
When the Economy Is Sick: Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on
the Regional Real Economy
Dmitry Rodnyansky
1a
, Elena Drobot
2,3 b
, Ivan Makarov
4,5 c
, Natalia Pakhomova
6d
and Marina
Titova
7e
1
Kazan Federal University, Kazan, Russia
2
PRIMEC Publishers, Moscow, Russia
3
Center of Additional Professional Education, Vyborg, Russia
4
Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, Lipetsk branch, Lipetsk, Russia
5
Institute of Business Career, Moscow, Russia
6
Lipetsk state technical University, Lipetsk, Russia
7
Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration, Lipetsk branch, Lipetsk, Russia
Keywords: Coronavirus, Economic Growth, Economic Decline, Gross Domestic Product, Pandemic, Real Economy,
Restrictive Measures.
Abstract: In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, an economic decline is observed in most regions of the world in
2020–2021. The restrictive measures caused a significant reduction in business activity. Falling incomes and
reduced demand of households should be considered as the main channel for the impact of coronavirus on the
economy. All above mentioned in turn causes a reduction yield and a feedback effect. Russian economy has
been significantly affected both by the deteriorating external economic conditions, such as drop in oil prices,
currency fluctuations, financial market volatility, and by the established accepted and voluntary restrictive
measures. The purpose of the article was to analyze the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the world
economy in general and Russia in particular. The authors examine macroeconomic statisticsЧ on gross
domestic product (GDP) fluctuations and assess possible economic downturns in the world and in Russia.
Changes in the real sector of the economy in the world and in Russia are revealed. The results of the study
can be used for further research on the impact of global virus attacks on the socio-economic systems at all
levels.
1 INTRODUCTION
The spread of the coronavirus and the restrictive
measures imposed everywhere, along with the self-
restrictions of the population, has had a rapid impact
on both national economies and the global economy
as a whole.
In the context of increasing external threats and
impact of the pandemic on business relations and on
the deformation of marketing communication fields
within the borders of different territorial entities, the
system quality in all segments and links of the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1389-1503
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5205-5455
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7698-1875
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5859-1374
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9618-1891
business sphere deteriorates. The instability of the
socio-economic sphere of society increases the
asymmetry of marketing behaviour of subjects and
multipolarity of the impact of different hierarchical
levels of regulation and management on key areas of
entrepreneurship in national economies. The
unbalanced modulating effects of various market
participants contribute to the deepening of
motivational and resource contradictions between the
subjects of relations in the conditions of uncertainty,
instability and increased crisis processes and
Rodnyansky, D., Drobot, E., Makarov, I., Pakhomova, N. and Titova, M.
When the Economy is Sick: Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Regional Real Economy.
DOI: 10.5220/0010588402150221
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 215-221
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
215

phenomena under the influence of an external
coronavirus pandemic explosion.
At the end of 2019 and in the first half of 2020 in
Russia the interest of researchers in reviewing the
state of the economy in the context of a pandemic has
increased.
Recently, there have been a lot of publications on
the main trends in the development of the world
economy as whole and individual countries in the
context of the crisis triggered by the COVID-19
pandemic. In this case the scientific researches of
such experts as Boccaletti et al. (Boccaletti, Ditto,
Mindlin, Atangana, 2020), Drobot et al. (Drobot,
2020; Drobot, Makarov, Nazarenko, Manasyan,
2020), Grigoryev et al. (Grigoryev, Pavlyushina,
Muzychenko, 2020), Grinberg, Pylin (Grinberg,
Pylin, 2020), Milovidov, Asker-Zade (Milovidov,
Asker-Zade, 2020), Varnavskii (Varnavskii, 2020)
should be mentioned.
The scientific papers by Akindinova et al.
(Akindinova, Dabrowski, Shirov, Belousov,
Voskoboynikov, Gurvich, 2020), Dynkin, Telegina
(Dynkin, Telegina, 2020), Kolodko (Kolodko, 2020),
Mau (Mau, 2020), Minakir (Minakir, 2019), Polbin et
al. (Polbin, Sinelnikov-Murylev, Trunin, 2020) were
devoted to the search for ways and means of economy
revitalization in the post-pandemic period.
