
Boolean Exponent Splitting
Michael Tunstall
1 a
, Louiza Papachristodoulou
2
and Kostas Papagiannopoulos
3 b
1
Rambus, 4453 North First Street, Suite 100, San Jose, California, U.S.A.
2
Fontys University of Applied Sciences, Rachelsmolen 1, Eindhoven, The Netherlands
3
University of Amsterdam, SNE-CCI, Science Park 904, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Keywords:
Exponent Splitting, Side-channel Attacks, Countermeasures.
Abstract:
A typical countermeasure against side-channel attacks consists of masking intermediate values with a random
number. In symmetric cryptographic algorithms, Boolean shares of the secret are typically used, whereas in
asymmetric algorithms the secret exponent is typically masked using algebraic properties. This paper presents
a new exponent splitting technique with minimal impact on performance based on Boolean shares, typically
requiring only an extra register and a few register copies per bit. We perform a security evaluation of our
algorithms using a mutual information framework and provide proofs that they are secure against first-order
side-channel attacks. The side-channel resistance of the proposed algorithms are also practically verified with
test vector leakage assessment performed on Xilinx’s Zynq zc702 evaluation board.
1 INTRODUCTION
Side-channel analysis as a method of extracting cryp-
tographic keys was first presented by Kocher (Kocher,
1996), who noted that timing differences in the execu-
tion time of a modular exponentiation could be used
to break instances of RSA (Rivest et al., 1978). Sub-
sequently, Kocher et al. (Kocher et al., 1999) observed
that the instantaneous power consumption could re-
veal information on intermediate states of any cryp-
tographic algorithm, since the instantaneous power
consumption has, in many cases, been shown to be
proportional to the Hamming weight of the data be-
ing manipulated (Brier et al., 2004), and it was later
shown that the electromagnetic emanations around a
device can be exploited in the same way (Gandolfi
et al., 2001; Quisquater and Samyde, 2001).
In public key cryptography, one typically uses
countermeasures based on redundant representations
to prevent side-channel leakage (Coron, 1999; Win
et al., 1998) (referred to as blinding). To protect an ex-
ponent used in a group exponentiation one would typ-
ically add a random multiple of the order of the group
to the exponent, providing a random bitwise repre-
sentation of the exponent. These countermeasures
can provide a strong resistance to Differential Power
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7107-8644
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5008-1756
Analysis (DPA), but are not convenient in some in-
stances. As noted by Smart et al. (Smart et al., 2008),
the random value used to blind an exponent needs to
have a bit length larger than the longest run of zeros
or ones in the bitwise representation of the the order
of the group. If we consider ECDSA (National Insti-
tute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 2009), for
example, the bitwise representations of the orders of
the groups used contain long runs of ones making this
countermeasure costly.
In this paper, we present a new countermeasure for
exponent splitting. We describe a method of splitting
an exponent into two Boolean shares, analogous to
the countermeasures that one would use for an imple-
mentation of a block cipher and similar to the coun-
termeasures used to prevent address-bit side-channel
attacks (Messerges et al., 1999; Messerges and Dab-
bish, 1999; Itoh et al., 2002). Having embedded de-
vices as our targeted implementation, and an adver-
sary able to get useful information from the length of
the exponent or the intermediate values, we provide a
number of secure algorithms against a broad range of
side-channel attacks.
At the same time, the modifications that are re-
quired to a group exponentiation algorithm have neg-
ligible effect on the time required to compute the ac-
tual group exponentiation, which is a significant ad-
vantage over previous examples of exponent split-
ting (Clavier and Joye, 2001; Ciet and Joye, 2003). In
Tunstall, M., Papachristodoulou, L. and Papagiannopoulos, K.
Boolean Exponent Splitting.
DOI: 10.5220/0010570903210332
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT 2021), pages 321-332
ISBN: 978-989-758-524-1
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
321

addition, our method can be efficiently combined with
blinding techniques applied to the input to a group ex-
ponentiation algorithm, in order to prevent leakage of
the intermediate values.
We present an evaluation of the method of
Boolean exponent splitting using the information-
theoretic framework of Standaert et al. (Standaert
et al., 2009) and a Test Vector Leakage Assessment
(TVLA) by Goodwill et al. (Goodwill et al., 2011).
We investigate the usual leakage models based on data
or location leakage and show that an adversary would
need either a second-order data attack or a third-order
location attack to successfully break the security of
our algorithms. In addition, we present for the first
time a hybrid model, where data leakage is combined
with location leakage, offering new exploitation op-
portunities. The rich interactions between data and lo-
cation leakage corroborates the need for holistic coun-
termeasures that encompass a wide spectrum of side-
channel attacks.
2 EXPONENT SPLITTING
METHODS
The critical operation in public key cryptographic al-
gorithms is exponentiation in a certain group G of or-
der µ, where the input message x ∈ G is raised by a
secret exponent κ and the result y = x
κ
is the pub-
lic output of the algorithm. When implementing a
group exponentiation algorithm the exponent is typ-
ically blinded by adding some random multiple of
the order of the group to the exponent. Trivially,
(rµ) + κ ≡ κ (mod µ) for r,κ ∈ Z where r is random.
Hence, computing x
κ+rµ
is equivalent to computing
x
κ
. While this randomizes the bitwise representation
of an exponent, the entire exponent is still equivalent
to the exponent in a given group. Examples of attacks
that have been proposed include analyzing a single
trace (from SPA (Kocher et al., 1999) to collisions
in manipulated values (Witteman et al., 2011; Kim
et al., 2010; Hanley et al., 2015)) or attempting to find
collisions in the random values used to then derive a
(blinded) exponent (Schindler and Itoh, 2011).
One method that can hinder these attacks, is to
split an exponent into two values whose bitwise rep-
resentations are random. Then one would compute
a group exponentiation where the combined effect of
the two values is equivalent to that of the desired ex-
ponent. Randomly splitting the value that manipu-
lates secret data was proposed initially by Chari et.
al in (Chari et al., 1999) as a generic technique to
provide provable resistant implementation to side-
channel attacks. By randomly splitting every bit of
the original computation into m shares, where each
share is equiprobably distributed and every proper
subset of m − 1 shares is statistically independent of
the encoded bit, the cryptographic computation can
then be performed securely by computing only the
shares, without ever reconstructing the original bit.
The leakage from every computation does not reveal
any useful information to the adversary, who needs
to perform m attacks to reconstruct the secret. There
are several methods of exponent splitting proposed by
Clavier and Joye (Clavier and Joye, 2001):
• Additive Splitting. For a random integer r with
bit-length smaller or equal to the exponent κ, we
can define κ = r +(κ − r). The output of the mod-
ular exponentiation y = x
κ
in G can be computed
by y = x
r
· x
κ−r
in G.
• Multiplicative Splitting. For some group G we
can define k
0
= k r
−1
mod |G| for some integer r.
Then the exponentiation y = x
k
in G can be com-
puted by using y = (x
r
)
k
0
mod |G|.
The same techniques can be applied to scalar multi-
plication algorithms for elliptic curves (ECs), in or-
der to hide the secret scalar. The problem with these
methods of exponent splitting is that one is required
to know the order of the group G, which may not be
available in some instances. They will also typically
double the time required to compute a group expo-
nentiation, because r is required to have a bit-length
similar to the exponent. A practical attack by Feix
et al. (Feix et al., 2014) demonstrates that a blinded
scalar can be determined if r is too small.
A further method described by Ciet and Joye (Ciet
and Joye, 2003) is:
• Euclidean Splitting. By writing the exponent as
k = bk/rcr+k mod r and letting s = x
r
for some r,
then y = x
k
can be computed by y = s
k
0
×x
k mod r
=
(x
r
)
k
0
× x
k mod r
, where k
0
= bk/rc.
