
AH-CID: A Tool to Automatically Detect Human-Centric Issues in App
Reviews
Collins Mathews
1
, Kenny Ye
1
, Jake Grozdanovski
1
, Marcus Marinelli
1
, Kai Zhong
1
,
Hourieh Khalajzadeh
2
, Humphrey Obie
2
and John Grundy
2
1
Faculty of Information Technology, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia
2
HumaniSE Lab, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia
{hourieh.khalajzadeh, humphrey.obie, john.grundy}@monash.edu
Keywords:
Human-centric Issues, App Reviews, Machine Learning, End-user, Human-centred Design.
Abstract:
In modern software development, there is a growing emphasis on creating and designing around the end-user.
This has sparked the widespread adoption of human-centred design and agile development. These concepts
intersect during the user feedback stage in agile development, where user requirements are re-evaluated and
utilised towards the next iteration of development. An issue arises when the amount of user feedback far
exceeds the team’s capacity to extract meaningful data. As a result, many critical concerns and issues may fall
through the cracks and remain unnoticed, or the team must spend a great deal of time in analysing the data that
can be better spent elsewhere. In this paper, a tool is presented that analyses a large number of user reviews
from 24 mobile apps. These are used to train a machine learning (ML) model to automatically generate the
probability of the existence of human-centric issues, to automate and streamline the user feedback review
analysis process. Evaluation shows an improved ability to find human-centric issues of the users.
1 INTRODUCTION
Software developers aim to deliver efficient and satis-
factory solutions to their end-users. However, fulfill-
ing the expectations of their diverse end-users is not
a straightforward task. Software systems are prone
to security and data breaches, massive cost over-
runs and project slippage, hard-to-deploy, hard-to-
maintain, and even dangerous solutions and hard-to-
use software (Grundy et al., 2020). These issues can
unintentionally arise due to the lack of understand-
ing of human-centric issues during the software en-
gineering process (Hartzel, 2003; Miller et al., 2015;
Stock et al., 2008; Wirtz et al., 2009). These human-
centric issues (HCIs) include the issue diverse users
face due to the lack of consideration of their age, gen-
der, culture, physical and mental impairments, socio-
economic status, and so on. When HCIs, such as age,
gender, disability and language are ignored, the abil-
ity of affected users to interact with the system may
be severely impacted (Grundy et al., 2020).
Software engineers are typically very different
from most end users - dominated by men; relatively
young; affluent; mostly proficient in English; having
less severe physical and mental impairments, and so
on (Grundy et al., 2020; Grundy et al., 2021). The
gap between developers and end-users leads to the
lack of understanding of the human-centric issues by
the developers. Some app users share their concerns
through app reviews, and therefore many mobile ap-
plications receive a huge number of user reviews.
These reviews collectively provide a lot of useful in-
formation to the development team from the end users
of the product. One set of insights that can be drawn
from user app reviews is the human-centric issues ex-
perienced by the users. However, the time and effort
required to extract meaningful insights from such a
large data source may exceed the capacity of a de-
velopment team (Mao et al., 2005). Therefore, a tool
to analyse and quantify HCIs, using Machine Learn-
ing (ML) would greatly aid developers designing and
improving systems around the end user (Mao et al.,
2005).
We collected a large number of reviews from 24
apps in different categories such as parking, social
media, COVID 19, education, fitness, and apps de-
veloped for people with dyslexia. The reviews were
classified by using eight human-centric tags identified
during our analysis as: Disability, Age, Emotional
(emotional impacts of the app), Language, Gender,
386
Mathews, C., Ye, K., Grozdanovski, J., Marinelli, M., Zhong, K., Khalajzadeh, H., Obie, H. and Grundy, J.
AH-CID: A Tool to Automatically Detect Human-Centric Issues in App Reviews.
DOI: 10.5220/0010576503860397
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Software Technologies (ICSOFT 2021), pages 386-397
ISBN: 978-989-758-523-4
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved

Location (or culture), Privacy, and Socio-economic
Status. The app reviews were initially tagged using
a semi-automated keyword-based tool (Obie et al.,
2021). They were then manually checked, revised
and used in training an ML model. We adopted a
binary relevance (BR) transformation method with a
base classifier of support vector machine (SVM) to
determine the percentage likelihood of the text input
to contain any of the 8 specified labels. Utilising this
ML model yields promising results and our perfor-
mance evaluations indicate a positive trend toward au-
tomating the user-feedback process as a viable option
to manual analysis of reviews.
The remainder of this paper is organised as fol-
lows. Section 2 details the motivation behind our
study. Section 3 provides an overview of our ap-
proach and tool. Section 4 shows the tool usage ex-
ample, and Section 5 discusses our evaluation results.
Section 6 discusses and reflects on the key findings.
Section 7 summarises key differences to the related
research. Finally, Section 8 draws conclusions and
proposes future work.
