
A Reinforcement Learning Approach for Traffic Control
Urs Baumgart and Michael Burger
Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Mathematics ITWM, Fraunhofer-Platz 1, D-67663 Kaiserslautern, Germany
Keywords:
Reinforcement Learning, Traffic Control, Microscopic Traffic Models, Radial Basis Function Networks.
Abstract:
Intelligent traffic control is a key tool to achieve and to realize resource-efficient and sustainable mobility
solutions. In this contribution, we study a promising data-based control approach, reinforcement learning
(RL), and its applicability to traffic flow problems in a virtual environment. We model different traffic networks
using the microscopic traffic simulation software SUMO. RL-methods are used to teach controllers, so called
RL agents, to guide certain vehicles or to control a traffic light system. The agents obtain real-time information
from other vehicles and learn to improve the traffic flow by repetitive observation and algorithmic optimization.
As controller models, we consider both simple linear models and non-linear radial basis function networks.
The latter allow to include prior knowledge from the training data and a two-step training procedure leading
to an efficient controller training.
1 INTRODUCTION
In view of steadily growing traffic flows and demand
for mobility services, intelligent vehicles and traffic
systems are becoming increasingly important. Com-
plex, partly networked driver assistance systems as
well as autonomous driving functions play a crucial
role and already cover more and more functionali-
ties. Intelligent traffic control systems and intelli-
gent infrastructure, as well as communication and co-
operation between road users and with infrastructure
elements, are equally important building blocks for
providing efficient and resource-saving mobility so-
lutions. Tools and methods of applied mathematics
and artificial intelligence may deliver decisive contri-
butions here in the development of innovative and ef-
ficient vehicle and mobility systems.
Today’s vehicle technology allows to collect an
increasing amount of data to improve the vehicle’s
performance, reliability and safety. Concerning mo-
bility infrastructure and communication technology,
larger and larger datasets can be transmitted faster ev-
ery year. This opens the opportunity to use (real-time)
data, communicated between cars and infrastructure,
to improve traffic flow in the future and, thereby, to
support holistic, efficient and sustainable mobility so-
lutions.
To achieve all those goals, efficient, intelligent and
sophisticated traffic flow controllers are needed that,
ideally, make use of established models as well as of
available data, and continue to learn from (new) data
and improve themselves constantly.
A promising technique that has the potential to
combine all mentioned characteristics is reinforce-
ment learning (RL). During the last years, reinforce-
ment learning approaches could achieve impressive
success, e.g., in playing games like Chess and Go
and, thereby, beating the best human players in these
games (Silver et al., 2018). Another field, in which
reinforcement learning has been applied successfully,
is robotics: here, RL-based controllers had been able
to learn and to perform very complex tasks with hu-
manoid robots (Kalashnikov et al., 2018; Rajeswaran
et al., 2018; Schulman et al., 2015). The core idea
of reinforcement learning is, roughly speaking, suc-
cessively repeating a task, or, more general, an in-
teraction with a certain environment. During those
repetitions that are steered by a databased controller,
the so-called agent, the controller evaluates the per-
formance of its actions in each repetition and uses that
information to adapt itself - the controller is enforced
to increase its own performance. This basic princi-
ple of (model-free) reinforcement learning goes back
to (Williams, 1992). However, the approach is attract-
ing more and more interest accompanied with success
stories in recent years, mainly due to increasing avail-
ability of data and increasing possibilities to measure
and to process data highly efficiently. Last, not least,
the increasing computing capacities that allow, e.g.,
rich and powerful databased controller models like
(deep) neural nets, is a decisive factor and accelera-
tor as well.
Baumgart, U. and Burger, M.
A Reinforcement Learning Approach for Traffic Control.
DOI: 10.5220/0010448501330141
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems (VEHITS 2021), pages 133-141
ISBN: 978-989-758-513-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
133

In this contribution, we present and discuss a
framework that allows to apply reinforcement learn-
ing to traffic flow control problems. That is, we
consider databased traffic controllers in a virtual,
simulation-based environment and the repetitive and
enforcing RL-technique to improve the traffic flow,
quantified here in terms of average speeds of in-
volved vehicles. We consider two different controller
types, the first one is guiding intelligently certain cars,
whereas the second one steers a traffic light systems,
see Sect. 2 for details. Both controllers act in a feed-
back mode making use of data that is provided from
involved (other) vehicles. For a general overview of
reinforcement learning as control approach, we refer
to (Recht, 2019).
Related Work. Since the first traffic flow mod-
els had been introduced in the last century, e.g., in
(Lighthill and Whitham, 1955; Gazis et al., 1961), op-
timal traffic control has been the subject of research
in several publications. Traffic can be controlled by,
e.g., speed limits and ramp metering (Lu et al., 2011)
or switching through phases of traffic lights (McNeil,
1968; De Schutter and De Moor, 1998). With the
emergence of (semi-) autonomous vehicles and an in-
creasing amount of traffic data, new controllers like
cruise control systems (Orosz, 2016) have been stud-
ied as well. In recent years, RL has been applied to
traffic control problems, too, including autonomous
braking systems (Chae et al., 2017), ramp metering
control (Belletti et al., 2017) and traffic light systems
(Wiering, 2000; Arel et al., 2010). In (Vinitsky et al.,
2018), benchmarks for different traffic control prob-
lems have been proposed.
In this work, besides RL-based traffic light con-
trol, we will apply RL to control the accelerations and
decelerations of one certain car, in a case study based
on the ring road experiment by (Sugiyama et al.,
2008). For this specific problem, the controllability
and stability have been studied (Wang et al., 2020;
Zheng et al., 2020), and solutions in a real-world set-
up (Stern et al., 2018) and with a RL controller (Wu
et al., 2017) have been presented.
