
Deep Learning for RF-based Drone Detection and Identification using
Welch’s Method
Mahmoud Almasri
a
LABSTICC, UMR 6285 CNRS, ENSTA Bretagne, 2 rue F. Verny, 29806 Brest Cedex 9, France
Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence, Deep Neural Network, Drone Identification and Classification, Welch.
Abstract:
Radio Frequency (RF) combined with the deep learning methods promised a solution to detect the presence
of the drones. Indeed, the classical techniques (i.e. radar, vision and acoustics, etc.) suffer several drawbacks
such as difficult to detect the small drones, false alarm of flying birds or balloons, the influence of the wind
on the performance, etc. For an effective drones’s detection, two main stages should be established: Feature
extraction and feature classification. The proposed approach in this paper is based on a novel feature extraction
method and an optimized deep neural network (DNN). At first, we present a novel method based on Welch
to extract meaningful features from the RF signal of drones. Later on, three optimized Deep Neural Network
(DNN) models are considered to classify the extracted features. The first DNN model can be used to detect the
presence of the drones and contains two classes. The second DNN help us to detect and recognize the type of
the drone with 4 classes: A class for each drone and the last one for the RF background activities. In the third
model, 10 classes have been considered: the presence of the drone, its type, and its flight mode (i.e. Stationary,
Hovering, flying with or without video recording). Our proposed approach can achieve an average accuracy
higher than 94% and it significantly improves the accuracy, up to 30%, compared to existing methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tackling malicious and dangerous Unmanned Aerial
Vehicles (UAVs) use requires the parallel devel-
opment of systems capable of detecting, tracking
and recognizing UAVs in an automatic and non-
collaborative way. Indeed, the development of drones
and the threats for sensitive sites make their detection
and identification critical. It is therefore necessary to
develop robust, reliable and inexpensive solutions to
locate and identify these drones. Several modalities
are available to deal with this problem, such as optical
or radar imagery, the detection of Radio-Frequency
(RF) communications or even acoustics. In (Bernar-
dini et al., 2017), acoustic drone localization and de-
tection has been proposed using support vector ma-
chines. In (Chang et al., 2018; Busset et al., 2015), the
authors propose to use the acoustic cameras method-
ology to detect and identify the drones. Video detec-
tion is also possible but quickly limited by the particu-
lar experimental conditions (Ramamonjy et al., 2016).
However, very high performance cameras should be
dedicated to this task, and require an initial localiza-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9106-4020
tion step to be able to target the drone beforehand.
In (Bisio et al., 2018), Radar imagery shows limited
performance due to little reflected radar signal portion
that mainly depends on the stealth technology.
RF signal emitted from UAVs is recently attracted
more attention to detect malicious drones and is suited
to be used in several scenarios (Azari et al., 2018).
This methodology is nor depends on the used wire-
less technologies of drones such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth,
4G, etc. RF combined with the Deep Neural Net-
work (DNN) may provide a more effective solution
for drones detection and classification. However, the
DNN model is widely suggested in several fields such
as speech recognition (Chan et al., 2016; Graves et al.,
2013), signal compression (Al-Sa’D et al., 2018), and
in other fields (LeCun et al., 2015).
The DNN model has emerged as the most impor-
tant and popular Artificial Intelligence (AI) technique
(Deng et al., 2018; Zhao and Gao, 2019).
In this paper, the two main challenges for drones de-
tection and identification are suggested: feature ex-
traction and feature classification. The aim of feature
extraction is to get a low dimensional representation
of the data without losing information of the original
data space. Then, the complexity of the data is re-
208
Almasri, M.
Deep Learning for RF-based Drone Detection and Identification using Welch’s Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0010530302080214
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications (DATA 2021), pages 208-214
ISBN: 978-989-758-521-0
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Split Data
Welch’s
Method
Noise
Elimination
Train Data
Test Data
Model Fit
&
Result Evaluation
Data are divided
into overlapping
segments
Add specified
windows to each
segments
FFT to
windowed
segments
Periodogram of each
windowed segment
is computed
All Periodograms
are averaged to
obtain Welch PSD
Data
Normalization
Figure 1: Flowchart of the entire process.
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
Time (s)
10
-3
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
Amplitude
10
4
RF Signal of Bebop
Figure 2: One segment of Bebop RF signal.
duced to a simple representation.
The second challenge, to classify the features vec-
tor gathered from the feature extraction stage in which
the classification in this work is performed using the
DNN model. Generally, the classification with a low
feature dimension can accelerate the model speed and
limit storage requirements. In this work, three DNN
models are developed:
• To detect the presence of a drone.
• To detect the presence of a drone, and identify its
type.
• To detect the presence of a drone, identify its type,
and finally determine its flight mode.
