
Financial Sustainability of the Region after the Pandemic and Factors
Affecting Its Characteristics
Lyuza Z. Bayguzina
a
, Zilya Z. Safina
b
and Asatur A. Sukyasyan
c
Bashkir State University, Karl Marx street 3/4, Ufa, Russian Federation
Keywords: Financial Sustainability, Region, Banking Sector, Pandemic, Evaluation Indicators, Innovation Products,
Biometric USB Tokens.
Abstract: The article reveals the theoretical essence of the category «financial stability of the region», has detected
distinctive features of the financial system in conjunction with the economic growth of the region. In the
authors' opinion, the most significant factors influencing the financial stability of the region after the pandemic
are highlighted. On the example of the subject of the Russian Federation - the Republic of Bashkortostan, the
banking factor and its recovery after the pandemic are considered. The authors cite domestic experience in
the development and implementation of banking services for remote customer service in the Republic of
Bashkortostan. The pandemic turned out to be the push that activated their internal mechanisms and launched
those processes that can no longer be stopped. In connection with the digitalization of the banking sector and
the development of digital technologies, society has a natural demand for new and modern banking products
and services. The emergence of new banking opportunities for the population and business that meet the needs
of the digital world increases the competitiveness of the country's economy in its entirety.
1 INTRODUCTION
The purpose of the article is to consider the factors
affecting the financial stability of a region after a
pandemic using the example of a certain region.
The issues of regional financial stability and the
role of state regulation in the processes of financial
stability have attracted great attention of the scientific
world community, which is reflected in numerous
studies of domestic and foreign academic economists.
First of all, two categories should be identified:
the first is sustainability and the second is financial.
2 RESEARCH METODOLOGY
Methodological approaches are complemented by
special methods of economic science: statistics,
methods of regression analysis, factor assessment of
the main directions of development of the financial
system, financial stability. A certain place supposed
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7830-8633
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9364-1311
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6389-8899
to be allocated to mathematical modeling associated
with the calculations of the banking factor to identify
financial stability.
Consider several definitions of «sustainability»
given by the following authors A. Bryachikhin
(Bryachikhin, 1997) defines that «the stability of the
region is connected with the restoration of a normal
social, economic and political situation in it. For this,
it is necessary that the territorial authorities more
fully and effectively identify local opportunities,
implement the needs, interests and expectations of
residents, firmly and consistently protect them from
negative influences, including competition, elements
and abuse of the wild market».
The author N. Timchuk (Timchuk, 1980) sees the
stability of the territorial system in the invariability of
its behavior until new goals appear. According to the
researcher, in hierarchical territorial systems,
subsystems of the lower levels are most susceptible to
changes for a number of reasons. At the upper levels,
due to diffusion and some mutual smoothing of the
292
Bayguzina, L., Safina, Z. and Sukyasyan, A.
Financial Sustainability of the Region after the Pandemic and Factors Affecting its Characteristics.
DOI: 10.5220/0010589602920297
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 292-297
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

unstable parameters of the lower structures, a
relatively high stability is achieved.
V. Leksin and A. Shvetsov (Leksin and Shvetsov,
1997) proposed an interdisciplinary interpretation of
sustainability. They believe that its most important
feature is «ong-term preservation of conditions for the
reproduction of the potential of the territory in the
mode of balance and social orientation».
Now let's look at the category «financial stability»
and try to identify the factors that affect it. Today
there is no clear interpretation of the category
«financial stability of the region” and many are trying
to associate it with «financial potential», «financial
attractiveness», «inancial condition», «budget», etc.
Author Zenchenko S.V. (Zenchenko, 2008)
«Financial sustainability refers to the balance of cash
incomes and expenditures of the region and their
proportional change under the influence of external
and internal factors in order to ensure the powers of
the regional government, its socio-economic and
political development in the current and long-term
conditions».
Another important concept is the economic space
of territories, its heterogeneity. Therefore, the authors
believe that «when considering economic systems,
economic ties, various processes in the economic
space, within the framework of regional studies, can
seen connection with geographic coordinates. The
geographical basis, due to the differences in the
geographical size of the units under consideration,
requires taking into account not only absolute
changes in indicators, but also operating with the
concept of density. So, analyzing indicators (total
income of the population, production and
investment), scientists often correlate their values
with the areas of these territories or population in
order to bring them into a comparable form (Grishin
et al., 2020).
