
A Hybrid Approach using Progressive and Genetic Algorithms for
Improvements in Multiple Sequence Alignments
Geraldo Francisco Doneg
´
a Zafalon
1,3 a
, Vitoria Zanon Gomes
1 b
, Anderson Rici Amorim
2,1 c
and Carlos Roberto Val
ˆ
encio
1 d
1
Department of Computer Science and Statistics, Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP),
Rua Crist
´
ov
˜
ao Colombo, 2265, Jardim Nazareth, S
˜
ao Jos
´
e do Rio Preto, SP, 15054-000, Brazil
2
Department of Computer and Digital Systems Engineering, Universidade de S
˜
ao Paulo (USP), Escola Polit
´
ecnica,
Av. Prof. Luciano Gualberto, Travessa 3, 158, Butant
˜
a, S
˜
ao Paulo, SP, 05508-010, Brazil
3
Department ICET, Universidade Paulista, Avenida Presidente Juscelino Kubitschek de Oliveira,
s/n, Jardim Tarraf II, S
˜
ao Jos
´
e do Rio Preto, SP, 15091-450, Brazil
Keywords:
Genetic Algorithm, Multiple Sequence Alignment, Hybrid Multiple Sequence Alignment, Bioinformatics.
Abstract:
The multiple sequence alignment is one of the main tasks in bioinformatics. It is used in different important bi-
ological analysis, such as function and structure prediction of unknown proteins. There are several approaches
to perform multiple sequence alignment and the use of heuristics and meta-heuristics stands out because of
the search ability of these methods, which generally leads to good results in a reasonable amount of time.
The progressive alignment and genetic algorithm are among the most used heuristics and meta-heuristics to
perform multiple sequence alignment. However, both methods have disadvantages, such as error propagation
in the case of progressive alignment and local optima results in the case of genetics algorithm. Thus, this work
proposes a new hybrid refinement phase using a progressive approach to locally realign the multiple sequence
alignment produced by genetic algorithm based tools. Our results show that our method is able to improve
the quality of the alignments of all families from BAliBase. Considering Q and TC quality measures from
BaliBase, we have obtained the improvements of 55% for Q and 167% for TC. Then, with these results we
can provide more biologically significant results.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, we can notice a constant growth in the
biological data available, thus, computational meth-
ods are essential to assist biological analysis (Baxeva-
nis et al., 2020). This fact originated bioinformatics,
which is a research field that provides computational
tools and methods to many biological problems, such
as SNP analysis (Elek et al., 2020), pattern recog-
nition (Kasabov, 2019; Martino et al., 2018; Agger
et al., 2017), phylogenetic analysis (Lemieux et al.,
2020; Zhang et al., 2018; Nascimento et al., 2017)
and sequence alignment (Gao and Skolnick, 2020;
Smirnov and Warnow, 2020; Suplatov et al., 2018).
The sequence alignment is a well-known method
in bioinformatics, because it is used in many bio-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2384-011X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4176-566X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7862-7530
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9325-3159
logical analysis, such as structure prediction of pro-
teins (Sievers and Higgins, 2020; Bawono et al., 2017;
Le et al., 2017), evolutionary studies (Zhang et al.,
2020a; Li et al., 2020; Edgar and Batzoglou, 2006),
phylogenetic analysis (Asnicar et al., 2020), among
others. We can cite the importance of sequence align-
ment methods on the efforts against the COVID-19
pandemic (Angeletti et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020b;
Tilocca et al., 2020; Ibrahim et al., 2020). Basically,
the sequence alignment consists in rearranging the nu-
cleotide or amino acid bases of the sequences, using
the systematic insertion of gaps, in order to optimize
metrics related to the biological significance of the
alignment (Amorim et al., 2018).
The best sequence alignment can be obtained
with dynamic programming approaches, such as
Needleman-Wunsch (Needleman and Wunsch, 1970),
to perform global sequence alignment, or Smith-
Waterman (Smith et al., 1981), to perform local align-
ment. However, due to the fact that these algorithms
were ideally developed to perform pairwise sequence
384
Zafalon, G., Gomes, V., Amorim, A. and Valêncio, C.
A Hybrid Approach using Progressive and Genetic Algorithms for Improvements in Multiple Sequence Alignments.
DOI: 10.5220/0010495303840391
In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2021) - Volume 2, pages 384-391
ISBN: 978-989-758-509-8
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

alignments, it is unfeasible, in terms of computational
complexity, to perform the alignment for more than
three sequences (Wang and Jiang, 1994). Thus, it
was necessary to develop new methods to deal with
many biological sequences simultaneously and per-
form Multiple Sequence Alignments (MSA), which
is high desired nowadays (Bawono et al., 2017). The
MSA algorithms are stochastic approaches that gener-
ally can produce results with relevant biological sig-
nificance in a feasible amount of time (Nute et al.,
2019).
