
Evaluating the Influence of Feature Matching on the Performance of
Visual Localization with Fisheye Images
Mar
´
ıa Flores
1 a
, David Valiente
2 b
, Sergio Cebollada
1 c
, Oscar Reinoso
1 d
and Luis Pay
´
a
1 e
1
Department of Systems Engineering and Automation, Miguel Hernandez University, Elche, Spain
2
Department of Communications Engineering, Miguel Hernandez University, Elche, Spain
Keywords:
Localization, Visual Odometry, Fisheye Camera, Adaptive Probability-oriented Feature Matching.
Abstract:
Solving the localization problem is a crucial task in order to achieve autonomous navigation for a mobile robot.
In this paper, the localization is solved using the Adaptive Probability-Oriented Feature Matching (APOFM)
method, which produces robust matching data that permit obtaining the relative pose of the robot from a pair
of images. The main characteristic of this method is that the environment is dynamically modelled by a 3D
grid that estimates the probability of feature existence. The spatial probabilities obtained by this model are
projected on the second image. These data are used to filter feature points in the second image by proximity
to relevant areas in terms of probability. This approach improves the outlier rejection. This work aims to
study the performance of this method using different types of local features to extract the visual information
from the images provided by a fisheye camera. The results obtained with the APOFM method are evaluated
and compared with the results obtained using a standard visual odometry process. The results determine
that combining the APOFM method with ORB as local features provides the most efficient solution both to
estimate relative orientation and translation, in contrast to SURF, KAZE and FAST feature detectors.
1 INTRODUCTION
Localization is one of the most crucial abilities that
a mobile robot must have for effective autonomous
navigation. Several techniques and sensors (Alatise
and Hancke, 2020) have been employed to obtain an
accurate position and orientation of the mobile robot.
Amongst the several types of sensors attached to the
mobile robot, researchers have shown a huge interest
in vision systems in recent years. This is due to the
fact that they can be employed to solve the localiza-
tion problem and perform other autonomous naviga-
tion tasks. Visual odometry is a localization technique
that relies only on the information provided by a cam-
era (Scaramuzza and Fraundorfer, 2011). In this pro-
cess, the position and orientation are incrementally
estimated from the changes caused by the motion in
the images (Aqel et al., 2016). This approach presents
some advantages, such as the fact that it is not affected
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1117-0868
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2245-0542
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4047-3841
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1065-8944
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3045-4316
by wheel slippage, and it can be employed in several
types of robots, not only in those that move on the
ground. For instance, Wirth et al. (2013) use a stereo
visual odometry process with images taken on board
of an Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV).
Using an omnidirectional camera is advantageous
in many robotic applications due to their larger field
of view. The main feature of these cameras is that
they can capture images with a field of view of 360
o
around the robot. A variety of systems can be used to
obtain omnidirectional images (Scaramuzza, 2014),
though the most acknowledged are the catadioptric
and fisheye systems. A catadioptric system is com-
posed of a conventional perspective camera with a
convex mirror mounted in front of it. This way, a
full 360-degree view (a complete sphere) is generated.
For instance, Rom
´
an et al. (2020) show the develop-
ment and evaluation of an incremental clustering ap-
proach to obtain compact hierarchical models of an
environment using a catadioptric vision system as in-
formation source. Another way to increase the field
of view is by combining a fisheye lens and a con-
ventional perspective camera. For example, Matsuki
et al. (2018) propose a method that extends the direct
sparse odometry to use the whole image even with
434
Flores, M., Valiente, D., Cebollada, S., Reinoso, O. and Payá, L.
Evaluating the Influence of Feature Matching on the Performance of Visual Localization with Fisheye Images.
DOI: 10.5220/0010555104340441
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2021), pages 434-441
ISBN: 978-989-758-522-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

strong distortion. To that end, the projection func-
tion is the omnidirectional model. In this work, the
approach proposed is evaluated using a sequence of
images taken by a fisheye camera. Comparing vision
systems with a wide field of view, the main difference
is that the field of view of a fisheye system is smaller
than the one provided by a catadioptric system. How-
ever, it is interesting to evaluate the performance of a
visual odometry algorithm using fisheye images since
this type of vision system presents some relevant fea-
tures compared to the catadioptric one, such as its re-
duced size and lightness. Besides, the catadioptric vi-
sion system is structurally more complex.
