
Agricultural Sector of the Republic of Kazakhstan in the Context of
Sustainable Development: Analysis of the General Condition and
Income Differentiation
Aitolkyn Sagynbayeva
a
, Abilda Symbat
b
and Saltanat Kondybayeva
c
Department of Economics, Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, Almaty, Republic of Kazakhstan
Keywords: Income Differentiation, Agriculture, Economic Growth, Agricultural Sector of Kazakhstan, Income
Inequality, Income of Agricultural Sector of Kazakhstan.
Abstract: The article is devoted to the agricultural sector of present Kazakhstan in the context of sustainable
development, as it considered as a significant part of the economic system. Agriculture has determinative
character in the economic development of the country. These days, the share of the population, who is working
in agriculture is declining as countries develop. The core aim of this research is to show a comprehensive
representation of the situation of agriculture in Kazakhstan, with a particular focus on income differentiation
and labor force developments in the agriculture sector. To achieve the goal of research work, a descriptive
method was used. The article reveals that due to low labor productivity and a large gap between income, there
is income differentiation in the agriculture sector of Kazakhstan. The achieved results from this article can be
used for evaluating the efficiency of various social policy tools both at the regional and national levels.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the vital parts of the country is agricultural
sector, as it participates in making the economic
security, as well as the country’s food encouraging,
but also it forms the labor and settlement potential of
rural areas. For many developing countries, the
agricultural sector is a driver of economic growth.
In the Kazakhstani and overseas literature, there
are several research works devoted to the study of
unevenness and differentiation of income. However,
the issue of the income differentiation in the
agricultural sector raised the attention of the authors.
Because since the beginning 90th, the improvement
of the agro-industry and ensuring the economic
security and the nation’s food encouraging in the
direction of “go green” and sustainable development
is the most significant strategic farm duties of the RK.
The literature research proved, that the works in the
analysis of income differentiation especially in the
agricultural sector and the clarifying of reasons
affecting its condition and dynamics are lack. The
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9910-7777
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2341-1921
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7781-9765
main purpose of our research paper is to define
answers to these issues.
The authors like S Kuznets, N Kaldor, A. Sen, E
Atkinson and others considered the issues inequality
and income differentiation and based the foundations
for measuring them (Malkina, 2015). Income
differentiation is an important macroeconomic
category that shows the result of sustainable
economic development of the country, as well as the
results of social state policy. For evaluating income
differentiation widely used the Gini coefficient of
variation, A Theil and E Atkinson indices. Moreover,
the construction of Lorentz curves shows the dynamic
in income differentiation. This article uses the Gini
coefficient, as it provided by the Ministry of National
Economy of Kazakhstan.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The research directed to analyze the situation of
agriculture in Kazakhstan from 2017 to 2019, with a
Sagynbayeva, A., Symba, A. and Kondybayeva, S.
Agricultural Sector of the Republic of Kazakhstan in the Context of Sustainable Development: Analysis of the General Condition and Income Differentiation.
DOI: 10.5220/0010590003190324
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 319-324
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
319

focus on agricultural income and labor force
development. Statistics were taken from the Ministry
of National Economy of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
This part introduces with a study of the significant
indicators, which belong to agricultural sector like the
growth dynamic, employment in this sphere and the
differentiation of incomes of the employees was
carried out. To achieve this research purpose authors
used descriptive research method
The important roles of agriculture in the country's
economic development are as follows (Kondybayeva,
2018):
As it mentioned previously, the agricultural
sector has an important strategic role, as it
participates in the economic growth direction
of the country.
In practice of developed countries, the
agricultural sector has already made a
significant contribution to the country's
economic prosperity.
The agricultural sector has a vital importance
for the Third World Countries.
In recent years, the growth rate of global
agricultural production and productivity has slowed.