Researchers are also interested in assessing the
impact of the pandemic on the well-being of the
individual, mental and physical health of the
population. Asai et al. (Asai, Konno, Ozaki, Otsuka,
Arai, Kitagawa, Ofusa, Yabumoto, Hirotsu, Eguchi,
Doki, Ishii, Taniguchi, Vecchione, 2020),
Conversano, Marchi, Miniati (Conversano, Marchi,
Miniati, 2020), Dheeraj (Dheeraj, 2020), Kuklin et al.
(Kuklin, Pecherkina, Tyrsin, Surina, 2017),
Mediawati et al. (Mediawati, Susanto, Nurahmah,
2020), Sharma (Sharma, 2020), and Welling et al.
(Welling, Batlle, Byrd, Burrell, South, Sparks, 2020)
addressed these issues in their articles.
The purpose of the research was to assess the
changes taking place in the real sector of the economy
in the world and in Russia, and to determine the
impact of the spread of coronavirus on the individual
economic sectors.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data from The International Monetary Fund (IMF),
Bloomberg, Bank of Russia, Ministry of Economic
Development of the Russian Federation, Federal State
Statistics Service of the Russian Federation (Rosstat),
etc. provided an empirical base of the study.
The research is based on the analysis of
macroeconomic statistics on gross domestic product
(GDP) and gross value added fluctuations as a whole
and by economic sectors.
The methodology of comparative economic
analysis, methods of induction and deduction based
on the provisions of neoclassical economic theory
were used.
3 RESULTS
3.1 The Outbreak of COVID-19
In 2020 the COVID-19 pandemic has become truly
globalized. The numbers of infected cases and death
globally are increasing so rapidly that the epicenter of
the pandemic is moving fast. Figures 1, 2 show the
total number of confirmed cases and deaths in the
world as a whole and in the G20 countries. According
to the data in September 2020, the numbers of
infected cases globally stand at 25,541,380, with
852,000 death cases. The number is stunningly high
when compared to other similar outbreak in the past;
for example, the SARS outbreak killed 774 and
infected 8,098 between November 2002 and July
2003. However, in September 2020 COVID-19’s
worldwide fatality rate stands at 3.33%, while
66.31% have so far recovered.
While the virus has already reached more than
200 countries and territories, the US, China, and the
Europe appear to be the biggest victims. The top
countries in terms of number of infected cases are the
United States, Brazil, India and Russia (Figure 1).
Initially China was the epicenter with a very high
number of infected and death cases, but that moved