There are different approaches to perform Mul-
tiple Sequence Alignment, based on many heuris-
tics and meta-heuristics, such as Progressive Align-
ment (Armstrong et al., 2020; Sievers and Higgins,
2018), Fast Fourier Transform (Katoh et al., 2002;
Rozewicki et al., 2019; Nakamura et al., 2018), Tabu
Search (Riaz et al., 2004), Simulated Annealing (Cor-
rea et al., 2012), Particle Swarm Optimization (Tran
and Wallinga, 2017; Zhang et al., 2014; Rasmussen
and Krink, 2003) Genetic Algorithms (GA) (Chen-
toufi et al., 2016; Kaya et al., 2016; Kumar, 2015),
among others. Some of the most used tools to per-
form MSA, such as Clustal family (Sievers and Hig-
gins, 2018; Thompson et al., 1994), Kalign (Lass-
mann, 2019) and MUSCLE (Edgar, 2004), are based
on Progressive Alignment. However, this heuristic
has known disadvantages, such as error propagation
(Gondro and Kinghorn, 2007) and order dependency
in the input sequences (Boyce et al., 2015), which
may lead to noisy results that could be improved.
On the other hand, GA based approaches do not face
these disadvantages, once the iterative nature of the
method may deal with the error propagation problem
(Gondro and Kinghorn, 2007). This fact lead GA to
be one of the most-used meta-heuristics to perform
MSA (Chowdhury and Garai, 2017). Nonetheless,
GA based tools have other disadvantages, such as lo-
cal optima solutions, which means that the produced
alignment is not the global best alignment and still
could be improved (Lee et al., 2008).
As we can notice, the advantages and disadvan-
tages of Progressive Alignment and Genetic Algo-
rithm methods are complementary. Thus, hybrid ap-
proaches can be used to smooth the disadvantages
of the methods, which may lead to better Multiple
Sequence Alignments in terms of biological signifi-
cance. Thus, this work aims to develop a hybrid re-
finement phase, based on Progressive Alignment, to
improve the quality of the alignments of Genetic Al-
gorithm based tools. With this, we are able to smooth
the local optima problem and to obtain results with
greater biological significance.
This work is organized as follows: in section 2 we
better explain the Multiple Sequence Alignment, in
section 3 we show the related works, in section 4 we
show our methodology, in section 5 we show the tests
and obtained results and, finally, in section 6 we show
our conclusions.
2 MULTIPLE SEQUENCE
ALIGNMENT
As we have aforementioned, the Multiple Sequence
Alignment is the alignment of three or more biolog-
ical sequences. The MSA problem can be defined
as a set of input sequences to be aligned. Theses se-
quences may be defined over an alphabet {A,T,C, G}
when dealing with nucleotide sequences and
{A,C, D, E, F, G,H, I, K, L, M, N, P,Q, R, S, T,V,W,Y }
when dealing with amino acids sequences. Thus, the
MSA is given by a new set where all input sequences
must have the same length and the alphabet is
defined over the old one plus the gap symbol (-).
The gap represents insertions and deletions on the
sequences and it is used to equal the length of the
input sequences.
This process is executed through the manipula-
tion of bases positions, using the gaps to make the
sequences length the same, in some systematic way.
The main goal is to optimize quality metrics, known
as objective functions. Examples of objective func-
tions optimization in MSA are maximize the num-
ber of correspondent bases, i.e. when bases at the
same column of the alignment are the same, minimize
the number of gaps in the sequences, among others.
When we consider its implementation, the MSA is
a matrix structure where the rows represent the se-
quences and the columns represent the aligned bases.
3 RELATED WORKS
The Genetic Algorithm is a meta-heuristic based on
the natural selection, where individuals of a popula-
tion are exposed to selection, mutation and recom-
bination processes, in order that only the best indi-
viduals are selected to the next generations. Thus,
as the process continues, the algorithm converge to
the optimal solution. When applied to solve the MSA
problem, each individual represent a possible Multi-
ple Sequence Alignment (Amorim et al., 2018). The
first tool that applied GA to MSA was SAGA, which
has implemented a complex group of 22 operators
of mutation and recombination (Notredame and Hig-
gins, 1996). However, other works showed that this
A Hybrid Approach using Progressive and Genetic Algorithms for Improvements in Multiple Sequence Alignments
385

complexity does not improve the quality of the align-
ment when compared with simpler GA (Thomsen and
Boomsma, 2004). Thus the MSA-GA tool was devel-
oped by Gondro and Kinghorn (2007) with a reduced
group of operators. The authors show that MSA-
GA is able to obtain better results when compared
to widely used tools, such as Clustal W (Thompson
et al., 1994).
We can notice many recent published works that
use GA to perform MSA. Fan et al. (2012) and Kaya
et al. (2014) proposed different GA approaches to
solve the MSA problem, focusing on improvements
in the genetic operators and also the objective func-
tions that evaluate the quality of the produced solu-
tion. Both works were able to produce good results,
but authors show that the results could be still refined
to reach greater biological significance.