Currently, many countries around the world have
high levels of food consumption per person, but
growth will be limited over time due to lack of
adequate resources. But at the same time, a high
proportion of the world and developing countries
remain in absolute poverty. This means that there is
not enough income to convert their needs into
sufficient demand. And development in the agrarian
sector has an important role in developing the
economy, as it caused the increase in the profits of the
poor by creating jobs on farms and stimulating
employment outside agriculture.
According to S Kuznets, at the early stages of
industrialization, the income inequality rises, since a
small part of the workforce is employed in the
industrial sector. However, as workers continue to
migrate to higher-wage sectors of the national
economy, these high levels of inequality eventually
decline over time (Kuznets, 1955).
According to the definition of the economist D
Ray, economic inequality is “a fundamental
imbalance in which one person can freely make
certain material decisions, while the other is denied
the opportunity to make exactly the same economic
choice” (Ray, 1998). The causes of disproportion
phenomena may include income inequality, a
consequence of accumulated a person wealth
inequality, situations in society and opportunities in
country, etc. The great researchers E Atkinson and F
Bourguignon pointed out the material and non-
material components of economic inequality.
According to their works, the objects of material
inequality consist of income, consumer spending and
accumulated wealth. Nevertheless, the researchers
considered the existing difference and defined:
income and expenses are economic, and accumulated
wealth is reserves (Atkinson, 2015).
Thus, the differentiation of incomes of the
population is one of the most important and
determinative socio-economic categories that
characterize the level of uneven distribution of
material wealth between the individuals of the
country. Depending on the prevailing production
relations, the principle of distribution of the quantity
and share of the social product between groups and
strata of the population will be determined. In
capitalist society, income differentiation and
inequality is determined by the relationship between
the exploitation of goods and class inequality. Since
representatives of different classes of society have a
different type of income, accordingly, the
differentiation of incomes shows the dynamics of the
share of working people in the share of capitalists in
social wealth in accordance with the general laws of
capitalist accumulation.
In a market economy, income is also the main
category that reflects the social status of an
individual. In this regard, in order to maintain the
long-term sustainable development of the economy,
the state needs to regulate the distribution of income
in the correct way so that status advantages are
effectively reflected.
A state with rational income differentiation, due
to the large number of the middle class and intensive
social mobility in society, has the greatest
sustainability of economic development, and also
provides a strong incentive for social advancement
and professional growth of the population (Bobkov,
2005).
In this way, income differentiation of the
population is the result of the distribution of incomes
of the population of the state, which describes the
uneven level of distribution of public goods of society
and the difference in the level of income of different
segments of the population. In society, income
differentiation arises and is formed in connection with
various types of activities, various industries, as well
as under the influence of demographic, social and
political factors.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
320

3 RESULTS
The changes in volume of the gross output of the
agrarian sector of Kazakhstan for time period from
2017 to 2019 inclusive is considered and analyzed in
this section of paper.
For this, we will use the diagram below (Figure
1), which clearly shows the dynamics of these
indicators for the analyzed time period. Statistical
data was taken from the reports of the Ministry of
National Economy of the Republic of Kazakhstan
Figure 1: Dynamics of gross output of the agricultural
sector of Kazakhstan (billion tenge) in 2017-2019.
As you can see from the above diagram for the
analyzed time period, the following changes and
transformations took place in the changes in volume
of the gross output of the sector of agriculture in
Kazakhstan:
the total gross output of the sector of
agriculture in the Republic of Kazakhstan
increased by 26.5% or 1080.2 billion tenge. In
2017 this indicator was 4070.9 billion tenge
and it increased to 5151.1 billion tenge at the
end of 2019, respectively;
at the same time, the share of the total gross
output of the sector of agriculture in the GDP
of Kazakhstan remained virtually unchanged,
decreasing from 7.49% in 2017 to 7.41% at the
end of 2019. A positive factor is the growth of
this indicator by the end of 2019 compared to
2018 by 0.17 percent, from 7.24% to 7.41%.
In general, the agricultural sector of Kazakhstan
determines an important role in economical balance
of Kazakhstan in key areas of development and it is
developing at the same level of the mining,
processing and heavy industries.
