
Factors of Innovative Development of Investment and Construction
Complex in the Processes of Industry - 4.0
I. A. Bachurinskaya
1a
, N. V. Vasileva
1b
, M. N. Yudenko
1c
, I. V. Fedoseev
1d
and S. N.
Maksimov
2e
1
Saint-Petersburg State University of Economics (SPbSUE), Sadovaya st., 21, SaintPetersburg, Russia
2
St Petesburg University (SPbU), Universitetskya Emb., 7-9, SaintPetersburg, Russia
Keywords: Investment and construction complex, Industry – 4.0, innovation potential, sustainability, economic and social
systems.
Abstract: The study goal which consists in the need to analyze the factors of innovative development of investment and
construction complex in the processes of Industry -4 is defined; the result on formation of digitalization
models for investment and construction company based on the experience of spreading Industry-4 trends in
Russia and foreign countries is achieved. The factors that contribute to sustainable development of the
investment and construction complex as a socio-economic system are identified. It is concluded that the
economic growth basis of the investment and construction complex are the processes of Industry-4, which
absolutely ensure its sustainability through implementation of processes of investment and construction
complex digitalization, ecology, innovation and location.
1 INTRODUCTION
The investment and construction complex
(hereinafter – the ICC) forms the basis for economy
and society development, creating the necessary
material objects for development of industry and
other economic activities, determining the
population's quality of life. The ICC's significant role
in the economy is confirmed by a number of statistical
indicators: scope оf work performed in 2020 by type
of activity “construction” amounted to 9.5 trillion
rubles, the average annual number of people
employed in construction – 6.4 million people or 9%
of the total number of people employed in the
country's economy. 439 thousand enterprises and
organizations are involved in the construction field,
which is 11.5% of their total number in the Russian
Federation.
At the beginning of 2021, the business confidence
index, which characterizes the business climate in
construction, had a negative value (-15), indicating a
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2296-5869
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0243-1317
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9994-8197
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7099-9495
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2709-2462
low business climate state in this type of economic
activity. The improvement of the business climate in
construction will be facilitated by enhancing
innovation in the investment and construction
complex.
The goal of this study is to analyze the factors of
ICC innovative development in the processes
Industry-4.0.
Within this analysis, an attempt is carried out to
confirm the hypothesis that the basis for progressive
economic growth of participants in the investment
and construction complex and its sustainability is the
increase their competitiveness in increasing the share
of the occupied construction market through the
introduction of Industry-4 processes.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
A significant number of scientific papers by
researchers and practitioners in this field are devoted
74
Bachurinskaya, I., Vasileva, N., Yudenko, M., Fedoseev, I. and Maksimov, S.
Factors of Innovative Development of Investment and Construction Complex in the Processes of Industry - 4.0.
DOI: 10.5220/0010683400003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 74-81
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

to the problems of development of the investment-
construction complex and innovations in
construction. The works presents general issues of
sustainable development of the investment and
construction complex as a complex economic and
social system and individual issues of analyzing the
possibilities of digitalization in the investment and
construction complex based on Industry-4.0.
The following articles prove the multidimensional
nature of the studied problem, the credibility and
correctness of the authors' attempts to prove the
inevitability of innovative development in
construction.
Ivanova and Zagidullina (2016) analyze the main
activation directions of innovation activity in the
investment and construction field, highlighting the
topical areas of innovation activity, which include:
modularity in manufacture and design, manufacture
robotization, increasing the manufacture flexibility,
development of modern monitoring systems, shows a
growing tendency to increase the innovative factors
role in the development of ICC and region's economy.
Khrustalev and Artamonova (2016) consider the
main aspects of ICC enterprises' development and
management, as well as the formation of an
innovative approach in the activities of enterprises of
investment and construction complex.
Separate issues are devoted to the concept of
Industry-4.0. Götz, Jankowska (2020) in the concept
of Industry - 4.0 describe specific Industry-4.0 tools
that are possible for ICC construction companies to
apply, such as an intelligent manufacturing network
in which physical manufacturing operations are
integrated with digital technology, machine learning
and big data, forming a holistic digital ecosystem.
