
Reframing the Fake News Problem: Social Media Interaction Design to
Make the Truth Louder
Safat Siddiqui and Mary Lou Maher
College of Computing and Informatics, University of North Carolina at Charlotte, NC, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Fake News, Misinformation, Intervention, Combat, Interaction, Design Principle, Social Media.
Abstract:
This paper brings a new perspective in social media interaction design that reframes the problem of misinfor-
mation spreading on social platforms as an opportunity for UX researchers to design interactive experiences
for social media users to make the truth louder. We focus on users’ interaction tendencies to promote 2 target
behaviors for the social media users: 1. Users interact more with credible helpful information, and 2. Users
interact less with harmful unverified information. The existing platform-based interventions assist users in
getting context and making informed decisions about the information they consume and share on the platform,
independently of users’ interaction tendencies on social platforms. But social media users exhibit different
interaction behaviors - active users on social platforms tend to interact with content and other users often. In
contrast, passive users prefer to avoid the interactions that produce digital footprints. This paper presents a
theoretical basis and 3 design principles to pursue the new research perspective - it builds on the Fogg behav-
ior model (FBM) to transform users’ interaction behaviors to mitigate the fake news problem, describes users’
active-passive interactions tendencies as a basis for design, and presents the 2 target interaction behaviors to
prompt on social platforms.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper presents a shift in focus for the mitigation
of fake news that has the goal to encourage social me-
dia users to share more credible information rather
than solely relying on stopping the spread of misin-
formation. Misinformation, one type of fake news
that refers to unintentional spreading of false infor-
mation, is responsible for increasing polarization and
the consequential loss of trust in science and media
(Lewandowsky et al., 2017). To reduce the spread
of misinformation, social media platforms are remov-
ing the accounts that spread misleading information
and the posts that contain false information. In ad-
dition to that effort, platforms are introducing new
indicators that facilitate the process of getting con-
textual information about posts that have question-
able veracity. The purpose of the indicators is to as-
sist users’ information verification process while con-
suming or before sharing the information with other
users. Though the intention of these indicators is to
minimize the spread of questionable content [(Smith,
2017); (Roth and Pickles, 2020); (Nekmat, 2020)],
the design aspects do not address users’ interaction
behaviors to leverage the interaction tendencies in
distributing credible information. In this paper, we
present users’ active-passive interactions tendencies
as the basis for design and provide 3 principles of
designing social media interaction that combat fake
news with a focus on making the truth louder on so-
cial platforms.
A focus on making the truth louder on social plat-
forms means that the interaction designs nudge users
toward distributing credible information and limiting
the spread of unverified information. Nudges, in the
form of suggestions or recommendations, intend to
steer users’ behaviors in particular directions with-
out sacrificing users’ freedom of choices [(Thaler and
Sunstein, 2009); (Acquisti et al., 2017)]. We iden-
tify that users’ interaction abilities on social media
can be described in the range from active to passive
- active users have a strong tendency to interact with
content and other users, whereas passive users have
the tendency to refrain from interactions [(Gerson
et al., 2017); (Chen et al., 2014); (Trifiro and Gerson,
2019)]. Users’ interaction behaviors could transform
overtime. Shao (Shao, 2009) has suggested that users
initially consume content and eventually start partic-
ipating on the platform and produce content. The
Reader-to-Leader Framework (Preece and Shneider-
158
Siddiqui, S. and Maher, M.
Reframing the Fake News Problem: Social Media Interaction Design to Make the Truth Louder.
DOI: 10.5220/0010658200003060
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications (CHIRA 2021), pages 158-165
ISBN: 978-989-758-538-8; ISSN: 2184-3244
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

man, 2009) indicates the evolution of a user from a
reader to a leader. This paper builds on our under-
standing of the active-passive continuum presented in
[ (Gerson et al., 2017); (Shao, 2009); (Preece and
Shneiderman, 2009)] to develop a theoretical basis for
nudging user behavior to adopt the 2 target interaction
behaviors that combat fakes news by making the truth
louder:
• Target Behavior 1 (TB1): Users interact to in-
crease the spread of verified and credible infor-
mation.
• Target Behavior 2 (TB2): Users interact to re-
duce the spread of unverified and questionable in-
formation.
We present 3 principles for designing social media
interaction that are grounded on users’ active-passive
tendencies and intend to increase users’ likeliness of
performing the 2 target behaviors. The design princi-
ples are inspired by the Fogg Behavior Model (FBM)
(Fogg, 2009) that suggests a change of behavior hap-
pens when individuals have 2 factors: 1. the abil-
ity to change the behaviors and 2. the motivation to
change the behaviors and overlays 3 types of prompts,
1. Signal, 2. Facilitator, and 3. Spark. In our design
principles, the factor ‘ability’ refers to individuals’ in-
teraction tendencies and the factor ‘motivation’ refers
to individuals’ motivation to contribute in making the
truth louder. The 3 design principles of social media
interaction for combating misinformation are:
1. Awareness on Making the Truth Louder: The
goal of this design principle is to remind users and
nudge their attention to perform the target behav-
iors that can make the truth louder. This design
principle is inspired from the Signal prompt in
FBM (Fogg, 2009) and appeals to social media
users who possess high ability to perform the be-
haviors and high motivation to contribute to mak-
ing the truth louder.