2 PROPOSED APPROACH FOR
FEATURE EXTRACTION
In this section, we present our proposed approach to
extract meaningful features, and prepare the dataset
for classification using an optimized DNN model. We
use an open access dataset of (Al-Sa’d et al., 2019),
that contains RF signals for three drones: Parrot Be-
bop, Parrot AR, and DJI Phantom 3. In (Al-Sa’d
et al., 2019), the acquisition is performed under differ-
Split Data
Pwelch
Method
Noise
Eimination
Train Data
Test Data
Model Fit
&
Result Evaluation
Data are divided
into overlapping
segments
Add specified
windows to each
segments
FFT to
windowed
segments
Periodogram of each
windowed segment
is computed
All Periodograms
are averaged to
obtain Welch PSD
Data
Normalization
Figure 3: Welch PSD algorithm.
ent modes: drones are off (i.e. Background activity),
on and connected, hovering, flying with and without
video recording.
Fig. 1 shows a flowchart of the entire proposed ap-
proach. At first, all data are split into small segments
(e.g. of 2.5 ms) in order to obtain a large amount of
the data that are required to train and test the DNN
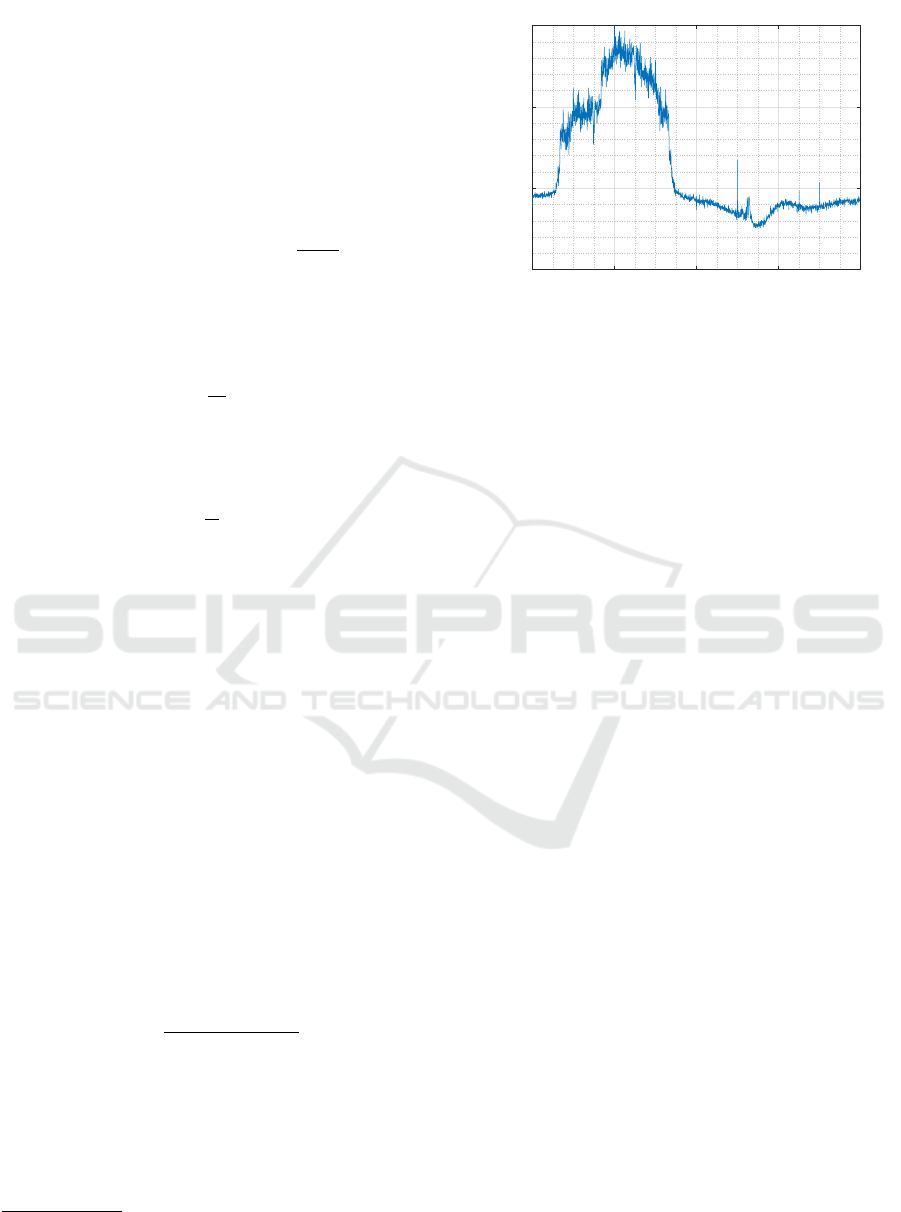
model. Fig. 2 represents a segment of the obtained
signal of Parrot Bebop.
For Fs = 40MHz, the number of samples in Fig.
2 (also in each segment) is 10
5
sample. In order to ex-
tract the most important features and reduce the num-
ber of samples in each segment, we focus on Welch’s
method.