The volume of crop and livestock production in
Kazakhstan has a stable growth and testifies to an
increase in demand in the home market and also in
foreign markets for products of the sector of
agriculture in the state.
To identify the advancement and development of
the crop production industry within the agrarian
sector of Kazakhstan, we will analyze the dynamics
of the gross harvest of the major agrarian crops in
Kazakhstan in 2017-2019. (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Gross harvest of major crops (thousand tons) in
Kazakhstan in 2017-2019.
As a result, it is possible to identify that the crop
production in agrarian sector of Kazakhstan, there is
a redistribution in favor of products with a high level
of added value - most crops (except for cereals)
demonstrate stable growth within the framework of
an increase in their gross harvest.
We will use the diagram below (Figure 3), which
clearly analyze the dynamics of exports of products
of the agrarian sector of Kazakhstan (million US
dollars) from 2017 to 2019 inclusive.
Figure 3: Dynamics of export of products of the agricultural
sector of Kazakhstan (million US dollars) in 2017-2019.
As you can see from the above diagram for the
analyzed time period, the following changes and
transformations occurred in the dynamics of export
volumes, products of the agrarian sector of
Kazakhstan from 2017 to 2019 time period:
the total volume of production of the agrarian
sector of Kazakhstan increased by 39.7% or
USD 808.1 million, from USD 2037.1 million
to USD 2845.2 million at the end of 2019,
respectively;
in the total amount of exports of Kazakhstan,
the overall level of total share of exports of
Agricultural Sector of the Republic of Kazakhstan in the Context of Sustainable Development: Analysis of the General Condition and
Income Differentiation
321

agricultural sector products increased by 0.7
percentage points. In 2017 this indicator was
4.2% and increased to 4.9% at the end of 2019,
respectively.
In the medium-term period of development of the
national economy agrarian sector of Kazakhstan has
a high degree of potential of this industry, which has
a stable growth in the volume of exports of products
of the agricultural sector and an increase of indicator
of volumes of exports of products of the agrarian
sector in the total volume of exports of Kazakhstan.
For the purpose of substantively disclose the
export orientation of agricultural products of
Kazakhstan to key markets, we will analyze the
export of products of the agricultural sector of
Kazakhstan for the time period from 2017 to 2019,
we will use the diagram below (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Structure of exports of products of the agricultural
sector of Kazakhstan (million US dollars) in 2017-2019.
In accordance with the above diagram, it can be
determined that in the structure of volumes, exports
of products of the agrarian sector of Kazakhstan from
2017 to 2019 time period, the following changes and
transformations took place:
the amount of exports of products of the sector
of agriculture in Kazakhstan to the CIS
countries increased by 56.4% or 545.3 million
US dollars. In 2017 this indicator was 967.3
million USD and at the end of 2019 increased
to 1512.6 million USD;
the amount of exports of products of the
agriculture of Kazakhstan to other countries
increased by 24.7%;
the share of exports of products of the sector of
agriculture in Kazakhstan to other countries
decreased by 5.7 percentage points, from
52.5% in 2017 to 46.8% at the end of 2019,
respectively.
In general, according to the research made it is
possible to determine that at the current time there is
a differentiated and systematic development process
of the agriculture of Kazakhstan. And It is manifested
in a stable growth in the volume of manufactured and
exported products of this sector of the national
economy.
4 DISCUSSION
After studying the development and position of the
agrarian sector of Kazakhstan, a descriptive analysis
was carried out on inequality and income
differentiation in this sector. The structure of
employment, the volume of income and wages has a
direct immediate effects and impact on the
differentiation of incomes and the welfare and
prosperity of the society and population, in addition
to the development of the economy as a whole.
Economic development, as well as income
differentiation is always influenced by the structure
of employment, income and wages level.
Income differentiation is an important
macroeconomic category that shows the result of
sustainable economic development of the country, as
well as the results of social state policy. The wages of
the population have an important and decisive
influence in determining the differentiation of
income, since wages are the main form of income for
the majority of the population that works in hired
labor and is part of the employed population.