2. Guidance on Making the Truth Louder: The
goal of this design principle is to provide users the
necessary interaction supports for performing tar-
get behaviors that lead to making the truth louder.
This design principle is inspired from the Facil-
itator prompt in FBM (Fogg, 2009) and appeals
to social media users who have low ability to per-
form the target behaviors but possess a high moti-
vation to contribute to making the truth louder.
3. Incentive on Making the Truth Louder: The
goal of this design principle is to provide incen-
tives and encourage users to perform the target
behaviors that can make the truth louder. This de-
sign principle is inspired from the Spark prompt
in FBM (Fogg, 2009) and appeals to social media
users who have the ability to perform the inter-
action behaviors but are not highly motivated to
participate in making the truth louder.
The organization of this paper is as follows: Sec-
tion 2 presents the related work and describes how the
design principles contribute to the research on com-
bating fake news. In Section 3, we discuss the dif-
ferences between active and passive users’ interaction
behavior and describe the connection of users’ inter-
action tendencies with the target behaviors that can
make the truth louder. Section 4 presents the 3 design
principles, provide prototypes to explain the princi-
ples and discusses the existing social media interven-
tions in the lens of these design principles. Finally,
we conclude the paper with a discussion of future re-
search for making the truth louder.
2 RELATED WORK
Social media companies are taking steps to reduce the
spread of fake news, such as misinformation (unin-
tentional misleading information) and disinformation
(intentional misleading information). They develop
algorithms and work with third parties to detect fake
content and the accounts who spread those fake in-
formation [(Rosen, 2021); (Rosen and Lyons, 2019)].
Platforms such as Facebook and Twitter remove fake
content and the accounts that display inauthentic ac-
tivities [(Roth and Harvey, 2018); (Gleicher, 2019)].
To reduce the spread of unverified information, the
platforms demote flagged posts and the content that
are detected to be spam or clickbait [(Babu et al.,
2017); (Crowell, 2017)]. In the research communi-
ties, a wide range of algorithms have been developed
to detect fake information by analyzing textual fea-
tures, network structure, and developing propagation
models [(Kumar and Shah, 2018)].
Despite the ongoing development of sophisticated
algorithms, misleading information is still posted and
spread on the platforms. Researchers have investi-
gated effective ways of correcting the misinformation
that has already spread, and identified the negative ef-
fects of fake information on individuals due to cog-
nitive biases, such as confirmation bias, continued in-
fluence, backfire effect [(Lewandowsky et al., 2017);
(Lewandowsky et al., 2012); (Mele et al., 2017)].
Studies have been conducted to understand how users
seek and verify the credibility of news on social media
[(Flintham et al., 2018); (Torres et al., 2018); (Bentley
et al., 2019); (Morris et al., 2012)], how they interact
with misinformation (Geeng et al., 2020), why and
how users spread fake news [(Marwick, 2018); (Star-
bird et al., 2018); (Starbird, 2017); (Arif et al., 2016)].
Reframing the Fake News Problem: Social Media Interaction Design to Make the Truth Louder
159

Those investigations provide a broader context of the
problem of fake news spreading on social media and
add value in developing communication and mitiga-
tion strategies for platform-based interventions.
The platform-based interventions create indicators
that assist users in making informed decisions on their
choices of information consuming and information
sharing on the platform. For example, Facebook pro-
vides an information (‘i’) button that shows details
about the source website of an article, and places
‘Related Articles’ next to the information that seems
questionable to the platform [(Hughes et al., 2018);
(Su, 2017); (Smith, 2017)]. Twitter warns users about
the information that could be misleading and harm-
ful, and directs users to credible sources (Roth and
Pickles, 2020); Twitter also introduces a community-
driven approach, Birdwatch, to identify misleading
information on the platform (Coleman, 2021). In
addition to the platform-based attempts, there exist
browser extensions [(Bhuiyan et al., 2018); (Perez
et al., 2020)] and media literacy initiatives [(Roozen-
beek and van der Linden, 2019); (Grace and Hone,
2019)] to assist users in identifying the credibility of
content.
However, the primary focus of existing design in-
terventions is to communicate to users about the cred-
ibility of the content. In this paper, we shift the focus
to create intervention designs that consider the differ-
ence between active and passive users and are adap-
tive to individual’s interaction tendencies. Preece et
al. (Preece and Shneiderman, 2009) have also sug-
gested the importance of various interface supports to
increase participation more generally, where our fo-
cus is on increasing participation to make the truth
louder. We provide 3 design principles for the UX re-
searchers to explore the design ideas with respective
design goals and address users’ active-passive ten-
dencies to increase users’ participation for combating
fake news.