Indeed, Welch represents one of the most popu-
lar method to calculate the Power Spectral Density
(PSD) for a given signal (Jahromi et al., 2018). Using
Welch’s method, on the one hand, can significantly
decrease the number of the features in the dataset; oth-
erwise, the DNN model will be trained for too long
time, and that may cause the model overfitting. On
the other hand, it is necessary to discard the noise
segments, that provide a low power; otherwise, the
accuracy will be significantly decreased because the
noise segments are used to train and test the DNN
model
1
. To perform Welch spectral analysis, Fig. 3
shows the different stages of the Welch’s method. Let
us begin to divide a given signal x into N sample:
x[0], x[1], ..., x[N − 1]. Then, all samples are splitted
into K overlapping segments that is considered, in
most cases, equal to 50%. Let M be the length of
each segment, N is the total number of segments, and
S is the number of samples to shift between segments.
Then, we obtain:
1
In our DNN model, there is a class for the noise (RF back-
ground activities) in order to train the DNN model to dif-
ferentiate the signal of the drone from the noise. Then, if
all classes contain noise segments, the accuracy will be
significantly decreased as in the case of (Al-Sa’d et al.,
2019).
Deep Learning for RF-based Drone Detection and Identification using Welch’s Method
209
Segment 1: x[0], x[1], . . . ,x[M − 1]
Segment 2: x[S], x[S + 1], ..., x[M + S − 1]
.
.
.
Segment K: x[N − M], x[N − M + 1], ..., x[N − 1]
For each segment k = 1, . . . , K, compute a windowed
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) as follows:
X
k
( f ) =
∑
m
x[m]w[m]exp
−
2π f j
M
m
(1)
where m = (k − 1)S, . . . , M + (k − 1)S − 1 and w[m]
represents the window function. Then, calculate the
periodogram P
k
( f ) for each segment as follows:
P
k
( f ) =
1
W
|X
k
( f )|
2
(2)
where W =
∑
m
w
2
[m]. Finally, average the peri-
odogram for each segments to obtain Welch’s PSD:
S
k
( f ) =
1
K
K
∑
k=1
P
k
( f ) (3)
After splitting the data and applying Welch’s method
on all segments, a threshold γ is established in order
to eliminate all segments with a low PSD
2
. Tab. 1
represents all segments in each class before and after
eliminate noise segments that have a PSD lower than
the threshold γ. To finalize the data preparation, all
segments should be normalized in order to make sure
that the different segments take on similar ranges of
values. Then, the necessary time to train the DNN
model is reduced while still providing the most accu-
rate results (Passalis et al., 2019). In (Sola and Sevilla,
1997), the authors show that the best normalization
method can be achieved when all segments are in the
same magnitude, and specially if they are in the or-
der of one. For this reason, after noise elimination, all
segments are normalized using the min-max method
that provides better results in most object classifica-
tion (Al Shalabi et al., 2006; Saranya and Manikan-