To solve the visual odometry, it is necessary to
extract and match relevant information from the im-
ages. The framework we use in the present work was
proposed in a previous research work (Valiente et al.,
2018) and is named Adaptive Probability-Oriented
Feature Matching (APOFM). The purpose of this ap-
proach is to solve the localization problem based on
the Standard Visual Odometry Method (SVOM) but
using probability information associated to the exis-
tence of feature points within the environment. This
information is provided by a scene model that estab-
lishes relations between 3D points with high probabil-
ity of existence and their projections on a pair of im-
ages. In this manner, these projections encode areas
of the images where the matches are more probable
to appear. The APOFM improves image processing
(detection and description of features and matching
search) in the visual odometry algorithm, obtaining
a robust matching search and outlier rejection. This
way, the localization solution obtained is more pre-
cise. In the previous work (Valiente et al., 2018) we
evaluated this method using the images captured by a
catadioptric system and using only SURF features to
extract the visual information.
Taking these facts into account, the present paper
considers fisheye images and different types of feature
points detectors and descriptors (SURF, ORB, FAST
and KAZE) and evaluates the influence of the type of
feature on the performance of the visual odometry us-
ing APOFM. The experimental section analyses both
the results of the matching process and the accuracy
of the visual odometry in the estimation of the posi-
tion and orientation of the robot, and these results are
compared with the SVOM. In order to conduct the ex-
periments, we use a publicly available dataset of fish-
eye images (Zhang et al., 2016).
The remainder of this paper is structured as fol-
lows. Section 2 presents the different types of local
feature detectors and descriptors used in this work.
In Section 3, the method to estimate the relative pose
using the probability information of the scene model
is described. The results achieved during the exper-
iments are shown in Section 4. Finally, Section 5
presents the conclusions of this work.
2 LOCAL FEATURE DETECTORS
AND DESCRIPTORS
In the related literature, two main frameworks can
be found to extract and describe relevant informa-
tion from the scenes: either global or local features.
On the one hand, in global appearance descriptors,
each image is described as a whole with a unique vec-
tor. This descriptor is expected to be invariant against
global changes. For instance, Amor
´
os et al. (2020)
present a comparison of global-appearance descrip-
tion techniques (including the use of colour informa-
tion) to solve the problem of mapping and localiza-
tion using only information provided by omnidirec-
tional images. On the other hand, the local features
are patterns or distinct structures (e.g. point, edge, or
small image patch) present in an image. They differ
from their immediate neighbourhood in terms of in-
tensity, colour, and/or texture (Tuytelaars and Miko-
lajczyk, 2008). Valiente Garc
´
ıa et al. (2012) compare
the results of a visual odometry method with omnidi-
rectional images by extracting the visual information
with these techniques.
Local features can be considered as the combina-
tion of a feature detector and a descriptor. Feature
detectors are used to find the essential features (i.e.
corners, edges of blobs) from the image, whereas de-
scriptors describe the features extracted and gener-
ate a descriptive vector. There are several types of
local features proposed in the literature. Joshi and
Patel (2020) present a survey of methods for detec-
tion and description. In the present paper, we have
employed the following four types of local features:
SURF (Bay et al., 2008) (based on blobs and real
descriptor vector), FAST (Rosten and Drummond,
2006) (corners and binary descriptor vector), ORB
(Rublee et al., 2011) (corners and binary descriptor
vector) and KAZE (Alcantarilla et al., 2012) (blobs
and real descriptor vector).
3 APOFM METHOD
This method consists in solving the localization prob-
lem based on SVOM but incorporating probability in-
formation provided by a scene model. The model is
a probability distribution that dynamically character-
izes the appearance of correspondences found in pre-
Evaluating the Influence of Feature Matching on the Performance of Visual Localization with Fisheye Images
435
Image
𝐼
!
Image
𝐼
!"#
Extract
features
Candidates
Matching
search
Essential
matrix
Extract
features
Relative
pose
Triangulation
Gaussian
Process
Scene
Model
2D projection
on 𝐼
!"#
Descriptors
features
Descriptors
features
Reprojection
on the image
𝑑(𝑥
#
!"#
, 𝑝
#
$
) > 𝑎
False positive counter
FP = FP + 1
𝑑 𝑥
%
!"#
, 𝑝
&
'
≥ 𝜒
⃗𝑥
%
!"#
𝜖 ℝ
(
⃗𝑝
&
'
𝜖 ℝ
(
𝑃
&
'
𝜖 ℝ
)
⃗𝑥
%
!