The impact on the time required to compute an ex-
ponentiation is lower than the other splitting methods
listed above. In fact, in (Ciet and Joye, 2003) the au-
thors evaluated this variant applied to Shamir’s dou-
ble ladder to have the same cost as the ‘double-and-
add-always’ algorithm (equivalent to the ‘square-and-
multiply-always’ for exponentiation). Precomputa-
tion of powers of s can reduce the exponentiation cost
compared to additive or multiplicative splitting. How-
ever, this method has the same constraints as adding
a multiple of the group order. That is, r needs to have
a bit length larger than the longest run of ones and
zeros in k and may have a significant impact on per-
formance (Smart et al., 2008). A secure division al-
gorithm is also required, see, for example, Joye and
Villegas (Joye and Villegas, 2002).
SECRYPT 2021 - 18th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
322

3 BOOLEAN EXPONENT
SPLITTING METHODS
In this section, we propose methods of exponent split-
ting based on XOR operation, and how an XOR-split
exponent can be applied to the Montgomery powering
ladder.
3.1 Montgomery Powering Ladder
The Montgomery Powering Ladder (MPL) was origi-
nally proposed as a means of speeding up scalar mul-
tiplication over ECs and later shown to be applica-
ble to multiplicative written Abelian groups (Mont-
gomery, 1987; Joye and Yen, 2002). We recall the
description of the MPL given by Joye and Yen (Joye
and Yen, 2002): We consider the problem of comput-
ing y = x
κ
in G for inputs x and κ. Let
∑
n−1
i=0
k
i
2
i
be
the binary expansion of κ with bit length n (for ease of
expression we shall also denote this as (k
n−1
,... , k
0
)
2
where convenient). Then, defining L
j
=
∑
n−1
i= j
k
i
2
i− j
and H
j
= L
j
+ 1, we have L
j
= 2 L
j+1
+ k
j
= L
j+1
+
H
j+1
+ k
j
− 1 = 2H
j+1
+ k
j
− 2 and so we obtain
(L
j
,H
j
) =
(2L
j+1
,L
j+1
+ H
j+1
) if k
j
= 0,
(L
j+1
+ H
j+1
,2H
j+1
) if k
j
= 1.
(1)
If we consider one register containing x
L
j
and another
containing x
H
j
then (1) implies that
(x
L
j
,x
H
j
) =
x
L
j+1
2
,x
L
j+1
· x
H
j+1
if k
j
= 0,
x
L
j+1
· x
H
j+1
,
x
H
j+1
2
if k
j
= 1.
(2)
Given that L
0
= k one can build an exponentiation
algorithm that requires two group operations per bit
of the exponent. Joye and Yen give several different
versions, one of which is shown in Algorithm 1. All
these methods are highly regular, meaning that a de-
terministic sequence of operations is executed for an
exponent of a given bit length.
Algorithm 1: Montgomery Ladder.
Input: x ∈ G, an n-bit integer κ =
∑
n−1
i=0
k
i
2
i
Output: x
κ
1 R
0
← 1
G
; R
1
← x ;
2 for i = n − 1 down to 0 do
3 R
¬k
i
← R
k
i
· R
¬k
i
;
4 R
k
i
← (R
k
i
)
2
;
5 end
6 return R
0
In applying an XOR-split exponent to MPL we use
one share to dictate the address accessed and the other
to act as the exponent. That is, we consider (1),
where the previous round may provide either (L
j
,H
j
)
or (H
j
,L
j
) and the computation changed accordingly.
Let S
0, j
= L
j
and S
1, j
= H
j
and
∑
n−1
i=0
a
i
2
i
be the
binary expansion of A with bit length n (i.e. the same
bit length as the exponent). Then we can use the val-
ues of a
i
to dictate whether a pair of registers holds
(L
j
,H
j
) or (H
j
,L
j
). Specifically, (1) can be rewritten
as:
(S
a
j
, j
,S
¬a
j
, j
) =
(2S
a
j
, j+1
,S
a
j
, j+1
+ S
¬a
j
, j+1
) if k
j
= 0,
(S
a
j
, j+1
+ S
¬a
j
, j+1
,2S
¬a
j
, j+1
) if k
j
= 1.
(3)
In (3), the values of L
j
and H
j
are assigned to S in
an order dictated by the binary expansion of A. Gen-
erating A as a random sequence of bits could provide
some side-channel resistance, but does not protect the
exponent.
We further consider
∑
n−1
i=0
a
i
2
i
and
∑
n−1
i=0
b
i
2
i
be
the binary expansion of A and B, respectively, where
κ = A ⊕ B of bit length n. We note that, as above,
∑
n−1
i=0
k
i
2
i
is the binary expansion of κ and k
i
= a
i
⊕b
i
for 0 ≤ i < n. Then (3) can be rewritten as:
(S
a
j
, j
,S
¬a
j
, j
) =
(2S
b
j
, j+1
,S
b
j
, j+1
+ S
¬b
j
, j+1
) if k
j
= 0,
(S
b
j
, j+1
+ S
¬b
j
, j+1
,2S
¬b
j
, j+1
) if k
j
= 1.
(4)
Rather than using the same value to control which or-
der L
j
and H
j
are assigned and read, we use the bits
of A to determine the order L
j
and H
j
are assigned,
and the bits of B to determine the order they are read.
The combined effect is that the order L
j
and H
j
are
assigned and read is dictated by the bits of κ.
(x
S
a
j
, j
,x
S
¬a
j
, j
) =
x
S
b
j
, j+1
2
,x
S
b
j
, j+1
· x
S
¬b
j
, j+1
!
if k
j
= 0,
x
S
b
j
, j+1
· x
S
¬b
j
, j+1
,
x
S
¬b
j
, j+1
2
!
if k
j
= 1.
(5)
From which we can define Algorithm 2, which oper-
ates in much the same way as the MPL, as it produces
a regular sequence of multiplications and squaring
operations. However, one more register is required
to allow the assignment in line 5 to affect R
0
or R
1
.
This algorithm is the basis that we use to present the
essence of Boolean-split exponent. Algorithm 2 is
largely equivalent to an algorithm proposed by Izumi
et al. (Izumi et al., 2010) where we set the multi-
plication in line 4 to operate in a random order as
it provides a better resistance to collision attacks, as
demonstrated by Kim et al. (Kim et al., 2010). We
discuss this further in Section 3.2.
The intermediate states of the registers are not ran-
domized in Algorithm 2 and would require additional
countermeasures to provide a secure implementation.
Boolean Exponent Splitting
323

Algorithm 2: Montgomery Ladder with XOR-Split
Exponent I.
Input: x ∈ G, n-bit integers A =
∑
n−1
i=0
a
i
2
i
and B =
∑
n−1
i=0
b
i
2
i
Output: x
κ
where κ = A ⊕ B
1 R
0
← 1
G
; R
1
← 1
G
; R
2
← 1
G
;
2 b
0
R
←− {0, 1} ; R
¬b
0
← x ;
3 for i = n − 1 down to 0 do
4 R
2
← R
a
i
· R
¬a
i
;
5 R
a
i
←
R
(b
i
⊕b
0
)⊕a
i
2
;
6 R
¬a
i
← R
2
;
7 b
0
← b
i
;
8 end
9 return R
b
0
For example, inexpensive solutions such as random-
izing projective points (Win et al., 1998) or Ebeid and
Lambert’s blinding method for RSA (Ebeid and Lam-
bert, 2010) can be used (see Section 5). If we as-
sume that the values held in registers {R
0
,R
1
,R
2
} do
not leak (i.e., we only consider whether the exponent
leaks) we can state the following:
Lemma 1. Assuming that the values held in registers
{R
0
,R
1
,R
2
} do not leak, an implementation of Algo-
rithm 2 is resistant to first-order side-channel analy-
sis.
