
‘This Student Needs to Stay Back’: To What Degree Would
Instructors Rely on the Recommendation of Learning Analytics?
Linda Mai, Alina Köchling and Marius Wehner
*
Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Germany
Keywords: Learning Analytics, Recommendation, Experimental Design, Adaptive Choice-based Experiment.
Abstract: Learning Analytics (LA) systems are becoming a new source of advice for instructors. Using LA provides
new insights on learning behaviours and occurring problems about learners. Educational platforms collect a
wide range of data while learners use them, for example, time spent on the platform, exams taken, and
completed tasks, and provide recommendations in terms of predicted learning success based on LA. In turn,
LA might increase efficiency and objectivity in the grading process. In this paper, we examine how instructors
react to the platform’s automatic recommendations and to which extent they consider them when judging
learners. Drawing on an adaptive choice-based experimental research design and a sample of 372 instructors,
we analyse whether and to what degree instructors are influenced by the recommendations of an unknown
LA system. We also describe which consequences an automatic judgment might have for both learners and
instructors and the impact of using platforms in schools and universities. Practical implications are discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Due to the increasing digitization in educational
institutions and the associated use of digital learning
platforms (Oliveira et al., 2016), a vast amount of data
is generated concerning the learning process, the
learning progress, the learning outcome, and the
learners themselves (Peña-Ayala, 2018). The
COVID-19 pandemic may have accelerated this
process (Rosenberg and Staudt Willet, 2020). Many
platforms evaluate data automatically and
additionally provide these for instructors to address
the problem of differentiation (Aguilar, 2018).
Learning analytics (LA) is defined as a systematic
analysis of large amounts of data about learners,
instructors, and learning processes to increase the
learning success and make teaching more effective
and efficient (Greller and Drachsler, 2012). Although
these objectives are oriented towards the pedagogical
context, problems can arise with grading. In 2020,
using an algorithm developed by England’s exam
regulator Ofqual which was based on historical grade
profiles revealed some obstacles (Paulden, 2020).
This event shows, that judgments are a very sensitive
issue with personal consequences. Given the
*
In this paper, we use the term ‘instructor’ for both
teachers and other lecturers and instructors with
numerous opportunities of LA, the focus was rather
on learners, their learning success and designing
activities (Peña-Ayala, 2018); however, the platforms
and LA might influence instructors as well.
Relying on the framework by Greller and
Drachsler (2012), instructors are involved as
stakeholders when using LA. Consequently, they
should not be overlooked when researching
stakeholders. This framework is the foundation on
which current research on the design process for LA,
for example, is built, because it takes ethical issues
into account (Nguyen et al., 2021). From an
instructor’s perspective, platforms provide access to
new information usually hidden in traditional
learning contexts, such as learning behaviour and
time spent with the offered materials online. This can
improve the planning of teaching activities (Siemens
and Long, 2011), but might influence the instructor’s
judgment.
Judgment accuracy is the instructors’ ability to
assess learners’ characteristics and adequately
identify learning and task requirements (Artelt and
Gräsel, 2009). In educational contexts, instructors can
be affected when it comes to assessments. They can
be biased by ethnic and social backgrounds (Tobisch
educational tasks in schools, high schools, and
universities.
Mai, L., Köchling, A. and Wehner, M.
‘This Student Needs to Stay Back’: To What Degree Would Instructors Rely on the Recommendation of Learning Analytics?.
DOI: 10.5220/0010449401890197
In Proceedings of the 13th Inter national Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2021) - Volume 1, pages 189-197
ISBN: 978-989-758-502-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
189

and Dresel, 2017), expectations (Gentrup et al.,
2020), halo effects (Bechger et al., 2010) and other
impacts that influence judgment accuracy (Urhahne
and Wijnia, 2021).
Despite the growing use in practice, research about
LA’s influence on instructors’ judgement is still
limited. Therefore, this study aims to examine to what
extent instructors might be influenced in a setting with
information and recommendations provided by LA.
We empirically analyse different evaluation
criteria. The analysis relies on an adaptive choice-
based conjoint analysis (ACBC) based on a sample of
372 instructors in Germany. The contributions of this
study are both theoretically and practically relevant.
2 THEORETICAL
BACKGROUND
2.1 Learning Analytics
LA is the measurement, collection, analysis, and
reporting of data about learners and their contexts to
understand and improve learning and the
environments in which it occurs (Gasevic et al., 2011;
Ferguson and Shum, 2012). This means a range of
educational (meta)data is analysed automatically to
provide more information about learners. Information
can be used to promote learners’ reflection, but they
are also interesting for prediction systems of learners’
success (Greller and Drachsler, 2012). The goal of
LA is to analyse learners and their learning behaviour
in such a way that learning practices can be
individually adapted to the needs of the learners and
thus become more effective (Aguilar, 2018). LA can
include machine learning methods to evaluate and
monitor learning activities (Bañeres et al., 2020).
Although all stakeholders have an interest in data and
learning success, Greller and Drachsler (2012)
distinguish between learners and instructors. Learners
come up with data and gain feedback on their
learning. Instructors receive data reports from the
platform and act accordingly. That means they can
adapt their behaviour to the learners’ requirements
and intervene.
