
Criminological Profile of Personality of a Professional Criminal:
Code-bound Thief as a Problem of Sustainable Development of
Society
Andrey A. Baybarin
1
a
and
Gennady P. Starinov
2 b
1
Department of Criminal Law, Faculty of Law, Southwest State University, 50 Let Oktyabrya Street 94, Kursk, Russia
2
Department of Public and Private Law, Faculty of Social and Humanitarian Studies, Komsomolsk-na-Amure State
University, Lenin’s Street 27, Komsomolsk-on-Amur, Russia
Keywords: Organized Crime, Professional Criminal, Criminogenic Environment, Criminal Subculture, Criminal Value
Orientations, Criminal Ideology, Special Subject of Crime.
Abstract: The article analyzes the main criminological characteristics of professional criminals - leaders of the criminal
community. The need to establish the causes and conditions for the emergence and development of criminal
qualities that form the prerequisites for committing a crime determines the analysis of the mechanism of an
individual’s criminal behavior. The works of Kh.A. Asatryan, M.P. Kleymionov, V.M. Anisimov, V.A.
Vladimirov, A.M. Lazarev and others examined the characterization of the personality of a criminal engaged
in organized criminal activity. They examined the spectrum of psychological qualities of a leader’s personality
required for organizing and directing one or another type of criminal activity. They made out the complex of
criminological characteristics of organized crime in business operation. They differentiated the organized
criminals’ composition by nationality. They indicated a problem of the positive perception of the criminal
subculture by young people. In order to counter the negative impact of the criminal "world" on the emerging
personality of a young man, they made some proposals to the current legislation. One can use the research
materials to form a criminological policy of modern society. The author has developed a legislative initiative
to implement it through amendments to the Code of Administrative Violations regarding administrative
offenses that encroach on public order and public safety.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to the “Strategy for Economic Security of
the Russian Federation for the period until 2030”, the
creation of effective criminological tools to prevent a
professional crime at the present stage of
development of our society is one of the strategic
directions for ensuring national security (Consultant
Plus, 2017).
The personality of a criminal is an integral
element of criminological research. The detailed
study of the personality of a criminal is required first
because of the fact that any commission with
elements of a crime largely depends on the
personalization of a particular criminal individual.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9183-3101
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7748-8954
The need to establish the causes and conditions for
the emergence and development of criminal qualities
that form the prerequisites for committing a crime
determines the further analysis of the mechanism of
an individual's criminal behavior.
2 METHODS
The environment exerts a strong influence on the
formation of the initial deviant behavior of a
particular person, which includes:
1) “External environment” formed from the
political, material and spiritual conditions of the
individual;
798
Baybarin, A. and Starinov, G.
Criminological Profile of Personality of a Professional Criminal: Code-bound Thief as a Problem of Sustainable Development of Society.
DOI: 10.5220/0010597807980803
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 798-803
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2) “Internal environment” as a form of immediate
social environment formed by the totality of criminal
elements that promote the ideology of a criminal
image.
The criminogenic environment, which has been
forming in the field of professional criminal activity
throughout the development of our society, has
implemented criminal moral standards, a criminal
subculture, the communications that ultimately
continued to improve the hierarchical criminal
structure, which ultimately negatively affected the
psychology and moral world of a specific individual.
The criminal environment has the greatest impact
on a particular person in places where the criminal
elements are concentrated (prison, pretrial detention
facilities, penal colony settlement) obliging to fulfill
all its requirements under the threat of inevitable
punishment (Kleymionov, 2011).
In our opinion, it seems advisable to consider the
criminological portrait of a professional criminal who
expresses his motivational activity in a categorically
negative attitude to the legal norms and values of our
society.
3 RESULTS
The personality of a professional criminal, the so-
called code-bound thief, contains criminal properties
at all stages of unlawful acts in full contact with
criminal communities that have a negative social
orientation not only in Russia but also abroad.
