
The Use of Analytical Tools in the Justification and Adjustment of the
Company's Strategic Guidelines
Olga Alexandrovna Polishchuk and Nadezhda Alekseevna Gracheva
Department of Economics, Management and Audit, Southwestern State University, Kursk, Russia
Keywords: Analysis, analytical tools, strategy, strategic guidelines, strategic management.
Abstract: The article shows the need to improve the strategic management of companies based on the development of
analytical tools for the development and implementation of the strategy. The authors clarified the concept of
strategy and strategic guidelines. The results of the study of corporate transparency of Russian companies on
the disclosure of information about strategic management in various aspects are summarized. The problems
in terms of analytical support of strategic management are identified and the need for its further development
is shown. The article presents the author's conceptual model of analytical support for strategic management
of production companies. It involves the formation of a set of analytical tools for strategic management,
focusing managers' attention on ensuring business continuity, minimizing risks, improving the efficiency of
the company as a whole and individual business processes, which will result in an increase in the value of the
business.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the context of a rapidly changing external
environment, fierce competition and the introduction
of sanctions, the determining factors for the success
of companies are to increase the efficiency of their
business and its development through the
achievement of their strategic goals. Therefore, many
Russian enterprises in the manufacturing sector of the
economy are forced to deal closely with issues of
strategic management. Quite a lot of foreign
publications (Ansoff, 1979; Drucker, 1969; Ferguson,
1993; Mintzberg, 1994; Porter, 1998; Thompson,
Strickland, 2007) and domestic authors (Vikhansky,
2002; Petrov, 2010; Khorin, 2006; Klochkov, 2010;
etc.) are devoted to the problems of developing,
implementing the strategy and evaluating its
effectiveness. These publications contain separate
analytical tools used in the process of developing
company strategies. At the same time, a
comprehensive approach is required to form
analytical tools that ensure the development and
implementation of the strategy, which will improve
the quality of the developed strategies and ensure
their implementation.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
General scientific methods were used in writing the
article: analysis, synthesis, complex and systematic
approaches, modeling. The article presents the results
of research on information transparency of Russian
companies on such an aspect of information
disclosure as strategic management (data from the
Russian Regional Network for Integrated Reporting).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Since there is no unambiguous position on the
concept of "strategy", we propose the following
definition of it, which was formulated, on the one
hand, by generalizing existing approaches, on the
other hand, based on the tasks solved by companies
in the process of strategic management. So, from our
point of view, the strategy for the development of a
production organization is a plan of action for the
future, supported by solutions to adapt companies to
the opportunities for obtaining competitive
advantages and to the threats of weakening their
competitive positions, in order to improve the
efficiency of activities based on risk management,
continuity, assets and business processes.
286
Polishchuk, O. and Gracheva, N.
The Use of Analytical Tools in the Justification and Adjustment of the Company’s Strategic Guidelines.
DOI: 10.5220/0010698800003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 286-290
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In practice, there are strategies with clearly
defined goals in quantitative terms, developed by the
management of companies, and strategies without
well-thought-out and clearly formulated goals, which
rather give an idea of the company's intentions. For
Russian companies, the second option is more typical,
especially for regional production organizations that
belong mainly to medium-sized businesses. Some
large companies do not disclose their strategic goals,
which means that it is difficult to form an idea of them
in this regard.
Since strategies are often cumbersome, vague and
insufficiently justified, it is difficult to evaluate them
and, consequently, to implement them. Therefore, it
is necessary to identify the key points of the strategy,
which will ensure the consistency of the interests of
owners and managers who implement the same
strategy, but at the same time have different interests.
In this regard, there is a need to develop the concept
of a "key strategic reference point", which will
become a "beacon" in strategic development for each
specific company. In our opinion, a key strategic
benchmark is a key indicator, the achievement of
which allows the organization to effectively develop
and implement a multi-vector policy.
