
Regional Dynamics of Self-employment Development in the Republic
of Sakha (Yakutia)
Nikolay Ivanov
1
, Natalya Rodnina
1
, Marina Tsynzak
1
and Olesya Popova
1
1
Department of Industrial Economics and Management,
Arctic State Agrotechnological University, Sergelyakhskoye sh.,
Yakutsk, Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), Russian Federation
Keywords: Self-employment, growth rates, small and medium-sized businesses, social responsibility, professional
income tax, types of economic activity, unemployed, employed.
Abstract: The article presents the main indicators identifying the seed stage of self-employment development in the
Yakutia. The study used summary and reporting data on the growth rate of small and medium-sized businesses
in municipalities. Chronological observation of the changes occurring within the framework of the
development of this business indicates that the heterogeneity of indicators for different administrative-
territorial units contributes to the emergence of the self-employed category of the population. In addition, the
article discusses the concept of self-employment and its status, which in the system of legislative regulation
may have different approaches to interpretation based on event facts. However, the status of the self-employed
is very vulnerable and imperfect, since the voluntary form of applying for professional income for taxation
will become more difficult to control and monitor, since only theoretically described and characterized
approaches that can be used to determine.
1 INTRODUCTION
A new tax agent appears in the microeconomic
environment of Russia, whose activities are legalized
by a special tax regime “tax on professional income”
or “special tax regime” for the self-employed.
However, the experiment on the introduction of a new
tax, which began on January 1, 2019, practically
introduces additional opportunities for the
development of medium and small businesses, and
researchers of this trend study the prospects and
practice of the new business format.
There is no doubt that the development of small
and medium-sized businesses is accompanied by
problems and prospects, the solution of priority tasks
and strategies, as well as a comprehensive analysis
and assessment of business efficiency. Obviously, the
tax innovation should have a positive effect not only
in solving microeconomic problems with the
employment of the population, but also guarantee the
prospect of retirement services for that category of
citizens who receive their modest income by
performing one-time jobs and providing personal
services typical of self-employed citizens.
The practical interest of the new tax agent is
limited by the fact that he is prohibited from hiring
personnel. In addition, a self-employed person cannot
be engaged in a number of economic activities
involving the involvement of other subjects of labor
relations in labor activities.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Since July 1, 2020, the expansion of the coverage of
the tax on professional income has affected the
territory of the subject of the Russian Federation - the
Republic of Sakha (Yakutia). During the time of its
influence on the regional space of the republic, the tax
innovation interested many supporters, who preferred
to take advantage of the experimental novelty
The grouping of data in Table 1 shows that since
July 10, 2020, the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) has
seen a 7-fold increase in the number of self-employed
citizens. At the beginning of September 2020, 2,573
tax agents were registered with the tax authority, who
declared themselves as self-employed citizens. In
absolute terms, in terms of the growth rate, it took
place in the Gorny municipal district, reaching an
indicator of 2900%, and in the city of Yakutsk, the
growth of officially self-employed citizens in terms
of quality was 1221 tax agents.
364
Ivanov, N., Rodnina, N., Tsynzak, M. and Popova, O.