Predictive outcomes can prevent failure, for
example, with early warning systems (Waddington et
al., 2016; Akçapınar et al., 2019). An early warning
system can be a powerful signal and might motivate
students to use support and intervention offers (Smith
et al., 2020). In the USA, universities need to focus
on successful students because they increase the
reputation and assure funding. In this regard, LA is a
powerful tool to identify those students who might
fail and to support students in achieving their learning
goals (Jones et al., 2020).
2.2 Learning Analytics in Germany
To use LA in schools and universities, the aspects of
pedagogy, complexity, ethics, power, regulation,
validity, and affect need to be considered (Ferguson
and Shum, 2012). These aspects are highly dependent
on the cultural framework. In Germany, individuality,
competition, performance, and success are important
cultural factors (Hofstede et al., 2010). In Germany,
education has a high impact on later opportunities and
careers.
Our study is motivated by the ongoing
digitization, promoted by the government, and
facilitated by the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany.
Although it would be technically possible, the use of
the platforms is not yet as widespread as, for example,
in the USA. In Germany, schools and universities are
increasingly using platforms to support the learning
processes and distance learning (Luckin and
Cukurova, 2019); however, these systems are mainly
used to provide materials and offer optional tests or
exams. Still, automatic recommendations by LA are
uncommon because (1) personal data are protected by
the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in
the European Union and (2) the majority of German
schools are rather traditional when it comes to digital
practices. Hence, instructors are not using all the
provided functions of platforms that are already
implemented. Nevertheless, future developments and
the COVID-19 pandemic will change the usage of
digital learning systems in Germany.
2.3 Influence on Instructors’ Judgment
Instructors are required to assess their learners’
abilities and competencies, but the accuracy of these
judgements is often unknown (Demaray and Elliot,
1998). In traditional education, systematic biases and
influences on judgment accuracy are well-studied
(Doherty and Conolly, 1985; Cadwell and Jenkins,
1986; Kaiser et al., 2015; Urhahne and Wijnia, 2021).
Biases lead to the problem of unfair grading in school
and university contexts. There is evidence that
instructors are biased by several personally
conditioned factors, such as judgment characteristics
and test characteristics, which in turn influence the
accuracy (Südkamp et al., 2012).
Learning platforms provide new information that
can be used for learners’ assessment and can
complement the face-to-face sessions (Romero and
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
190

Ventura, 2013). Additionally, LA offers data and
analyses about learners and provides insight for the
educators, students, and other stakeholders
(Buckingham Shum and Deakin Crick, 2016). Hence,
recommendations about learners’ success are
additional factors when taking the influence of learning
platforms on instructors into consideration. To find out
how instructors react to the prediction of platforms, we
designed a conjoint experiment that offers different
kinds of information about the learners.
3 METHOD
3.1 Adaptive Choice-based Conjoint
Experiment
Our study uses conjoint analysis that has been applied
in numerous judgment and decision-making studies
among various disciplines (Green et al., 2004).
Developed from a psychological context with the idea
of using ordinal information only to focus on
composing rules (Krantz and Tversky, 1971), this
method was also used in recruiting and educational
contexts in the recent years (e.g., Blain-Arcaro et al.,
2012; Oberst et al., 2020). This methodological
approach has several advantages concerning
challenges associated with the research context: As
this method allows researchers to stimulate
respondent’s decision processes in real-time, it is in
several ways superior to commonly used post-hoc
methods, which may suffer from participants’
tendency to rationalise their decisions retrospective
(Shepherd and Zacharakis, 1999; Aiman-Smith et al.,
2002). Moreover, since adaptive choice-based
conjoint analysis is primarily an experimental design,
it makes causal inference a realistic goal. The
adaptive choice-based method is particularly suited to
our research question since it produces a decision
context that is close to the day-to-day decision
context of instructors. Both the experiment and the
daily job of participants require a judgment based on
a set of observable characteristics.
In a conjoint experiment, participants are asked to
judge a series of theory-driven profiles, combinations
of parameter values for several attributes. From the
preferences revealed in this way, conclusions can be
drawn about the contribution of each attribute’s
parameter values to the overall valuation a certain
1
Algorithms from Sawtooth Software that use a balanced
overlap design strategy that tracks the simultaneous
occurrence of all pairs of feature levels to produce an
approximately orthogonal design for each respondent
profile receives (Shepherd and Zacharakis, 1999).
Fortunately, previous research provides considerable
evidence for the external validity of conjoint studies
(Louviere and Hout, 1988; Zacharakis and Shepherd,
2018). We specifically conducted an adaptive choice-
based conjoint experiment since adaptive choice-
based conjoint experiments, in contrast to traditional
conjoint analysis, come close to the real-life situation
of instructors. In general, ACBC choice tasks of
selecting alternatives require low cognitive effort
(Balderjahn et al., 2009). All aspects help to increase
both the validity and response rate of the study. The
application of this research method to our study is
presented in the following paragraphs. An important
trade-off in designing an ACBC is making the
experiment as realistic as possible while ensuring
1
that it is manageable for respondents. Hence, we
decided to restrict each scenario to two students with
a maximum of five attributes. Consequently, we
selected five attributes based on the research
question, we aimed to answer. The design of the
experiment is such that all student attributes that do
not explicitly vary are equal. Thus, provided the
experiment is carefully conducted, the omitted
variables do not affect the results.