very fast to the Europe making Italy the next
epicenter. At the latest, the US tops the list with
6,088,672 confirmed cases and 183,066 deaths,
making the country the latest epicenter of the
diseases, according to the data in September 2020.
Except for the USA, Brazil, India, Mexico, Great
Britain, Italy, France and Spain leads by the number
of deaths caused by COVID-19 (Figure 2).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
216
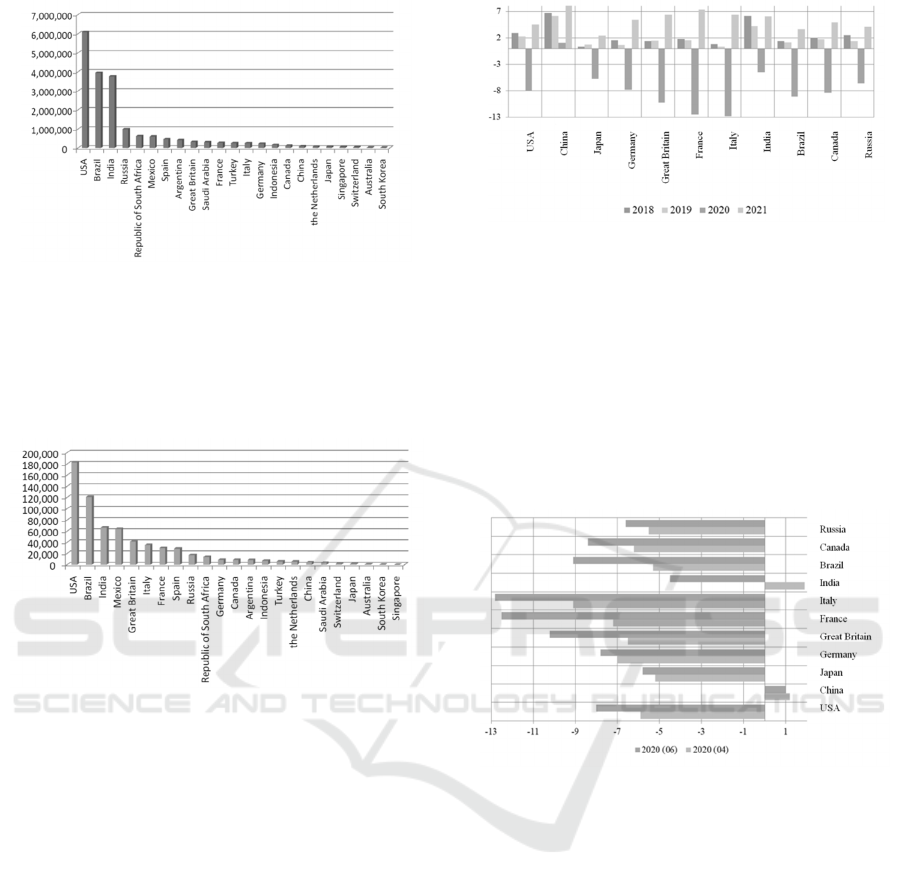
Figure 1: Numbers of COVID-19 infected cases in G20
countries, September 2020
Source: compiled by the authors according to: Trading
Economics. URL:
https://ru.tradingeconomics.com/
(Date of access 07.08.2020).
Figure 2: Numbers of deaths caused by COVID-19 in G20
countries, September 2020
Source: compiled by the authors according to: Trading
Economics. URL:
https://ru.tradingeconomics.com/
(Date of access 07.08.2020).
3.2 A Crisis Like No Other: Impact in
Figures
The constant updating data indicate deterioration in
long-term forecasts. Thus, the current situation is
more complex than it has been previously estimated.
This situation was very clearly described in the
headline of the IMF Bulletin in June 2020 “A Crisis
Like No Other”. By the way, the IMF itself
significantly revised its forecast in an unfavorable
direction. Thus, according to the IMF forecast, only
China will maintain positive GDP growth in 2020
(Figure 3).
Figure 3: Real and
projected
GDP growth/decline, %
Source: compiled by the authors according to the IMF.
Many countries suffered from several types of
crises both in the economic and health sectors in the
first and second quarter of 2020.
According to the IMF experts, the total loss of
global GDP in 2020–2021 will reach about $9 trillion.
And this is more than the combined size of the
Japanese and German economies (Figure 4).
Figure 4: The IMF forecasts for GDP decline, April – June
2020, %
Source: compiled by the authors according to the IMF.
The negative impact of the pandemic on
employment in percentage terms is more than it is in
relation to GDP (Walmsley, Rose, Wei, 2020). This
is due to the fact that most service sectors, especially
in the most economically developed countries such as
the United States and Europe, tend to be more labour-
intensive. And their closure has a more negative
impact on employment than on the main sectors of the
economy.
The uncertainty increases with each new forecast
for the impact of coronavirus on national economies.
In addition, the lack and lag of data significantly
complicate the objective assessment of changes.
