
Estimation of Sustainable Development of the Far Eastern Regions of
Russia in Terms of Advancing the Implementation of the Growth
Strategy
Vilena A. Yakimova
a
and Sergey V. Khmura
b
Department of Finance, Amur State University, Ignatievskoe St., Blagoveshchensk, Russian Federation
Keywords: Economic Growth, Advanced Development Zones, Sustainable Development, Economic Development
Model, Investments, Region Economy.
Abstract:
The article studies the problems of sustainable economic development of the Far Eastern regions of Russia,
implementing the economic growth strategy. In the course of the regression analysis, multifactor models were
formed and the key factors, stimulating the economic growth of the regions, were identified. The models show
the influence of the factor of capital assets and investments, on the formation of which the increase in
industrial production depends. In an insignificant part of the regions, favorable growth factors are socio-
demographic capital and exports. Starting from 2015, the economic growth of the regions have been ensured
from the positive effect from the implementation of the development strategy ahead of the others in
comparison with the average Russian level. In the course of the research, the type of development of the
regions, in which the advanced development zones function, was determined, based on the analysis of the
interrelations between the indicators of the stability of the region's economy with the generalized indicators
of residents of the advanced development zones. For four Far Eastern regions (Yakutia, Kamchatka,
Khabarovsk Territory, Chukotka Autonomous District), an intensive type of development is characteristic,
which contributes to the growth of GRP by increasing sales by enterprises, entering the advanced development
zones, effective use of investments, and resources. The results of the research can be used to improve the
mechanism for managing the factors of sustainable development of the regions of the Russian Far East.
1 INTRODUCTION
The stability of the region's economic system is
characterized by dynamic transformations, that form
the vector of long-term economic growth. The
priority task for the development of the Russian
economy is the strategy of stimulating the economic
growth of the Far Eastern regions, which have a high
resource potential, a favorable geographical location,
high competitive advantages, but lagging behind in
terms of their development. Since 2015, the advanced
development zones have been functioning on the
territory of the macroregion, which solve the
problems of creating a comfortable living
environment for the population and modernizing less-
developed industries. Economic growth is facilitated
by the inflow of private and budgetary investments,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5866-5652
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0704-8755
cluster regional policy, and a set of tools to support
the business climate.
The concept of "sustainability of the economic
system" and "sustainable development" is quite
multifaceted, but, as a rule, it is based on an effective
combination of production, technological and human
capital in a socially-oriented policy, rational use of
natural resources, and environmental protection. The
growth of the gross regional product does not
guarantee the stability of the economy, a balance of
the components of the system and a fixation on
meeting the needs of the population, living in the
territory, are required.
The evolutionary concept of stability presupposes
such an equilibrium position of a stationary point, at
which a change in the set of parameters does not
change the stability of the entire system as a whole
(Balakina and Oydup, 2012). The level of stability of
332
Yakimova, V. and Khmura, S.
Estimation of Sustainable Development of the Far Eastern Regions of Russia in Terms of Advancing the Implementation of the Growth Strategy.
DOI: 10.5220/0010590203320338
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 332-338
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

the system is formed as a combination of internal and
external factors, that stimulate or restrain the
equilibrium state of the region's economy. The
stability of the region's economy is ensured through
ecologization, national security, equitable resource
management, and competitive advantages of socio-
economic development.
By sustainable development of the territorial-
economical system, we mean the equilibrium state of
the production, investment, socio-demographic,
technical and technological, ecological spheres, when
positive changes in a particular sphere do not restrain
the development of any other sphere, but contribute
to the achievement of a general economic equilibrium
of the entire system of the region.
In the scientific literature, there are a number of
indicators and models for estimating the stability of
economic systems. To rate the sustainable
development of the territory, indicators, developed by
the UN (human capital index) and the World Bank (an
indicator of net savings), are used. In the methods of
economists, a set of socio-ecological indicators of
stability is used: socio-demographic, financial and
economic, technological, natural and ecological
(Bezdenezhnykh et. al., 2015), institutional,
geographic, demographic determinants (Moral-
Benito, 2009), economic, social and ecological
factors (Rahman and Velayutham, 2020), exports
(Kahouli and Kadhraoui, 2012). For regions, where
territories with a special economic status operate, an
important development factor is the development of
institutions, that provide access to funding sources,
reducing administrative barriers, and receiving tax
incentives (Pankova and Yakimova, 2020).