Thus, the concept of «financial stability» can be
presented in the form of a comparative characteristic
in table 1.
Table 1: Differences between the concepts of «financial
stability of the region» and «stability of the regional
financial system».
Сomparison
signs
Financial stability
of the region
Stability of the
regional financial
system
Category
conten
t
financial social-economical
Concept general economic
equilibrium
sustainable
developmen
t
Subject
(sphere)
formation and use
of financial
resources of the
region
systemic signs and
structural and
functional
characteristics of
financial relations in
the region
An object financial position
of the region
(financial
resources, their
sources, result of
use)
integral property of
the financial system
as a driver of
economic growth
and development of
the regio
n
Subjects of
management
Central Bank of
the Russian
Federation,
Ministry of
Finance in the
region and others
a special body for
monitoring and
systemic
management within
the regional Ministry
of Economy and
Investment
Developmen
t
Criteria for
evaluation
effective
functioning and
development of
local financial
subsystems of the
region
socio-economic,
budgetary and tax,
investment,
structural and
functional
Assessment
indicators
quantitative and
qualitative
indicators of
various financial
sub-systems
(banking, fiscal,
insurance, etc.)
arterial indicators of
stability of the
regional financial
system, comparison
with threshold values
*compiled by the author (Zotova, 2015)
As noted by the author A.I. Zotova (Zotova, 2015)
the financial system of the region should be
considered as a single entity, and not just a union of
various (banks, budget) subsystems, albeit
interconnected, as their real interaction aimed at
effective and sustainable development of the territory
in the interests of solving social and economic
problems. We fully adhere to the opinion of the
author.
Thus, in our opinion, one of the qualitative
properties of the financial system of the country and
the regions is stability, which in general is interpreted
as the ability of the system to maintain its structure
under the influence of disturbing factors or return to
its previous state after a violation.
Financial Sustainability of the Region after the Pandemic and Factors Affecting its Characteristics
293

3 MAIN PART RESEARCH
RESULTS
In our opinion the financial stability of the region
depends on the following factors:
The tax factor shows the role of budgetary and tax
policy in the region. In this factor, on the one hand,
there are enterprises, small and medium-sized
businesses that generate financial resources, which
are the main taxpayers. On the other hand, business
entities influence the formation of the financial
system of the region and the processes taking place in
it, there are government bodies that create a
regulatory framework, mechanisms and incentives
for the development of financial potential, public-
private partnership, the real sector of the economy,
including getting rid of tax mechanisms. Improving
the efficiency of the functioning of the financial
system of the region largely depends on the budgetary
system of the region, the volume of fiscal powers of
state authorities and local self-government, as well as
the efficiency and effectiveness of spending budget
funds, including financial.
In support of the above, we present the arguments
of the authors (Mol-Gomez-Vazquez et al., 2020) The
promotion of a more stable European banking system
has become a priority which, not doubt, will bring
important benefits to firms. However, bank stability
comes with stronger regulations that could harm the
access to finance of small and medium-sized
enterprises (SMEs), which are highly dependent on
bank financing. We provide new evidence on the
association between the stability of a country's
banking system and SMEs access to finance through
the study of borrower discouragement. We analyze
20,207 observations gathered among 16,382 firms
operating in the EU-28 during the period 2011-2018.
Applying multilevel methodology, our results show
that SMEs operating in countries with more stable
banking systems are less likely to be discouraged
from applying for a loan. Working to achieve a more
stable banking system does not seem to harm the
access to finance of SMEs.
The investment factor shows the level of
investment activity in the region, the role of financial
and non-financial organizations in this process.
Relative financial self-sufficiency and independence
as attributes of the regional financial system are
directly related to the system's ability to
independently generate the required volumes.
As part of the article, we will consider the
investment factor and highlight the banking sector.
The first factor influencing financial stability is
the banking sector.
The decrease in the number of commercial banks
and the weakening of competitive positions in the
regional banking market are signals of the crisis state
of the region as an integral developing system.