Proof. It suffices to consider each intermediate state
and verify that at least one random mask is ap-
plied. Verifying this for an entire group exponenti-
ation would be tedious, but can be simplified if we
consider two rounds of Algorithm 2. That is, if we
consider round m, where 0 ≤ m ≤ n − 2, then the fol-
lowing operations are performed:
1. R
2
← R
a
m
· R
¬a
m
2. α ← b
m
⊕ b
0
3. β ← α ⊕ a
m
4. R
a
m
← R
β
2
5. R
¬a
m
← R
2
6. R
2
← R
a
m+1
· R
¬a
m+1
7. α ← b
m+1
⊕ b
m
8. β ← α ⊕ a
m+1
9. R
a
m+1
← R
β
2
10. R
¬a
m+1
← R
2
Let the proposition P (n) be that round n > 0 is re-
sistant to first-order side-channel analysis for the n-th
treated bit of the exponent. If we consider the first
round, we wish to show P(1) is true and, in the above
code fragment, b
0
is set to a random value from {0,1}.
Then, it is easy to see that:
• the results of the operations in lines 1, 4, 5, 6,
9 and 10 are dependent on the random values
{R
0
,R
1
,R
2
}.
• the results of the operations in lines 2, 3, 7 and 8
are uniformly distributed on {0,1}.
If we assume that P (m) is true for all m ∈ {1,... , n},
then we consider P (n + 1) where b
0
is set to b
n
. As
b
n
is one share of a previously treated exponent bit, it
is indistinguishable from a random value from {0,1}.
The above statements regarding the results of the op-
erations apply. Hence, by induction we have shown
P (n) is true for all n > 0. To complete the proof, we
simply note that only half of the code fragment above
will need to be considered in the last round.
Remark. In (Itoh et al., 2003), the authors present the
randomized addressing method (RA), in order to pro-
vide protection against address-based DPA and elim-
inate the correlation between an exponent bit and the
register where the result of an operation is stored. In
this work, we do not limit our countermeasure to work
only against address-based DPA. Our goal is to per-
form operations on different exponent shares, in a way
that an adversary would need a combination of leak-
ages (such as higher-order DPA combined with tem-
plate attacks) in order to recover the exponent.
3.2 Using Inverses
In this section we propose an algorithm more suited
to groups where inversions can be readily computed.
Le Duc et al. (Le et al., 2015) propose a straight-
forward variant of the Montgomery powering ladder
that requires the computation of inverses. They note
that (1) can be rewritten as:
(L
j
,H
j
) =
(H
j
− 1, L
j+1
+ H
j+1
) if k
j
= 0,
(L
j+1
+ H
j+1
,L
j
+ 1) if k
j
= 1.
(6)
From which we can define Algorithm 3. If we let
T
0, j
= L
j
and T
1, j
= H
j
, or T
0, j
= H
j
and T
1, j
= L
j
and
store the ordering in another variable we can rewrite
(6) as:
(T
0, j
,T
1, j
) =
(
(L
j
,H
j
) if k
j
= 0
(H
j
,L
j
) if k
j
= 1
=
(
(L
j+1
+ H
j+1
,L
j
− 1) if k
j
= 0,
(L
j+1
+ H
j+1
,L
j
+ 1) if k
j
= 1.
(7)
From which we can define Algorithm 4.
Following the previous notation, we notice that T
0, j
should contain the sum of the registers in the previous
round
1
. Therefore, (7) can be rewritten as follows:
(T
0, j
,T
1, j
) =
(T
b
0
, j+1
+ T
¬b
0
, j+1
,T
0, j
− 1) if k
j
= b
0
= 0,
(T
b
0
, j+1
+ T
¬b
0
, j+1
,T
0, j
+ 1) if k
j
= b
0
= 1.
(8)
1
The algorithms are left-to-right, so j + 1 indicates the
round preceding j.
SECRYPT 2021 - 18th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
324

Algorithm 3: Variant with Inverses I.
Input: x ∈ G, an n-bit integer κ =
∑
n−1
i=0
k
i
2
i
Output: x
κ
1 R
0
← 1
G
; R
1
← x ;
2 U
0
← x
−1
; U
1
← x ;
3 for i = n − 1 down to 0 do
4 R
¬k
i
← R
k
i
· R
¬k
i
;
5 R
k
i
← R
¬k
i
·U
k
i
;
6 end
7 return R
0
Algorithm 4: Variant with Inverses II.
Input: x ∈ G, an n-bit integer κ =
∑
n−1
i=0
k
i
2
i
Output: x
κ
1 R
0
← 1
G
; R
1
← x ;
2 U
0
← x
−1
; U
1
← x ;
3 for i = n − 1 down to 0 do
4 R
0
← R
0
· R
1
;
5 R
1
← R
0
·U
k
i
;
6 end
7 return R
¬k
0
We note that to treat k
j+1
, b
0
= k
j
. However, if we let
k
j
= a
j
⊕b
j
, for a
j
,b
j
∈ {0,1} and h = a
j
⊕b
j
⊕b
j−1
,
we can modify (8) as follows:
(T
0, j
,T
1, j
) =
(
(T
¬h, j+1
+ T
h, j+1
,T
0, j
− 1) if a
j
= b
j
,
(T
¬h, j+1
+ T
h, j+1
,T
0, j
+ 1) if a
j
= ¬b
j
.
(9)
By using the above equations as exponents of x, we
can define Algorithm 5.
Algorithm 5: Montgomery Ladder with XOR-Split
Exponent II.
Input: x ∈ G, n-bit integers A =
∑
n−1
i=0
a
i
2
i
and B =
∑
n−1
i=0
b
i
2
i
, r ∈
R
Z
Output: x
κ
where κ = A ⊕ B
1 R
0
← 1
G
; R
1
← 1
G
; U
0
← x ; U
1
← x
−1
;
2 b
0
R
←− {0, 1} ; R
¬b
0
← x ;
3 for i = n − 1 down to 0 do
4 R
0
← R
b
i
⊕b
0
· R
(b
i
⊕b
0
)⊕a
i
;
5 R
1
← R
0
·U
b
i
;
6 b
0
← b
i
;
7 end
8 return R
b
0
Algorithm 5 follows the same sequence of instruc-
tions with the MPL. Its correctness can be verified by
the fact that at every round the difference R
0
/R
1
= x
or R
1
/R
0
= x, as for the usual ladder step. The ad-
vantage of Algorithm 5 compared to Algorithm 2,
and consequently previously proposed algorithms by
Izumi et al. (Izumi et al., 2010), is the elimination of
the auxiliary register R
2
. Instead, the auxiliary regis-
ters U
0
,U
1
manipulate the known fixed value x or x
−1
for computational purposes, and they do not require
additional computational power or updates when the
algorithm is executed.
As previously, if we assume that the values held
in registers {R
0
,R
1
} do not leak we can state the fol-
lowing:
Lemma 2. Assuming that the values held in regis-
ters {R
0
,R
1
} do not leak, an implementation of Algo-
rithm 5 is resistant to first-order side-channel analy-
sis.
Proof. It suffices to consider each intermediate state
and verify that at least one random mask is ap-
plied. Verifying this for an entire group exponenti-
ation would be tedious, but can be simplified if we
consider two rounds of Algorithm 5. That is, if we
consider round m, where 0 ≤ m ≤ n − 2, then the fol-
lowing operations are performed:
1. α ← b
m
⊕ b
0
2. β ← α ⊕ a
m
3. R
0
← R
α
· R
β
4. R
1
← R
0
·U
b
m
5. α ← b
m+1
⊕ b
m
6. β ← α ⊕ a
m+1
7. R
0
← R
α
· R
β
8. R
1
← R
0
·U
b
m+1
Let the proposition P (n) be that round n > 0 is re-
sistant to first-order side-channel analysis for the n-
th treated bit of the exponent. If consider the first
round, we wish to show P(1) is true and, in the above
code fragment, b
0
is set to a random value from {0,1}.
Then, it is easy to see that:
• the results of the operations in lines 3, 4, 7 and 8
are dependent on the random values {R
0
,R
1
}.
• the results of the operations in lines 1, 2, 5 and 6
are uniformly distributed on {0,1}.
If we assume that all P (m) is true for m ∈ {1,... , n},
then we consider P (n + 1) where b
0
is set to b
n
. As
b
n
is one share of a previously treated exponent bit, it
is indistinguishable from a random value from {0,1}.
