
Knowledge Graph Analysis of Russian Trolls
Chih-yuan Li
1
, Soon Ae Chun
2
and James Geller
1
1
Department of Computer Science, New Jersey Institute of Technology, Newark, NJ 07102, U.S.A.
2
City University of New York, College of Staten Island, New York City, NY 10314, U.S.A.
Keywords: Relationship Analysis of Troll Tweets, Entity Extraction, Triple Extraction, Sentiment Analysis.
Abstract: Social media, such as Twitter, have been exploited by trolls to manipulate political discourse and spread
disinformation during the 2016 US Presidential Election. Trolls are users of social media accounts created
with intentions to influence the public opinion by posting or reposting messages containing misleading or
inflammatory information with malicious intentions. There has been previous research that focused on troll
detection using Machine Learning approaches, and troll understanding using visualizations, such as word
clouds. In this paper, we focus on the content analysis of troll tweets to identify the major entities mentioned
and the relationships among these entities, to understand the events and statements mentioned in Russian Troll
tweets coming from the Internet Research Agency (IRA), a troll factory allegedly financed by the Russian
government. We applied several NLP techniques to develop Knowledge Graphs to understand the
relationships of entities, often mentioned by dispersed trolls, and thus hard to uncover. This integrated KG
helped to understand the substance of Russian Trolls’ influence in the election. We identified three clusters of
troll tweet content: one consisted of information supporting Donald Trump, the second for exposing and
attacking Hillary Clinton and her family, and the third for spreading other inflammatory content. We present
the observed sentiment polarization using sentiment analysis for each cluster and derive the concern index for
each cluster, which shows a measurable difference between the presidential candidates that seems to have
been reflected in the election results.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the activities of Russian internet trolls were
discovered in the 2016 US Presidential elections, the
influence of trolls has been studied (Linvill et al.,
2019). Social media, e.g., Facebook and Twitter, have
become influential platforms of political discourse,
but were also misused by “trolls” who manipulated
the political exchanges. Trolls are users who create
social media accounts in order to post or retweet
misleading messages to negatively influence the
political process.
Different definitions of "troll" exist. Mojica
(2016) focuses on the intentions of the user, while
Kumar et al. (2014) use the term "trolling" when a
user posts and spreads disinformation. Addawood et
al., (2019) defined trolls as user accounts whose sole
purpose is to sow conflict and deception, and Jachim
et al. (2020) consider trolls as users who identify
themselves with a group that wants to cause
disruption and trigger conflict in discourse. The
Russian Trolls (RTs) were 2,752 Twitter handles
(accounts) identified by Twitter that were allegedly
tied to the Internet Research Agency (IRA), known to
be a troll farm sponsored by the Russian government,
attempting to sow discord among Americans and
influence the 2016 US election by spreading
disinformation. The networks of these trolls posted
inflammatory tweets, such as claims that Democrats
are practicing witchcraft. Some trolls created bogus
personae pretending to be BLM activists and posted
aggressive tweets. Trolls also connected with
influencers, e.g. celebrities, to manipulate them and
to amplify their malicious intents.
With the rapid data sharing on social media, the
impact of trolls can be quite damaging. Thus, the
troll-related research challenges include: (1) methods
for troll detection for distinguishing troll posts from
non-troll posts, and (2) the in-depth analysis of the
content of troll posts to further uncover the underlying
entities and their relationships in distributed posts by
different trolls. With the advances of Machine
Learning, models for the detection of trolls or their
posts were trained with high accuracy (e.g., Chun et
al., 2020).
Li, C., Chun, S. and Geller, J.
Knowledge Graph Analysis of Russian Trolls.
DOI: 10.5220/0010605403350342
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications (DATA 2021), pages 335-342
ISBN: 978-989-758-521-0
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
335

In this paper, we present new approaches of in-
depth analyses of the Russian Troll dataset, linking
disparate tweets to understand the involved entities,
and their semantic relationships. We applied several
NLP techniques including Named Entity Recognition
and Triple Extraction to derive relationships between
entities and construct a Knowledge Graph based on
the triples for the semantic analysis of troll tweets.
We also performed unsupervised clustering to
discover major clusters of troll tweets and to construct
a knowledge graph for each cluster that consists of
entities, the relations between the entities, and the
sentiments expressed by the troll tweets to get more
in-depth insights into the operations of RTs. We:
• Integrate the distributed microblog posts (tweets)
by different trolls into a Knowledge Graph to
understand the entities and their relations/events
between entities. The Knowledge Graph allows to
focus on the semantic relationships of entities
existing in different trolling posts that are not
directly visible and therefore usually ignored.
• The semantic approaches include NER and triple
extraction, leading to an understanding not only of
entities, but also of asserted statements by trolls.
• The interactive visualization of these entity-
relationship triples (Subject, Predicate, Object)
allows the users to uncover prominent events or
claims by trolls.