𝜖 ℝ
(
𝑃
%
𝜖 ℝ
)
𝑝
#
$
𝑃
#
⃗𝑥
#
!"#
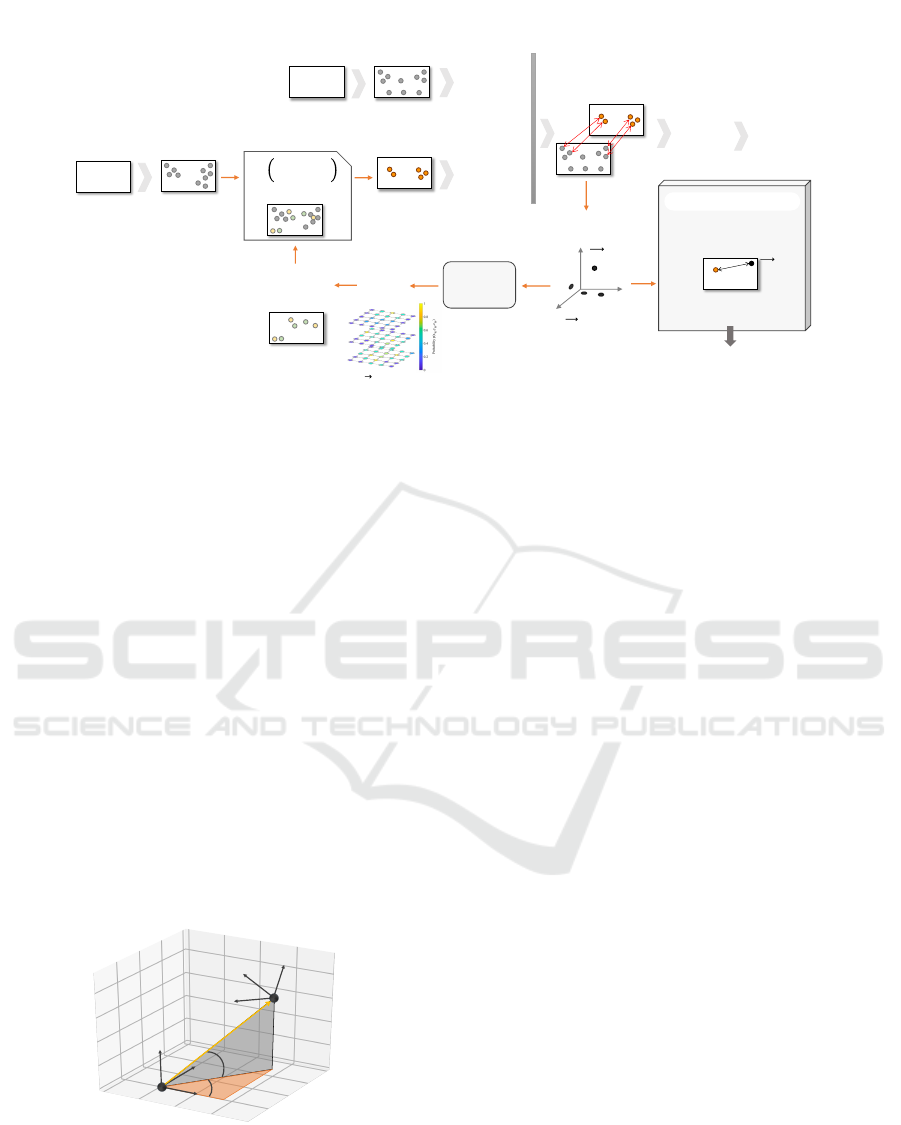
Figure 1: Block diagram of the APOFM method.
vious iterations. The technique employed for this pur-
pose is the Gaussian Process (GP) (Williams and Ras-
mussen, 2006). In Figure 1, all steps of this method
are shown.
In the first iteration (t = 1), the relative pose is
estimated by solving the SVOM since all the projec-
tions of 3D scene points have the same probability
of being a correspondence. Therefore, the first three
steps are to detect the feature points in each image (I
0
and I
1
), extract the descriptor vector of these points
and search correspondences according to a distance
measure between descriptors. The similarity measure
used for the binary feature descriptors is the Ham-
ming distance and the Squared Euclidean distance for
other description formats. This way, a set of 2D to 2D
correspondences has been obtained. from it, the next
step consists in estimating the relative motion through
the epipolar geometry. It corresponds to the two last
blocks in the diagram of Figure 1: essential matrix
and relative pose.
𝝓
𝜷
𝝆
𝐙
𝐭
𝐙
𝐭
"
𝟏
𝐘
𝐭
𝐗
𝐭
𝐗
𝐭
"
𝟏
𝐘
𝐭
"
𝟏
Figure 2: The relative translation expressed by two angles,
φ and β, and a scale factor ρ.