3.2 Sample
The targeted sample for our online survey were 372
instructors in Germany in the summer of 2020. The
mean age was 45 years. 66 per cent of the instructors
were female and 33 per cent male, one respondent
was divers. They all work professionally in
educational contexts. The average number of years in
the school system was 16 years. 60 per cent of the
participants have already gained experience with a
digital learning platform.
3.3 Experimental Design and
Attributes
Prior to the empirical examination, we pretested the
experiment with 15 participants to obtain feedback and
refine the survey design. The pre-test led us to change
the wording of the attribute levels and the introduction
to make them more familiar and understandable for
instructors. The participants of the pre-test confirmed
that the number of choice tasks was indeed
manageable, realistic, and understandable.
concerning the main effects, but also allows a degree of
level overlap within the same task to allow for the
measurement of interactions between features.
‘This Student Needs to Stay Back’: To What Degree Would Instructors Rely on the Recommendation of Learning Analytics?
191
Participants accessed the experiment online. First,
participants were asked to read the text thoroughly
and imagine themselves in the described situations
(see the appendix for the introduction text). The
participants were supposed to give grades to their
students at the end of the school year. We chose a
grading situation because it reflects a common
situation in everyday school life.
In 16 rounds, the instructors were shown the
fictitious profiles of two learners with different
attributes. They had to choose the one they estimated
to be the better performer. The attributes were the
given name, the learning behaviour, the number of
completed online exams, the extent of parental
support, the learner’s picture, and the automatic
recommendation by the platform. Each attribute was
associated with different levels (Table 1).
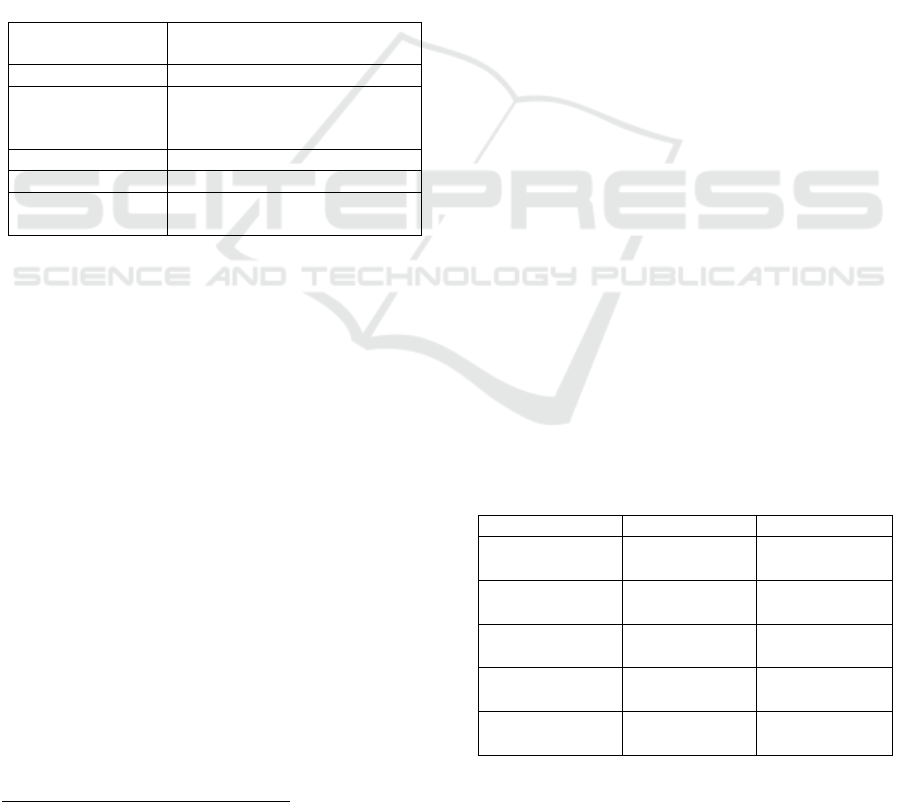
Table 1: Learners’ attributes and attributes levels.
Name Maximilian, Mohammed,
Sophie, Layla
Picture generated by AI
Learning
behaviour
activity:
never, before an exam,
permanent
Exams taken 3/18, 9/18, 17/18
Parental support little, moderate, high
Automatic
recommendation
Promotion is recommended,
Promotion is endangered
To represent different cultures, the given names were
typically German and Turkish. The Turkish minority
is the largest in Germany, which is why all instructors
should classify these names. Name and picture
belonged together to prevent the blending of a female
name with a male picture and vice versa. The pictures
have been generated by an AI
2
and are highly likeable
to eliminate perception errors that occur through
physiognomy (see the appendix for exemplary
pictures) (Aharon et al., 2001; Pound et al., 2007).