• The sentiment analysis performed on major troll
tweet clusters uncovers the comparative
polarizations existing in different troll clusters.
These methods can be applied to any other electoral
Twitter dataset for insights.
Section 2 explores previous work on troll
research, e.g., troll detection and discovery,
especially of right- and left-wing trolls. In Section 3,
we detail the dataset used in this work and the text
preprocessing steps. In Sections 4 and 5, we introduce
the methods used, e.g., Named Entity Recognition,
Text Clustering, Sentiment Analysis and Triple
Extraction, followed by the results, findings, and
future work.
2 RELATED WORK
A number of approaches using AI and Machine
Learning (ML) models have been used to classify troll
and non-troll tweets. (Chun et al., 2019) trained
several ML models and applied them to decide
whether a given tweet is a troll tweet. (Addawood et
al., 2019) identified linguistic cues as potential
markers of deceptive language to distinguish between
troll and non-troll tweets. (Monakhov, 2020)
proposed a quantitative measure for detecting troll
contents, which focused on certain sociolinguistic
limitations of troll speech, and discussed two
algorithms that both require only 50 tweets to
distinguish whether a message is ‘genuine’ and ‘troll-
like.’ In (Jachim et al., 2020), two automated
reasoning mechanisms for detecting and evading
trolling detection are presented, TrollHunter and
TrollHunter-Evader. While the former reached an
accuracy of 98.5% identifying trolls, the latter
undermined the performance of the former by 40%,
by manipulating the text and hashtags in the tweets.
(Seah et al., 2015) detected troll users from the
sentiments of the textual content. (Ghanem et al.,
2020) identified trolls by studying the effect of a set
of text-based features, including affective ones, and
proposed ML models that take into account topic
information. (Cambria et al., 2010) used Sentic
Computing, a new paradigm for the affective analysis
of natural language text, to extract semantics and
sentics from web-posts and hence protect web-users
from getting emotionally hurt by malicious posts.
To deal with troll contents that are not written in
English, (Miao et al., 2020) detected troll tweets in a
bilingual English and Russian corpus. (Mutlu et al.,
2016) measured the awareness level of users in
Turkey and around the world in regard to terrorism,
based on the results of troll detection. To prevent
trolls from influencing public opinion with fake
information, methods for discovering or deactivating
suspected troll accounts on Twitter have been studied.
(Im et al., 2020) developed ML models to predict
whether a Twitter handle is a Russian Troll, and the
findings imply that many RTs are likely still active
today.
The features and semantic patterns of troll tweets
have been explored. In (Chun et al., 2020), they not
only worked out troll detection, but also successfully
classified specific tweets as coming from left trolls or
right trolls. (Atanasov et al., 2019) automated the
analysis of different behavioral patterns (Left, Right,
Newsfeed) observable in the online traces of trolls, by
using ML in a realistic setting, in a supervised
learning scenario and in a distant supervision
scenario. (Iqbal et al., 2020) found patterns and topics
in tweet contents and categorized the trolls as left
trolls or right trolls.
Dynamic Exploratory Graph Analysis was
proposed (Golino et al., 2020) to discover latent
topics in the left troll and right troll tweets. Common
topics posted by right trolls include support for
Donald Trump and defending political agendas
aligned with Trump’s proposed policies, including
pro-gun, pro-police, anti-terrorism, and anti-Islam
DATA 2021 - 10th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
336

policies, etc. These tweets also "expose" and attack
Hillary Clinton. As for left trolls, the main topics are
Black Lives Matter (BLM), activities against police
brutality, and support of black culture and music.
Another study (Etudo et al., 2020) showed that the
timing of tweets about police brutality by RTs
coincided with periods of increased BLM activities.
(Badawy et al., 2018) found that RTs had a mostly
conservative, pro-Trump agenda and conservatives
amplified trolls’ messages much more often than
liberals.
As we have been looking into political trolls’
behavior, political psychology is also worthy of
exploration. (Alizadeh et al., 2019) revealed that
extremists show lower positive emotions and higher
negative emotions than partisan users, but their
differences in certainty are not significant. Moreover,
while left-wing extremists express more anxiety than
liberals, right-wing extremists were lower than
conservatives on the scale.
3 DATASET
The dataset we used is derived from the RT tweets
made available by NBC News (Popken, 2018). Under
the House Intelligence Committee investigation into
how RTs have influenced the 2016 US Election,
Twitter released almost 3,000 Twitter handles
believed to be associated with Internet Research
Agency (IRA). These accounts as well as their data
were suspended and deleted by Twitter. A team at
NBC News was able to reconstruct a dataset
consisting of a subset of the deleted data for their
investigation and were able to show how these troll
accounts went on the attack during the election
period. The dataset is freely available and includes
203,482 tweets from 454 Twitter handles.
We used this dataset to understand the underlying
entities and relationships among the trolls. In the first
step of preprocessing, we removed URLs, Twitter
handles and Non-ASCII characters from the tweets,
using the ‘re’ package of Python (McKinney, 2017).