Over the past few years, there has been a tendency
to reduce the growth rates of developed and
When the Economy is Sick: Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Regional Real Economy
217
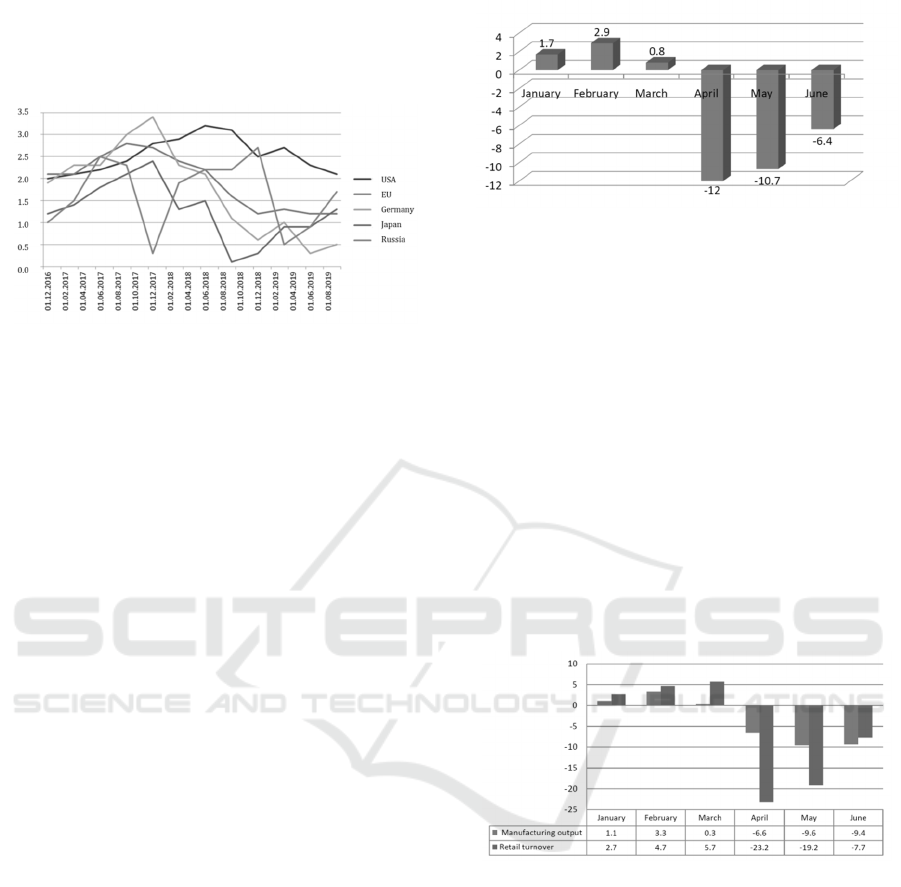
developing countries (Figure 5), which, in the context
of the combined impact of the pandemic and the
aggravation of the situation in the oil market, has a
negative synergistic effect on the Russian economy.
Figure 5: GDP growth rates in developed economies and
the Russian Federation, quarterly data, %
Source: compiled by the authors according to Rosstat, Bank
of Russia, and Bloomberg.
The Russian economy has been significantly
affected both by the deteriorating external economic
conditions (drop in oil prices, currency fluctuations,
financial market volatility) and by the restrictive
accepted and voluntary measures. Falling incomes
and reduced demand of households should be
considered as the main channel for the impact of
coronavirus on the economy. All above mentioned in
turn causes a reduction yield and a feedback effect.
The assessment of the decline in economic
activity in Russia remains very ambiguous: from -
4.3% in the HSE consensus forecast to -6% in the
World Bank forecast and -6.6% according to the IMF
forecast.
In our opinion, the main effect of restrictive
measures will be reflected in the reduction of
consumer demand and investment, which accordingly
determines the main vector of anti-crisis measures.
The restrictive measures and lockdown caused a
significant reduction in business activity.
Thus, according to the Russian Ministry of
Economic Development, GDP decreased by 12% in
April 2020 compared to the corresponding period of
the 2019. The decline was about 10.7% in May 2020
and 6.4% in June 2020 (Figure 6). The gradual
dropping of restrictions contributed to the
improvement of dynamics in May – June 2020. At the
same time, according to the Bank of Russia, the
annual decline in GDP may reach 9–10% in the
second quarter of 2020.
Figure 6: GDP growth/decline rate in 2020,
as a
percentage of the
previous year's corresponding period
level
Source: compiled by the authors according to the data of the
Ministry of Economic Development of Russia.
The decline in industrial production had a
corresponding dynamics. The largest decline
occurred in the manufacturing, as the restrictions
were added to the reduction in demand in related
industries. As a result, production decreased by -10%
in April 2020 and -7.2% in May 2020.