The above statements regarding the results of the op-
erations apply. Hence, by induction we have shown
P (n) is true for all n > 0. To complete the proof, we
simply note that only half of the code fragment above
will need to be considered in the last round.
Boolean Exponent Splitting
325

3.3 Boolean Scalar Splitting
In the above, we define group exponentiations appli-
cable to any multiplicatively written group G. How-
ever, specific groups may have particular character-
istics that means the algorithms above are not suit-
able as described. In this section, we discuss the al-
gorithms in the context of a group formed from the
points on an elliptic curve (EC). We define the EC E
over a finite field F
q
, for a large prime q. E consists of
points (x,y), with x,y in F
q
, that satisfy, for example,
the short Weierstraß equation
E : y
2
= x
3
+ a x + b
with a, b ∈ F
q
, and the point at infinity denoted O
O
O. The
set E(F
q
) is defined as E (F
q
) = {(x, y) ∈ E | x,y ∈
F
q
}∪ {O
O
O}, where E(F
q
) forms an Abelian group un-
der the chord-and-tangent rule and O
O
O is the identity
element. Alternative equations with different repre-
sentations of a neutral element are also used in cryp-
tographic algorithms, such as Edwards curves (Ed-
wards, 2007; Bernstein and Lange, 2009) and Mont-
gomery curves (Montgomery, 1987). The scalar mul-
tiplication of a given point is a group exponentiation
in E that uses elliptic curve arithmetic, i.e. addition
between points or scalar multiplication [κ]P
P
P for some
integer κ < |E|, and is an important part of many
cryptographic algorithms.
The algorithms presented above cannot be se-
curely implemented as described because of the neu-
tral element. In the short Weierstraß example, the
neutral element 1
G
is represented in E as the point at
infinity O
O
O and cannot be manipulated in a regular way.
That is, one would typically be obliged to test for a
numerical representation of O
O
O and conduct a different
operation if it is detected. In practice, one would im-
plement the algorithm such that the most significant
bit (assumed to be set to one) is already treated by the
pre-processing. For example, Algorithm 2 can be im-
plemented as shown in Algorithm 6, and Algorithm 5
as shown in Algorithm 7.
As previously, if we assume that the values held
in registers {R
0
,R
1
,R
2
} do not leak we can state the
following:
Corollary 1. Lemma 1 implies that an implementa-
tion of Algorithm 6 is resistant to first-order side-
channel analysis.
Corollary 2. Lemma 2 implies that an implementa-
tion of Algorithm 7 is resistant to first-order side-
channel analysis.
The exponent splitting methods detailed in this paper
do not modify the intermediate states generated and
one would expect that randomizing projective points
Algorithm 6: Montgomery Ladder with XOR-Split
Scalar on an EC.
Input: E, F
q
, P
P
P ∈ E , n-bit integers
A =
∑
n−1
i=0
a
i
2
i
and B =
∑
n−1
i=0
b
i
2
i
Output: Q
Q
Q = [κ]P
P
P where κ = A ⊕ B
1 R
R
R
0
← P
P
P ; R
R
R
1
← P
P
P ; R
R
R
2
← P
P
P ;
2 b
0
R
←− {0, 1} ;
3 R
R
R
¬b
0
← 2P
P
P ;
4 for i = n − 2 down to 0 do
5 R
R
R
2
← R
R
R
a
i
+R
R
R
¬a
i
;
6 R
R
R
a
i
← 2R
R
R
(b
i
⊕b
0
)⊕a
i
;
7 R
R
R
¬a
i
← R
R
R
2
;
8 b
0
← b
i
;
9 end
10 return R
R
R
b
0
Algorithm 7: Montgomery Ladder with XOR-Split
Scalar II on an EC.
Input: E, F
q
, P
P
P ∈ E , n-bit integers
A =
∑
n−1
i=0
a
i
2
i
and B =
∑
n−1
i=0
b
i
2
i
Output: Q
Q
Q = [κ]P
P
P where κ = A ⊕ B
1 R
R
R
0
← P
P
P ; R
R
R
1
← P
P
P ;
2 U
U
U
0
← P
P
P ; U
U
U
1
← −P
P
P ;
3 b
0
R
←− {0, 1} ;
4 R
R
R
¬b
0
← 2P
P
P ;
5 for i = n − 2 down to 0 do
6 R
R
R
0
← R
R
R
b
i
⊕b
0
+R
R
R
(b
i
⊕b
0
)⊕a
i
;
7 R
R
R
1
← R
R
R
0
+U
U
U
b
i
;
8 b
0
← b
i
;
9 end
10 return R
R
R
b
0
would be adequate to provide a secure solution (Win
et al., 1998). However, such multiplicative mask-
ing can be problematic if an attacker can choose and
input that could produce a point with a coordinate
set to zero, which cannot be blinded using a mul-
tiplication (Goubin, 2003). Hence, one would need
to combine our algorithms with Coron’s countermea-
sures (Coron, 1999) and add a small multiple of the
order of the group to the private key before it is used.
The bit length of the multiplier needs to be chosen
such that an attacker cannot predict the location of a
zero-coordinate with sufficient reliability to make it
visible in a side-channel attack. Having a 16-bit mul-
tiplier may be sufficient, depending on the signal-to-
noise ratio of the platform. The advantage of combin-
ing these countermeasures is that one does not need to
consider the longest runs of ones or zeros in the order
of the group.
SECRYPT 2021 - 18th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
326

4 SECURITY EVALUATION
In this section, we discuss the security of the algo-
rithms presented previously, first by making a com-
parison with the state-of-the-art algorithms and then
by providing a security evaluation of Algorithm 2,
proposed in this paper.
4.1 State-of-the-Art Comparison
In this section, we compare our proposed algorithms
with a selection of algorithms discussed in the previ-
ous sections and summarize our observations in Ta-
ble 1.
The first block of algorithms in Table 1, con-
tain exponentiation algorithms using the Montgomery
power ladder without splitting the exponent (Algo-
rithm 1), with additive splitting or with variations of
XOR-splitting (Algorithms 2, 3, 4). Multiplicative or
Euclidean splitting are not included in this table, be-
cause in terms of security they have the same side-
channel resistance as an algorithm with additive split-
ting. In terms of performance, the number of opera-
tions is the similar, unless the values s
k
0
are precom-
puted and stored in memory.
The second block of algorithms summarizes the
behavior of the corresponding scalar multiplication
algorithms
2
. Algorithms 8 and 9 are presented in Sec-
tion 5.
We note that none of the algorithms in their cur-
rent form can prevent leakage from observing the in-
termediate values. However, intermediate values can
be blinded with a random value as previously de-
scribed.
4.2 Mutual Information-based Security
Evaluation
Having established that the proposed exponent split-
ting algorithms are probing-secure against first-order
side-channel attacks, we proceed to analyze the noise
amplification stage of the proposed countermeasure.
Analytically, we perform an evaluation of Boolean
exponent splitting (as described by Algorithm 2) us-
ing the information-theoretic framework of Standaert
et al. (Standaert et al., 2009). Analogous approaches
2
We do not count XORs, which can be implemented al-
most for “free” compared to the cost of multiplications (M),
squaring operations (S) and modular inversions (I) in the
chosen field or point additions (A) and doubling operations
(D) on an elliptic curve. The subtraction of points on an
elliptic curve has the same cost as an addition, so we do not
count them separately.
can be conducted for all exponent splitting algo-
rithms, yielding very similar results. Our analysis
considers two sources of leakage, namely data-based
leakage and location-based leakage (also known as
address leakage). Using these two leakage sources,
we demonstrate three possible attack paths against
Algorithm 5, covering all possible combinations be-
tween leakage sources. Thus we show the noise am-
plification stage when only data-based leakage is ex-
ploited (data attack), when only location-based leak-
age is exploited (location attack) and finally the noise
amplification stage when the adversary combines data
and location leakage (hybrid attack).
4.2.1 Notation & MI Metric
In this subsection, random variables are denoted with
capital letters. Instances of random variables and con-
stant values are denoted with lowercase letters. Cap-
ital bold letters are used for random variable vec-
tors and matrices and calligraphic font denotes sets.