3 TARGET BEHAVIORS FOR
THE USERS WITH DIFFERENT
INTERACTION TENDENCIES
To make the truth louder, our design principles focus
on promoting 2 target behaviors for social media users
possessing interaction tendencies ranging from active
to passive. In this section, we present the relationship
between 2 target behaviors and users’ interaction ten-
dencies on social platforms.
3.1 Users’ Interaction Tendencies on
Social Platforms
Social media users have different interaction tenden-
cies on social platforms. Some users play an active
role by participating in various interactions, such as
posting comments, sharing content and creating their
own content and posts, uploading photos and videos.
These users are known as active users [(Khan, 2017);
(Chen et al., 2014)]. Chen et al. (Chen et al., 2014)
identified 25 active users’ interactions on social me-
dia and categorized those into 4 dimensions: Content
Creation, Content Transmission, Relationship Build-
ing, and Relationship Maintenance. Conversely, some
social media users do not like to interact with so-
cial media that produces a digital footprint - they are
known as passive users [(Gerson et al., 2017);(Non-
necke and Preece, 1999)]. Passive users prefer to
seek information and entertainment on social plat-
forms and they are more involved in the interactions
that are required to consume information - that type
of interactions can be identified as Content Consump-
tion. According to (Shao, 2009), users first consume
content, then start participating and become the mem-
bers who can produce content. Shao’s (Shao, 2009)
suggestion indicates that users are initially involved in
the interactions related to content consumption, and
over time, users start using interaction items related
to the dimension of relationship building, relationship
maintenance, and content transformation. When users
develop relationships with other users and get habit-
uated to interacting with content, they proceed using
interaction items related to content creation.
The passive and active users have different pref-
erences towards the interaction dimensions because
of their interaction tendencies [(Gerson et al., 2017),
(Trifiro and Gerson, 2019)]. Though the users are
similar in the dimension of content consumption,
the interaction preference between active and passive
users starts to differ in other dimensions of interac-
tions, such as content creation and content transmis-
sions. In comparison to active users, passive users
have less preference for interaction items that are
not related to content consumption. The design af-
fordance that helps users to get context and verify
information are related to the interactions of con-
tent consumption dimension, where interaction pref-
erences between active and passive users remain sim-
ilar. We focus on the interactions of content transmis-
sions where active users are more likely to participate
than passive users and provide 3 design principles of
social media interaction adaptive to users’ interaction
tendencies.
CHIRA 2021 - 5th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
160

3.2 Difference between Users’ Abilities
to Perform the Target Behaviors
The ability to perform the 2 target behaviors will be
different for the users due to their interaction tenden-
cies. Active and passive users on social media demon-
strate the opposite ability because of their online in-
teraction tendencies, making target behavior 1 (TB1)
easier for active users but difficult for passive users,
and target behavior 2 (TB2) easier for passive users
but difficult for active users.
The ability to contribute to the spread of verified
information (TB1) demands interactions with content
and other social media users - such ability is high for
the active users but low for the passive users. Due to
active users’ natural inclination, they are habituated
to perform high levels of interactions, such as shar-
ing information with other users, making comments,
or sending love/like reactions to the content - these
interactions contribute to the distribution of verified
information. But passive users hesitate to perform
such interactions and have low levels of interactions
on social platforms, which makes adopting the target
behavior 1 challenging for passive users.
In contrast, limiting the spread of unverified in-
formation (TB2) is easier for passive users to adopt
compared to active users as it requires users to interact
less with the unverified content. For target behavior 2,
passive users get an advantage as they have the gen-
eral tendency to interact less with social media con-
tent. However, active users have to be reflective about
their activities on social platforms so that they do not
interact with any unverified content because of their
natural behavioral tendencies, which makes adopting
target behavior 2 harder for active users.
Figure 1: The design principles addresses the differences
between active and passive users to perform the target be-
haviors.
The design principles address the differences be-
tween active and passive users’ online interaction ten-
dencies to direct their interactions to make the truth
louder on social media, as illustrated in Figure 1. Ac-
tive users have high interaction abilities, and passive
users have low interaction abilities. As users’ inter-
actions (e.g., shares, comments, likes) on social plat-
forms lead to the distribution of the content in that
platform, the principles intend to assist active users in
adopting the target behavior to interact only with the
credible information and not to interact with unveri-
fied or questionable information. Similarly, the prin-
ciples intend to support passive users to increase their
interactions with credible information that can make
the truth louder on social platforms.
4 DESIGN PRINCIPLES THAT
ADDRESS USERS’
INTERACTION TENDENCIES
We present 3 design principles that address users’ in-
teraction tendencies: Awareness, Guidance, and In-
centive on making the truth louder. In this section, we
describe the design principles that appeal to the users
of different levels of interaction abilities and motiva-
tion, and discuss the existing design interventions in
reference to these principles.