To summarize, there are a few applications of
RL-approaches to traffic flow problems and with our
work, we contribute to that area. In particular, the
main contribution of our paper is twofold. First, we
consider controller models that have not been applied
to traffic flow problems and analyse their capabilities
and their performance potential. It is worth pointing
out here that the considered radial basis function net-
works provide the possibility to include prior knowl-
edge, while maintaining a non-linear structure. Sec-
ond, as one of our case-studies, we consider a virtual
version of a real-world road network.
The remaining part of the paper is organized as
follows. First, in Sect. 2, we describe human-like traf-
fic modelling in terms of microscopic car-following
models and the set-up of road networks in the mi-
croscopic simulation software SUMO (Lopez et al.,
2018). In Sect. 3, we define reinforcement learn-
ing in the framework of Markov Decision Processes
(MDPs) and introduce linear model as well as radial
basis function network policies. Finally, in Sect. 4, we
present and discuss the results of two different traffic
control experiments. We close the paper with a short
summary, some concluding remarks and a sketch of
open problems, Sect. 5.
2 TRAFFIC CONTROL
PROBLEMS
We model different traffic networks, in which agents
aim to improve traffic flows by repetitive observation
and algorithmic optimization. These agents can either
control connected automated vehicles or traffic guid-
ance systems, such as traffic lights and obtain real-
time information from other vehicles in the scenario.
2.1 Car-following Models
To set up those experiments, we model traffic with
microscopic car-following models (Orosz et al., 2010;
Treiber and Kesting, 2013). In these models, traffic is
described by individual driver-vehicle units that form
a traffic flow. We consider pairs of following and lead-
ing vehicles: the follower’s longitudinal actions, ac-
celerations and decelerations on the current lane, de-
pend on observations of the leading vehicle. To de-
scribe this mathematically, we define the dynamics of
each following vehicle by a system of ordinary differ-
ential equations (ODEs)
˙s
i
(t) = v
i
(t),
˙v
i
(t) = f (s
i
(t),s
i+1
(t),v
i
(t),v
i+1
(t))
(1)
where s
i
(t),s
i+1
(t),v
i
(t),v
i+1
(t) are the front-bumper
positions and speeds at time t of the following and
leading car, respectively. In some applications it is
desirable to describe the dynamics of the headway be-
tween the vehicles in terms of the bumper-to-bumper
distance, so, we define the headway as follows
h
i
= s
i+1
−s
i
−l
i+1
(2)
with l
i+1
being the length of the leading vehicle.
Then, the dynamics are given by
˙
h
i
(t) = v
i+1
(t) −v
i
(t),
˙v
i
(t) = f (h
i
(t),v
i
(t),v
i+1
(t)).
(3)
VEHITS 2021 - 7th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
134

For the right hand side f that determines the acceler-
ation of the following vehicle, there are several dif-
ferent choices. One of them is the Intelligent Driver
Model (IDM) (Treiber and Kesting, 2013) that we will
use for modelling of human-driven vehicles. In the
IDM, the equation for the acceleration of the i-th ve-
hicle is given by
˙v
i
= a
max
"
1 −
v
i
v
des
δ
−
h
∗
(v
i
,∆v)
h
i
2
#
,
h
∗
(v
i
,∆v) = s
0
+ max
0,v
i
T +
v
i
∆v
2
√
a
max
b
,
(4)
with ∆v = v
i
−v
i+1
. The crucial point here is the
comparison of the current speed v
i
with a given de-
sired speed v
des
and the current headway h
i
with the
desired headway h
∗
. The model is determined by
a set of parameters β
IDM
= [v
des
,T, h
min
,δ,a
max
,b],
which allows to represent different aspects of driv-
ing behaviour and different driver types. These pa-
rameters can be fitted based on real-world traffic data.
However, for typical values and a detailed description
of the parameters, we refer to (Treiber and Kesting,
2013).
2.2 Traffic Modelling
To build traffic scenarios with car-following models,
we use the microscopic traffic simulation software
SUMO (Lopez et al., 2018) as it provides a lot of op-
tions to implement own models and allows real-time
control of all objects, e.g., vehicles, traffic lights, in
the created traffic scenarios. Thereby, we can simu-
late various traffic scenarios ranging from synthetic
networks up to real-world traffic situations, (real net-
works may be imported via an OpenDRIVE (ASAM,
2020) interface or from OpenStreetMap (OSM) data
(OpenStreetMap, 2020). Moreover, SUMO provides
a traffic control interface (TraCI) that allows to re-
trieve information about the traffic system and change
values of the objects at each time step. As program-
ming environment, we use Python and with the cor-
responding TraCI application programming interface
(API), we can, for example, observe speeds and posi-
tions of a follower/leader pair, then calculate the fol-
lowing vehicles speed at the next time step and pass it
to the SUMO configuration.
2.3 Traffic Control Scenarios
One traffic scenario that has become famous in recent
years is based on a real-world experiment (Sugiyama
et al., 2008): several human driven vehicles are placed
at equal distances between each other on a ring road
and told to follow a given speed for a certain time
period. It has been shown that, without any external
effects like traffic lights or lane changes, human driv-
ing behaviour alone leads to stop-and-go waves and
congestions. In our study, the main idea is to replace
one human-driven vehicle (or several vehicles) by an
intelligently, RL-based controlled vehicle, called au-
tonomous vehicle (AV), that gets information about
the speeds and positions of all vehicles in the system.