The pictures showed two female and two male
learners at the age of about 12 years. The attribute
learning behaviour was shown as a curve,
representing the time spent on the platform. The
curves showed low activity, a high activity before an
exam, and permanent high activity. Information about
exams taken was just demonstrated by the absolute
number (3, 9, or 17 of a maximum of 18 exams), but
no information about the level of difficulty or the
content was given. There were three levels of parental
support (little, moderate, high). This attribute
represents additional exercises at home and support
with homework. There is little evidence for primary
2
generated.photos
school pupils that parents start to support their
children when problems occur (Luplow and Smidt,
2019). Therefore, parental support can be interesting
for instructors working with younger learners. The
automatic recommendation was expressed with
“Promotion is recommended” and “Promotion is
endangered”. No information on how the algorithm
generated the recommendation was provided. This
means the participants did not know which attributes
had been rated by the underlying algorithm.
4 RESULTS
With the participants’ different preferences, we
analysed which information about learners had the
highest impact on the choice. Using the sawtooth
software on this ACBC design, the dominance of a
few attributes occurred. The exact results are shown
in Table 2. Firstly, the participants showed the
strongest reaction to the exams taken (32.56 per cent
of total variability). The more exams a learner had
done, the better was the participant’s judgment.
Consequently, high activity on the platform and the
motivation to take optional exams had a strong effect
on the instructors.
Secondly, the participants relied on the platform’s
recommendation. They were highly affected by the
label “Promotion is recommended” (26.32 per cent of
total variability). Furthermore, a positive
recommendation led to a positive appraisal.
Thirdly, there is little evidence that the
participants preferred low parental support. For
instance, learners with high parental support were
devalued and disadvantaged. Ethnicity, represented
by typical names, had a low impact on the
participants’ judgment. Likewise, learning behaviour
and gender had a neutral effect on the participants.
Table 2: Relative importance of learner’s attributes.
Attributes R I
Exams taken 1 32.56
[12.11]
Platform’s
recommendation
2 26.32
[13.14]
Learning
behaviour
3 20.73
[9.10]
Parental support 4 12.48
[9.82]
Name and
picture
5 7.91
[6.59]
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
192
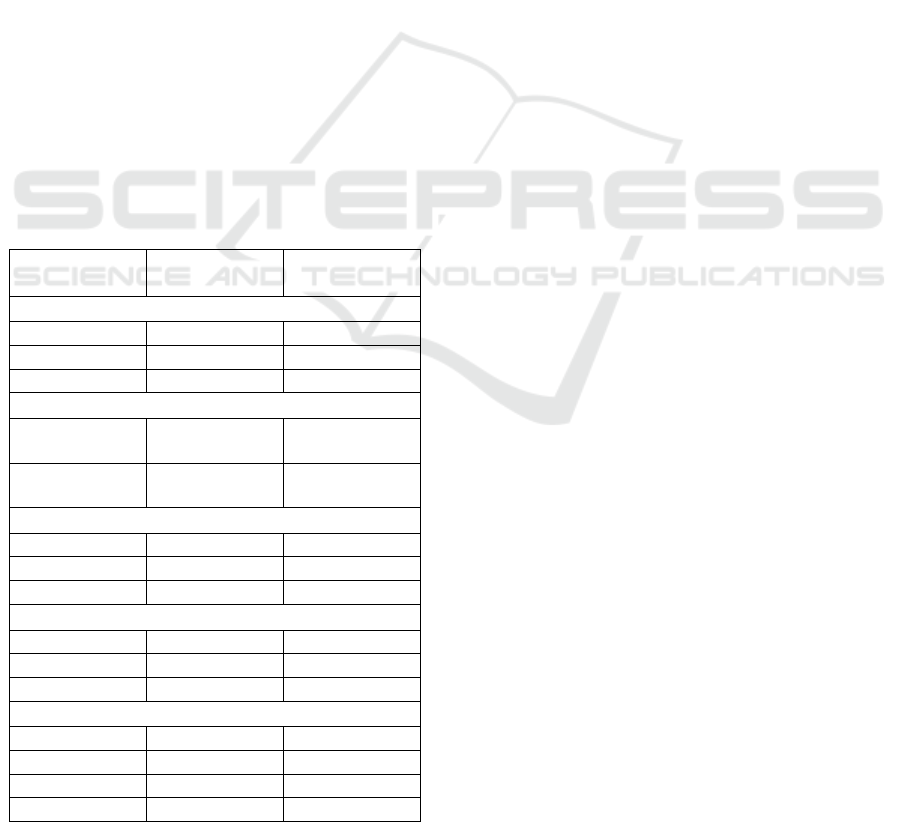
Attributes are ranked in order of their importance. R
is the rank of each attribute’s importance. I is the
relative importance of each attribute expressed as a
percentage of the total variability (high to low) across
utility coefficients. Importance scores add to 100.00.
The standard deviation is shown in the brackets. The
importance of “exams taken” explains 32.56 per cent
of the overall preferences. Importance scores show
the mean preferences of all participants. It is not
possible to infer the differences in the sample from
the importance score. The standard deviation shows
the variability across the sample. It is not possible to
make the statement that this ranking applies to all
participants. But in general, there is a tendency to link
one’s preferences to the attribute “exams taken”. The
same applies to the attribute “platform’s
recommendation”. There is evidence that this
attribute explains an overall preference for 26.32 per
cent, but the standard deviation of 13.14 shows that
this may not be true for every single participant.