Rani and Ramyachitra (2017) proposed a GA to
perform MSA, focused on the parameters of the re-
combination operators. The quality of the solutions is
computed through a multi-objective approach, which
simultaneously optimizes different characteristics of
the alignment. One of the main contributions of this
work is that the authors showed that the horizontal
crossover operator is better to improve the MSA qual-
ity when compared to other crossover operators. The
proposed method was able to obtain good results, but
in some cases other consistency-based tools, such as
T-Coffee (Notredame et al., 2000), were able to pro-
duce better results. Thus, authors claim that a hybrid
approach may produce better results.
With this, Chatterjee et al. (2019) proposed a hy-
brid GA and Chemical Reaction Optimization (CRO)
to perform MSA. The GA executes the routine and
produce the Multiple Sequence Alignments, then, the
CRO is called as a refinement phase after each GA it-
eration. The authors show that the method obtained
good results, but it still face problems to correctly
align less similar sequences sets.
To smooth this problem, Rubio-Largo et al. (2016)
proposed a hybrid scheme, based on Progressive
Alignment, to locally refine the MSA produced by
an Artificial Bee Colony Optimization (ABCO) ap-
proach, using the Kalign tool (Lassmann, 2019). The
authors show that the method was able to obtain better
results and claim that the refinement phase was essen-
tial to the quality improvement.
Thus, once GA and ABCO are population-based
approaches with the same nature, the improvements
reached by the ABCO through this hybrid approach
may also be extended to Genetic Algorithm based
tools.
4 MATERIAL AND METHODS
4.1 The MSA-GA Tool
In this work, we choose the MSA-GA as GA based
tool to perform the Multiple Sequence Alignments.
This choice is due to the fact that MSA-GA has a
simpler GA scheme when compared with other GA
tools and it is able to produce good results, even better
than some Progressive Alignment based tools, such as
Clustal W (Gondro and Kinghorn, 2007).
In the MSA-GA, the population is initial-
ized based on pairwise alignments, computed with
Needleman-Wunsch. After that, the fitness of each
individual is calculated with the Weighted Sum-of-
Pairs (WSP) scoring function. A tournament phase is
executed, selecting the individuals based on their fit-
ness, as a ranking scheme, in order to expose them to
the genetic operators. In the MSA-GA, it was imple-
mented two crossover operators: horizontal crossover
and vertical crossover. The first one selects two in-
dividuals to recombine, defines a horizontal cut point
and selects entire sequences from both individuals to
generate new ones. The vertical crossover selects two
individuals, apply a vertical cut point, separating the
sequences into two parts, and generate new individ-
uals based on these parts. Moreover, the MSA-GA
tool implements three types of mutation operators to
optimize the gap positions: gap opening, gap exten-
sion and gap reduction. The first one randomly se-
lects a position and a block of gaps is inserted into the
sequence. The second one randomly selects a block
of gaps and then a gap position is inserted into the
sequence. Finally, the third one randomly selects a
block of gaps and a gap position is deleted from it.
The GA executes this process over the iterations
until a stop criteria is reached, such as maximum
number of generations. After that, the best individ-
ual is given as output as the best MSA found. Thus,
we have developed a refinement stage into the MSA-
GA tool to deal with eventual alignments trapped in a
local optima position, based on a hybrid scheme with
Progressive Alignment.
4.2 Hybrid Refinement Phase
Initially, we must define when our refinement phase
will be called into the GA routine. Thus, we have set
a user-defined parameter responsible for calling the
refinement routine after n iterations without any fit-
ness improvement in the best individual of the GA.
We find this is a good way to tell if a MSA is trapped
in a local optima position.
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
386

We can see in the Figure 1 the flowchart of the
proposed method. The basic idea of our refinement
phase is to locally realign a region of the MSA, based
on the Progressive Alignment heuristic.
When the refinement routine is called, initially we
define the part of the MSA that will be realigned. The
size of this part is randomly defined over an interval
between 5% and 25% of the MSA size. Once the size
was defined, the correspondent part of the alignment
is randomly selected. After that, we take the selected
part of the alignment, delete all gap positions and gen-
erate a new file with sequences related to the selected
bases, without the gaps. Thus, we give this file as
an input to the Kalign tool (Lassmann, 2019), which
will realign the selected part. In this work, we choose
the Kalign tool as a hybrid scheme because it is able
to quickly and precisely realign local parts of a MSA
(Rubio-Largo et al., 2016). Once Kalign realigned the
given part, we take this output and reinsert it into the
original MSA. All this realignment process is illus-
trated in Figure 2. After that, we evaluate the fitness
of the new individual and replace the old one in case
of fitness improvement. When the refinement phase
finishes its execution, the GA routine continues its ex-
ecution normally and the number of iterations without
any improvement is set to zero.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
5.1 Benchmark and Test Parameters
In this work, we have used the test cases from BAl-
iBase (Thompson et al., 2005), which is a benchmark
widely used to validate MSA methods. The BAliBase
contains different test case with different biological
characteristics, such as sequence similarity and size,
divided into different families. The BAliBase bench-
mark also provides reference alignments, which are
considered the correct alignments. This is important
because we are able to compare the produced align-
ments with the ideal ones.