Repetitive punctuations and spaces were also
eliminated. Then we separated camel case words and
"sticky" numbers and letters and used other data
cleansing steps as needed. Table 1 shows an example.
After standard text pre-processing, we were left with
201,366 troll tweets stored in a Python list with
2,624,037 words and 15,586,691 characters.
Table 1: Tweet before and after preprocessing.
Before Preprocessing After Preprocessing
IGetDepressedWhen someone says
he doesn’t have
any options except for voting for
Trump
I Get Depressed When
someone says he doesnt
have any options except
for voting for Trump
4 METHODS
4.1 Named Entity Recognition
Named Entity Recognition (Named-entity
recognition, n.d.) finds and classifies named entities
in text into pre-defined categories, such as person,
organization, location, date, time, quantity, etc. We
utilized spaCy (spaCy 101, n.d.) to assign named
entity labels to our tweets. SpaCy is a powerful, free
library for Natural Language Processing (NLP) in
Python. Its features include linguistic and more
general ML functionalities. There are features that
require statistical models (spaCy models, n.d.) to be
loaded so that spaCy will be able to predict linguistic
annotations, e.g., whether a word is a noun or a verb.
Different languages are supported by spaCy. ML
models also differ in format of input data, accuracy,
size, speed, etc. Users can choose the model
depending on individual cases and the input.
Normally a small or default model is a proper option
to start with. There are 18 types (Data formats, n.d.)
that spaCy can recognize, such as person, event,
location, etc. We used the (displaCy Named Entity
Visualizer, n.d.) to visualize the labeled entities.
Types are color-coded.
4.2 Troll Tweet Clustering
Clustering (Koch, 2020) is used for grouping troll
tweets based on their text into groups that contain
similar objects. We used K-Means Clustering (k-
means clustering, n.d.). As it requires numerical data
for similarity and distance measures, we used TF-
IDF, which uses term frequency and inverse
document frequency. To implement TF-IDF and
clustering, we used scikit-learn tools. We also
performed preprocessing for text clustering by
removing stop words, numbers, and punctations.
4.3 Sentiment Analysis of Trolls
To understand how Twitter users feel about politics,
we measured sentiments expressed by the collected
tweets. We used the sentiment analysis tool in the
Stanford NLP (Sentiment Analysis, n.d.) package,
Knowledge Graph Analysis of Russian Trolls
337
which uses fine-grained analysis based both on words
and labeled phrasal parse trees to train a Recursive
Neural Tensor Network (RNTN) model. The model
computes the sentiment expressed by a sentence,
based on how words compose the meaning of longer
phrases. Then the sentiments of the nodes
(representing phrases) in the parse tree are composed
to predict a sentiment value for the whole sentence.
Previous work has indicated that it is possible to
achieve an accuracy for fine-grained sentiment labels
above 80% (Socher et al., 2013).
The RNTN model works with a single sentence at
a time. To analyze tweets that include more than one
sentence, we converted periods, question marks and
exclamation marks into semicolons. Then tweets are
labeled either as "Very negative," "Negative,"
"Neutral," "Positive" or "Very positive" (Table 2).
Table 2: Sentiment analysis of example trolls.
Tex
t
Sentiment
Sore loser Obama turns to Russian hacking to
delegitimize Trump's triumph;
Very
negative
Hillary Clinton And you have turned the Middle
East into a living hell;
Negative
Trump Signs Obamacare Executive Orde
r
Neutral
In light of Hillary's FBI investigation you can
change your early vote in these states;
Positive
real Donald Trump is brilliant and has amazing
insight; He's going to be a fantastic President;
Very
positive
We analyzed the degree of negative polarization
toward a candidate. The higher the negative
polarization, the bigger the negative influence the
readers were exposed to with regards to the candidate,
thus, became more likely to vote against him/her. To
characterize the degree of negative polarization in
normalized sentiments, we used the concern index,
that we previously defined (Ji et al., 2013), as follows:
CI = N/(N+P)
N is the count of negative tweets + very negative
tweets; P = #(positive + very positive tweets).
4.4 Triple Extraction
To understand the semantic relations between two
entities, we use a triple which codifies a statement
about the entities in the form of subject–predicate–
object (Hitzler et al., 2014). To determine the
relations between entities in tweets (e.g., between two
people), we extracted such triples from tweets. We
used the Stanford Open Information Extraction
system (Stanford Open Information Extraction, n.d.)
for this. Multiple triples can be extracted from one
tweet through repeated split operations to capture
several relations in a tweet. Tweets are parsed into
sentences. Traversing a dependency parse tree
recursively, the algorithm predicts at each step
whether an edge should yield an independent clause
(Angeli et al., 2015).
