
Personnel Security: Personnel Addictive Behavior
N. S. Mikhailova
a
, V. A. Lyubina
b
and S. A. Verkhoturov
c
The Zabaikal’sk Institute of Rail Transport – the branch of Irkutsk State Transport University, Chita, Russian Federation
Keywords: Personnel safety, risk-based management, personnel risks, job satisfaction, behavior, addiction, addictive
behavior, addictive reaction, deviant behavior, prevention of alcoholism, mental disorders, psychoactive
substances, drugs, alcohol.
Abstract: The article deals with the issues of personnel security related to the problems of addictive behavior of
personnel who ensure the organization's activities in the implementation of production processes. The study
aims to determine the influence of addictive behavior on the management process and the efficiency of the
use of personnel in production activities. The authors set the task of reducing and limiting the presence in the
production and in management structures of persons who are potentially and actually included in a certain
risk group associated with the use of alcoholic beverages or being in the workplace in a state of alcoholic
intoxication. We conducted theoretical and empirical studies, reflecting statistical data on the drunkenness of
workers, alcohol dependence of personnel, and facts of alcohol consumption for the first time among
employees of railway enterprise divisions. The results of the study allowed us to determine the vector of
measures that ensure the reduction of personnel risks associated with deviant behavior.
1 INTRODUCTION
The classical theory of management defines the main
resources that support the activities of the enterprise,
which include financial, material and technical,
human, and information resources. The efficiency of
the use of resources depends more on the level of
competence of the manager. The executor of the
functional processes is the personnel who have the
necessary qualifications. Human resource
management is part of a special risk area called
personnel risks. Unlike other types of risks, personnel
risks are quite difficult to calculate in advance, since
human actions are unpredictable, and actions and
motives are determined both at the conscious and
unconscious levels (at the level of emotions). The
elements of uncertainty inherent in the functioning
and development of many processes cause the
emergence of situations that do not have an
unambiguous outcome.
In risk-based management, personnel risks are
considered at the entry to the organization, during the
performance of direct functional duties, and at the
stage of dismissal of employees from the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0316-2879
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1976-8488
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9775-3097
organization. Depending on the degree of uncertainty,
there are situations of risk and situations of
uncertainty. At the same time, the situation of risk,
being a kind of uncertainty, is characterized by the
fact that each action can have different results. Most
managers are concerned with risk minimization and
strategic risk planning processes.
The anti-crisis policy is developed in conditions
of full or partial uncertainty. Human behavior is
difficult to imagine in the form of any prescribed
management algorithm since personnel risks are
manifested in two ways. On the one hand, the
personnel affects the efficiency of doing business and
ensuring its safety, on the other hand, personal well-
being and safety. Under such conditions of
interaction, both wins and losses can be observed on
the part of the organization and the employee. The
company can thrive due to the presence of a person
with specific competencies, or vice versa, become
bankrupt when making an incorrect management
decision. The human factor is very often the cause of
any losses. Therefore, risk orientation enables to find,
eliminate or protect the most vulnerable places in the
management field (Melnyk, Shuprudko, and
172
Mikhailova, N., Lyubina, V. and Verkhoturov, S.
Personnel Security: Personnel Addictive Behavior.
DOI: 10.5220/0010695900003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 172-178
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Kolosovska, 2020). Back in the early 20th century,
Henry Ford said that if all his car factories were taken
away from him but people were left behind, he could
rebuild his car empire. And if he only had factories
without people, then he couldn't do anything (Ford,
1993).
Today, Russian companies implement a variety of
employee management tools: adaptive technologies,
certification system, competence-based approach,
grading system, and many other personnel policy
tools. The use of personnel management technologies
is not enough for efficient personnel management.
The work process is of great importance in terms of
the resources used by employees, presented
professional qualifications, motivation and ability to
adapt to changes in the environment, and factors
affecting people's behavior.
