
Theoretical Foundations of Training Students in the Building
Information Modeling in the Context of Sustainable Development of
the Construction Industry
Anastasia Vilisova
a
and Lyudmila Mironova
b
Ural Federal University named after the First President of Russia B.N. Yeltsin, Institute of Construction and Architecture,
Department of Hydraulics, Mira street, Yekaterinburg, Russian Federation
Keywords: Building Information Modeling, Information Modeling in Construction, Teaching Students to Work in BIM,
Minor, Training to Work in BIM.
Abstract: In connection with the implementation of the state program «Digital Economy of the Russian Federation»,
there is an increase in demand for engineers who have competence in the field of building information
modeling (BIM). Only such professional staff will be able to ensure the sustainable development of the
construction industry in the context of its digitalization. The article is devoted to the problem of insufficient
teaching of bachelors and masters for BIM design. The purpose of the article is to develop a minor in the form
of an online course «Building Information Modeling Technologies», designed for students studying
bachelor’s and master’s programs at the Institute of Construction and Architecture. The method used is a
general scientific method, namely, the analysis of scientific and methodological literature and normative
documents on the topic of the study. The practical value of the work lies in the development of the structure
of the minor academic plan and its content, which can later be used in universities to teach students for
professional activities in the field of BIM design of construction objects.
1 INTRODUCTION
The state program «Digital Economy of the Russian
Federation» is being implemented in the Russian
Federation with the aim of creating a digital economy
ecosystem in which digital data is a key factor of
production in all spheres of socio-economic activity,
including construction.
It is obvious that the sustainable development of
the construction industry in the context of the
digitalization of the economy involves the use of
personnel employed in this field, developed
platforms, technologies, institutional and
infrastructure environment.
A number of researchers (Rothenbusch et al.,
2021) call BIM (building information modeling)
technology one of the trends in the construction
industry digitalization.
It is obvious that specialists who are trained for
professional activity in the construction objects
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6357-9764
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3675-6008
design should be confident in the technology of
information modeling.
The demand for specialists in this field is also
determined by the trend towards the mass
introduction of BIM technology in Russian
enterprises according to the action plan for the
implementation of the assessment of the economic
efficiency of investment justification and information
modeling technologies, approved by the Government
of the Russian Federation on April 11, 2017, No.
2468p-P9.
However, an analysis of the academic plans of
universities that train future builders has shown that
the training of students in BIM technology is not
intended. This circumstance determines the problem
of the study.
The implementation of the state program «Digital
Economy of the Russian Federation» requires close
cooperation between the state, business, and science,
which will inevitably entail the formation of state
order for universities to train personnel who would
Vilisova, A. and Mironova, L.
Theoretical Foundations of Training Students in the Building Information Modeling in the Context of Sustainable Development of the Construction Industry.
DOI: 10.5220/0010594505950600
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 595-600
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
595

have the necessary competencies to work with
information modeling technology. This determines
the relevance of the research topic.
The purpose of the article is to develop and offer
a minor in the form of an online course «Building
Information Modeling Technologies».
To achieve the goal of the research, it is necessary
to solve the following tasks: to analyze scientific
articles in this field; to determine the competencies
that a specialist in information modeling in the field
of construction should have; to develop a basic
academic plan and content of the minor; to propose
methods for monitoring and evaluating the results of
the formation of competence in the field of BIM
technology application, as well as recommendations
for the formation of staff who teach students BIM
technology.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The problem of training specialists in higher
educational institutions with a certain level of
competence to work with BIM technology is an
urgent problem, which is confirmed by a number of
studies.
Thus, over the past decade, the global
construction industry has demonstrated an obvious
and urgent need for professionals who know the
technology of building information modeling (Chen
et al., 2020).
The studies (Goldobina and Orlov, 2017;
Yakshina et al., 2019) speak about the need to
improve the system of training and implementation of
BIM technology in the process of training civil
engineers as part of the strategic development of the
construction industry.
However, despite the increasingly widespread
adoption of building information modeling
technology, a steady stream of graduates ready to
work with BIM, required to meet the demand in the
industry, still cannot be identified (Casasayas et al.,
2021).
The study (Maharika et al., 2020) notes that most
of the current BIM implementation models are
focused more on the construction industry (consulting
firms and contractors) and less on higher education
institutions. Responsibility for BIM education should
be shared between industry and academia (Sampaio,
2021). Many researchers want cooperation between
universities and industry (Chen, Lu, Wang, 2020).