Vertakova and Plotnikov (2019) note that
sustainable development is a priority in the modern
world and one of its effective tools is the development
of a green economy. Scientists propose priorities and
directions for green economy development in order to
achieve the main goal – sustainable development in
Russia.
The social and economic benefits of green
technologies in the construction field are known and
given in articles by domestic and foreign scientists
Bachurinskaya, Vasileva, Yudenko, and Nikolikhina
(2020), Acemoglu, Aghion, Bursztyn, and Hemous
(2012), Zhineng Tong (2020).
Gizem Erdoğan (2019) in article presents a study
aimed at the assumption of significant influence of
location factors of industrial enterprises, including the
ICC objects on the development of territories within
Industry 4.0, the hypothesis is put forward that the
existing manufacturing sites will be moved from
urban centers in the process of Industry 4.0, and urban
settlements will be changed by transforming the land
selection criteria, taking into account new
requirements.
The analysis of scientific works allowed to
conclude that scientists and practitioners share one
view about the fact that the ICC innovative
development is an important element in solving
socio-economic problems, is closely connected with
the problems of sustainable development and green
economy and has a significant impact on
competitiveness and economic growth of the country
as a whole, as well as on the prospects of innovative
development of ICC as a functioning mechanism and
industry development.
The article's research method is based on a
qualitative analysis of the observable innovative
development factors of the investment and
construction complex, realities and facts of their
interaction. Collecting data on the investment and
construction complex development is a complex
process, the implementation of which is helped by
usual terminology (investment and construction
complex as a socio-economic system,
redevelopment); tendency, trends and integrated
concepts (for example, Industry - 4 and trends in its
development in construction); abstractions in the
form of simplified models (for example, digitalization
models in construction).
The authors of this study consider Industry-4 as an
innovative factor in construction, without denying
that the path to Industry-4.0 will be an evolutionary
process. Existing basic technologies and experience
should be adapted to the specific requirements for the
investment and construction complex, and innovative
solutions for new territories and new markets in this
type of economic activity should be studied.
2.1 Tendency in the Impact of
Industry - 4 Processes on the
Sustainability of the Investment
and Construction Complex as a
Socio-economic System
How do the processes of Industry-4 in construction
affect the stability of the investment and construction
complex as a socio-economic system? According to
the authors, the development of Industry - 4 processes
should be aimed at increasing productivity (as a result
of functional connection between man and machine),
the utilization efficiency of fixed assets (the ability of
system to make autonomous decisions) and efficiency
as a whole (integration of manufacture and IT
systems). And we consider it important to refer to the
Factors of Innovative Development of Investment and Construction Complex in the Processes of Industry - 4.0
75

concept of entropy as a qualitative measure of
disorder. The proposed digitalization model in the
investment and construction complex, as the socio-
economic system, will contribute to the system
ordering and self-organization, i.e., the growth of its
stability. Entropy characterizes the event and process
tendencies, and if the probability of implementing
such models increases, then activities within such
models begin to occur more often and entropy
decreases.
ICC as the socio-economic system refers to
dissipative systems that have both stable and unstable
states. The sequence of these states is determined by
the control parameters by which the external world
determines its relationship with the system. By
controlling through ICC external influence and
choosing certain control parameters, we can manage
the development tendency of ICC as a system, in our
case, the development tendency of the investment and
construction complex. Such control parameters
include models of digitalization of investment and
construction complex organizations within Industry-
4.
The evolutionary process of Industry-4 uses all
the resources of increasing entropy. One can speak of
evolution towards entropy as a progressive evolution
(Prangishvili, 2015). The evolutionary growth of
entropy of ICC organizations in the Industry-4
processes means an increase in the probability of
emergence of more and more progressive
development directions of such organizations and an
increase in the prevalence of digitalization models
(Table 1), and the high prevalence means the
adaptability of such models in construction. And in
this case, the investment and construction complex
stability as the socio-economic system increases.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The success of various approaches to stimulating the
innovative ICC development largely depends on the
study of factors that affect this process. The concept
“factor” is disclosed in literature as the cause, the
driving force of a process, a phenomenon,
determining its nature or its individual features, an
essential circumstance in any process. The study of
these driving forces and significant circumstances is
the key to making effective and innovative decisions
for the ICC development and the growth of its
sustainability.