With these information, the AV aims to improve traf-
fic flow for all vehicles in the system by outbalancing
the stop-and-go waves with optimal accelerations and
decelerations. If we assume the human-driven vehi-
cles are controlled by car-following models, this leads
to an optimal control problem constrained by a cou-
pled system of ODEs. Instead of solving this problem
with classic solution methods, we apply an RL ap-
proach where the controlled vehicle tries to maximize
its reward (objective function) by repetitive simula-
tion of the traffic situation.
As already indicated, we consider a second con-
troller type as well, namely an agent that controls one
or several traffic lights. In that set-up, every time step,
the agent has to decide, if each traffic light stays at the
current traffic light phase or switches to the next one.
The goal is to lead traffic flows as fluently as possible
through a given road network with persistently leav-
ing and entering vehicles. Again, the agent, i.e., the
traffic light(s) controller, obtains real-time informa-
tion about the vehicles and roads in the system and
optimizes the traffic flow by repetitive simulation.
3 REINFORCEMENT LEARNING
Reinforcement learning has achieved huge success in
different areas and in recent years, it has been applied
to a few applications in traffic control (Chae et al.,
2017; Belletti et al., 2017; Vinitsky et al., 2018). As
described, RL controllers work usually by repeating a
task several times to learn applying optimal actions in
different situation. With higher computational power
available, this gets more and more applicable to a lot
of scenarios and is a competitive approach to optimize
traffic flows.
3.1 General Concepts
The mathematical framework for (model-free) RL is
given by a Markov Decision Process (MDP) (Puter-
man, 1994; Feinberg and Shwartz, 2002; Sutton and
Barto, 2018). It describes the ongoing interaction be-
tween an agent (controller) and its environment (dy-
namical system). The agent aims to iteratively gain
knowledge about the system and control it optimally.
A Reinforcement Learning Approach for Traffic Control
135
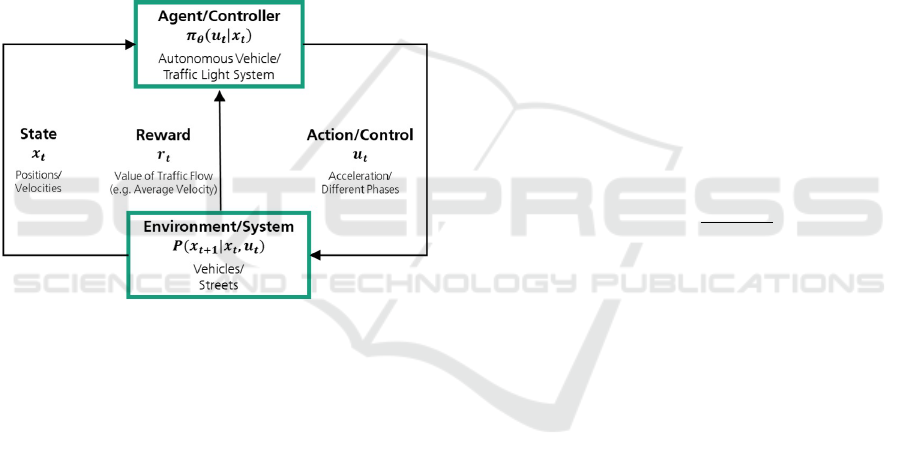
MDPs are defined by a tuple (X, U,P,r,ρ
0
,γ,t
f
) con-
sisting of the state space X, action (or control) space
U, transition probability function P : X ×U ×X →
[0,1], reward function r: X ×U →R, initial state dis-
tribution ρ
0
: X →[0,1], discount factor γ ∈(0, 1] and
time horizon t
f
∈ R
>0
(Duan et al., 2016).
At the beginning of each MDP episode with dis-
crete time steps, the environment is described by an
initial set of states x
0
, given by initial distribution,
x
0
∼ ρ
0
. Then, at each time step t the environment
generates a new state following the transition prob-
ability function P(x
t+1
|x
t
,u
t
) and the action u
t
cho-
sen by the agent. To evaluate the current combi-
nation of state and action, the environment also re-
turns a reward r
t
= r(x
t
,u
t
). Finally, the trajectory
data of one episode or rollout is summarized by τ =
(x
0
,u
0
,x
1
,u
1
,...,x
t
f
).
Figure 1: MDP interaction between agent and environment
for traffic control scenarios.
3.2 Model-free Reinforcement Learning
In contrast to model-based RL, where, basically, a
model for the environment is learned first, in model-
free RL, the agent typically determines its actions by
a deterministic policy u
t
= µ
θ
(u
t
,x
t
) or by sampling
from a stochastic policy u
t
∼ π
θ
(u
t
|x
t
). Both choices
for the policy are parametrized by a vector θ and the
goal is to find the policy parameters that optimize the
following maximization problem
max
θ
E[
t
f
−1
∑
t=0
γ
t
r(x
t
,u
t
)]. (5)
To build such a policy, we assume real-valued state
and action spaces with dimensions n and p (X = R
n
and U = R
p
). Then, we define a function f
θ
: X →
U parametrized by θ and the deterministic policy is
given by
µ
θ
= f
θ
(x). (6)
For the stochastic policy, typically, Gaussian distribu-
tions with mean f
θ
(x) and a fixed covariance matrix
Σ ∈ R
p
×R
p
are chosen
π
θ
∼ N( f
θ
(x),Σ). (7)
One common choice for f
θ
in RL are deep neural nets
like Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs) that have already
been applied to control traffic networks with RL (Wu
et al., 2017). In this contribution, we show that it
is possible to obtain satisfying results with structures
like linear models or radial basis function (RBF) net-
works. For the linear model policy, we define
f
θ
(x) = W x +b, (8)
with W ∈ R
n×p
and b ∈ R
p
that leads to parameter
vector θ ∈R
(n+1)p
storing the entries of W and b.