4.1 Awareness on Making the Truth
Louder
The purpose of the Awareness design principle is to
assist social media users in recognizing verified and
unverified content that appears in their social media
feeds and remind users to perform the target behavior
that can make the truth louder. This design principle
is a Signal prompt in the FBM (Fogg, 2009) that is ef-
fective for individuals who have high motivation and
high ability to perform the target behavior. When ac-
tive users on the platform have the motivation to par-
ticipate in making the truth louder, they can respond
positively to the intervention designs that follow the
Awareness design principle promoting the target be-
havior 1. Likewise, passive users can respond easily
to the interventions that follows the Awareness design
principle to promote the target behavior 2 - requesting
limited interactions with the unverified and question-
able content.
Most of existing interventions can be described
using the Awareness design principle as the focus
of these interventions is to inform users about the
context and validity of the information. For exam-
ple, social media platforms, such as Facebook and
Twitter, provide related fact-checkers’ information so
that users can get the context of the information.
Reframing the Fake News Problem: Social Media Interaction Design to Make the Truth Louder
161

Facebook shows an indicator to related articles when
the platform detects any questionable content [(Su,
2017); (Smith, 2017)]. Twitter warns users if the plat-
form identifies any harmful content (Roth and Pick-
les, 2020). The accuracy nudging intervention (Pen-
nycook et al., 2020) draws users’ attention to the
accuracy of the content, and NudgeFeed (Bhuiyan
et al., 2018) applies visual cues to grab users’ at-
tention to the credibility of the information source -
whether the information source is mainstream or non-
mainstream. These platform-based interventions edu-
cate users about the context of the information when
users are involved in content consumption interac-
tions. Some interventions, such as Facebook, alert
users when they interact to share any questionable
content (Smith, 2017). These interventions follow the
Awareness design principle as the purpose is to make
users aware of the context before they share the infor-
mation on social media.
To describe the Awareness design principle, we
present a design prototype that promotes the target
behavior 1, illustrated in Figure 2. The prototype
use the standard signifiers ‘Like’, ‘Comment’, and
‘Share’ buttons of Facebook that signal users can per-
form interactions to like the information, make com-
ments about that information, and share that informa-
tion with other users. The credible information in
Figure 2 is collected from (Pennycook et al., 2020)
study, and we add ‘More information about this link’
and ‘Related Articles’ sections that assist users in
getting the context of the content. Figure 2 follows
the Awareness design principle that uses texts in the
‘More information about this link’ section to commu-
nicate with users about the credibility of information
and information source, and have related fact-checked
articles in ‘Related Articles’ section to provide more
contextual information. This prototype focuses on in-
forming the active users about context of the infor-
mation so that the subset of active users who posses
the motivation to contribute in making the truth louder
become aware to share the verified information.
Figure 2: Prototype describing the Awareness design prin-
ciple for promoting target behavior 1.
4.2 Guidance on Making the Truth
Louder
The purpose of the Guidance design principle is to
simplify the interactions for the users to increase their
ability to interact on social platforms and educate
users about the interactions that can lead to the distri-
bution of credible information and limit the spread of
unverified harmful information. This design principle
is a Facilitator prompt in the FBM (Fogg, 2009) that
is effective for individuals who have high motivation
but low ability to perform the target behaviors. This
design principle focuses on promoting target behav-
ior 1 among passive users by simplifying the interac-
tion steps for them that assist their interactions for dis-
tributing credible information. Likewise, this design
principle can promote target behavior 2 among the ac-
tive users by designing interaction and affordance that
assist them limiting their interactions with unverified
content.
To describe the Guidance design principle, we
present a design prototype that promotes the target
behavior 1 by simplifying sharing interactions, illus-
trated in Figure 3. The prototype follows the Guid-
ance design principle that increases users’ interac-
tion ability with credible information by reducing the
number of interaction steps required for sharing cred-
ible information. The Share button has the biggest
impact on digital footprints as this functionality al-
lows users to share the information with the users of
their network; the Comments and Like buttons have
smaller digital footprints compared to that. Facebook
includes different sharing options, such as share pub-
licly or privately, and users get those sharing options
when they press the share button. In addition to the af-
fordance presented in Figure 2, this prototype has dif-
ferent sharing options upfront and reduces the num-
ber of interaction steps for sharing. The prototype
includes the privately sharing option to facilitate the
motivated passive users’ interactions toward the cred-
ible information. As passive users have a natural in-
clination to avoid digital footprint, the motivated pas-
sive users will feel comfortable sharing credible in-
formation privately to their friends rather than sharing
publicly with the whole network. The prototype also
includes additional 2 sharing options that enable users
to share the verified fact-checked information with a
single step of interaction. The design can apply visual
cues on those buttons or use text to guide users about
the interactions that lead to the distribution of credible
information on the social platform.
