
Fast Gamification Approach: Increase of the Motivation in Remote
Classes
P. Pernelle
1
, T. Carron
2
a
, S. Talbot
3
and D. Wayntal
3
1
University of Lyon 1, F-69221 Villeurbanne, France
2
LIP6, Sorbonne University, CNRS, F-75005 Paris, France
3
University of Savoie Mont Blanc, F-73000 Chambery, France
Keywords:
Collaborative RPG Serious Game, Fast Gamification, Remote Class, Distance Learning.
Abstract:
Serious Games are considered as effective incentive tools for academic training. However, it remains a difficult
challenge to use and generalize in university degrees. This paper aims at presenting a hybrid fast gamification
approach for different training modules in order to improve the motivation context and involve non-game-
specialist teachers. Thus, in various experiments, we have been able to show that a serious game with a unique
and same storyboard increases motivation even in different formations. In the first part, we present the game
scenario modeling. Then, in a second part, we detail integration mechanisms of several training modules into
this scenario. Finally, in a third part, we present the experiments carried out and the results obtained from this
approach used in distance learning, during the COVID-19 crisis.
1 INTRODUCTION
Serious games are effective tools to motivate learn-
ers in their formations. However, they remain very
marginally deployed in vocational university training
(Vlachopoulos and Makri, 2017). There are a vari-
ety of reasons for this. In addition to overcoming
strong resistance to change inherent in the academic
system, the difficulty of creating a playful scenario
also known as gamification (Kapp, 2012; Bíró, 2014;
Deterding et al., 2011)) and the lack of simple tools
are the main obstacles.
Moreover, the quarantine and the closure of uni-
versity campuses have imposed the need and the gen-
eralization of distance learning. In this difficult con-
text, for teachers and especially for students, motiva-
tional tools such as serious games appear to be essen-
tial to maintain students’ attention and to avoid the
phenomenon of dropping out (Muratet et al., 2012).
This article presents a hybrid approach called
rapid gamification. The main point of this gamifica-
tion consists in being able to create a same game con-
text for one or more existing training modules very
quickly. This approach relies on a simplified model
of the interactions between a fun activity and an edu-
cational activity. Thanks to this approach, the teacher,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6982-7055
who is not a serious game specialist, integrates his
teaching activities into a fun framework initially pre-
pared by a serious game specialist, regardless of the
field of use that will be made of it. The first part of
this article presents the modeling used to build this
type of playful scenario and the dedicated modeling
tool.
In the second part, we present the experiments
achieved during the quarantine. Indeed, this approach
has been tested on different teacher modules in a re-
mote classes context. The last part describes the out-
comes collected in different vocational training ses-
sions: Imperative Programming, Database, Control
Theory. Moreover, this approach has been experi-
mented in various university degrees.
2 FAST GAMIFICATION
APPROACH
2.1 Playful Scenario vs Pedagogical
Scenario
Classic script-writing approaches are generally based
on the gamification of an educational process (Botturi
et al., 2006) (Kim et al., 2018). In this type of ap-
282
Pernelle, P., Carron, T., Talbot, S. and Wayntal, D.
Fast Gamification Approach: Increase of the Motivation in Remote Classes.
DOI: 10.5220/0010461702820287
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2021) - Volume 2, pages 282-287
ISBN: 978-989-758-502-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

proach, the trainer and the game designer try to build a
playful scenario from their educational and / or play-
ful experience, or even from a learning path estab-
lished elsewhere. To do this, they can use models that
will describe the steps of a player-learner’s progress.
In literature, we can find the following models:
• IMS-LD-SG (Tran et al., 2010) is a modified ver-
sion of IMS-LD in order to design serious game
(SG) scenarios by adding specific types of re-
sources dedicated to the SG;
• SGORM (Bisognin et al., 2010) is an extension of
SCORM allowing to define playful components;
• MoPPLiq (Marne et al., 2013) corresponds to a
specific model for representing SG scenario that
can be easily modified;
• SG-LOM (El Borji and Khaldi, 2014) focuses on
metadata scheme and proposes an application pro-
file of IEEE LOM. It takes into account the differ-
ent evaluation studies and relies on a SG classifi-
cation.
