
Sustainable Development of the Health System through the Prism of
Patient Participation in HTA in Bulgaria
Claudia I. Georgieva
a
, Antonia Y. Yanakieva
b
and Alexandrina Vodenicharova
c
Department of Health Technology Assessment, Faculty of Public Health, Medical University - Sofia, Bulgaria
Keywords: Patients, Health Technology Assessment, Sustainable Development, Health System.
Abstract: Background: Several countries worldwide are developing policies aimed at patient participation in healthcare
as a critical element for sustainable development in the field. HTA is an essential part of sustainable
development strategies, and patient involvement as an expert is a mechanism for ensuring transparent, fair,
and equitable healthcare. Aim: The study aims to determine the readiness of patients and patient organizations
in Bulgaria to be included in the HTA process and outline the challenges for their implementation. Materials
and Methods: The study was based on two questionnaires conducted from September 2019 - May 2020. They
involved 563 patients and 53 patient organizations in the Republic of Bulgaria. Various analytical approaches
have been applied for data processing. Results: Patients in Bulgaria are willing to participate in the HTA
process. The survey proves that 67.1% of the respondents would participate in training organized for them.
64.2% would meet with representatives of the HTA institution. 61.2% are willing to assist in the preparation
of HTA strategies and work plans. The main challenge for implementing patients in the process is the low
level of competence in the field, which does not allow equal participation in HTA. For this purpose, it is
necessary to conduct training campaigns and promote the process among patients in our country and allocate
funds to support the inclusion of patients in HTA. Conclusions: Stimulating close cooperation between
patients, HTA institutions, manufacturers, and users of health technologies is the basis for the modern health
system's sustainable development.
1 INTRODUCTION
The sustainable development goals are now steering
the global health and development agendas (Hone,
2018). There is an extensive body of literature
available on sustainable development. Definitions
vary, but in the main they draw out environmental,
economic and social dimensions of the concept,
emphasizing that progress to date has been achieved
at huge cost. The 2005 UK sustainable development
strat- egy sets out five principles (HM Government.
Delivering sustainable development together: shared
UK principles for sustainable development, 3 March
2021) which resonate strongly with the practice of
public health:
living within environmental limits;
ensuring a strong healthy and just society;
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3738-6598
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6418-2788
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4133-0132
achieving a sustainable economy;
promoting good governance;
using sound science responsibly (Adshead,
2006).
Health status in general, as well as, the mortality
rate at various stages of life in developed, developing,
and least developed countries vary based on several
factors. The government/health insurance/private
funds (out-of-pocket, NGOs, private corporations)
spending in health (health expenditures) are few of
the factors that mortality rate varies greatly from
country to country (OECD. Health spending
(indicator), 3 February 2021).
Life expectancy, the morbidity of the population,
quality of life are among the indicators that determine
how effectively a health system functions
(Department of the Environment, Food and Rural
Affairs. Sustainable development indicators in your
Georgieva, C., Yanakieva, A. and Vodenicharova, A.
Sustainable Development of the Health System through the Prism of Patient Participation in HTA in Bulgaria.
DOI: 10.5220/0010586400730080
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 73-80
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
73

pocket. London, 27 February 2021). Among the main
goals of the National Health Strategy of Bulgaria is to
reduce mortality and increase life expectancy while
ensuring the sustainability of the implemented
measures and policies, allowing 2025 Bulgaria to
reach the current European average levels of
demographics (National Health Strategy 2020, 3
March 2021). One of the plan's priority policies to
achieve these objectives is to build and manage a fair,
sustainable development, and efficient health system
focused on quality and results (Ministry of Health of
the Republc of Bulgaria Action Plan for
implementation of the National Health Strategy 2020,
8 March 2021). One of the modern approaches for
implementing the development strategy is the
inclusion of the patient's experience and opinion in
decision-making at different health policy levels. The
process includes integrating patients' competencies at
various decision-making levels and other state
institutions, the National Health Insurance Fund,
HTA institutions, professional organizations, and the
non-governmental sector.
The concept of sustainable development health
care is defined by elements, among which the patient
occupies an important place, namely:
1. The health literacy of the population and the
resulting choices for leading a healthy lifestyle,
sharing responsibility for disease prevention, active
participation of patients in treatment, shared with the
professional skills and care of medical professionals,
skills and readiness for taking care of personal health;
2. Awareness of the population and knowledge of
the rights and obligations of patients;
3. Active participation of patients, which are also
leading aspects for establishing the concept of
sustainable development.