The obstacles that make it difficult to prepare
graduates of the appropriate level in the field of BIM
technology proficiency were highlighted (Casasayas
et al., 2021):
The gap between the educational sphere and the
construction industry;
Problems of managing changes in the
educational process;
Limitations of educational and thematic plans
and program content;
Lack of teachers with the necessary
qualifications.
It is quite obvious that these problems require
finding solutions with the joint participation of
representatives of higher educational institutions and
the construction sector. However, some researchers
associate a number of questions with these problems,
to which there are no answers yet. For example, how
both parties can contribute to the collaboration to
achieve high-quality student learning (Chen et al.,
2020).
The inclusion of BIM in university academic
plans, along with core engineering disciplines, has
been gaining momentum in recent years. BIM’s
models of integration into the learning process vary
significantly from country to country in terms of the
approaches, strategies, and methods applied to the
professional and academic environment (Isanović
and Colakoglu, 2020). According to the authors of
this article, high-quality training of students to work
with information modeling technology is a
determining factor for the further sustainable
development of construction, architecture, and other
engineering areas within the framework of
digitalization of the construction industry in Russia.
The implementation of the minor «Building
Information Modeling Technologies» is one of the
tools for the formation of a competitive construction
industry that meets high standards of quality and
efficiency, working on the basis of modern financial,
economic, technical and managerial mechanisms.
3 METHOD
The interdisciplinary character of the article covers
research at the intersection of pedagogical, economic
and engineering sciences. In this connection, it was
necessary to analyze a wide range of issues affecting
the theoretical foundations of the digitalization of the
construction sector and the training of BIM
technology in the educational process of higher
educational institutions.
To achieve the goal of the study, a general
scientific method was used, namely, the analysis of
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
596

scientific and methodological literature and
regulatory documents on the issues of digitalization
of construction and the development of BIM
technology.
Within the framework of the study, a target group
of people was identified for whom the proposed
minor «Building Information Modeling
Technologies» is designed ‒ it includes students
studying bachelor’s and master’s educational
programs in the field of construction.
The purpose of the minor program is to develop
student’s competence (relevant knowledge, skills,
and experiences) to perform professional activities in
the field of investment and construction project
management using BIM technology.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Minor «Building Information Modeling
Technologies» is focused on professional standards
for construction and design: Architect, Head of a
construction organization, Specialist in the field of
assessment and expertise for urban planning,
Specialist in the field of engineering and technical
design for urban planning, Organizer of design
production in construction and professional standard
for IT ‒ Information Technology Manager.
The list of competencies that a specialist in
information modeling in the field of construction
should have:
Availability of knowledge about the features of
information modeling of construction objects
with the use of special computer programs;
Ability to develop project documentation based
on the results of engineering and technical
design;
Ability to develop the architectural section of
project documentation in investment and
construction projects.
The minor developed in the framework of the
research is focused on the formation of the basics of
the listed competencies in students.
4.1 Minor Structure
To learning the minor «Building Information
Modeling Technologies», 72 hours are required,
including 18 hours – lectures, 36 hours – laboratory
classes, 18 hours – independent work.
The form of implementation of the minor is full-
time and part-time, with the use of distance
educational technologies (e-learning), 4-6 hours a
week.
The form of assimilation control of the minor is a
test.
4.1.1 Content
The minor «Building Information Modeling
Technologies» includes 6 topics.
Topic 1. Introduction to the Autodesk Revit
software. Interface. Opportunities.
Topic Content 1: Software Interface. Basic
principles of working in the Autodesk Revit
environment. Developing of project and working
documentation in Autodesk Revit.
Topic 2. Basic principles of working with families
in the information model project.
Topic Content 2: Defining a family.
Classification of families. Templates for creating
families. Learning the interface of the family editor.
The creation of a family, the download to the project,
and location. The graphics of the family and creating
specifications. Creating parameters.
Topic 3. Studying the features of data exchange
between information modeling programs.
Topic Content 3: Import of drawings from CAD
(computer-design automation systems). Export of
project information to calculation complexes.
Topic 4. Visual programming: learning the basics.
Topic Content 4: Features of creating code for
automating work on an investment and construction
project. Interaction with project elements. Creating
objects along a complex trajectory. Features of the
placement of components. Finishing depending on
the parameters of the projected object.