Most of these models integrate playful elements
into an educational logic. Finally, there is an inter-
dependence in the design of the educational scenario
and the playful scenario (Buckingham and Burn,
2007). These approaches produce good results but the
constraints are very strong. On the one hand, they re-
quire a high level of expertise; on the other hand, they
often induce long production time and some very spe-
cific developments.
The modeling approach that we have chosen cre-
ates a decoupling between the playful and educational
facets (Abed et al., 2018). In particular,this allows the
models to be produced in parallel and independently,
by different people.
2.2 Fast Gamification Approach (FGA)
Modeling
We therefore opted for an opposite approach to the
previously mentioned approaches. Indeed we have
deliberately modeled a playful scenario with a pro-
gression in the game independently of any pedagogi-
cal consideration.
2.2.1 Playful Model
The playful modeling is based on a decomposition ap-
proach by aggregation around the following concepts:
universe, activity, scenario, quest and task. The uni-
verse characterizes the playfulcontext in a thematic or
dreamlike coherence (example: a medieval-fantastic
universe). The activity represents a play unit (exam-
ple: a set of multitouch table activities, a 3D game, a
2D Web Game, a VR game session). These two con-
cepts are mainly categorical elements that help game
designer (and as we will see later teacher) to identify
the granularity.
The structural modeling of a scenario can be bro-
ken down into several quests, each quest being able to
be broken down into tasks. The dynamic of the play-
ful scenario is characterized by the sequence of quests
and tasks whose links are based on predicates.
Figure 1 describes the model used with UML no-
tation.
Figure 1: FGA playful model.
Figure 2 illustrates an extract from the scenario
model which was produced for the experiments in a
University and in an Institute of Technology. We de-
veloped a web tool: a simple graphical editor called
ScenarFab to facilitate the global visualisation of each
scenario.
Figure 2: Quest modeling example.
2.2.2 Pedagogical Model
In order to get/reinject existing pedagogical content
(exercises, video, documents, questionnaire), we only
add one concept: the "integration task". The educa-
tional model represents a simple extension of certain
elements of the playful model (see Figure 3). Thus,
the quests include exercises or video capsules. Some
exercises can be detailed, if necessary, by breaking
them down into tasks.
Fast Gamification Approach: Increase of the Motivation in Remote Classes
283
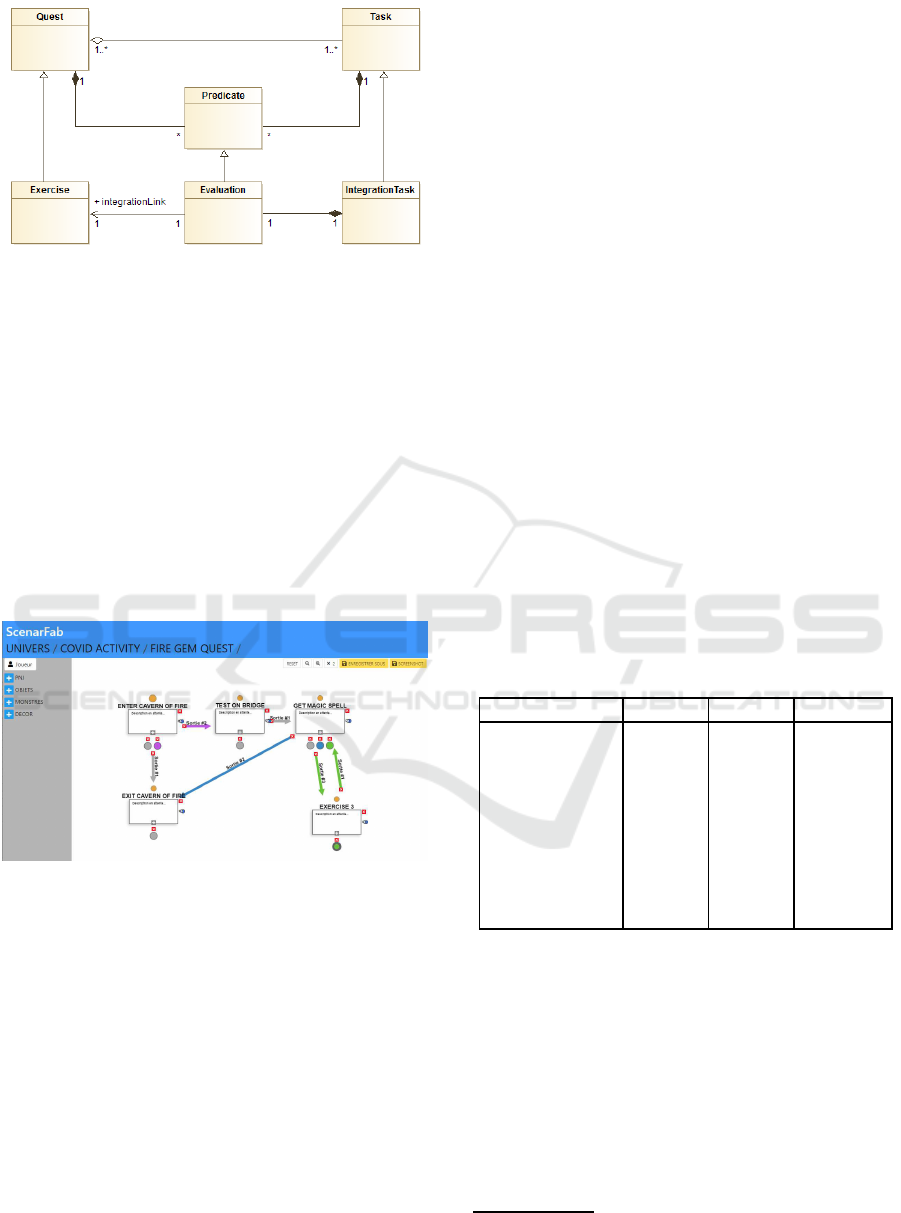
Figure 3: Extension of playful model FGA.
The pedagogical-playful integration is thus natu-
rally done through the integration tasks and their eval-