2 MOTIVATION
Software systems are created through production
pipelines and techniques aiming to efficiently deliver
solutions to the users. However, many software solu-
tions are developed by professionals who do not inti-
mately understand the human-centric needs of their
users and do not have the tools to find and access
this information (Grundy et al., 2020). This results in
software solutions not meeting the users needs, often
leading to dissatisfaction and extra costs if the client
wishes to resolve these issues. From a software pro-
duction perspective, it is in their best interest to gauge
HCIs quickly and accurately, in order to improve the
quality of their software system.
Human-centred Design: Human-centred design
is a methodology in which product developers create
solutions in conjunction with the people in which they
want to impact (Farooqui et al., 2019). Having a tool
that can gather HCIs from reviews could greatly im-
prove the efficiency of human-centred design work-
flows. Thus, instead of creating a product for people,
the goal is to create the product with people through-
out continuous iterations. Farooqui et. al. stated
that most developers underestimate the importance of
user experience and usability and merely focus on
developing more features or content. Many of the
human-centred design workflows discussed by (Fa-
rooqui et al., 2019) used iterative production where
prototypes were built and users were asked to give
their feedback. This continuous research allowed de-
signers to create in-depth personas of its end users
giving developers guidance on understanding the real
user requirements (Farooqui et al., 2019).
Diversity of Users: End user diversity is often
not sufficiently considered in the development pro-
cess by many software development teams (Grundy
et al., 2021). Spending time with the potential users
and understanding the context in which they use soft-
ware can greatly improve the understanding of prob-
lems and use cases when developing solutions. How-
ever, for general use software, it is not always clear
who the users are. Online reviews provide a diverse
dataset, as users express their concerns and opinions
regarding the system. This provides a platform for
users that were not originally considered in the de-
sign process to effectively communicate their needs.
The challenging aspect for developers is synthesising
large amounts of reviews into meaningful data for im-
proving their original solution. In addition to this, de-
velopers must ensure that the HCIs of minority users
do not get lost in the process. Having a tool which can
condense this data into usable information regarding
HCIs would aid in the inclusion of a diverse set of
users (Farooqui et al., 2019).
Developer Empathy: Empathy is an extremely
important skill for developers in order to create effec-
tive software solutions. The ability to show concern,
empathy, and a positive attitude may influence an en-
gineer’s overall career success and technical compe-
tence (Levy and Hadar, 2018). A reciprocal relation-
ship between emotional intelligence or social cogni-
tion and reasoning about the mechanical properties of
a system is shown by (Jack et al., 2013). Being able to
connect developers and users consistently and effec-
tively is critical to achieving technical excellency. De-
velopers who can visualise their impacts on users are
more likely to stay motivated and develop a more tai-
lored software experience. As a result, software teams
can build their emotional intelligence in tandem with
technical expertise.
Process & Cost: Both developers and stakehold-
ers are consistently looking for ways to improve the
effectiveness of the development process along with
avoiding costly changes that come with large scale re-
structuring (Farooqui et al., 2019). Farooqui et. al de-
scribes the evaluation of human-centred design and its
associating benefits compared to a conventional soft-
ware development process. A tool to consolidate user-
based feedback without requiring a manual review
process will ensure that developing software systems
will meet the requirements of the end user by high-
lighting HCIs. This can be achieved effectively dur-
ing every stage of development which will greatly re-
AH-CID: A Tool to Automatically Detect Human-Centric Issues in App Reviews
387

duce the time consuming process of such a review.
3 OUR APPROACH
We have developed a tool, Automated Human-Centric
Issues Detector (AH-CID), for detecting human-
centric discussion in app reviews. Based on our litera-
ture review, BR problem transformation method with
a SVM multi-label learning approach was selected as
the best approach for our problem. AH-CID develop-
ment process is shown in Figure 1. It is composed on
a machine learning component and a software devel-
opment component conducted in parallel. Details of
the stages are summarised below.
Dataset: For the training of the model, a multil-
abel binary marked dataset was required. A total of
171,048 user reviews were collected from 24 apps:
Firefox Browser, parking (Cellopark, Paystay), so-
cial media (Pinterest, Tiktok), COVID 19 (COVID-
safe, Aarogya Setu India, NZ Covid Tracer), ed-
ucation (Moodle), fitness (Fitbit), and apps devel-
oped for people with dyslexia (Dyslexia Reading
Test, Eye games Dyslexia, Speechify, SmartyNote
Notepad, Augmenta11y, Mighty Fonts, Omoguru,
Ridit, Dyslexia learn letters, Nessy Learning, KOBI,
TintVision, Dyslexic Font for FlipFont, Cool Fonts
Text Free, HexaDyslexia).