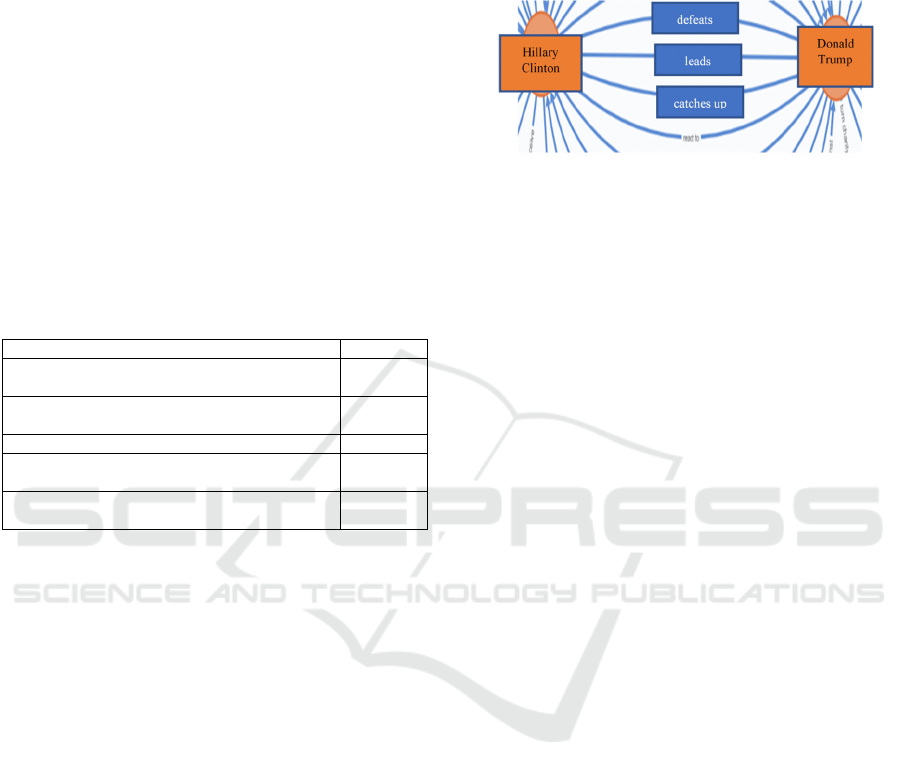
Figure 1: Donald Trump (Subject) relates to Hillary Clinton
(Object) with different relations (excerpt from Neo4j
visualization, post-edited for readability).
Clauses are shortened into fragments, and
fragments are segmented into OpenIE triples. For
example, triples extracted from “Born in Boston, he
is a US citizen” would be (he, Born in, Boston) and
(he, is, US citizen). The triples (typically) retain the
core semantics of the original sentence. A set of
triples is stored as a CSV file with three columns.
4.5 Knowledge Graph for
Relationships
A large triple set with information about the same
entity spread out over many rows is not conducive to
comprehension. We used Knowledge Graph and
visualization to collect all information about one
entity (one concept as one node) at one place, for
understanding the entity-to-entity relationships.
A Knowledge Graph represents a collection of
interlinked entity descriptions. Inside the graph there
are entities such as real-world objects and events or
abstract concepts stored, and they are interlinked with
relations to form a network. As the semantic web is
developing, Knowledge Graphs are often associated
with linked data, focusing on the connections between
entities and concepts. (Ehrlinger & Wöß, 2016; Soylu
et al., 2020)
In our work, the transformation from text to a
Knowledge Graph (KG) is achieved as follows. Every
subject and every object becomes a node in the graph.
Every relation becomes a link, forming larger graphs
with overlapping nodes in several steps. For example,
two triples (Anthony Wiener, Criticize, Hillary
Clinton) and (Hillary Clinton, Delete, Email),
together can form a larger KG by sharing "Hillary
Clinton."
In a visual representation of such a graph in Neo4j
nodes appear commonly as ovals and links as arrows
pointing from the subject node to the object node.
DATA 2021 - 10th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
338
When a specific entity occurs in many rows of the
CSV file (in our case, e.g., "Hillary Clinton"), we
want to represent all instances by the same node.
Neo4j offers a setting that automatically merges
identical entities into one node. The graph data is
accessible by its own query language, called Cypher
(Cypher (query language), n.d.). Having a graph
representation makes it possible to answer many
questions of interest about a tweet set with little visual
effort. For example, we can determine which entities
have many relations, what kinds of relations they are,
and whether more of these relations are outgoing or
incoming. For instance, Figure 1 shows the Neo4j
relations between Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton,
such as "defeats," "leads," and "catches up to", etc.,
(entity labels are represented in textboxes for
readability). Collecting all these relations next to each
other in a graph provides a rich picture of how two
entities in the real world connect to each other,
according to the opinions of Twitter users. Similarly,
the conceptual distance between two entities can be
seen in a graph as the minimal number of links that
have to be traversed to get from one entity to the
other.
Figure 2: Named Entity Recognition and Label
Visualization.