The strategy in the process of its implementation
is forced to undergo adjustments under the influence
of various factors. Leaving the strategic guidelines
the same or not radically changing them, it is
advisable to adjust the intermediate parameters of the
strategy, the action plan. Significant adjustments to
the strategy are allowed only in crisis situations and
in case of drastic changes in business conditions. The
study of the strategic guidelines of Russian
corporations is usually carried out within the
framework of studying the system of goals put
forward by them and building corporate strategies
(Polishchuk, 2019).
An integral part of the Russian Regional Network
for Integrated Reporting (RRN) transparency studies
of Russian companies is the study of the disclosure of
strategic management information by major
companies.
Thus, the report for 2013 presented the results of
a survey of public reports of 100 companies from 24
industries. At the same time, 100% of the companies
disclosed information about the strategy and its
implementation. The best information is about the
industry/market situation. However, some aspects are
not sufficiently described: only 34% of companies
describe their strategic goals in quantitative terms;
38% of companies describe the resources needed to
implement the strategy. The contribution of the
reporting year to the achievement of strategic goals is
disclosed by 82% of companies, while in the reports
of 70% of companies this contribution is covered in
both quantitative and qualitative descriptions. Among
the leading industries in the disclosure of information
about strategic management are the chemical,
petrochemical and ferrous industries [Russian
Regional Network for Integrated Reporting].
The RRN report on corporate transparency of the
largest Russian companies for 2015 presented the
following results. For such an aspect of transparency
as strategic management, data on 182 companies that
disclose information in excess of the requirements of
Russian legislation are presented. Of these, 174
companies (96%) disclose information on the basis of
which it is possible to judge their further
development. The most disclosed information is the
company's position in the industry/market. 138
companies (76%) have a strategy description, only 78
companies (43%) describe their strategic goals in
quantitative terms; 51 companies (28%) disclose the
resources needed to implement the strategy – this is
the least disclosed aspect of strategic management.
The contribution of the reporting year to the
implementation of the strategy was described by 78
companies (43%) [Russian Regional Network for
Integrated Reporting].
In 2016, 184 companies were surveyed, of which
103 (56%) disclosed information about the strategy
and its implementation. RRN reports on company
transparency for subsequent years are not publicly
available. There is an acute problem of access to this
kind of information, since the transparency of a
number of Russian companies still remains poorly
illuminated in the media and the Internet space. The
imposition of sanctions against Russian companies
has also affected their willingness and ability to
disclose information about their strategic goals, as
well as the resources used to achieve them.
Unfortunately, many Russian manufacturing
companies do not have an effective and clearly
formulated long-term development strategy or their
strategic goals are not quantified. The reasons for this
situation are:
1. Lack of close attention to the development
strategy on the part of the company's owners.
2. Lack of highly qualified specialists in strategy
development.
3. Insufficient alignment of the achievement of
the company's strategic goals with the system
of remuneration of top managers.
The Use of Analytical Tools in the Justification and Adjustment of the Company’s Strategic Guidelines
287
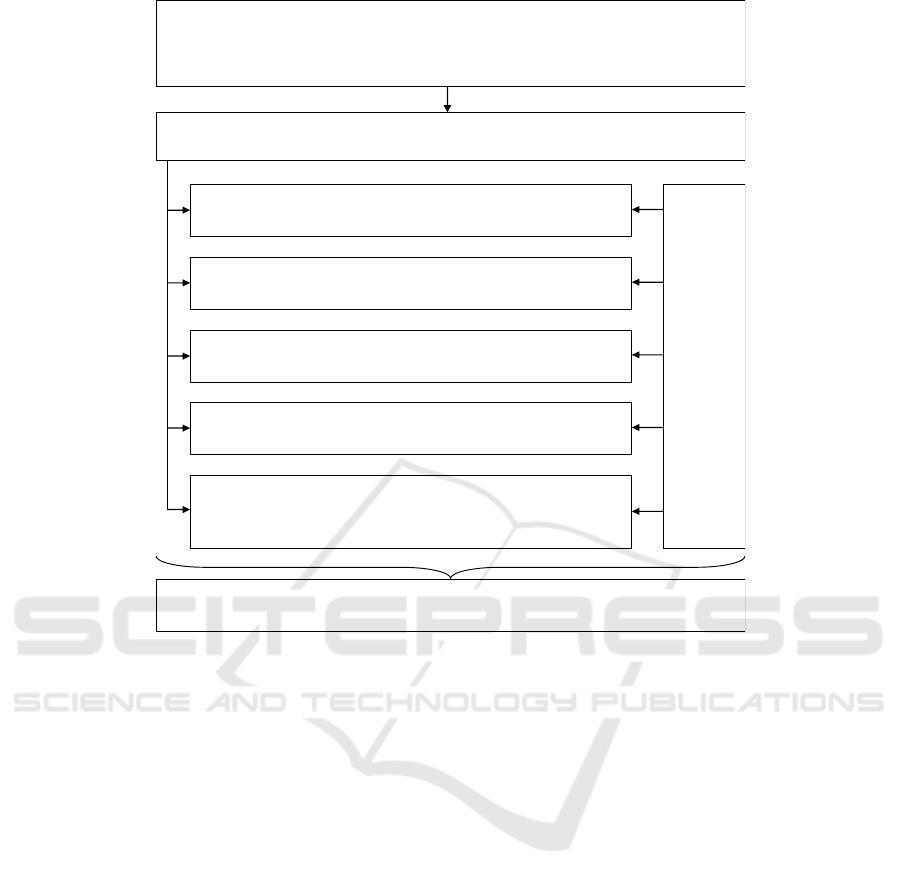
Figure 1: Model of analytical support for strategic management of production companies.
4. Poor alignment of the company's strategy with
the development strategies of the regions and