Further, as a second controller model example,
we introduce non-linearity into the policy represen-
tation by considering a representation with RBF net-
works. They have been used in several areas of ma-
chine learning (Bishop, 2006; Murphy, 2012) as well
as in RL (Deisenroth, 2010). The representation of
a policy by a RBF network consists of the centres
c
i
∈R
n
, radii r
i
∈R, bias b ∈R
p
and weighting matrix
W ∈R
m×p
where m is the number of centres. First, we
define the Gaussian radius function
h
i
(x) = exp
−
k
x −c
i
k
2
2
2r
2
i
!
. (9)
Then, similarly to the linear model, those RBF func-
tions are combined to a weighted sum
f
θ
(x) = W h(x) + b (10)
with h(x) = [h
1
(x),...,h
m
(x)]
T
and the parameter
vector θ ∈ R
(n+1)m+(m+1)p
contains all values c
i
, r
i
and the entries in W and b.
Most RL algorithms work by iteratively updat-
ing the policy parameters θ to maximize the objective
function (cf. Eq. (5)) (Duan et al., 2016). If θ con-
tains a lot of parameters or the state and control space
have high dimensions, this results in a huge number
of computations. Therefore, instead of optimizing all
parameters of the RBF network, we first derive cen-
tres c
i
and radii r
i
and fix them, in order to only update
the entries of W and b by the RL-technique.
The Gaussian radius function as defined in Eq. (9)
measures for each state x the distance to centres c
i
.
If we already have sampled data of the state space
{x
1
,...,x
N
}, e.g., from previous simulations, we can
choose centres such that the distances are small.
To find centres with small distances, we apply a k-
means clustering algorithm (Bishop, 2006). Such an
approach does not only reduce the number of opti-
mization parameters but also tackles the problem of
VEHITS 2021 - 7th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
136

finding suitable initial parameters θ
0
. In contrast to
randomly chosen parameters, we can further decrease
computational costs, leading to desirable results with
less iterations, as we will show in Sect. 4. This is a
substantial benefit of RBF networks as control poli-
cies compared to, e.g., standard MLP neural nets.
In our experiments, we use policy update algo-
rithms that optimize the policy parameters iteratively
without having exact information about the dynamics
of the environment. That is, we can derive a policy π
θ
and then a trajectory τ with the corresponding states
and actions will be created following the episodic set-
ting of MDPs. After each episode, we can evaluate
the collected rewards and change the parameters of
θ with the goal to improve the value of the objective
function defined in Eq. (5).
In particular, in our experiments, we apply an aug-
mented random search (ARS) method as stated in
(Mania et al., 2018).
4 EXPERIMENTS AND
CASE-STUDIES
In this section, we present the application of specific
RL-based controllers to two different virtual traffic
scenarios. As a first case-study, we control several
vehicles in the so-called ring road experiment. In the
second study, we consider a virtual version of a real
road network, in which an RL-agent steers the traffic
light systems.
4.1 Ring Road
Figure 2: Representation of the ring road in SUMO where
the blue vehicle is controlled by an autonomous vehicle.
The ring road is an artificial traffic scenario that has
revealed insufficiencies of human driving behaviour
and how connected autonomous vehicles (AVs) can
be used to improve traffic flow (Sugiyama et al., 2008;
Stern et al., 2018). While deep RL has already been
applied to this scenario (Wu et al., 2017), here, we ap-
ply and analyse an RL controller with RBF network
policy.
We set up the ring road with radius 50m in SUMO
and describe it in the framework of MDPs. The envi-
ronment’s state space consists of the speeds and two-
dimensional positions of N = 22 vehicles in the sys-
tem
x = (v
1
,...,v
N
,s
1
1
,s
2
1
...,s
1
N
,s
2
N
) ∈ R
3N
. (11)
At each time step the AVs are controlled by an RL
agent that determines the vehicles’ longitudinal accel-
erations and decelerations with a parametrized policy
π
θ
. We aim to find policy parameters that maximize
the objective function (cf. Eq. (5)), whereby the re-
ward is set to be the average speed over all vehicles
r(x, u) =
1
N
N
∑
i=1
v
i
. (12)
We use a RBF network policy with m = 20 cen-
tres. If the RL agent only controls one AV, the ac-
tion space dimension is p = 1 and, therefore, θ ∈
R
(3N+1)m+(m+1)p
= R
1361
, i.e., the number of opti-
mization parameters is 1361. By obtaining the centres
c
i
with clustering as described in Sect. 3 and fixing
all radii to r
i
= 1, only the weighting matrix W and
the bias b have to be optimized. The decreased num-
ber of parameters leads to less computational costs
as well as to faster convergence of solutions because
prior knowledge of the system is put into the policy
by the clustering from previous simulations.
Then, after determining initial parameter vector θ
0
with the clustering technique, different situations are
simulated by changing the parameters that lead to dif-
ferent rewards. We update the parameters with the
ARS algorithms to iteratively improve the traffic flow
by maximizing the value of the objective function.
Experimental Set-up. All human drivers (HDs)
that are not controlled by the agent follow the IDM
with parameters β
IDM
= [v
des
,T, h
min
,δ,a
max
,b] =
[8,0.1,2,4,1,1.5] as described in Eq. (4). We con-
sider three different scenarios:
• HD Only: First, all vehicles are assumed to be
HDs. The vehicles are placed randomly on the
lane and the parameters β
IDM
are chosen to model
realistic human driving behaviour leading to the
stop-and-go behaviour observed in the real-world
scenario.
A Reinforcement Learning Approach for Traffic Control
137

• One AV: Then, one of the HDs is replaced by an
AV that obtains real-time information from all ve-
hicles in the system.