5 RESULTS
5.1 Named Entities in Trolls
The six most common entity types recognized in our
dataset are shown in Table 3. Figure 2 shows
examples of the occurrences of different types of
entity labels.
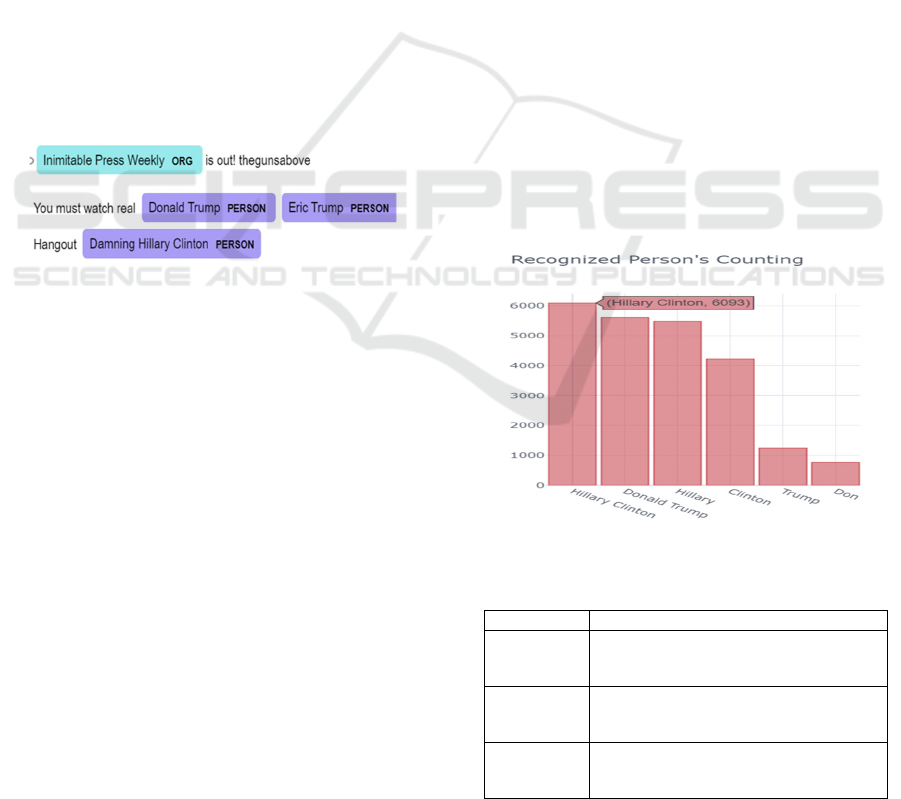
Figure 3 shows the counts of person entities
extracted, with the two presidential candidates
topping the frequencies of being mentioned, and
“Hillary Clinton” appearing more often than “Donald
Trump.” This confirms the hypothesis that this dataset
is election-related. According to the aggregated
statistics "Clinton" appears more often than "Trump,"
thus we can say that Clinton (and family) are more of
a target of Russian Trolls than Trump (and family).
Table 3: Six of 18 Named Entity types.
Entity Type Count
Person 99,273
Org 60,596
G
p
e
(
Geo
p
olitical location
)
30,466
Cardinal 30,354
Date 23,727
Norp (Nation/Religion) 17,455
5.2 Clustering of Trolls
In the K-Means algorithm, the value of K depends on
how many clusters we want to partition the set of all
tweets into. This requires a trial-and-error approach.
In the beginning we set K=6, however, results were
not intuitive. As we stepwise reduced K to 3, this
dataset was naturally grouped into three clusters. One
resulting cluster of 16,851 tweets is mainly about
Clinton. Another cluster of 30,111 tweets is about
Trump. The largest cluster with 154,404 tweets
relates to Obama and other topics. This result enabled
us to separately look into how each of these three
person entities was portrayed by RTs. We collected
the top 15 terms of each cluster to obtain a general
understanding of the topic (Table 4). We can easily
identify in Cluster 1 the Trump-related tweets, Cluster
2 contains Clinton-related tweets and Cluster 3 is on
Obama and others. Figure 4 shows the word clouds
for Clinton and Trump.
Figure 3: Top 6 Frequencies of ‘PERSON’ entity.
Table 4: Top 15 terms in each cluster.