individual sectors of the economy.
5. Introduction of sanctions against Russian
companies.
At present, companies' strategic guidelines need
to be further aligned with regional development
strategies, and in some cases with the country's
development strategy as a whole, since these
strategies are not sufficiently developed in all regions
and are not fully provided with resources, including
financial ones, which makes it difficult to develop and
implement them. Nevertheless, there are serious
theoretical developments concerning various aspects
of regional development that are of practical interest
both for regional managers and for those companies
that consider it necessary and profitable to take into
account the vector of regional development in their
goal-setting [Belyaeva, Kozieva, 2019; Bessonova,
2018; Vertakova, 2016]. The alignment of the
companies' strategies with the strategic plans for the
development of the territories will increase their
efficiency, increase the investment attractiveness of
the companies, and increase their value.
Improving the process of developing and
implementing the strategy makes it necessary to
create a model of analytical support for strategic
management of companies, which should be based on
the modernization and development of a set of
analytical tools used to justify, adjust and implement
the development strategy of production
organizations.
The proposed model (Fig. 1) and its
implementation will improve the efficiency of the
company as a whole and individual business
processes, ensure the continuity of the company's
functioning, take into account and minimize risks,
and accelerate the achievement of goals. Many
manufacturing companies need to improve the
effectiveness of their development strategy. This
should also be aimed at improving the analytical
support of the strategic management process.
Let's look at the individual analytical tools of this
model.
In our view, the starting point for the
implementation of the strategic priorities of the
production company should be ensuring the
continuity of its activities. This is necessary to reduce
Modernization of analytical tools for development and
implementation of the development strategy a production
organization
A model for improving the efficiency of strategic management of production
companies based on analytical tools for developing and implementing their
development strategies
Analytical support system for strategic management of production organizations in order to increase
their efficiency
Assessment of the business continuity of a production organization
The end result of the implementation of the model: development of measures to achieve
strategic targets, including to increase the value of the business
Assessment of internal risks of the production organization to
minimize the degree of their impact
Analysis of the effectiveness of the activities and individual business
processes of the production organization
SWOTanalysis
PESTanalysis
Building a scheme for integrating financial and
non-financial indicators that forms the process of creating added
business value
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
288

the risks of business interruption and the negative
consequences of such failures, and restore the
business to an acceptable level. Therefore, the
assessment of the continuity of the company's
activities should be interlinked with the corporate
strategy and the strategies of the business units. It is
also important to rely on an understanding of the
specifics of business processes in various
organizations, taking into account their industry
affiliation. It is advisable to integrate the continuity
assessment into the organization's risk management
system (diagnostics of bankruptcy risk). Equally
important is which business unit will conduct the
continuity assessment. Most often, the assessment of
the continuity of the company's activities is difficult
due to the lack of a unified methodological approach
to its conduct and a quantitative assessment of the
factors that threaten it.