Topic 5. Working with projects: review, analysis,
and verification.
Topic Content 5: Program formats. Performing a
project build. Performing a check for intersections
(collisions). Visualization in a software environment.
Topic 6. Working together on projects.
Topic Content 6. Basic principles of working
together on a project. Storage of information in the
cloud storage. Ways to link files for collaboration, a
common coordinate system. Features of the
distribution of functions between the specialists of the
project department. Exploring of the «Collaboration
panel».
4.1.2 Academic Plan
Table 1 shows the Academic plan of the minor
«Building Information Modeling Technologies»
developed by the authors of the article.
Theoretical Foundations of Training Students in the Building Information Modeling in the Context of Sustainable Development of the
Construction Industry
597
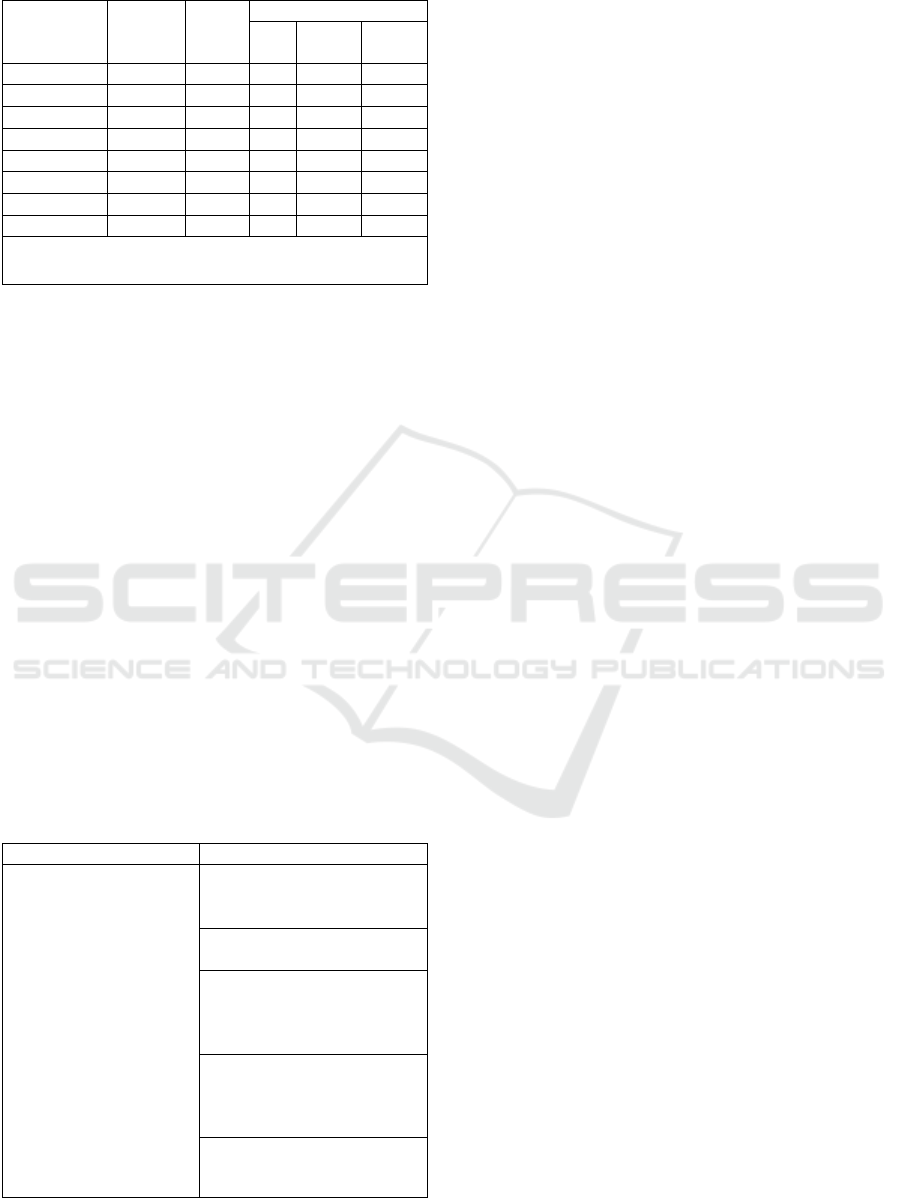
Table 1: Academic plan.