Innovation activity in ICC has its own specifics,
which is manifested in the fact that at each stage of
the investment and construction project innovation
may have different objectives, volumes and sources.
This fact distinguishes them from most industrial
innovations and requires a systematic approach to the
organization of innovation throughout the life cycle
of the investment and construction project.
The global tendency in the field of innovative
development of the construction industry includes
scientific research aimed at reducing energy
consumption and withdrawal of natural resources for
the production of building materials, reducing the
construction period of buildings and other objects,
providing recycling of construction waste, efficient
use of investment and construction activities.
Let's highlight the most relevant and significant
factors of ICC innovative development. These factors
include:
- technological modernization of building
materials manufacture, construction and
installation work performance;
- ICC greening;
- introduction of innovative approaches to the
ICC management and the financing of
investment and construction projects;
- providing the investment and construction
complex with highly qualified personnel;
- ICC digitalization and introduction of Industry-
4.0 technologies.
Technological modernization of manufacture
processes in construction as a factor of innovative
development provides for the introduction of new
technologies and equipment at construction
enterprises, the production of innovative building
materials. Enterprises will be able to create a more
technologically sophisticated final product that
replaces imports on the domestic market or is able to
compete on the foreign market. The need for
technological modernization not only in relation to a
separate field of activity, but also to the economy as
a whole, is considered as a factor of innovative
development and other researchers (Boyko I.V.,
2018).
ICC greening is the most relevant trend that
encourages innovative solutions, the use of
innovative materials for building structures, the
introduction of energy-saving technologies (energy-
efficient house, energy-efficient city, etc.), the
creation of “smart networks” and energy-information
systems. Of particular importance in this direction is
the widespread use of secondary material resources in
ICC - waste production and consumption, which not
only reduces CO2 emissions and saves natural
resources, but also reduces the construction cost.
The defining factor of innovative development, in
our view, is the introduction of innovative approaches
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
76
to the ICC management. It is about the introduction
of multidimensional project management systems
that use extensive information bases and digital twins
of ICC objects, which will allow to make
management decisions reasonably and within a short
time, and that will contribute to the capacity building
of ICC innovative development. ICC innovative
development requires more complex management
models for both the state and business, associated
with investing in projects for the development of high
technologies and human capital development projects
with payback time that go far beyond the long-term
limits established in the market.
Among the main factors of the ICC innovative
development is the availability of highly qualified
personnel. In the last decade, the availability of
personnel has significantly decreased, according to
the Ministry of Construction of the Russian
Federation by almost 1.5 times. Innovative
development involves the formation of innovative
competencies and the effective use of potential of
highly skilled workers. In this direction, it is
necessary that the competencies formed in the process
of education meet the objectives of innovative
development of construction and installation
materials industry, which can be achieved by
strengthening the interaction between higher
education institutions and construction companies. It
is especially important to create an effective system
for the formation of innovative competencies in the
field of system engineering, organization and
construction management.
A powerful factor of innovative development is
the use of modern digital technologies, primarily
Building Information Modeling (BIM) technologies,
which allow to automate labour intensive processes,
simplify the project adjustment, to make decisions
based on cost estimates not only for construction but
also for the facility operation. Such technologies are
aimed at creating a unified scientific, technical and
technological, regulatory and information
environment for intelligent management of the life
cycle of construction projects.
3.1 Industry-4.0 Processes in the
Investment and Construction
Complex
In the fourth industrial revolution, various economic
activities of manufacture are undergoing a series of
transformations: robots are working in factories, the
internet of things is regulating the use of resources,
and new technologies are changing the labor process.
Unfortunately, construction has been very slow to
transform in this direction, and many construction
sites differ little from those of the early 20th century.