Regional Dynamics of Self-employment Development in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
DOI: 10.5220/0010705400003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 364-375
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
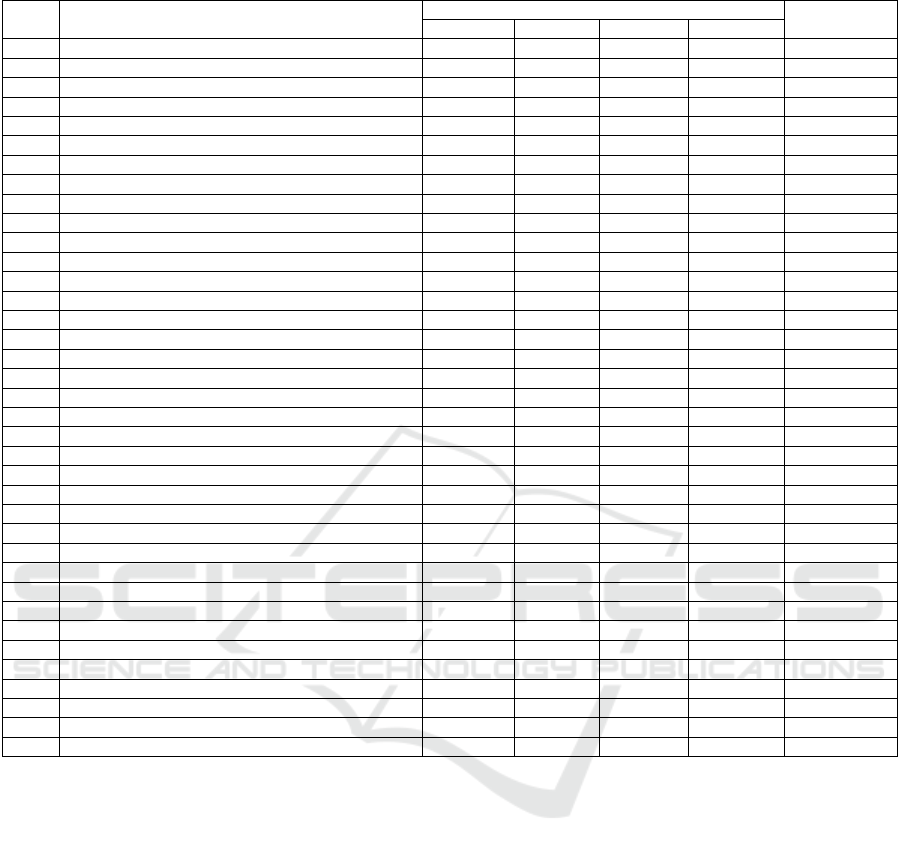
Table 1: Dynamics of the number of self-employed citizens in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) as of October 16, 2020
No.
The name of the municipal formation (municipal
district)
Critical dates 2020
Growth rate,
%
10.07 04.09 02.10 16.10
1 Abyysky 1 1 1 5 500
2 Aldan 15 51 68 84 560
3 Allaihoskiy 1 3 3 3 300
4 Amginsky 3 16 28 35 1167
5 Anabar national (Dolgan-Evenk) 1 2 7
6 Bulunsky 4 7 9 11 275
7 Verkhnevilyuisky 5 18 32 41 820
8 Verkhnekolymsky 5 7 7
9 Verkhoyans
k
1 13 20 20 2000
10 Vilyuisky 5 21 29 41 820
11 Mountainous 1 15 26 29 2900
12 City of Yakuts
k
195 759 1061 1221 626
13 Zhatay 4 14 17 22 550
14 Zhiganskiy national Even
k
3 12 14 15 500
15 Kobyaysky 15 22 25 1250
16 Lensky 17 53 79 92 541
17 Megino-Kangalassky 11 47 68 87 791
18 Mirninsky 21 126 180 210 791
19 Momsky 2 6 8 11 550
20 Namsky 8 27 33 41 513
21 Neryungri 26 108 146 179 654
22 Nizhnekolymsky 2 4 5 5 250
23 Nyurba 5 27 45 54 1080
24 Oymyakonsky 1 8 12 12 1200
25 Olekminsky 3 16 29 37 1233
26 Olenek Evenk national 1 2 4 4 400
27 Srednekolymsky 2 5 6 600
28 Suntarsky 5 30 42 51 1020
29 Tattinsky 5 21 31 33 660
30 Tomponsky 3 11 15 18 600
31 Us
t
-Aldansky 4 21 34 43 1075
32 Us
t
-Maisky 2 5 4 9 450
33 Us
t
-Yansky 2 6 8 8 400
34 Khangalassky 8 43 62 76 950
35 Churapchinsky 4 22 31 40 1000
36 Even-Bytantai National 1 2
Total 369 1538 2180 2573 697
Source: the data in the table are compiled from the reporting data of the administrations of municipalities (municipal districts)
of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) as of 16.10.2020
Analysis of the situation in the development of
medium and small business allows us to note some
aspects. In particular, the problems faced by small
and medium-sized businesses in the context of
globalization and the transformation of market and
economic relations force the owners of small and
medium-sized businesses to make not entirely
adequate decisions.
One problem of the Russian medium and small
business, which is highlighted by the young
researcher, reflects the essence of the fact that “The
main problem in the implementation of tax policy is
the lack of division by tax legislation of business
participants into real entrepreneurs (who deliberately
chose this path, developing , who successfully and
effectively operate, understand and accept all the
risks associated with activities "at their own peril and
risk"), and those for whom small business is self-
employment, an attempt to somehow survive in
difficult economic conditions on their own and feed
their families. This means that both must pay taxes on
an equal footing, although the financial situation and
opportunities for activities are different” (Tereshkina,
2014).