The entry of society into the information phase of
its development, market globalization and
competition, and many other factors have
significantly influenced people's behavior. The ideas
of experts and scientists about human behavior
received a particularly successful and rapid
development in the early twentieth century when
behaviorists declared it a subject of psychological
science. Behavior was initially understood as any
observed external reactions: motor, vegetative,
speech, which function according to the stimulus-
response scheme. In general, behavior can be defined
as "inherent in living beings, interaction with the
environment mediated by their external and internal
activity" (Mendelevich, 2016). Behavior that
corresponds to the rules accepted in society is
considered the norm, and non-compliance is
considered a deviation.
1.1 Problem Statement
One of the tasks of a modern enterprise is to limit the
presence in the production and in management
structures of persons who are potentially and actually
included in certain risk groups. In the modern world,
many scientific fields are engaged in the study of
interdependencies, or addictions, including medical,
sociological, psychological, and other schools. On the
edges of such studies, an unusual science has formed
– addictology, or the science of addictions. Currently,
the science of addictology studies a wide range of
human addictions, such as alcohol, narcotic,
toxicological, tobacco, pharmacological, chemical,
computer, gambling, including computer games,
various types of labor addictions, as well as food,
sexual, dependence on people, objects, actions, and
many others. The basis of addictive behavior is the
desire of a person to change the state of their
consciousness and thereby escape from reality. The
types of specific addictions differ depending on the
mechanisms used to escape from reality (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Types of human addictions.
When a person leaves reality, they experience
strong emotional overload and experiences, and at the
same time, their inner state actually depends on
emotions. That is, emotions, conventionally called
individual indicators of personnel security, are an
integral part of the dependence (Karzaeva and
Davydova, 2020). Is it legitimate to consider the
presence of people with addictions in the company as
an opportunity to develop personnel risks? Yes, it is
possible since the risks of personnel security can lead
to the following consequences:
external management of a dependent
employee who is at risk can lead to the destabilization
of the company by disclosing secrets, luring
customers, losing vigilance, etc.;
ability of a dependent employee to spread their
habits and addictions to the internal environment of
the company by organizing a group of like-minded
people and sympathizers;
satisfaction of personal addictions through the
use of various material and stratification resources of
the organization;
destabilization of the work of a well-
coordinated team, destruction of team spirit;
tendency to commit offenses and criminal acts
both for the sake of achieving their goals and as a
result of the consequences that have arisen.
Let's consider the most common form of human
addiction – alcoholism. Alcoholism is the use of
alcohol-containing beverages, that is, a mental and
physiological craving for alcohol. People with such
an addiction are a great danger to society, especially
when applying for a job. One can detect signs of
alcohol intoxication in a candidate for a vacant
position or a full-time employee both with the help of
medical and psychological methods and by external
signs.
Typical signs of alcoholism of a person are
represented by a fairly wide range of examples:
Personnel Security: Personnel Addictive Behavior
173
uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic
beverages at business meetings and entertainment
events;
appearance of external signs in preparation for
alcohol consumption: increased fussiness, irritability
or emotional elation, rubbing of hands and nose;
changes in certain facial features (redness of
the nose tip, swelling of the face, swelling of the
eyelids, changes in the color of the face skin);
speech signs, such as loss of sentence
meaning, limited vocabulary, stuttering, etc.;
memory lapses, changes in external behavior,
loss of "human appearance" and much more.
To determine the predisposition of people to
alcoholism, various medical methods are used.
Alcohol abuse negatively affects the entire system of
the human body, and at the same time, the negative
influence of an alcoholic on the organization is
expressed mainly in characteristic changes in their
personal qualities, their physical and emotional state.
The consequences of such changes are quite obvious:
significant losses of working time and,
consequently, economic losses;
constant threat to industrial and information
security, including the threat of accidents;
collapse of the team, involvement in the
drinking of alcoholic beverages of young people,
colleagues;
committing criminal acts or omissions,
causing bodily harm to colleagues and other persons,
etc.
