
Development of a Methodology for Assessing the Performance of
Financial Mechanisms to Support SMEs
Maxim Alekseevich Kostyukhin
1
, Tatiana Sergeevna Sobol
1
, Nadezhda Vladislavovna Sergeeva
2
and
Irina Vladimirovna Razinkina
3
1
Moscow Witte University, Moscow, Russian Federation
2
Moscow Polytechnic University, Moscow, Russian Federation
3
Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russian Federation
Keywords: Small and medium business, financial support mechanisms.
Abstract: The purpose of the study was to develop a methodology for assessing the performance of financial
mechanisms to support small and medium-sized businesses based on the analysis of statistical data. The
authors proposed the use of a composite index, which allows to assess the effect of the implemented
mechanisms in three aspects: the quality of the entrepreneurial environment development, budget efficiency
and the impact on the labor market. Each aspect was assessed based on a set of macroeconomic indicators
that form the corresponding evaluation index. The final assessment was carried out using a composite index,
which includes an integral index of the quality of development of small and medium-sized businesses, an
integral index of the efficiency of the use of state budget resources, an integral index of social efficiency of
small and medium-sized businesses. The results of the study allow us to draw conclusions about the
connection between individual measures of financial support and their impact on the quality of the business
environment
.
1 INTRODUCTION
Support for SMEs is a priority of the state economic
policy (Franquesa, Vera, Kakembo, Abduh, Salleh,
Mendy, Mittal, Raman, 2021).
As of December 01, 2019, the number of SMEs,
information about which is contained in the Unified
Register, is 5.9 million units (-118.2 thousand or -2%
to the same date in 2018): 2.5 million legal entities (-
183.5 thousand or -6.8% relative to 2018) (hereinafter
also - "LE") and 3.4 million individual entrepreneurs
(+65.3 thousand or + 2.0% by 2018) (hereinafter also
- "IE") (42.5% and 57.5% of the total number of
SMEs, respectively).
The majority of SMEs is engaged in services and
trade (80.0%). At the same time, over the period
2016-2019, there is an increase in the service sector
with a simultaneous reduction in the trade sector. So,
if, according to the Unified Register, as of December
01, 2016, 40.6% of the total number of SMEs were
engaged in trade, and 39.9% - in the service sector,
then as of December 01, 2019, the share of SMEs
engaged in trade amounted to 37.6%, in the service
sector - to 42.4%.
The largest number of SMEs is concentrated in
Moscow and St. Petersburg, as well as in the
Moscow, Sverdlovsk regions and Krasnodar
Territory, the smallest - in the Chukotka, Nenets and
Jewish Autonomous Districts.
When evaluating the distribution of funds from
the federal budget and the budget of Moscow in
dynamics (Rudenko, 2021), we can note an increase
in concentration on a limited number of more priority
measures of financial support for SMEs in Moscow,
the total amount of funding for which is growing
every year.
Nevertheless, there are a number of issues despite
the growth of financing for small and medium-sized
businesses.
In particular, there is no clear understanding of
how much and in what areas funds are spent to
support SMEs (Bykova, Rudenko, 2019). State
structures are not able to track and summarize data on
the number and volume of financial support measures
in the Russian Federation (Rudenko, 2021).
Kostyukhin, M., Sobol, T., Sergeeva, N. and Razinkina, I.
Development of a Methodology for Assessing the Performance of Financial Mechanisms to Support SMEs.