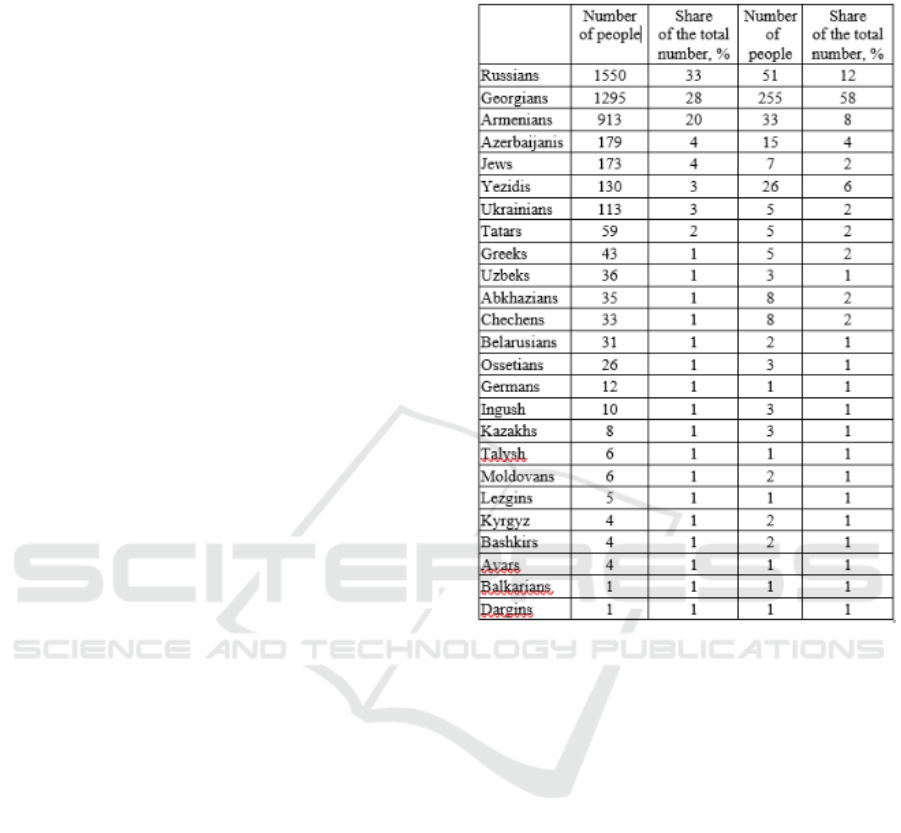
A huge number of ethnic organized criminal
communities – Georgian, Ingush, Chechen, and
Azerbaijani – are engaged in crimes in Russia. The
criminal activity of the Chinese and Tajik diasporas
is intensifying, ultimately creating a threat to the
national security of our society.
The multinational composition of professional
criminals – code-bound thieves allows concluding
about the international interaction of "criminal world"
(Table 1).
Table 1: The National Composition of Professional
Criminals.
Source: the author compiled the table based on the data
from the site of Prime Crime Information Agency (Prime
Crime-1 IA, 2020).
A diverse range of criminal activities determines
a wide range of psychological qualities of a leader’s
personality, which are necessary to lead various types
of criminal activity.
Typical personality characteristics inherent with
code-bound thieves committing common crimes and
leaders of organized crime groups operating in the
field of criminal business operation differ a little
(Asatryan, 2014). A leader of the criminal
community, organizing crimes in economic activity,
is a highly educated criminal, unconventionally
approached to the search for new opportunities for
criminal business operation.
The business qualities inherent with a
professional criminal - a code-bound thief include:
initiative in making a certain decision; decisiveness in
making high-risk decisions; ability to influence
people used in the criminal business process; high
level of professional training; charismatic abilities
that allow to manage a criminal society.
Criminal professional training of professional
criminals creates the conditions for the preparation
Criminological Profile of Personality of a Professional Criminal: Code-bound Thief as a Problem of Sustainable Development of Society
799

and commission of a crime, using the opportunities
for latent receipt of criminal profit in the process of
committing illegal actions (Samsonov and Sergeev,
2014). They have extensive connections that go far
beyond criminal contacts, including corrupt law
enforcement officials.
A criminal offender connects crimes of a
corruption nature with the deliberate use of his
official authority in order to obtain material and other
advantages, for personal criminal enrichment or for
third parties performing managerial functions in a
commercial or other organization and receiving
illegal remuneration (Onufrienko, 2014).
Such people, having a certain legal status, both in
government and in business, and in business
operation, are usually pragmatic and are striving for
specific criminal results, often using the capabilities
of representatives of the “thieves' world” -
professional criminals (Izvestia, 2018).
The public danger of a corrupt criminal also
comes out in legal discrediting of law through
lobbying of criminal bills and interference in law
enforcement, artificially blocking social projects in
the interests of code-bound thieves.
Professional criminals strive for personal
independence in any circumstances, realizing their
high level through domination in the criminal and
business operational environment.
The most authoritative in the criminal community
leaders of the "criminal world" define the status of a
professional criminal as a code-bound thief at their
gathering.
All the business qualities of a professional
criminal ultimately form the criminal value
orientations and distorted moral foundations of
behavior for direct perpetrators of criminal activity,
and ultimately increase the social danger of a
particular code-bound thief (Kudryavtseva, 2005).