To cover human-centric issues related to the end-
users’ age, gender, language, culture, physical and
mental impairments, emotions, and privacy concerns,
we considered eight human-centric tags as:
• Disability: reviews related to the issues with the
app usage due to the end-users physical and men-
tal impairments
• Age: issues related to the age of the end-users,
including elderly and very young users
• Emotional: the negative emotional impacts that an
app have on the end-users
• Language: not considering the language of dif-
ferent users accessing the app, such as translating
the app into different languages and considering
the issues due to translation
• Gender: not taking into account gender specific
features in the design of the app
• Location (or culture): issues related to the loca-
tion that the users access the app from
• Privacy: privacy related concerns that the end-
users raise through app reviews
• Socio-economic Status: issues related to the cost
and technology required to be able to use the app
Due to the large number of app reviews, a semi-
automated keyword-based tool (Obie et al., 2021)
was first utilised to filter any samples that did not
contain at least one keyword that was in relation to
the labels. Keywords include all the synonyms and
antonyms of the labels and can be accessed online
through (Mathews et al., 2021). A total sample size
of 8,965 was then remained from all the apps. This
combined dataset was then manually labelled by five
of the authors to ensure the reviews discuss HCIs only
related to the 8 categories. A total of 1,315 sam-
ple was then detected as app reviews discussing these
human-centric issues. A sample subset app reviews
discussing HCIs can be seen in Table 1.
Text Processing: We then carried out pre-
processing tasks including stop words removal and
stemming to each sample in our dataset to provide
cleaned text that can be vectorised for the multi-label
classifier. The CountVectorizer and TfidfTransformer
classes from the Scikit-Learn Python library were
used to vectorise the data into Term-Frequency and
then Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency
features, respectively.
Model Training: The training of the model was
handled by Scikit-Multilearn in conjunction with
Scikit-Learn Python libraries. Scikit-Multilearn’s Bi-
naryRelevance classifier was instantiated with Scikit-
Learn’s svm.SVC learning method to provide the basis
for the model to be trained from. The vectorised data
was placed into a 3:1 train/test split and the training
dataset was passed into the classifier. The resultant
learning model to be used for AH-CID was pickled
via the use of Pandas into a pickle (.pkl) file to be
loaded into the tool. The learning model was then
tested on the testing dataset via metrics from Scikit-
Learn’s metrics package.
User Interface: A web-based user interface was
built with Django, which follows the model-template-
view architectural pattern. The user can choose both
text entry and CSV file upload. If they need to check a
single sample, they may use the text entry, however if
they would like to investigate multiple samples, they
may upload a CSV file with these samples. User input
is validated and read into a Pandas DataFrame object,
where the pre-processing and vectorisation is han-
dled as above. The trained BR model is used to pre-
dict from the user input the resultant probabilities for
the multi-label classification using Scikit-Multilearn’s
predict proba method. If the user entry consisted of
a CSV file, a new results file is saved with the ini-
tial dataset given by the user, concatenated with the
resultant probabilities. The resulting prediction vari-
ables are then passed as Django context variables to
the frontend.
ICSOFT 2021 - 16th International Conference on Software Technologies
388

Dataset
extraction
(n=171,048)
Dataset filtering with
keyword-based tool
Dataset selection
(n=8,965)
Dataset manual
labelling
Vectorisation
Text
preprocessing
Model training
Saved model
Metrics analysis
User interface
creation
User interface
update
Prototype
development
Final working
tool
Deployment
EC2 Instance
Requirements
clarification
Machine Learning Component
Website development component
Human-centric
Dataset
(n=1,315)
Figure 1: AH-CID tool development process.
The ChartJS JavaScript package is utilised to dis-
play the results of the multilabel classification to the
user with dynamic bar chart visualisations. If the
user entry consisted of a CSV file, multiple bar charts
would be displayed dependent on the user input, along
with a download link to the aforementioned results
file. Any caught errors in user input validation would
be handled by a new HTML page displaying the na-
ture and description of the error, communicated be-
tween frontend-backend via Django context variables.
Deployment: The deployment of the Django full-
stack application was done on an AWS EC2 instance.
Port 80 was then allowed as an inbound rule to all
sources which allows HTTP request over the internet,
making AH-CID publicly accessible. Nginx, Guni-
corn and Supervisor frameworks were used to host the
Django application. Collectively, Supervisor would
control a Gunicorn process (on launch) that would tar-
get the Django application and bind it to a Unix socket
located at the root directory. Nginx would then point
to the same Unix socket and host it as a HTTP server,
allowing public internet access to the entire applica-
tion.
4 AH-CID TOOL USAGE
EXAMPLE
Upon loading of AH-CID, the user is displayed a
home page, as shown in Figure 2, and is then able
to select between two options in the form of tabs, i.e.,
“Text Entry” and “CSV Entry”. In the “Text Entry”
tab, the user may enter latin1 encoded text into the
text area and select the GENERATE button. The tool
will then display another page showing the resulting
label probabilities for the text that the user has entered
as shown in Figure 3.
In the “CSV Entry” tab, the user may enter a CSV
file of the data that they wish to obtain label proba-
bilities for. There are three optional form parameters
and two required form parameters for the user to fill.