CHIRA 2021 - 5th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
162
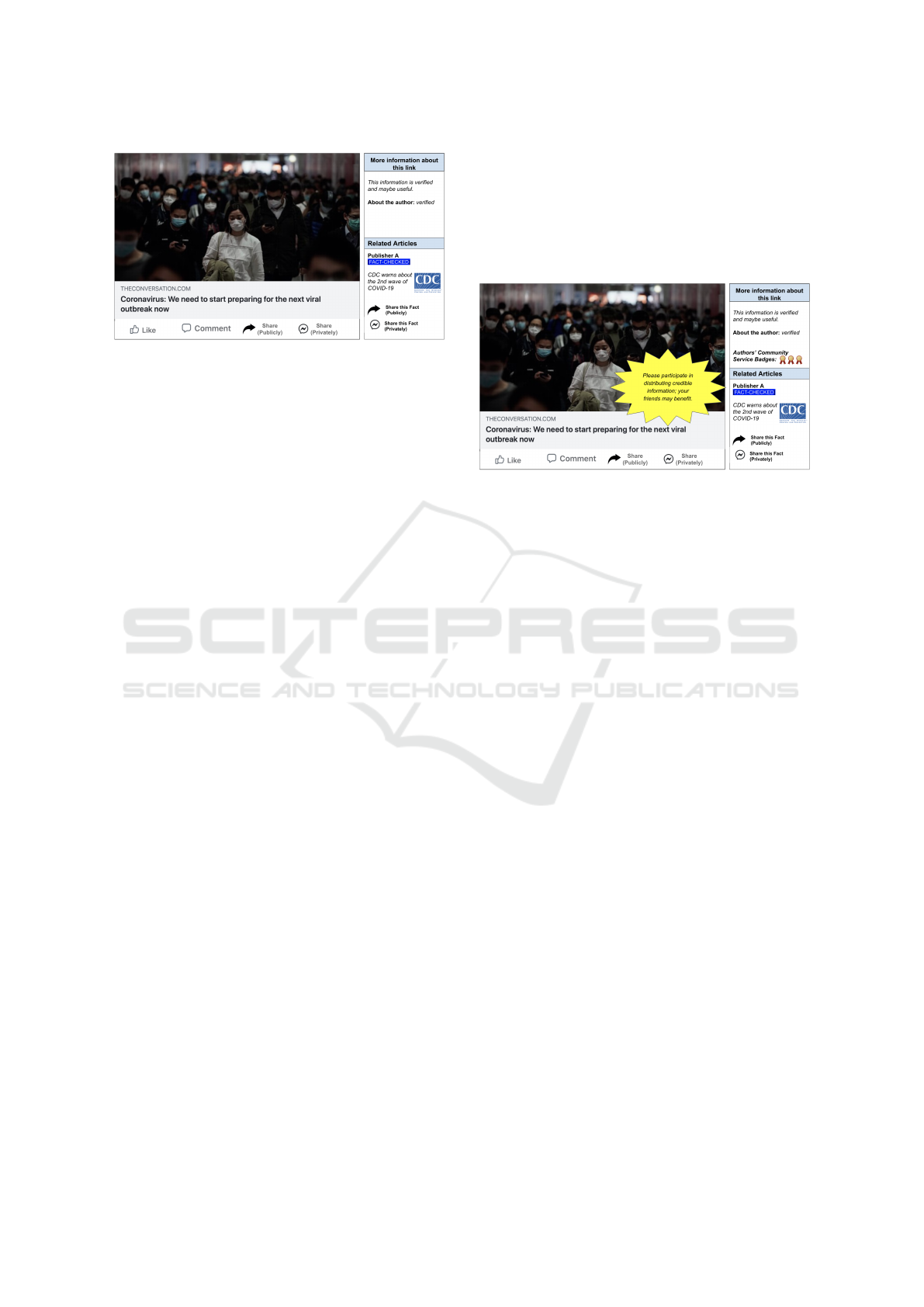
Figure 3: Prototype describing the Guidance design princi-
ple for promoting target behavior 1.
4.3 Incentive on Making the Truth
Louder
The purpose of Incentive design principle is to en-
courage and motivate users to orient their interaction
behavior in a direction that can make the truth louder
on the platform. The Incentive design principle is a
Spark prompt in the FBM that is proven effective for
the individuals who have the high ability but low mo-
tivation to perform the target behaviors. This design
principle can prompt the less motivated active users
to perform target behavior 1 and the less motivated
passive users to perform target behavior 2.
To describe the Incentive design principle, we
present a design prototype that promotes the target be-
havior 1 by providing users badges, illustrated in Fig-
ure. 4. The concept of ‘Community Service Badges’
can demonstrate a way to incentivize social media
users to increase their motivation for performing the
target behaviors. When users perform social media
interactions for making the truth louder, they will re-
ceive badges. The platform can add benefits to the
badges, such as prioritizing the content posted by
users who have the badges, suggesting other users
to follow the individuals who hold the badges due to
the contribution in distributing credible information.