• Three AV: Further, to show the impact of several
AVs in mixed-traffic networks, three HDs are re-
placed by AVs.
For both RL scenarios the agents are optimized on an
eight-core Intel Xeon Gold 6248R processor. We use
Python for optimization and to interact with SUMO,
see Sect. 2.2. As for the ARS algorithm differ-
ent rollouts of one iteration can be calculated at the
same time, we use Python package multiprocessing to
compute rollouts simultaneously on each of the eight
cores of the processor. Thereby, we can calculate an
optimization with 50 iterations and 32 rollouts in ap-
proximately two hours.
Results. After optimization, we observe the vehi-
cles’ average speed in each scenario for time horizon
t
f
= 300s, see Figure 3. For the HD only scenario
the vehicles accelerate at the beginning but due to the
emerging stop-and-go wave, several vehicles have to
slow down leading to a lower average speed for the
rest of the time horizon.
In contrast, the AV in the second scenario does not
accelerate as fast as the HD leading to the formation
of a platoon behind the AV. Then, the AV accelerates
more smoothly and stabilizes the traffic flow around
an equilibrium speed.
For the third scenario, we observe a faster in-
crease of the average speed. As the three AVs have
been equally distributed among the HDs, each AV can
outbalance more inefficient human acceleration be-
haviour. Then, all three vehicles increase their speed
faster than the single AV in the previous scenario and,
finally, they stabilize the traffic flow around the same
average speed as in the second scenario.
Figure 3: Average speed [m/s] for the different scenarios
over time horizon t
f
= 300s.
Figure 4: Opel-Roundabout in Kaiserslautern, Germany
(OpenStreetMap, 2020).
4.2 Opel-roundabout
The Opel-roundabout is a real-world road network in
Kaiserslautern, Germany. It can be seen as a round-
about with six incoming and outgoing lanes and the
traffic flow is controlled by several traffic lights as
shown in Figure 4.
In our virtual set-up these traffic lights are con-
trolled by switching through different phases with
fixed durations. Such static behaviour leaves room for
improvement and in the last decades, several solutions
for optimal traffic light control have been proposed
(McNeil, 1968; De Schutter and De Moor, 1998). In
recent years, RL has been applied to this kind of prob-
lem, too, and solutions controlling one or several traf-
fic lights simultaneously have been presented (Wier-
ing, 2000; Arel et al., 2010; Vinitsky et al., 2018).
We apply our RL approach to this traffic scenario
by aggregating the traffic lights to six different traffic
control units, which can switch between two phases
showing either green for one or the other direction,
see Figure 4. Every time step the RL agent decides
for all units whether to stay at the current phase or
to switch to the next one. Thus, following the RL
procedure as presented in Sect. 3, the traffic flow is
optimized iteratively from run to run by optimizing a
linear model policy in the RL agent.
The traffic situation can be set up in SUMO as the
simulation software contains a build-in tool that al-
lows to convert OpenStreetMap data to SUMO net-
works. For five of the six traffic light units, there are
two incoming lanes and for the one at the top right
there are three incoming lanes which totals in thirteen
lanes that are directly heading to the units. For all
of them, the RL agent observes the density (number
of vehicles on the lane), the minimum distance of the
closest vehicle to next traffic light unit, the number
of waiting vehicles in front of the traffic light (speed
v < 0.1m/s), the time since the last change has oc-
curred and a binary variable indicating whether the
VEHITS 2021 - 7th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
138
upcoming traffic light is green or not. This leads to
an environment, represented by a state space with di-
mension n = 65.
The agent determines its action u
t
∈ R
6
for each
of the six traffic light unit with a linear model policy.
We define a fixed value u
switch
such that, if u
i
t
> u
switch
for time step t and unit i, the traffic light unit switches
to the next phase and, if u
i
t
≤ u
switch
, it stays at the
current one. Then, the policy parameters θ consist of
the entries of W ∈ R
65×6
and b ∈ R
6
.
To decrease the number of optimization parame-
ters, we set entries of W to zero such that each con-
trol unit only receives information from lanes directly
heading to it. The remaining parameters of vector θ
are optimized with the ARS algorithm and we choose
the same reward function (Eq. (12)) as in the ring road
experiment.
Experimental Set-up. To obtain a realistic traffic
scenario, vehicles are entering and leaving the net-
work persistently over a fixed time horizon. We as-
sume that all of them are HDs that obtain their speeds
from car-following models. There are six incoming
and six outgoing lanes and we determined realistic
frequencies f
i j
indicating the probability of a vehi-
cle entering the network on lane i and leaving it on
lane j. For each time step, we draw samples z
i j
of a
uniform distributed random variable Z ∼U(0, 1) and,
if z
i j
≤ f
i j
, a vehicle starts driving from lane i to lane
j. We use stochastically chosen frequencies for the
training of the controller to model different traffic sce-
narios and make it less prone to changes of the envi-
ronment. Additionally, it seems more realistic to as-
sume that vehicles are not entering the system in equal
time periods. The entries f
i j
are summarized in a fre-
quency matrix F.
The RL controller is trained in stochastic scenar-
ios based on frequency matrix F and we compare it
with a typical static traffic light switching program.
This static controller is based on a realistic fixed cy-
cle time of 90s and aims at avoiding collisions and
achieving high values of traffic flow.