To measure the quality of the alignments, we have
used the qscore tool
1
to calculate the Q and TC scores,
which are metrics related to the biological signifi-
cance of the alignment. This tool compares the pro-
duced alignment with the reference alignment and
gives a score between 0 and 1, for both of Q and TC
metrics. The greater the value, more biologically sig-
nificant is the MSA.
The tests were executed in a computer with
Windows 10 Pro 64 bits, Intel Core i3-6100
1
https://www.drive5.com/qscore/
CPU@3.70GHz processor and 8GB of RAM. The pa-
rameters of the MSA-GA are the default values de-
scribed by Gondro and Kinghorn (2007).
5.2 Results
We have executed test cases from all BAliBase fami-
lies: RV11, RV20, RV30, RV40, RV50. The first one
is related to sequence sets with less than 20% of sim-
ilarity; the second one is related to sequence sets with
similarity between 20% and 40%; the third one is re-
lated to sequence sets with at least one divergent se-
quence; the fourth one is related with more than 40%
of similarity but less than 20% with other families; the
fifth one is related to sequence sets with many inser-
tions.
We have compared the results obtained by the
original MSA-GA and the MSA-GA with our hybrid
refinement stage, here named HMSA-GA. Due to the
stochastic nature of GA, we have executed each test
case ten times and the considered value is the average
of all the ten executions.
In Table 1 we can see the Q scores obtained by
the original MSA-GA and our method. We can notice
that HMSA-GA is able to reach better results in all
the five families when compared to MSA-GA. More-
over, we can see the that average improvement of the
alignment quality for Q score is 55%.
We can see in the Table 2 the TC scores obtained
by the original MSA-GA and our HMSA-GA. Here,
we can notice that our method is able to refine the
alignments and reach also better results in all the five
