
Development of the Agri-Food Market of the Krasnodar Territory in
the Context of Food Security in the Region
O. N. Kolomyts
1
, I. G. Ivanova
2
and R. F. Bakirov
2
1
Kuban State Technological University, Russia
2
Kuban State Agrarian University named after I.T. Trubilin, Russia
Keywords: Agri-Food Market, Food Security, Region, Consumers, Balance, Production and Consumption.
Abstract: The purpose of this study is to develop a holistic concept for the formation and sustainable development of
the regional agri-food market of the Krasnodar krai, mechanisms for the management and improving its
efficiency to reduce the asymmetry of its functioning and increase the level of food security in the region.
Within the framework of the study, the essential characteristics of the agri-food market that have a "vector of
market orientation" and the features of its formation were clarified; the level and intensity of the development
of the regional agri-food market were analyzed in dynamics; the balance of the agri-food market of the
Krasnodar krai was assessed. The results obtained can be used by regional authorities, the Ministry of
Agriculture, and the Ministry of Economic Development in the development of complex projects and targeted
programs for the development of the agro-industrial complex; in updating the regulatory framework of
regional agricultural policy; in justifying management decisions in the field of regulating the growth of a
certain branch of the economy of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation and improving its food
security, as well as in the business activities of business entities.
1 INTRODUCTION
The sustainable functioning and development of the
agri-food complex of the Russian Federation as one
of the priority national economic complexes of the
country is the determining vector of socio-economic
development, determining the vital activity of
society.
The agri-food market (AFM) is an important
segment of any national economy, the globalization
of which affects economic systems, thereby
determining their further development. The European
integration vector in the development of Russia
changes the structure of the market, its role, and
functions (Vlasov, 2018). The process of
development of the agri-food market in modern
conditions is complex and multifaceted, and
phenomena and processes associated with it acquire
new features that correspond to the needs of the
entities of the modern environment.
These trends are becoming more pronounced and
often repeated in the context of a globalized economy.
The processes of change in market systems are
dynamic, irreversible, and multilateral in the global
environment, which significantly affects all related
systems that are also the elements of state regulation
(Gaiduk, 2018).
The main aspects in the development
of economic systems are industry-specific features.
The already achieved level of development of the
agri-food market currently lags behind the indicators
of most European countries. At the same time, the
Krasnodar krai has significant potential, enabling to
occupy a leading position in the agri-food market on
a global scale.
The development of the agri-food market attracts
the attention of many scientists. Thus, the general
scientific study of the essence for the category
"development" is considered in the papers of O.
Khubar, V. Virchenko, A. Kuzmenko, Yu. Prikhozhi
na, A. Toynbi, O. Spengler, et al.
The sectoral aspects of the national agri-food
markets are traced in the papers of O. Berezin, N.
Datsenko, E. Kirilyuk, et al.
The main aspects of the nature and structure of the
agri-food market are considered in the research by
Samoylik.
It is also important to pay attention to the scientific
contribution of foreign authors (T. Burns, DeVille, I.
Skavronska, Ya. Mazurek, I. Meltsova, M. Sholtes,
Mamedov, et al., Dedina and Sánova, Vilmantas, and
Melnikas, et al.), studying the development of
agricultural markets in other countries.
316
Kolomyts, O., Ivanova, I. and Bakirov, R.
Development of the Agri-Food Market of the Krasnodar Territory in the Context of Food Security in the Region.
DOI: 10.5220/0010700400003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 316-322
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

All of the above determines the emergence of
modern determinants and mechanisms for the
development of the regional agri-food market, which
require additional research.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Abstract-logical and formalized methods were used
to study the essence, formulate the characteristics and
identify the most significant factors of the "agri-food
market" category, and establish the patterns of its
development.
Generalization and description of facts and
events, projection of patterns of functioning of the
agri-food market of the region, methods of analogy,
and general scientific methods of theoretical and
empirical knowledge were used.
Comparison of indicators and trends,
identification of similarities and differences, as well
as identification of the most significant aspects and
factors of the formation and development of the AFM
were carried out by methods of comparative and
causal analysis.
The use of a systematic approach in the study
complements the traditional analysis with methods
that enable to study socio-economic processes in their
totality and interaction, considering the regional agri-
food market as an integral object consisting of
interrelated and interdependent elements (entities,
infrastructure, market conditions, etc.).
The author's personal observations and
developments, data from the Federal State Statistics
Service and Krasnodarstat, and official Internet
websites served as information and empirical basis
for testing the proposed hypothesis.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The agri-food market (AFM) integrates the
agricultural and food markets, where the sale of
agricultural raw materials, products of processing
industries, agricultural and processing industries,
public catering and wholesale and retail trade is
carried out.