The
number
of to
p
ic
Hours T.U.*
Includin
g
**
L. L.C. I.W.
1 12 3 6 3
2 12 3 6 3
3 10 3 4 3
4 12 3 6 3
5 12 3 6 3
6 12 3 6 3
Attestation 2 0 0 2 0
Total 72 1 18 36 18
List of abbreviations: * T.U. ‒ test units; ** L. ‒lectures;
L.C. ‒laboratory classes; I.W. ‒ independent work.
A feature of the learning process within the
framework of the minor is its pronounced practice-
oriented orientation. The increased volume of
laboratory classes, the transfer of part of the
educational process to independent
work allows
students to consistently master the basics of
information modeling technology without
interrupting the main educational process.
4.1.3 Monitoring and Evaluation of Results
The current control over the development of the
minor is carried out by testing at different stages of
training. The final control is carried out in the form of
a test and a final laboratory work, for the performance
of which the student receives a «pass test».
The development of test tasks is at the
competence of the staff of the minor. Table 2 shows
the criteria developed by the article authors for
evaluating the results of students in the minor
program development.
Table 2: Results and evaluation criteria.
Student results Criteria for evaluation
1. Knows the
methodology of
information modeling
of project elements.
2. Knows how to
exchange data between
programs that are used
in the design and
implementation of
calculations.
3. Knows the
methodology of
working together on
p
rojects.
Demonstrates management
of the information modeling
environment elements.
There is a more complex
element of the project.
The model created in
Autodesk Revit was
imported into another
software
p
acka
g
e
(
an
y
one
)
.
Demonstrates management
of the «Collaboration
panel» functionality in
Autodesk Revit.
Answered correctly on at
least 70% of the test tasks.
After passing the test and completing the final
laboratory work, students sum up the results of
training in the minor, taking into account the level
approach in determining the level of competence
formation (Paharenko and Zol’nikova, 2012):
High level of BIM competence: the training
material is fully mastered, the student fully
understands the methodology of information
modeling of project elements, methods of data
exchange between programs, and methods of
joint work on projects.
Basic level of BIM competence: the training
material of the minor is sufficiently mastered,
the student is familiar with the methodology of
information modeling of project elements,
knows the ways of data exchange between
programs and the methodology of joint work on
projects, but makes minor mistakes. It is
recommended to pay attention to independent
work in programs for information modeling of
construction objects.
Average level of BIM competence: the training
material of the minor is not sufficiently
mastered, the student at the initial level knows
the methodology of information modeling of
project elements, methods of data exchange
between programs, and methods of joint work
on projects while making significant mistakes.
It is recommended to pay attention to the
repeated study of the theory, independent work
in programs for information modeling of
construction objects.
Low level of BIM competence: the training
material of the minor is poorly mastered by the
student, the information modeling
methodology is insufficiently studied, and
allows a significant number of errors. It is
recommended to pay attention to the repeated
study of the theory and additional literature, as
well as to independent work in programs for
information modeling of construction objects.
4.2 Faculty Members
When implementing the minor, the combined
teaching staff is recommended. It is advisable that
lectures for students studying in the field of
construction should be conducted by teachers of the
main engineering disciplines. It is advisable to
conduct laboratory classes for invited teachers-
employees of construction organizations specializing
in design using BIM technology.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
598

This approach to the formation of teaching staff
in the study of BIM technology has several
advantages.
Firstly, the professional competencies of teachers
of engineering disciplines allow students to easily
present lecture materials in the field of building
information modeling. Secondly, in the laboratory
classes, students who master the minor have the
opportunity to get answers to questions related to
information modeling technology from practical
teachers in this field.
Thus, the involvement of combined teaching staff
in the implementation of the minor allows students to
comprehensively master the advanced capabilities of
digital technologies in the development of
information models of buildings.
4.3 Requirements for the Results of
Passing the Minor
The results of the development of the minor are:
Knowledge of the methodology of modeling
information model project elements using
special computer programs;
Ability to apply the basic principles of data
exchange between computer programs for
designing and performing calculations;
Practical knowledge of the technology for
performing joint work on an information model
in an investment and construction project.
The totality of these results determines the
competence that is necessary for a competitive specialist
of building information modeling.
The following advantages are provided by students
studying BIM technology at universities without
interrupting the main educational process:
Mastering the technology of information
modeling even before the beginning of
professional activity;
Lectures, laboratory classes, and independent
work in the complex allow students to master
the theory and practice of using BIM;
Interaction between students and teachers-
employees of project organizations contributes
to the establishment of new professional
contacts in the future.