DOI: 10.5220/0010703000003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 347-353
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
347
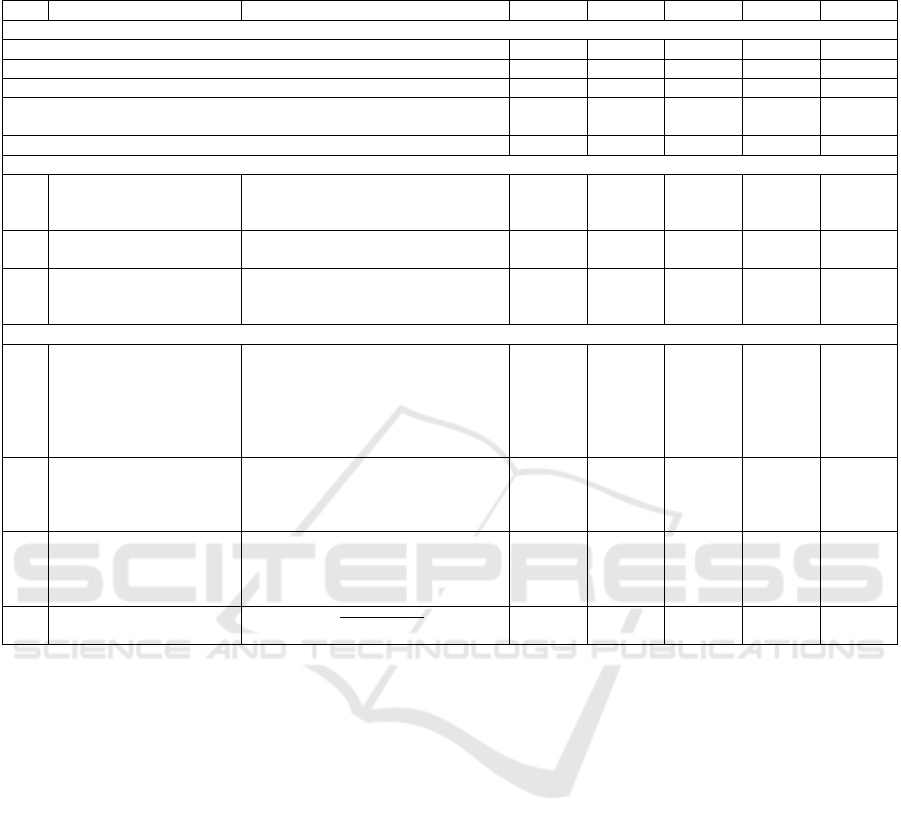
Table 1: Source data for determining the integral quality index of the development of SMEs in Moscow for the period 2016–
2019
No. Indicators Calculation method 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Source data
The number of enterprises and organizations, units 1009747 1010064 1039834 1045258 1094198
Number of SMEs, units 320160 324254 355350 385029 529221
SME turnover, RUB bln 4533.75 4460.28 4492.83 4618.38 2909.04
Average headcount of SME employees (excluding external part-time
workers), thousand people
226.7 229.6 229.1 226.6 292.8
Population, thousand people 12463 12468 12471 12470 12472
Calculation parameters
1
Number of SMEs per 100
thousand people of
population
Number of SMEs / population (in
thousand persons)
25.689 26.007 28.494 30.876 42.433
2
Share of SMEs in the total
number of enterprises
Number of SMEs / Number of
enterprises and organizations
0.317 0.321 0.342 0.368 0.484
3
The volume of SMEs
turnover per person
employed by SMEs
SME turnover / Average headcount of
people employed in SMEs
19.999 19.426 19.611 20.381 9.935
Indexes
i
11
Index of change in the
number of SMEs per 100
thousand people of the
population
The number of SMEs per 100 thousand
people of the population
t
/ The number
of SMEs per 100 thousand people of
the population
t-1
- 1.012 1.096 1.084 1.374
i
12
Index of change in the
share of SMEs in the total
number of enterprises
The share of SMEs in the total number
of enterprises
t
/ The share of SMEs in
the total number of enterprises
t-1
- 1.012 1.065 1.078 1.313
i
13
Index of change in the
volume of turnover per one
person employed in SME
The volume of turnover per one person
employed in SME
t
/ The volume of
turnover per one person employed in
SME
t
-1
- 0.984 1.007 1.028 0.630
I
QD
Integral index of quality of
development of SMEs
𝑖
∗𝑖
∗𝑖
- 1.003 1.055 1.063 1.044
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study consists in analyzing key macroeconomic
indicators of a small and medium-sized business
entity, reflecting the quality of the business
environment, government spending on financing
various forms of support for small and medium-sized
entrepreneurs, as well as changes in the labor market
among those employed in small and medium-sized
businesses.
An integral assessment based on indices was
carried out to assess the effectiveness of the
implemented financial mechanisms of small and
medium-sized entrepreneurs
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
One of the methods for assessing the performance of
SME support policy is an integral assessment based
on indices [2, 6]. Based on the available statistical
data, it is proposed to establish a composite index
based on three integral indices: an integral index of
the quality of SME development, an integral index of
the efficiency of using budget resources, and an
integral index of social efficiency of SMEs.
1. The initial data for calculating the Moscow
SME development quality index are shown in Table
1.
The results of calculating the integral quality
index of the development of SMEs in Moscow and its
components are presented in Figure 1.
The graphic interpretation of the analysis results
allows us to state the presence of positive changes in
the sphere of SMEs in Moscow from 2015 to 2019.