All simulations in this section are carried out with
the identity leakage function. Observable data-based
leakages of a certain intermediate value v are denoted
using subscript L
v
. Likewise, observable location-
based leakages caused by accessing register R
i
(where
i the index) are denoted using subscript L
R-i
. To
distinguish between data-based leakage and location-
based leakage we use superscript L
data
and L
loc
. In
addition, we assume that different sources of leakage
(data, location) have different noise levels i.e. we as-
sume homoscedastic data noise N
data
∼ N (0, σ
2
data
)
and homoscedastic location noise N
loc
∼ N (0,σ
2
loc
).
We use the following formula to compute the MI met-
ric.
MI(S;L) = H[S] +
∑
s∈S
Pr[s] ·
∑
m∈M
d
Pr[m] ·d
(10)
where d =
R
l∈L
(d+1)
Pr[l|s, m] · log
2
Pr[s|l] dl and
Pr[s|l] =
∑
m
∗
∈R
Pr[l|s,m
∗
]
∑
s
∗
∈S
∑
m
∗
∈R
Pr[l|s
∗
,m
∗
]
, and random variable S
denotes the secret exponent bit, L denotes the leakage
vector and M is a d-dimensional randomness vector
that we need to sum over when randomization is in
place, i.e. d is the attack order.
4.2.2 Data Leakage Attack
The first obvious way to recover k
n−1
is by observ-
ing the data leakage of the values b
n−1
and a
n−1
at
the same time. We run the algorithm for the first
two rounds and note the intermediate values that can
leak information. We let b
0
be a random value from
R{0,1}, then:
Boolean Exponent Splitting
327
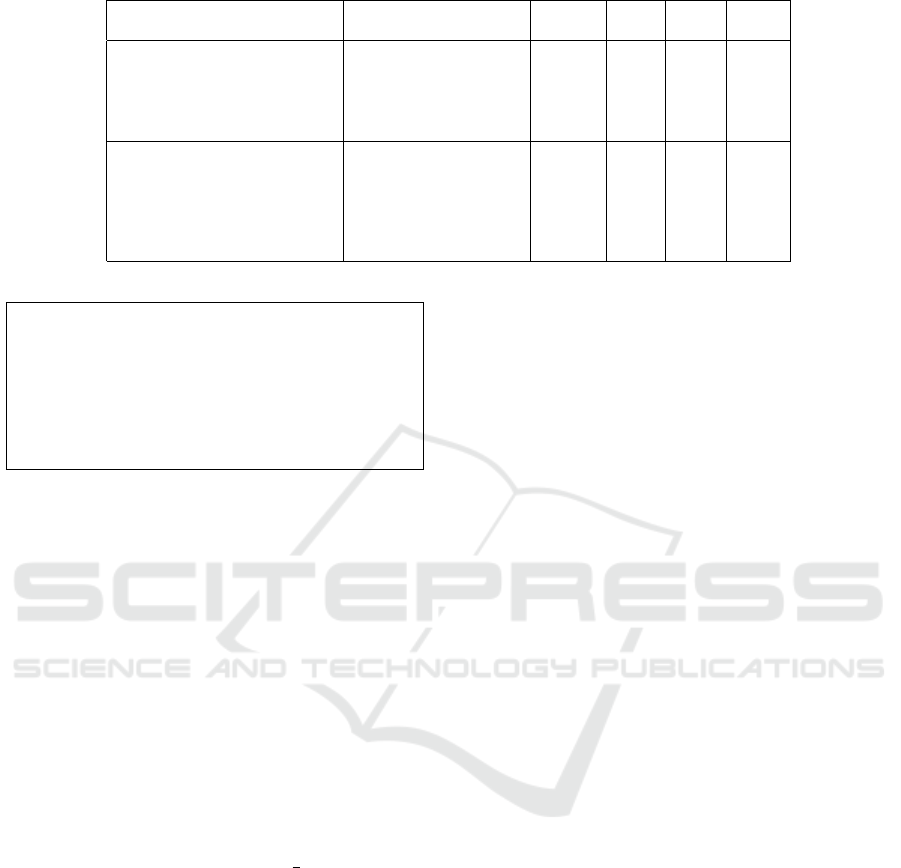
Table 1: Comparison Table.
Algorithm ]operations ]registers Hide ADPA Interm.
length Values
Algorithm 1 n · M + n · S 2 7 7 7
Clavier-Joye (Clavier and Joye, 2001) 2(n · M + n · S) 2 7 7 7
Algorithm 2 n · M + n · S 3 3 3 7
Algorithms 3–4 2n · M 4 3 3 7
Algorithm 5 2n · M 4 3 3 7
Algorithm 6 (n − 1) · A + (n − 1) · D 3 3 3 7
Algorithm 7 2 · (n − 1) · A 4 3 3 7
Itoh et al. (Itoh et al., 2003) Alg. 8 (n − 1) · D + (n − 1) · A + 1 · I 3 7 3 7
Izumi et al. (Izumi et al., 2010) Alg. 2 (n − 1) · D + (n − 1) · A 3 7 3 7
Algorithm 8 n · D + n · A 3 3 3 7
Algorithm 9 2 · n · A 4 3 3 7
i = n − 1
1. b
m
= b
n−1
⊕ b
0
2. a
m
= b
m
⊕ a
n−1
3. R
0
= R
b
m
· R
a
m
4. R
1
= R
0
·U
b
n−1
5. b
0
= b
n−1
i = n − 2
6. b
m
= b
n−2
⊕ b
0
7. a
m
= b
m
⊕ a
n−2
8. R
0
= R
b
m
· R
a
m
9. R
1
= R
0
·U
b
n−2
10. b
0
= b
n−2
As can be observed in above, the value b
n−1
is ac-
cessed in the first iteration (i = n−1) three times, once
when b
m
is calculated (line 1), once implicitly for the
index of U
b
n−1
(line 4) and finally for b
0
(line 5). The
value a
n−1
is accessed once during the first iteration
(i = n − 1) and it is not used in the second iteration
(i = n − 2). We notice that the value b
n−1
is used im-
plicitly again in the second iteration, since it is equal
to b
0
. An attacker observing the power leakage of
this algorithm should be able to probe at two different
points in time, in order to observe both leakages L
data
a
n−1
,
L
data
b
n−1
and eventually the key, i.e. we conclude that a
second-order attack is possible for this scheme. Note
also that the an adversary with ability to conduct hor-
izontal side-channel attacks (Battistello et al., 2016)
could observe the leakage of b
n−1
multiple times, av-
erage them by computing
¯
L
data
b
n−1
=
1
4
∗
∑
4
j=1
L
data
b
n−1
in
order to reduce the noise level and finally perform a
second-order attack. The results of the MI evaluation
are visible in Figure 1. As expected, the exponent
splitting scheme performs noise amplification and has
a different slope compared to an unprotected expo-
nentiation (Algorithm 1). In addition, we observe the
curve’s horizontal shift to the right caused by the hor-
izontal exploitation of the available leakage, i.e. we
can quantify the effect of multiple leaky points for
b
n−1
.
4.2.3 Location Leakage Attack
Let us assume that the adversary can distinguish
between the manipulation of registers according to
which address is accessed, similar to the address-bit
DPA attack described in (Izumi et al., 2010). If the
adversary can distinguish between accesses to, U
0
and U
1
for example, a direct consequence is recovery
of value b
n−1
. To mount a successful attack against
Algorithm 5 using solely location-based leakage, we
need the simultaneous observation of the address of
U
i
1
and R
i
2
and R
i
3
, for indexes i
1
= b
n−1
(line 4) and
i
2
= b
m
(line 3) and i
3
= a
m
(line 3). Thus, in order
to recover k
n−1
, we need to observe leakage vector
L
loc
= [L
loc
U-i
1
,L
loc
R-i
2
,L
loc
R-i
3
], i.e. perform a third-order at-
tack. The results are visible in Figure 2, where we can
observe the noise amplification effect that increases
the curve’s slope. Naturally, a third-order attack us-
ing only location-based leakage tends to be less ef-
fective compared to a second-order attack using only
data-based leakage. However, depending on the de-
vice, exploiting the address dependency may be more
effective than exploiting the data dependency. That
is, the third-order attack can become more efficient if
σ
data
> σ
loc
.