Such platform-based benefits can attract active users
to become reflective about their social media interac-
tions and perform interactions only with credible in-
formation.
The platform-affordances can communicate with
users and encourage them to participate in making the
truth louder as a part of their responsibilities for cre-
ating personal, social, and societal impacts. Figure
4 includes the text “Please participate in distribut-
ing credible information; your friends may benefit”
to communicate with social media users and inspire
their motivation. As the community service badges
indicate individuals’ effort to make the truth louder
on social platforms, the badges can gather positive
impressions from other social media users, which can
attract the platform’s active users to attain the badges.
The platform-based interventions can identify useful
information and harmful information by relying on
the fact-checking services and assist users in devel-
oping the interaction habits by rewarding them with
the badges.
Figure 4: Prototype describing the Incentive design princi-
ple for promoting target behavior 1.
In summary, we present 3 design principles to
make the truth louder that are adaptive to users’ in-
teraction tendencies. The relationships between the
design principles and the credibility of the post, the
target behaviors, and the user’s interaction tendencies
is shown in Table 1. These design principles encour-
age UX researchers to design and create affordances
on the social media posts that are adaptive to individ-
uals’ interaction tendencies.
5 FUTURE WORK
We are developing alternative design instances that
follow these design principles as a basis for evalu-
ating the effectiveness of those instances on users’
achieving the target behaviors considering their ac-
tive passive tendencies. In our evaluation studies, we
plan to collect information about participants’ social
media usage and identify their interaction tendencies
with a self report survey. We will ask participants to
report their level of motivation to adopt the 2 target
behaviors and compare their self-reported responses
with the observations data that we collect in the study.
In the study, participants will see social media posts
containing both credible and questionable informa-
tion and will be divided into experiment conditions so
that we can compare the results between controlled
and treatment conditions. The findings of the study
can be the basis for developing an AI model that
presents effective intervention designs in response to
users’ interaction tendencies to optimize making the
truth louder.
Reframing the Fake News Problem: Social Media Interaction Design to Make the Truth Louder
163
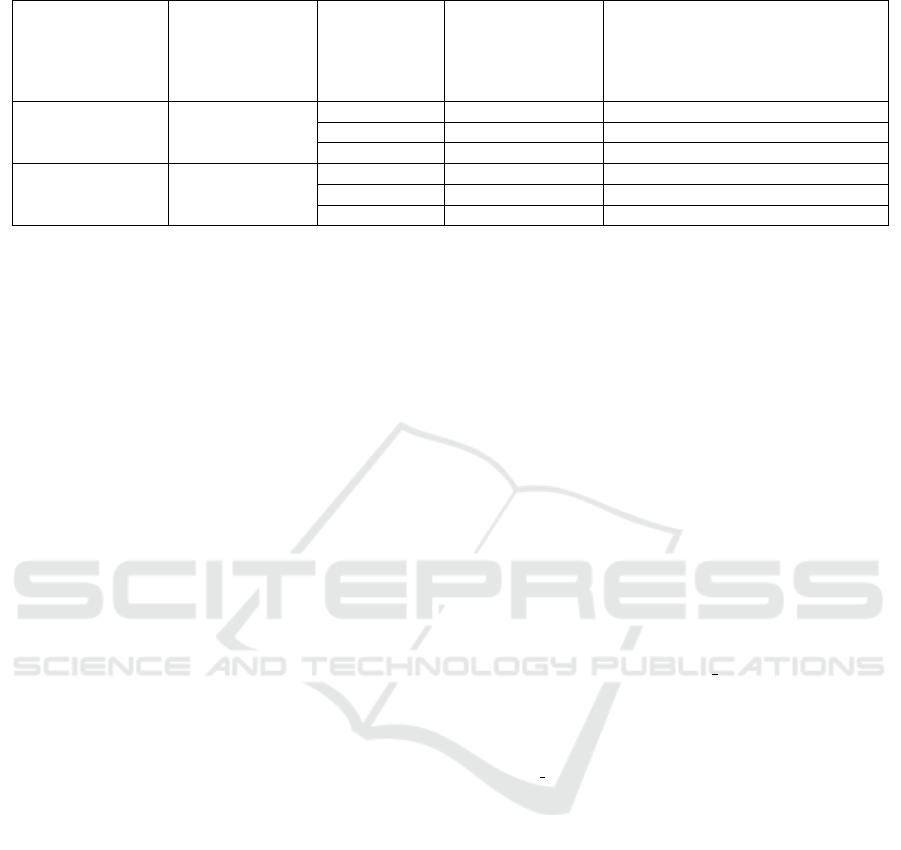
Table 1: The design principles can measure the effectiveness of intervention designs for making the truth louder.