At the same time, however, despite the increase in the
indices of change in the number of SMEs per 100
thousand of the population and the change in the share
of SMEs in the total number of enterprises, the drop
in the index of change in the volume of turnover per
person employed by SMEs led to a decrease in the
integral index of the quality of SME development by
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
348

10% in 2019 compared to 2018. This indicates a
decline in the quality of SME development in
Moscow under the influence of macroeconomic
factors, which led to a significant reduction in the
turnover of SMEs in 2019 (– 37% compared to the
previous year), and the need to review the policy of
state support.
The source data for calculating the resource
efficiency index of the Moscow budget are presented
in Table 2
. The results of the calculation of the
integrated index of budget resource use efficiency in
Moscow and components thereof are shown in Figure
2.
Figure 1: Integral quality index of development of SMEs in Moscow for the period 2016–2019 and its components.
Figure 2: Integrated index of budget resource use efficiency in Moscow and components thereof for the period 2015–2019.
Table 3: Sources and volumes of SME development support programs in Moscow in 2016–2019, in thousand rubles
Funding sources
Funding volumes
2016 2017 2018 2019
Total budgetary allocations, including
1291680 4404040 1803200 1681760
regional budget funds
460000 926440 460000 443440
federal budget funds 831680 3477600 1343200 1238320
Development of a Methodology for Assessing the Performance of Financial Mechanisms to Support SMEs
349
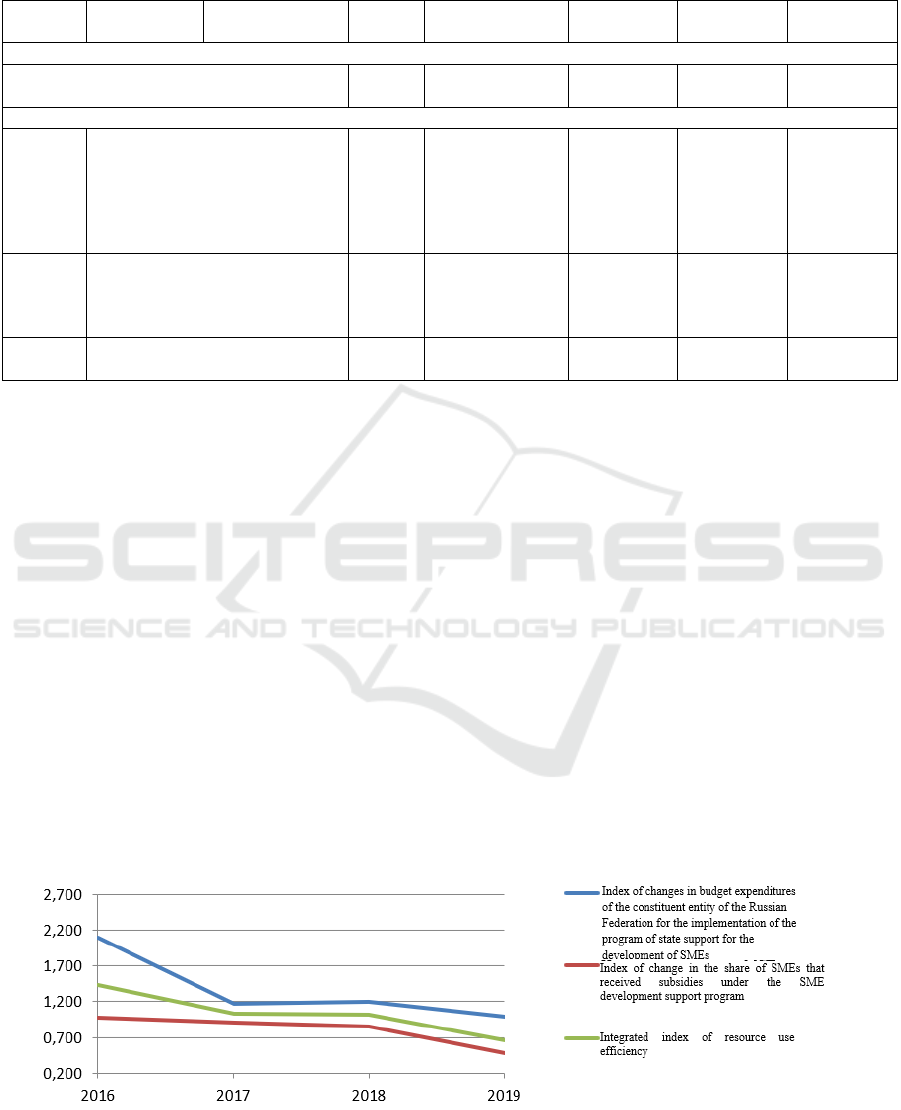
Table 4. Source data for calculation of the integrated index of budget resource use efficiency in Moscow for the period 2016-
2019 (with the author's adjustments for the amount of funding for the SME development support programs in Moscow in
2017)
No. Indicators Calculation
metho
d
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Source data
Amount of financing of the state program for
the develo
p
ment of SMEs, thousand rubles
617320 1291680 2898000 1803200 1681760
Indexes
i
21
Index of changes in budget
expenditures of the constituent
entity of the Russian Federation
for the implementation of the
program of state support for the
develo
p
ment of SMEs
2.0924 1.1660 1.1973 0.9327
i
22
Index of change in the share of
SMEs that received subsidies
under the SME development
su
pp
ort
p
ro
g
ra
m
0.9776 0.9034 0.8577 0.4745
I
RUE
Integrated index of resource use
efficienc
y
1.4302 1.0263 1.0134 0.6652