The problems of studying various aspects of the
development of the agri-food market are covered by
many researchers and scientists (Paramonov, 2016;
Ushachev, 2015; Zeldner, 2018; Kuchumov, 2018;
Mikhalko, 2017), but there is no unified interpretation
of the concept under consideration today.
The critical analysis and systematization of
existing points of view, variety of approaches, and
numerous modifications of the definition of "agri-
food market" allowed us to understand the agri-food
market based on the use of commodity-money
relations, as a set of relations of economic entities of
industry markets involved in the process of
production, distribution, exchange, and consumption
of food products and their promotion from producers
to consumers (auth.).
The agri-food market (Cole, 2018; Alston, 2000)
integrates three independent but interrelated markets,
each of which has its own characteristics (Figure 1).
Thus, the agri-food market is a multisectoral
complex ecosystem that includes the sphere of
circulation of agri-food products and ensures the
relationship between the production and consumption
of agri-food products, continuity, and integrity of the
reproduction process. The foundation of the AFM is
commodity-money relations that develop in the
processes of production, distribution, exchange, and
consumption of agri-food products, the structural and
functional organization of which is based on a set of
organizational, financial, economic, and social
institutional forms (Buks, 2016; Pérez-Escamill,
2017).
Within the framework of the study, the authors
consider the AFM as a system that covers a wide
range of economic relations that are manifested in the
process of interaction between agricultural producers,
processing enterprises, intermediaries, and other
market participants regarding the movement of agri-
food resources, as well as end users (Figure 2).
The functioning of the agri-food market is
impossible without state participation since it
coordinates the interaction of all market participants
through state support for agricultural producers and
various regulatory and legislative mechanisms
(Charles, 2014; Campbell). that allow regulating
market relations and smoothing their negative
aspects.
The concluded transactions between the entities of
the AFM in terms of the supply and sale of
manufactured products to meet the needs of the
population in accordance with the effective demand
and obtaining a socio-economic effect represent the
result of the functioning of the agri-food market
(Pingali, 2005). The foundation of management, the
basic component of the sustainability and efficiency
of agro-industrial production are the relations that
arise between the entities of the agri-food market,
which determine the structure, forms of product sales,
production costs, strategic directions of development,
etc.
Development of the Agri-Food Market of the Krasnodar Territory in the Context of Food Security in the Region
317
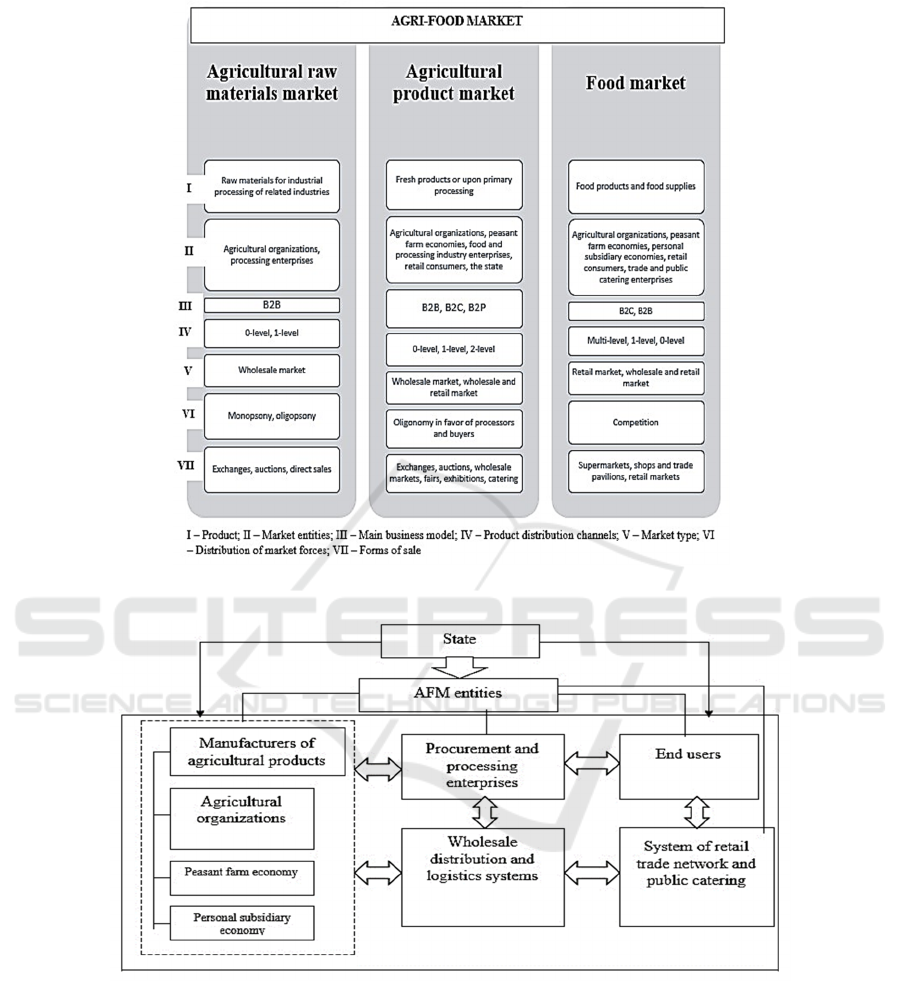
Figure 1: Agri-food market structure.