Factual status
of the post
that appears on
user’s social
media feed
Target behavior
to promote
User’s
interaction
tendencies on
the platform
User’s motivation
to contribute in
making the truth
louder
Appropriate design principle
to apply on the post
to promote the target behavior
for the user
When information
of the post
is credible
Target behavior 1
High Low
Incentive principle for active user
High High
Awareness principle for active user
Low High
Guidance principle for passive user
When information
of the post
is questionable
Target behavior 2
Low Low
Incentive principle for passive user
Low High
Awareness principle for passive user
High High
Guidance principle for active user
6 CONCLUSION
This paper provides a theoretical basis for structur-
ing the design space around misinformation interven-
tions, which addresses users’ active-passive tenden-
cies as behavior, develops design principles to trans-
form the interaction behavior, and identifies 2 interac-
tion behaviors to promote to make the truth louder on
social media. We develop 3 design principles of social
media interactions and present associated prototypes
to explain the design principles - those principles can
be used to evaluate the effectiveness of design in-
stances for combating misinformation. We interpret
the problematic issue of misinformation spreading on
social platforms as a design challenge for UX re-
searchers to create platform-based affordances that
encourage users to adopt new interaction behaviors:
interact more with credible content and interact less
with harmful content. Instead of solely relying on re-
ducing the spread of misinformation, we encourage
UX researchers to explore design ideas of the 3 de-
sign principles and address the difference between ac-
tive and passive users to create affordances that nudge
users’ interactions to distribute credible information.
REFERENCES
Acquisti, A., Adjerid, I., Balebako, R., Brandimarte, L.,
Cranor, L. F., Komanduri, S., Leon, P. G., Sadeh, N.,
Schaub, F., Sleeper, M., et al. (2017). Nudges for pri-
vacy and security: Understanding and assisting users’
choices online. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR),
50(3):1–41.
Arif, A., Shanahan, K., Chou, F.-J., Dosouto, Y., Starbird,
K., and Spiro, E. S. (2016). How information snow-
balls: Exploring the role of exposure in online rumor
propagation. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM Con-
ference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work &
Social Computing, pages 466–477. ACM.
Babu, A., Liu, A., and Zhang, J. (2017). New up-
dates to reduce clickbait headlines. (may 2017).
https://about.fb.com/news/2017/05/news-feed-fyi-
new-updates-to-reduce-clickbait-headlines/.
Bentley, F., Quehl, K., Wirfs-Brock, J., and Bica, M. (2019).
Understanding online news behaviors. In Proceed-
ings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors
in Computing Systems, pages 1–11.
Bhuiyan, M. M., Zhang, K., Vick, K., Horning, M. A., and
Mitra, T. (2018). Feedreflect: A tool for nudging users
to assess news credibility on twitter. In Companion
of the 2018 ACM Conference on Computer Supported
Cooperative Work and Social Computing, pages 205–
208.
Chen, A., Lu, Y., Chau, P. Y., and Gupta, S. (2014). Classi-
fying, measuring, and predicting users’ overall active
behavior on social networking sites. Journal of Man-
agement Information Systems, 31(3):213–253.
Coleman, K. (2021). Introducing birdwatch, a community-
based approach to misinformation (january 2021).
https://blog.twitter.com/en\ us/topics/product/
2021/introducing-birdwatch-a-community-based-
approach-to-misinformation.html.
Crowell, C. (2017). Our approach to bots and misin-
formation. (june 2017). https://blog.twitter.com/
en\ us/topics/company/2017/Our-Approach-Bots-
Misinformation.html.
Flintham, M., Karner, C., Bachour, K., Creswick, H.,
Gupta, N., and Moran, S. (2018). Falling for fake
news: investigating the consumption of news via so-
cial media. In Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Confer-
ence on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pages
1–10.
Fogg, B. J. (2009). A behavior model for persuasive design.
In Proceedings of the 4th international Conference on
Persuasive Technology, pages 1–7.
Geeng, C., Yee, S., and Roesner, F. (2020). Fake news
on facebook and twitter: Investigating how people
(don’t) investigate. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI
conference on human factors in computing systems,
pages 1–14.
Gerson, J., Plagnol, A. C., and Corr, P. J. (2017). Passive
and active facebook use measure (paum): Validation
and relationship to the reinforcement sensitivity the-
ory. Personality and Individual Differences, 117:81–
90.
Gleicher, N. (2019). Removing coordinated inauthentic be-
CHIRA 2021 - 5th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications
164

havior from china. (august 2019). https://about.fb.
com/news/2019/08/removing-cib-china/.
Grace, L. and Hone, B. (2019). Factitious: Large scale com-
puter game to fight fake news and improve news liter-
acy. In Extended Abstracts of the 2019 CHI Confer-
ence on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pages
1–8.
Hughes, T., Smith, J., and Leavitt, A. (2018). Helping peo-
ple better assess the stories they see in news feed with
the context button. (2018). https://about.fb.com/news/
2018/04/news-feed-fyi-more-context/.
Khan, M. L. (2017). Social media engagement: What moti-
vates user participation and consumption on youtube?
Computers in Human Behavior, 66(4):236–247.