Economists (Hall, Jones, 1999, Bennett, 2019,
Zubarevich, 2017) distinguish infrastructural and
transport, and logistics factors as catalysts for the
growth of regional economies and opportunities for
developing resource and production capacity. In
models of sustainable growth, national income, the
level of accumulation of human and physical capital,
the growth in the population of the territory, the share
of the economically active population, and life
expectancy are used as determinants (Rahman and
Velayutham, 2020). Sustainable development of the
social sphere is achieved thanks to social equality, the
satisfaction of the population with living in the
territory, social infrastructure, and opportunities to
receive social benefits at a quality level. The
ecological component of sustainable development
reflects the efficient use of natural resources,
preservation of natural potential, prevention of
ecosystem dysfunctions, and loss of biodiversity.
Equilibrium is achieved by the stable development of
natural capital and lean technologies.
On the brink of the economic development of the
region, an important task is to maintain static and
dynamic stability, not only in the short term but also
in the medium and long term. Innovations and
investments are catalysts for long-term stability and
economic growth, employment and a high level of
value added (Goridko and Nizhegorodtsev, 2018).
The rational allocation of investments in projects,
implemented in the region, guarantees an increase in
the gross income of the region, and the creation of
transport and logistics facilities, housing construction
creates a comfortable living environment for the
population of the region.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Equilibrium growth is observed in the case of a one-
time growth in all components of sustainable
development: investment, economic, production,
socio-demographic, ecological. Regional growth is
determined by the growth in sales of manufacturing
industry products, investments in capital assets,
growth in fixed assets of enterprises, exports, and
socio-demographic factors. The standard model is as
follows:
BbKbKacb
EbFbIbQbbGRD
876
43210
(1)
where GRD is GRP per head, Q is the volume of shipped
products of manufacturing industries in the region, I is
investments in capital assets of the region, F is the cost of
fixed assets of enterprises in the region, E is exports, d is
the demographic load factor (disabled persons per 1000
employable persons in the region ), Kac is the employed
population, K is the population, living in the region, B is the
emissions of pollutants into the air.
The standard of a multifactor model of socio-
economic development takes into account a set of
factors, that form the preconditions for achieving
sustainable equilibrium growth. The sustainable
development model includes a set of resources,
interacting with each other in the interests of
increasing the efficiency of the entire socio-economic
system of the region in the direction of the trend of
economic growth.
Estimation of Sustainable Development of the Far Eastern Regions of Russia in Terms of Advancing the Implementation of the Growth
Strategy
333

3 MODEL AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Sustainable Development Model of
Regions
Based on the standard model, multifactor models of
socio-economic development of the Far Eastern
regions of Russia are constructed. The method of
stepwise multifactor regression analysis in the
applied SPSS program made it possible to exclude
insignificant factors and eliminate multicollinearity.
The resulting models are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Sustainable development models of the Far Eastern
regions of Russia.
Region Sustainable development model
of the re
g
ion
R
2
Investment and technolo
g
ical t
yp
e
Republic
of Sakha
(Yakutia)
I
FGRD
911,0
22,0145649,7
F (0.001) I (0.031)
0.9
7
Technical and technolo
g
ical t
yp
e
Kamchatka
Territory
FGRD 92,0162807,3
F (0.006)
0.9
3
Chukotka
Autonomo
us District
FGRD 141,6381703,744
F (0)
0.9
0
Ex
p
orts and technolo
g
ical t
yp
e
Sakhalin
Region
EF
GRD
545,63370459,0
6-331421,91
F (0) E (0.01)
0.9
1
Jewish
Autonomo
us Region
E
FGRD
227105,951
669,0127654,734
F (0) E (0.03)
0.9
7
Socio-technological type
Khabarovs
k Territory
F
dGRD
072,0
12984-545014,54
d(0) F(0)
0.9
9
Socio-investment type
Primorsk
Territory
IKac
dGRD
277,01434
1220872765,95
d
(
0
)
Kac
(
0
)
I
(
0.003
)
0.9
9
Structural and production type
Amur
Region
QGRD 872,8-75671,75
Q(0)
0.9
3
Note: The significance of the factor in the model, according
to the t-statistic criterion, is indicated within brackets. The
decision on the statistical adequacy is made at <0.05.