uation link. These tasks will define the pedagogi-
cal attachment points which will then be used by the
trainer. Figure 4 shows an example of integration with
an exercise in ScenarFab. An important feature of
ScenarFab is the recursive aspect: game designer and
teacher may zoom into each level of granularity (play-
ful activity, scenario, quest) in order to get a clear vi-
sion of that part of the scenario. ScenarFab generates
a JSON file with the full scenario but currently we are
not yet able to directly generate the game from this
JSON file.
Figure 4: Integration example.
With this approach, the creation of the exercises is
totally decoupled from the playful scenario. This al-
lows the trainer in particular to work in parallel with
the game designer. Another advantageis that the same
scenario frame can be used for different training mod-
ules.
3 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
This section presents the experiments carried out with
FGA. The approach allowed us in particular to very
quickly offer a context of motivation during the health
crisis of COVID-19.
3.1 Experiments Context
We tested our approach on three different learning
modules in two different training courses.
• first cohort with 56 students (Computer Science
bachelor)
– a module on imperative programming in C
language: Imperative Programming, functions,
separate compilation, pointers.
– a database training module: Relational DBMS,
SQL
• second cohort - 80 students - Institute of tech-
nology diploma GMP (mechanical and production
engineering department).
– control module : Linear system, identification,
PID
The table 1 presents the characteristics and condi-
tions of these experiments and in particular the dis-
tribution of hours worked face-to-face (before the
COVID crisis) and hours worked in remote class con-
text (during quarantine). The duration represents the
effective game play including briefings and debrief-
ings. We did not take into consideration gender be-
cause most of these students are male in the degrees
for these experiments. Average age is around twenty-
one.
Table 1: Characteristics of modules using serious play.
Module (total) C Lang DBMS Control
Total 24 24 16
before COVID 20 h 16h 7 h
during COVID 1 x 4 h 2 x 4 h 3 x 3 h
SG Duration 2 h 2 h 2.5 h
Quests Nb 7 9 7
Exercise Nb 5 7 5
E-learning Moodle Moodle Claroline
Discord yes yes yes
LAWEB yes yes yes
The three scenarios have been modified with FGA
and the ScenarFab tool (cf. Figure 5). It is important
to note that the first and the second scenario (of the
C.S. Bachelor cohort) are part of the same scenario
background although they involve two totally inde-
pendent modules in training.
These scenarios have been implemented in the
LAWeb platform. LAWeb is a collaborative-RPG
game platform running within a simple web browser
1
.