“A large part of the population is involved in this
system and to the point organized crime, controlled
by professional criminals, is an alternative society
with its highly profitable economy, social and
spiritual spheres, its systems of governance, security,
the formation of the young generation, the courts, its
domestic and foreign policies” (Nomokonov, 2010).
Organized crime comes out in the complex of its
criminological characteristics in business operation:
1) The criminalization of economic relations
expressed in the merger of economic and ordinary
criminal activity;
2) The active manifestation of corruption
components, which are a prerequisite, on the one
hand, and one of the manifestations of organized
crime, on the other hand, a means of disguising it;
3) The formation of a reserve of organized
criminal communities from among who serving
criminal sentences in places of deprivation of liberty;
4) The elimination of most forms of social control
because of political instability of society, aggravation
of interethnic, ethnic, religious conflicts;
5) The deformation of the moral position of the
population, affecting the criminal potential;
6) Gaps in the criminal, criminal procedure,
criminal executive and administrative legislation;
7) The weakening of the role of state bodies of
legislative and executive power in the legal regulation
of business operation, in the formation of civilized
market relations.
A specific feature of professional crime is a high
degree of criminal latency that causes enormous
damage to society.
The latency of professional crime is a big social
problem, a detailed study of which allows revealing
of crime statistics close to the truth based on:
1) The real development of methods for the
prevention of crimes in the field of business
operation;
2) Identifying the causes and conditions
conducive to the commission of economic crimes,
and their timely elimination;
3) The implementation of the principle of the
inevitability of punishment for committing unlawful
acts and evening-out the educational impact of
criminal law;
4) The ability to predict economic crime and
develop comprehensive programs for its prevention;
5) Reducing of such a negative phenomenon as
the self-determination of economic crime, that is the
preventive effect on its self-reproduction due to the
growth of recidivism.
An analysis of criminological policy in Russia
allows concluding that the fact that our society allows
professional criminals to manage youth policy
unpunishably and legally in order to prepare for them
a new generation of perpetrators of criminal
intentions also facilitate the spread of criminal
ideology and the strengthening of the positions of
organized criminal groups (TASS, 2016).
In this case, the criminal subculture, being an
integral part of the ideological values of the criminal
community, creates the prerequisites for a negative
impact on the younger generation, which is the basis
for the further development of our society (Vologdina
et al., 2020).
Creating a positive perception of the criminal
lifestyle of professional criminals in the youth
environment makes it possible to legalize the cultural
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
800

phenomena studied in criminology as a criminal
subculture (Kleymionov, 2018).
The implementation of distorted value
orientations of youth, based on a positive perception
of the criminal subculture, is gradually becoming an
integral part of the personality of offenders,
displacing elements of legal consciousness
(Anisimkov and Koroliova, 2007).
The low level of social well-being of the
mainstream youth environment allows professional
criminals to stupefy young people with “thieves'
romance”, followed by involving juveniles in
criminal activity (NEWSru.com, 2016).
4 DISCUSSION
The idea of ways to violate the law sequentially
comes to citizens of our society as an inevitable
attribute of business activity. For example, Russian
code-bound thieves legalized the site "Prime Crime",
having registered it as a mass media outlet, all
materials of which are protected by copyright (Prime
Crime-2 Information Agency, 2020).
Public ideologists of the thieves' movement have
gathered a huge amount of material on propagating
the history of the “thieves' world” based on the
formation of an allegedly positive image of criminal
authorities (Beloglazov, 2006).
The imperfection of the legislation and the
inefficiency of the criminological policy of the state
in the sphere of the lawful behavior of an individual
makes the basis for the further spread of criminal
ideology among young people (Tseveleva et.al.,
2020).
5 CONCLUSIONS
In order to negatively perceive the criminal “world”
at the stage of personality formation and counteract
the formation of professional criminal communities,
include the article 20.3.1 in chapter 20 of the Code of
Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation
(Administrative Offenses encroaching on public
order and public safety). Name it "Advocacy of the
ideology of criminal subculture and the criminal way
of life among juveniles".
«A public demonstration of the symbols of
belonging to the criminal world, the performance of a
song repertoire praising the social significance of the
criminal environment, the public use of slang phrases
of the criminal world, the creation of sites and groups
on social networks with the aim of spreading and
propagating criminal ideology among juveniles».
The proposed legislative initiative will be one of
the forms for the implementation of Federal Law No.
436-FZ dated 12/29/2010 “On the Protection of
Children from Information Harmful to Their Health
and Development”. It will be the form of legal
consolidation of the constitutional principles for the
protection of childhood, proposed for public
discussion by the President of the Russian Federation.