Beyond that, it is important to differentiate
between the attribute levels to gain a deeper
understanding of the instructors’ preferences (Table
3). The different values for the attribute levels show
mean and standard deviation. Mean values add to 0
and show which level had a strong influence.
Table 3: Adaptive Choice-based Conjoint Utility
Descriptive Statistics.
Attributes and
levels
M SD
Exams taken
3/18
-75.70 41.10
9/18
0.42 14.46
17/18
75.28 44.62
Platform’s recommendation
Promotion is
endangered
-57.56 45.81
Promotion is
recommended
57.56 45.81
Learning behaviour
Never -42.74 34.12
Before an exam -1.04 16.46
Permanent 43.77 37.84
Parental support
Little 18.99 35.28
Moderate 2.89 14.97
High -21.88 32.10
Name and picture
Maximilian -5.30 19.65
Mohammed 0.248 19.47
Sophie -0.85 19.78
Layla 5.90 19.65
The attribute of exams had a strong influence with a
small and a high number (mean -75.70 and 75.28), but
it was negligible with a medium number of exams
taken. The automatic recommendation had a strong
impact (mean -57.56 and 57.56). The SD value shows
that this impact may not be relevant to everyone. The
same pattern as the exams had learning behaviour and
parental support. There was a low impact of the level
“before an exam” and higher impacts of “never” and
“permanent”. We also found a low impact of
“moderate” and higher impacts of “little” and “high”.
Finally, typical German names had only small
negative impact.
5 DISCUSSION
This study aimed to examine the influence of LA’s
recommendations on instructors’ judgement in the
educational context. Besides the number of exams
taken, results showed that instructors heavily rely on
LA’s recommendation about the promotion of a
learner to the next grade as well as her/his depicted
learning behaviour. Parental support and the name
with the picture of the learner had only little influence
on instructors. The results reflect the mean of all
participants and are therefore generalised.
Preferences may vary, but the attitude towards
automatic recommendations becomes visible.
The high degree of influence by LA’s
recommendations is surprising because participants
in our study had no additional information about how
the LA system was trained, how the system predicted
the learning success or what information was used to
make this recommendation. Although one might
assume higher objectivity in assessing and evaluating
learning outcomes by a computer system rather than
a human, the literature discussed the problems of
potential biases and discrimination of machine
learning systems (Roscher et al., 2020). Besides the
LA recommendation, learning behaviour ranked third
in the relative importance for instructors to evaluate
learners. This might also lead to biases and, for
example, to a disadvantage for offline learners
because LA systems cannot analyse offline-learning
activities. Standard measures cannot map the
complexity of activities (Dyment et al., 2020). These
findings have several implications for theory,
practice, and future research.
5.1 Theoretical Implications
Using algorithms in learning contexts can be useful to
generate deeper insights into the learning processes
‘This Student Needs to Stay Back’: To What Degree Would Instructors Rely on the Recommendation of Learning Analytics?
193

(Baker and Yacef, 2009). But algorithms’ accuracy is
highly dependent on the training data, and the results
are not comprehensible. This leads to the problem of
opacity when using algorithms. Opacity means that
users get a result without knowing the relationship
between data and the algorithm (Burrell, 2016). But
taking the platform’s recommendation without giving
it serious consideration can over- and underestimate
a learner’s learning success. Consequently, learners
do not get the right support, or their learning
performance is rated too low. Leaving all the
decisions to the platform means a high risk of unfair
judgment (Scholes, 2016).
Therefore, there is a need for transparency when
using algorithms for decision-making. This means
users should be informed about the data which is used
for decisions. Adding transparency to algorithms is
difficult because high transparency complicates the
use and can encourage misuse of the system (Eslami
et al., 2019). Nevertheless, auditing of systems is
necessary, and suitable concepts will be developed
with increasing use.
5.2 Practical Implications
Instructors have an important role in education
success (Roorda et al., 2011), but they are influenced
by several personally conditioned factors, e. g. from
self-fulfilling prophecies (Gentrup et al., 2020).
Urhahne and Wijnia (2021) recommend relying on
valid and observable indicators to improve judgment
accuracy. At first glance, the results of LA systems
seem to be such indicators. This leads to the
importance of the context in which the results are
used. Specific patterns in the learner’s online
behaviour can be integrated into an early warning
system to ensure that their learning success is
endangered. If the algorithmic decision is used for
judgment, the aspects of equal opportunities must be
taken into consideration. Algorithms can support
decision-making, but the outcome can be biased
depending on the training data and the chosen model
(Murphy, 2012).
To understand the operations of platforms, it is
necessary to know how algorithms work and predict
certain outcomes. Therefore, educational institutions
need to develop the instructors’ knowledge and train
their digital competencies about LA systems and
algorithms (Jones, 2019) because a limited
understanding of these new technologies in
combination with little experience will lead to
unwanted effects, such as reproducing stereotypes,
biases, and discrimination. There are ongoing
processes to develop measurable concepts like AI
literacy (Long and Magerko, 2020) that represent the
basic skills and abilities. If instructors are aware of
these emerging problems, platforms can create
learning success through better internal
differentiation in the classroom and focus on the
specific problems revealed by data.