In this paper, the relative pose is expressed by five
angular parameters (θ, γ, α, φ, β) and a scale factor
(ρ). Three of the angular parameters are associated
with the orientation (θ, γ, α). The other two (φ, β),
along with the scale factor ρ are associated with the
translation expressed in spherical coordinates (Figure
2), where ρ is the relative distance between both cam-
era centers (except for a scale factor), φ is the polar
angle and β the elevation angle from the x-y plane. In
the experimental section, the values of these angular
parameters are estimated. At the end of this first itera-
tion, the information about feature correspondences is
obtained. The steps considered by the APOFM to use
this information are explained in the following sub-
sections.
3.1 3D Probability Model
To create the model, first, the 3D coordinates of each
pair of correspondences must be recovered, solving
the triangulation problem. In this sense, given a pair
of images, if the matching feature points are actually
the projection of the same 3D point, their rays must
intersect at this 3D point. However, this fact does not
always occur due to the presence of several types of
noise (e.g. error by non-precise calibration parame-
ters or noise during the feature detection). Therefore,
the triangulation problem is reduced to finding the
best solution, for instance, using the midpoint method
where the 3D point is assumed to be the midpoint of
the common perpendicular to both 3D lines.
However, the two 3D lines do not intersect in some
cases because the match of this pair of feature points
is a false positive, which means that they are not the
projection of the same 3D point though their descrip-
tor vectors are similar and therefore, they have been
wrongly associated during the matching search step.
To improve the SVOM regarding the false positives,
we have added a block, denominated false positive
ICINCO 2021 - 18th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
436

counter in the algorithm (see Figure 1), to evaluate
the effectiveness of the APOFM with respect to the
SVOM. In this block, given a 3D point
−→
P
1
whose
coordinates have been obtained with the pair of corre-
spondences (
−→
x
t
1
and
−→
x
t+1
1
), it is re-projected on the
second image
−→
p
0
1
using the camera model and if it is
near enough the feature point
−→
x
t+1
1
, it means that the
feature point is the projection of this 3D point and the
matched point is a true positive, otherwise it is a false
positive.
After solving the triangulation problem, the next
step to estimate the relative pose is to create the scene
model. To that end, the GP has been employed. The
GP block receives training input data that corresponds
to the set of 3D coordinates and training output data
that are a vector of ones indicating that the projec-
tion of these 3D points on the pair of images has been
considered as a matching point. Besides, there is a
set of test points that corresponds with the 3D points
that define the model. The output of the GP is the
mean and covariance of the predicted conditional dis-
tribution for the test points. The objective is to create
a probability model of the environment
−→
P
M j
, so this
prediction must take values between zero and one. To
that end, a logistic function (sigmoid) is employed.
Finally, the global map is updated using a Bayesian
Committee Machine (BCM).
3.2 Selecting Candidate Feature Points
Once the 3D scene model with probability is created
(t = 1) or updated (t > 1), the mobile robot moves
to a new position, and an image I
t+1
is taken. Then,
the feature points are detected. The next step con-
sists in projecting the 3D probability information on
this new image. To that end, both intrinsic and ex-
trinsic camera parameters must be known. The in-
trinsic ones have been previously obtained with the
calibration process. The extrinsic parameters are es-
timated by employing the vehicle model and apply-
ing the transformation from the mobile robot frame to
the camera frame (it is known since the camera is in-
stalled in the same position on board the mobile robot
at every moment). This odometry data is only used
for mapping from 2D to 3D points and from 3D to
2D.
At this stage of the algorithm, a two-set of
pixel points are obtained: one with image informa-
tion (feature points) and another with probability for
the search of correspondences (projection of the 3D
model scene). The selecting candidate features step
is given by a search for the nearest point in the sec-
ond set to each point in the first set. This search is
based on a metric measure, concretely on the City-
Block and the technique to find the nearest neighbor
is the Kd-tree algorithm.
A feature point will be considered as a candidate if
the calculated distance is lower than a specific thresh-
old (χ) whose value is given by the chi-square inverse
cumulative distribution function. If the feature point
is classified as a candidate to find a matching in the
image I
t
, the probability of the nearest projected point
is associated with this feature point. The candidate
points can then be filtered according to the probabil-
ity value associated, obtaining a set of candidate fea-
ture points whose probability to represent a matching
is higher than a minimum probability (ρ
min
).
The following steps correspond to the SVOM
(matching search, essential matrix and relative pose),
as explained for the first iteration. However, the de-
scriptor vectors are only extracted from the candi-
date points since this is the set of features used in the
matching search.
4 EXPERIMENTS
As stated in Section 3, the APOFM method estimates
the relative pose from local feature points. Consider-
ing it, the experiments performed in this paper have
two main objectives: (a) evaluating the behaviour of
the APOFM with various local feature types to de-
termine which of them provides a more precise rela-
tive pose estimation; and (b) performing a comparison
between the APOFM and SVOM in order to assess
the improvement achieve with the APOFM method.