The pandemic also had a significant impact on
retail sales. And as it was expected, the decline was
more in non-food products sector (-36.4% in April
2020 and -29.2% in May 2020, compared to the
corresponding period of 2019) (Figure 7).
Figure 7: Growth/decline rates of industrial production and
retail trade turnover in 2020,
as a percentage of
the
previous year's corresponding period level
Source: compiled by the authors according to the data of the
Ministry of Economic Development of Russia.
Food retail turnover was less affected by the
decline, with a drop of 9.2% and 8.6%, respectively.
The reduction of the retail sales decline in June 2020
was mainly due to a gradual recovery in demand for
non-food products, which in turn has had a positive
impact on the accordingly oriented manufacturing
industries
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
218

Investment activity also suffered a significant
negative impact of lockdown. The level of investment
in 2020 was the lowest in the previous five years.
Similar trends are observed in the production of
investment goods, transportation, and import of
machine-building products. It should be taken into
account that the growth rate of investment in fixed
assets in Russia has been declining recently. Even in
the updated macroeconomic forecast of the Ministry
of Economic Development of the Russian Federation,
published on September 30, 2019, expectations for
the growth of investment in fixed assets in the coming
years were lowered for various reasons. The forecast
for investment dynamics was lowered from 3.1% to
2.0% in 2019.
At the same time, it is worth paying attention to
the observed heterogeneity in the growth rates by
industry or sector. A significant increase in
investment activity in some sectors is taking place
against the background of a significant slowdown in
others.
Considering the dynamics of investment by
industry or sector (Figure 8), we jump into
conclusion that many outsider industries are included
in the list approved by the Government of the Russian
Federation that are most affected by the deterioration
of the situation as a result of the new coronavirus
infection.
Figure 8: Growth rates of investment in fixed assets in
Russia by economic sectors in 2019,
as a percentage of
the
2018 level
Source: compiled by the authors according to Rosstat data.
According to experts, the COVID-19 pandemic in
Russia affected about 4.17 million companies and
individual businessmen out of a total 6.05 million,
i.e. about 67% of small, medium-sized and large
enterprises and individual businessmen.
A reduction in the number of SMEs, a decrease in
production volumes and financial indicators
deterioration can also lead to a decrease in the share
of SMEs’ production in GDP.
According to a joint study by NAFI and Forbes in
June 2020, 76% of companies reported revenue
reduction, 66% noted demand reduction in, and
36.5% indicated reduction in the number of suppliers.
The impact of the coronavirus pandemic has a
serious impact on the internal labour forces. In
particular, the coronavirus affected the motivation of
employees to implement their work activity and
professional adaptability to the challenges of a
changing unstable market.
The motivation of the labour resource to implement
its innovation capacity has decreased by 23–25%. For
example, experts estimate that a 22.4% drop in
employment in the United States over the three-
month closing period means 35.2 million workers
over that period (Walmsley, Rose, Wei, 2020).
4 DISCUSSION
The vulnerability of certain countries as a result of the
negative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic is
explained to a certain extent by the lack of mutual
international support to ensure sustainable
development (Barbier, Burgess, 2020).
The COVID-19 pandemic contributed to a serious
disruption in global value chains and pushed the
world economy into recession (Coveri, Cozza,
Nascia, Zanfei, 2020), distorting established ties and
destroying the balance of interests, which became
more focused on political rather than economic
conditions. At the same time, the pandemic has
revealed opportunities for revising industrial and
economic policies in managing the development of
national economies, without looking at the pressure
of the multidirectional forces of globalization and
deglobalization.
Thus, the study of the impact of the pandemic
on socio-economic processes in the economies of
different countries (including Russia) indicates
destructive phenomena in the industry segments of
national economy that hinder the innovative
development and form an increasing internal
antagonistic tension in the system of relations
between different stakeholders, i.e. between business
and employees, between business and government,
between stratification classes and society, etc.