The development and justification of a business
development strategy must necessarily be
accompanied by the identification and assessment of
the level of risks. Performing the risk analysis for the
purposes of strategic management, it is proposed to
divide them into three groups: risks of strategic
management zones and the external business
environment; internal risks; risks of a separate project
(product) [Petrov, 2010]. In our opinion, the
company's internal risks deserve close attention,
which can be diagnosed in a timely manner and then
managed.
Currently, in the context of a decline in production
in certain sectors of the economy and the introduction
of sanctions, many companies are experiencing the
need to identify points of potential tension, the
presence of which can lead to a violation of the
balance within the organization and conflicts, and as
a result, to the inability to achieve their strategic
goals. One of the methods for diagnosing internal
risks is the standard model of the internal riskiness
calculator of an organization, modified by us
[Polishchuk, 2019], which can be used to identify,
track, control and minimize points of tension in
companies through corrective management actions.
Its use is aimed at achieving strategic goals.
The classic analytical tools used in strategic
management are SWOT analysis, PEST analysis,
GAP analysis, which should be used to more clearly
take into account the industry specifics of the
organization and its position in the commodity
markets.
The analysis of the achievement of strategic goals
should include an assessment of the performance of
companies: whether their achievement is
accompanied by an increase in key performance
indicators, whether the remuneration of top managers
is linked to the implementation of the set strategic
goals and objectives. For the company, it is necessary
to create key performance indicators, the system of
which can be represented by performance indicators
grouped by its types of activities, by functional zones,
by areas of asset use, and other characteristics. The
effectiveness of the company's activities and its
progress towards the set goals is seriously affected by
the effectiveness of individual business processes of
the organization, which strongly affects the coherence
of the actions of the company's divisions in the
process of implementing the strategy.
When evaluating the implementation of
companies' strategic plans, it is necessary to analyze
the achievement of corporate performance targets.
The target indicators can be the size and rate of profit
growth, sales growth, an increase in the share of
products in the market, indicators of return on assets
and equity, and capitalization growth. "In achieving
long-term goals, EVA, EBITDA and performance
indicators calculated on their basis are indispensable.
The company's goals may be to increase the value
added of equity capital (SVA), market value added
(MVA)." [Gracheva, 2016].
To link strategic goals with business processes
and personnel actions at each level of the company's
management, it is advisable to use such a tool as the
balanced system of organizational performance
indicators (BSC). It combines financial and non-
financial performance indicators, as well as the
achievement of strategic indicators and development
plans of the company. To determine the company's
prospects, goals and indicators, as well as the links
between them, it is necessary to develop a strategic
map. A strategic map with a description of non-
financial quantitative goals (for example, increasing
the company's market share, reducing the length of
the production cycle of manufacturing products,
increasing the satisfaction of both customers and
staff) allows you to imagine the process of creating
added value. Non-financial indicators should account
for about 80% of the indicators. The optimal ratio of
indicators is as follows: customers - 22%, internal
business processes - 34%, training and development -
22%, finance - 22%. The strategic map identifies
causal relationships that indicate how intangible
assets (for example, the availability of highly
qualified personnel, customer bases, brands) are
transformed into tangible results (attracting new
customers, providing increased revenue from the sale
of new products and services, increasing profits and
increasing the value of the company). Thus, the BSC
allows the company to describe its strategy in an
The Use of Analytical Tools in the Justification and Adjustment of the Company’s Strategic Guidelines
289

accessible way in the form of a map and translate
strategic goals into a clear plan of operational
activities of departments and key employees for
subsequent evaluation of results using key
performance indicators (KPI). Ultimately, the KPI
system used in the company should be aimed at
ensuring the growth of the business value through the
management of the factors that affect it.