Cluste
r
Frequent terms
1 (Trump)
trump, donald, real, president, vote,
politics, say, america, clinton, maga, win,
media, make, obama, pence
2 (Clinton)
hillary, clinton, trump, email, campaign,
vote, prison, president, trust, obama, thing,
debate, say, politics, crooked
3 (Others)
obama, word, make, people, day, like,
thing, say, know, love, news, black, life,
new, want
Knowledge Graph Analysis of Russian Trolls
339
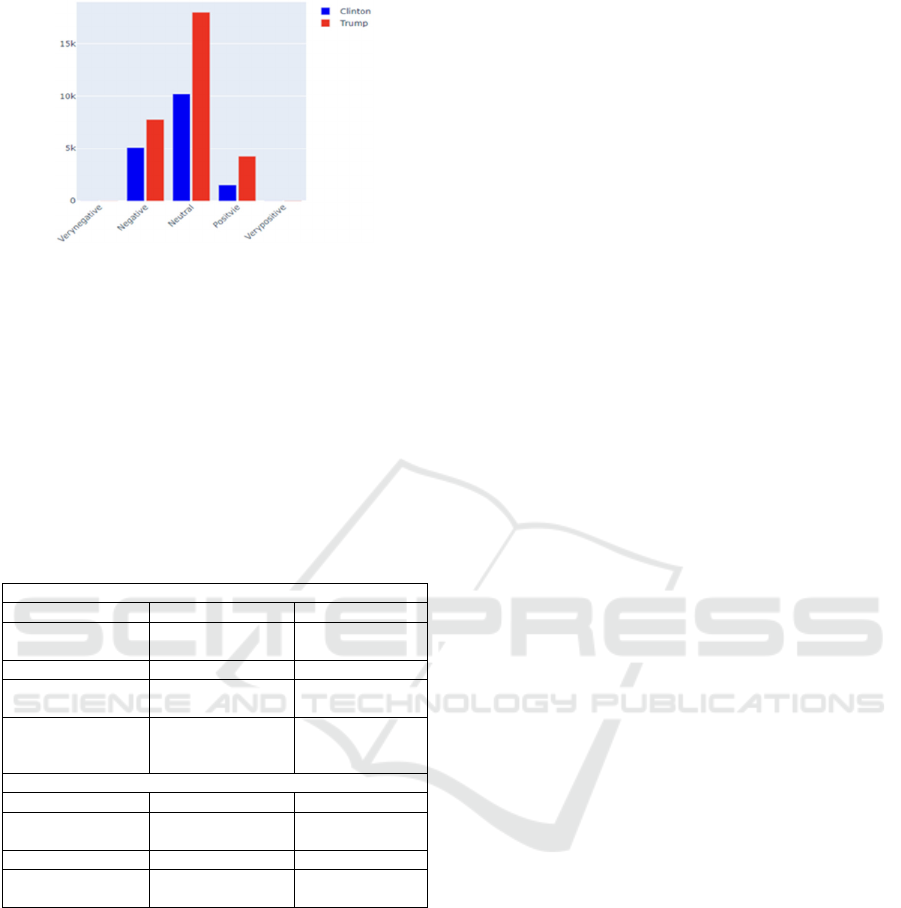
Figure 5: The sentiment distribution in Trump cluster (red),
and in Clinton cluster (blue).
We extracted 428,729 triples from our dataset of
201,365 troll tweets. The triples directly and
concisely show entities, e.g., persons or
organizations, and the relations between them. Table
5 shows examples of extracted triples with entities
from the Clinton and Trump clusters, including
relations between Clinton and email, between Clinton
and foundation, between Trump and media, and
between Trump and presidency.
Table 5: Example triples extracted from the tweets.
Example Triples from Clinton cluster
subject relation object
Hillary Clinton
delete
email
Clinton order destruction email
Clinton foundation is most corrupt
enterprise in
political history
Clinton foundation employ
Muslim
brotherhood
official
Example Triples from Trump cluster
Trump lash out a
t
media
Trump trash
mainstream
media
Trump is worst president
Trump
Keep workplace
protection fo
r
LGBTQ
Americans
The Knowledge Graph of triples (visualization of
the graph is omitted) shows the frequent relations
existing between "Trump" and "media." With main
relations such as "trash," "lash out at," and "attack,"
Russian Trolls tried to create the impression that there
existed conflicts between Trump toward and the
media.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
An elaborate combination of Knowledge Graph and
Natural Language Processing methodologies, such as
Named Entity Recognition, (subject, predicate,
object) triple extraction, and sentiment analysis, has
been applied in this paper to further understand the
semantic relationships among entities in trolls. The
Knowledge Graph approach has been conducted to
further understand the events or statements expressed
in the triple relationships among different entities in
troll tweet sets from the 2016 Presidential Election.
The trolls targeted one candidate, Hillary Clinton, and
her family, by repeatedly accusing her of the "email-
gate scandal" and of misuse of the Clinton foundation,
etc. The concern index in the Clinton cluster of troll
tweets was the highest, and over 10% higher than in
the other two clusters, which shows that Russian
Trolls had used many more negative terms portraying
Clinton than Trump.
We plan to further validate the effectiveness of the
Knowledge Graph approach to integrating micro-
blogging posts that are often not connected to each
other, as they are coming from many different
accounts. We seek to uncover more of the underlying
semantic relationships among entities in such
Knowledge Graphs.