(Shchepakin, Gubin, Khandamova, 2019). Russia
accepted the challenge of the pandemic as an
objective reality, which strongly dictated the
requirement for all stakeholders of the socio-
economic process to seek a consensus of interests not
When the Economy is Sick: Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Regional Real Economy
219

only within the country, but also at the level of the
world community.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The pandemic and related restrictions have had a
negative impact on macroeconomic indicators. There
is a recession in all regions of the world. And like any
economic crisis, it is characterized by economic
decline and reduction in business activity,
unemployment increase, and decrease in investment
activity.
Sudden outbreak of coronavirus disease in 2019
led to a global commodity downfall
(Rajput, Changotra, Rajput et al., 2020). And it
greatly affected the demand, as well as the supply of
goods. The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a major
disruption to global value chains (Coveri, Cozza,
Nascia, Zanfei, 2020).
The oil market had been severely damaged by a
sharp collapse in demand, mainly due to travel
restrictions, which also led to a sharp drop in oil
prices. Prices of precious and industrial metals also
fell down, although the drop in prices was less than
that of oil prices. The agricultural sector is still one of
the least affected by this pandemic because of its
indirect link to economic activity. However, the final
impact of the COVID-19 pandemic will largely
depend on the severity and duration of its spread, but
it is expected to have long-term consequences
(Rajput, Changotra, Rajput et al., 2020).
An effective program of state support measures
will be required to overcome this situation.
It seems that by the end of 2021, the
macroeconomic situation may change, both for the
better and for the worse. But an improvement in
Russia's macroeconomic situation can be expected if
the optimistic forecast of an increase in oil prices on
world markets to the pre-crisis level of $100–150 per
barrel comes true.
As for the time scale of the Russian economy
recovery in terms of GDP growth, there are two
possible scenarios.
In accordance with an optimistic scenario (with
oil prices growth), the Russian economy will be able
to recover to pre-crisis level of 2019 by mid-2021. If
we consider a pessimistic scenario, which, in our
opinion, looks more realistic, then it will take at least
three years to overcome the consequences of the
crisis, and only by the middle of 2023 Russia will be
able to cope with the crisis in the economy.
REFERENCES
Akindinova, N.A., Dabrowski, M.P., Shirov, A.A.,
Belousov, D.R., Voskoboynikov, I.B., Gurvich, E.T.
(2020). The prospects of Russian economic growth
recovery (Proceedings of the roundtable discussion at
the XXI April international academic conference on
economic and social development). Voprosy
Ekonomiki, 7:5–50. doi: 10.32609/0042-8736-2020-7-
5-50. (In Russ.)
Asai, A., Konno, M., Ozaki, M., Otsuka, C., Arai, T.,
Kitagawa, T., Ofusa, K., Yabumoto, M., Hirotsu, T.,
Eguchi, H., Doki, Y., Ishii, H., Taniguchi, M.,
Vecchione, A. (2020). COVID-19 drug discovery using
intensive approaches. International Journal of
Molecular Sciences, 21(8):2839.
Barbier, E.B., Burgess, J.C. (2020). Sustainability and
development after COVID-19. World Development, 11.
doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105082.
Boccaletti, S., Ditto, W., Mindlin, G., Atangana, A. (2020).
Modeling and forecasting of epidemic spreading: the
case of COVID-19 and beyond Chaos. Solitons &
Fractals, 135:109794.
Conversano, C., Marchi, L., Miniati, M. (2020).
Psychological distress among healthcare professionals
involved in the COVID-19 emergency: vulnerability
and resilience factors. Clinical Neuropsychiatry, 17(2):
94–96.
Coveri, A., Cozza, C., Nascia, L., Zanfei, A. (2020).
Supply chain contagion and the role of industrial policy.
Journal of Industrial and Business Economics,
47(3):467–48. doi: 10.1007/s40812-020-00167-6.
Dheeraj, K. (2020). Analysing COVID-19 news impact on
social media aggregation. International Journal of
Advanced Trends in Computer Science and
Engineering, 9(3):2848–2855.
Drobot, E.V. (2020). The impact of the pandemic COVID-
19 on the US labour market. Ekonomika truda, 7 (7):
577–588. doi: 10.18334/et.7.7.110715. (In Russ.)
