghi, P.,
Ream, E., and Chrysanthaki, T. (2018). Technology
integrated health management for dementia. British
Journal of Community Nursing, 23:502–508.
Solis-Quispe, J. M., Quico-Cauti, K. M., and Ugarte, W.
(2021). Chatbot to simplify customer interaction in
e-commerce channels of retail companies. In Interna-
tional Conference on Information Technology & Sys-
tems, pages 1–6.
Ugarte, W., Boizumault, P., Loudni, S., Cr
´
emilleux, B., and
Lepailleur, A. (2015). Soft constraints for pattern min-
ing. J. Intell. Inf. Syst., 44(2):193–221.
Xu, M., Feng, G., Ren, Y., and Zhang, X. (2020). On cloud
storage optimization of blockchain with a clustering-
based genetic algorithm. IEEE Internet Things J.,
7(9):8547–8558.
ICT4AWE 2021 - 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
186