Therefore, a total of eight tests have been performed
as a result of the combination of the two methods and
the four local features: (1) SURF-SVOM, (2) SURF-
APOFM, (3) ORB-SVOM, (4) ORB-APOFM, (5)
FAST-SVOM, (6) FAST-APOFM, (7) KAZE-SVOM
and (8) KAZE-APOFM. In the figures, the results ob-
tained with SVOM are shown in orange colour and
with the APOFM method in grey colour.
Figure 3: An example of fisheye image available in the
dataset (Zhang et al., 2016).
To evaluate the influence of the kind of features,
we have carried out a study regarding the following
Evaluating the Influence of Feature Matching on the Performance of Visual Localization with Fisheye Images
437
aspects: the number of features detected with each lo-
cal feature and how many of them have been found as
a match on the other image (Section 4.1); the preci-
sion obtained in the matches search (Section 4.2); the
error during the estimation of the relative pose (Sec-
tion 4.3); and the computation time (Section 4.4). In
each figure, the result shown is the average of the val-
ues obtained with each pair of images. All experi-
ments have been carried out with a PC with a CPU
Intel Core i7-10700 R at 2.90GHz and Matlab as soft-
ware.
With respect to the images, we have used an open-
source and publicly available dataset (Zhang et al.,
2016). This dataset provides a set of fisheye im-
ages model (see Figure 3), and an output file with the
camera positions where each image is taken (ground
truth). The camera followed a trajectory from which
the number of images taken is 200, with a resolution
of 640x480 pixels.
4.1 Number of Feature Points and
Matches Detected
As mentioned throughout this paper, both the SVOM
and the APOFM method solve the localization prob-
lem using local feature points detected on two images
and a set of correspondences between them. There-
fore, we will study it in this subsection.
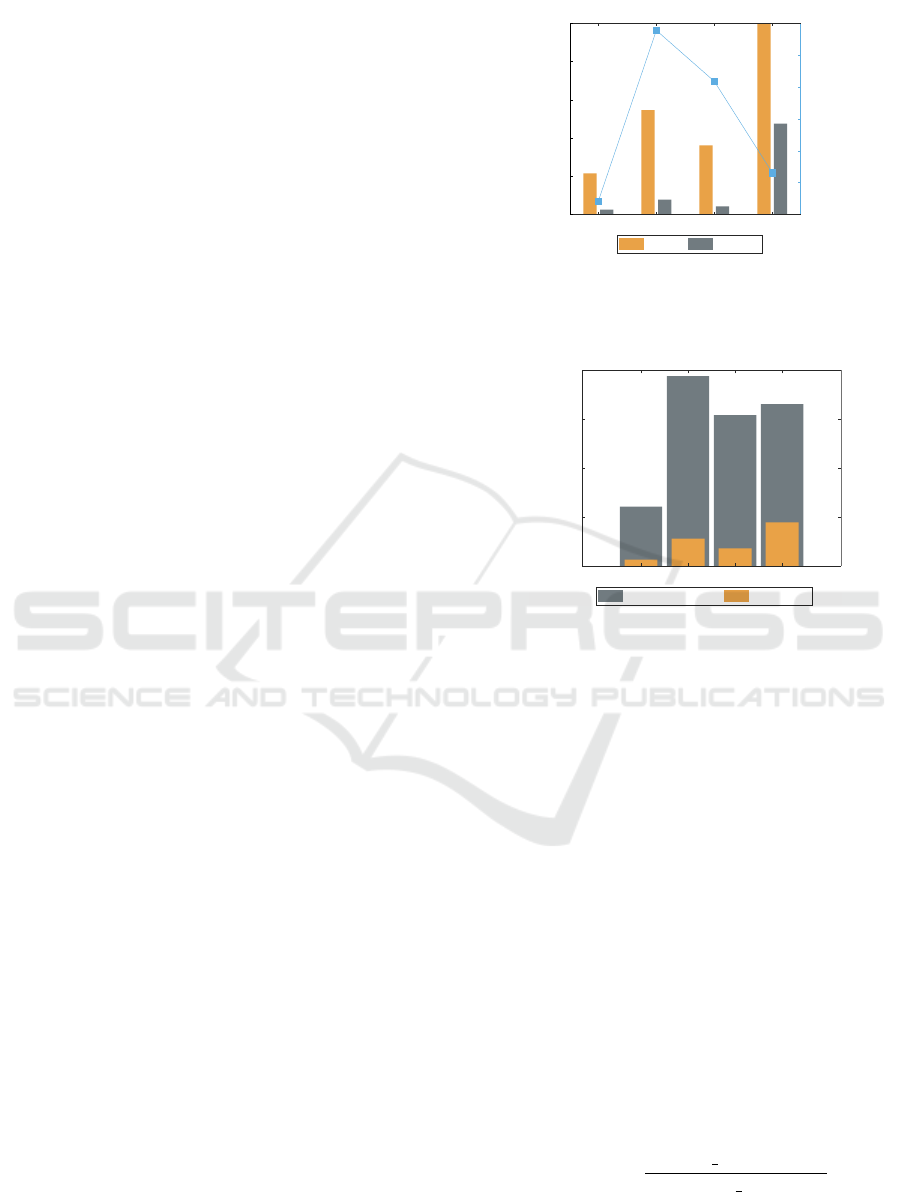
First, Figure 4 shows the performance of the eight
combinations points/odometry method. The right ver-
tical axis of Figure 4 and the blue tendency show the
number of local feature points detected. Concerning
this, there is no distinction according to the odom-
etry method employed since the number of feature
points is independent of it, which means that it is the
same in both cases. The parameters of the features
have been chosen sin order to detect a high number
of points. Second, the number of these points that
finally have found their corresponding point on an-
other image is represented on the left axis of Figure
4. In this case, the number of matches depends on the
odometry method employed so, the number obtained
with each one is represented by a different bar. After
analyzing Figure 4, we can conclude that the highest
number of local feature points is obtained using ORB
and FAST. On the contrary, SURF provides the lowest
number of matches with both methods. In contrast,
when KAZE is employed, more feature points result
in matching points, although the number of points de-
tected on the image is not as elevated as using ORB or
FAST. As for the odometry methods, we can observe
that the SVOM algorithm finds more matches than