dan, 2013):
x =
x − min(x)
max(x) − min(x)
(4)
After performing Welch’s method and the seg-
ment normalization on the signal of the Bebop in Fig.
2, we obtain Fig. 4.
2
This threshold level can be chosen with respect to the RF
background activities where there is no-drone signal.
2400 2420 2440 2460 2480
Frequency (MHz)
-150
-100
-50
0
dB
Pwelch of Bebop for one segment
Figure 4: Welch based estimates, Hamming window, 2050
samples long segment, 50% overlap, min-max normaliza-
tion.
3 DEEP NEURAL NETWORK
MODEL
Deep Neural Network (DNN) has shown surpass-
ing results in various cognitive tasks such as speech
recognition, object detection and identification, etc.
At first, we present the DNN concept and general ar-
chitecture. Later on, we optimize the architecture of
the DNN model in order to accelerate the training
time and also to achieve a better accuracy. A DNN
model has an input layer, hidden layers and an out-
put layer. For a given DNN model, the mathemati-
cal input-output relationship can be expressed as fol-
lows(He and Xu, 2010):
z
l
k
= f
l
(W
l
z
(l−1)
k
+ b
l
), (5)
W
(l)
=
w
(l)
11
w
(l)
12
·· · w
(l)
1H
(l−1)
w
(l)
21
w
(l)
22
·· · w
(l)
2H
(l−1)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
w
(l)
H
(l)
1
w
(l)
H
(l)
2
·· · w
(l)
H
(l)
H
(l−1)
(6)
z
l
k
is the output of layer l and the input to layer
l + 1 for the k
th
segment; z
(l−1)
k
represents the out-
put of layer (l − 1) and the input to layer l; for in-
stance, z
0
k
stands for the k
th
segment at the input layer
and z
L
k
represents the classification vector for the k
th
segment where L is the output layer; f
l
is the acti-
vation function of layer l; This later can be any lin-
ear or non-linear function, such as: the rectified linear
unit (ReLU), Sigmoid, Softmax, TanH, etc. W
l
is the
weight matrix of layer l; w
l
pq
is the weight between
the p
th
neuron of layer l and the q
th
neuron of layer
l −1; b
l
= [b
l
1
, b
l
2
, . . . , b
l
(H
l
)
] is the bias vector of layer
DATA 2021 - 10th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
210
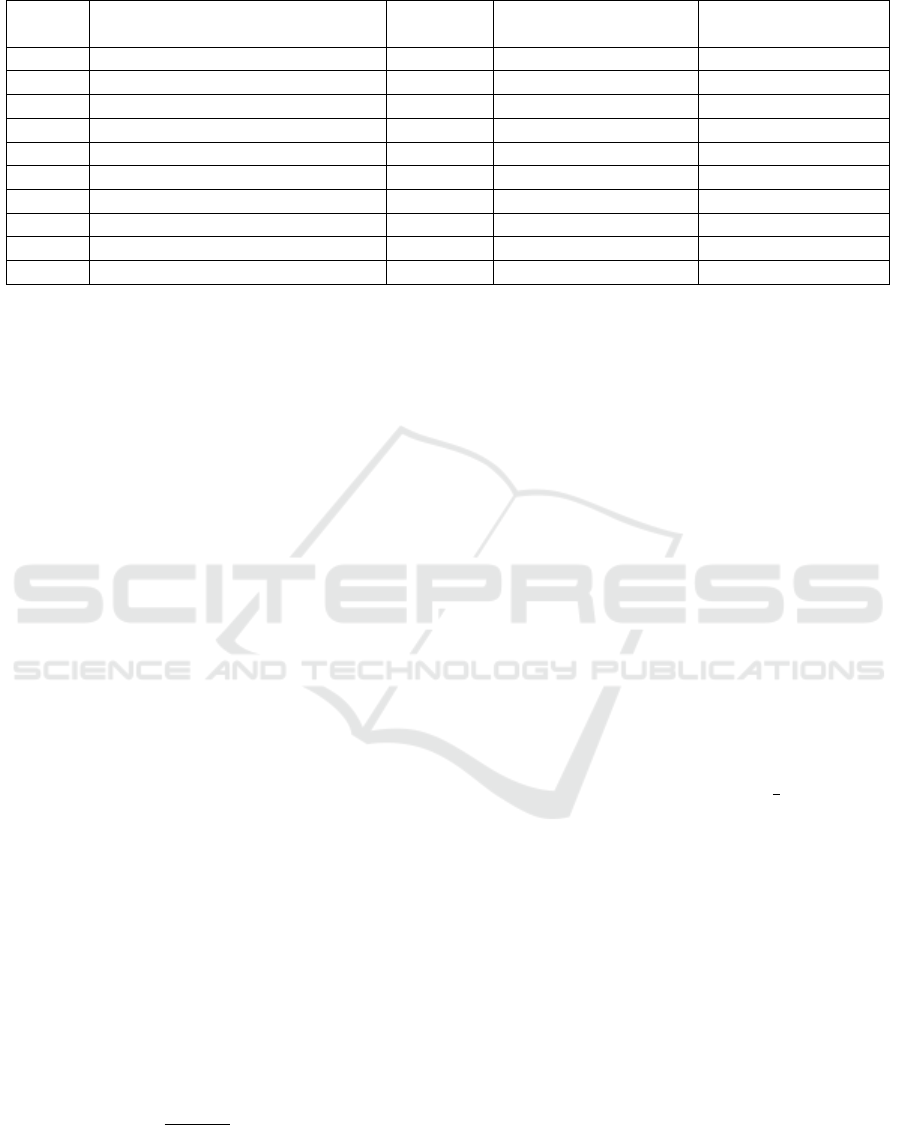
Table 1: Class Labels, Acronyms, and Class Sample Rate before and after the Preprocessing.
Classes Class Name Acronyms nb. of segments before nb. of segments after
the preprocessing the preprocessing
1 No-Drone (Background activities) ND 4100 4100
2 Bebop Static BS 2100 832
3 Bebop Hovering BH 2100 695
4 Bebop Flying BF 2100 720
5 Bebop Flying & Video recording BFV 2100 696
6 AR Static AS 2100 659
7 AR Hovering AH 2100 526
8 AR Flying AF 2100 566
9 AR Flying & Video recording AFV 1800 886
10 Phantom Static PS 2100 1627
l; H
l
is the total number of neurons in layer l; for in-
stance, H
0
is the number of features at the input and
H
L
is the number of classes in the classification vector
at the output.
3.1 DNN Model Optimization
In a DNN model, the weight and biases are updated
through a supervised learning process with respect
to minimizing the classification error (Bottou, 2010).