Figure 2: Agri-food market entities.
Economic crises negatively affect the income of
the population and, as a result, the consumption of
food. The social state, like the Russian Federation,
guided by the Constitution is obliged to ensure the
well-being of the population, its security, and
improvement of the standard of living. The standard
of living largely depends on the ability to meet
primary needs, including food (Kolomyts, 2019).
In the context of the pandemic, when due to the
suspension of the activities of a large number of
enterprises, a significant part of the population's
income has decreased; the state has taken a whole
range of measures aimed at maintaining the declining
incomes of the population.
The parity of the production-consumption ratio of
food products should be observed, since if production
volumes of some products are higher than the demand
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
318

volumes, then it is necessary to export them, and vice
versa, if the population's demand for any products is
not satisfied, then it is necessary to organize its import
(Keyzer, 2007; Velinov, 2016).
The assessment of the factors of the regional food
market conjuncture involves the analysis of dynamics
of the import and export of food products (Figure 3).
The results obtained show that there is a
fluctuation in import volumes over certain years in
the study period. So, in 2019, compared to 2015, there
was a reduction in the import of sugar by 83.4%,
cheese by 48.1%. There is an increase in imports for
other types of food.
The main suppliers of food products to the
Krasnodar krai are the Belgorod, Pskov, Vladimir,
Moscow, Chelyabinsk, and Orenburg regions. The
total volume of imported products from these regions
is more than 80% of the total import of food products.
Figure 3: Import of main types of food products, t (GKS).
Table 1: Export of main types of food products, t (GKS).
Indicators 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Meat 5,271 8,405 5,772 6,874 6,542
Sausage products 14,188 11,234 11,623 11,312
11,235
Butter 1,190 1,222 820 1,104 1,398
Cheese 434 4,039 4,387 1,906 2,176
Development of the Agri-Food Market of the Krasnodar Territory in the Context of Food Security in the Region
319
Table 2: Balance of import and export of basic food products (GKS).
Indicators 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Meat 101,286 102,561 131,825 129,478 93,483
Sausage products 27,012 57,960 41,185 34,732 49,038
Butter 693 1,435 1,887 2,096 1,448
Cheese 41,422 33,389 15,614 16,298 19,123
Flour -21,678 57,428 23,221 93,308 87,750
Cereal -26,061 -81,524 11,349 -109,047 -69,993
Sugar -618,320 -751,278 -802,204 -621,619 -874,020
The increase in the export of food products in the
study period in physical terms was: for cheeses – five
times; for tea – nine times; for meat semi-finished
products – nine times; for cereals – almost twice; for
milk (except raw) – one and a half times; for
confectionery products – thirty-seven percent.
The export volumes of some food products
decreased: flour – by 3.2 times, canned meat – by
39.1%, sausage products – by 20.8%.
Enterprises of the Krasnodar krai produce a fairly
large volume of meat products, which affects the
decline in the production of producers from other
regions in the domestic market. Thus, the volume of
imported meat for the period from 2015 to 2019
decreased by 6.1% due to the redistribution of
commodity flows. It should be noted that now most
of the products produced are sold on the territory of
the Krasnodar krai.
The Krasnodar krai supplies more than 80% of
food products to Moscow and the Moscow region, as
well as to St. Petersburg and the Rostov region.
The negative balance of import-export of the
studied groups of food products indicates that the
volume of export of cereals and sugar exceeds the
volume of import. Thus, the export of cereals in 2019
exceeded the import by 2.3 times, sugar by more than
180 times.
To determine the level of balance of the regional
food market, it is necessary to assess the production
and consumption of basic food products using
integral estimates of the volume of production and
consumption of food products by the population of
the Krasnodar krai.