4.2.4 Hybrid Leakage Attack
Lastly, we analyze the scenario in which an adver-
sary can observe both data-based and location-based
leakage. Using this information the adversary can use
leakage vector
L = [L
data
a
n−1
,L
loc
U-b
n−1
]
to carry out a second-order attack that uses data leak-
age to recover bit a
n−1
and location leakage with re-
gard to register U to recover bit b
n−1
. Since data
and location leakage imply different noise levels, i.e.
(σ
data
6= σ
loc
), we need to represent the available in-
formation as a three-dimensional plot, as in Figure 3.
The wave-like plot quantifies the attainable informa-
tion with regard to a particular data and location noise
level. Thus, it assists the side-channel evaluator to
analyze the scheme’s security in a more holistic way
that factors in location leakage and demonstrates the
SECRYPT 2021 - 18th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
328
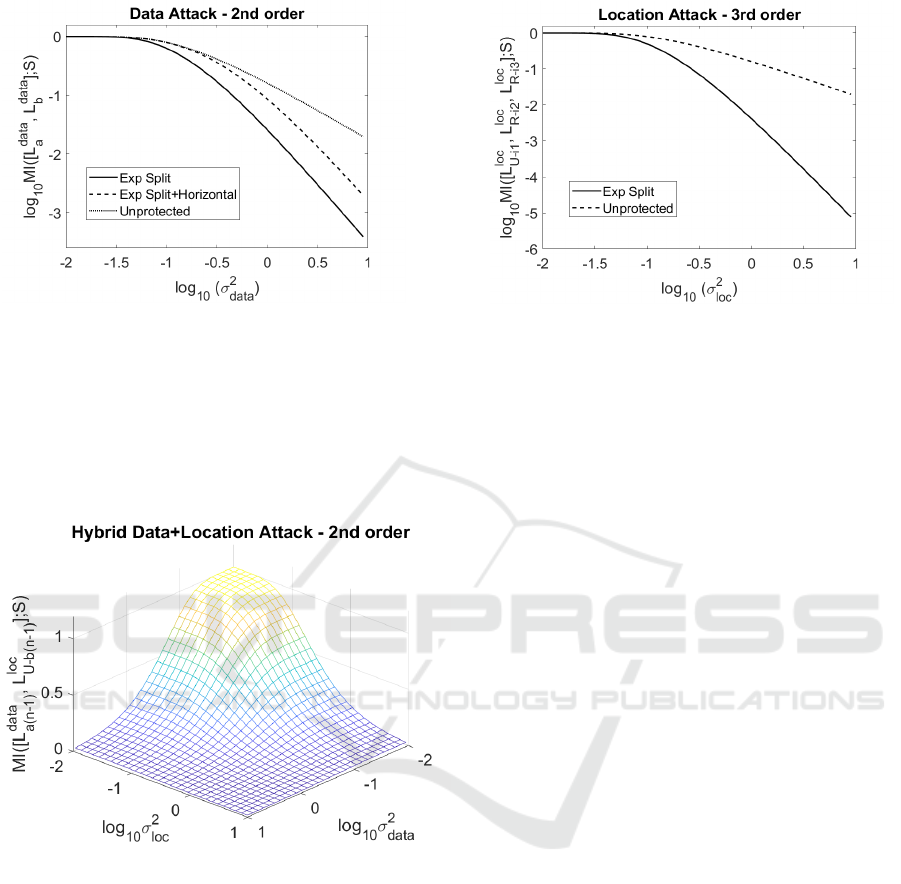
Figure 1: MI evaluation for Algorithm 2, using a data
leakage attack, with and without horizontal exploitation.
Observed leakage vector L = [L
data
a
n−1
,L
data
b
n−1
].
Figure 2: MI evaluation for Algorithm 2, using a lo-
cation leakage attack. Observed leakage vector L =
[L
loc
U-i
1
,L
loc
R-i
2
,L
loc
R-i
3
].
tradeoff between data noise and location noise. If for
instance σ
loc
σ
data
in the target device, the adver-
sary can directly opt for the hybrid attack, instead of
pursing a data-only attack route.
Figure 3: MI evaluation for Algorithm 5 exponent splitting,
using a hybrid leakage attack. Observed leakage vector L =
[L
data
a
n−1
,L
loc
U-b
n−1
].
5 IMPLEMENTATION
CONSIDERATIONS
In this section, we describe the results of applying
Test Vector Leakage Assessment (TVLA) (Goodwill
et al., 2011) to implementations of some of the al-
gorithms above. We further describe modifications
required to achieve a secure implementation where
the hardware architecture can mean that variables that
should be independent leak at the same time, poten-
tially unmasking a secret value (Balasch et al., 2015).
Our implementations were developed using Xil-
inx’s Zynq zc702 evaluation board. The Zynq zc702
microprocessor contains two ARM7 cores and an
FPGA fabric. We used one ARM7 core for our imple-
mentations, clocked at 667 MHz, and the FPGA pro-
vided a means of triggering an oscilloscope at a con-
venient point in our implementations. We acquired a
trace of the electromagnetic emanations around one
of the coupling capacitors.
The test that we used from TVLA is to determine
whether there are statistically significant differences
in the mean traces of two sets of traces, one acquired
with a fixed scalar and the other with random scalar.
One would typically randomly interleave acquisitions
so that environmental effects are the same for both
sets and there are no erroneous indications of leakage,
caused, for example, by the least significant bit of a
variable used to count the number of acquisitions. In
applying this, one would take two sets of data, and
conduct Welch’s t-test point-by-point to determine
whether there is evidence against the null hypothesis
that the sets are the same. We determine that leakage
is present if we observe values above 6.63σ which
gives the probability of indicating leakage where no
leakage is present, often referred to as a Type I error,
of approximately 1 × 10
5
when using traces contain-
ing 3 × 10
5
samples. The interested reader is referred
to Goodwill et al. (Goodwill et al., 2011) and Schnei-
der and Moradi (Schneider and Moradi, 2015) for a
thorough description.
We made a straightforward implementation of Al-
gorithm 6 using NIST’s P192 curve and conducted a
test where we compared a set of traces with a fixed
scalar compared to a set of traces with a random
scalar. The elliptic curve points were implemented
as homogeneous projective points. We use the x and
z-coordinates in conjunction with so-called x-only al-
Boolean Exponent Splitting
329

gorithms for point arithmetic (Brier and Joye, 2002),
as one would for an implementation of ECDH. The
instantaneous electromagnetic emanations around the
targeted capacitor were measured during the execu-
tion of the first 20 rounds of the implementation. The
top-left trace in Figure 4 shows the result of a TVLA
analysis with 1×10
3
traces where leakage can be seen
in numerous places.
A straightforward implementation of Algorithm 6
was tested in the same way. The algorithm is sim-
ilar to that proposed by Izumi et al. (Itoh et al.,
2003) but with masking conducted before the execu-
tion of the scalar multiplication, rather than on-the-
fly. The resulting TVLA traces is shown in the top-
right of Figure 4, where we note that significant leak-
age is present with 1 × 10
6
traces. This is caused by
the microprocessor combining values held in regis-
ters because of the architecture chosen by the design-
ers (Balasch et al., 2015).
A more secure implementation can be made by
computing some of the required indices before the ex-
ecution of the main loop of the scalar multiplication,
as shown in Algorithm 8. We set C to B ⊕
B
2
such
that individual bits of B are masked by adjacent bits.