It will be the legal consolidation in normative acts
of the instructions of the President of the Russian
Federation expressed in the Address to the Federal
Assembly on 15.01.2020. It will be the legal basis for
the implementation of Recommendation No. CM /
Rec (2018) 7 of the Cabinet of Ministers of the
Council of Europe “On the observance, protection
and implementation of the rights of children in the
digital environment”, which stipulates the need to
identify the relevant crimes committed in the digital
environment and criminal liability for them
(ConsultantPlus-1, 2019; State Duma, 2020;
President of Russia, 2020; Recommendation, 2018).
Fixing the unlawful ideological activity of the
leaders of the criminal “world” within the framework
of administrative legislation will create legal
prerequisites in the process of subsequent criminal
liability under paragraph 1 of Article 210 of the
Criminal Code of the Russian Federation for
“...occupying a higher position in the criminal
hierarchy”. It will allow the law enforcement
authorities to classify this category of persons as the
“special subject of crime”, since the signs themselves
directly follow from the content of the article,
although not directly indicated in it (ConsultantPlus,
2020; ConsultantPlus-2, 2019).
This will primarily relate to the fact that the
criminalization of criminal policy to increase
responsibility for the creation and leadership of the
criminal community has forced authoritative code-
bound thieves to implement a set of preventive
counteractions aimed at practical imparting to the
conspiracy of a criminal organization.
Their counter-actions include the development of
measures for career-oriented nomination of their legal
representatives in business structures and state
authorities in order to create corrupt schemes.
In particular, summarizing the multifaceted
opinions of specialists regarding the definition of the
status of a special subject, Yu.V. Tarasova (2004)
concretizes the fact that there is no single
understanding on this issue in the theory of criminal
law.
Criminological Profile of Personality of a Professional Criminal: Code-bound Thief as a Problem of Sustainable Development of Society
801

For example, A.M. Lazarev, G.N. Borzenkov
(1981), defines a special subject as the person who
has both common features and additional qualities.
V.A. Vladimirov, G.A. Levitsky (1964)
concretize a special subject as the one who has the
specific features listed in the disposition of the article.
Accordingly, when classifying the characteristics
of a special subject, we propose to take into account
the characteristics of the legal status of the subject
depending on the role that he plays in the commission
of the crime: organizer / leader (DeKeseredy and
Dragiewicz, 2012).
In this case, enumeration for the meaning of the
features of a special subject is as follows:
1) Optional features forming the components of
crime
2) Acting as qualifying features
3) The implication for the individualization of
punishment, aggravating criminal liability.
Controlling common criminal and economic
crime in the course of their criminal activity,
professional criminals participate in criminal
business operations actively, making fabulous profits
from the criminal arms trade, trafficking and sale of
drugs, sale of innards, organizing of the sex-work
sector and the total control of the smuggling of goods
across the border (Gondolf, 2012).
Professional criminals are legal co-founders of a
significant part of the economic sphere of business,
continuing further work on the legalization of capital
acquired by illegal means, trying to take control of the
economy of the city, region, concentrating tax-free
money in the criminal community. It means that they
are the most active participants in the formation of the
“shadow” economies and constitute a real threat to
the national security of the country.
We believe that the knowledge of the personality
of a criminal - the code-bound thief, who, being the
most important link in the entire mechanism of
criminal behavior of criminal communities creates
problems for the stabilization of our society, makes
the base for the effective counteraction against
professional crime.
REFERENCES
Anisimkov, V.M. and Koroliova, E.V. (2007). Criminal
Subculture: A Brief History of the Matter, Its Impact on
the Formation of the Offender’s Personality. Bulletin of
the Vladimir Law Institute, 3(4): 142-146.
Asatryan, Kh.A. (2014). Characterization of the Personality
of a Criminal Engaged in Organized Criminal Activity.
Criminological Magazine of the Baikal State University
of Economics and Law, 3: 40-48.
Beloglazov, E.G. (2006). Modeling of a Criminal
Environment Management System. Bulletin of the
Moscow University of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of
the Russian Federation named after V.Ya. Kikotya,
pages 39-41.
Consultant Plus (2017). Decree of the President of the
Russian Federation dated May 13, 2017 N 208 “On the
Strategy for Economic Security of the Russian
Federation for the period until 2030”. URL:
http://www. consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW
_216629/ (data accessed: 15.05.2020).
Consultant Plus (2020). Federal Law N 63-FZ dated
06/13/1996 “Criminal Code of the Russian Federation”
(as amended on 02/18/2020). URL:
http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_
10699/ae9d07f27fd0e736d95f0da92e5d62311e7ea7f5/
(data accessed: 19.03.2020).