Drobot, E.V., Makarov, I.N., Nazarenko, V.S., Manasyan,
S.M. (2020). Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the
real economy. Ekonomika, predprinimatelstvo i pravo,
10 (8):2135–2150. doi: 10.18334/epp.10.8.110790. (In
Russ.)
Dynkin, A., Telegina, E. (2020). Pandemic Shock and the
World after Crisis. World Economy and International
Relations, 64(8):5–16. doi: 10.20542/0131-2227-
2020-64-8-5-16.
Grigoryev, L.M., Pavlyushina, V.A., Muzychenko, E.E.
(2020). The fall into 2020 recession... Voprosy
Ekonomiki, 5:5–24. doi: 10.32609/0042-8736-2020-5-
5-24. (In Russ.)
Grinberg, R.S., Pylin, A.G. (2020). Eurasian Economic
Union: Main Development Trends amid Global
Uncertainty. Economy of Region, 16(2):340–351. doi:
10.17059/2020-2-1.
Kolodko, G.W. (2020). After. Economics and politics of the
post-pandemic world. Voprosy Ekonomiki, 5:25–44.
doi: 10.32609/0042-8736-2020-5-25-44. (In Russ.)
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
220

Kuklin, A.A., Pecherkina, M.S., Tyrsin, A.N., Surina, A.A.
(2017). Methodological Tools for Detection of Risks to
the Welfare of the Individuals and the Territory of
Residence. Economy of Region, 13(4):1030–1043.
Mau, V.A. (2020). Economics and politics in 2019–2020:
Global challenges and national answers. Voprosy
Ekonomiki, 3:5–27. doi: 10.32609/0042-8736-2020-3-
5-27. (In Russ.)
Mediawati, A.S., Susanto, R., Nurahmah, E. (2020). The
routes of COVID-19 transmission: a literature review.
Journal of Critical Reviews, 7(6): 722–724.
Milovidov, V., Asker-Zade, N. (2020). Protectionism 2.0:
New Reality in the Age of Globalisation. World
Economy and International Relations, 64(8):37–
45. doi: 10.20542/0131-2227-2020-64-8-37-45.
Minakir, P.A. (2019). Russian Economic Space: Strategic
Impasses. Economy of region, 15(4):967–980. doi:
10.17059/2019-4-1. (In Russ.)
Polbin, A.V., Sinelnikov-Murylev, S.G., Trunin, P.V.
(2020). The economic crisis of 2020: Reasons, policies
to deal with and further development of the Russian
economy. Voprosy Ekonomiki, 6:5–21. doi:
10.32609/0042-8736-2020-6-5-21. (In Russ.)
Rajput, H., Changotra, R., Rajput P. et al. (2020). A shock
like no other: coronavirus rattles commodity markets.
Environment Development and Sustainability, 8. doi:
10.1007/s10668-020-00934-4. URL:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10668-020-
00934-4 (Date of access 03.09.2020).
Sharma, A.K. (2020). Novel coronavirus disease (COVID-
19). Resonance, 25(5):647–668.
Shchepakin, M. B., Gubin, V.A., Khandamova, E.F.
(2019). Marketing-resource approach to crisis
management of a priori unstable socio-economic
systems. Vestnik of Astrakhan State Technical
University. Series: Economics, 1:113–136. doi:
10.24143/2073-5537- 2019-1-113-136. (In Russ.)
Varnavskii, V. (2020). Drivers of Global Economy. World
Economy and International Relations, 64(7):5–16. doi:
10.20542/0131-2227-2020-64-7-5-16.
Walmsley, T.L., Rose, A., Wei, D. (2020). Impacts on the
US macroeconomy of mandatory business closures in
response to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Applied
Economics Letters, 8. doi:
10.1080/13504851.2020.1809626. URL:
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/135048
51.2020.1809626 (Date of access 03.09.2020).
Welling, P.A., Batlle, D., Byrd, J.B., Burrell, L.M., South,
A.M., Sparks, M.A. (2020). Rigor before speculation in
COVID-19 therapy. American Journal of Physiology -
Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology,
318(5):L1027–L1028.
When the Economy is Sick: Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Regional Real Economy
221