The analysis findings show that there is no general
trend in the effective use of budget funds to support
the development of SMEs. A significant increase in
the index of changes in budget expenditures occured
in 2017 and, as a result, increase of the integral index,
followed by an even sharper decline in 2018 (the drop
in the integral index in 2018 compared to 2017 was
66%) and a slight improvement in the index value in
2019. This is due to significant changes in the amount
of funding for SME development support programs
Table 3 presents the distribution of funding
volumes depending on funding sources.
An analysis of the volume of budget funding and
the direction of program expenditures suggests that an
increase in funding from the regional budget in 2017
(by 457,240 thousand rubles compared to the
previous year) and from the federal budget (by
2,645,920 rubles (more than 3 times)) is associated
with funding within the SME support program of the
Moscow Fund for Assistance to Lending to Small
Entrepreneurship (457,240 thousand rubles were
allocated for its development in 2017 from the
regional budget and 2,645,920 thousand rubles - from
the federal budget). Thus, most of the expenses for
the support and development of SMEs in Moscow in
2017 are related to the funding of the Fund's work.
Since the allocation of such a large amount of
financial resources is a one-time event, it causes a
little distortion in the results of constructing the
integral index. Accordingly, it would be useful to to
compare the previously obtained data with the results
that can be obtained from the analysis without the
amount of funds for one-time funding of the Fund
(namely, 579,600 thousand rubles from the regional
budget and 2,318,400 thousand rubles from the
federal budget, i.e. 2,898,000 thousand rubles in
2013). The results of the calculation of the integral
index of resource efficiency are presented in Table 4
and Figure 3.
Figure 3. Source data for calculation of the integrated index of budget resource use efficiency in Moscow and components
thereof for the period 2016-2019 (with the author's adjustments for the amount of funding for the SME development support
programs in Moscow in 2017)
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
350
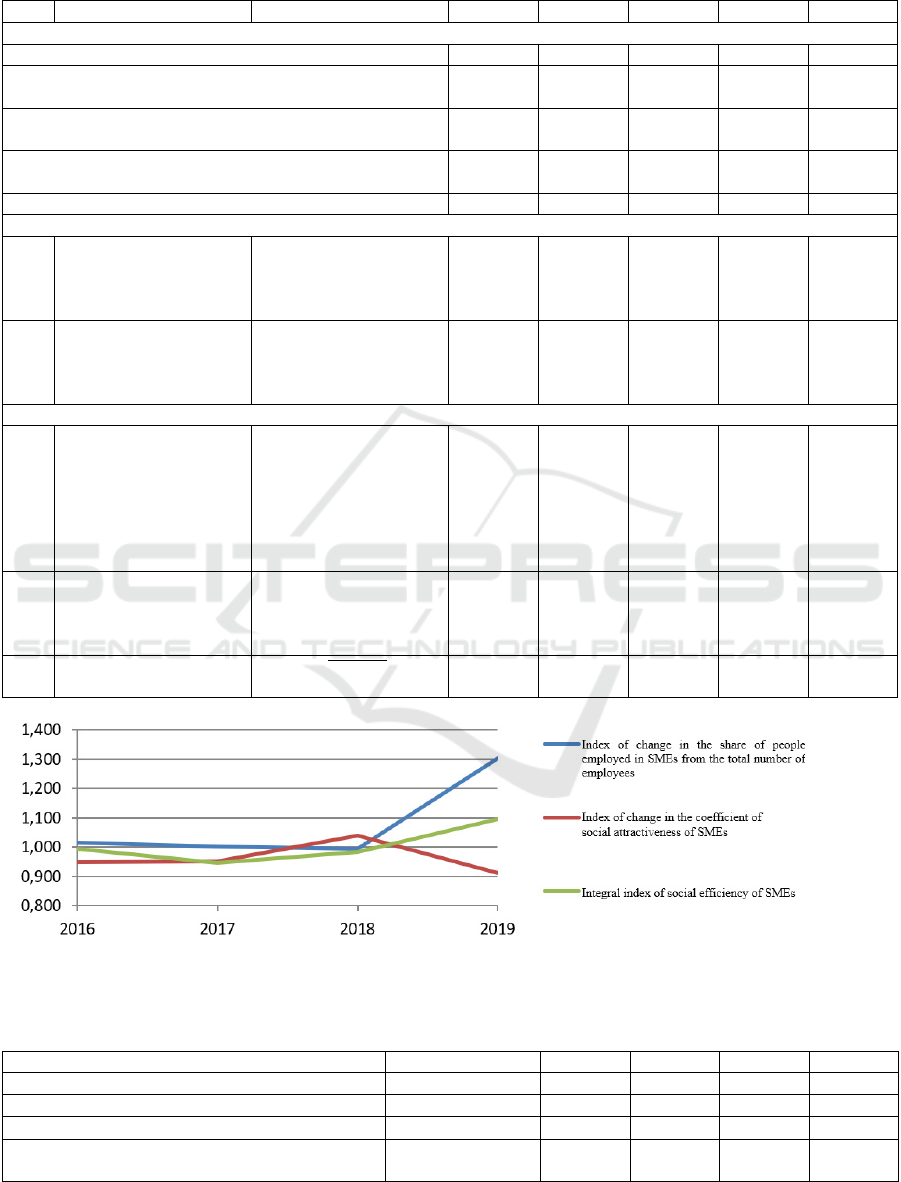
Table 5. Source data for determining the social efficiency index of the development of SMEs in Moscow for the period 2016–
2019.
No. Indicators Calculation metho
d
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Source data
Number of SMEs, units 320160 324254 355350 385029 529221
Average headcount of SME employees (excluding external
p