4. An adequate level of health literacy gives
patients self-confidence and confidence in dealing
with illness and making decisions concerning their
health. Personal choice is a leading moral aspect for
establishing the concept of sustainable development
healthcare development.
Health Technology Assessment (HTA) plays an
essential role in decision-making and the allocation of
available resources in modern health systems. Health
technology assessment (HTA) is the process of
systematic evaluation of the properties and effects of
health technology, focusing on its direct and expected
impact and its indirect and unintended consequences
(HTAGlossary, 27 February 2021). The goals of
HTA are achieved by assessing health technologies
against their clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness,
safety, social and economic characteristics (EUR-
ASSESS Steering Committee, 13 Desember 2020)
(Government of Australia. Review of Health
Technology Assessment in Australia, 16 November
2020). HTA has evolved as a key element to support
the distribution of healthcare budgets (Priftis, 2017).
In this sense, the HTA process is an essential part of
sustainable development strategies, and patient
participation as an expert is a mechanism for ensuring
transparent, fair, and equitable healthcare.
Specific practical benefits for the sustainable
development of the health system through the prism
of patient participation in HTA can be identified,
namely:
Fairness - the status of patients as an equal
party in the HTA process, along with other
stakeholders and access to strategies that allow
effective engagement, would prove to the
general public that the decisions taken
regarding the evaluation and reimbursement of
essential health technologies are a fair and just
process;
Equality - the participation of patients in HTA
contributes to the equality of all those in need,
understanding the specific health problems. In
a balanced health system, resources are
distributed fairly among all consumers;
Legitimacy - patient participation in HTA
contributes to greater transparency,
accountability, and trust in healthcare decision-
making;
Capacity building - overcoming the barriers to
patient participation in HTA and joint work
between patients and HTA institutions would
contribute to the sustainable development of
the field based on capacity building of experts
in HTA decision making (Guidance for patient
involvement in HTA, 20 September 2020).
HTA contributes to the distribution and
expenditure of financial resources in the health sector
in growing consumption conditions. The main idea of
the assessment is to give evidence-based point of
view to policy-making (Georgiev, 2017). The
inclusion of the patient as an equal party in HTA is
essential for achieving a balanced health system and
the sustainable development of health care in general.
That is why the present study focuses on patients in
Bulgaria. It is interesting to study their attitudes and
real opportunities for inclusion in HTA.
2 METHODS
The study aims to show patients' attitudes to
participate in the HTA process and the challenges
before their implementation. Involving patients in the
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
74

process would encourage open communication
between different stakeholders in HTA.
The object of this review is patients and patient
organizations in the territory of the Republic of
Bulgaria. The study is multicomponent and complex.
The first component includes research and
analysis of information provided by patients about the
HTA process in Bulgaria. We collected the data based
on a questionnaire in open pharmacies. The survey
questions were answered by 567 patients with various
diseases, giving information about their level of
awareness regarding HTA, their willingness to share
experience and point of view, and to assist HTA
institutions.
The second component includes a survey among
patient organizations in Bulgaria on their point of
view and position related to patients' inclusion in
HTA. Based on 53 responding organizations,
demographic characteristics, general knowledge, and
interest in HTA, activity in training, preparation of
reports, etc., were analyzed.
The survey was conducted in the period
September 2019 to May 2020. Various analytical
approaches have been applied for data processing.
Descriptive statistics are mainly used. Quantitative
variables are represented by the arithmetic mean
(Mean) - a characteristic for estimating the central
trend and a standard deviation (SD) - a characteristic
for estimating the scattering. For categorical
variables, the results are presented by absolute
frequencies (n) - the number of units in a single group
and relative frequencies (%) - the number of units in
a single group relative to the total number of units in
the population.
The Chi-square test or Fisher's Exact Test were
also performed - to study the relationship between
descriptive (category) data with two or more
categories. The study established a connection
between the survey's different questions by
determining Spearman's rho rank correlation
coefficient.
3 RESULTS
Surveyed patients were 567, of which 62.8% (356
patients) were men and 37.2% (211 patients) were
women. The average age of men is 45.03 years, and
women are 48.87 years (Table 1).
Table 1: Age and gender structure of the respondents (Mean
- arithmetic mean, SD - standard deviation, Min - minimum
value, Max - maximum value).