Several classification loss functions are adapted to
DNN models and widely used in the literature, such as
Mean Square Error (MSE), cross-entropy, etc. Cross-
entropy is the most commonly used loss function for
multi-class classification problems (Nielsen, 2015),
(Zhu et al., 2020) and (Nasr et al., 2002). Cross-
entropy for a multi-class classification task measures
the dissimilarity between the target label distribution
y
j
and the predicted one ˆy
j
, and can be expressed as
follows:
L(y
j
, ˆy
j
) = −
C
∑
j=1
y
j
log( ˆy
j
) (7)
In eq. (7), the Cross-entropy is configured with C
class (C = H
L
), and a ‘Softmax‘ activation function
should be used at the output layer in order to pre-
dict the probability for each class (Liu et al., 2016;
Kobayashi, 2019; Agarwala et al., 2020). While for
hidden layers, we use the rectified linear unit (ReLU)
that represents the most used activation function by
default for performing a majority of the deep learning
tasks. Softmax and ReLU functions are respectively
expressed in eq. (8) and (9):
f (x
i
) =
e
x
i
∑
C
j=1
e
x
j
, for i=1,...,C (8)
f (x
i
) =
(
x
i
x
i
> 0
0 x
i
≤ 0
(9)
Let’s start to determine the best number of layers
and neurons in the hidden layers. For the input layer,
the number of neurons is equal to 2050 that repre-
sents the number of samples in each segment. While
the number of neurons at the output is equal to 2, 4 or
10 classes for the first, second, and third DNN model.
For hidden layers, until now, there were no-definitive
rules for choosing the number of hidden layers, and
the best number of neurons in each hidden layer. Sev-
eral methods are used without providing an exact for-
mula for determining the number of hidden layers as
well as the number of neurons in each hidden layer.
For the number of hidden layers, the best hidden lay-
ers is achieved when the number of layers ranges from
1-5 (Arifin et al., 2019). However, adding more un-
necessary hidden layer can significantly increase the
complexity of the network.
For the number of neurons in hidden layers, several
works attempt different methods trying to maximize
the model accuracy, and some rules are suggested:
• The required hidden neurons are
2
3
(or from 70%
to 90%) of the size of the input layer (Boger and
Guterman, 1997).
• The number of hidden neurons should be less than
twice of the number of neurons in the input layer
(Berry and Linoff, 2004).
• The number of hidden neurons can be as high as
the number of training segments (Huang, 2003).
• The number of hidden neurons should be between
the input layer neurons and the output layer ones
(Blum, 1992).
Based on the above discussion, and to reduce the com-
plexity of the DNN model, we consider three layers
with the following number of neurons: 256, 128 and
64.
Deep Learning for RF-based Drone Detection and Identification using Welch’s Method
211

Fold 1
Fold 2
Fold 10
𝐷
𝑣𝑎𝑙,1
𝐷
𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛,1
Figure 5: 10-fold cross-validation. The data is randomly
partitioned into 10 blocks, each of them contains 10% of the
data. 90% of the data are used to train the model training
and 10% for model validation.
3.2 K-fold Cross-Validation
K-fold Cross-Validation represents one of the most
used technique for model evaluation in machine learn-
ing practice. However, machine learning models
sometimes cannot generalize well on unseen data that
has not been trained yet. To ensure that the model is
relevant and can perform well on new data, K-fold
Cross-Validation is recommended. As well, it en-
sures that all RF segments in the dataset has the same
chance to be in training and test set. In K-fold Cross-
Validation, RF segments are divided into K blocks
with equal size. Then, one block is used for the vali-
dation while the other K −1 blocks contribute to train
the DNN model, and a validation performance can
be calculated. The operation is repeated K times, by
selecting another validation block, in order to obtain
a model that have both low bias and variance. The
global cross-validated performance can be obtained
by averaging the K performance measurements.
Fig. 5 illustrates the K-fold cross validation for
K = 10 where D
val,1
in the first fold represents the
data validation and blocks D
train,1
serve as training
data. In (Raschka, 2018), the experiments show that
K = 10 represents a good choice for K.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this section, we use several metrics in order to eval-
uate the performance of our proposed method: Ac-
curacy, Precision, recall, error, false discovery rate
(FDR), false negative rate (FNR) and F1 scores via
confusion matrices. These metrics are defined as fol-
lows:
Accuracy =
T P + T N
T P + T N + FP + FN
(10)
Precision =
T P
T P + FP
(11)
Recall =
T P
T P + FN
(12)
Error = 1 −Accuracy (13)
FDR = 1 −Precision (14)
FNR = 1 −Recall (15)
where T P, T N, FP and FN are true positives, true
negatives, false positives and false negatives respec-
tively. We develop three DNNs models for drones
detection and identification. The Confusion Matrix
of the three DNN models for 2-class, 4-class and 10-
class are respectively shown in Figs. 6a, 6b and 6c.