The resulting TVLA trace is shown in the bottom-left
of Figure 4, where we observe that there is only one
place where we see significant leakage with 1 × 10
6
traces. This leakage occurs because the initial state of
{R
R
R
0
,R
R
R
1
} contain {P
P
P,2P
P
P} in some random order. In
the first loop of the scalar multiplication {R
R
R
0
,R
R
R
1
} is
overwritten with {2P
P
P,3P
P
P} or {3P
P
P,4P
P
P}, in some ran-
dom order, depending on whether the second most-
significant bit of κ is set to 0 or 1, respectively. When
2P
P
P overwrites 2P
P
P the side-channel leakage will be
significantly different to any other possible combina-
tion, since the Hamming distance will be zero.
A fully secure implementation can be achieved by
randomizing the point produced by the doubling op-
eration, by multiplying the x and z-coordinate of the
resulting point by a random value. In implementing
Algorithm 8, this was achieved by randomizing R
R
R
0
and R
R
R
1
before the main loop of the scalar multipli-
cation. The resulting TVLA trace is shown in the
bottom-right of Figure 4, where we observe that there
is no significant leakage with 1 ×10
6
traces. An alter-
native would be to set the coordinates of R
R
R
a
i
to zero
before setting R
R
R
a
i
to R
R
R
2
. Algorithm 9 shows the same
arguments applied to Algorithm 7. However there is
no need to randomize any points during the loops of
scalar multiplication. If the redundant representation
of the point assigned to R
R
R
0
and R
R
R
1
is randomized sep-
arately to that applied toU
U
U
0
an overwrite with a Ham-
ming distance of zero cannot occur.
Algorithm 8: Montgomery Ladder with XOR-Split
Scalar on EC.
Input: E, F
q
, P
P
P ∈ E , n-bit integers
A =
∑
n−1
i=0
a
i
2
i
, B =
∑
n−1
i=0
b
i
2
i
Output: Q
Q
Q = [κ]P
P
P where κ = A ⊕ B
Uses: C =
∑
n−1
i=0
c
i
2
i
1 R
R
R
0
← P
P
P ; R
R
R
1
← P
P
P ; R
R
R
2
← P
P
P ;
2 C ← B ⊕
B
2
;
3 b
0
← b
n−1
;
4 R
R
R
¬b
0
← 2P
P
P ;
5 for i = n − 2 down to 0 do
6 R
R
R
2
← R
R
R
a
i
+R
R
R
¬a
i
;
7 R
R
R
a
i
← 2R
R
R
a
i
⊕c
i
;
8 R
R
R
¬a
i
← R
R
R
2
;
9 end
10 return R
R
R
b
0
Algorithm 9: Montg. Ladder with XOR-Split
Scalar II on EC.
Input: E, F
q
, P
P
P ∈ E , n-bit integers
A =
∑
n−1
i=0
a
i
2
i
, B =
∑
n−1
i=0
b
i
2
i
Output: Q
Q
Q = [κ]P
P
P where κ = A ⊕ B
Uses: C =
∑
n−1
i=0
c
i
2
i
and D =
∑
n−1
i=0
d
i
2
i
1 R
R
R
0
← P
P
P ; R
R
R
1
← P
P
P ;
2 U
U
U
0
← P
P
P ; U
U
U
1
← −P
P
P ;
3 C ← B ⊕
B
2
; D ← C ⊕ A;
4 b
0
← b
n−1
, R
R
R
¬b
0
← 2P
P
P ;
5 for i = n − 2 down to 0 do
6 R
R
R
0
← R
R
R
c
i
+R
R
R
d
i
;
7 R
R
R
1
← R
R
R
0
+U
U
U
b
i
;
8 b
0
← b
i
;
9 end
10 return R
R
R
b
0
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we show how an exponent can be split
into two shares, where the exponent is the XOR sum
of the two shares and the cost is typically an extra reg-
ister and some register copies per bit. A significant
advantage over previously proposed exponent split-
ting methods, which can have a prohibitive impact on
performance (Clavier and Joye, 2001). Our method
can also be applied to groups whose order contains
long runs of bits set to 0 or 1 without any penalty on
performance or security. Indeed, one does not need
to know the order of the group; a significant advan-
tage if, for example, one wished to implement RSA
SECRYPT 2021 - 18th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
330
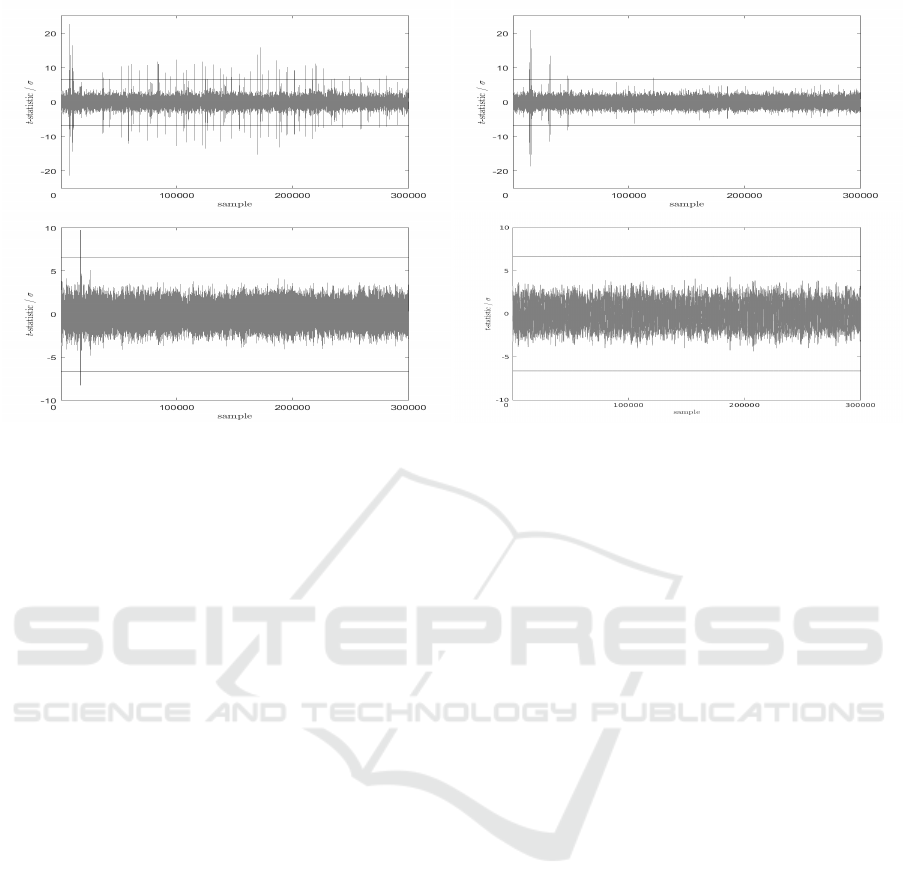
Figure 4: From top left to bottom right we show: an unmasked implementation showing leakage after 1 × 10
3
traces, a na
¨
ıve
implementation of Algorithm 6 and a more secure variant both showing leakage after 1 × 10
6
traces, and an implementation
of Algorithm 8 that does not show leakage after 1 × 10
6
traces.
without using the Chinese remainder theorem.
We show that our algorithms are secure using for-
mal methods, MI-based evaluation and TVLA on an
implementation of Boolean exponent splitting. We
note that our method does not prevent an attacker
from using the intermediate states generated by the al-
gorithms as a means of attack. However, inexpensive
solutions such as randomizing projective points (Win
et al., 1998) or Ebeid and Lambert’s blinding method
for RSA (Ebeid and Lambert, 2010) can be com-
bined with our method to provide a high level of side-
channel resistance.
The algorithms presented above will be more ef-
ficient than adding a multiple of the group order to
the exponent, since the bit length of the exponent is
not increased. Moreover, the resistance to collision
attacks is superior, since one would need to conduct
several attacks to derive each share and reconstruct
the exponent. Where one is adding a random mul-
tiple of the exponent any bits recovered directly re-
late to bits of the exponent used. It has not yet been
shown that one can derive an exponent from gaining
partial information on a series of blinded exponents,
but significant advances have been made (Schindler
and Itoh, 2011; Joye and Lepoint, 2012; Schindler,
2014; Schindler and Wiemers, 2014).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Lauren De Meyer and
Michael Hamburg for their helpful comments.