The second or classical problem is associated with
the analysis, which “showed that the activities of
small and medium-sized enterprises are accompanied
by a low level of liquidity and a high level of
entrepreneurial risk. This is primarily due to a
decrease in sales volumes due to poor study of
demand, lack of a sales network, advertising;
mismanagement of working capital; ignorance of
how much and how to produce and sell, so that the
Regional Dynamics of Self-employment Development in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
365

proceeds not only cover the costs, but also bring
profit” (Mashrapov, 2015).
The problem at the meta-economic level, which
reinforces a special problem in the interaction of the
traditional type of economic system in the modern
digital economy, is reflected in the fact that “A
significant layer of the mass agricultural economy is
not considered as a subject of an investment project -
small business, microbusiness - is deleted from state
support for investments. Herewith, the existing
methodology for assessing the efficiency of the state
program does not provide for a serious analysis of the
return on the spent state budget funds” (Chistyakova,
2018).
In the face of meta-economic stratification, a
problem is quite serious, which corresponds to the
experience of survival of small and medium-sized
businesses in conditions of intense competition and
the dominance of big business. Therefore, “It is very
tragic, for representatives of small and medium-sized
businesses in Yakutia, the problem with the “profit
hunger”, as it is commonly called in their circles,
should be pointed out. If in previous periods the
average monthly net income of an entrepreneur in this
sector of the economy was 40-45 th RUR, today,
businessmen call the amounts 2-3 times less,
complaining that the market has become too
oversaturated, and the main contingent of consumers
finds other sources of making a purchase ”(Lavrova,
2014).
It is highly likely that there is a lack of
entrepreneurial literacy among medium and small
businesses, which are characterized by typical errors
and mistakes in professional activity. Therefore, it is
advisable if “an agrarian business specializing in
raising cattle with a dairy focus is quite rationally
capable of making a scenario calculation pursuant to
the accepted methodological formats of financial and
economic activities, in which representatives of the
urban population may become co-owners of a part of
the herd. This method of attracting investment and
consumer interest of a city dweller quite rationally
contributes to solving issues of ensuring economic
security, a guaranteed flow of products by regular
buyers, getting rid of per capita costs for intermediary
services, creating a stable sales market and receiving
financial resources for the provision of additional
services” (Lavrova, 2013). This vision of the situation
leads to the fact that self-employed citizens in rural
areas, who are able to feed and maintain cattle, may
quite reasonably provide services of this kind for
citizens who do not have such abilities and
opportunities, that is, mainly for city dwellers.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Self-employment of Citizens and
Professional Income Tax
Numerous studies of market instability and social
injustice respond to a high degree of dissatisfaction
with the economic reality of the population, who are
forced to solve their problems in non-standard ways.
For the most part, it is the desire to acquire and
consume new, seductive and requiring a large amount
of money spending, the most practical and smart
citizens receive incomes that need to be declared and
make payments to the budget at the personal income
tax rate.
However, there is an opinion that “There is a large
group of self-employed citizens in Russia, defined by
us, as we suggest,“ informal entrepreneurs ”, which
does not fall under any of the categories of small
business provided for by the current legislation. There
are many citizens in the country who, having their
main occupation, find the opportunity to fulfill some
orders that correspond to their interests, hobbies, the
need for additional income, for instance, they may
teach to draw, conduct tutoring, and therapeutic
gymnastics. Such hobbies of a citizen may be
associated with a commercial interest” (Chernysheva,
2010). Opinions of this nature are quite consistent
with the following definition: “Self-employment is
understood as an independent organization and
conduct of entrepreneurial activity” (Pavlovskaya,
2015).
Accordingly, the fiscal innovation, introduced
from July 1, 2020, updates the tax status “Self-
employed citizen” and interprets it in the academic
environment as similar to those assigned to a specific
category of person, which “conducts a freely
regulated type of business. It is worth considering that
this sector in the segment of working citizens is
difficult to establish, since it includes both individuals
and individual entrepreneurs. The alienation of the
self-employed population is primarily associated with
the development of a small form of business that does
not require a staff of employees, and, consequently, a
large number of costs, that is, it implies a simplified
structure of business relations” (Ageeva, 2019).