families. In this case, we can see an average improve-
ment of 167%.
In order to verify whether the improvements
are statistically significant, we have execute the
Wilcoxon signed-rank test (Woolson, 2007). This
non-parametric test is well-suited to Multiple Se-
quence Alignment because the test cases do not fol-
low a normal distribution (Rubio-Largo et al., 2016).
We have used a confidence level of 1% (p
value <
0.01), once this value is considered appropriate to val-
idate MSA (Rubio-Largo et al., 2016).
In our hypothesis statistic test, when we com-
pared the differences between the results of MSA-GA
and our HMSA-GA, we have obtained a p value of
0.0013. Once the obtained p value is less than 1%,
we can say that the obtained improvements are statis-
tically significant.
Thus, the better results reached by HMSA-GA
show the ability of our refinement stage to improve
the quality of the MSA computed by Genetic Algo-
rithms.
A Hybrid Approach using Progressive and Genetic Algorithms for Improvements in Multiple Sequence Alignments
387
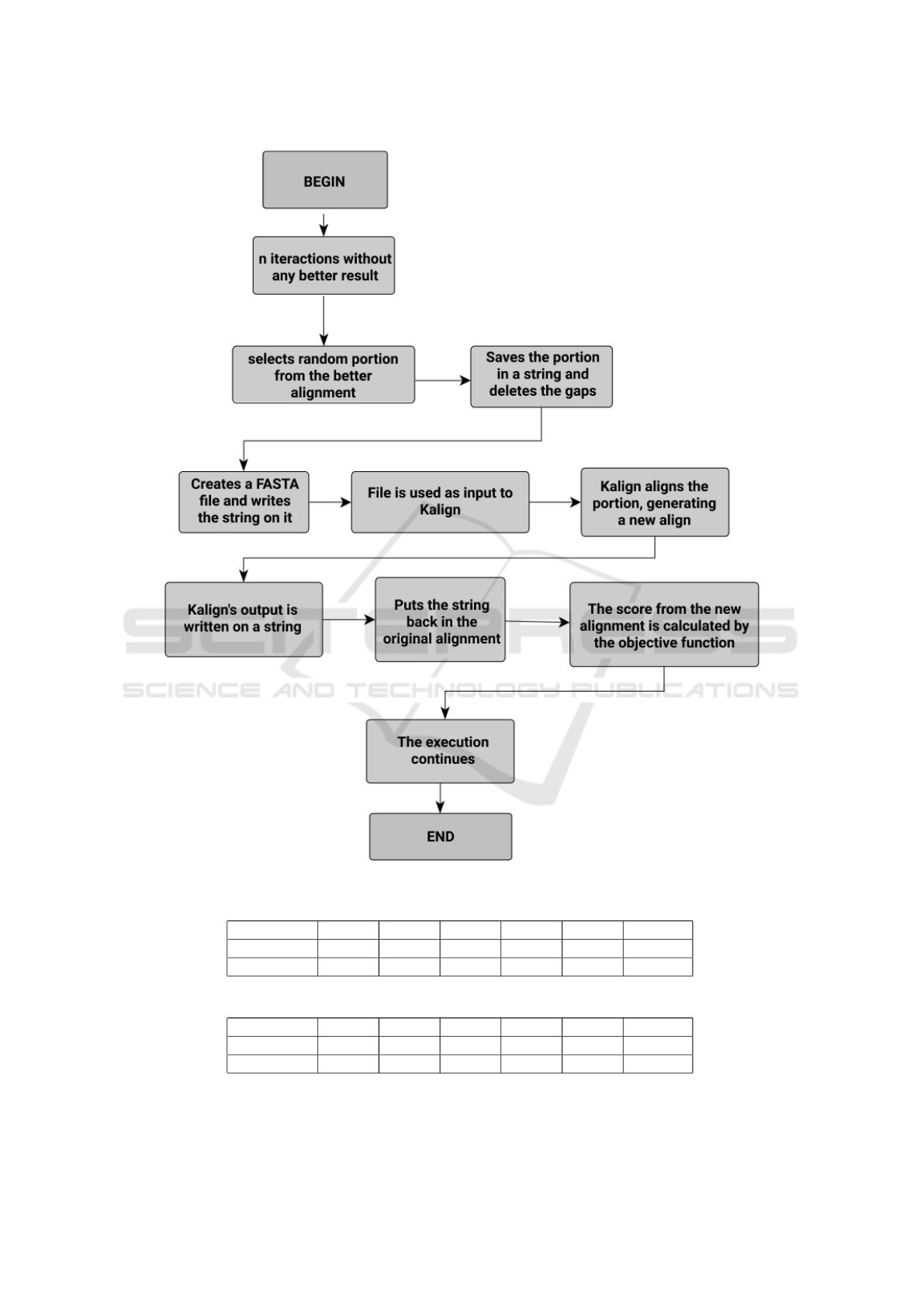
Figure 1: Refinement phase flowchart.
Table 1: Q scores obtained for all families of BAliBase.
RV11 RV20 RV30 RV40 RV50 Average
MSA-GA 0.2369 0.2507 0.2667 0.3626 0.3261 0.2886
HMSA-GA 0.3408 0.4470 0.4110 0.5611 0.4791 0.4478
Table 2: TC scores obtained for all families of BAliBase.
RV11 RV20 RV30 RV40 RV50 Average
MSA-GA 0.0971 0.0013 0.0024 0.0353 0.0135 0.0299
HMSA-GA 0.1150 0.0351 0.0303 0.1852 0.0341 0.0799
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
388
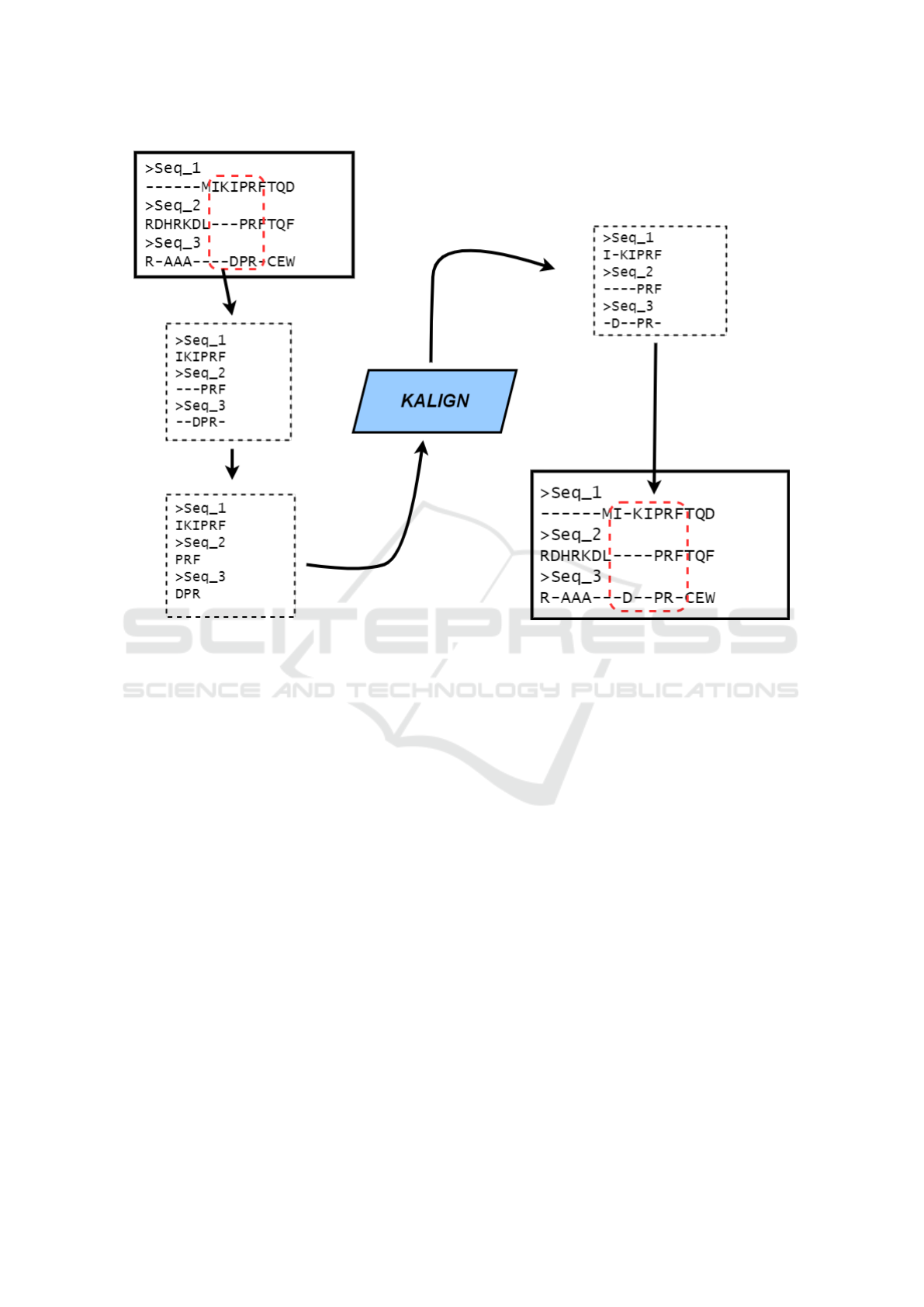
Figure 2: The local realignment process.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we presented a new hybrid refinement
phase, based on Progressive Alignment, to improve
the quality of the alignments produced by GA. We
have used the Kalign tool to systematically realign
parts of the alignment that may be responsible for a
local optima trap.