However, how much effective a bank-supported
economic recovery will be depends on the soundness
and health of the commercial banks themselves.
Losses from loan defaults and increases in risk-
weighted assets will deplete banks' capital. The extent
will depend on the spread of COVID-19 and the
effectiveness of the public health response and
mitigation measures.
The crisis which was caused by coronavirus has
highlighted the shortcomings of the European Union
(EU), which manifested itself after the global
financial crisis. It should be highlighted that self-
imposed restrictions within the EU have prevented
recovery over the past decade. However, the
suspension of the Stability and Growth Pact and
recent measures by the European Central Bank have
broken the shackles. We recommend national
governments use the restored sovereignty within the
EMU and not wait for common European decisions.
In addition, we provide policy suggestions in line
with EU's current structure (Ehnts and Paetz, 2020).
Reinders, H. J., Schoenmaker, D., & Van Dijk, M.
A. (Reinders et al., 2020). It should be clear that a
quick return to pre-COVID-19 policies in the EU
would have devastating consequences for economic
and political reasons. If governments would try to
consolidate their budgets, as they did during the years
after the financial crisis, a long-lasting depression is
the most likely outcome.
Southern European countries have already been in
a bad economic shape before COVID-19. The
unemployment rates in 2019 for Spain (14.1%), Italy
(10.0%) and Greece (17.3%) were in the double
digits, with a recession in Germany looming at the
end of the year. In Greece and Italy, real GDP per
capita was still lower in 2019 than in 2007. If this
countries would be forced to return to austerity
measures, they might prefer to leave the Euro.
Austerity policy cannot be successful within the next
few years for the same reason it has not been
successful in the past decade: It exacerbates the
economic downturn and the substantial fall in income
increases both public deficits and debt-to-GDP ratios
(Saez and Zucman, 2020).
According to the review of the banking sector of
the Bank of Russia for May 2020, the profit of
Russian banks fell to 45.4 billion rubles from 51.2
billion rubles in April and from 218.5 billion rubles
in March. At the same time, there was a significant
increase in deductions to reserves from 47 billion
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
294

rubles to 106.5 billion rubles, which, possibly, was
one of the main reasons for the decline in profit.
However, it should be noted that the growth of
overdue debt was not catastrophic (plus 22 billion
rubles only due to the retail sector).
Currently, the situation in the Russian financial
sector has begun to improve compared to the
beginning of the pandemic. However, the economic
downturn, decrease in the income of organizations
and the population led to an increase in credit risks.
Regulatory measures have facilitated loan
restructuring and allowed borrowers to improve their
financial position. A significant part of the Bank of
Russia's measures in connection with the pandemic
was planned for the period from March 1, 2020 to
September 30, 2020. At the same time, it is planned
that the way out of the emergency situation will be
gradual, so that banks adapt and are not forced to
reduce lending to the economy.
Compared to the beginning of the pandemic, the
liquidity situation in the banking sector has begun to
improve. In June and July 2020, the number of
citizens' ruble deposits began to increase
(Sokolinskaya and Zinov'yeva, 2020).
The volume of highly liquid assets participating in
the calculation of the short-term liquidity ratio on the
balance sheets of systemically important credit
institutions increased from March 1, 2020 to July 1,
2020 by 1.3 trillion rubles and amounted to 8.9 trillion
rubles. The Bank of Russia switched to a soft
monetary policy, lowering the key rate to 4.25%, as a
result of which banks have the opportunity to reduce
interest rates on loans, including for small and
medium-sized businesses.
The coronavirus pandemic served as a kind of
catalyst for the digital transformation of the banking
sector. Judging by the experience of recent months, it
is digital transformation that sets the vector for the
development of their business processes for banks.
During the pandemic, many citizens are convinced of
the benefits of remote services and plan to use them
after it ends.
Consider the banking factor at the regional level
of the Republic of Bashkortostan (Bayguzina et al.,
2019).
One of the innovations is the calculated economic
benefits of implementing multi-factor authentication
based on biometric USB tokens. Nevertheless, there
are still restrictions and some drawbacks of such
systems. Even interfaces of the best Russian Internet
banks come up with some absurd solutions with
regard to the end user, which is mainly imposed by
various severe restrictions of software modules and
platforms.