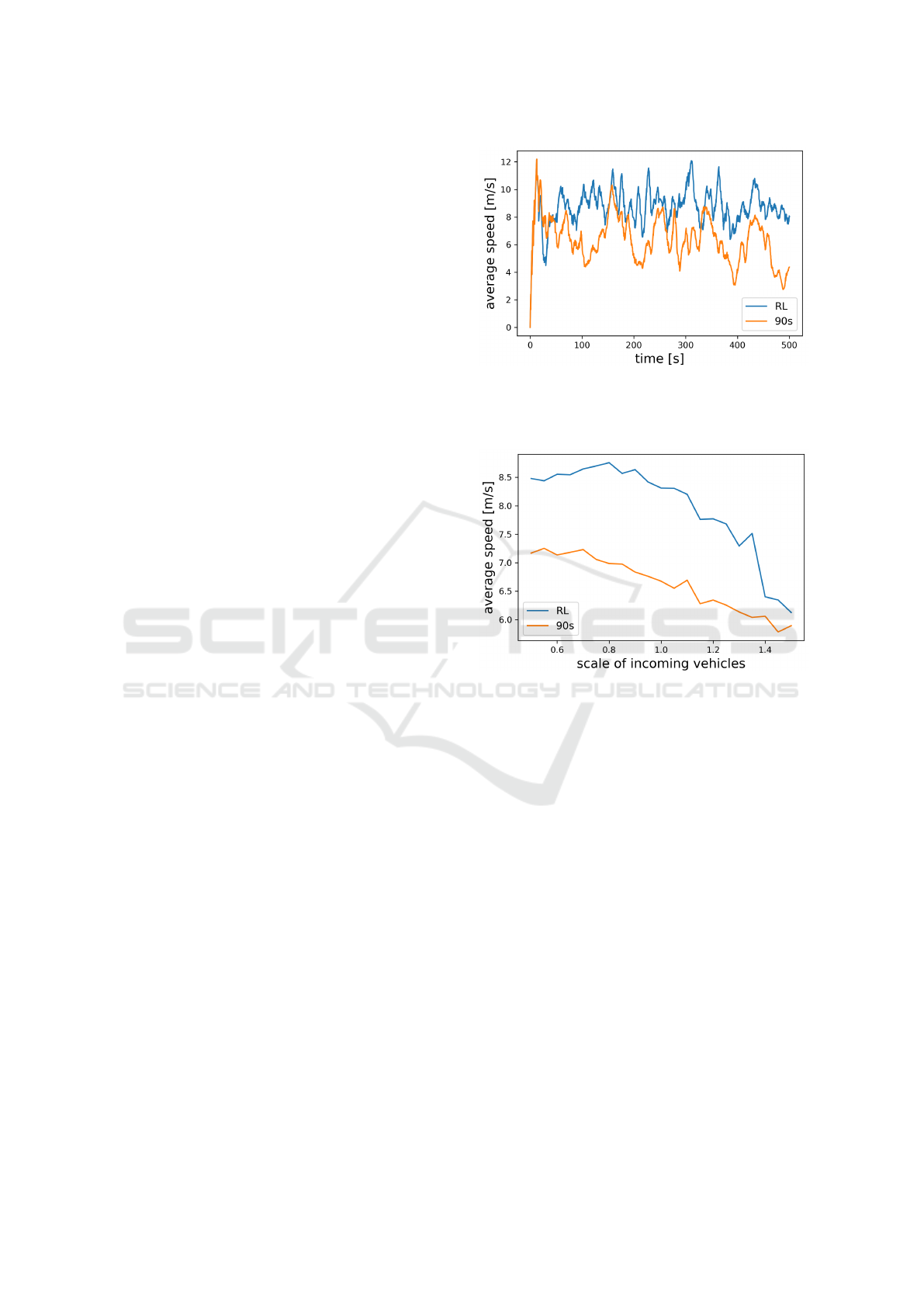
Results. First, in Figure 5, results are shown from
both a scenario with the static controller and with the
RL-based controller. Most of the time steps, the RL
controller achieves a higher average speed over all ve-
hicles which indicates that it can outperform the static
controller on a frequency that it is trained on.
Next, we compare both controllers on differ-
ent frequencies of incoming vehicles. That is, we
multiply each entry of F with a fixed value k ∈
{0.5,0.55,0.6,...,1.45,1.5} and simulate 20 scenar-
ios for each scaling step. In Figure 6, we compare
Figure 5: RL agent and static 90s controller in terms of the
average speed [m/s] over all vehicles for one scenario that
was created with frequency matrix F and fixed stochastic
seed.
Figure 6: The RL controller is trained on frequency matrix
F of incoming vehicles and the frequencies are scaled from
0.5F up to 1.5F. For each scaling step 20 simulations are
calculated and the RL agent and the static 90s controller are
compared in terms of the average [m/s] over all vehicles
and simulations.
the average speed over all vehicles and the entire time
horizon of all simulations for each value k. We ob-
serve that the RL controller increases traffic flow es-
pecially for low frequencies of incoming vehicles but
also outperforms the static controller for all other sim-
ulated scenarios. As the RL agent obtains real-time
information about its traffic environment, it is more
capable of adjusting the phases to scenarios where ve-
hicles are entering more frequently from one direction
or with varying time gaps.
For a higher number of incoming vehicles, the
impact of these effects decreases, and, because the
RL agent has been trained on frequency matrix F, it
is more often confronted with scenarios that not oc-
curred during training. However, the results are very
remarkable as the RL agent optimized traffic flow
without any insights about the traffic environment
before optimization such that the observations made
during several rollouts were sufficient to achieve de-
A Reinforcement Learning Approach for Traffic Control
139

sirable results for all considered scenarios.
5 SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION
After introducing microscopic car-following models
and reinforcement learning (RL) in the framework of
Markov Decision Processes (MDPs), we have com-
bined them, to optimize traffic flows with RL agents.
We have shown that these agents are able to control
autonomous vehicles or traffic lights, to lead other ve-
hicles more fluently through different road networks.