The main goal of the implementation of the KPI
system is to ensure the growth of the overall
efficiency of the company, due to the fact that each of
the employees will understand the relationship
between their specific responsibilities and the
strategic goals of the company. Managing a company
using a system of key performance indicators allows
you to look at the current situation in the company
through the prism of a strategic perspective.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Further research is required on strategic management,
in particular, on analytical support for the
development and implementation of company
strategies. The model developed by the authors
provides for the formation of a set of analytical tools
for strategic management, which will improve the
efficiency of the company as a whole and individual
business processes, ensure the continuity of the
company's functioning, take into account and
minimize risks, and accelerate the achievement of
strategic goals.
REFERENCES
Ansoff, H. I., 1979. Strategic Management, The MacMillan
Press.
Drucker, P., 1969. The age of discontinuity, Heinemann.
Ferguson, Marylin., 1993. The New Paradigm: Emerging
Strategic for Leadership and Organizational Change.
New Consciousness Reader.
Mintzberg, H., 1994. The rise and the fall of strategic
planning. N.Y. The Free Press.
Porter, M. E., 1998. Competitive Strategy: Techniques for
Analyzing Industries and Competitors. N.Y.: The Free
Press.
Thompson, Jr., Arthur A., Strickland III, A. J., 2007.
Strategic Management: Concepts and Situations for
Analysis, 12
th
. M.: Publishing house "Williams". p. 928.
Fleischer, K., and Bensussan, B., 2005. Strategic and
competitive analysis. Methods and means of
competitive analysis in business. M.: BINOM.
Knowledge Lab. p. 541.
Vihansky, O. S., 2002. Strategic Management, M.:
Gardariki. p. 296.
Petrov A. N., 2010. Strategic Management, St. Petersburg:
Peter, p. 496.
Horin, A. N., 2006. Strategic analysis. Moscow: Eksmo. p.
288.
Klochkov, A. K., 2010. KPI and personnel motivation, M.:
Eksmo. p. 160.
Polishchuk, O. A., Gracheva, N. A., 2019. Analytical
support for the strategic management of a production
organization. Kursk, CJSC "University book".
Gracheva, O. A., Ponomareva, T. V., 2011. Formalization
and reengineering of business processes of an industrial
enterprise in order to increase the efficiency of its
activities. In Economics, Statistics, and Computer
Science. Bulletin of the UMO. 3. pp. 34-41.
Gracheva, N. A., Polishchuk, O. A., 2012. Methodological
approaches to assessing and managing the value of
companies from the perspective of risk management
and business process optimization. In Bulletin of the
Samara State University of Economics. 9(95). pp. 18-
25.
Gracheva, N., 2016. Analysis in corporate governance. In
Economic magazine-XXI. 157. 3-4-1. pp. 85-87.
Belyaeva, T., Kozieva, I., 2019. Diagnostics of strategic
spatial development scenarios of the national economy.
In Economic magazine-XXI. 11-12. pp. 122-129.
Vertakova, Yu. V., Klevtsov, S. M., Klevtsova, M. G.,
2016. Sustainability of territory development:
morphology of economic space. In Proceedings of
Southwest State University. Series: Economy.
Sociology. Management. 18(1). pp. 89-96.
Bessonova, E., Alekseeva, V., Milgunova I., 2018.
Development of the assessing method of investment
attractiveness for the regional socio-economic system.
In Proceedings of the 32nd International Business
Information Management Association Conference,
IBIMA 2018 - Vision 2020: Sustainable Economic
Development and Application of Innovation
Management from Regional expansion to Global
Growth. pp. 5864-5876.
Russian Regional Network for Integrated Reporting, 2013.
http://transparency2013.downstream.ru.
Russian Regional Network for Integrated Reporting, 2015.
http://transparency2015.downstream.ru.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
290