The two required form parameters are Samples Col
and CSV File. The three optional form parameters are
Likes Col, Dislikes Col and Rating Col. Descriptions
for each form parameter can be seen in Figure 4.
An example of ‘covidsafereviewsresults.csv’
dataset can be seen in Table 2. We take the content
column (6th indexed column) as Samples Col param-
eter, thumbsUpCount column (8th indexed column)
AH-CID: A Tool to Automatically Detect Human-Centric Issues in App Reviews
389
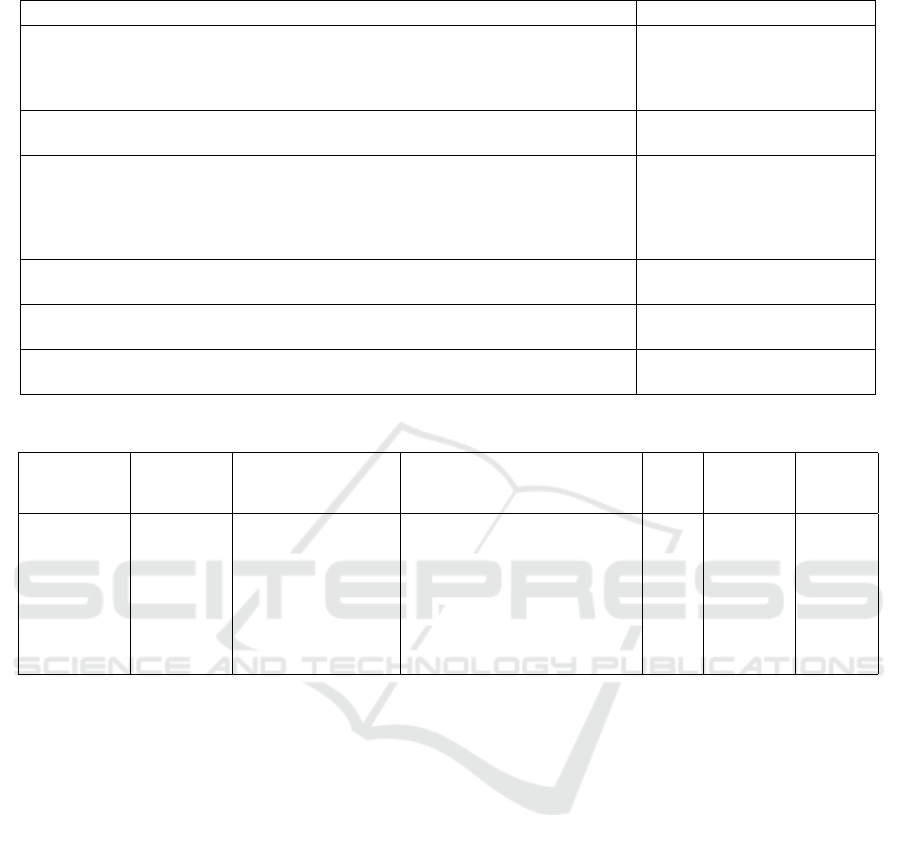
Table 1: Example of app reviews discussing human-centric issues.
User review Human-centric issue
I downloaded the app while another colleague downloaded it nearby. I was very
shocked to see that his app was pre-populated with all my personal details de-
spite different emails addresses and bluetooth disabled. Total breach of my pri-
vacy and I am deleting the app. Absolutely hopeless.
Privacy
I m disappointed I can t install it on an older Android phone. That must cut out a
portion of the population
Socio-Economic
Where is input choice for women s cycles of women with hysterectomy Where
are choices for DISABLED WOMEN who can do partial body workouts only This
is NOT an inclusive app offers little variety at all for those outside the fully
physically able bodied normal people INCREDIBLY DISAPPOINTING as it s
such a HUGELY MISSED OPPORTUNITY
Gender, Disability, Emotional
App cannot be found if your Google account is registered in another country, so
how are you tracing visitors?
Location
Does not accept norwegian keyboard as default when LL THE apps. Have to use
spaceward to swap. Worked fine before. EXTREMLY FRUSTRATERING????.
Language, Emotional
I can’t log in because by the time I find the code on the phone it’s too late to enter
it. This is too quick for older people!
Age
Table 2: Example data of covidsafereviewsresults.csv.
reviewId userName userImage content score
thumbs
UpCount
review
Created
Version
xx:XXxxXX John Smith
https://example.com/
userimage
The new UI is terrible!
Not user friendly at all.
Especially for older folks who
I would install it for on their
devices. I want to revert to
older versions on all of my
and client devices and hope
it does not pose a security risk.
1 97 68.10.1
asLikes Col parameter and score column (7th indexed
column) as Rating Col parameter. The user may then
select the GENERATE button once they are satisfied
with the form parameters. AH-CID will then display
another page showing different metrics about the data
in the CSV file as shown in Figure 5.