In all 8 regions under study, the sustainable
development model differs significantly from the
standard one, since they use a maximum of three
components.
At the same time, in all regions, with the
exception of the Primorsk Territory and the Amur
Region, the key factors include (F) the cost of fixed
assets of enterprises in the region, which may be due
to the predominance of capital-intensive industries
(mining industry). An insignificant share is accounted
for by manufacturing industries.
In two regions (Sakhalin and Jewish Autonomous
Region), the export component belongs to the main
components of the sustainable development model of
the region, which is associated with a high export
component in the GRP of the regions; in the case of
the Sakhalin Region, this is the extraction of oil
products, and the Jewish Autonomous Region - of
iron stone.
Also, it should be noted, that only two regions
(Khabarovsk and Primorsk Territory) have social
components. This fact indirectly confirms the
presence of socio-demographic problems in the Far
East and associated with difficult living conditions, as
well as the constant migration outflow of the
population.
3.2 Estimation of the Impact of the
Advanced Development Zones on
the Stability of the Regional
Economy
The formation of territories with a special economic
status in the Far Eastern regions is intended to ensure
economic growth through the creation of new
industries and the consolidation of the manufacturing
industry in the Far East. However, on the brink of
stimulating development, there are a number of
challenges and factors, restraining development. In
such conditions of instability, the issues of estimating
the impact of ASEDZ activities on the level of
stability of the economic systems of the Far Eastern
regions are relevant. The results of the regression
analysis are presented in Table 2.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
334

Table 2: Regression analysis of the relation between the
economic indicators of the Far Eastern regions of Russia
and the indicators of ASEDZ in the regions.
The region where the
ASEDZ was
established
Statistical estimation parameters
Interrelation between investments and invested
capital of ASEDZ residents
Interrelation between GRP and the volume of
products, sold by ASEDZ residents
Interrelation between the volume of shipped
products of the agricultural sector of the region
and ASEDZ residents
Republic of Sakha
(Yakutia)
R2 0.288 0.983 0.361
T-
st
0.46
(
Н
)
0.09 0.4
(
Н
)
re
g
1.37 0.09 54.28
Kamchatka Territory R2 0.951 0.9 0.677
T-
st
0.025 0.047 0.177
(
Н
)
re
g
0.203 0.09 0.195
Primorsk Territory R2 0.664 0.811 0.613
T-
st
0.19
(
Н
)
0.1
(
Н
)
0.217
(
Н
)
reg 0.581 0.01 5.22
Khabarovsk
Territory
R2 0.986 0.956 0.055
T-
st
0.07 0.022 0.764
(
Н
)
reg 0.810 0.04 0.526
Amur Region R2 0.922 0.767 -
T-
st
0.04 0.12
(
Н
)
-
reg 0.333 0.01 -
Sakhalin Region R2 0.03 0.468 0.995
T-
st
0.945
(Н)
0.32
(Н)
0.02
reg 0.059 0.107 0.374
Jewish Autonomous
Region
R2 0.37 0.02 -
T-
st
0.391
(Н)
0.86
(Н)
-
reg 2.187 0.214 -
Chukotka
Autonomous District
R2 0.988 0.979 0.507
T-
st
0.06 0.011 0.288
(Н)
reg 0.794 0.045 0.681
Note: R
2
, t-statistics (the decision on statistical
adequacy is made at <0.05), reg is the regression
coefficient. H - the model has no statistical significance
(based on t-statistics and R
2
). Significant parameters are
highlighted in gray.
Based on the results of regression analysis, it can
be concluded, that in Yakutia, Kamchatka and
Khabarovsk Territories, Chukotka Autonomous
District, there is an relation between the region's GRP
and the volume of products, sold by ASEDZ
residents, which is due to the fact, that a large number
of projects, implemented by ASEDZ residents have
already been completed, and they are in operation.
In Kamchatka Territory, Khabarovsk Territory,
Amur Region and Chukotka Autonomous District, a
high correlation between investments in the regional
economy and investments in ASEDZ projects is noted
due to the active investment phase of individual large
projects. At the same time, investments can be made
in projects, that are implemented from the initial stage
(for example, the Amur gas processing plant in
ASEDZ "Svobodny" in the Amur Region), and aimed
at modernizing an existing production (for example,
gold mining at NGK "Resurs" in ASEDZ
"Nikolaevsk" Khabarovsk Territory).