It is essential to present some statistical data in
order to make the study verifiable. The paper presents
economic benefits from multifactor authentication
based on biometric USB-tokens. Initially, it is
suggested to introduce such systems only for legal
entities since they represent the target group when
dealing with cyberattacks due to large sums of money
available in accounts. The study of the market of
biometric USB-tokens was carried out. According to
its results, a solution of ISBC group - ESMART
Token GOST - was selected. This represents a
cryptographic protection of information with
hardware support of Russian cryptographic
algorithms based on domestic MIK 51 chip
manufactured by JSC NIIME and Mikron Plant.
The group of companies known as Mikron created
the entire production chain from design to production
of the ultimate product, which allows producing the
whole range of high-tech products and solutions
aimed at the mass market: RFID chips and tags, SIM
cards, transit and bank cards with a chip, protected
microchips for social cards and state identification
documents. Mikron annually produces more than 400
million RFID tags, 50 million bank chips, 30 million
bank cards, more than 5 million chips for the
production of biometric passports and electronic
documents. Mikron is also the largest Russian
exporter of industrial microchips - more than 500
million microchips manufactured by Mikron are
annually exported to Europe and South-East Asia for
enterprises that produce various electronic
equipment. The choice of tokens based on
microelectronics produced by Mikron is justified by
its ability to provide the necessary volume of
production, without purchasing ready-made foreign
solutions and technologies. Moreover, it eliminates
the need to purchase an expensive license for their
production and use, which is especially complicated
under sanctions. This token exemplifies how
biometrics allows effectively solving different tasks
related to information security and protection. The
advantages of such tokens include low cost, ability to
be used as an electronic signature, and, in comparison
with smart cards, there is no need for special readers,
the cost of which is several times higher than the cost
of USB-Tokens, with the same level of security
provided. The secure controller, embedded in
ESMART Token GOST, provides protection against
attacks such as SPA, DPA, DFA. The intrusion
sensors, light, impulse noise, voltage, temperature, as
well as hardware integrity control sensors and
erasability of EEPROM secure key information to
protect against breaking the chip and unauthorized
access. EEPROM is an electrically erasable
Financial Sustainability of the Region after the Pandemic and Factors Affecting its Characteristics
295
reprogrammable permanent storage device and one of
the types of nonvolatile memory.
Bashsomsnabbank accounts for 5% or from 500
million to 30 billion rubles. This indicator was
calculated on the basis of data obtained from
Marswebb lnternet Banking 2016 concerning the
level of penetration of the Internet banking among
legal entities and data of Bashkomsnabbank, which
indicate approximately 5% (formula 1) of legal
entities.
(75318/4.5 *0.35)*100=4.79 (1)
where 75138 – number of clients (mln) – legal
entities, using remote banking services of
Bashkomsnabbank;
4.5 mln – number of registered legal entities in
Russia;
0.35 – level of penetration of the Internet banking
amongst legal entities in Russia.
Based on the estimates of Group-IB and the
Sberbank of Russia for 2018-2019, the legal entities
in Russia suffered losses from cyberattacks making
from 10 to 400 billion rubles, depending on
evaluation as such. Proceeding from this assumption,
one assumes that the distribution of cyberattacks in
general will coincide with the number of users of the
Internet banking and will make from 500 million to
20 billion rubles for Rosselkhozbank.