5.3 Limitations and Future Research
Firstly, the choice experiment approach brings unique
advantages for studying decision criteria, but it comes
with caveats. Conjoint analysis research reduces the
social desirability and retrospective reporting biases
associated with self-reports of judgments. Judgments
are made in a relatively controlled environment. But
one cannot be sure that participants were mentally
able to keep all other start-up attributes equally. These
limitations are true for all choice experiments, and we
have paid particular attention to designing the
experiment as realistically as possible to alleviate
these concerns. Although we selected the most
essential attributes identified by previous literature,
the choice experiment approach implies that we can
study only a limited set of start-up attributes.
Importantly enough, this feature does not affect the
results. The results show the relative contribution of
attribute levels for the sample, not for the individual
decision. Not everyone may be affected by the
platforms’ recommendation, but there is evidence
that the impact is very high.
Secondly, the tested setting assumed that the
instructors evaluated the learners only based on the
information provided by the platform. In everyday
school life, however, it is more conceivable that the
platform could be used to support the learning
processes. Therefore, instructors at school would
supplement their own impression of the learners with
the information rather than relying solely on it. The
situation at universities is different. There is usually a
less strong personal relationship between lecturers
and students due to the high number of students. This
means that the use of learning platforms can have a
different impact in the university context, which is
more similar to our experiment than schools with
smaller classes.
Third, different current social discourses may
influence the result, for instance, the reactions to the
Black Lives Matter movement since May 2020.
Maybe, our participants were aware that learners and
students of colour are often discriminated against in
educational contexts. This might explain the positive
impact on Turkish names, but further research is
needed to explain these differences because
minorities can be discriminated against. For instance,
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
194

there is evidence for the underrepresentation of
students of colour in gifted programs in the USA
(Grissom and Redding, 2016).
Finally, our research was conducted in only one
country (Germany). Thus, the question of cross-
national generalization remains open due to a
different school and university systems, different
levels of digitization of educational institutions and
cultural differences (Hofstede et al., 2010). Future
research, therefore, should be conducted in different
cultures to fully assess generalization.
6 CONCLUSIONS
We sought to increase the current understanding of
LA algorithms in educational contexts. Driven by the
current challenges due to the COVID-19 pandemic,
teaching routines in schools and universities may
change, and so may the impact of platforms. Our
work showed that instructors heavily relied on the
recommendations by the LA system. Instructors may
be open to supposedly more objective evaluation
methods, but they need to be aware of the threats and
bias in using these new methods without knowing
their training data or underlying models. The use of
platforms enables instructors to get access to hidden
patterns of learning behaviour. For practice, these
insights provide a better allocation of personal
support. Furthermore, using algorithms means
focusing on measurable online activities. Other
relevant activities may be important for learning
success but are not captured within the system
(Dyment et al., 2020). However, if instructors have
limited knowledge on which data the algorithm made
a recommendation, their complete reliance on the
recommendation may lead to unfairness and biased
decisions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from
the Federal Ministry of Education and Research in
Germany (Project number 01JD1812B).
REFERENCES
Aguilar, S.J., 2018. Learning Analytics: at the Nexus of Big
Data, Digital Innovation, and Social Justice in
Education. TechTrends 62, 37–45.
Aharon, I., Etcoff, N., Ariely, D., Chabris, C.F., O'Connor,
E., Breiter, H.C., 2001. Beautiful Faces Have Variable
Reward Value. Neuron 32, 537–551.
Aiman-Smith, L., Scullen, S.E., Barr, S.H., 2002.
Conducting Studies of Decision Making in
Organizational Contexts: A Tutorial for Policy-
Capturing and Other Regression-Based Techniques.
Organizational Research Methods 5, 388–414.
Akçapınar, G., Altun, A., Aşkar, P., 2019. Using learning
analytics to develop early-warning system for at-risk
students. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 16.
Artelt, C., Gräsel, C., 2009. Diagnostische Kompetenz von
Lehrkräften. Zeitschrift für Pädagogische Psychologie
23, 157–160.
Baker, R.S., Yacef, K., 2009. The State of Educational Data
Mining in 2009: A Review and Future Visions.
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3554657.
Balderjahn, I., Hedergott, D., Peyer, M., 2009. Choice-
Based Conjointanalyse. In: Baier, D., Brusch, M. (Eds.)
Conjointanalyse. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin,
Heidelberg, pp. 129–146.
Bañeres, D., Rodríguez, M.E., Guerrero-Roldán, A.E.,
Karadeniz, A., 2020. An Early Warning System to
Detect At-Risk Students in Online Higher Education.
Applied Sciences 10, 4427.
Bechger, T.M., Maris, G., Hsiao, Y.P., 2010. Detecting
Halo Effects in Performance-Based Examinations.
Applied Psychological Measurement 34, 607–619.
Blain-Arcaro, C., Smith, J.D., Cunningham, C.E.,
Vaillancourt, T., Rimas, H., 2012. Contextual
Attributes of Indirect Bullying Situations That
Influence Teachers' Decisions to Intervene. Journal of
School Violence 11, 226–245.