Inter-sectoral and intra-sectoral differentiation of
wages is a crucial and important factor in the
differentiation of population by income.
Inter-sectoral differentiation in wages arises in
connection with the intensive growth of wages in
priority sectors and spheres that have great export
demand and potential (fuel and energy complex) and
the financial and economic sector, and on the other
hand, due to stable wages in social spheres (like
education, culture, health care) and agricultural
sector.
Intra-industry differentiation of incomes
unjustified differentiation of wages in each sector of
the economy is also growing significantly.
The changes in volume of employment in
agriculture in the Republic of Kazakhstan has a
negative trend, as there is a small outflow of labor
(Figure 5).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
322
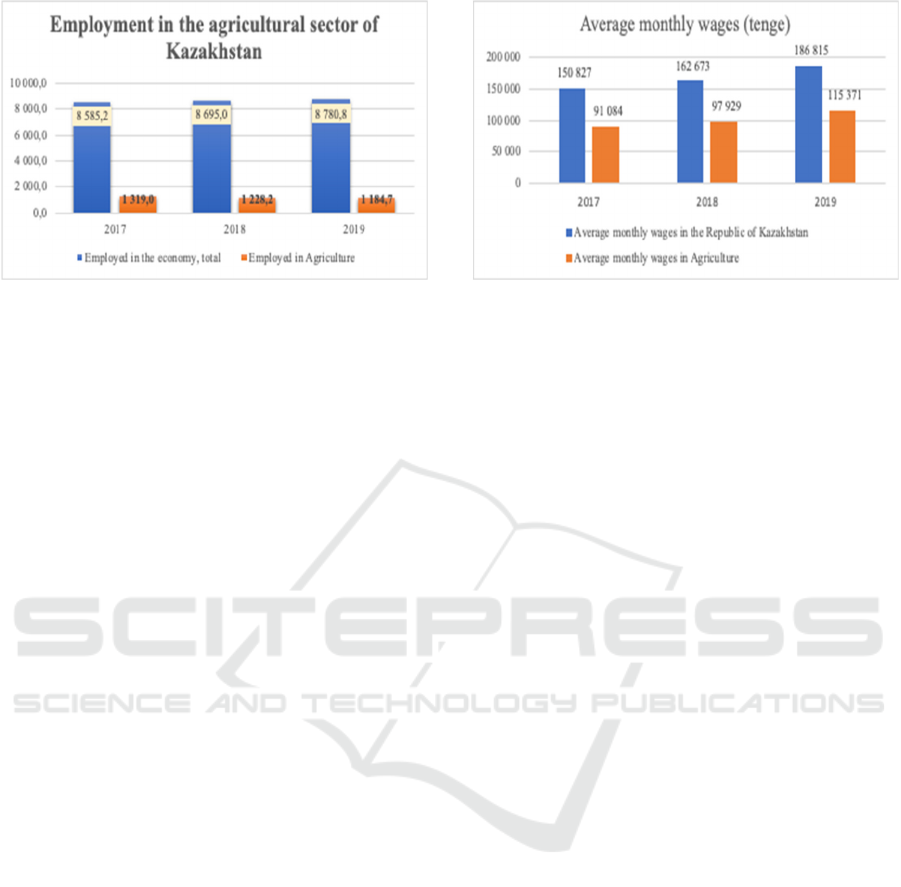
Figure 5: Employment in the agrarian sector.
As stated in the report of Ministry of National
Economy of Kazakhstan, since 2009 there has been
an outflow of labor by almost 2.2 times. In this sector,
the average annual growth rate of employment
decrease from 2009 to 2019 time period was 6.4%,
which is a very high indicator compared to other
sectors of the economy. According to statistics in
2019, employment in agriculture is 1.2 million
people.
The peculiarity of the agrarian sector in
Kazakhstan is that there is a large number of self-
employed (64.6%).