Studies have found that a person who abuses
alcoholic beverages has a demoralizing effect on
people from the immediate environment. Despite this,
it is possible to exclude the harmful influence of such
employees on the organization. It all depends on the
degree of alcoholism. The more acute the stage of
alcoholism, the more obvious the reason for getting
rid of such an employee becomes. As a rule, the
dismissal of such an employee with a negative
attitude of the team to alcoholics does not carry a
social danger.
1.2 Results of Theoretical and
Empirical Studies
The basis for the formation of any addiction is a clear
sequence of non-standard psychological states, which
are the source of replacing various negative feelings
in a person with positive ones; for example, the
feeling of loneliness and anxiety is replaced by a
positive feeling of solidarity. At the same time, the
path of acquiring a new sensation and eliminating
troubles remains in the person's mind for a long time,
and the person feels safe and quite calm. Such a
subjective tactic of a person is called an addictive
reaction.
The negative consequences of drunkenness and
alcoholism are multidimensional and widely known.
These are millions of broken destinies, a huge number
of victims, violent crimes, motor vehicle accidents
(drunk drivers are the culprits of every fourth road
accident), increased mortality, injuries, degradation,
unfavorable heredity, loss of the health of the nation.
From 2010 through 2019 only, Russia has lost about
1 million people due to reasons related to
drunkenness and alcoholism. About 40 thousand
people die from ethanol poisoning every year. Factors
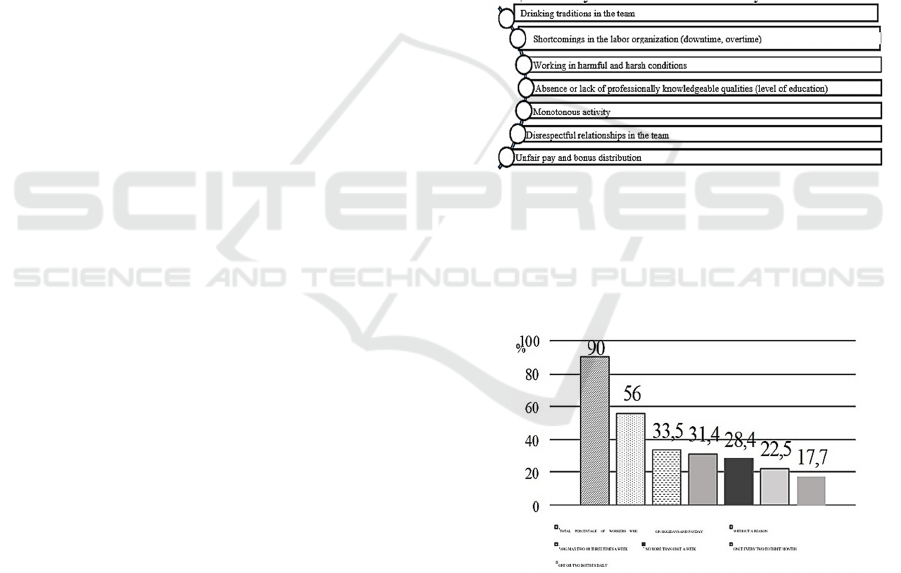
that contribute to the drunkenness of workers (Figure
2) were developed during the Soviet era, and they are
still relevant today.
Figure 2: Factors contributing to personnel deviant
behavior.
This problem has been around for a century.
Statistical data on the drunkenness of workers in 1935
(Figure 3).
Figure 3: Statistical data on the drunkenness of workers
(1935).
According to a survey conducted by the Russian
Statistics Office in 2019, the use of alcoholic
beverages in 73% of Russian citizens is associated
with the tradition of celebrating holidays with
alcohol. The second most popular answer was
"pleasure experienced as a result" according to 27.8%
of respondents. The feeling of calmness and
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
174
carelessness was indicated by 25.3% of respondents.