REFERENCES
Balasch, J., Gierlichs, B., Grosso, V., Reparaz, O., and Stan-
daert, F. (2015). On the cost of lazy engineering for
masked software implementations. In CARDIS 2014,
volume 8968 of LNCS, pages 64–81. Springer.
Battistello, A., Coron, J., Prouff, E., and Zeitoun, R. (2016).
Horizontal side-channel attacks and countermeasures
on the ISW masking scheme. In CHES 2016, volume
9813 of LNCS, pages 23–39. Springer.
Bernstein, D. J. and Lange, T. (2009). A complete set of
addition laws
for incomplete edwards curves. Cryptology ePrint
Archive, Report 2009/580. https://eprint.iacr.org/
2009/580.
Brier, E., Clavier, C., and Olivier, F. (2004). Correlation
power analysis with a leakage model. In CHES 2004,
volume 3156 of LNCS, pages 16–29. Springer.
Brier, E. and Joye, M. (2002). Weierstraß elliptic curves
and side-channel attacks. In PKC 2002, volume 2274
of LNCS, pages 335–345. Springer.
Chari, S., Jutla, C. S., Rao, J. R., and Rohatgi, P. (1999). To-
wards sound approaches to counteract power-analysis
attacks. In CRYPTO ’99, volume 1666 of LNCS, pages
398–412. Springer.
Ciet, M. and Joye, M. (2003). (virtually) free randomiza-
tion techniques for elliptic curve cryptography. In
ICICS 2003, volume 2836 of LNCS, pages 348–359.
Springer.
Boolean Exponent Splitting
331

Clavier, C. and Joye, M. (2001). Universal exponentiation
algorithm. In CHES 2001, volume 2162 of LNCS,
pages 300–308. Springer.
Coron, J. (1999). Resistance against differential power anal-
ysis for elliptic curve cryptosystems. In CHES 1999,
volume 1717 of LNCS, pages 292–302. Springer.
Ebeid, N. M. and Lambert, R. (2010). A new CRT-RSA
algorithm resistant to powerful fault attacks. In WESS
2010, page 8. ACM.
Edwards, H. M. (2007). A normal form for elliptic curves.
In Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society,
volume 44, pages 393–422.
Feix, B., Roussellet, M., and Venelli, A. (2014). Side-
channel analysis on blinded regular scalar multiplica-
tions. In INDOCRYPT 2014, volume 8885 of LNCS,
pages 3–20. Springer.
Gandolfi, K., Mourtel, C., and Olivier, F. (2001). Electro-
magnetic analysis: Concrete results. In CHES 2001,
volume 2162 of LNCS, pages 251–261. Springer.
Goodwill, G., Jun, B., Jaffe, J., and Rohatgi, P. (2011). A
testing methodology for side channel resistance vali-
dation. NIST non-invasive attack testing workshop.
Goubin, L. (2003). A refined power-analysis attack on ellip-
tic curve cryptosystems. In PKC 2003, volume 2567
of LNCS, pages 199–210. Springer.
Hanley, N., Kim, H., and Tunstall, M. (2015). Exploiting
collisions in addition chain-based exponentiation al-
gorithms using a single trace. In CT-RSA 2015, vol-
ume 9048 of LNCS, pages 431–448. Springer.
Itoh, K., Izu, T., and Takenada, M. (2002). Address-bit
differential power analysis of cryptographic schemes
OK-ECDH and OK-ECDSA. In CHES 2002, volume
2523 of LNCS, pages 129–143. Springer.
Itoh, K., Izu, T., and Takenada, M. (2003). A practical coun-
termeasure against address-bit differential power anal-
ysis. In CHES 2003, volume 2779 of LNCS, pages
382–396. Springer.
Izumi, M., Ikegami, J., Sakiyama, K., and Ohta, K. (2010).
Improved countermeasures against address-bit DPA
for ECC scalar multiplication. In DATE 2010, pages
981–984. IEEE.
Joye, M. and Lepoint, T. (2012). Partial key exposure on
RSA with private exponents larger than N. In IS-
PEC 2012, volume 7232 of LNCS, pages 369–380.
Springer.
Joye, M. and Villegas, K. (2002). A protected division al-
gorithm. In CARDIS 2002. USENIX.
Joye, M. and Yen, S.-M. (2002). The Montgomery pow-
ering ladder. In CHES 2002, volume 2523 of LNCS,
pages 291–302. Springer.
Kim, H., Kim, T. H., Yoon, J. C., and Hong, S. (2010).
Practical second-order correlation power analysis on
the message blinding method and its novel counter-
measure for RSA. ETRI Journal, 32(1):102–111.
Kocher, P. (1996). Timing attacks on implementations of
Diffie-Hellman, RSA, DSS, and other systems. In
CRYPTO ’96, volume 1109 of LNCS, pages 104–113.
Springer.
Kocher, P., Jaffe, J., and Jun, B. (1999). Differential power
analysis. In CRYPTO ’99, volume 1666 of LNCS,
pages 388–397. Springer.
Le, D.-P., Tan, C.-H., and Tunstall, M. (2015). Randomiz-
ing the Montgomery powering ladder. In WISTP 2015,
volume 9311 of LNCS, pages 155–170. Springer.
Messerges, T. S. and Dabbish, E. A. (1999). Investigations
of power analysis attacks on smartcards. In Smartcard
1999. USENIX Association.
Messerges, T. S., Dabbish, E. A., and Sloan, R. H. (1999).
Power analysis attacks of modular exponentiation in
smartcards. In CHES’99, volume 1717 of LNCS,
pages 144–157. Springer.
Montgomery, P. L. (1987). Speeding the Pollard and elliptic
curve methods of factorization. Mathematics of Com-
putation, 48(177):243–264.
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
(2009). Recommended elliptic curves for federal
government use. In the appendix of FIPS 186-
3, available from http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/fips/
fips186-3/fips
186-3.pdf.
Quisquater, J.-J. and Samyde, D. (2001). Electromagnetic
analysis (EMA): Measures and counter-measures for
smart cards. In E-smart 2001, volume 2140 of LNCS,
pages 200–210. Springer.
Rivest, R., Shamir, A., and Adleman, L. M. (1978). Method
for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryp-
tosystems. Communications of the ACM, 21(2):120–
126.
Schindler, W. (2014). Exclusive exponent blinding may not
suffice to prevent timing attacks on RSA. Cryptol-
ogy ePrint Archive, Report 2014/869. http://eprint.
iacr.org/.
Schindler, W. and Itoh, K. (2011). Exponent blinding does
not always lift (partial) SPA resistance to higher-level
security. In ACNS 2011, volume 6715 of LNCS, pages
73–90. Springer.
Schindler, W. and Wiemers, A. (2014). Power attacks in
the presence of exponent blinding. J. Cryptographic
Engineering, 4(4):213–236.
Schneider, T. and Moradi, A. (2015). Leakage assessment
methodology - A clear roadmap for side-channel eval-
uations. In CHES 2015, volume 9293 of LNCS, pages
495–513. Springer.
Smart, N., Oswald, E., and Page, D. (2008). Randomised
representations. IET Proceedings on Information Se-
curity, 2(2):19–27.
Standaert, F., Malkin, T., and Yung, M. (2009). A unified
framework for the analysis of side-channel key recov-
ery attacks. In EUROCRYPT 2009, volume 5479 of
LNCS, pages 443–461. Springer.
Win, E. D., Mister, S., Preneel, B., and Wiener, M. J.
(1998). On the performance of signature schemes
based on elliptic curves. In ANTS 1998, volume 1423
of LNCS, pages 252–266. Springer.
Witteman, M. F., van Woudenberg, J. G. J., and Menarini, F.
(2011). Defeating RSA multiply-always and message
blinding countermeasures. In CT-RSA 2011, volume
6558 of LNCS, pages 77–88. Springer.
SECRYPT 2021 - 18th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
332