For this purpose, we used the method of N.V.
Shalanova:
where x
ij
is the value of the j-th indicator in the
year t
i
of the analyzed period;
σ is the standard deviation of the j-th exponent;
ɑ
j
is the weight of indicators;
The algorithm for calculating the integral estimate
is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Algorithm for calculating the integral estimate.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
320
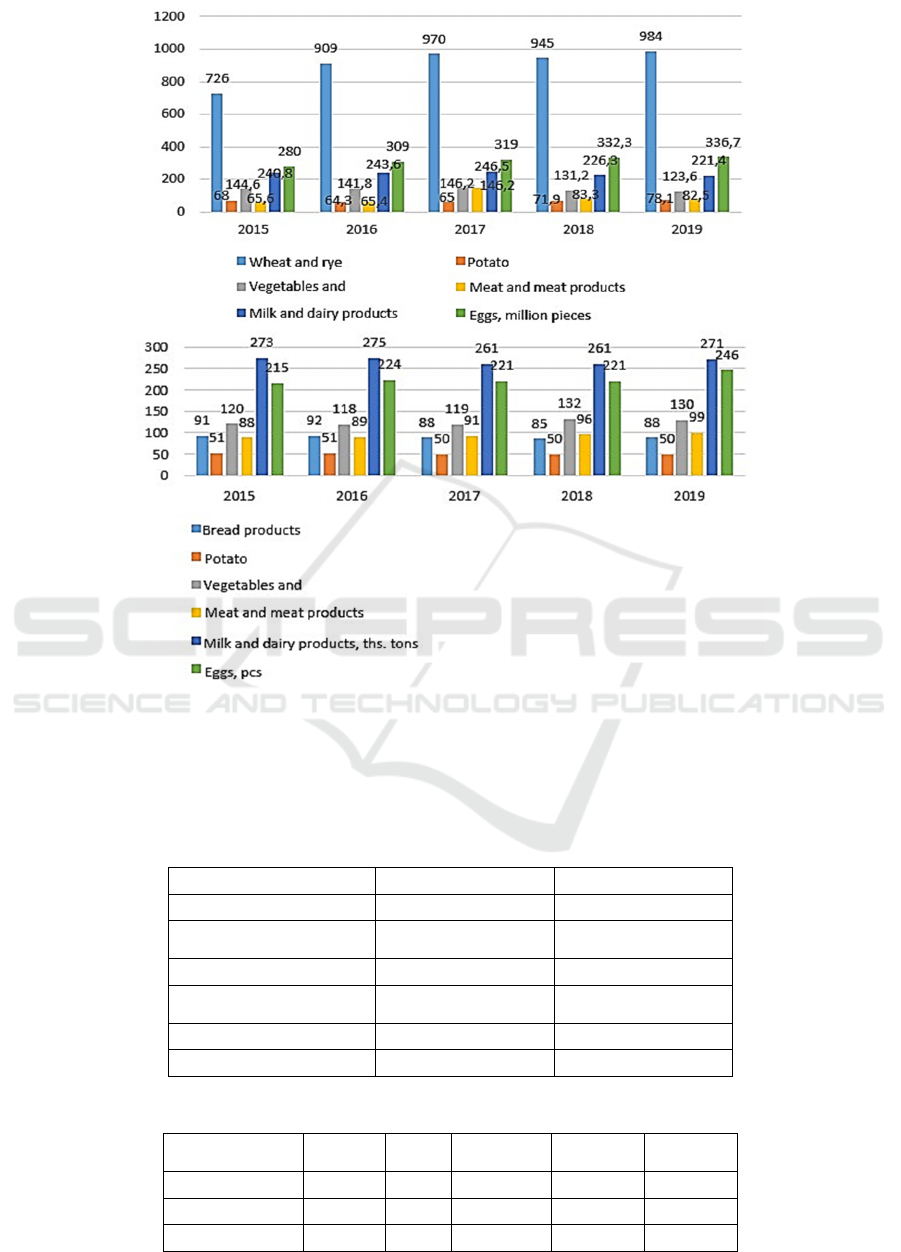
Figure 5: Average per capita consumption of basic food products, kg. (Krasnodarstat, 2019).
To assess the balance of the regional food market
of the Krasnodar krai, the recommended norms of
food consumption were used (Table 3).
The results of the calculation of the integrated
assessment of the potential of the agri-food market
are summarized in Table 4.
Table 3: Recommended norms of consumption of basic food products, on average per capita in Russia (GKS).
