
Methodological Foundations for Managing Commercial Activities of
Small Businesses
Aleksander Aleksandrovich Popov, Elena Vladimirovna Lapteva
and Aleksandra Vyacheslavovna Kuzmicheva
Orenburg branch of the Plekhanov Russian University of Economics, 50/51-53, Leninskaya Ul./Pushkinskaya Ul.,
Orenburg, Russia
Keywords: small business entities, business management, management principles
Abstract: The article reveals the factors that affect the effectiveness of the management of the commercial activities of
small businesses; gives the legal basis, brief characteristics and advantages of small businesses; considers the
essence, goals, objectives, principles and methods of managing the commercial activities of small businesses;
reveals the content of the main elements of the commercial management process.
1 INTRODUCTION
Currently, the problems of effective management of
the commercial activities of small businesses are
caused by:
1. Business globalization. In these conditions, the
competition of small businesses with large
diversified companies operating, sometimes in
different regions (countries), in many cases
leads to disappointing consequences for small
businesses and even to the bankruptcy of some
of its representatives;
2. The lack of methodological unity in
understanding the essence and content of the
process of managing the commercial activities
of the organization;
3. The neglect on the part of many leaders of
small businesses to the most important aspects
of the organization's commercial activities and
to the vision of the prospects for commercial
development, etc. (Bagiev, 2016).
In Russia, the activities of small businesses are
regulated by Federal Law No. 209-FL dated July 24,
2007 "On the development of small and medium-
sized businesses in the Russian Federation", which
specifies the criteria by which you can determine
whether an enterprise belongs to a small business.
Among these criteria are: the maximum number of
employees of the organization; the maximum amount
of annual income; compliance with the requirements
for shareholders of enterprises.
In some cases, the process of creation of small
business enterprises is greatly facilitated, they are
allowed simplified accounting, they are given
benefits and supported by the government.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Currently, small businesses in Russia are represented
by the following structures:
- joint stock companies;
- limited liability companies;
- individual enterprises that carry out their
production and commercial activities without
forming a legal entity;
- consumer cooperatives;
- farming enterprises.
At the same time, for example, depending on the
number of employees, small business enterprises are
divided into:
- microenterprises with no more than 15
employees;
- small enterprises with at least 16 employees
and no more than 100 employees;
- middle-size enterprises with at least 101
employees and no more than 250 employees.
Among significant advantages of small business
there are: he possibility of self-registration, moreover,
it can be done remotely or in a simplified form; the
possibility of using simplified, including electronic
Popov, A., Lapteva, E. and Kuzmicheva, A.
Methodological Foundations for Managing Commercial Activities of Small Businesses.
DOI: 10.5220/0010697800003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 241-245
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
241

document management; exemption from certain
types of scheduled inspections, etc.
The activity of any enterprise does not happen
spontaneously, it is managed by specific people
(managers). The management of commercial
activities contributes to the improvement of the
effectiveness of all commercial and trade processes,
allows to direct the joint efforts of the employees of
the organization in order to achieve the planned
objectives.
Thus, the main objective of commercial
management is the rational use of the available labor,
material, technical, financial and other resources in
the organization to achieve the intended commercial
result of its activities (for example, increasing sales,
obtaining a certain profit, etc.) (Popov, 2019).
Specialists in the field of commerce among the
priorities of modern management of commercial
activities of the organization often include:
1. Study of goal market conditions and
forecasting of market demands;
2. Analysis of existing and potential producers
and resellers;
3. Optimization of procurement activities in the
organization based on the rational selection of
suppliers of necessary products and
establishment of economic relations with them;
4. Development of a system of measures aimed at
improving the effectiveness of the pricing
policy;
5. Analysis of the existing product range and its
rationalization taking into account consumer
demand;
6. Taking effective measures to improve the
organization's inventory management process;
7. Development of measures to improve the
efficiency of the sales process of goods;
8. Improving the quality of the offered services;
9. Search for efficient ways of positioning and
promotion of goods (services), including
advertising and information activities to
implement them and create a positive image of
the organization itself, etc.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Commercial management is considered as a specific
type of activity or an integral part of the entire
management system¬ of an organization. Such
activities are closely interconnected with economic,
technological and financial¬ processes. That is why,
when creating an effective commercial management¬
system, it is necessary to find a harmonious
combination of all its elements within the overall
management system.