Our results show that our method was able to con-
siderably improve the quality of the alignments for all
the families of BAliBase when compared to the re-
sults obtained by the GA. Thus, we can conclude that
our method is able to refine the results of the MSA
produced by GA based tools and provide more bio-
logically significant alignments.
Moreover, the statistic hypothesis test show that
the difference between the obtained results are sta-
tistically significant and so are the obtained improve-
ments.
As future work, we propose to use other heuris-
tics, such as consistency based methods, in our hybrid
scheme. This may allow us to smooth other difficul-
ties and to obtain even better alignments.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank S
˜
ao Paulo Research
Foundation (FAPESP) for the financial support, un-
der grant 2019/00030-3, and Universidade Paulista
(Unip/ICET) to partially support this research under
grant number 7-03/1116/2019.
REFERENCES
Agger, J. W., Busk, P. K., Pilgaard, B., Meyer, A. S., and
Lange, L. (2017). A new functional classification of
glucuronoyl esterases by peptide pattern recognition.
Frontiers in microbiology, 8:309.
Amorim, A. R., Neves, L. A., Val
ˆ
encio, C. R., Roberto,
G. F., and Zafalon, G. F. D. (2018). An approach
for coffee objective function to global dna multiple se-
quence alignment. Computational biology and chem-
istry, 75:39–44.
Angeletti, S., Benvenuto, D., Bianchi, M., Giovanetti, M.,
Pascarella, S., and Ciccozzi, M. (2020). Covid-2019:
the role of the nsp2 and nsp3 in its pathogenesis. Jour-
nal of medical virology, 92(6):584–588.
Armstrong, J., Hickey, G., Diekhans, M., Fiddes, I. T.,
Novak, A. M., Deran, A., Fang, Q., Xie, D., Feng,
A Hybrid Approach using Progressive and Genetic Algorithms for Improvements in Multiple Sequence Alignments
389

S., Stiller, J., et al. (2020). Progressive cactus is
a multiple-genome aligner for the thousand-genome
era. Nature, 587(7833):246–251.
Asnicar, F., Thomas, A. M., Beghini, F., Mengoni, C., Ma-
nara, S., Manghi, P., Zhu, Q., Bolzan, M., Cumbo,
F., May, U., et al. (2020). Precise phylogenetic
analysis of microbial isolates and genomes from
metagenomes using phylophlan 3.0. Nature commu-
nications, 11(1):1–10.
Bawono, P., Dijkstra, M., Pirovano, W., Feenstra, A., Abeln,
S., and Heringa, J. (2017). Multiple sequence align-
ment. In Bioinformatics, pages 167–189. Springer.
Baxevanis, A. D., Bader, G. D., and Wishart, D. S. (2020).
Bioinformatics. John Wiley & Sons.
Boyce, K., Sievers, F., and Higgins, D. G. (2015). Instabil-
ity in progressive multiple sequence alignment algo-
rithms. Algorithms for molecular biology, 10(1):26.
Chatterjee, S., Hasibuzzaman, M., Iftiea, A., Mukharjee,
T., Nova, S. S., et al. (2019). A hybrid genetic al-
gorithm with chemical reaction optimization for mul-
tiple sequence alignment. In 2019 22nd International
Conference on Computer and Information Technology
(ICCIT), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Chentoufi, A., El Fatmi, A., Bekri, A., Benhlima, S.,
and Sabbane, M. (2016). Solving multiple rna se-
quences alignment by multi-objective genetic algo-
rithm method based on pareto optimality. In 2016 11th
International Conference on Intelligent Systems: The-
ories and Applications (SITA), pages 1–5. IEEE.
Chowdhury, B. and Garai, G. (2017). A review on multiple
sequence alignment from the perspective of genetic al-
gorithm. Genomics, 109(5-6):419–431.