Gender N %
Age
Mean SD Min Max
Male 356 62,8 45,03 12,89 22,00 81,00
Female 211 37,2 48,87 14,21 18,00 86,00
Total 567 100,0 46,46 13,51 18,00 86,00
The majority of respondents have higher
education - 60.5%, 37.4% have primary, and 2.1%
have secondary education (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Educational status of the respondents.
The active patients who took part in the study
were mainly aged between 41 and 60 years. These are
people of active working age, carriers of the disease
(acute or chronic), or disease symptoms. The study
shows that patients with this profile would be most
useful for the HTA process.
To be included in evaluation procedures, it is
crucial to what extent the average patient is familiar
with HTA. 43% of respondents show a complete lack
of knowledge in the field, and 37.4% - "somewhat
low" awareness. The data show that most respondents
are not familiar with the concept of HTA (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Level of knowledge of the concept of Health
Technology Assessment.
Statistical analysis reveals a relationship between
the level of competence in the field of HTA and the
age of patients. The confidence interval p<0.001
indicates the result's statistical significance (Table 2).
2,10%
37,40%
60,50%
Primaryeducation
Secondaryeducation
Highereducation
Veryhigh
8%
High
12%
Somewhatlow
37%
Missing
43%
Sustainable Development of the Health System through the Prism of Patient Participation in HTA in Bulgaria
75
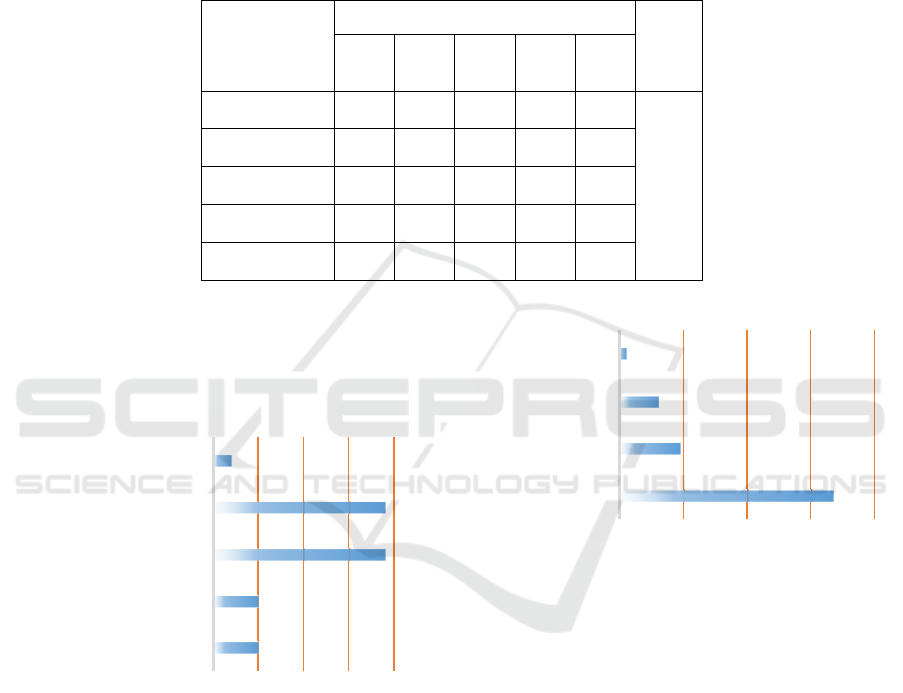
The respondents indicate the highest level of
knowledge of the process under the age of 31. 14.9%
state that they have knowledge at a "very high" and
18.4% in a "high" degree. With age, the percentage of
patients who know the process to a more significant
extent decreases. Younger patients have greater
access to information technology and social
networks. This access allows easier finding of
information and communication with various
specialists, which is essential for higher competence.
There is a tendency for the age group of patients to
increase the percentage of respondents with "low" or
"missing" awareness in the field of HTA.
Table 2: Relationship between the level of knowledge of the concept of HTA and the respondents' age group.