Indicators
Per year, kg
Per day, g
Meat and meat products
73
200
Milk and dairy products
translated into mil
k
325
890
Eggs, pcs.
260
0.7
Bread and bread products
translated into flou
r
96
263
Potato
90
247
Vegetables and melons
140
384
Table 4: Integrated assessment of production and consumption of basic food products for 2015-2019.
Integral
estimation
2015
2016 2017 2018 2019
Production
15.7
15.8 15.3 15.8 15.7
Consumption
12.5
12.9 12.0 12.3 12.1
Balance sheet
3.2
2.8 3.3 3.5 3.6
Development of the Agri-Food Market of the Krasnodar Territory in the Context of Food Security in the Region
321

During the study period, the production of the
main types of food exceeded consumption. Almost all
product groups are produced in the region in
sufficient quantities. Today, the Krasnodar krai meets
the needs of the population in basic food products at
the expense of its own capacities. Export is carried
out if the production exceeds the demand.
Indicators of meat products and milk and dairy
products are slowing down and lagging behind the
recommended standards. Accordingly, their
insufficient production should be compensated by the
import of these products.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The results of the study indicate that most of the
indicators are within their acceptable values, which
characterizes the state of regional food security as
fairly stable, within the normal range. The threat is a
decrease in the potential of the agro-industrial
complex, social tension, which is manifested in a
significant income gap, low real incomes, and high
food prices, which reduces the availability of food
and increases social discontent.
The priority direction and basic task from the
point of view of providing the population with food
should be the improvement of regional agri-food
policy, and its solution should be accompanied by
import substitution of food, state support for
agricultural enterprises, integration processes in
agriculture, revision and adjustment of the current
doctrine of ensuring food security
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The study was carried out with the financial support
of the RFBR and the Krasnodar krai in the framework
of the scientific project No. 19-410-230041.
REFERENCES
A. G. Zeldner, 2018. Economic mechanism of ensuring
food security in the conditions of investment
restrictions: experience and problems. p. 160.
Agriculture of the Krasnodar krai: Statistical collection.
Krasnodarstat, 2019. p. 234.
Alston, J., 2000. Agricultural R&D, Technological Change,
and Food Security. pp. 50-55.
Buks, J., 2016. Environmental externalities and food
security. In J. of Agribusiness and Rural Development.
2(40). pp. 257-264.
Campbell, H. Breaking new group in food regime theory:
Corporate environmentalism, ecological feedbacks and
the "Food from Somewhere" Regime? In Agriculture
and Human Values. 4. pp. 9-19.
Charles, H., 2014. Food security and sustainable
intensification. In Philosophical Transactions. The
royal society. pp. 2-11.
Cole, M. B., 2018. The science of food security. In Science
of Food. 2(14). pp. 45-49.
Federal State Statistics Service, http://www.gks.ru.
Food market of the Krasnodar krai: analytical note. p. 54.
Gaiduk, V. I., 2018. Food security of Russia in the context
of sanctions: challenges and priorities. In Economics,
labor, and management in agriculture. 3(36). pp. 19-
24.
Keyzer, M. A., 2007. The Millennium Development Goals,
how realistic are they? In De Economist. 154(3). pp.
443-466.
Kolomyts, O. N., Prokhorova, V. V., Ivanova, I. G., 2019.
Advantages and prospects of creating regional high-
tech agrarian clusters. In Indo-American J. of
Pharmaceutical Sciences. 6(3). pp. 6881-6885.
Kuchumov, A.V., 2018. Food security of the regions as the
basis of food security in Russia. p. 160.
Mikhalko, E. R., 2017. Food security: global community,
agriculture, economic expansion. p. 704.
Paramonov, P. F., Egorov, E. A., Artemova, E. I., et al.,
2016. Agri-food market of the region: theory and
practice. p. 429.
Pérez-Escamilla, R., 2017. Food security measurement and
governance: Assessment of the usefulness of diverse
food security indicators for policymakers. In Global
Food Security. pp. 95-104.
Pingali, P., 2005. Food security in complex emergencies:
enhancing food system resilience. In Disasters. 29. pp.
5-24.
Ushachev, I. G., Altukhov, A. I., Bespakhotny, G. V., et al.,
2015. Import substitution in the agroindustrial complex
of Russia: problems and prospects. p. 447.
Velinov, E., Ponomarev, M., 2016. Organizational
development of Russian SMEs: current trends. In J. of
Eastern European and Central Asian Research
(JEECAR). pp. 86-96.
Vlasov, V. A., 2018. The concept and indicators of food
security: federal and regional levels. In Agrarian and
Land Law. 5(161). pp. 34-41.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
322