2.4% of respondents mentioned the cause of alcohol
consumption as they simply could not imagine their
lives without alcohol.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
There are many tests available to identify employees
who are prone to deviant behavior. To determine this
behavior, in particular, to identify deviations from
normal behavior, predisposition to alcoholism, the
collection questionnaire by K.K. Yakhin and V.D.
Mendelevich is used for detecting earlier signs of
alcoholism (Mendelevich, 2016). This questionnaire
is aimed at conducting diagnostic studies to determine
the levels of alcoholization of the individual –
domestic drunkenness, when the constant use of
alcoholic beverages is a habit in a person but has not
yet led to the development of addiction and chronic
alcoholism, when the body is intoxicated with alcohol
and there is a persistent psychological and physical
dependence on it.
To keep a person from developing alcoholism and
from consequences in case of constant alcohol
consumption – serious health problems, inability to
build a career and achieve success in life, loss of
human appearance, and early death, it is necessary to
reveal the content of this disease and indicate safe
ways to have a sober lifestyle.
To identify the proportion of people who are
prone to deviant behavior, we conducted testing
among the persons of one of the structural divisions
of the Trans-Baikal Railway.
The survey involved 120 employees, of which 40
people are "managers, specialists, employees" and 80
people are "workers".
The level of propensity to alcoholism is as
follows:
the level of development of alcoholism is
below -12.8 points;
the level of development of domestic
drunkenness ranges from +12.8 to -12.8;
the level of health status is above +12.8
points.
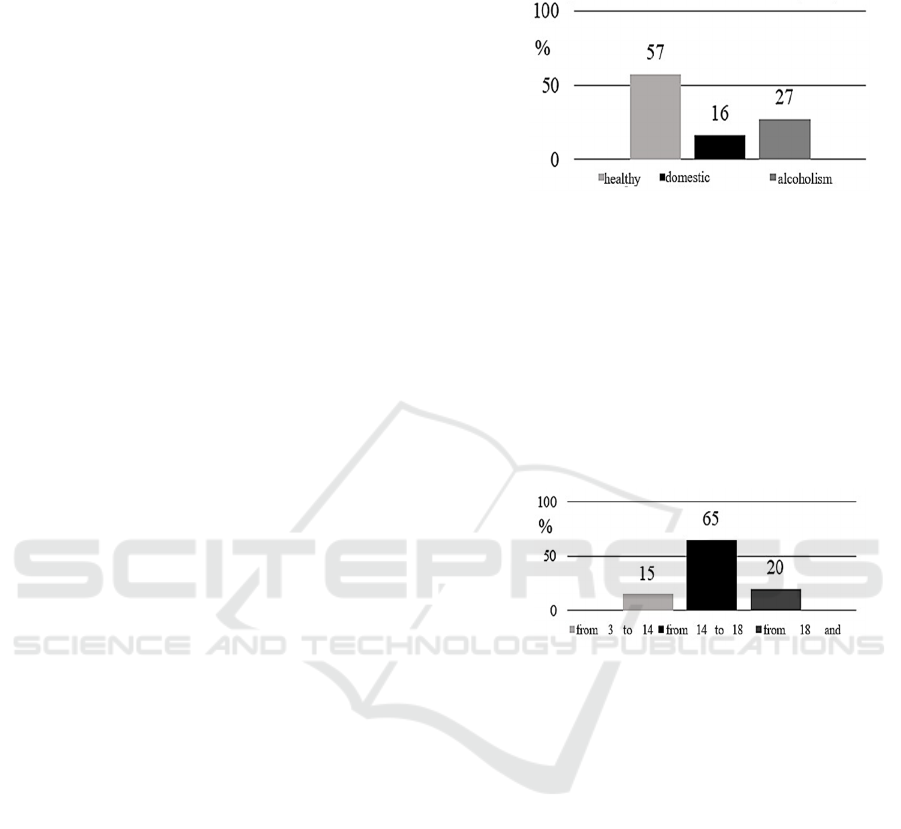
According to the results of the survey to identify
early signs of alcoholism, it was found that:
57% of respondents are healthy;
16% of respondents suffer from a domestic
form of drunkenness;
27% of respondents have alcoholism.