In that figures, the rows of the inner 2x2, 4x4 and
10x10 matrices represent the predicted class while the
columns correspond to the true class. The diagonal
cells, exhibited in green, represent the number of seg-
ments that are correctly classified, while the red cells
refer to the incorrectly classified segments. As well
as, each cell show the number of segments and the
percentage of the total number of segments. The gray
cells in the right column show the precision and FDR
in green and red respectively. Furthermore, the gray
cells in the row at the bottom illustrate the recall in
green, and FNR in red. In addition, the blue cell in the
bottom right of the plot shows the overall accuracy in
green, and the error in red. Moreover, the yellow col-
umn and row on the far left and top show the F1 scores
for predicting each class in green and its complemen-
tary in red, (1-F1 score), for completeness. Finally,
the orange cell in the upper left of the plot shows the
averaged F1 score for all classes in green and its com-
plementary in red. The first DNN model in Fig. 6a,
for two classes, shows that the average accuracy is
about of 99.7%, average error of 0.3% and average F1
score of 99.7%. Fig. 6b depicts the classification per-
formance of the second DNN model, which detects
the presence of a drone and identifies its type. Results
demonstrate an average accuracy of 97.7%, average
error of 2.3%, and average F1 score of 97.5%.
We should notice that the average accuracy is
significantly improved using our approach based on
Welch’s method compared to the proposed methods in
(Al-Sa’d et al., 2019; Al-Emadi and Al-Senaid, 2020;
Allahham et al., 2020). Indeed, the achieved accura-
cies in the latter references, for 4 classes, are respec-
tively: 84.5%, 85.8 % and 94.6 %.
Finally, Fig. 6c illustrates the classification per-
formance of the third DNN model which detects the
presence of a drone, identifies its type, and determines
its flight mode. Results demonstrate an average accu-
racy of 94.5%, average error of 5.5%, and average
DATA 2021 - 10th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
212

No-Drone Drone
Target Class
No-Drone
Drone
Output Class
4082
36.1%
18
0.2%
99.6%
0.4%
16
0.1%
7191
63.6%
99.8%
0.2%
99.6%
0.4%
99.8%
0.2%
99.7%
0.3%
99.6%
0.4%
99.8%
0.2%
99.6%
0.4%
99.8%
0.2%
99.7%
0.3%
(a) Confusion Matrix of the
first DNN model
ND B A P
Target Class
ND
B
A
P
Output Class
4084
36.1%
8
0.1%
5
0.0%
3
0.0%
99.6%
0.4%
8
0.1%
2859
25.3%
68
0.6%
8
0.1%
97.1%
2.9%
4
0.0%
107
0.9%
2523
22.3%
3
0.0%
95.7%
4.3%
1
0.0%
23
0.2%
18
0.2%
1585
14.0%
97.4%
2.6%
99.7%
0.3%
95.4%
4.6%
96.5%
3.5%
99.1%
0.9%
97.7%
2.3%
99.6%
0.4%
96.2%
3.8%
96.1%
3.9%
98.2%
1.8%
99.6%
0.4%
96.2%
3.8%
96.1%
3.9%
98.2%
1.8%
97.5%
2.5%
(b) Confusion Matrix of the second
DNN model
ND BS BH BF BFV AS AH AF AFV PS
Target Class
ND
BS
BH
BF
BFV
AS
AH
AF
AFV
PS
Output Class
4085
36.1%
4
0.0%
0
0.0%
4
0.0%
1
0.0%
0
0.0%
0
0.0%
1
0.0%
2
0.0%
3
0.0%
99.6%
0.4%
4
0.0%
786
7.0%
8
0.1%
2
0.0%
0
0.0%
22
0.2%
3
0.0%
3
0.0%
1
0.0%
3
0.0%
94.5%
5.5%
0
0.0%
1
0.0%
650
5.7%
6
0.1%
1
0.0%
7
0.1%
19
0.2%
6
0.1%
2
0.0%
3
0.0%
93.5%
6.5%
4
0.0%
5
0.0%
5
0.0%
647
5.7%
26
0.2%
1
0.0%
16
0.1%
15
0.1%
0
0.0%
1
0.0%
89.9%
10.1%
1
0.0%
0
0.0%
8
0.1%
26
0.2%
654
5.8%
0
0.0%
1
0.0%
5
0.0%
1
0.0%
0
0.0%
94.0%
6.0%
1
0.0%
11
0.1%
4
0.0%
2
0.0%
0
0.0%
604
5.3%
11
0.1%
11
0.1%
13
0.1%
2
0.0%
91.7%
8.3%
0
0.0%
1
0.0%
8
0.1%
8
0.1%
1
0.0%
21
0.2%
409
3.6%
60
0.5%
17
0.2%
1
0.0%
77.8%
22.2%
1
0.0%
2
0.0%
1
0.0%
6
0.1%
4
0.0%
14
0.1%
44
0.4%
470
4.2%
21
0.2%
3
0.0%
83.0%
17.0%
0
0.0%
2
0.0%
3
0.0%
1
0.0%
0
0.0%
19
0.2%
28
0.2%
40
0.4%
793
7.0%
0
0.0%
89.5%
10.5%
1
0.0%
2
0.0%
14
0.1%
6
0.1%
2
0.0%
3
0.0%
5
0.0%
8
0.1%
1
0.0%
1585
14.0%
97.4%
2.6%
99.7%
0.3%
96.6%
3.4%
92.7%
7.3%
91.4%
8.6%
94.9%
5.1%
87.4%
12.6%
76.3%
23.7%
75.9%
24.1%
93.2%
6.8%
99.0%
1.0%
94.5%
5.5%
99.6%
0.4%
95.5%
4.5%
93.1%
6.9%
90.6%
9.4%
94.4%
5.6%
89.5%
10.5%
77.0%
23.0%
79.3%
20.7%
91.3%
8.7%
98.2%
1.8%
99.6%
0.4%
95.5%
4.5%
93.1%
6.9%
90.6%
9.4%
94.4%
5.6%
89.5%
10.5%
77.0%
23.0%
79.3%
20.7%
91.3%
8.7%
98.2%
1.8%
90.8%
9.2%
(c) Confusion Matrix of the third DNN model
Figure 6: Confusion matrix of the three DNN models. Fig. 6a represents two classes: No-Drone and Drone. Fig. 6b depicts the
performance of the second DNN model for 4 classes: ND (No-drone), B (Bebop), A (AR) and P (Phantom). The Acronyms
in Fig. 6c are shown in Tab. 1.