Dependent on the active tab selected underneath
Options, bar charts will be shown representing the
composition of the data based on the probabilities
given by the metric outlined in the active tab. In Fig-
ure 5, a bar chart of total label probabilities is shown
based on the count of samples. In Figure 6, a cate-
gorical bar chart of total label probabilities is shown
based on the rating it was given. The user may also
select the ‘Use Threshold?’ checkbox to instead have
the bar charts be based on a probability threshold such
that samples that have a label that is above or equal to
the threshold are only considered.
The user may also download the probability la-
belled data by selecting the ‘Download labelled’ link,
which will prompt the user to save a CSV file. An ex-
ample of this downloaded CSV dataset can be seen in
Table 3. Any errors using AH-CID, such as inputting
incorrect column parameters in ‘CSV Entry’, will re-
sult in an error page being shown with a description of
the error, such as ”Column values are out of bounds”.
5 EVALUATION
The contents of our dataset included labeled reviews
of 24 apps with a combined sample size of n=1,315.
The dataset was put in a 3:1 train(n=986)/test(n=329)
split. The model was then trained 100 times with
different training/testing dataset splits with the aver-
aged metrics of hamming loss, accuracy and micro F1
score used to evaluate the effectiveness of the model.
Accuracy refers to how well the set of labels pre-
dicted (for the test subset) exactly matched with the
corresponding set of true labels for the test subset.
Hamming loss refers to the fraction of labels that are
incorrectly predicted. F1 score can be interpreted as
the weighted average between precision and recall.
Micro F1 score is an extension of F1 score which
involves calculating metrics globally by counting the
ICSOFT 2021 - 16th International Conference on Software Technologies
390

Figure 2: AH-CID user interface.
Figure 3: Text entry results page for AH-CID.
total true positives, false negatives and false positives.
Given our model and both training and testing
datasets, the following metrics were found:
accuracy score = 0.914
hamming loss = 0.021
micro F1 score = 0.63
Based on these metrics, the following results can be
concluded. Given a sample from the test dataset:
• the model has a probability of ≈91.0% of assign-
ing all labels (as either 1 or 0) correctly
• the model has a probability of ≈2.1% of assigning
a single label (as either 1 or 0) incorrectly
• the new model has a moderate-high effectiveness
in assigning the samples with the correct label (as
1)
While the accuracy score and hamming loss dis-
play positive connotations for the effectiveness of the
learning model, the micro F1 score also indicates that
the dataset is relatively balanced and contains no in-
herent biases as used in the model. The results for
four apps are shown in Figure 7 with the X axis show-
ing the 8 human-centric categories. Dependent on the
active tab selected underneath Options, bar charts will
represent the composition of the data based on the
probabilities given by the metric outlined in the ac-
tive tab. In Figure 7, for COVIDSafe and Firefox, the
total label probabilities is shown based on the count
of samples (Y axis). For Fitbit and Paybyphone apps,
the ‘Use Threshold?’ checkbox with a threshold rat-
ing of 0.5 is selected to instead have the bar charts
be based on a probability threshold such that number
of app reviews that have a label above or equal to the
threshold (Y axis). The results show that the model
is effective in predicting human-centric discussion in
text.
AH-CID: A Tool to Automatically Detect Human-Centric Issues in App Reviews
391

Figure 4: CSV entry example for AH-CID.
Figure 5: CSV entry results page with ‘By Count’ option selected.
6 DISCUSSION
6.1 What are the Common HCIs in App
Reviews?
As Figure 7 indicates, the human-centric issues vary
among different apps. For example, privacy and loca-
tion were the main concerns among users of COVID
19 and Firefox Browser mobile apps, that conse-
quently affects their emotions, making them frus-
trated or disappointed. COVIDSafe, being an app
created and maintained by the governments, incites
conversation amongst the storage and handling of the
user’s location and data by the government. Fitbit and
Paybyphone, on the other hand, seem to be developed
in a gender and language biased way. These indicate
the need for more research on human-centric aspects
in app development, that we aim our AH-CID tool
would facilitate.
COVIDSafe, being an app created and maintained
by the Australian Government (AustralianGovern-
ment, 2020), incites conversation amongst the stor-
age and handling of the user’s location and data by
the government. This was expressed by many users
within the dataset, as seen in Table 4. The Firefox
Browser app is marketed as a leading browser in pri-
vacy protection. A segment of the app description on
the Google Play store is captured below.
“Firefox for Android browser gives you effortless
privacy protection with lighting-fast page loads.
Enhanced Tracking Protection automatically blocks
over 2000 known online trackers from invading your
privacy and slowing down your pages.” (GooglePlay,
2020)
ICSOFT 2021 - 16th International Conference on Software Technologies
392

Table 3: Example of Results CSV file.
Text Likes Ratings Disability Age Emotional Language Location Privacy
Socio-
economic
Status
The new UI is terrible!
Not user friendly at all.
Especially for older
folks who I would
install it for on their
devices. I want to
revert to older versions
on all of my and client
devices and hope it does
not pose a security risk.