The level of income in the agricultural sector is
directly dependent on labor productivity. According
to statistics, in 2019 labor productivity amounted to
2,077 thousand tenge. This indicator has an annual
positive growth rate, but labor productivity in
agrarian sector by way of comparison with other
sectors of the economy is lower.
In the agrarian sector of Kazakhstan, there is a low
level of wages (Figure 6). In agriculture, in 2019, the
average monthly wage was 115,371 tenge, and
compared to 2018 year the growth rate was 17.8%.
This indicator for the time duration from 2017 to 2019
rised up by 1.3 times. Thus, the country's agricultural
sector is the leader in terms of average annual wage
growth rates and is 11.4%. However, the average
monthly wage of population in the state is 186,815
tenge, but there is a gap, which is about 71 000 tenge,
and it is 1.6 times more than salary in agricultural
sector.
Figure 6: Average monthly wages (amount in tenge).
Social inequality, which is measured by income
differentiation, depends not only on the industry and
the development of the country, but there are also
many social factors, such as the level of education in
the studied industry. The agricultural sector of
Kazakhstan and also of the countries around the
world is defined by a less highly skilled labor force.
Almost half of all employed in agriculture (47%)
have only primary, basic, secondary general
education. According to statistics, only 13% of
employers has higher education in the sector of
agriculture in Kazakhstan. The study revealed the
socio-economic stratification of the regions of the
Republic of Kazakhstan, as well as a large inequality
in wages of the population by industry and spheres of
the economy.
5 CONCLUSION
Our research can be concluded that the number of
people employed in agriculture is decreasing every
year. Such a negative tendency is observed not only
in Kazakhstan, but also in every countries around the
world. According to this fact, there is an uneven
distribution, a large level of income gap compared
with other sectors of the economy, as well as low
labor productivity affects to the income
differentiation of the population of Kazakhstan.
In general, according to the research made it is
possible to determine that at the current time there is
a differentiated and systematic development process
of the agriculture of Kazakhstan. And It is manifested
in a stable growth in the volume of manufactured and
exported products of this section of the national
economy.
Agricultural Sector of the Republic of Kazakhstan in the Context of Sustainable Development: Analysis of the General Condition and
Income Differentiation
323

REFERENCES
Malkina, M. (2015). Evaluation of the Factors of Intra-
Regional Income Differentiation of the Russian
population. Spatial Economics, 3
Ministry of National Economy of the Republic of
Kazakhstan. Retrieved from: https://stat.gov.kz
Kondybayeva, S., Nurgazy, S., Ospanov ,S.,
Mukhamediyev, B. and Sadykhanova, G. (2018). Food
Market of Kazakhstan: Current State and Innovative
Development Directions. Proceedings of the 31st
International Business Information Management
Association Conference, Milan, Italy 25-26 April, P.,
4312-4317
Summary report of FAO World agriculture: towards
2015/2030. Retrieved from: http://www.fao.org/3/a-
y3557e.pdf
Ray, D. (1998). Development Economics. New Jersey:
Princeton University Press, 848.
Atkinson, A. and Bourguignon, F. (2015). Income
Distribution Today. Handbook of Income Distribution,
vol. 2, pp. xvii-lxiv.
Kuznets, S. (1955). Economic growth and income
inequality. The American Economic Review, 45(1): 1-
28
Bobkov, V. (2005). Differentiation of welfare, The
Economist.
Report of Agency of Strategic planning and reforms of
the Republic of Kazakhstan Bureau of National
statistics. Taken from:
https://stat.gov.kz/api/getFile/?docId=ESTAT105377
Statistical yearbook of Foreign trade of the Republic of
Kazakhstan. Agency of Strategic planning and reforms
of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Retrieved from:
https://stat.gov.kz/api/getFile/?docId=ESTAT392576
Statistical yearbook of Agriculture in the Republic of
Kazakhstan. Retrieved from:
https://stat.gov.kz/api/getFile/?docId=ESTAT386870
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
324