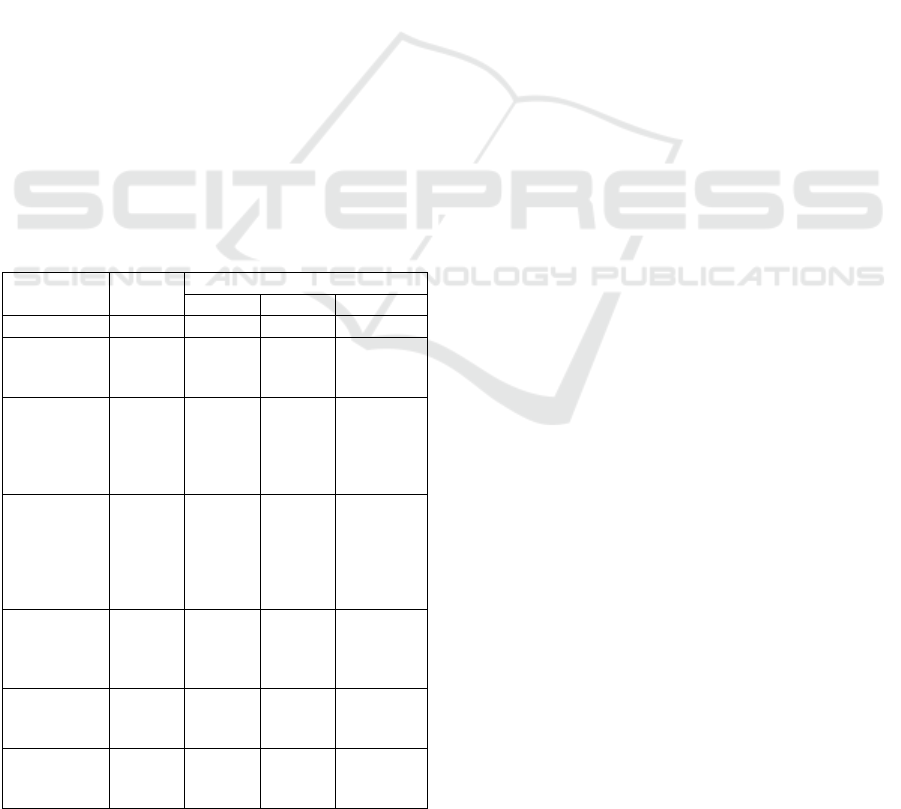
Table 2: Intended economic effect from introducing USB-
tokens ESMART Token GOST with biometrics.
Indicator Total
Scope of introduction
2018 2019 2020
1 2 3 4 5
Number of
connected
clients
75,138
USB token
ESMART
Token
GOST/USB,
pcs.
80,000 25,000 25,000 30,000
Price per unit
of USB token
ESMART
Token
GOST/USB,
rubles
- 1,486 1,545 1,607
License value
per software
unit (for 3
years)
- 1,634 1,699 1,767
Expenses on
potential
losses (7%)
1,822,371 5,460,000 5,677,770 7,085,941
Total
expenses,
rubles
2,785,629 8,346,000 8,678,870 108,313,669
*Developed by the author
The above calculations allow concluding that the
share of costs related to the transition of legal entities
to the system of multifactor authentication, including
biometrics, makes from 55.7% to 1.4% of potential
losses on 50 cyberttacks. Therefore, it seems
advisable and reasonable to install this system.
In this regard, the development of RBS protection
systems is aimed at the maximum possible cost and
time associated with attacks. Such strategy excludes
those people who cannot afford organizing and
implementing attacks due to their poor financial
potential. Maintaining the adequate level of
information security requires a systematic approach
and investments from a particular bank. Otherwise, a
bank puts trustworthiness and loyalty of its customers
at risk, since the latter ones perceive the Internet
banking as a necessary tool of any bank they are
dealing with.
At present, in terms of security of individuals,
Bashsomsnabbank provides its customers with
reliable security of remote banking operations, which
is continuously ensured through leading domestic
developments
4 THE DISCUSSION OF THE
RESULTS
Currently, the banking sector is focused on customer
focus. All current transformations and innovations,
first of all, take place for clients, for the convenience
of providing them with services, for increasing their
confidence in the banking sector.
The pandemic turned out to be the push that
activated their internal mechanisms and launched
those processes that can no longer be stopped. In
connection with the digitalization of the banking
sector and the development of digital technologies,
society has a natural demand for new and modern
banking products and services. The emergence of
new banking opportunities for people and businesses
that meet the needs of the digital world increases the
competitiveness of the country's economy as a whole.
The rapid development of the banking sector,
building ecosystems, digitalization and globalization
at all levels of the system are what awaits us in the
near future.
The pandemic has become a factor pushing the
digitalization of banking services and the transition to
online. With the introduction of the self-isolation
regime, banks were forced to more actively improve
their digital capabilities, although before that this
process was quite intense. Back in 2019 (compared to
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
296

2018), the number of bank customers who used online
services increased by more than one and a half times.