As we can see, from the data in Figures 4, 5, the
category of "domestic drunkenness" makes up a
larger percentage of respondents (16%), and those
suffering from alcoholism come second (27%).
Figure 4: Results of the survey on alcoholism of personnel.
Such data confirms that the problem of alcoholism
is present in the organization and requires a solution.
The analysis of the specialized questionnaire
allowed us to formulate the following results.
Alcoholism in adolescence can develop due to
dissatisfaction with modern living conditions and
everyday life. According to the survey, the proportion
of young people who drink alcohol during their
school years is 65%, but this was not considered
drunkenness.
Figure 5: Results of the "Age when you first tried alcohol"
survey.
By drinking alcohol, young men tend to weaken
their characteristic state of timidity, uncertainty and
get rid of excessive indecision. Often parents, friends,
and peers show negative examples related to
drinking. One of the reasons for the use of alcoholic
beverages is the poor organization of recreation and
leisure activities of young people, family relations,
domestic problems, financial difficulties, lack of
employment opportunities, etc. (Yakovleva,
Gaponenko [et al.], 2020). Such circumstances as
prolonged illness, loss of relatives and friends, and
conflicts in the family can also lead to domestic
drunkenness.
In the organization, as well as in society as a
whole, it is possible to identify many different factors
that lead to alcoholization of personnel, such as a
wide range of wine and vodka products, low level of
anti-alcohol policy at the enterprise, development of
negative traditions, for example: when meeting
friends and acquaintances to drink alcohol, "pop the
Personnel Security: Personnel Addictive Behavior
175
cork" for the appointment to a new position or the
birth of a child, etc.
According to scientists, since there is no obvious
pronounced predisposition to alcoholism at a young
age (although foreign scientists do not agree with
this), the assimilation of alcohol habits is carried out
mainly in small groups, such as family, social circuit,
and friends. Alcoholism is recognized in the modern
world as one of the most tragic and dangerous forms
of deviant behavior, which poses a serious threat to
the life of the population, the health and creative well-
being of both individual employees and the workforce
as a whole. The consequences of the development of
drunkenness are enormous, it negatively affects all
aspects of human activity, including labor discipline,
performance of official duties, etc.
The appearance of an official at the workplace in
a state of alcohol or drug intoxication negatively
affects the reputation of the enterprise, hinders its
normal functioning, entails organizational and
production risks, and also affects the success of the
company.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A set of psychological, organizational, and other
measures aimed at preventing alcoholism is carried
out by the organization's officials. In addition, work
is being carried out to identify the circle of
subordinates who are prone to this form of behavior.
Team conversations are held about the negative
consequences of drinking alcoholic beverages during
working hours, which can lead to both downtime in
the work of the organization and more serious
consequences (loss of a workplace or, even worse,
health or death, both in the workplace and outside it).
These activities should be carried out within the
framework of social work and should be attributed to
one of the current important tasks.