Other future work includes: (1) applying the
Knowledge Graph approach to other election and troll
datasets, such as tweets from Alt-Right and Alt-Left
groups; (2) building more accurate Machine Learning
models that are location and language sensitive (e.g.,
by country) and comparing their influences; (3)
distinguishing between professional trolls and
amateur trolls; (4) an analysis of statistical
significance of differences observed; (5) semantic
deduplication (i.e., which "Trump" is "Donald
Trump" and which is another member of the Trump
family); (6) extension to non-Russian trolls; and (7) a
deeper analysis of insights that can be gained from the
KGs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work partially supported with grants from NSF
CNS 1747728, NSF CNS1624503, and NRF-Korea:
2017S1A3A2066084.
REFERENCES
Addawood, A., Badawy, A., Lerman, K., and Ferrara, E.
(2019). Linguistic Cues to Deception: Identifying
Political Trolls on Social Media. Proceedings of the
International AAAI Conference on Web and Social
DATA 2021 - 10th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
340

Media, 13(01), 15-25. Retrieved from
ojs.aaai.org/index.php/ICWSM/article/view/3205
Alizadeh, M., Weber, I., Cioffi-Revilla, C. et al. Psychology
and morality of political extremists: evidence from
Twitter language analysis of alt-right and Antifa. EPJ
Data Sci. 8, 17 (2019). https://doi.org/
10.1140/epjds/s13688-019-0193-9
Angeli, G., Premkumar, M. J. J, Manning, C. D. (2015).
Leveraging Linguistic Structure for Open Domain
Information Extraction. Proc. of the 53rd Ann. Mtg. of
the ACL and the 7th Int. Joint Conference on Natural
Language Processing (V. 1) (pp. 344–354). Beijing,
ACL.
Atanasov, A., Morales, G., & Nakov, P. (2019). Predicting
the Role of Political Trolls in Social Media. ArXiv,
abs/1910.02001.
Badawy, A., Ferrara, E., and Lerman, K., (2018)
"Analyzing the Digital Traces of Political
Manipulation: The 2016 Russian Interference Twitter
Campaign," IEEE/ACM Int. ASONAM, pp. 258-265,
2018.
Cambria, E., Chandra, P., Sharma, A., Hussain, A. (2010).
Do Not Feel The Trolls. CEUR Workshop Proceedings.
664.
Chun, S. A., Holowczak, R., Dharan, K. N., Wang, R.,
Basu, S., & Geller, J. (2019). Detecting political bias
trolls in Twitter data. In A. Bozzon, F. J. D. Mayo, & J.
Filipe (Eds.), WEBIST 2019 - Proc. of the 15th Int.
Conf. on Web Information Systems and Technologies
(pp. 334-342).
Cypher (query language). (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cypher_(query_language
)
Data formats. (n.d.). Retrieved from spacy.io:
https://spacy.io/api/data-formats#named-entities
displaCy Named Entity Visualizer. (n.d.). Retrieved from
explosion.ai/: https://explosion.ai/demos/displacy-ent
Ehrlinger, L. and Wöß, W. (2016). Towards a Definition of
Knowledge Graphs.
Etudo, U., Yoon, V.Y., Yaraghi, N. (2019). From Facebook
to the Streets: Russian Troll Ads and Black Lives
Matter Protests. HICSS.
Fivethirtyeight, Russian-troll-tweets, https://github.com/
fivethirtyeight/russian-troll-tweets/ Retr. 1/ 2019.
Ghanem B., Buscaldi D., Rosso P. (2020). TexTrolls:
Identifying Trolls on Twitter with Textual and
Affective Features. In: Proc. Workshop on Online
Misinformation- and Harm-Aware Recommender
Systems (OHARS), Co-located with RecSys 2020,
CEUR Workshop Proceedings.CEUR-WS.org, vol.
2758, pp. 4-22
Golino, H., Christensen, A., Moulder, R., Kim, S., Boker,
Steven. (2020). Modeling latent topics in social media
using Dynamic Exploratory Graph Analysis: The case
of the right-wing and left-wing trolls in the 2016 US
elections. 10.31234/osf.io/tfs7c.
Hitzler, P., Lehmann, J., Polleres, A. (2014). Logics for the
Semantic Web, Editor(s): Jörg H. Siekmann, Handbook
of the History of Logic, North-Holland, Volume 9,
Pages 679-710.
Im, J., Chandrasekharan, E., Sargent, J., Lighthammer, P.,
Denby, T., Bhargava, A., Hemphill, L., Jurgens, D., &
Gilbert, E. (2020). Still out there: Modeling and
Identifying Russian Troll Accounts on Twitter. 12th
ACM Conference on Web Science.
Iqbal, S., Keshtkar, F., Chun, S. A. (2020) Extract Semantic
Pattern from Trolling Data, FLAIRS-33 (pp. 509-514).
Iqbal, S., Chun, S. A., Keshtkar, F. (2020) Using
Computational Linguistics to Extract Semantic Patterns
from Trolling Data.Proceedings of IEEE 14th
International Conference on Semantic Computing
(ICSC 2020): 369-374
Jachim, P., Sharevski, F., Treebridge, P. (2020).