But there is still some progress.
Construction is a type of economic activity,
which is characterized by limitations associated with
rising prices of construction materials, high rate of
credit, high level of debt between participants in the
investment and construction process, which forces
builders to optimize their production, accelerate
production processes. The answer to solving the
objectives can be Industry-4.
The article's authors, having studied and
summarized the progressive experience of Industry-
4.0 in construction, proposed a list of models within
Industry-4 (Table 1).
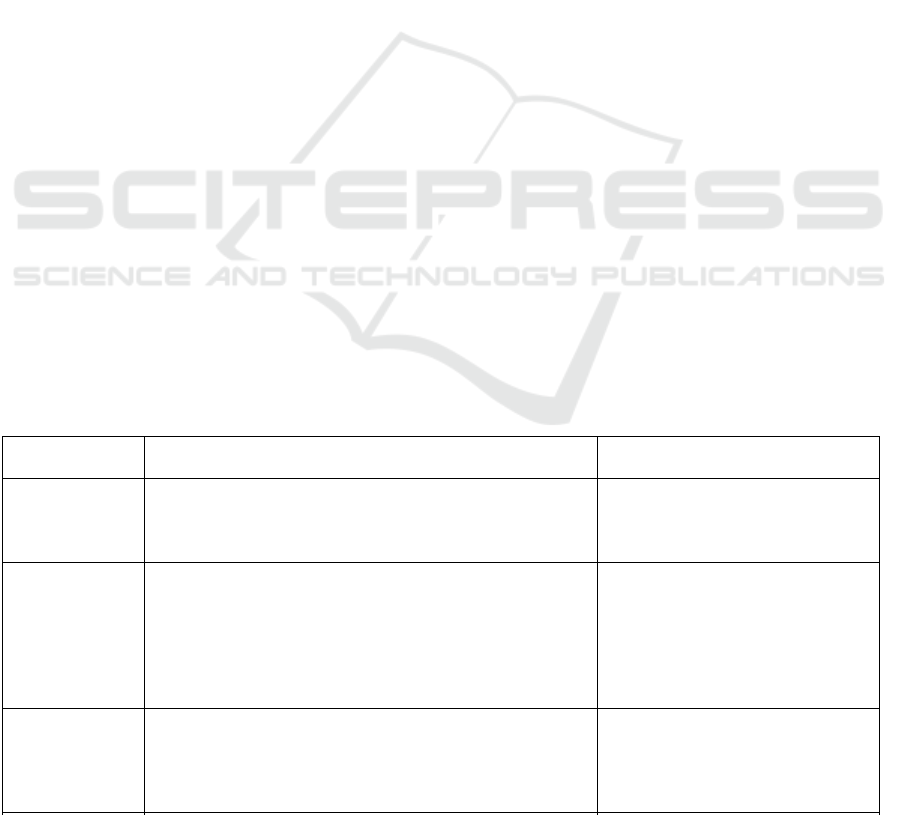
Table 1: Digitalization models of ICC organizations within Industry-4.
Model name Content Participants of the investment and
construction market
Construction
information
classifier (CIC).
Translation of various construction documents into
machine-readable format, i.e. document capture
Etalon Group, Platforma
stroitelnykh servisov LLC, YUIT
Sankt-Peterburg JSC, SiSOFT
Develo
p
ment JSC
Ecological
safety of
buildings as a
megatrend in
construction,
green
construction
Reducing CO
2
emissions from their own activities and their
own investment projects. Striving for carbon-neutral
operation. Availability of licensed software product.
Secondary use of water, purification of meltwater and
rainwater, automatic control of signals through control
room, lighting control in common areas and street lighting.
YIT House, MirLand Development,
Millhouse company
Artificial
intelligence and
machine
learning
Machine learning helps teams identify the most critical
safety and quality risks on a construction site that require
immediate attention.
Banks, financial organizations,
energy companies, retail,
telecommunications.
Construction companies have a low
start-u
p
base.