Аge group
p
Up to
30
years
31-40
years
41-50
years
51-60
years
Over
60
years
Very high 13
(14,9)
11
(8,7)
4
(2,9)
12
(9,4)
5
(5,8)
<0,001
High 16
(18,4)
23
(18,3)
7
(5,0)
11
(8,6)
9
(10,5)
Somewhat low 20
(23,0)
41
(32,5)
56
(40,0)
67
(52,3)
28
(32,6)
Missing 38
(43,7)
51
(40,5)
73
(52,1)
38
(29,7)
44
(51,2)
Total 87
(100)
126
(100)
140
(100)
128
(100)
86
(100)
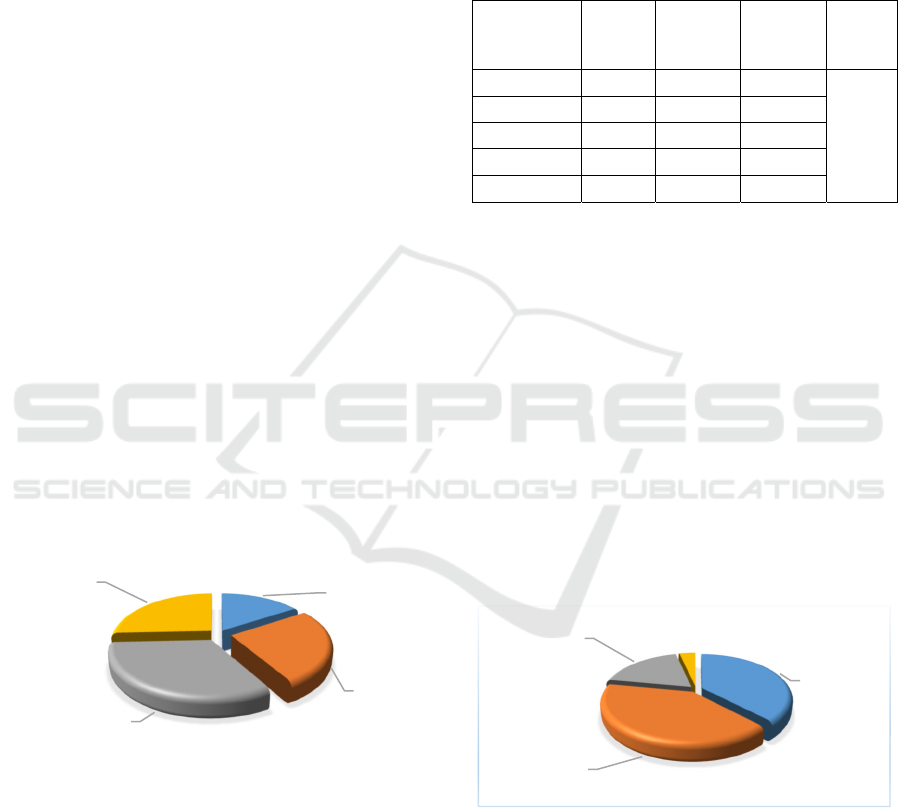
The situation is similar with patient organizations.
For most of them, the concept of HTA is relatively
little known. 38% show "low" and 10% "very low"
competence in the field (Figure 3).
Figure 3: To what extent is your organization familiar with
Health Technology Assessment?
The lack of knowledge and interest on the part of
patient organizations is mainly due to the fact that
they have not had contact or need so far to contact an
HTA institution. 67% of the respondents have never
participated or were not interested in HTA
procedures, and 19% have taken part in such activities
from 1 to 2 times (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Has your organization been directly involved in
making specific health technology assessments?
The results clearly show a low level of knowledge
of the HTA process by patients and patient
organizations in Bulgaria. The lack of information is
also the first challenge for the implementation of
patients in the process. It can overcome the Bulgarian
patient's low factual competence by organizing
training that will increase both their level of
competence and society as a whole. Only in this way
could the patient be an equal member of HTA
committees in decision-making and contribute to
sustainable development in the sector.
Several countries around the world are setting a
positive example in this regard. The Center for Drug
Evaluation (HTA) is the main body in Taiwan dealing
with HTA procedures in which the patient is active.
The institution organizes training seminars for
patients, focused on the legislative framework and the
rules for implementing HTA in the country. Part of
10%
10%
38%
38%
4%
Ican'tjudge(therehasbeen
anysuchneedsofar)
Verylow
Low
High
Veryhigh
67%
19%
12%
2%
Never
From1to2times
From3to5times
Оver5times
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
76
the initiatives to stimulate patient participation is the
convening of an international conference discussing
the global experience in HTA to support and promote
patient activity in local HTA procedures (Center for
Drug Evaluation (CDE), Taiwan, 20 September
2020).