ConsultantPlus-1 (2019). Federal Law N 436-FZ dated
December 29, 2010 “On the Protection of Children
from Information Harmful to Their Health and
Development” (as amended on May 01, 2019). URL:
http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_
108808/ (data accessed: 20.05.2020).
Consultant Plus-2 (2019). Federal Law dated 01.04.2019 N
46-FZ “On Amendments to the Criminal Code of the
Russian Federation and the Criminal Procedure Code of
the Russian Federation with Regard to Organized
Crime Prevention”. URL: http://www.consultant.ru/
document/cons_doc_LAW_3214 11/ (data accessed:
19.03.2020).
DeKeseredy, W. and Dragiewicz, M. (2012). Critical
criminology: Past, present, and future. Handbook of
critical criminology. Routledge. New York.
Gondolf, E. (2012). The future of batterer programs:
Reassessing evidence-based practice. Northeastern
University Press. Boston.
Kleymionov, M.P. (2018). Personality of a Professional
Criminal Personality of a Criminal and Its
Criminological Study. Russian Criminological
Association Publ. Moscow.
Kudryavtseva, V.N. (2005). Criminology. Norma.
Moscow.
Lazarev, A.M. (1981). Subject of Crime. RIO VUZI.
Moscow.
NEWSru.com (2016). The Human Rights Council told
about the AUE youth group, which requires children in
18 regions of the Russian Federation to donate “money
to the common fund for the prison camp”. URL:
http://www.newsru.com/crime/13jul2016/unity.html
(data accessed: 27.07.2020).
Nodelman, V. (2018). Portrait of a Corrupt Official:
Energetic, Educated 40-year-old Family Man. Izvestia.
URL: https://iz.ru/821066/valeriia-nodelman/portret-
korruptcionera-energichnyi-obrazovannyi-40-letnii-
semianin (data accessed: 09.04.2020).
Nomokonov, V.A. (2010). Transnational Organized
Crime. Far Eastern Federal University Publ.
Vladivostok.
Onufrienko, A.V. (2014). The Role of the Prosecution
Authorities of the Russian Federation in the Fight
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
802

against Corruption. Bulletin of the Moscow Finance
and Law University, 4: 133-143.
President of Russia (2020). The President’s Message to the
Federal Assembly. URL: http://www.kremlin.ru/
events/president/news/ 62582 (data accessed:
01.04.2020).
Prime Crime-1 Information Agency (2020). People. URL:
https://www.primecrime.ru/ characters / top / (data
accessed: 20.03.2020).
Prime Crime-2 Information Agency (2020). About the
project. URL: https://www.primecrime.ru / about /
(data accessed: 10.03.2020).
Recommendation (2018). Recommendation No. CM/Rec
(2018)7 of the Cabinet of Ministers of the Council of
Europe “On Observance, Protection and
Implementation of the Rights of Children in the Digital
Environment” (Adopted on 07/04/2018 at the 1321st
meeting of representatives of ministers)”. Bulletin of
the European Court of Human Rights, 12: 112-126.
Samsonov, V.A. and Sergeev, S.M. (2014). Law
Enforcement Counteraction to Ethnic Organized
Criminal Groups. East Siberian Institute of the Ministry
of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation Publ.
Irkutsk.
State Duma (2020). On the Amendment to the Constitution
of the Russian Federation. URL:
http://duma.gov.ru/news/48045/ (data accessed:
29.03.2020).
Tarasova, Yu.V. (2004). The Concept and Characteristics
of a Special Subject of Crime. Russian Investigator, 10:
13-16.
TASS (2016). HRC is concerned about the “thieves'
movement” among children, considers it a threat to
national security. URL: http://tass.ru/obschestvo/2
621038 (data accessed: 25.04.2020).
Tseveleva, I.V., Starinov, G.P. and Pershina, E.Yu. (2020).
Foresight System in the Structure of Criminological
Forecasting of Corruption in the Business Environment
in Multicultural Space of Russia. In Smart Innovation,
Systems and Technologies, 172: 379-390.
Vladimirov, V.A. and Levitsky, G.A. (1964). Subject of
Crime under Soviet Criminal Law. Lecture. NIiRIO
VSh MOOP RSFSR. Moscow.
Vologdina, E.S., Kuzmina, O.A. and Matyuschko, A.V.
(2020). Experience of Implementing State Policy on
Life and Adaptation of Families of Agricultural
Migrants from the European Part of Russia to the Far
East in the 20-30s of the 20th Century. Advances in
Economics, Business and Management Research, 128:
584-588.
Criminological Profile of Personality of a Professional Criminal: Code-bound Thief as a Problem of Sustainable Development of Society
803