Besides LAWeb, the students also had an audio virtual
room to communicate within their team (figure 6).
1
It can be seen as a layered build based on an editor
software of 2D game called RPG Maker.
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
284
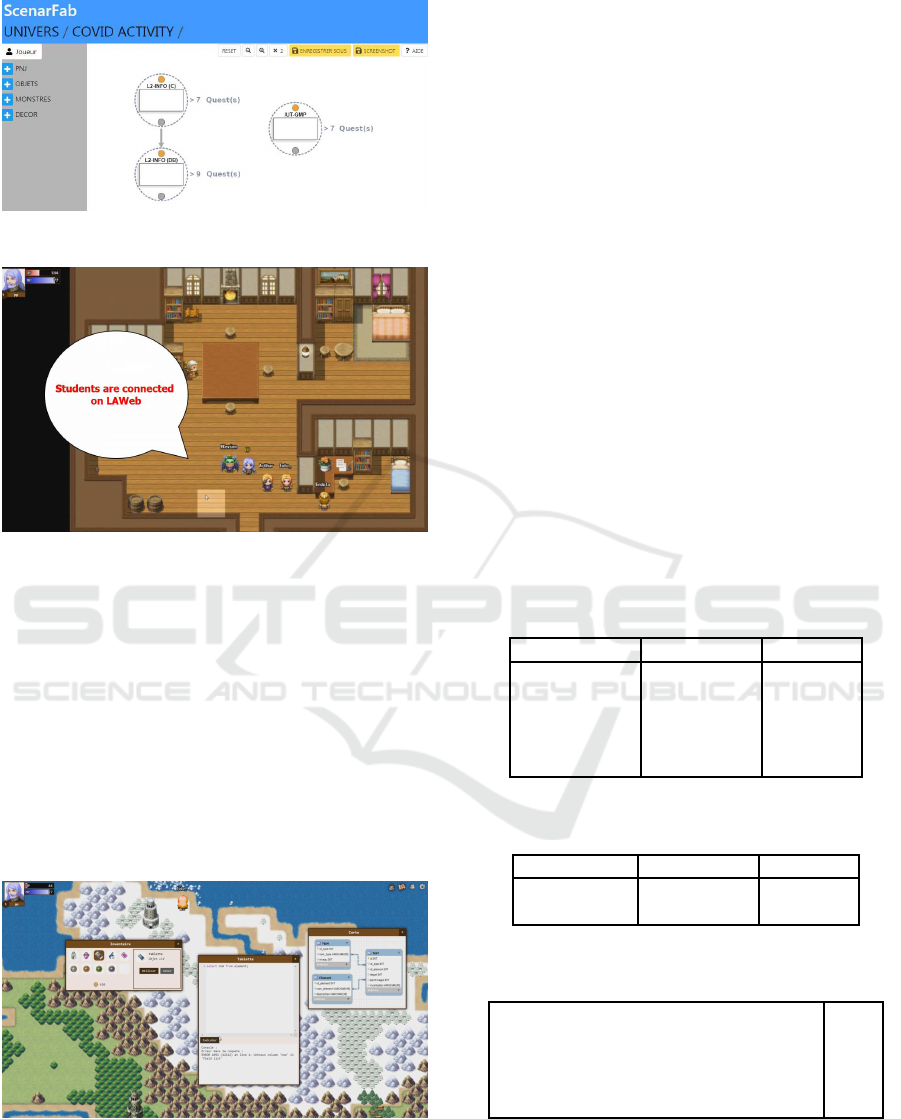
Figure 5: Extract from the scenario model with ScenarFAb.
Figure 6: Used gaming tools : LAWeb.
Table 1 also summarizes the quests and integra-
tion tasks of the different scenarios. As we indicated
in the previous paragraph, the trainer defines the exer-
cises. As part of these experiments, we integrated ex-
ercise evaluation mechanisms with two different ap-
proaches.
The first approach is based on online tests within
an LMS (Learning Management System) platform.
The second approach is based on a shell/CLI (Com-
mand Line Interpreter) assessment engine (the an-
swers are compared with a correct test set): the input
interface is available within the game (Figure 7).
Figure 7: Global evaluation on C and SQL modules.
Here, the role of the trainer is simply to provide a
set of exercises with assessable results.