APOFM. This fact was expected in advance since the
second method does not use all the feature points de-
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
Number of points
Matching
SURF ORB FAST KAZE
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
Number of matches
SVOM APOFM
Figure 4: The number of feature points detected is repre-
sented in the right axis, and the number of them that have
found a correspondence in the left axis.
Candidate points
SURF ORB FAST KAZE
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
num points
Features detected Candidates
Figure 5: APOFM method. The initial number of features
detected and number of them considered as matching can-
didates are shown to highlight how this method filters them
considering their probability of existence.
tected in this step, only those that have been consid-
ered as matching candidates due to their probability
of existence. Figure 5 is dedicated exclusively to the
APOFM method. It shows the number of features de-
tected, and how many of them have been considered
as matching candidates, this way, we can observe that
the matching search step using this method consid-
ers a lower number of feature points corresponding to
I
t+1
since the initial feature set has already been fil-
tered by probability of existence.
4.2 Precision in the Matching Search
In addition to the study of the number of feature cor-
respondences, it is necessary to analyse how many of
these matchings are true positives or false positives.
To that purpose, the precision of the matching pro-
cess is calculated as:
Precision =
matches number − FP
matches number
(1)
where FP is the number of false positives, that is, pairs
of correspondences whose feature points are wrongly
ICINCO 2021 - 18th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
438

associated as the projection of the same 3D point. The
block added to the algorithm (false positive counter,
in Figure 1) returns this value. The precision is repre-
sented on the right axis of Figure 6 and the blue ten-
dency, and it is normalized from 0 to 1. The left axis
of Figure 6 shows, by means of bars, the ratio between
the number of feature points detected and the num-
ber of matches. The closer to one the precision value
is, the more accurate it is. Figure 6 shows that the
matching step using SURF is less accurate than using
the other local features. The precision difference is
considerable, taking into account that the precision in
the other features is higher than 0.99 and near to one
while in the case of SURF, it is lower than 0.98.
Ratio and precision
SURF ORB FAST KAZE
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
Matches/points
0.95
0.96
0.97
0.98
0.99
1
precision
SVOM APOFM
Figure 6: The ratio (left axis) and the precision (right axis)
during the matching search step.
4.3 Error Estimating the Relative Pose
The objective is to estimate the relative pose with the
highest accuracy. Therefore, the error must be stud-
ied to determine how a localization method performs
depending on the sort of feature points utilized as in-
put. In this subsection, the figures show, using bars,
the error of each odometry method with respect to the
ground truth.