The agency's main priority in Australia
(Australian Department of Health and Aging) is to
decide on the reimbursement of medical devices. The
country's health system's sustainable development is
linked to the profitable consumption of private health
funds. The patient's inclusion guarantees the
observance of public values and compliance with
ethical, legal, and financial norms. The HTA
institution finances a "Health Forum", where patient
representatives (based on illness, membership in
patient organizations) are selected to participate in the
HTA process. "Health Forum" is a place where
patients can exchange experiences with each other,
raise their awareness in the field, and get acquainted
with the methodology of HTA in an understandable
and accessible language (Government of Australia,
16 November 2020).
Of interest for the study is the extent to which
patients in Bulgaria have participated in decision-
making affecting their own health statuses, such as
upcoming manipulations, health activities, or choice
of health technology (Figure 5). 25.7% have never
faced such decisions, and 32.6% say they have met a
selection of different alternatives to a "low" degree.
25.9% were patients who reported a "high" degree of
participation in this type of activity.
Figure 5: Degree of participation in decision-making
concerning forthcoming manipulations or health activities
(needs) related to the patient's own health condition.
The analyzes established a statistically significant
relationship between the frequency with which
patients participated in decision-making and their
educational status (the level of statistical significance
p<0.001) (Table 3). Patients with the lowest
education level most often made decisions in a
"somewhat low" group - 75%. Among patients with
higher education, "high" and "somewhat low" activity
is reported to approximately the same extent when
participating in decision-making affecting their
personal health - 29.2% and 29.4%, respectively.
Patients with secondary education most often answer
"lack" participation in such activities - 36.8%.
Table 3: To what extent have you been involved in
decision-making concerning upcoming manipulations or
health activities (needs) related to your health condition?
Primary
education
n(%)
Secondary
education
n(%)
Higher
education
n(%)
p
Very high 2 (16,7) 13 (6,1) 74 (21,6)
<0,001
High 1 (8,3) 46 (21,7) 100 (29,2)
Somewhat low 9 (75) 75 (35,4) 101 (29,4)
Missing 0 (0) 78 (36,8) 68 (19,8)
Total 12 (100) 212 (100) 343 (100)
Trends show that the majority of patients have not
been involved in making decisions about their health.
The lack of such practices is dictated by established
medical institutions' policies or passivity on the part
of patients.
In order to be honored by experts in decision-
making, the patient must be willing to share personal
experiences and experiences gained in the course of a
disease or care to a loved one with specific disease
symptoms. 40% of patients state that they are fully
prepared, and 37.9% have a "very high" degree of
readiness to share their experience and opinion on
issues affecting their health. (Figure 6). There is a
willingness on the part of patients to openly share
their experience in different approaches to treatment
and therapy.
Figure 6: Willingness of patients to share experiences and
opinions about their medication or therapy.
It has been proven that in order to achieve
sustainable development in the field of healthcare
with the active participation of patients, it is necessary
to conduct training activities.
To the question "Do you want to participate in
pieces of training or seminars organized by an HTA
Very
high
16%
High
26%
Somewhatlow
32%
Missing
26%
Very
high
38%
High
40%
Somewhat
low
19%
Missing
3%
Sustainable Development of the Health System through the Prism of Patient Participation in HTA in Bulgaria
77

institution?", 42.9% answered with a "high" degree of
desire to participate, and 24.2% have a "very high"
desire. "Somewhat low" and "no" willingness to
participate indicate 22.2% and 10.8%, respectively
(Figure 7). The majority of the surveyed patients
would participate in pieces of training organized by
an HTA institution. Patients today are open to new
knowledge. They want to enrich their healthcare
knowledge to more easily overcome the disease or
disease symptoms with which they live.
Figure 7: Patients' desire to participate in training or
seminars organized by the HTA institution.
The survey proves that 67.1% of all respondents
would participate in training organized for them,
64.2% would meet with representatives of the HTA
institution, and 61.2% are willing to assist in
preparing HTA strategies and work plans (Figure 8).
Figure 8: Willingness of patients to engage in activities
related to HTA.
To the question "What is your attitude to
participate in the Health Technology Assessment
process? 46.4% of the respondents give a "high"
answer. "Very high" is the attitude of 18.5% (Figure
9). The majority of respondents have a positive
attitude to participate in the process and are ready to
be involved as an active part in decision-making in
HTA.