Although “the position of state authorities,
management and control is such that self-employed
citizens, for the purposes of accounting, tax and other
obligatory contributions to the budget of the Russian
Federation, include individuals: 1) personally
providing services to other individuals for personal
and household needs; 2) those engaged in the
production and sale of goods on the basis of personal
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
366

labor; 3) not registered as individual entrepreneurs; 4)
receiving income on their own; 5) not attracting hired
workers and employees; 6) receiving a patent for the
right to conduct a particular labor activity; 7)
submitting a notice of tax registration” (Berdnikova,
2019).
The likelihood of self-employed status is fixed in
the academic environment, “But at the moment in the
domestic legislation there is no definition of the legal
status of self-employed individuals, as well as the
procedure for registration as such” (Krivin, 2020).
However, there is a gap that is not legally supported,
which is reflected in a complex and controversial
aspect as fixing the minimum and maximum income
limit calculated by self-employed for a certain period
of time.
De jure, the self-employed is limited by a number
of legal norms, based on which the authors
confidently assume that the size of the maximum
possible annual income of a self-employed cannot
exceed 8 RUR mln. Since the law on the development
of medium and small businesses establishes the
criterion for a micro-enterprise that may employ up to
15 employees, when, pursuant to the decree of the
Government of the Russian Federation of 2016, the
maximum income limit for a micro-enterprise is
regulated in the amount of 120 RUR mln. The ratio of
these parameters allows us to justify the maximum
income limit for the self-employed. In this context,
mention should be made of the entry into force from
January 1, 2021 of the amendment to Art. 224 of the
Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax rate is
15%, which is levied, from some types of income
exceeding 5 RUR mln per calendar year for personal
income tax.
Based on economic and legal information
obtained by a logical method of calculation, the
maximum income limit for self-employed may vary
within 5-8 RUR mln. per calendar year, provided that
the self-employed is over 5 RUR mln of annual
income will be forced to perform tax deductions at a
rate of 15%. Although the law on the tax on
professional income defines the maximum amount of
income considered when determining the tax base for
the tax under study, which does not exceed 2.4 RUR
mln in the current calendar year.
Thus, a tax innovation means a triad constraint
that identifies the self-employed status for taxation
along the following trajectories:
- compliance with the tax on professional
activities within 2.4 units in RUR mln;
- in the same dimension within 2.4 and 5 units in
RUR mln at a personal income tax rate of 13% in the
general tax regime;
- also within the limits of 5 and 8 units in RUR
mln in the general taxation regime at the personal
income tax rate of 15%;
- and over 8 RUR mln, the self-employed taxpayer
status must be converted into microenterprise status.
The following tendency arises, requiring
additional clarification of the legal status of the self-
employed. In addition to the restrictions on self-
employed citizens included in the law and pursuant to
paragraph 1 of Art. 3 dated 19.04.1991 # 1032-1 RF
Law “On Employment in the Russian Federation” an
unemployed person is a citizen who does not have a
job or earnings, therefore it is categorically
impossible to recognize him as self-employed. If an
unemployed person gets a job, he loses his desired
status, which makes it possible to orient the social
responsibility of the state on the problems of
unemployment, providing for the opportunity for the
unemployed to receive assistance in social adaptation
as a self-employed person.
Table 2: List of organizations that exchange information with the Federal Tax Service of Russia
Item
No.
Legal name of the organization
Trade name of the
organization
INN Partner site
1 Alfa-Bank JSC Alfa-Bank 7728168971 https://samozanyat. roketbank.ru
2 PJSC "Sberbank of Russia" Sberban
k
7707083893 https: /
/
prostobank.onlain
3 PJSC "AK Bars" BAN
K
AK Bars Ban
k
1653001805 https://www.akbars.ru
4 Bank "Cube" (JSC) Prosto Ban
k
7414006722 https://samozanyat. roketbank.ru
5 Investment Bank "Vesta" LLC Vesta Bank 6027006032 https: /
/
prostobank.onlain
6 JSC "Kiwi Bank" KIBI Bank, Rocketban
k
3123011520 https://samozanyat. roketbank.ru
Source: [2, p.136]
Accordingly, supporting the opinion of other
researchers who have formulated an exhaustive
answer to the natural question "How does a self-
employed person work?" In particular, “The working
conditions are simple and straightforward. A person
downloads the My Tax application and registers in it
as a payer of professional income tax. To do this, one
does not need to draw up any paperwork and go to the
tax office, everything is done through the My Tax
mobile application, or in the taxpayer’s personal
account on the official website of the Federal Tax
Service of Russia, or in a special bank application.