Factors of Innovative Development of Investment and Construction Complex in the Processes of Industry - 4.0
77
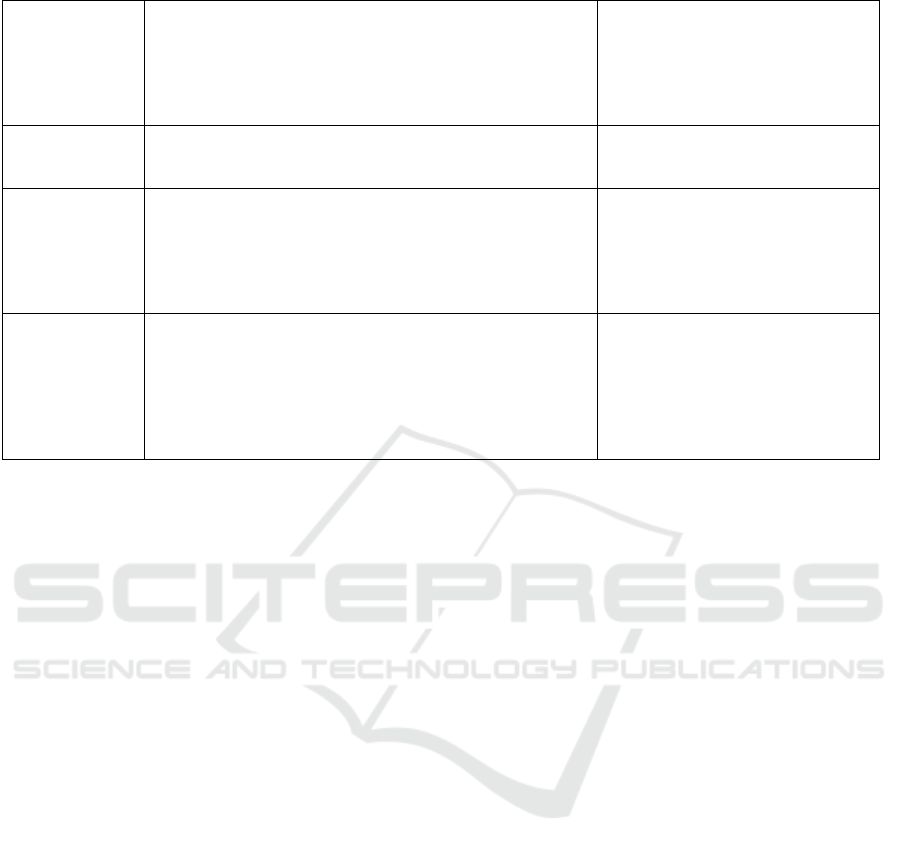
Table 1: Digitalization models of ICC organizations within Industry-4.
Programmed
(automatic)
devices for
operating
machines and
mechanisms
For example, sensors attached to working equipment will
transmit real-time data about its use and possible problems
to the supplier. So it will be possible to prevent breakdowns
and repairs. Real-time data will also provide the ability to
download automatic adds.
Construction companies have a low
start-up base.
“Live” materials
in construction
Examples include: self-healing biocement, self-replicating
concrete substitute, and mycelium-based composites for
construction and packaging
Experimental tests
3D printing in
construction
Process of creating a three-dimensional model of buildings
and structures
Single projects.
Pilot construction Apis Cor
Company (the city of Stupino,
Moscow region). Spetsavia
company (residential building).
Robots at
construction site
Application in emergency rescue, renovation, construction
and dismantling works in harsh environments.
The first group consists of manipulators, robots for
installation work performance. The second group consists of
construction manipulators and robots for concrete work. A
large group of construction manipulators and robots are the
means of finishing works robotization, etc. (Shagina, 2014)
Mostly – foreign experience.
In Russia – Victoria GC
Construction information classifier (CSI). On
December 1, 2020, the provisions of Article 57.6 of
the Urban Planning Code of the Russian Federation
entered into force, which defined the scope of the
construction information products. This is an
information resource formed as a result of a large
scientific research. At the moment, all housing
projects of YIT (the largest Finnish and one of the
largest Northern European construction companies)
use information modeling technologies, which allows
to automate the processes of creating standard
construction documentation and reduce labor costs
for manual information processing. Without a doubt,
the CIC implementation is a factor that determines the
system's ability to maintain its current state under the
effect of external influences.