97 1
0.01184
3356798
142966
0.9939
560908
192195
0.06591
875754
51285
0.00169
9474286
364846
0.00493
300658
4214907
0.47160
126164
387484
0.002770
9282290
950773
Figure 6: CSV entry results page with ’By Rating’ option selected.
Table 4: Subset of COVIDSafe app reviews concerning pri-
vacy.
Content
Now you require my location This was my biggest
fear about downloading the app I need to protect my
whereabouts So you have made this app useless to me
Uninstalling
After the latest update this APP has now become a
TRACKING APP It no longer just requires Bluetooth
It now requires Vocation Data The government is now
tracking you so if you don’t want that which you
shouldn’t then uninstall this app It is now a risk to
your privacy and your security
As such, Firefox could be assumed to attract users
more concerned with their privacy, and updates that
threaten to take away this security provoke reviews
detailing users’ frustrations, as seen with the subset
shown in Table 5.
6.2 How Can We Create a Tool That
Accurately Detects and Categorises
Human-centric Issues in Text?
AH-CID is an initial attempt to create a tool that ac-
curately detects and categorises human-centric issues
in text. The web-based user interface provides a user-
friendly interface that can be used by developers. The
model in which the tool is based on is deemed effec-
tive in categorising human-centric discussion in text.
With the metrics from our model, it may be inferred
that our dataset has no bias towards any of its labels,
hence the model is effective in predicting human-
centric discussion in text. This research provides a
baseline and aims to encourage the future research on
more effective and accurate automatic tools to detect
human-centric issues in app reviews.
AH-CID: A Tool to Automatically Detect Human-Centric Issues in App Reviews
393

Figure 7: Results of the training dataset passed through AH-CID for four different apps, with and without setting the threshold.
Table 5: Subset of Firefox Browser app reviews concerning
privacy.
Content
AWU NEW UPDATE!!! ONE REBOOTS EVE
TIME I The AND SERC OR ANYTHING!!!!! Up-
dated review after your response: It had nothing to do
with my speed, this app shut down my phone every
time I tried to open it after the last update and was do-
ing unsettling things to my phone which I did not like
or felt safe with. Moved to another web browser as I
no longer trust your app after the latest update.
Never gave camera access to this app and I am us-
ing pour camera phone, all of sudden camera popped
up and closed for a second while browsing. Then
checked app permission, it had camera access which
I never gave. No privacy in this app. It is not safe.
Installed and formatted mobile.
Doses as a browser, but spams in notifications with
political, pro-censorship agenda, even if notifications
are disabled. Ca not be trusted anymore.
6.3 How AH-CID Can Help Developers
and End-users?
Results from (Alshayban et al., 2020) reflect the im-
portance of accessibility-related awareness to make
app developers becoming ambassadors of accessibil-
ity in their organisations. As discussed in the intro-
duction, the differences between developers and end-
users in terms of HCIs, including age, gender, culture,
and disabilities make it difficult for developers to un-
derstand the end-users’ needs (Grundy et al., 2021).
AH-CID aims to fill in this gap by facilitating the au-
tomatic detection of end-users’ human-centric issues
reported through app reviews by developers. This
would ultimately help end-users to get access to easy
to use software tailored based on their human-centric
needs.
6.4 Threats to Validity
Our study has several limitations, as reported below.
6.4.1 Internal Validity
There are internal threats to the validity of our results.
The first one is the selection of our 24 studied apps.
We considered a wide range of apps with large-scale
and vulnerable end-users to be able to cover as many
human-centric issues as possible. Moreover, since the
manual labeling of all the app reviews was not possi-
ble, we adopted a keywords-based tool to select the
relevant reviews, and therefore this introduces bias
toward our keywords list. However, we have made
our keywords list available to encourage further future
work on it. Furthermore, manually analysis of the app
ICSOFT 2021 - 16th International Conference on Software Technologies
394

reviews may have introduced some bias. However,
the main objective of this paper is to build a dataset
that can be used to train our machine learning tool,
which can be trained on any kind of datasets in fu-
ture. Finally, we selected BR transformation method
with a base classifier of SVM, as the suitable ma-
chine learning algorithm for our problem, based on
the review of the existing algorithms. This paper is
the first attempt in using a machine learning tool to
detect human-centric issues in app reviews and in fu-
ture, other algorithms can be explored and be com-
pared with our method as the baseline.
6.4.2 External Validity
Our findings may not be generalised to all differ-
ent types of app reviews. Moreover, not all users
share their human-centric issues through app reviews,
and therefore we might have missed some essential
human-centric issues. Furthermore, the identified cat-
egories of human-centric issues are exclusive to the
apps we selected and the app reviews we analysed.
This can encourage future research on exploring other
apps and looking into other human-centric aspects
that may not have been covered in our work.
7 RELATED WORK
There have been several works on the mining and
classification of user reviews to understand the feed-
back from users and to provide information to soft-
ware developers to help in the evolution and mainte-
nance of their software applications.