By all means, the RL agents in our set-ups rely on
data that, right now, is typically not fully accessible
on a real-time basis like we assumed in the experi-
ments. But currently, there are huge developments on
both, the vehicle and network technology side, and,
therefore, it seems realistic to expect the experiments
of this work, to be applicable to real-world situations
in the near future.
We stress that, in our view, the results are very re-
markable because the agents do not rely on any prior
knowledge about the traffic environment, but only on
observations they have made during several simula-
tions. For complex road networks like the consid-
ered Opel-roundabout, static traffic light systems have
to be optimized over years by applying heuristic ex-
perience and very costly analysis or time-consuming
observations. Hence, we expect RL (or other data-
driven) controllers, that have been trained and opti-
mized with simulations, to be capable of outperform-
ing static controllers for different road networks in
real-world applications.
It is important and crucial to point out that the
transfer and the application, respectively, of RL con-
trollers to the real world is a substantial challenge,
which is far from being understood and fully solved.
The classical training requires the possibility to run
controllers with poor performance, which is in reality
and, especially, in safety-relevant situations, like traf-
fic with humans involved, merely impossible. Train-
ing in a virtual environment, as we have done it
here, and transferring the trained controller afterwards
would require a very good and guaranteed match be-
tween the virtual environment and reality. In litera-
ture, there are approaches and investigations that are
concerned with so-called offline reinforcement learn-
ing (Levine et al., 2020). Moreover, it is necessary to
guarantee both accuracy and stability for the RL con-
trollers, which is, at least partially, an open task as
well. Last, not least, even the reproducibility of RL
training approaches is currently an ongoing research
(Henderson et al., 2018).
In this work we have shown, that RL can be ap-
plied to traffic control with methods, that are rather
straightforward to implement and that are able to
achieve satisfying results with limited computational
capacity. In the RL field, however, currently there are
several different optimization algorithms, that have
proven, to reach even better results in other applica-
tions (Duan et al., 2016). Accordingly, more sophisti-
cated structures like deep neural nets could also be ap-
plied here for the policy representation in traffic flow
control. While they are able to model more complex
relations between state and control space, on the one
hand, they also lead, on the other hand, to an increase
of parameters in the policy vector θ and may lead
to more time-consuming computations. Additionally,
complex structures can decrease the explainability of
the obtained solution.
As future work, we plan to investigate the perfor-
mance, robustness and stability of the proposed ap-
proach, especially for extreme traffic scenarios (e.g.
vehicles only enter the traffic network from one lane
or occurrence of emergency vehicles). Moreover, we
intend the application of further controller models as
well as a detailed comparison to existing approaches.
Furthermore, we will study the enhancement of the
model-free and data-driven RL approach, as consid-
ered in this paper, with physics-based traffic mod-
elling and control, to improve both, the controller’s
performance and interpretability.
REFERENCES
Arel, I., Liu, C., Urbanik, T., and Kohls, A. (2010). Rein-
forcement learning-based multi-agent system for net-
work traffic signal control. IET Intelligent Transport
Systems, 4:128–135.
ASAM (2020). ASAM OpenDRIVE. https://www.asam
.net/standards/detail/opendrive/. Accessed Dec.18,
2020.
Belletti, F., Haziza, D., Gomes, G., and Bayen, A. (2017).
Expert Level Control of Ramp Metering Based on
Multi-Task Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE
Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,
19(4):1198–1207.
Bishop, C. M. (2006). Pattern Recognition and Machine
Learning. Springer-Verlag New York.
Chae, H., Kang, C. M., Kim, B., Kim, J., Chung, C. C.,
and Choi, J. W. (2017). Autonomous braking system
via deep reinforcement learning. In 2017 IEEE 20th
International Conf. on Intelligent Transportation Sys-
tems (ITSC), pages 1–6.
De Schutter, B. and De Moor, B. (1998). Optimal Traf-
fic Light Control for a Single Intersection. European
Journal of Control, 4(3):260 – 276.
Deisenroth, M. P. (2010). Efficient Reinforcement Learn-
ing using Gaussian Processes. PhD thesis, Karlsruhe
Institute of Technology (KIT).
VEHITS 2021 - 7th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
140

Duan, Y., Chen, X., Houthooft, R., Schulman, J., and
Abbeel, P. (2016). Benchmarking Deep Reinforce-
ment Learning for Continuous Control. In Proceed-
ings of The 33rd International Conference on Ma-
chine Learning, volume 48 of Proceedings of Machine
Learning Research, pages 1329–1338.
Feinberg, E. and Shwartz, A. (2002). Handbook of
Markov Decision Processes: Methods and Applica-
tions. Springer US.
Gazis, D. C., Herman, R., and Rothery, R. W. (1961). Non-
linear Follow-the-Leader Models of Traffic Flow. Op-
erations Research, 9(4):545–567.
Henderson, P., Islam, R., Bachman, P., Pineau, J., Precup,
D., and Meger, D. (2018). Deep Reinforcement Learn-
ing that Matters. arXiv: 1709.06560.
Kalashnikov, D., Irpan, A., Pastor, P., Ibarz, J., Herzog,
A., Jang, E., Quillen, D., Holly, E., Kalakrishnan,
M., Vanhoucke, V., and Levine, S. (2018). Scal-
able Deep Reinforcement Learning for Vision-Based
Robotic Manipulation. In Proceedings of The 2nd
Conf. on Robot Learning, vol. 87 of Proceedings of
Machine Learning Research, pages 651–673.
Levine, S., Kumar, A., Tucker, G., and Fu, J. (2020). Of-
fline Reinforcement Learning: Tutorial, Review, and
Perspectives on Open Problems. arXiv: 2005.01643.