The errors estimating the relative translation are
represented in Figure 7 and Figure 8. The first one is
related to the parameter φ, whereas the second figure
is associated with the parameter β. Analyzing both
figures, we can observe that the error is higher with
SURF. This fact was expected in advance due to its
worse precision commented in Section 4.2 and the
lowest number of points detected and matches. As
for the parameter φ (Figure 7), the APOFM method
presents a lower error with respect to SVOM in all
cases, except when using KAZE. However, there
is not a considerable error difference between both
methods in this case, though, concerning the standard
deviation, APOFM presents better results. The best
localization solution has been obtained with the com-
bination of the APOFM method and ORB, being the
Translation error
SURF ORB FAST KAZE
-20
0
20
40
60
80
angular error (
°
)
SVOM APOFM std
Figure 7: Error estimating the translation parameter φ.
Translation error
SURF ORB FAST KAZE
-20
0
20
40
60
angular error (
°
)
SVOM APOFM std
Figure 8: Error estimating the translation parameter β.
error in φ around 4
◦
. In contrast, the APOFM pro-
vides a lower error estimating the parameter β, inde-
pendently on the local feature type.
The relative orientation is expressed by three an-
gles (θ, γ and α), so Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure
11 show the error estimating these parameters. As for
the method used, the APOFM estimates the orienta-
tion with more precision than SVOM. Similarly that
in the translation, the best localization solution, that
is, the one that provides lowest error, is obtained with
the ORB local feature.
Rotation error (Z-axis)
SURF ORB FAST KAZE
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
angular error (
°
)
SVOM APOFM std
Figure 9: Error estimating the rotation parameter θ.
Evaluating the Influence of Feature Matching on the Performance of Visual Localization with Fisheye Images
439

Rotation error (Y-axis)
SURF ORB FAST KAZE
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
angular error (
°
)
SVOM APOFM std
Figure 10: Error estimating the rotation parameter γ.
Rotation error (X-axis)
SURF ORB FAST KAZE
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
angular error (
°
)
SVOM APOFM std
Figure 11: Error estimating the rotation parameter α.
4.4 Computation Time
Finally, it is also necessary to analyse the computation
efforts required by each of the combinations studied
in the previous subsections. Figure 12 compares the
computation times.
The time used during the relative pose estimation
is lower for the APOFM when the local features are
SURF, ORB and FAST. This is due to the fact that, in
the case of APOFM, the number of feature points cor-
responding to I
t+1
that have to find a match is lower
than in the case of SVOM since the feature points
have been filtered (candidates). This way, the time
associated with this step and the features SURF, ORB
and FAST is also lower, except when using KAZE.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, the information from the environment
is acquired by a fisheye camera, and the localization
problem is solved using publicly available images.
We have studied the performance of our former
method (APFOM, (Valiente et al., 2018)) when differ-
ent sets of feature detectors and descriptors are con-
sidered as inputs. The APOFM characterizes the en-
Computation time
SURF ORB FAST KAZE
0
5
10
15
time (s)
SVOM APOFM
Figure 12: The computation time of each test is shown.
vironment by dynamically modelling 3D points with
certain probability of feature point existence. In this
manner, feature correspondences can be found in spe-
cific areas of the images. Such dynamic model is
obtained by an inference technique, the GP. In (Va-
liente et al., 2018), the authors evaluate this method
using images taken by a catadioptric vision system
and SURF features solely.
The present work has evaluated the behaviour of
the localization technique by means of an experimen-
tal setup consisting in: a total of eight tests accord-
ing to the combination of the method (the SVOM and
the APOFM) and the local feature type (SURF, ORB,
FAST and KAZE). For each one, we have studied sev-
eral aspects, such as the number of features detected
and matches; the precision regarding the correspon-
dences found and the pose estimation (by means of
the error made in each localization parameter), and
the time consumed to calculate the relative pose (con-
sidering all the steps of the algorithm).
From the analysis of the results, we can conclude
that the APOFM method has outperformed consider-
ably the SVOM with regards to the localization solu-
tion and the computation time when the local features
are SURF, ORB and FAST. The difference between
both methods when they use KAZE is slight, and the
error using the APOFM method is a little higher. The
combination of the APOFM method and ORB pro-
vides a more precise localization (the error is around
4
◦
for the translation parameter φ) besides a lower
computation time with respect to the SVOM.
In summary, the localization problem solved using
the APOFM method has been improved by employing
other feature point types, concretely ORB.
As future work, it will be interesting to evalu-
ate this method with other local feature points, such
as ASIFT (Yu and Morel, 2011), which is invariant
to affine transformations. Moreover, another future
work will consider extending these comparative re-
sults to other non-linear image models.