Successful implementation of commercial
activity management processes is hardly possible
without relying on scientifically based and verified by
modern practice principles¬ and methods of
commercial management.
Recently, such principles¬ of management in the
field of commerce as (Buneeva, 2017) have become
increasingly widespread in the practical activities of
small businesses:
- the principle of reliability of sources of
information necessary for analysis and
management decisions on commercial issues;
- the principle of purposeful aspiration in
achieving the final results of commercial
activities;
- the principle of elasticity in commercial
management, timely adaptation of the system
to dynamically changing environmental
conditions and the requirements of the target
market;
- the principle of objectivity of forecasts and
timely response to possible manifestations of
commercial risks;
- the principle of concentration (focusing) of
efforts on priority aspects of commercial
activity;
- the principle of high responsibility of all
personnel for the fulfillment of their
obligations to ensure commercial transactions;
- the principle of effective coordination
(ensuring the required level of interaction) of
commercial activities¬ with the main activities
of the organization. It should not be forgotten
that commercial activities¬ are formed and
implemented taking into account the interests
of consumers and the needs of the market;
- the principle of complexity in commercial
management, taking into account all factors of
the external and internal environment of the
organization in question in the interests of
developing sound management decisions
aimed at optimizing commercial work, etc.
The methods of management (administrative,
economic and socio-psychological), through which
the impact on commercial processes is carried out,
should not be in dialectical contradiction. They
should be harmoniously combined and take into
account the existing conditions of the functioning of
the organization. The essence of the listed methods is
analyzed in (Popov, 2013).
The specific function of managing the commercial
activities of a small business entity is a continuous
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
242
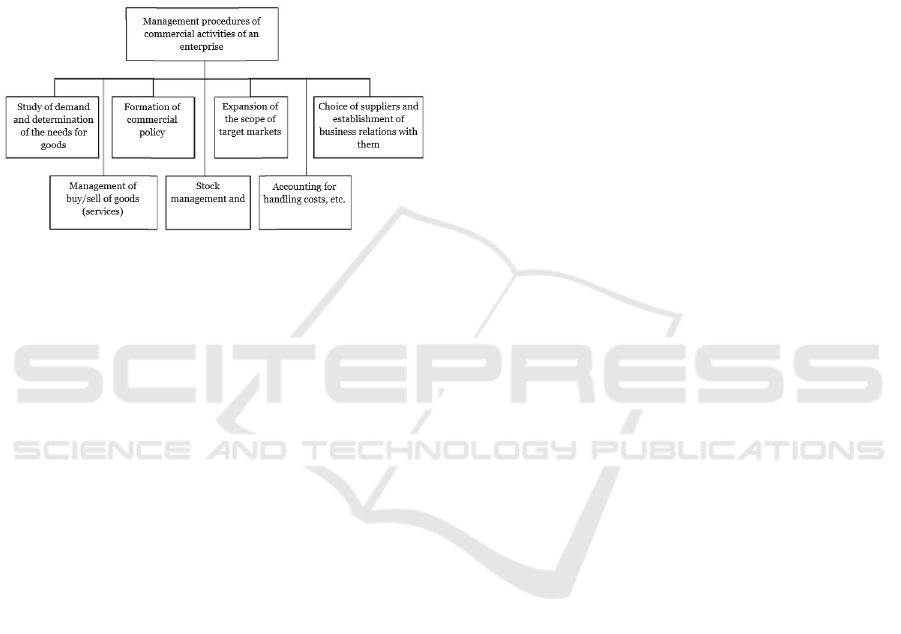
process of influence of the organization's
management on its personnel. All procedures of
management of commercial activities of the
organization should be reflected in this process.
In its turn, implementation of each management
procedure involves the execution of a certain
sequence of actions (operations) on the part of the
governing bodies, aimed at the formation and rational
use of the organization's resources. The content of the
procedures for managing the commerce of small
business entities is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Procedure of management of commercial
activities of a small business entity
Management procedures of commercial activities
of an enterprise
Study of demand and determination of the needs
for goods
Formation of commercial policy
Expansion of the scope of target markets
Choice of suppliers and establishment of business
relations with them
Management of buy/sell of goods (services)
Stock management
Accounting for handling costs, etc.
Let us describe in detail each procedure for
managing the commercial activities of small
businesses.
The purpose of studying demand and determining
the needs for goods is to identify problems and make
timely management decisions to fully or partially
eliminate emerging problems in order to increase
success in the field of commerce (Zhukova, 2017).