art-time workers), thousand people
2086 2112 2108 2085 2694
Average annual number of employed people, thousand
p
eo
p
le
15443 15391 15337 15281 15158
Average monthly wages of SME employees, thousand
rubles
36.6 39 42.3 47.4 46.2
Avera
g
e monthl
y
wa
g
es
p
er em
p
lo
y
ee, thousand rubles 60.06 67.5 76.95 83.04 88.92
Calculation
p
arameters
1 Share of people
employed in SMEs in
the total number of
em
p
lo
y
ees
The average number of
employees in SME /
Total average number of
em
p
lo
y
ees
0.1351 0.1372 0.1374 0.1364 0.1777
2 Social attractiveness of
SMEs
Average monthly salary
of SME employees /
Average monthly salary
in the econom
y
0.6095 0.5778 0.5497 0.5708 0.5195
Indexes
i
31
Index of change in the
share of people
employed in SMEs from
the total number of
employees
Share of people
employed in SMEs from
the total number of
employees
t
/ Share of
people employed in
SMEs from the total
number of em
p
lo
y
ees
t-1
1.0162 1.0013 0.9927 1.3027
I
32
Index of change in the
coefficient of social
attractiveness of SMEs
Social attractiveness of
SMEs
t
/ Social
attractiveness of SMEs
t-
1
0.9479 0.9514 1.0383 0.9102
I
SE
Integral index of social
efficiency of SMEs
𝑖
∗𝑖
0.9942 0.9649 0.9844 1.0960
Figure 4: Integral quality index of development of SMEs in Moscow and components thereof for the period 2016–2019
Table 6. Results of calculations of integral and composite indices characterizing the quality of development, social efficiency,
and resource efficiency within the SME state support policy in Moscow for the period 2016-2019.
Indicato
r
Desi
g
nation 2016 2017 2018 2019
Integral index of quality of development of SMEs
𝐼
КР
1.003 1.055 1.063 1.044
Integrated index of resource use efficienc
y
𝐼
ЭИР
1.4302 1.0263 1.0134 0.6652
Integral index of social efficiency of SMEs
𝐼
СЭ
0.9942 0.9649 0.9844 1.0960
Composite index of the effectiveness of the SME
state support polic
y
𝐼
сводн
1.1256 1.0147 1.0198 0.9130
Development of a Methodology for Assessing the Performance of Financial Mechanisms to Support SMEs
351

Thus, without considering the funding of the
Moscow Fund for Assistance to Lending to Small
Entrepreneurship, but taking into account only the
activities of the authorities related to financial,
property, and information support of SMEs, we can
obviously note the negative dynamics of the change
in the integral index. This fact underlines the
expediency of spending budget funds not only on
traditional types of state support for SMEs, but also
on infrastructure facilities for supporting SMEs, the
funding of which contributes to improving the values
of the integral index of budget efficiency.