The interrelation between the volume of shipped
agricultural products of the region and ASEDZ
residents is observed only in the Sakhalin region,
which is caused by the low level of development of
agriculture in this region due to its island location and
adverse climatic conditions. In other regions, the level
of development of agriculture is much higher and
projects, implemented by ASEDZ residents in
agriculture, have an insignificant share.
Investment growth is determined by federal and
regional policies, the situation in the country, market
conditions, credit policy, aimed at the preferential use
of borrowed sources of financing, the fiscal system,
return on investment and the rate of return.
Estimation of Sustainable Development of the Far Eastern Regions of Russia in Terms of Advancing the Implementation of the Growth
Strategy
335
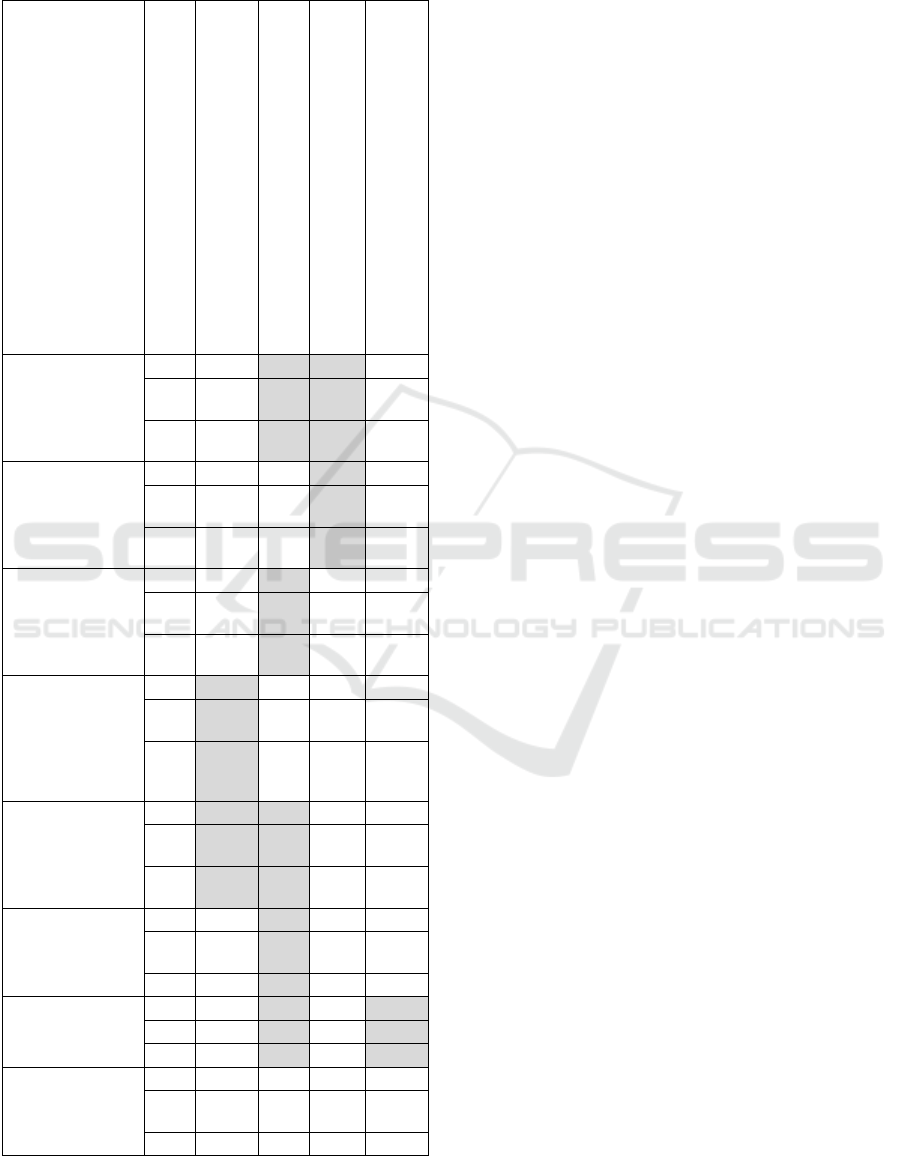
Table 3: Regression analysis of the relation between socio-
economic indicators of the Far Eastern regions of Russia
and indicators of ASEDZ in the regions.