The logical consequence of the pandemic has
become the intensification of competition in the
development of digital services: the overwhelming
majority of banks have taken measures to expand the
functionality of mobile applications, which have
become the main element of the digital
transformation of banking services. The emphasis is
placed on the maximum use of innovative
technologies, as well as on constant renewal and
modernization, which directly affects the
competitiveness of the bank. The functionality of
applications began to include not only the possibility
of remote registration of banking products, but also
the receipt of certificates, statements, transaction
histories. The quality and usability of apps began to
seriously affect the quality of customer service.
5 CONCLUSION
According to the results of calculations, it can be
concluded that the share of the costs of transferring
clients - legal entities to multifactor authentication
systems including biometrics - will be from 55.7% to
1.4% of possible losses from 50 hacker attacks. Based
on this, we can conclude that the introduction of this
system is advisable.
In this regard, the development of RBSprotection
systems is aimed at making the cost and time spent on
carrying out attacks as high as possible. Such a
strategy excludes those for whom the cost of
organizing and conducting an attack on the remote
banking system is higher than their financial
capabilities.
Maintaining a sufficient level of information
security requires a systematic approach and
investment on the part of the bank, otherwise the bank
risks losing the trust and loyalty of its customers, who
refer Internet banking to the list of necessary services
provided by the bank in which they are served.
In the field of Internet banking security for
individuals, to date, Bashkomsnabbank provides high
security of operations in the RBS system, ensured by
constant improvement of the current system and the
use of leading domestic developments.
REFERENCES
Analysis of methods for assessing the financial potential of
the region (2008). Collection of scientific works of
SevKav GTU. Ser. "Economy, 8.
Bayguzina, L.Z., Galimova, G.A., Nurdavlyatova, E.F. and
Ponomareva, L.N. (2019). Globalization of financial
system and its synergetic effect at regional levelsocial
and cultural transformations in the context of modern
globalism. European Proceedings of Social and
Behavioural Sciences, 58: 209-216.
Bryachikhin, A. (1997). Western Administrative.
Economics Institute Public Policy Brief, 133.
Ehnts, D. and Paetz, M. (2020). COVID-19 and its
economic consequences for the Euro Area. Eurasian
Economic Review.
Grishin, K.E., Kazakova, O.B., Kuzminykh, N.A. and
Timeryanova N.A. (2020). Economic space:
approaches to research and the form of presentation.
Economics and Management: scientific and practical
journal, 3(153): 4-11.
Leksin, V.N. and Shvetsov, A.N. (1997). State and regions.
Theory and practice of state regulation of territorial
development, pages 27-28.
Mol-Gomez-Vazquez, A., Hernandez-Canovas, G. and
Koeter-Kant, J. (2020). Banking stability and borrower
discouragement: a multilevel analysis for SMEs in the
EU. Small Business Economics.
Reinders, H. J., Schoenmaker, D. and Van Dijk, M. A.
(2020). Is COVID-19 a threat to fnancial stability in
Europe? CEPR, DP14922
Saez, E. and Zucman, G. (2020). The triumph of injustice—
taxes and inequality in the 21st century. New York:
Norton and Company.
Sokolinskaya, N. E. and Zinov'yeva, Y. A. (2020).
Bankovskiy sektor do i posle pandemii. Finasovvyy
rynok i banki.
The Bank of Russia made a decision on regulatory
concessions and macroprudential measures. [Electronic
resource]. URL:
https://cbr.ru/press/pr/?file=10082020_163109pr_0.ht
m17.
Timchuk, N.F. (1980). City and region. Regulation of
integrated development, 19.
What is happening in the Russian banking sector after the
pandemic. [Electronic resource]. URL:
https://2stocks.ru/2.0/russian/stocks/ news / chto-
proishodit-v-rossiyskom-bankovskomsektore-posle-
pandemii.
Zotova, A.I. and Kirichenko, M.V. (2015). Financial
system of the region: structural and functional aspect.
Modern science: actual problems of theory and
practice. Series: Economics and Law, 11–12: 82–86.
Financial Sustainability of the Region after the Pandemic and Factors Affecting its Characteristics
297