3.2 Results Analysis
The results presented here are extracted from an
anonymous survey carried out at the end of serious
gaming sessions. The response rate for the first co-
hort is 57% (same response rate for both scenarios).
The response rate of the second cohort is 48%.
Table 2 presents general student opinions on seri-
ous gaming, for the C programming module and for
the Database module. The results are mostly posi-
tive. We note that at the end of the first scenario,
the students wish to continue the game for another
module (74%). The fact of continuing the scenario
for the second module did not modify their opinion
in a negative way. Moreover, 94% of students would
be ready to continue on a third module (cf. Tables 3
4). These results show that the “pedagogical discon-
tinuity” (in the same game environment, sequence of
modules from different domains or subjects studied
in remote class) has no impact on the already known
contribution of serious games. More accurately, the
learners considered as positive to find the same envi-
ronment again and to continue to explore it, to already
master the use of the interface, to find the same NPCs
(Non Playable Characters) again.
Table 2: What is your general impression about use a seri-
ous game in this module?
module C Language DataBase
Very Bad 0 0.03
Bad 0.04 0.03
Without view 0 0.10
Good 0.19 0.38
Very Good 0.65 0.58
Table 3: Would you like to play another game in a different
module?
after module C Language DataBase
No 0.26 0.06
Yes 0.74 0.94
Table 4: Has your opinion changed compared to the previ-
ous module?
No my opinion has not changed 0.48
Yes my opinion has changed but it’s
more positive
0.45
Yes my opinion has changed but it’s
more negative
0
The results (cf. Tables 5 7) were obtained for
the first cohort (C.S. Bachelor) and for the second co-
hort (Institute of Technology Diploma). They show
that the main interest of serious games remains an in-
crease in motivation. Nevertheless, the students do
Fast Gamification Approach: Increase of the Motivation in Remote Classes
285

not think that this directly facilitates their learning.
However, even without a direct impact, many studies
(Prensky, 2001; Connolly et al., 2012; Westera, 2019)
have shown that motivation is a determining factor in
the ability to learn, and with these very difficult pan-
demic contexts, motivation become a crucial criteria
to avoid the dropout.
Table 5: Do you think this serious game is an asset for this
module?
cohort C.S. Bachelor IUT
No 0.06 0.08
Yes 0.94 0.92
Table 6: If you think serious play is an asset, which one do
you think is most representative?
cohort C.S. Bachelor IUT
It’s motivating 0.70 0.75
It changes my view on
the module
0.18 0.25
This helps to better un-
derstand
0.12 0
Figure 8: Ratings compared with and without serious game.
This pedagogical point is confirmed by the results
of Figure 8 since the scores of the groups who per-
formed the module before quarantine (without the se-
rious game) are more or less the same as the groups
who did the module remotely with serious games.
This finding was not observed in the other modules
of the training.
Table 7 shows that the distance had no impact in
serious game. For the two cohorts, the results are
roughly the same. An important point is that for the
second cohort, the serious game session took place
over two sessions by dividing the cohort into two
groups (around 40 students per group). Thus, thanks
to the “MMO” game (not really massive but multi-
player and online), it was possible to manage two
sessions of 40 students in distance learning, instead
of the four that would have been necessary in face-
to-face or even more with current (post-confinement)
pandemic risk restrictions in the universities.
Table 7: Because the COVID containment, you followed
this scenario in distance learning, what is your opinion on
this point?
cohort C.S. Bachelor IUT
It was not a problem 0.94 0.71
I have no opinion 0.03 0.25
It was problematic not to
be in presential
0.03 0.04
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this article, we have proposed an approach to
quickly implement a motivation context thanks to se-
rious gaming. In order to involve the non-game-
specialist teachers, this approach is based on a sce-
nario construction approach decoupled from educa-
tional aspects. The pedagogical link is carried out a
posteriori by using points of attachment on some spe-
cific tasks thanks to a graphical editor called Scenar-
Fab. This method allows the work of the designer and
the trainer to be done simultaneously. Furthermore,
the results obtained show that there is no playful dis-
sonance and that the pedagogical discontinuity is not
seen as a hindrance on motivation feeling. Moreover,
the results clearly present an effect of increased mo-
tivation in distance learning that makes a lot of sense
especially in these times of pandemic uncertainty.