Correa, J. M., de Melo, A. C. M. A., Jacobi, R. P., and
Boukerche, A. (2012). Parallel simulated annealing
for fragment based sequence alignment. In 2012 IEEE
26th International Parallel and Distributed Process-
ing Symposium Workshops & PhD Forum, pages 641–
648. IEEE.
Edgar, R. C. (2004). Muscle: multiple sequence align-
ment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic
acids research, 32(5):1792–1797.
Edgar, R. C. and Batzoglou, S. (2006). Multiple sequence
alignment. Current opinion in structural biology,
16(3):368–373.
Elek, Z., Kov
´
acs, Z., Keszler, G., Szab
´
o, M., Csanky, E.,
Luo, J., Guttman, A., and R
´
onai, Z. (2020). High
throughput multiplex snp-analysis in chronic obstruc-
tive pulmonary disease and lung cancer. Current
Molecular Medicine, 20(3):185–193.
Fan, H., Wu, R., Liao, B., and Lu, X. (2012). An im-
proved genetic algorithm for multiple sequence align-
ment. Journal of Computational and Theoretical
Nanoscience, 9(10):1558–1564.
Gao, M. and Skolnick, J. (2020). A novel sequence align-
ment algorithm based on deep learning of the protein
folding code. Bioinformatics.
Gondro, C. and Kinghorn, B. P. (2007). A simple genetic
algorithm for multiple sequence alignment. Genetics
and Molecular Research, 6(4):964–982.
Ibrahim, I. M., Abdelmalek, D. H., Elshahat, M. E., and
Elfiky, A. A. (2020). Covid-19 spike-host cell receptor
grp78 binding site prediction. Journal of Infection.
Kasabov, N. K. (2019). Computational modelling and pat-
tern recognition in bioinformatics. In Time-Space,
Spiking Neural Networks and Brain-Inspired Artificial
Intelligence, pages 505–543. Springer.
Katoh, K., Misawa, K., Kuma, K.-i., and Miyata, T. (2002).
Mafft: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence
alignment based on fast fourier transform. Nucleic
acids research, 30(14):3059–3066.
Kaya, M., Kaya, B., and Alhajj, R. (2016). A novel multi-
objective genetic algorithm for multiple sequence
alignment. International Journal of Data Mining and
Bioinformatics, 14(2):139–158.
Kaya, M., Sarhan, A., and Alhajj, R. (2014). Multiple
sequence alignment with affine gap by using multi-
objective genetic algorithm. Computer methods and
programs in biomedicine, 114(1):38–49.
Kumar, M. (2015). An enhanced algorithm for multiple se-
quence alignment of protein sequences using genetic
algorithm. EXCLI journal, 14:1232.
Lassmann, T. (2019). Kalign 3: multiple sequence align-
ment of large datasets. Bioinformatics, 36(6):1928–
1929.
Le, Q., Sievers, F., and Higgins, D. G. (2017). Protein
multiple sequence alignment benchmarking through
secondary structure prediction. Bioinformatics,
33(9):1331–1337.
Lee, Z.-J., Su, S.-F., Chuang, C.-C., and Liu, K.-H. (2008).
Genetic algorithm with ant colony optimization (ga-
aco) for multiple sequence alignment. Applied Soft
Computing, 8(1):55–78.
Lemieux, J. E., Siddle, K. J., Shaw, B. M., Loreth, C.,
Schaffner, S. F., Gladden-Young, A., Adams, G., Fink,
T., Tomkins-Tinch, C. H., Krasilnikova, L. A., et al.
(2020). Phylogenetic analysis of sars-cov-2 in boston
highlights the impact of superspreading events. Sci-
ence.
Li, X., Wang, W., Zhao, X., Zai, J., Zhao, Q., Li, Y., and
Chaillon, A. (2020). Transmission dynamics and evo-
lutionary history of 2019-ncov. Journal of medical
virology, 92(5):501–511.
Martino, A., Giuliani, A., and Rizzi, A. (2018). Granu-
lar computing techniques for bioinformatics pattern
recognition problems in non-metric spaces. In Com-
putational Intelligence for Pattern Recognition, pages
53–81. Springer.
Nakamura, T., Yamada, K. D., Tomii, K., and Ka-
toh, K. (2018). Parallelization of mafft for large-
scale multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics,
34(14):2490–2492.
Nascimento, F. F., dos Reis, M., and Yang, Z. (2017). A bi-
ologist’s guide to bayesian phylogenetic analysis. Na-
ture ecology & evolution, 1(10):1446–1454.
Needleman, S. B. and Wunsch, C. D. (1970). A gen-
eral method applicable to the search for similarities
in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. Journal
of molecular biology, 48(3):443–453.
Notredame, C. and Higgins, D. G. (1996). Saga: sequence
alignment by genetic algorithm. Nucleic acids re-
search, 24(8):1515–1524.
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
390

Notredame, C., Higgins, D. G., and Heringa, J. (2000). T-
coffee: A novel method for fast and accurate multiple
sequence alignment. Journal of molecular biology,
302(1):205–217.