ICINCO 2021 - 18th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
440

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported in part by the Spanish
Government through the Project DPI 2016-78361-
R (AEI/FEDER, UE) ”Creaci
´
on de mapas mediante
m
´
etodos de apariencia visual para la navegaci
´
on de
robots”, and in part by the Generalitat Valenciana
through the Grant ACIF/2020/141 and the Project
AICO/2019/031 ”Creaci
´
on de modelos jer
´
arquicos y
localizaci
´
on robusta de robots m
´
oviles en entornos so-
ciales”.
REFERENCES
Alatise, M. B. and Hancke, G. P. (2020). A review on chal-
lenges of autonomous mobile robot and sensor fusion
methods. IEEE Access, 8:39830–39846.
Alcantarilla, P. F., Bartoli, A., and Davison, A. J. (2012).
KAZE features. In Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Per-
ona, P., Sato, Y., and Schmid, C., editors, Computer
Vision – ECCV 2012, pages 214–227, Berlin, Heidel-
berg. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Amor
´
os, F., Pay
´
a, L., Mayol-Cuevas, W., Jim
´
enez, L. M.,
and Reinoso, O. (2020). Holistic descriptors of om-
nidirectional color images and their performance in
estimation of position and orientation. IEEE Access,
8:81822–81848.
Aqel, M. O. A., Marhaban, M. H., Saripan, M. I., and Is-
mail, N. B. (2016). Review of visual odometry: types,
approaches, challenges, and applications. Springer-
Plus, 5(1):1897.
Bay, H., Ess, A., Tuytelaars, T., and Van Gool, L. (2008).
Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURF). Computer
Vision and Image Understanding, 110(3):346–359.
Similarity Matching in Computer Vision and Multi-
media.
Joshi, K. and Patel, M. I. (2020). Recent advances in lo-
cal feature detector and descriptor: a literature survey.
International Journal of Multimedia Information Re-
trieval, 9(4):231–247.
Matsuki, H., von Stumberg, L., Usenko, V., St
¨
uckler, J.,
and Cremers, D. (2018). Omnidirectional DSO: Di-
rect Sparse Odometry With Fisheye Cameras. IEEE
Robotics and Automation Letters, 3(4):3693–3700.
Rom
´
an, V., Pay
´
a, L., Cebollada, S., and Reinoso,
´
O. (2020).
Creating incremental models of indoor environments
through omnidirectional imaging. Applied Sciences,
10(18).
Rosten, E. and Drummond, T. (2006). Machine learning
for high-speed corner detection. In Leonardis, A.,
Bischof, H., and Pinz, A., editors, Computer Vision
– ECCV 2006, pages 430–443, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Rublee, E., Rabaud, V., Konolige, K., and Bradski, G.
(2011). ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or
SURF. In 2011 International Conference on Com-
puter Vision, pages 2564–2571.
Scaramuzza, D. (2014). Omnidirectional Camera, pages
552–560. Springer US, Boston, MA.
Scaramuzza, D. and Fraundorfer, F. (2011). Visual odom-
etry [tutorial]. IEEE Robotics Automation Magazine,
18(4):80–92.
Tuytelaars, T. and Mikolajczyk, K. (2008). Local in-
variant feature detectors: A survey. Foundations
and Trends
R
in Computer Graphics and Vision,
3(3):177–280.
Valiente, D., Pay
´
a, L., Jim
´
enez, L. M., Sebasti
´
an, J. M.,
and Reinoso,
´
O. (2018). Visual information fusion
through bayesian inference for adaptive probability-
oriented feature matching. Sensors, 18(7).
Valiente Garc
´
ıa, D., Fern
´
andez Rojo, L., Gil Aparicio, A.,
Pay
´
a Castell
´
o, L., and Reinoso Garc
´
ıa, O. (2012). Vi-
sual odometry through appearance-and feature-based
method with omnidirectional images. Journal of
Robotics, 2012.
Williams, C. K. and Rasmussen, C. E. (2006). Gaussian
processes for machine learning, volume 2. MIT press
Cambridge, MA.
Wirth, S., Carrasco, P. L. N., and Codina, G. O. (2013).
Visual odometry for autonomous underwater vehi-
cles. In 2013 MTS/IEEE OCEANS-Bergen, pages 1–6.
IEEE.
Yu, G. and Morel, J.-M. (2011). ASIFT: An Algorithm for
Fully Affine Invariant Comparison. Image Processing
On Line, 1:11–38.
Zhang, Z., Rebecq, H., Forster, C., and Scaramuzza, D.
(2016). Benefit of large field-of-view cameras for vi-
sual odometry. In 2016 IEEE International Confer-
ence on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pages 801–
808.
Evaluating the Influence of Feature Matching on the Performance of Visual Localization with Fisheye Images
441