TrollHunter [Evader]: Automated Detection [Evasion]
of Twitter Trolls During the COVID-19 Pandemic.
New Security Paradigms Workshop (pp. 59-75). New
York, NY: ACM.
Ji, X., Chun, S. A., and Geller, J., "Monitoring Public
Health Concerns Using Twitter Sentiment
Classifications," 2013 IEEE International Conference
on Healthcare Informatics, Philadelphia, PA, USA,
2013, pp. 335-344, doi: 10.1109/ICHI.2013.47.
Kersting, J., Geierhos, M. (2020). Neural Learning for
Aspect Phrase Extraction and Classification in
Sentiment Analysis. The 33rd International FLAIRS
(pp. 282-285).
K-means clustering. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-means_clustering
Koch, K., 2020. A Friendly Introduction to Text Clustering,
https://towardsdatascience.com/a-friendly-introduction
-to-text-clustering-fa996bcefd04, Retrieved Jan. 29,
2021.
Kumar, S., Spezzano, F., Subrahmanian, V.S., 2014.
Accurately detecting trolls in slashdot zoo via
decluttering. In Proc. of ASONAM ’14, 188–195,
Beijing, China.
Lewinski, D., Hasan, M. R., “Russian Troll Account
Classification with Twitter and Facebook Data”, arXiv
e-prints, 2021.
Linvill, D., Boatwright, B., Grant, W., Warren, P. (2019).
“The Russians are Hacking my Brain!” investigating
Russia's internet research agency twitter tactics during
the 2016 US presidential campaign. Computers in
Human Behavior. 99. 10.1016/j.chb.2019.05.027.
Miao, L., Last, M., Litvak, M. (2020). Detecting Troll
Tweets in a Bilingual Corpus. Proc. of the 12th
Language Resources and Evaluation Conf. (pp. 6247–
6254). Marseille, France: European Language
Resources Association.
McKinney, W., 2017. Python for Data Analysis, Data
Wrangling with Pandas, NumPy, and IPython. O'Reilly.
Mojica, L. G., 2017. A Trolling Hierarchy in Social Media
and a Conditional Random Field for Trolling (Richard
Socher, 2013) Detection, arXiv:1704.02385v1 [cs.CL].
Monakhov, S. (2020) Early detection of internet trolls:
Introducing an algorithm based on word pairs / single
words multiple repetition ratio. PLoS ONE 15(8):
e0236832. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0236
832
Knowledge Graph Analysis of Russian Trolls
341

Mutlu, B., Mutlu, M., Oztoprak, K., Dogdu, E. (2016).
Identifying Trolls and Determining Terror Awareness
Level in Social Networks Using a Scalable Framework.
10.1109/BigData.2016.7840796.
Named-entity recognition. (n.d.). Retrieved from
wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Named-entity
recognition
Popken, B "Twitter deleted 200,000 Russian troll tweets.
Read them here.," (2018). Available: https://www.nbc
news.com/tech/social-media/now-available-more-200-
000-deleted-russian-troll-tweets-n844731.
Seah, C. W., Chieu, H. L., Chai, K. M. A., Teow, L., Yeong,
L. W. "Troll detection by domain-adapting sentiment
analysis," 2015 18th International Conference on
Information Fusion (Fusion), Washington, DC, USA,
2015, pp. 792-799.
Socher, R., Perelygin, A., Wu, J., Chuang, J., Manning, C.
D., Ng, A., Potts, C. (2013). Recursive Deep Models for
Semantic Compositionality Over a Sentiment
Treebank. Proc. of the 2013 Conf. on Empirical
Methods in Natural Language Processing (pp. 1631–
1642). Seattle, Washington.
Soylu, A., Corcho, O., Elvesaeter, B., Badenes-Olmedo, C.,
Yedro, F., Kovacic, M., Posinkovic, M., Makgill, I.,
Taggart, C., Simperl, E., Lech, T., Roman, D. (2020).
Enhancing Public Procurement in the European Union
through Constructing and Exploiting an Integrated
Knowledge Graph.
Roeder, O., 2018. Why We’re Sharing 3 Million Russian
Troll Tweets https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/why-
were-sharing-3-million-russian-troll-tweets/, retrieved
6/3/2019.
Sentiment Analysis. (n.d.). Retrieved from stanford:
https://nlp.stanford.edu/sentiment/
spaCy 101: Everything you need to know. (n.d.). Retrieved
from spacy.io: https://spacy.io/usage/spacy-101
Stanford Open Information Extraction. (n.d.). Retrieved
from https://nlp.stanford.edu/software/openie.html
Trained Models & Pipelines. (n.d.). Retrieved from
spacy.io: https://spacy.io/models
Wikipedia contributors, 2019. Internet Research Agency. In
Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. https://en.wikipe
dia.org/w/index.php?title=Internet_Research_Agency
&oldid=900092717, Retrieved June 3, 201.
DATA 2021 - 10th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
342