Ecological safety of buildings and green
construction.
At the Summit of Leaders on Climate Issues, the
President of the Russian Federation noted that Russia
intends to increase the volume of associated gas
utilization; implement a large-scale program of
environmental modernization and energy efficiency
in all economy sectors; ensure the capture, storage
and use of carbon dioxide from all sources.
Programmed (automatic) devices for operating
machines and mechanisms. Professor and British
engineer Paul Newman believed that increasing
automation
is met with excitement and fear in equal measure.
But the benefits of autonomy for humanity are
enormous. At Volvo Construction Equipment, a
survey of 205 workers at the construction site yielded
the following results – nearly half of all construction
workers fear that the reliability and safety of their
jobsites could be compromised by the artificial
intelligence introduction and machines and
equipment automation.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning. The
technologies exist and are used by innovative
companies to mark visual data and analyze it for
potential threats, as well as to reduce all possible
risks.
According to McKinsey Global Energy &
Materials Practice research, artificial intelligence
techniques are used very little in the construction
industry. And in heavy industry, many companies
have spent years creating and storing big data, but still
have not revealed its full value. In fact, the authors'
research shows that more than 75% have tried some
form of artificial intelligence, but less than 15 % have
implemented a meaningful scalable impact (Agarwal,
Buckley, Samek, Somers, Hoey, Niel, and Wells,
2021).
What are the limiting factors that make it difficult
to use artificial intelligence in construction? These
factors include:
– that, if violated, can lead to substantial fines,
and the US Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
has issued a notice that it may hold
organizations accountable for spreading bias or
inequality through artificial intelligence;
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
78

– shortage of process specialists, in part due to
the retirement of full-time employees and a
lack of young candidates for employment;
– lack of funds for R&D.
“Live” materials in construction. The choice of
building materials for construction purposes is based
on profitability and quality in the implementation of
investment and construction projects. “Materials for
life” is a sustainable system that includes materials
and structures that constantly monitor, regulate and
repair themselves without external interference.
Davies, Kanellopoulos, Pilegis, and Trupti (2015)
note in their study that their team is developing a
multi-scale system that uses a number of
interdisciplinary technologies to promote and enable
self-healing in cement materials. The individual
healing methods under consideration are designed to
eliminate damage at various scopes of duration and
time and are encapsulated heal over agents, bacterial
heal over, crack close up using shape memory
polymer tendons.
In Russia, one of the main building materials is
concrete, which is affected by humidity, and therefore
scientists Yudenko, Chepachenko, Polovnikova and
Nikolikhina (2019) concluded that it is necessary to
adapt concrete to a wet environment. In such an
environment, self-produced concrete can be used to
fill cracks in roads, walls, and sidewalks.
3D printing in construction. If from January 1,
2022 the use of BIM technologies is mandatory for all
objects of state order from January 1, 2022, then the
use of 3D printing in the Russian market is a
promising direction of digitalization, but has a limited
application field. This technology is mainly applied
for low-rise house building, the creation of small
architectural forms, children's playgrounds and sport
venues. The advantage of 3D printing is not only
reduced expenses and time required for project
construction, but also reduced dependence on
humans. So far, most printers are adapted to the
manufacture of small parts.
Robots at a construction site. At the end of 2020,
an experiment began in Moscow to introduce the
technology of digital duplication of workers'
activities at the construction site. This is a joint
project of the Department of Urban Planning Policy
and the Department of Information Technology. As
an experiment, a special suit and a software and
hardware complex were developed that can
significantly increase working efficiency.