Kumar, S. and Shah, N. (2018). False information on
web and social media: A survey. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1804.08559.
Lewandowsky, S., Ecker, U. K., and Cook, J. (2017). Be-
yond misinformation: Understanding and coping with
the “post-truth” era. Journal of applied research in
memory and cognition, 6(4):353–369.
Lewandowsky, S., Ecker, U. K., Seifert, C. M., Schwarz,
N., and Cook, J. (2012). Misinformation and its
correction: Continued influence and successful debi-
asing. Psychological science in the public interest,
13(3):106–131.
Marwick, A. E. (2018). Why do people share fake news?
a sociotechnical model of media effects. Georgetown
Law Technology Review, 2(2):474–512.
Mele, N., Lazer, D., Baum, M., Grinberg, N., Friedland,
L., Joseph, K., Hobbs, W., and Mattsson, C. (2017).
Combating fake news: An agenda for research and ac-
tion. Retrieved on October, 17:2018.
Morris, M. R., Counts, S., Roseway, A., Hoff, A., and
Schwarz, J. (2012). Tweeting is believing? under-
standing microblog credibility perceptions. In Pro-
ceedings of the ACM 2012 conference on computer
supported cooperative work, pages 441–450.
Nekmat, E. (2020). Nudge effect of fact-check alerts:
Source influence and media skepticism on sharing of
news misinformation in social media. Social Media+
Society, 6(1):2056305119897322.
Nonnecke, B. and Preece, J. (1999). Shedding light on lurk-
ers in online communities. Ethnographic Studies in
Real and Virtual Environments: Inhabited Informa-
tion Spaces and Connected Communities, Edinburgh,
123128.
Pennycook, G., McPhetres, J., Zhang, Y., Lu, J. G., and
Rand, D. G. (2020). Fighting covid-19 misinforma-
tion on social media: Experimental evidence for a
scalable accuracy-nudge intervention. Psychological
science, 31(7):770–780.
Perez, E. B., King, J., Watanabe, Y. H., and Chen, X.
(2020). Counterweight: Diversifying news consump-
tion. In Adjunct Publication of the 33rd Annual ACM
Symposium on User Interface Software and Technol-
ogy, pages 132–134.
Preece, J. and Shneiderman, B. (2009). The reader-to-leader
framework: Motivating technology-mediated social
participation. AIS transactions on human-computer
interaction, 1(1):13–32.
Roozenbeek, J. and van der Linden, S. (2019). Fake news
game confers psychological resistance against online
misinformation. Palgrave Communications, 5(1):1–
10.
Rosen, G. (2021). How we’re tackling misin-
formation across our apps (2021). https:
//about.fb.com/news/2021/03/how-were-tackling-
misinformation-across-our-apps/.
Rosen, G. and Lyons, T. (2019). Remove, reduce, inform:
New steps to manage problematic content. (april
2019). https://about.fb.com/news/2019/04/remove-
reduce-inform-new-steps/.
Roth, Y. and Harvey, D. (2018). How twitter is fight-
ing spam and malicious automation. (june 2018).
https://blog.twitter.com/en\ us/topics/company/
2018/how-twitter-is-fighting-spam-and-malicious-
automation.html.
Roth, Y. and Pickles, N. (2020). Updating our approach to
misleading information. https://blog.twitter.com/en\
us/topics/product/2020/updating-our-approach-to-
misleading-information.html.
Shao, G. (2009). Understanding the appeal of user-
generated media: a uses and gratification perspective.
Internet research, 19(1):7–25.
Smith, J. (2017). Designing against misinformation. (de-
cember 2017). https://medium.com/facebook-design/
designing-against-misinformation-e5846b3aa1e2.
Starbird, K. (2017). Examining the alternative media
ecosystem through the production of alternative nar-
ratives of mass shooting events on twitter. In Eleventh
International AAAI Conference on Web and Social
Media.
Starbird, K., Arif, A., Wilson, T., Van Koevering, K., Yefi-
mova, K., and Scarnecchia, D. (2018). Ecosystem or
echo-system? exploring content sharing across alter-
native media domains. In Proceedings of the Inter-
national AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media,
volume 12.
Su, S. (2017). New test with related articles (2017).
https://about.fb.com/news/2017/04/news-feed-fyi-
new-test-with-related-articles/.
Thaler, R. H. and Sunstein, C. R. (2009). Nudge: Improving
decisions about health, wealth, and happiness. Pen-
guin.
Torres, R., Gerhart, N., and Negahban, A. (2018). Combat-
ing fake news: An investigation of information veri-
fication behaviors on social networking sites. In Pro-
ceedings of the 51st Hawaii international conference
on system sciences.
Trifiro, B. M. and Gerson, J. (2019). Social media usage
patterns: Research note regarding the lack of universal
validated measures for active and passive use. Social
Media+ Society, 5(2):2056305119848743.
Reframing the Fake News Problem: Social Media Interaction Design to Make the Truth Louder
165