F1 score of 90.8%. While, the obtained accuracies
in (Al-Sa’d et al., 2019; Al-Emadi and Al-Senaid,
2020; Allahham et al., 2020) are respectively: 46.8%,
59.2% and 87.4%. Then, the average accuracy of our
proposed method, for 10 classes, can be greatly en-
hanced by 47%, 35% and 7% compared to the pro-
posed methods in the latter references.
5 CONCLUSION
In Intelligent detection and identification techniques
have emerged vastly by the rise of data driven algo-
rithms, such as neural networks. In the Deep Neural
Network (DNN), extracting features from given data
represents a critical importance for the successful ap-
plication of machine learning. In this work, we pro-
posed a novel approach based on Welch’s method for
feature extraction in order to enhance the classifica-
tion performance of multi-class and maximize the av-
erage accuracy. Using Welch’s method, the number
of extracted features at the input of the DNN model
can be reduced. Moreover, it can estimate if a given
segment of data contains an useful information or not,
so that the noise segments can be eliminated. Three
DNN models have been used to classify the extracted
features, and then detect the presence of a drone, iden-
tify its type and finally determine its flight mode. In
the first DNN model, for two classes, the achieved
average accuracy is about of 99.7%. By increasing
the number of classes in the second DNN model, 4
classes are used, the average accuracy is slightly de-
creased to 97.7%. In the last DNN model with 10
classes, the obtained accuracy is about of 94.5% that
is enhanced up to 47% compared to existing methods.
In the future work, another important feature ex-
traction methods can be used in the frequency or time
domains, such as Entropy, Skewness, kurtosis, etc.
Another potential research direction is to apply an-
other powerful machine learning technologies to ad-
dress the fundamental visual feature extraction issue.
REFERENCES
Agarwala, A., Pennington, J., Dauphin, Y., and Schoen-
holz, S. (2020). Temperature check: theory and prac-
tice for training models with softmax-cross-entropy
losses. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.07344.
Al-Emadi, S. and Al-Senaid, F. (Doha, Qatar, February,
2020). Drone detection approach based on radio-
frequency using convolutional neural network. In
IEEE International Conference on Informatics, IoT,
and Enabling Technologies, pages 29–34.
Al-Sa’d, M. F., Al-Ali, A., Mohamed, A., Khattab, T., and
Erbad, A. (2019). Rf-based drone detection and iden-
tification using deep learning approaches: An initia-
tive towards a large open source drone database. Fu-
ture Generation Computer Systems, 100:86–97.
Al-Sa’D, M. F., Tlili, M., Abdellatif, A. A., Mohamed,
A., Elfouly, T., Harras, K., O’Connor, M. D., et al.
(2018). A deep learning approach for vital signs com-
pression and energy efficient delivery in mhealth sys-
tems. IEEE Access, 6:33727–33739.
Al Shalabi, L., Shaaban, Z., and Kasasbeh, B. (2006). Data
mining: A preprocessing engine. Journal of Computer
Science, 2(9):735–739.
Allahham, M. S., Khattab, T., and Mohamed, A. (Doha,
Deep Learning for RF-based Drone Detection and Identification using Welch’s Method
213

Qatar, February, 2020). Deep learning for rf-based
drone detection and identification: A multi-channel 1-
d convolutional neural networks approach. In IEEE
International Conference on Informatics, IoT, and En-
abling Technologies, pages 112–117.
Arifin, F., Robbani, H., Annisa, T., and Ma’arof, N. (2019).
Variations in the number of layers and the number of
neurons in artificial neural networks: Case study of
pattern recognition. In Journal of Physics: Confer-
ence Series, volume 1413, page 012016.
Azari, M. M., Sallouha, H., Chiumento, A., Rajendran, S.,
Vinogradov, E., and Pollin, S. (2018). Key technolo-
gies and system trade-offs for detection and localiza-
tion of amateur drones. IEEE Communications Mag-
azine, 56(1):51–57.
Bernardini, A., Mangiatordi, F., Pallotti, E., and Capodi-
ferro, L. (2017). Drone detection by acoustic signature
identification. Electronic Imaging, 2017(10):60–64.