Thus, students who have been trained in the minor
«Building Information Modeling Technologies» are
prepared for professional activities in organizations
focused on designing with the use of BIM technology.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The use of BIM technology in construction
companies today is carried out on an initiative basis
since in this area in the Russian Federation there is no
state-mandated requirement for its mandatory
implementation (Chikovskaya, 2013).
However, due to the trend towards the mass
implementation of BIM technology in Russian
enterprises, according to the action plan approved by
the Government of the Russian Federation on April
11, 2017, No. 2468p-P9, the demand for specialists
who own BIM is growing every year.
The article specifies the competencies that a
specialist in information modeling in the construction
field should have. On their basis, the academic plan
and minor content were developed in the online
course form «Building Information Modeling
Technologies» for master’s and bachelor’s degree
students studying in the construction field, which
allows us to state that the goal of the study has been
achieved.
The analysis of scientific articles in this field has
shown that there are problems that make it difficult to
teach information modeling technologies to students
in higher educational institutions.
However, these problems can be solved by
organizing the educational process through the joint
efforts of the higher educational teachers and the
construction sector specialists.
Methods of monitoring and evaluating the results
of the minor study were developed.
Recommendations on the teaching staff formation are
given.
The study of the minor is aimed at forming the
necessary professional competence of future
developers of investment and construction projects
based on information modeling technology. In the
future, this will facilitate the selection of personnel
for design organizations specializing in BIM
technology, which will contribute to the sustainable
development of the construction industry in the
context of its digitalization in accordance with the
state program «Digital Economy of the Russian
Federation».
We hope for the introduction of this minor in
Russian higher educational institutions for high-
quality training of specialists in the field of
information modeling of construction objects.
Theoretical Foundations of Training Students in the Building Information Modeling in the Context of Sustainable Development of the
Construction Industry
599

REFERENCES
Berlak, J., Hafner, S. and Kuppelwieser, V.G. (2021).
Digitalization’s impacts on productivity: a model-based
approach and evaluation in Germany’s building
construction industry. Production Planning and
Control, 32(4).
Casasayas, O., Hosseini, M.R., Edwards, D.J., Shuchi, S.
and Chowdhury, M. (2021). Integrating BIM in Higher
Education Programs: Barriers and Remedial Solutions
in Australia. Journal of Architectural Engineering,
27(1).
Chen, K., Lu, W. and Wang, J. (2020). University–industry
collaboration for BIM education: Lessons learned from
a case study. Industry and Higher Education, 34(6):
401‒409.
Chikovskaya, I. (2013). BIM implementation ‒ experience,
scenarios, mistakes, conclusions. CAD and graphics,
8(202): 18‒22.
Goldobina, L.A. and Orlov, P.S. (2017). Bim technology
and experience of their introduction into educational
process for training bachelor students of major 08.03.01
«construction». Journal of Mining Institute, 224: 263‒
272.
Isanović, H. and Çolakoğlu, B. (2020). Students’
perceptions of bim learning scenario in architectural
education. A/Z ITU Journal of the Faculty of
Architecture, 7(3): 195‒209.
Maharika, I.F., Irsan, A., Al Athas, S.I., Susanto, A., Abma,
V. and Yuriandala, Y. (2020). Building information
modelling (BIM) adoption model for architectural
education. Journal of Design and Built Environment,
20(3).
Paharenko, N.V. and Zol’nikova, I.N. (2012). Model for
determining the level of formation of general cultural
and professional competencies. Modern problems of
science and education, 6.
Rothenbusch, S. and Kauffeld, S. (2020). Potential for
change through the digitalization of the cross-trade
cooperation of small and medium sized organizations in
the construction industry toward Building Information
Modeling (BIM)‒a case report. Gruppe. Interaktion.
Organisation, 51(3): 299‒317.
Sampaio, A.Z. (2021). BIM Education Required in
Construction Industry. Advances in Science.
Technology and Innovation, pages 3‒9.
Yakshina, A., Vasilovskaya, G., Berseneva, M., Danilovich,
E. and Hoffman, O. (2019). Bim technology in the
educational process. 22nd International Scientific
Conference on Construction the Formation of Living
Environment, FORM 2019, 97.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
600