Nute, M., Saleh, E., and Warnow, T. (2019). Evaluating sta-
tistical multiple sequence alignment in comparison to
other alignment methods on protein data sets. System-
atic biology, 68(3):396–411.
Rani, R. R. and Ramyachitra, D. (2017). Application of
genetic algorithm by influencing the crossover param-
eters for multiple sequence alignment. In 2017 4th
IEEE Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference
on Electrical, Computer and Electronics (UPCON),
pages 33–38. IEEE.
Rasmussen, T. K. and Krink, T. (2003). Improved hidden
markov model training for multiple sequence align-
ment by a particle swarm optimization—evolutionary
algorithm hybrid. Biosystems, 72(1-2):5–17.
Riaz, T., Wang, Y., and Li, K.-B. (2004). Multiple se-
quence alignment using tabu search. In Proceedings of
the second conference on Asia-Pacific bioinformatics-
Volume 29, pages 223–232.
Rozewicki, J., Li, S., Amada, K. M., Standley, D. M., and
Katoh, K. (2019). Mafft-dash: integrated protein se-
quence and structural alignment. Nucleic acids re-
search, 47(W1):W5–W10.
Rubio-Largo,
´
A., Vega-Rodr
´
ıguez, M. A., and Gonz
´
alez-
´
Alvarez, D. L. (2016). Hybrid multiobjective artificial
bee colony for multiple sequence alignment. Applied
Soft Computing, 41:157–168.
Sievers, F. and Higgins, D. G. (2018). Clustal omega
for making accurate alignments of many protein se-
quences. Protein Science, 27(1):135–145.
Sievers, F. and Higgins, D. G. (2020). Quantest2:
benchmarking multiple sequence alignments using
secondary structure prediction. Bioinformatics,
36(1):90–95.
Smirnov, V. and Warnow, T. (2020). Magus: Multiple se-
quence alignment using graph clustering. Bioinfor-
matics.
Smith, T. F., Waterman, M. S., et al. (1981). Identifica-
tion of common molecular subsequences. Journal of
molecular biology, 147(1):195–197.
Suplatov, D. A., Kopylov, K. E., Popova, N. N., Voevodin,
V. V., and
ˇ
Svedas, V. K. (2018). Mustguseal: a server
for multiple structure-guided sequence alignment of
protein families. Bioinformatics, 34(9):1583–1585.
Thompson, J. D., Higgins, D. G., and Gibson, T. J. (1994).
Clustal w: improving the sensitivity of progres-
sive multiple sequence alignment through sequence
weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight
matrix choice. Nucleic acids research, 22(22):4673–
4680.
Thompson, J. D., Koehl, P., Ripp, R., and Poch, O. (2005).
Balibase 3.0: latest developments of the multiple se-
quence alignment benchmark. Proteins: Structure,
Function, and Bioinformatics, 61(1):127–136.
Thomsen, R. and Boomsma, W. (2004). Multiple sequence
alignment using saga: investigating the effects of op-
erator scheduling, population seeding, and crossover
operators. In Workshops on applications of evolution-
ary computation, pages 113–122. Springer.
Tilocca, B., Soggiu, A., Musella, V., Britti, D., Sanguinetti,
M., Urbani, A., and Roncada, P. (2020). Molecular
basis of covid-19 relationships in different species: a
one health perspective. Microbes and Infection.
Tran, Q.-N. and Wallinga, M. (2017). Ups: A new approach
for multiple sequence alignment using morphing tech-
niques. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on
Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pages 425–
430. IEEE.
Wang, L. and Jiang, T. (1994). On the complexity of mul-
tiple sequence alignment. Journal of computational
biology, 1(4):337–348.
Woolson, R. (2007). Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Wiley en-
cyclopedia of clinical trials, pages 1–3.
Zhang, C., Zhang, F.-m., Li, F., and Wu, H.-s. (2014). Im-
proved artificial fish swarm algorithm. In 2014 9th
IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Ap-
plications, pages 748–753. IEEE.
Zhang, D., Gao, F., Jakovli
´
c, I., Zou, H., Zhang, J., Li,
W. X., and Wang, G. T. (2020a). Phylosuite: an
integrated and scalable desktop platform for stream-
lined molecular sequence data management and evo-
lutionary phylogenetics studies. Molecular ecology
resources, 20(1):348–355.
Zhang, S.-f., Tuo, J.-l., Huang, X.-b., Zhu, X., Zhang,
D.-m., Zhou, K., Yuan, L., Luo, H.-j., Zheng, B.-j.,
Yuen, K.-y., et al. (2018). Epidemiology characteris-
tics of human coronaviruses in patients with respira-
tory infection symptoms and phylogenetic analysis of
hcov-oc43 during 2010-2015 in guangzhou. PloS one,
13(1):e0191789.
Zhang, T., Wu, Q., and Zhang, Z. (2020b). Probable pan-
golin origin of sars-cov-2 associated with the covid-19
outbreak. Current Biology.
A Hybrid Approach using Progressive and Genetic Algorithms for Improvements in Multiple Sequence Alignments
391