Li et al. developed a framework for analysing
user reviews to understand user satisfaction as an in-
put to support software evolution (Li et al., 2010).
A related study utilised topic modelling and senti-
ment analysis to extract useful topics for the purpose
of requirements engineering (Carre
˜
no and Winbladh,
2013). To minimise the effort required in analysing
user reviews, Di Sorbo et al. introduced a tool for
summarising app reviews into explanatory summaries
for developers (Di Sorbo et al., 2016).
Moreover, in the area of reviews classification,
Panichella et al. introduced a taxonomy for clas-
sifying reviews using a hybrid of natural language
processing techniques, text analysis, and sentiment
analysis (Panichella et al., 2015). Similarly, another
study applied probabilistic methods to classify re-
views into four categories, namely, bug reports, fea-
ture requests, user experiences, and ratings (Maalej
and Nabil, 2015). Finally, the reflection and violation
of human values in app reviews is explored by (Obie
et al., 2021). Their results show that a quarter of the
22,119 analysed app reviews contain perceived viola-
tion of human values in mobile apps, supporting the
recommendation for the use of app reviews as a poten-
tial source for mining values requirements in software
projects (Obie et al., 2021). Our work complements
the studies discussed above, as we also aim to stream-
line the feedback review analysis process. However,
we focus on the automatic detection and classification
of human-centric issues in app reviews.
When it comes to multi-label learning, there pri-
marily exists two main methods to solve the prob-
lem: problem transformation methods and algorithm
adaptation methods. Problem transformation meth-
ods transform multi-label problems into single-label
problem(s) which are then used against models pri-
marily suited for the classification of multi-class la-
bels. Conversely, algorithm adaptation methods use
algorithms directly extended for the use of multi-label
learning (Madjarov et al., 2012). However, problem
transformation methods are simpler and more gener-
alised when categories are stochastically independent
of each other. The human-centric discussion labels
that we have elected to use share no or minor de-
pendencies between them giving warrant to preferring
problem transformation methods.
(Belyakov et al., 2020) utilised several ML tech-
niques to classify bug reports and service support re-
quests. In their study, support vector machine yielded
the highest accuracy based off the proportion of true
positive and true negatives over the total number of
instances. In the study carried out by (Rahmawati and
Khodra, 2015), the authors compared multiple com-
binations of feature selection and multi-label classi-
fication approaches to determine which combination
was most effective in categorising Indonesian news
articles. They found that the problem transforma-
tion algorithms, binary relevance and calibrated la-
bel ranking, using support vector machine (SVM) as
its base learning algorithm, obtained the highest F1
scores. Algorithm adaption models were significantly
improved using feature selection methods which in-
cluded information gain, symmetrical uncertainty and
correlation coefficient while problem transformation
approaches only saw small increases.
Despite large improvements in the algorithm
adaption models, problem transformation approaches
exhibited greater F1 scores (Rahmawati and Khodra,
2015). binary relevance (BR), used by (Cherman
et al., 2011), has low computational complexity in
comparison with other problem transformation meth-
ods. BR scales linearly with the number of binary
classifiers, meaning it is more effective on datasets
with a small number of binary classifiers. However,
AH-CID: A Tool to Automatically Detect Human-Centric Issues in App Reviews
395

the BR method is limited by its strong assumption of
independent labels.
While we have discussed different approaches to
multi-label learning, the main contribution of this
work is not the technical approach applied, but rather
we draw attention to the critical human-centric issues
affecting the users’ experience of software applica-
tions, and the use of app reviews as a valuable proxy
to detect these issues.
8 CONCLUSION
This paper presents AH-CID, a novel tool that has the
means of detecting and analysing human-centric is-
sues in text, to allow developers to ascertain which
issues are adversely affecting their diverse user base.
Using a machine learning approach, a model was con-
structed and deployed with 91.4% accuracy and a
2.1% hamming loss. Also, the training data was bal-
anced resulting in a moderate-high F1 score.
In the future, we plan to investigate a larger set of
apps reviews and human-centric issues using our tool.
Additionally, an empirical study with users on their
perception of human-centric issues is another area for
our future work. We also plan to extend the tool and
add a user review feature for the end-users to use the
tool and detect HCIs in different apps to be able to se-
lect and download apps more wisely, from a human-
centric aspect.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Support for this work from ARC Laureate Program
FL190100035 and ARC Discovery DP200100020 is
gratefully acknowledged.
REFERENCES
Alshayban, A., Ahmed, I., and Malek, S. (2020). Acces-
sibility issues in android apps: State of affairs, sen-
timents, and ways forward. In Proceedings of the
ACM/IEEE 42nd International Conf. on Software En-
gineering, ICSE ’20, page 1323–1334, New York,
USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
AustralianGovernment (2020). Background to covidsafe. In
https://covidsafe.gov.au/background.html.