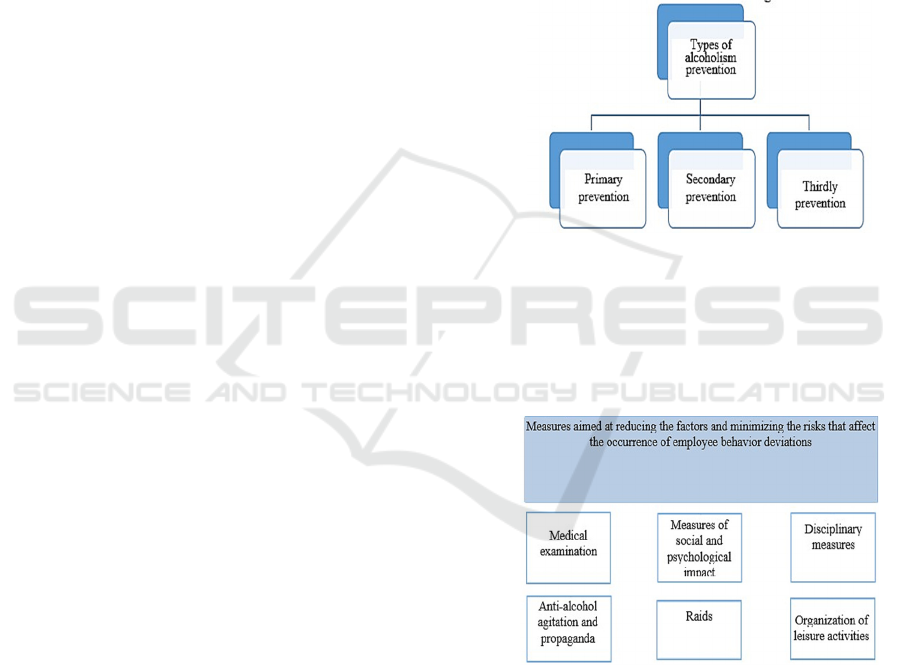
The main types of preventive measures against
alcoholism (Figure 6) include:
- primary prevention aimed at reducing the risk of
alcohol consumption by non-drinkers, especially
young people. This type of prevention of alcoholism
can be carried out among the circle of people with
mental disorders, prone to depression and mood
swings, since they are often prone to various
addictions;
- secondary prevention, which consists of helping
people with alcoholism. These activities are aimed at
making people aware that they should give up
alcohol. Most often, people suffering from
alcoholism do not understand that they are sick and
do not take this problem seriously. They are sure that
they have everything under control, and they can give
up this addiction at any time. At the same time, they
perceive such obvious signs of addiction as an
unhealthy appearance, an unpleasant smell and
fumes, and inappropriate behavior as normal;
- tertiary prevention, which consists of helping
people who have given up alcohol. This type of
preventive measures is aimed at reducing the risks of
returning to this addiction. Although it is important to
note that this type of activity is less efficient than the
previous two since any stressful situation can return a
former alcoholic to drinking alcohol.
Figure 6: Types of alcoholism prevention.
As a solution to the problem of deviant behavior
at the enterprise, the authors propose a set of
measures aimed at reducing the factors and
minimizing the risks that affect the occurrence of
employee behavior deviations (Figure 7).
Figure 7: Set of measures aimed at reducing the factors and
minimizing the risks that affect the occurrence of employee
behavior deviations.
One of the most efficient measures, in our opinion,
is the conduct of medical examinations aimed at
identifying alcohol and drug intoxication. The labor
legislation allows for mandatory daily medical
examinations for employees engaged in the harmful
and dangerous production, which includes the railway
transport industry. The algorithm for conducting a
medical examination is shown in Figure 8.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
176

Figure 8: Algorithm for conducting a medical examination.
The periodic medical examination includes the
measurement of the pulse and blood pressure, the
general assessment of the person's state of health, the
clarity of consciousness, and is conducted during the
working time. If alcohol or drug intoxication is
suspected, the employee is obliged to pass an express
test, and in case of positive results, he/she is
suspended from work. In addition, the reason for
suspension from work may be general malaise or
pressure drops.
Disciplinary measures include the method shown
in Figure 9. This method is used in practice by one of
the Far Eastern companies. At the initial appearance
at the workplace in a state of alcoholic intoxication,
the employee is reprimanded, and he/she is deprived
of 50% of the bonus. In case of repeated violation of
labor discipline, the employee is already deprived of
100% of the bonus, and the next time he/she will be
dismissed. This method is efficient in those industries
where there is an acute shortage of personnel, and
there is no possibility of dismissal of employees.
Figure 9: Disciplinary measures.
Figure 10 shows the methods of socio-
psychological impact.
Figure 10: Methods of socio-psychological impact.
One of the most efficient tools related to measures
of socio-psychological impact is the prosecution of
persons who have allowed the use of alcoholic
beverages in the workplace, with the analysis of such
cases at the general meeting of the team to create
intolerance to such violations of labor discipline.