The region where
the ASEDZ was
established
Statistical estimation parameters
The interrelation between the volume of shipped products of
regional enterprises and ASEDZ residents of the
manufacturing industry
The interrelation between the value of the region's fixed
assets and the fixed assets of the ASEDZ residents
The interrelation between the region's exports and the
proceeds from the sale of ASEDZ resident-exporters
The interrelation between the number of employed
population in the region and the number of ASEDZ resident-
employees
Republic of Sakha
(Yakutia)
R
2
0.88 0.926 0.971 0.819
T-st 0,62
(Н)
0.038 0.015 0,28
(Н)
reg 2.73 38.93
5
0.01 6.96
Kamchatka
Territory
R
2
0.06 0.67 0.911 0.04
T-st 0,923
(Н)
0,182
(Н)
0.045 0,96
(Н)
reg -4.54 10.57
2
0 0
Primorsk Territory
R
2
0.796 0.933 0.805 0.896
T-st 0,108
(Н)
0.034 0.1
(Н)
0,21
(Н)
reg 1.665 10.65 0.0000
7
-12
Khabarovsk
Territory
R
2
0.99 0.758 0 0.505
T-st 0.005 0,129
(Н)
1 (Н) 0,497
(Н)
reg 5.616 62.49 -
0.0000
3
-15
Amur Region
R
2
0.947 0.999 0.707 0.745
T-st 0.027 0 0,159
(Н)
0,337
(Н)
reg 1.504 1.215 0.0000
2
-4
Sakhalin Region
R
2
0.758 0.988 0.625 0.907
T-st 0,129
(Н)
0.01 0,21
(Н)
0,198
(Н)
reg 35.85 36.47 0 -5
Jewish
Autonomous
Region
R
2
0.01 0.902 0 0.999
T-st 0.9 (Н) 0.05 1 (Н) 0.017
reg 2.64 108.7 0 94.5
Chukotka
Autonomous
Region
R
2
0.779 0.714 0.242 0.01
T-st 0.117
(Н)
0.155 0.51
(Н)
0.936
reg 1.127 7.191 0 -0.043
The data in Tables 2 and 3 show the degree of
influence of the ASEDZ indicators on the level of
sustainable development of the regions and the
contribution of residents of the territories to the
indicators of the socio-economic development of the
region.
As a result of the performed regression analysis, a
relation between the volume of shipped products of
enterprises in the region and ASEDZ residents in the
manufacturing industry in the Khabarovsk Territory
and the Amur Region was revealed. This relation is
due to a large number of projects in the field of
manufacturing industries in the Khabarovsk Territory
(milling plant of LLC "Amur Timber Company", a
plant for processing polymers and the production of
plastic products, etc.), as well as large manufacturing
industries in the Amur Region (vegetable oil
extraction mill for advanced processing of soybeans).
The relation between the exports of the region and
the proceeds from the sale of resident-exporters is
observed in the Kamchatka Territory and Yakutia. In
the regions, projects are being implemented in the
field of fisheries, processing and manufacturing of
jewelry.
The correlation between the number of the
employed population of the region and the number of
ASEDZ resident-employees is observed only in the
Jewish Autonomous Region, which is associated with
the small size of the region and the size of the
population living in it. In other regions, this
interrelation has not been identified, including due to
the fact, that most of the projects, implemented by
residents, do not require significant labour power
intake due to the use of new and automated
equipment.
In the Primorsk Territory, economic development
is due to the growth of industries, that are not included
in ASEDZ. It should be noted, that the largest share
in the GRP structure of the Primorsk Territory is held
by trade, as well as transportation and storage.
Moreover, in the regions of the Far East,
development is taking place due to the development
of various sectors of specialization of ASEDZ
territories and “anchor investors”. The analysis
allowed the studied regions to be divided into three
groups, depending on the type of development (Table
4).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
336

Table 4: Type of sustainable development of ASEDZ in the
region.