Buckingham Shum, S., Deakin Crick, R., 2016. Learning
Analytics for 21st Century Competencies. Learning
Analytics 3, 6–21.
Burrell, J., 2016. How the machine ‘thinks’: Understanding
opacity in machine learning algorithms. Big Data &
Society 3, 205395171562251.
Cadwell, J., Jenkins, J., 1986. Teachers’ Judgments About
Their Students: The Effect of Cognitive Simplification
Strategies on the Rating Process. American Educational
Research Journal 23, 460–475.
Demaray, M.K., Elliot, S.N., 1998. Teachers' judgments of
students' academic functioning: A comparison of actual
and predicted performances. School Psychology
Quarterly 13, 8–24.
Doherty, J., Conolly, M., 1985. How Accurately can
Primary School Teachers Predict the Scores of their
Pupils in Standardised Tests of Attainment? A Study of
some non‐Cognitive Factors that Influence Specific
Judgements. Educational Studies 11, 41–60.
Dyment, J., Stone, C., Milthorpe, N., 2020. Beyond busy
work: rethinking the measurement of online student
engagement. Higher Education Research &
Development 39, 1440–1453.
Eslami, M., Vaccaro, K., Lee, M.K., Elazari Bar On, A.,
Gilbert, E., Karahalios, K., 2019. User Attitudes
towards Algorithmic Opacity and Transparency in
‘This Student Needs to Stay Back’: To What Degree Would Instructors Rely on the Recommendation of Learning Analytics?
195

Online Reviewing Platforms. In: Brewster, Fitzpatrick
et al. (Hg.) – Proceedings of the 2019 CHI, pp. 1–14.
Ferguson, R., Shum, S.B., 2012. Social learning analytics,
in: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on
Learning Analytics and Knowledge - LAK '12. the 2nd
International Conference, Vancouver, British
Columbia, Canada. 29.04.2012 - 02.05.2012. ACM
Press, New York, New York, USA, p. 23.
Gasevic, D., Conole, G., Siemens, G., Long, P., 2011.
LAK11: International Conference on Learning
Analytics and Knowledge. Banff, Canada 27.
Gentrup, S., Lorenz, G., Kristen, C., Kogan, I., 2020. Self-
fulfilling prophecies in the classroom: Teacher
expectations, teacher feedback and student
achievement. Learning and Instruction 66, 101296.
Green, P.E., Krieger, A.M., Wind, Y., 2004. Thirty Years
of Conjoint Analysis: Reflections and Prospects. In:
Eliashberg, J., Wind, Y., Green, P.E. (Eds.) Marketing
Research and Modeling: Progress and Prospects,
vol. 14. Springer US, Boston, MA, pp. 117–139.
Greller, W., Drachsler, H., 2012. Translating learning into
numbers: A generic framework for learning analytics.
Journal of Educational Technology & Society 15, 42–
57.
Grissom, J.A., Redding, C., 2016. Discretion and
Disproportionality. AERA Open 2, 233285841562217.
Hofstede, G., Hofstede, G.J., Minkow, M., 2010. Cultures
and organizations: software of the mind: intercultural
cooperation and its importance for survival. New York:
McGraw-Hill.
Jones, K.M.L., 2019. “Just because you can doesn’t mean
you should”: Practitioner perceptions of learning
analytics ethics. portal: Libraries and the Academy
19(3).
Jones, K.M.L., Rubel, A., LeClere, E., 2020. A matter of
trust: Higher education institutions as information
fiduciaries in an age of educational data mining and
learning analytics. Journal of the Association for
Information Science and Technology 71, 1227–1241.
Kaiser, J., Möller, J., Helm, F., Kunter, M., 2015. Das
Schülerinventar: Welche Schülermerkmale die
Leistungsurteile von Lehrkräften beeinflussen. Z
Erziehungswiss 18, 279–302.
Krantz, D.H., Tversky, A., 1971. Conjoint-measurement
analysis of composition rules in psychology.
Psychological Review 78, 151–169.
Long, D., Magerko, B., 2020. What is AI Literacy?
Competencies and Design Considerations. In:
Bernhaupt, Mueller et al. (Hg.) – Proceedings of the
2020 CHI, pp. 1–16.
Louviere, J.J., Hout, M., 1988. Analyzing decision making:
Metric conjoint analysis. Sage.
Luckin, R., Cukurova, M., 2019. Designing educational
technologies in the age of AI: A learning sciences‐
driven approach. Br J Educ Technol 50, 2824–2838.
Luplow, N., Smidt, W., 2019. Bedeutung von elterlicher
Unterstützung im häuslichen Kontext für den
Schulerfolg am Ende der Grundschule. Z
Erziehungswiss 22, 153–180.
Murphy, K.P., 2012. Machine learning: A probabilistic
perspective.
Nguyen, A., Wandabwa, H., Rasco, A., Le, L.A., 2021. A
Framework for Designing Learning Analytics
Information Systems, in: Proceedings of the 54th
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences.