Berry, M. J. and Linoff, G. S. (2004). Data mining tech-
niques: for marketing, sales, and customer relation-
ship management. John Wiley & Sons.
Bisio, I., Garibotto, C., Lavagetto, F., Sciarrone, A., and
Zappatore, S. (2018). Blind detection: Advanced
techniques for wifi-based drone surveillance. IEEE
Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 68(1):938–
946.
Blum, A. (1992). Neural networks in C++: an object-
oriented framework for building connectionist sys-
tems. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Boger, Z. and Guterman, H. (Orlando, FL, USA, October,
1997). Knowledge extraction from artificial neural
network models. In IEEE International Conference
on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Computational
Cybernetics and Simulation, volume 4, pages 3030–
3035.
Bottou, L. (Paris France, August, 2010). Large-scale ma-
chine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In In-
ternational Conference on Computational Statistics.
Busset, J., Perrodin, F., Wellig, P., Ott, B., Heutschi, K.,
R
¨
uhl, T., and Nussbaumer, T. (2015). Detection and
tracking of drones using advanced acoustic cameras.
In Unmanned/Unattended Sensors and Sensor Net-
works XI; and Advanced Free-Space Optical Commu-
nication Techniques and Applications, volume 9647,
page 96470.
Chan, W., Jaitly, N., Le, Q., and Vinyals, O. (Shanghai,
China, March, 2016). Listen, attend and spell: A
neural network for large vocabulary conversational
speech recognition. In IEEE International Conference
on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing.
Chang, X., Yang, C., Wu, J., Shi, X., and Shi, Z. (Sheffield,
UK, July, 2018). A surveillance system for drone
localization and tracking using acoustic arrays. In
IEEE Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Process-
ing Workshop (SAM).
Deng, C., Liao, S., Xie, Y., Parhi, K. K., Qian, X., and Yuan,
B. (Fukuoka, Japan, October, 2018). Permdnn: Effi-
cient compressed dnn architecture with permuted di-
agonal matrices. In Annual IEEE/ACM International
Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO).
Graves, A., Abdelrahman, M., and Hinton, G. (Vancouver,
Canada, 2013). Speech recognition with deep recur-
rent neural networks.
He, X. and Xu, S. (2010). Artificial neural networks. Pro-
cess neural networks: theory and applications, pages
20–42.
Huang, G.-B. (2003). Learning capability and storage
capacity of two-hidden-layer feedforward networks.
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 14(2):274–
281.
Jahromi, M. G., Parsaei, H., Zamani, A., and Stashuk, D. W.
(2018). Cross comparison of motor unit potential fea-
tures used in emg signal decomposition. IEEE Trans-
actions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engi-
neering, 26(5):1017–1025.
Kobayashi, T. (Cardiff, UK, September, 2019). Large mar-
gin in softmax cross-entropy loss. In British Machine
Vision Conference.
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learn-
ing. nature, 521(7553):436–444.
Liu, W., Wen, Y., Yu, Z., and Yang, M. (New York City,
USA, June, 2016). Large-margin softmax loss for con-
volutional neural networks. In International Confer-
ence on Machine Learning.
Nasr, G. E., Badr, E., and Joun, C. (2002). Cross entropy er-
ror function in neural networks: Forecasting gasoline
demand. In FLAIRS conference, pages 381–384.
Nielsen, M. A. (2015). Neural networks and deep learn-
ing, volume 2018. Determination press San Francisco,
CA.
Passalis, N., Tefas, A., Kanniainen, J., Gabbouj, M., and
Iosifidis, A. (2019). Deep adaptive input normaliza-
tion for time series forecasting. IEEE Transactions on
Neural Networks and Learning Systems.
Ramamonjy, A., Bavu, E., Garcia, A., and Hengy, S. (Le
Mans, France, 2016). D
´
etection, classification et
suivi de trajectoire de sources acoustiques par capta-
tion pression-vitesse sur capteurs mems num
´
eriques.
In Congr
`
es de la Soci
´
et
´
e Franc¸aise d’Acoustique-
CFA16/VISHNO.
Raschka, S. (2018). Model evaluation, model selection,
and algorithm selection in machine learning. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1811.12808.
Saranya, C. and Manikandan, G. (2013). A study on
normalization techniques for privacy preserving data
mining. International Journal of Engineering and
Technology, 5(3):2701–2704.
Sola, J. and Sevilla, J. (1997). Importance of input data
normalization for the application of neural networks
to complex industrial problems. IEEE Transactions
on nuclear science, 44(3):1464–1468.
Zhao, C. and Gao, X.-S. (2019). Qdnn: Dnn with
quantum neural network layers. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1912.12660.
Zhu, Q., He, Z., Zhang, T., and Cui, W. (2020). Improv-
ing classification performance of softmax loss func-
tion based on scalable batch-normalization. Applied
Sciences, 10(8):2950.
DATA 2021 - 10th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
214