Belyakov, S., Bozhenyuk, A., Kacprzyk, J., and Rozenberg,
I. (2020). Intelligent planning of spatial analysis pro-
cess based on contexts. In International Conf. on In-
telligent and Fuzzy Systems, pages 10–17. Springer.
Carre
˜
no, L. V. G. and Winbladh, K. (2013). Analysis of
user comments: An approach for software require-
ments evolution. In ICSE.
Cherman, E. A., Monard, M. C., and Metz, J. (2011). Multi-
label problem transformation methods: a case study.
CLEI Electronic Journal, 14(1):4–4.
Di Sorbo, A., Panichella, S., Alexandru, C. V., Shima-
gaki, J., Visaggio, C. A., Canfora, G., and Gall,
H. C. (2016). What would users change in my app?
summarizing app reviews for recommending software
changes. In FSE.
Farooqui, T., Rana, T., and Jafari, F. (2019). Impact of
human-centered design process (hcdp) on software
development process. In 2019 2nd International Conf.
on Communication, Computing and Digital systems
(C-CODE), pages 110–114. IEEE.
GooglePlay (2020). Firefox browser: fast, private & safe
web browser - google play.
Grundy, J., Khalajzadeh, H., and Mcintosh, J. (2020). To-
wards human-centric model-driven software engineer-
ing. In ENASE, pages 229–238.
Grundy, J., Khalajzadeh, H., McIntosh, J., Kanij, T., and
Mueller, I. (2021). Humanise: Approaches to achieve
more human-centric software engineering. In Eval-
uation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering:
15th International Conf., ENASE 2020, Prague, Czech
Republic, May 5–6, 2020, Revised Selected Papers 15,
pages 444–468. Springer International Publishing.
Hartzel, K. (2003). How self-efficacy and gender issues
affect software adoption and use. Communications of
the ACM, 46(9):167–171.
Jack, A. I., Dawson, A. J., Begany, K. L., Leckie, R. L.,
Barry, K. P., Ciccia, A. H., and Snyder, A. Z. (2013).
fmri reveals reciprocal inhibition between social and
physical cognitive domains. NeuroImage, 66:385–
401.
Levy, M. and Hadar, I. (2018). The importance of empathy
for analyzing privacy requirements. In 2018 IEEE 5th
International Workshop on Evolving Security & Pri-
vacy Requirements Engineering (ESPRE), pages 9–
13. IEEE.
Li, H., Zhang, L., Zhang, L., and Shen, J. (2010). A user
satisfaction analysis approach for software evolution.
In PIC, volume 2.
Maalej, W. and Nabil, H. (2015). Bug report, feature re-
quest, or simply praise? on automatically classifying
app reviews. In RE.
Madjarov, G., Kocev, D., Gjorgjevikj, D., and D
ˇ
zeroski,
S. (2012). An extensive experimental comparison of
methods for multi-label learning. Pattern recognition,
45(9):3084–3104.
Mao, J.-Y., Vredenburg, K., Smith, P. W., and Carey, T.
(2005). The state of user-centered design practice.
Communications of the ACM, 48(3):105–109.
Mathews, C., Ye, K., Grozdanovski, J., Marinelli, M.,
Zhong, K., Khalajzadeh, H., Obie, H., and Grundy,
J. (2021). AH-CID: A Tool to Automatically Detect
Human- Centric Issues in App Reviews [Data set].
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4475066.
Miller, T., Pedell, S., Lopez-Lorca, A. A., Mendoza, A.,
Sterling, L., and Keirnan, A. (2015). Emotion-led
ICSOFT 2021 - 16th International Conference on Software Technologies
396

modelling for people-oriented requirements engineer-
ing: the case study of emergency systems. Journal of
Systems and Software, 105:54–71.
Obie, H. O., Hussain, W., Xia, X., Grundy, J., Li, L.,
Turhan, B., Whittle, J., and Shahin, M. (2021). A
first look at human values-violation in app reviews.
In ICSE-SEIS.
Panichella, S., Di Sorbo, A., Guzman, E., Visaggio, C. A.,
Canfora, G., and Gall, H. C. (2015). How can I im-
prove my app? classifying user reviews for software
maintenance and evolution. In ICSME.
Rahmawati, D. and Khodra, M. L. (2015). Automatic mul-
tilabel classification for indonesian news articles. In
2015 2nd International Conf. on Advanced Informat-
ics: Concepts, Theory and Applications (ICAICTA),
pages 1–6. IEEE.
Stock, S. E., Davies, D. K., Wehmeyer, M. L., and Palmer,
S. B. (2008). Evaluation of cognitively accessi-
ble software to increase independent access to cell-
phone technology for people with intellectual dis-
ability. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research,
52(12):1155–1164.
Wirtz, S., Jakobs, E.-M., and Ziefle, M. (2009). Age-
specific usability issues of software interfaces. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEA, volume 17.
AH-CID: A Tool to Automatically Detect Human-Centric Issues in App Reviews
397