Lighthill, M. J. and Whitham, G. B. (1955). On kinematic
waves. II. A theory of traffic flow on long crowded
roads. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A, 229:317–345.
Lopez, P. A., Behrisch, M., Bieker-Walz, L., Erdmann, J.,
Fl
¨
otter
¨
od, Y.-P., Hilbrich, R., L
¨
ucken, L., Rummel,
J., Wagner, P., and Wießner, E. (2018). Microscopic
Traffic Simulation using SUMO. In The 21st IEEE
Intl. Conf. on Intelligent Transportation Systems.
Lu, X.-Y., Varaiya, P., Horowitz, R., Su, D., and Shladover,
S. E. (2011). Novel Freeway Traffic Control with
Variable Speed Limit and Coordinated Ramp Meter-
ing. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the
Transportation Research Board, 2229(1):55–65.
Mania, H., Guy, A., and Recht, B. (2018). Simple random
search provides a competitive approach to reinforce-
ment learning. arXiv: 1803.07055.
McNeil, D. R. (1968). A Solution to the Fixed-Cycle Traffic
Light Problem for Compound Poisson Arrivals. Jour-
nal of Applied Probability, 5(3):624–635.
Murphy, K. P. (2012). Machine Learning: A Probabilistic
Perspective. The MIT Press.
OpenStreetMap (2020). https://www.openstreetmap.org.
Accessed Dec.18, 2020.
Orosz, G. (2016). Connected cruise control: modelling, de-
lay effects, and nonlinear behaviour. Vehicle System
Dynamics, 54(8):1147–1176.
Orosz, G., Wilson, R. E., and St
´
ep
´
an, G. (2010). Traffic
jams: dynamics and control. Philosophical Transac-
tions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical
and Engineering Sciences, 368(1928):4455–4479.
Puterman, M. L. (1994). Markov Decision Processes: Dis-
crete Stochastic Dynamic Programming. John Wiley
& Sons, Inc., 1st edition.
Rajeswaran, A., Kumar, V., Gupta, A., Vezzani, G., Schul-
man, J., Todorov, E., and Levine, S. (2018). Learn-
ing Complex Dexterous Manipulation with Deep Re-
inforcement Learning and Demonstrations. In Pro-
ceedings of Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS).
Recht, B. (2019). A Tour of Reinforcement Learning:
The View from Continuous Control. Annual Re-
view of Control, Robotics, and Autonomous Systems,
2(1):253–279.
Schulman, J., Levine, S., Moritz, P., Jordan, M., and
Abbeel, P. (2015). Trust Region Policy Optimization.
In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conf. on In-
ternational Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 37
of ICML’15, pages 1889–1897.
Silver, D., Hubert, T., Schrittwieser, J., Antonoglou, I., Lai,
M., Guez, A., Lanctot, M., Sifre, L., Kumaran, D.,
Graepel, T., Lillicrap, T., Simonyan, K., and Hass-
abis, D. (2018). A general reinforcement learning
algorithm that masters chess, shogi, and Go through
self-play. Science, 362(6419):1140–1144.
Stern, R. E., Cui, S., Delle Monache, M. L., Bhadani, R.,
Bunting, M., Churchill, M., Hamilton, N., Haulcy,
R., Pohlmann, H., Wu, F., Piccoli, B., Seibold, B.,
Sprinkle, J., and Work, D. B. (2018). Dissipation
of stop-and-go waves via control of autonomous ve-
hicles: Field experiments. Transportation Research
Part C: Emerging Technologies, 89:205 – 221.
Sugiyama, Y., Fukui, M., Kikuchi, M., Hasebe, K.,
Nakayama, A., Nishinari, K., Tadaki, S.-i., and
Yukawa, S. (2008). Traffic jams without bottle-
necks—experimental evidence for the physical mech-
anism of the formation of a jam. New Journal of
Physics, 10(3):033001.
Sutton, R. S. and Barto, A. G. (2018). Reinforcement Learn-
ing: An Introduction. Adaptive Computation and Ma-
chine Learning. MIT Press, 2nd edition.
Treiber, M. and Kesting, A. (2013). Traffic Flow Dynamics.
Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Vinitsky, E., Kreidieh, A., Flem, L. L., Kheterpal, N., Jang,
K., Wu, C., Wu, F., Liaw, R., Liang, E., and Bayen,
A. M. (2018). Benchmarks for reinforcement learning
in mixed-autonomy traffic. In Proceedings of The 2nd
Conf. on Robot Learning, vol. 87 of Proceedings of
Machine Learning Research, pages 399–409.
Wang, J., Zheng, Y., Xu, Q., Wang, J., and Li, K.
(2020). Controllability Analysis and Optimal Control
of Mixed Traffic Flow With Human-Driven and Au-
tonomous Vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent
Transportation Systems, pages 1–15.
Wiering, M. (2000). Multi-Agent Reinforcement Leraning
for Traffic Light Control. In Proceedings of the Sev-
enteenth Intl. Conf. on Machine Learning, ICML ’00,
pages 1151–1158.
Williams, R. J. (1992). Simple statistical gradient-following
algorithms for connectionist reinforcement learning.
Machine Learning, 8(3):229–256.
Wu, C., Kreidieh, A., Parvate, K., Vinitsky, E., and Bayen,
A. M. (2017). Flow: Architecture and Benchmarking
for Reinforcement Learning in Traffic Control. arXiv:
1710.05465.
Zheng, Y., Wang, J., and Li, K. (2020). Smoothing Traf-
fic Flow via Control of Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE
Internet of Things Journal, 7(5):3882–3896.
A Reinforcement Learning Approach for Traffic Control
141