Figure 9: What is your attitude to participate in the Health
Technology Assessment process?
The willingness of institutions to cooperate is
largely linked to the patient's desire for his voice to
be heard and contribute to the health sector's
sustainable development. The general attitude is that
the patient has the right to express their views on the
therapy and to share any inconveniences, side effects,
or unpleasant sensations during treatment. Patient
participation in HTA would lead to active
communication and dialogue with the specialist and
selecting the best therapeutic approach. Such an
attitude is precious for HTA institutions because the
inclusion of the patient's point of view ensures open
communication between stakeholders and ultimately
the most rational decisions in the field.
One of the next challenges to the useful inclusion
of patients in HTA is the lack of sufficient resources
(tangible and intangible). Patient organizations were
asked if they had the funds to fund staff to engage in
the HTA process activities. 86% of them state that
they do not have the financial means for such
activities. Only 14% of the respondents have the
necessary funds (Figure 10). Despite the availability
of time, desire, and human resources (patients,
members of the organization), this is not enough.
Additional funds are needed to engage staff to plan
and implement HTA methodologies in participation
in the process. Additional funds are required both for
a direct financial incentive for other staff and for
increasing the knowledge and competence in HTA
practices. Additional funding will allow participation
in training, seminars, purchase of specialized
literature, consulting, etc.
Figure 10: Does your organization have the resources to
fund staff involved in coordinating and contributing to the
Health Technology Assessment process?
Very
high
24%
High
43%
Somewhat
low
22%
Missing
11%
67,10%
64,20%
61,20%
Patientswouldliketake
apartintrainings
organizedforthem
Patientswouldliketo
meetwith
representativesofthe
HTAinstitution
Patientsarewillingto
assistinthepreparation
ofHTAstrategiesand
workplans
Very
high
18%
High
47%
Somewha
tlow…
Missing
9%
14%
86%
Closertoyes
Closertono
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
78

In several countries, patient participation is
financially supported by providing fees for seminars,
transport costs, seat fees, hotel stays, etc. The Dutch
Health Care Institute (the Dutch HTA agency)
conducts an open and transparent process through
collaboration between patients and professionals,
ensuring the reimbursement of patient costs
associated with their involvement in the process.
Patient organizations were asked what they see as
a basic need in their organization for more effective
involvement in HTA. 52% categorically stating
"compiling registers of patients and their
diseases"(Figure 11). 31% believe that one of the
main needs of patient organizations to participate in
HTA is "increasing knowledge and competence in
HTA methodologies". Many believe that they need a
"financial incentive from public authorities to provide
information on HTA" - approximately 15%.
Figure 11: What do you see as your organization's basic
needs for more effective involvement in HTA processes?
4 DISCUSSION
The main goal of the HTA process is to provide
quality, safe and effective health technologies in the
presence of limited resources. Decision-making in
HTA must ensure optimal spending of the financial
resources available to a country's health system. At
the same time, society's vital needs must be met,
which will ensure the health, prosperity, and well-
being of citizens, which is the basis for the sustainable
development of health care in modern countries.
Involving the patient in the HTA process is key to
achieving the principles of sustainable development
in healthcare, namely fair distribution of health
resources, equal access to health care, quality health
technologies with optimal financial resources. The
sustainable development of healthcare links the
economic with the ecological efficiency of social
production. It affirms the principle of equality and
justice by increasing human possibilities and civic
consciousness.
One of the main challenges to the sustainable
development of healthcare is strengthening patients'
participation and role in the care of their health by
increasing health literacy, health responsibility, and
public solidarity. The study shows that patients in
Bulgaria desire and are willing to cooperate with
institutions through their perspective and experience.
Still, the main obstacle to this is the low competence
and knowledge related to the methods of HTA. 43%
of the respondents lack any knowledge in the field,
and 37.4% have insufficient knowledge. At this level
of competence, patients in Bulgaria would not be able
to participate as a legitimate party in the process if
they are not further trained for this purpose.
Patients show a willingness to increase their
knowledge in the field, aware of their contribution to
society, and the chance to help other patients with
their personal experience. The analysis proves a
positive attitude of patients to participate in the HTA
process. In 46.6% of patients, the attitude to
participation is "high", and in 18.5%, it is "very high".