Oberst, U., Quintana, M. de, Del Cerro, S., Chamarro, A.,
2020. Recruiters prefer expert recommendations over
digital hiring algorithm: a choice-based conjoint study
in a pre-employment screening scenario. MRR ahead-
of-print.
Oliveira, P.C. de, Cunha, C.J.C.d.A., Nakayama, M.K.,
2016. Learning Management Systems (LMS) and e-
learning management: an integrative review and
research agenda. JISTEM 13, 157–180.
Paulden, T., 2020. A cutting re‐mark. Significance 17, 4–5.
Peña-Ayala, A., 2018. Learning analytics: A glance of
evolution, status, and trends according to a proposed
taxonomy. WIREs Data Mining Knowl Discov 8,
e1243.
Pound, N., Penton-Voak, I.S., Brown, W.M., 2007. Facial
symmetry is positively associated with self-reported
extraversion. Personality and Individual Differences
43, 1572–1582.
Romero, C., Ventura, S., 2013. Data mining in education.
WIREs Data Mining Knowl Discov 3, 12–27.
Roorda, D.L., Koomen, H.M.Y., Spilt, J.L., Oort, F.J.,
2011. The Influence of Affective Teacher–Student
Relationships on Students’ School Engagement and
Achievement. Review of Educational Research 81,
493–529.
Roscher, R., Bohn, B., Duarte, M.F., Garcke, J., 2020.
Explainable Machine Learning for Scientific Insights
and Discoveries. IEEE Access 8, 42200–42216.
Rosenberg, J.M., Staudt Willet, K.B., 2020. Balancing'
privacy and open science in the context of COVID-19:
a response to Ifenthaler & Schumacher (2016).
Educational technology research and development:
ETR & D, 1–5.
Scholes, V., 2016. The ethics of using learning analytics to
categorize students on risk. Educational technology
research and development: ETR & D 64, 939–955.
Shepherd, D.A., Zacharakis, A., 1999. Conjoint analysis: A
new methodological approach for researching the
decision policies of venture capitalists. Venture Capital
1, 197–217.
Siemens, G., Long, P., 2011. Penetrating the fog: Analytics
in learning and education. EDUCAUSE review 46, 30.
Smith, B.I., Chimedza, C., Bührmann, J.H., 2020. Global
and Individual Treatment Effects Using Machine
Learning Methods. Int J Artif Intell Educ 30, 431–458.
Südkamp, A., Kaiser, J., Möller, J., 2012. Accuracy of
teachers' judgments of students' academic achievement:
A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology
104, 743–762.
Tobisch, A., Dresel, M., 2017. Negatively or positively
biased? Dependencies of teachers’ judgments and
expectations based on students’ ethnic and social
backgrounds. Soc Psychol Educ 20, 731–752.
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
196

Urhahne, D., Wijnia, L., 2021. A review on the accuracy of
teacher judgments. Educational Research Review 32,
100374.
Waddington, R.J., Nam, S.J., Lonn, S., Teasley, S.D., 2016.
Improving Early Warning Systems with Categorized
Course Resource Usage. Learning Analytics 3, 263–
290.
Zacharakis, A., Shepherd, D.A., 2018. Chapter 7 Reflection
on Conjoint Analysis. In: Katz, J.A., Corbett, A.C.
(Eds.) Reflections and Extensions on Key Papers of the
First Twenty-Five Years of Advances, vol. 20. Emerald
Publishing Limited, pp. 185–197.
APPENDIX
Introduction for the Participants
The school year is coming to an end, and the summer
vacations are approaching. In a few days, you will
have to enter the grades for your 10th class consisting
of 32 students to write the reports afterwards.
For grading purposes, the school's internal
learning platform provides you with the name, a
picture and the type of learning type of each student.
A distinction is made between three different types.
The learning type "not at all" describes students who
do not repeat the school material independently and
do not prepare for exams. They hardly or not at all use
the school's internal learning platform. Students who
are "permanently" learning to learn the relevant
content regularly throughout the school year and
actively use the school's internal learning platform for
this purpose. The learning type "always before
exams" refers to students who learn only in a short
period before exams or exams or who use the school's
internal learning platform. In the remaining time of
the school year, they have a low learning activity.
Furthermore, you know to what extent parents
support their children in terms of school success. A
distinction is made between no, moderate and much
support from the parents. Parents who provide a lot of
support are informed about the subjects, contents, and
current school events. They regularly talk to their
children about these topics and help with any
problems the children may have with the content or
social issues. In contrast, parents who do not provide
support have little knowledge of their children's
school situation and development. They do not
support their children in case of content-related or
social difficulties. Moderate support from parents
corresponds to an occasional commitment. The
parents are informed about the general situation at
school and help in major difficulties with the content
or social problems.
You can also see which learners have been
classified as "at-risk" by the digital learning platform.
According to the platform, those students are at risk
of not being transferred. Indicators for such a threat
are the extent of reading activity, adherence to due
dates, participation in forums and written
submissions.
In the following, you will be presented 16 times
with two students, each with the above information,
and you will be asked to choose which one you rate
better. Afterwards, you will be asked some more
questions.
‘This Student Needs to Stay Back’: To What Degree Would Instructors Rely on the Recommendation of Learning Analytics?
197