Another promising field is robot masons. The
robot of the Australian company Fastbrick Robotics
is capable of laying out up to 225 bricks per hour
without human intervention, that is, 4 times faster
than an ordinary builder. And the updated model of
the device is able to lay out up to 1000 bricks per
hour. Swiss engineers, together with architects,
materials scientists and robotics specialists, are
developing a mobile robot builder to carry out
construction work directly on the site. The device can
build objects with various tools with an accuracy of
up to 5 mm, reach high walls and work in semi-
autonomous mode. The architect remotely manages
the system, adjusting the construction plan.
3.2 Redevelopment Role in the
Industry-4.0 Processes
When forming the Industry-4.0 concept within ICC
management, it is necessary to pay special attention
to the location selection of investment and
construction complex enterprises. This statement is
confirmed by the research carried out by Gizem
Erdoğan (2019). The study suggests that existing
production sites will be moved from urban centers in
the Industry 4.0 process, and urban settlements will
be changed by transforming the criteria for land
selection to meet new requirements. At the same time,
special attention should be paid to the redevelopment
processes of urban areas with the choice of sites for
the transfer of industrial enterprises from central part
of city's territories.
The issues immediacy of urban areas
redevelopment in the ICC management processes is
due to such reasons as the physical and moral
obsolescence of the urban real estate fund (residential
and industrial buildings), changes in the structure of
urban land use due to structural changes in the urban
economy (reduction in the share of industrial
manufacture and increase in the share of service
industry, including trade), low efficiency of the use of
urban areas, relatively low density of development in
areas of cities built up with houses of the first
industrial series, the so-called houses of the
Khrushchev and Brezhnev era. For example, in St.
Petersburg, according to estimates of the Urbanika
Institute, the building density in areas built up in the
1950s-1960s was about 6000-10000 sq. m per
hectare, while in the central areas it is more than 20
000 sq. m of buildings per hectare.
The general tendency of changes in the structure
of urban land use, for example, in St. Petersburg is a
gradual reduction of industrial land. Thus, according
to the Committee on Land Resources and Land
Management of St. Petersburg, as of 2011, industrial
land accounted for 19 thousand hectares or 13.6% of
the city's territory. In 2016, their share was already
13% or 13.3 thousand hectares. At the same time, it
Factors of Innovative Development of Investment and Construction Complex in the Processes of Industry - 4.0
79

should be kept in mind that the practice of urban
planning develops faster than changes are made to the
documentation on territorial zoning. Former
industrial areas are increasingly becoming the object
of redevelopment with their transformation into
public and business or, even more often, residential
development. In general, this process should affect
about 6 thousand hectares belonging to the so-called
“gray zone” of St. Petersburg.
The implementation of redevelopment projects of
industrial territories has been carried out up to the
present time, mainly on the basis of the acquisition
(or equity participation) of industrial land by
investors interested in using it for the development of
commercial or residential facilities without direct
government participation in the implementation of
such projects. And in cases where the case touched on
territories with a single owner, such decisions are
quite possible. But where the territory has a complex
structure of use and ownership (many small plots of
land with different functional uses, many owners and
holders of other rights to land, buildings, premises,
etc.), the decision to redevelop is taken at big
expenses, and often hangs in mid-air.
Bachurinskaya I A, Vasileva N V, Maksimov S
N, and Yudenko M N (2020) proposed a unified
methodological foundation for the formation and
implementation of territorial development programs
from the perspective of their integrated development
in a major city. As a methodological basis for the
formation of a system of criteria and performance
indicators, it is proposed to use the concept of the best
and most efficient use of land, which is well-known
in the field of economics and real estate valuation,
which will allow, when choosing a location for ICC
enterprises within Industry-0, to comply with the
principles of energy efficiency and environmental
standards, as well as ensure the social, urban planning
and economic efficiency of using the territories.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The article considers the main factors of ICC
innovative development in the Industry-4.0
processes. The following characteristics of the most
significant factors are given: technological
modernization of building materials manufacture,
construction and installation work performance; ICC
greening; introduction of innovative approaches to
the management of ICC and financing of investment
and construction projects; provision of ICC with
highly qualified personnel; ICC digitalization and the
introduction of industry 4.0 technologies.