Type of
development
Characteristic Regions of
the Far
Eastern
Federal
District
Intensive type
of
development
GRP growth,
ensured by an
increase in
investments, high
attractiveness for
new residents,
investors, labor
force. Effective use
of factors of
production and
networking in the
s
y
stem
Republic of
Sakha
(Yakutia)
Kamchatka
Territory
Khabarovsk
Territory
Chukotka
Autonomous
District
Intensive type
for the
development
of industries of
specialization
Development of the
production and
resource potential
of certain industries
of specialization,
which is caused by
a high inflow of
investments and the
effective use of
individual factors of
p
roduction
Sakhalin
Region
Amur Region
Extensive type
of
development
High accumulated
resource potential,
investments, but no
growth of GRP is
observed. Economic
returns are possible
in the lon
g
ter
m
Primorsk
Territory
Jewish
Autonomous
Region
The first group, which includes Yakutia,
Kamchatka and Khabarovsk Territories, Chukotka
Autonomous District, is the most successful and has
signs of intensive development, since investments are
made in various industries and there is a return on
these investments. Territorial economic systems have
an complex and systematic approach, and there is a
balance in key spheres of sustainable development.
The second group, consisting of the Sakhalin and
Amur regions, also has signs of intensive
development, but specific selective industries. In the
Sakhalin region, the bulk of the GRP is formed by the
oil extraction industry, in addition residents are
implementing major projects in the field of tourism
and agriculture. The specification of the economy of
the Amur Region is agriculture and mining, while
large projects of ASEDZ residents are aimed at
manufacturing industries.
The third group of regions, represented by the
Primorsk Territory and the Jewish Autonomous
Region, has an extensive type of development, which
is associated with a low return on projects,
implemented by ASEDZ residents, since most are
still in the investment stage.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The economy of the Far Eastern regions of Russia is
unbalanced and has a clear raw material orientation,
which made it possible, after the collapse of the
Soviet Union, to actively sell natural resources to the
developing countries of the Asia-Pacific region. At
present, the resource orientation of most sectors of the
regional economy prevents the comprehensive
development and growth of manufacturing industries,
in particular.
As a result of constructing of sustainable
development models of regions, a significant
deviation from the standard model in favor of one or
two components, which are key in the region's GRP,
as well as practically no social factors in these
models, was revealed.
The tool of the advanced socio-economic
development zones, introduced in 2015 in the Far
East, despite its short application period, shows its
effective impact on regional indicators. At the same
time, in each region, the effect of the creation of the
advanced development zones has its own
characteristics due to differences in the field of
activities, size, and stage of development of ASEDZ
projects.
REFERENCES
Balakina, G.F. and Oydup, T.M. (2012). Features of the
formation of a system of sustainable development of
the region. National interests: priorities and security,
19: 29-36.
Bennett, D.L. (2019). Infrastructure investments and
entrepreneurial dynamism in the U.S. Journal of
Business Venturing, 5.
Bezdenezhnykh, T.I., Kormanovskaya, I.R. and
Kadnichanskaya, M.O. (2015). Factorial approach to
assessing the risks of regional development (on the
example of the Nizhny Novgorod region). Regional
economy: theory and practice, 32: 32-44.
Goridko, N.P. and Nizhegorodtsev, R.M. (2018). Growth
points of the regional economy and regression
assessment of sectoral investment multipliers.
Economy of the region, 1: 29-42.
Estimation of Sustainable Development of the Far Eastern Regions of Russia in Terms of Advancing the Implementation of the Growth
Strategy
337

Hall, R. and Jones, Ch. (1999). Why Do Some Countries
Produce So Much More Output per Woker than
Others? Quarterly Journal of Economics, CXIV, pages
83-116.
Kahouli, B. and Kadhraoui, N. (2012). Consolidation of
regional groupings and economic growth: empirical
investigation by panel data. Int. J. Euro-Mediterr. Stud.,
5: 71–92.
Moral-Benito, E. (2009). Determinants of Economic
Growth: A Bayesian Panel Data Approach. World Bank
Policy Research Working, 4830.
Pankova, S.V. and Yakimova, V.A. (2020). Formation of
analytical tools for investment activities audit of
priority development areas. Smart Innovation, Systems
and Technologies, 172: 295-316.
Rahman, M.M. and Velayutham, E. (2020). Renewable and
non-renewable energy consumption-economic growth
nexus: New evidence from South Asia. Renewable
Energy, 147: 399-408.
Zubarevich, N.V. (2017). Development of the Russian
space: barriers and opportunities for regional policy.
The world of the new economy, 2: 46-57.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
338