Raids are also an efficient method for preventing
alcoholism. In this case, the employees of the
organization responsible for conducting this event
periodically go around the workplace and check the
labor discipline in terms of drinking alcoholic
beverages. Raids and medical examinations are
carried out at different times, without warning the
organization's personnel.
Anti-alcohol agitation and propaganda of a
healthy lifestyle is a fairly efficient method of
preventing alcoholism. This method helps to reduce
alcohol consumption among low-drinkers and may
encourage an employee with alcoholism to seek
treatment. This method is quite efficient in visual
agitation with the use of medical knowledge (one can
give an example of the harmful effects of alcohol on
the human body, show photos or videos on this topic).
To implement this method, doctors, psychologists,
social workers, or representatives of the Alcoholics
Anonymous Society can be invited to the company.
The development of organizational culture and the
organization of leisure time for employees is also an
important method of preventing alcoholism
(Osetrova, Prykhodko and Glazunov [et al.], 2019).
Properly organized leisure time of the organization's
personnel contributes to team cohesion, the
realization of the needs of the organization's
personnel in rest.
Game is the most common form of leisure. Based
on the conducted research, experts distinguish the
game in the broad and narrow sense of the word. The
game form of activity is a simulation and
reproduction of any actions or practical activities of a
person that contribute to their development and
improvement as an employee of a particular
organization (Hussain, Qazi, and Ahmed [et al.],
Personnel Security: Personnel Addictive Behavior
177
2018). The functional orientation of games is shown
in Figure 11.
Figure 11: Functional focus of games.
Thus, using the game as an organization of
corporate leisure, one can create a healthy and
creative atmosphere, provide the team with active,
interesting, and healthy rest.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The use of modern mechanics in personnel
management allows developing a set of personnel
strategies to prevent or minimize risks by changing
the perception of employees about the ideal model
and trajectory of behavior in the labor market, as well
as about the career strategy. By creating conditions
for the implementation of preventive measures to
minimize the factors that contribute to the
manifestation of negative addictions, it is possible to
get an efficient employee who meets the requirements
of the company.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors express their gratitude to the director of
the Trans-Baikal Institute of Railway Transport for
organizing surveys at railway transport enterprises, as
well as to the management and employees of the
divisions of Russian Railways JSC directly
participating in the surveys.
REFERENCES
Andrunik, A.P., 2020. HR security: innovative technologies
of personnel management: Textbook. p. 508.
Ford, G., 1993. My life, my achievements. p. 204.
Hussain, S., Qazi, S., Ahmed, R. R., [et al.], 2018.
Employee management: Evidence from gamification
techniques. In Montenegrin J. of Economics. 14(4). pp.
97-107.
Karzaeva, N. N., 2020. Methodological approaches for
creating a system of security indicators for company´s
personnel. In Utopia y Praxis Latinoamericana. 25(6).
pp. 219-228.
Kostenko, E. P., 2018. Modern trends in personnel
management: domestic and foreign experience. J. of
Economic Regulation (Issues of Economic Regulation).
9(4). p. 118.
Melnyk, S., Shuprudko, N., Kolosovska, I., et al., 2020.
Anti-crisis personnel management in the process of
ensuring the economic security of the enterprise. In
Business: Theory and Practice. 21(1). pp. 272-281
Mendelevich V. D., 2016. Psychology of deviant behavior:
Textbook. p. 392.
Osetrova, O., Prykhodko, O., Glazunov, S., et al., 2019.
Organizational culture as a component of personnel
security of the enterprise. In J. of Security and
Sustainability Issues. 9. 1(11). pp. 107-121.
Yakovleva, T. P., 2020. Morbidity and mortality trends
associated with the use of alcohol and psychoactive
substances (pas) in the young people (AGED 15-19) in
Russia. In AD ALTA: J. of Interdisciplinary Research.
1(11). pp. 140-143.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
178