The development features of Industry-4.0
technologies are revealed, such as the growth of labor
productivity (as a result of functional connection of
man and machine), the efficiency of use of fixed
assets (system ability to make decisions
independently) and efficiency in general (integration
of production and IT systems) in application to the
formation of models of ICC organization
digitalization within Industry-4.0.
It is noted that the proposed digitalization models
in the investment and construction complex, as the
socio-economic system, will contribute to the system
ordering and self-organization, i.e., the growth of its
stability. From the point of ICC management view,
the necessity of implementing multidimensional
project management systems that use extensive
information bases and digital twins of ICC objects is
justified, which will allow to make management
decisions reasonably and within a short time, and that
will contribute to the capacity building of ICC
innovative development.
Attention is drawn to the fact that when forming
the concept of Industry-4.0 within ICC management,
it is necessary to pay special attention to the choice of
location for enterprises of investment and
construction complex and as a methodological basis
for this choice of location concept of the most
effective use is proposed. Thus, within the framework
of the conducted research, the hypothesis that the
Industry -4.0 processes are the stability and
development basis of the investment and construction
complex is confirmed.
REFERENCES
Boyko, I.V., 2018. Spatial and technological diversification
of the Russian economy. In Management consulting. 6.
pp. 68-76.
Acemoglu, D, Aghion, P, Bursztyn, L, Hemous, D., 2012.
The environment and directed technical change
American Economic Review. 102.
Gizem, Erdoğan, 2019. Land selection criteria for lights out
factory districts during the industry 4.0 process. In
Journal of Urban Management. 8. 3.
Götz, M., Jankowska, B., 2020.Adoption of Industry 4.0
Technologies and Company Competitiveness: Case
Studies from a Post-Transition Economy. In Foresight
and STI Governance. 14. 4.
Bachurinskaya, I.A., Vasileva, N.V., Yudenko, M.N.,
Nikolikhina, S.A., 2020. “Green” technologies in
housing: the experience of Russia. IOR IOP Conference
Series: Materials Science and Engineering . p. 913.
Bachurinskaya, I. A, Vasileva, N. V, Maksimov, S. N,
Yudenko, M. N., 2020. Programs implementation
prospects for the large city territories development in
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
80

Russia: institutional aspec. IOP Conference Series:
Materials Science and Engineering. 1083.
Zhineng, Tong, 2020. Discussion on Application of Energy
Saving Technology in Green Building. IOP Conference
Series: Earth and Environmental Science. p. 446.
Jay, Agarwal, Sean, Buckley, Robert ,Samek, Ken, Somers,
Michel van, Hoey, Joris Van, Niel, Ian, Wells, 2021.
Adopting a smart data mindset in a world of big data.
https://www.mckinsey.com/
Davies, Robert, Kanellopoulos, Antonios, Pilegis,
Martins, Sharma, Trupti, 2015. Materials4Life (M4L)
research aims to improve the sustainability and
resilience of the built environment. Conference:
International Conference Self-Healing Materials.
https://www.cardiff.ac.uk/
Yudenko, M.N., Chepachenko, N.V., Polovnikova, N.A. ,
Nikolikhina, S.A., 2019. Innovative materials in
construction and their role in improving of the
efficiency of organizations. IOR Conference Series:
Materials Science and Engineering. p. 698.
Shagina E.S., 2014. Robotization as a method of improving
the construction manufacture safety. In Construction of
unique buildings and structures. 6(21).
Prangishvili I.V., 2005. System approach and
management efficiency improvement. Moscow: Nauka.
p. 442.
Ivanova, R.M., Zagidullina, G.M., 2016. The main
directions of innovative activation in the investment
and construction field. In Russian enterprise. 17. p. 21.
Investment and construction complexes: theory and
practice of creation and development: collective
monograph. endorsed by Doctor of Economics
Sciences, prof. B.B. Khrustaleva and Candidate of
Economic Sciences Yu.S. Artamonova. Penza:
PGUAS. 2016.
Factors of Innovative Development of Investment and Construction Complex in the Processes of Industry - 4.0
81