Study of demand may be carried out in two
directions:
- analysis of the group assortment and the overall
level of demand;
- analysis of the intra-group assortment and
quality ratings of consumers.
Information about customer demand is necessary
for the rational formation and timely product
extension.
The analysis of customer demand can be carried
out using various methods. For example, in retail
enterprises, such methods as those listed below are
widely used:
1. Assessment of turnover of goods and stocks;
2. Analysis of realized (unrealized) consumer
demand from the population.
Turnover is an expression of demand that reflects
only the realized customer needs. However, there are
objectively unfulfilled needs, that is, unmet demand,
the main reasons for which are the lack of the
necessary goods on sale, the excessively high price of
the goods, etc.
In order to study the unsatisfied demand, the
following can be used: lists of unsatisfied needs;
control sheets that are filled in by customers; counting
orders for goods that are not available for sale;
holding days of accounting for unsatisfied needs, etc.
Methods of analysis of realized demand include:
continuous statistical survey; sample survey; balance
method (the most used method of demand analysis).
Demand is a form of manifestation of needs in the
market. That is why, commercial organizations
should not only monitor changes in customer
demand, but also actively influence them using
effective marketing techniques (depending on the
current market situation).
The formation of a commercial policy should, first
of all, be aimed at developing correct long-term and
current goals and objectives of commerce, identifying
effective ways to achieve them. Such a policy is
developed taking into account the state of the
commodity market and its characteristics, as well as
on the basis of the formulated general goals, strategies
and real capabilities of the considered small business
entity.
We believe that the main content of developing a
commercial policy for a small enterprise is:
- formulation of reasonable goals and objectives
of commercial activity;
- development of assortment policy (product
strategy);
- formulation of pricing policy (strategies of
pricing);
- development of a policy (strategy) for the
promotion and sale of goods.
The main goal of commercial work is to ensure
the process of product distribution to consumers and
improve the quality of their customer service, taking
into account the established requirements of the target
market.
The main tasks of commercial activity for small
businesses include:
- study of consumer demand;
- increasing influence and penetration into new
markets;
Methodological Foundations for Managing Commercial Activities of Small Businesses
243

- maintaining its position in this market;
- expansion of the product range;
- rational organization and management of the
processes of purchase and sale of goods, etc.
Another procedure for developing the
management policy of small businesses is the
formation of an assortment policy. Its role in the
competitive struggle of rival parties is constantly
growing, since with the increase in the variety of
goods sold on the market that can satisfy the needs of
buyers, the company's competitive position is
strengthened.
The objective of forming a product range is to
establish a balanced product range. At the same time,
the balance of the company's product range becomes
one of the most important requirements. Since
changes in demand lead to the need to adjust the
assortment in order to ensure its balance, there is a
tight connection between demand and the product
range.
In order to carry out effective assortment policy,
it is advisable to pay attention to the rationality of
using the following types of product strategy:
- strategy for the development and introduction
of new products to the market, which involves
a certain sequence of actions, starting with the
development of a commercial idea and ending
with the commercialization of the innovation;
- strategy of product variation, within which it is
possible to modify it, change its individual
properties and quality parameters;
- strategy of elimination or withdrawal of the
good that lost its its competitiveness from the
market.
The goal of formulating a pricing policy and
choosing an effective pricing strategy is to achieve
the organization's planned profit level, to expand
(maintain) the market share by setting optimal prices
for the products sold. A "fair" price contributes to the
maximum attraction of buyers to the goods, forms
stable consumer preferences for both existing and
potential buyers. In the end, a competent pricing
policy allows you to achieve the required level of
return on investment.
The main stages (content) of the process of
formation of a pricing policy by small business
entities are (Popov, 2010):
- carrying out organizational measures to
develop a pricing policy (establishing
responsibility, clarifying the duties of officials,
etc.);
- formulation of objectives, goals and principles
to develop a pricing policy;
- development of a pricing strategy, the order of
actions of the organization in this aspect,
depending on changes in market conditions;
- determination of effective methods of price
competition;
- selection of an expedient method for
monitoring the price situation, etc.
The point of the product promotion process is to
convince potential buyers to make their first purchase
and remind regular customers to make regular
purchases.
The procedure for promoting a product involves
its positioning in the market and the use of effective
means of influence.