Among the perspectives to be developed, we wish
to bring an increased and deeper adaptability of the
educational and play paths. Currently, the educational
hooks are linked to an exercise. In fact, there is no
pedagogical adaptation apart from the possibility of
putting optional play tasks. We wish to study the
possibility that the attachment points are no longer
linked to an exercise but to an exercise pool so that
the learner can do exercises according to a level of
difficulty. Another point concerns the real-time moni-
toring of the scenario by the trainer. Experimentshave
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
286

shown that it is necessary to have suitable indicators
in order to be able to monitor a large group of students
in real time and react at the right time.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thank to the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region for their
support in the implementation of our platforms.
REFERENCES
Abed, H., Pernelle, P., Carron, T., Talbot, S., Wayntal, D.,
and Amar, C. B. (2018). A gamification approach for
serious games. In 2018 IEEE International Confer-
ence on Teaching, Assessment, and Learning for En-
gineering (TALE), pages 551–558. IEEE.
Bíró, G. I. (2014). Didactics 2.0: A pedagogical analysis
of gamification theory from a comparative perspec-
tive with a special view to the components of learning.
Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 141:148–
151.
Bisognin, L., Carron, T., and Marty, J.-C. (2010). Learning
games factory: construction of learning games. using
a component-based approach. In Actes de 4th Euro-
pean Conference on Games Based Learning, pages
19–30.
Botturi, L., Derntl, M., Boot, E., and Figl, K. (2006).
A classification framework for educational modeling
languages in instructional design. In 6th IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Advanced Learning Technolo-
gies (ICALT 2006), pages 1216–1220.
Buckingham, D. and Burn, A. (2007). Game literacy in the-
ory and practice. Journal of Educational Multimedia
and Hypermedia, 16(3):323–349.
Connolly, T. M., Boyle, E. A., MacArthur, E., Hainey, T.,
and Boyle, J. M. (2012). A systematic literature re-
view of empirical evidence on computer games and
serious games. Computers & Education, 59(2):661 –
686.
Deterding, S., Dixon, D., Khaled, R., and Nacke, L. (2011).
From game design elements to gamefulness: defin-
ing gamification. In Proceedings of the 15th inter-
national academic MindTrek conference: Envisioning
future media environments, pages 9–15. ACM.
El Borji, Y. and Khaldi, M. (2014). An ieee lom application
profile to describe serious games «sg-lom». Interna-
tional Journal of Computer Applications, 86(13).
Kapp, K. M. (2012). The gamification of learning and
instruction: game-based methods and strategies for
training and education. John Wiley & Sons.
Kim, S., Song, K., Lockee, B., and Burton, J. (2018). What
is Gamification in Learning and Education?, pages
25–38. Springer International Publishing.
Marne, B., Carron, T., Labat, J.-M., and Marfisi-Schottman,
I. (2013). Moppliq: a model for pedagogical adapta-
tion of serious game scenarios. In Advanced Learning
Technologies (ICALT), 2013 IEEE 13th International
Conference On, pages 291–293. IEEE.
Muratet, M., Delozanne, E., Torguet, P., and Vial-
let, F. (2012). Serious Game and Students’
Learning Motivation: Effect of Context Us-
ing Prog&Play, volume 7315, chapter Serious
Game and Students’ Learning Motivation: Effect
of Context Using Prog&Play, pages 123–128.
http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-
642-30950-2 16.
Prensky, M. (2001). Digital Game-Based Learning.
McGraw-Hill.
Tran, C., George, S., and Marfisi-Schottman, I. (2010).
Edos: An authoring environment for serious games.
design based on three models. In Proceedings
of ECGBL 2010 The 4th European Conference on
Games Based Learning. 4 th ECGBL, pages 393–402.
Vlachopoulos, D. and Makri, A. (2017). The effect of
games and simulations on higher education: a system-
atic literature review. International Journal of Educa-
tional Technology in Higher Education, 14(22).
Westera, W. (2019). Why and how serious games can be-
come far more effective: Accommodating productive
learning experiences, learner motivation and the mon-
itoring of learning gains. Journal of Educational Tech-
nology & Society, 22(1):59–69.
Fast Gamification Approach: Increase of the Motivation in Remote Classes
287