The initial data for calculating the social
efficiency index of the Moscow SMEs are presented
in Table 5, and the results are shown in Figure 20.
In general, we can consider the dynamics of
changes in the integral index of social efficiency of
SMEs in Moscow for the period 2016–2019 as
positive, which is primarily due to the stable growth
in the number of SMEs and average wages (until
2018). Separately, we should consider the results of
the construction of the integral index in 2019: a
significant increase in the number of employees of
SMEs (by 29.2% compared to 2018) was a key factor
in improving the integral index.
However, we should note that the index of
changes in the coefficient of social attractiveness fell
significantly, which is due to the manifestation of
inconsistency in the change in wages in small
enterprises and in the economy as a whole: while the
average monthly salary in the region increased (by
7% compared to 2018), in SMEs – decreased (by 2.5
%). This indicates a high sensitivity of SMEs to
economic shocks. The manifestation of this kind of
phenomena in combination with a relatively small
level of the integral rating (for all years (except for
2019) below 1) is the basis for strengthening and/or
revising the policy of state support for SMEs in
Moscow. Based on the constructed integral indices,
the composite index (Table 6) can be calculated using
the formula:
𝐼
сводн
𝐼
КР
∙𝐼
ЭИР
∙𝐼
СЭ
(1)
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the data obtained, we can conclude that
there is insufficient consistency in the changes in the
integral indices, which indirectly indicates that there
is quite a small connection between the use of
resources within the SME state support policy and the
quality of SME development and its social
attractiveness in Moscow in the period 2016-2019.
Due to the fact that currently, state bodies refuse
to directly subsidize the costs of SMEs in favor of
creating an institutional environment for expanding
the access of SMEs to financial resources, the author
analyzed the activities of the regions of the Russian
Federation to create and improve the work of
microfinance organizations that provide loans to
SMEs, and developed a system of proposals for the
development of the Moscow microfinance
organization established in 2019.
The areas of improvement of state support for
SMEs in terms of microfinancing of SMEs are
grouped as follows:
1) expansion of access for SMEs to the
microfinance system (in particular, expansion of
SMEs activities subject to microfinance and lending
purposes; reduction of the minimum threshold value
of the SMEs operation period (in order to involve
start-up entrepreneurs); formation of infrastructure
for access to microfinance, etc.);
2) expanding opportunities for SMEs, which
receive funding (increasing the term, volume of loans,
differentiation of loan products, the possibility of debt
restructuring, etc.).
The author justified the expediency of increasing
the maximum volume of microcredit to 3 million
rubles and made a forecast, according to which the
incorporation of the proposed recommendations in
the activities of the microfinance organization of
Moscow would improve the results of the
implementation of the SME state support policy in the
region.
REFERENCES
Bykova, O. N., Rudenko, L. G., 2019. Support system for
socially-oriented small and medium-sized businesses.
In Economics and Entrepreneurship.
Franquesa, J., Vera, D., 2021. Small business debt
financing: the effect of lender structural complexity. In
J. of small business and enterprise development.
Kakembo, S. H., Abduh, M., PMHAPHM, S., 2021.
Adopting Islamic microfinance as a mechanism of
financing small and medium enterprises in Uganda.
Mendy, J., 2021. Performance management problem of four
small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs): towards a
performance resolution.
Mittal, V., Raman, T.V., 2021. Financing woes: estimating
the impact of MSME financing gap on financial
structure practices of firm owners. In South asian
journal of business studies.
Munyuki, T., CMP, J., 2021. The nexus between financial
literacy and entrepreneurial success among young
entrepreneurs from a low-income community in Cape
Town: a mixed-method analysis.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
352

Nicolas, T., 2021. Short-term financial constraints and
SMEs' investment decision: evidence from the working
capital channel.
Rudenko, L. G., 2021. Organizational and economic
mechanism for the implementation of state
management of infrastructural support for small
businesses. In Moscow Economic J.
Development of a Methodology for Assessing the Performance of Financial Mechanisms to Support SMEs
353