Against this data's background, 25.7% of Bulgaria
patients have never participated in decision-making
affecting their health, and 32.6% have participated in
such activities to a somewhat low degree. The lack of
experience on the part of patients in the choice of
healthy alternatives can be another challenge for the
health system and HTA institutions due to the
impossibility of building patients' capacity with
expert opinion.
The creation of registers is of paramount
importance for patient organizations' work and their
effective participation in HTA. To be of maximum
benefit to the process, HTA institutions must target
patients appropriately. When assessing a specific
health technology, participants must have some
"technical" knowledge. Usually, these are patients in
the field they represent (orthopedics, urology,
cardiovascular diseases), providing expert opinions
Increasingthetime
availableto
employees/expertsto
engagemoreactively
withHTA
Financialincentivefrom
publicauthoritiesto
provideinformationon
HTA
Increasingknowledge
andcompetenceinHTA
methodologies
Compilingregistersof
patientsandtheir
diseases
2%
15%
31%
52%
Sustainable Development of the Health System through the Prism of Patient Participation in HTA in Bulgaria
79

and advice from the patient's perspective living with
the disease.
In summary, the contribution of patient
participation in HTA to achieving sustainable
development in the health sector requires several
legislative changes to stimulate the consideration of
the patient's point of view in his treatment. Changes
are needed in the health policy of medical institutions
and health institutions in the direction of active
involvement of patients in the treatment process,
choice of therapy, treatment specialists, procedures,
and manipulations to become a legitimate participant
in HTA.
5 CONCLUSION
The involvement of patients in healthcare and, in
particular, in the general practice of development and
evaluation of health technologies allows new and
valuable products to be developed and to be directly
addressed to patients and their unmet needs. Patients'
participation in the HTA process is an initial step to
be recognized as a key figure in revealing the
evaluated health technologies' full value. Stimulating
close cooperation between patients, HTA institutions,
manufacturers, and users of health technologies is the
basis for the modern health system's sustainable
development.
REFERENCES
Hone, T., Macinko, J. and Millett, C. (2018). Revisiting
Alma-Ata: what is the role of primary health care in
achieving the Sustainable Development Goals?. The
Lancet, 392(10156), 1461-1472.
HM Government. Delivering sustainable development
together: shared UK principles for sustainable
development, Available from: /http://www.sustainable-
development.gov.uk/what/ principles.htmS.
Adshead, F., Thorpe, A. and Rutter, J. (2006). Sustainable
development and public health: A national perspective.
Public health, 120(12): 1102-1105.
OECD. Health spending (indicator). 2019 Available from:
/https://data.oecd.org/healthres/health-spending.htm.
Department of the Environment, Food and Rural Affairs.
Sustainable development indicators in your pocket.
London, DEFRA, 2006. /http://www.sustainable-
development.
gov.uk/progress/documents/sdiyp2006_a6.pdfS
National Health Strategy 2020.
https://www.mh.government.bg/bg/politiki/strategii-i-
kontseptsii/strategii/nacionalna-zdravna-strategiya-
2020/
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Bulgaria Action Plan
for implementation of the National Health Strategy
2020.
/https://www.mh.government.bg/media/filer_public/20
16/09/12/plan_za_deistvie-nzs_2020.pdf, Accessed 8
March 2021.
HTAGlossary.net. Health Technology Assessment (HTA)
2016.
http://htaglossary.net/health+technology+assessment+
%28HTA%29.
EUR-ASSESS Steering Committee. Health technology
assessment 2009.
https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/technolog
y_assessment/docs/2014_strategy_eucooperation_hta_
en.pdf.
Government of Australia. Review of Health Technology
Assessment in Australia, Available from:
https://info.australia.gov.au, Accessed 16 November
2020.
Priftis, S., Grigorov, E., Georgiev, S. and Yanakieva, A.
(2017). Health Technology Assessment of medical
devices, Health policy and management, 17(2): 68-73.
Guidance for patient involvement in HTA, Available from:
https://www.eupati.eu/health-technology-
assessment/guidance-for-patient-involvement-in-hta/.
Georgiev, S., Yanakieva, A. and Priftis, S. (2017).
Opportunities and challenges related to number of
experts of HTA. 1st International Conference on Public
Health, Proceeding Book, ISBN 978-954-9318-87-6.
Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE), Taiwan, Available
from: /https://www.cde.org.tw/eng/.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
80