Product positioning on the market is ensured
through the use of such marketing techniques as
intensive or passive marketing, selective or wide
market penetration, etc.
The "driving tools" of influence include: "public
relations", advertising, sponsoring, direct marketing,
personal selling, branding, product placement.
Sales as the final procedure of commercial
activity of a small business entity is aimed at directly
providing consumers with the necessary goods
(services). Its goal: formation and maintenance of
rational system of goods movement from the
manufacturer to the consumer. Such a system
involves timely planning and reasonable choice of
ways to sell goods.
In general, a rationally formulated commercial
policy allows small businesses to expand their
influence in the market, find new market segments,
balance the trading range, improve the level of service
to the people.
Expansion of the scope of target markets involves
searching for new sales markets in order to increase
sales. There are several ways to achieve this goal:
- capture of new segments in the existing market;
- extension of the scope of small business entities
to other regions;
- search for new channels of distribution;
The correct choice of suppliers and the
establishment of economic ties with them allows a
small business to carry out mutually beneficial
commercial transactions and trade operations related
to the purchase and sale of goods, as well as to form
and maintain the required level of product assortment.
At the same time, the reliability of economic relations
depends on the ability of the interacting parties to
strictly comply with their contractual obligations.
The process of managing buy/sell of goods
(services) consists in the implementation of
commercial operations (transactions), commodity-
money exchange with suppliers and consumers and in
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
244

the sale of goods and services provided in the target
market. At the same time, purchasing activity is
becoming one of the most important commercial
functions, the essence of which consists in purchasing
goods that are intended for the subsequent sale.
Effective organization of procurement activities
by a small business entity allows to significantly
reduce commercial risks (Ivanov, 2016).
An element of commercial work is also the sales
service and provision of additional services to clients.
The provided services accompany the process of
purchase of goods and can include after-sales service
of the sold goods. It is necessary to pay special
attention to the quality of provided services and the
prospects of their diversification in customer service.
Inventory management contributes to the solution
of an important commercial¬ problem: the formation
and maintenance of the range of goods at the proper
level in order to meet customer demand.
Inventory management¬ involves: determination
of the optimal size of the inventory; operational
inventory accounting and effective control over their
condition; regulation of inventory at the enterprise.
The need for inventory management¬ is due to the
fact that the demand for goods is influenced by
many¬ factors. Therefore, there are errors¬ that take
place, which lead to the formation of surplus or lack
of the inventory, which is undesirable. When there is
the surplus of goods, the organization's¬ costs for
their storage, lending, etc. increase. Shortage of
inventory leads to unsatisfied customer demand and,
as a result, to a deterioration in the economic¬
condition of the organization.
Accounting for the costs associated with
commercial activities is the basis for the commercial
success of a small business entity and is determined
by the ratio between expenses and income received
from commercial activities. And this, in turn, is
associated with mutually beneficial transactions, with
the competence and enterprise of the organization's
leaders.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Thus, small business is a part of entrepreneurial
activity, which is based on small organizations, small
enterprises that are not formally included in any
associations.
Management of the business activities of an
organization is quite a complex process that can
create many problems for small businesses if there is
insufficient attention to it on the part of entrepreneurs.
REFERENCES
G. L. Bagiev, N. P. Ketova, 2016. Marketing in industries
and spheres of activity: Textbook for bachelors in the
direction of training "Management". SPB: Asterion.
p.340.
A. A. Popov, E. V. Lapteva, 2019. Development of a highly
specialized company strategy. In Audit statements. 4.
pp. 152–154.
R. I. Buneeva, 2017. Commercial activity. Organization
and management. M: Phoenix. p. 368.
A. A. Popov, D. A. Popov, O. N. Arguneeva, 2013.
Management: Textbook for bachelor students. p. 540.
T. N. Zhukova, 2017. Commercial activity. p. 256.
A. A. Popov, O. D. Dimov, D. A. Popov., 2010. Strategic
Company Management: Textbook. Orenburg:
Publishing center of the Orenburg State Agrarian
University. p. 344.
G. G. Ivanov, 2016. Organization and technology of
commercial activity. 272.
E. V. Lapteva, 2014. Policy and practice of the largest
Russian banks in the banking services market. In the
collection: Regional innovation economy: essence,
elements, problems of formation. Materials of the Fifth
All-Russian Scientific Conference with International
Participation. pp. 145–148.
Methodological Foundations for Managing Commercial Activities of Small Businesses
245