Regional Dynamics of Self-employment Development in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
367

Sberbank and other banks have this” (Samitov, 2020).
This opinion is supported by the information given in
Table 2
The informative value of Table 2 confirms the
interest of some banking structures, which have
included in their economic activities customer service
under the status of self-employed. Moreover, the
attractiveness of working with such clients is due to
the fact that “A new tax regime was introduced for the
self-employed with a rate of 4% when working with
individuals and 6% with legal entities. The
registration process is simple and does not require
visiting tax authorities, everything may be done
through a mobile application, checks are generated
without cash registers” (Bakirova, 2020). Perhaps
they saw the prospects for further development of
events, which reveal the horizons of charging
commissions for servicing banking and monetary
transactions that are made by the self-employed.
There are some peculiarities related to the fact that
“If the income is not constant, then the application of
the NPD does not create an additional tax burden: in
the absence of income during the tax period,
mandatory, minimum or fixed payments do not arise.
Herewith, the self-employed may receive free
medical care, since they are members of the
compulsory health insurance system” (Konkin,
2020). It is also likely that there are certain
shortcomings of the private order, which prescribe
mandatory rules, not to fulfill orders from the
previous employer and provide him with services
within 2 years after registration as self-employed,
prudently adopted by the legislator in order to prevent
the mass transfer of workers to the status of self-
employed. Otherwise, the violation of this imperative
will be recognized as an employment relationship.
In the publication aspect of scientific works, one
may come across such conclusions, reflecting the
following conclusions: “The reasons for the
introduction of this tax are easy to determine if looked
at the average unemployment rate in the country,
which now stands at 5.4%. A clear discrepancy
between the number of those laid off and this
percentage of unemployed may be seen. This may
only be explained by the fact that citizens start a
business in the shadow economy, which is not
reflected in official statistics. Therefore, the state
needs to legalize self-employed citizens"(Kurnosova,
2020). It is on these explanations that the authors’
approach is confirmed, which concludes the tax
innovation in the triad limitation of the self-
employed.
Of course, the self-employed status will be subject
to certain rankings. For example, “In the rating of the
reasons for the attractiveness of self-employed status
for Russians, the first place is taken by the
opportunity to devote more time to the family, the
second place is given by the respondents to the
emergence of greater interest in their work, and the
third is the financial benefits from the new
employment format. The fourth and fifth places are
shared by the opportunity to choose their own
customers and draw up their own work schedule on
their own “ (Safonov, 2020). Thus, the likelihood of
the group dynamics of an increase in the number of
self-employed is alarming, the consequences of
which may affect the personnel shortage, provoked
by an artificial means. Therefore, it is strategically
required to perform on-line monitoring in order to
timely prevent problems with personnel in the
business environment.
3.2 Self-employment in the Analysis of
the Current State and Development
of Medium and Small Businesses
The analysis of the current state and development of
small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) is based
on statistical indicators based on the results of
economic activity for 2017 and 2019. taking into
account the indicators of self-employment. The
characteristic by type of economic activity within the
distribution of individual entrepreneurs reflects the
growth of SMEs as of January 1 of the current year.
It is required to highlight some sectors of the regional
economy, in particular, information technology and
mining, hotels and catering, which statistically
confirm real growth. However, in the economic
structure of individual entrepreneurship such as
activities in the field of health and social services;
agriculture, forestry, hunting, fishing and fish
farming; financial and insurance activities, there is a
decrease in the number of SMEs (tab. 3)
The informativeness of the tabular data may be
interpreted in a comparative assessment of two
critical indicators pursuant to the criterion of the
maximum - "activity in the field of information and
communication" and the minimum - "activity in the
field of health and social services", the gap between
which is insignificant in quantitative terms, but
significant in qualitative terms. There is also a
noticeable quantitative statics, which is not uniform
in its influence on the qualitative dynamics.
The Regional Center for Employment of the
Population states data on the number of unemployed
citizens, in particular for November 2020, in
quantitative terms, equal to 32,986 unemployed,
which in qualitative terms was fixed at 133% as of
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
368
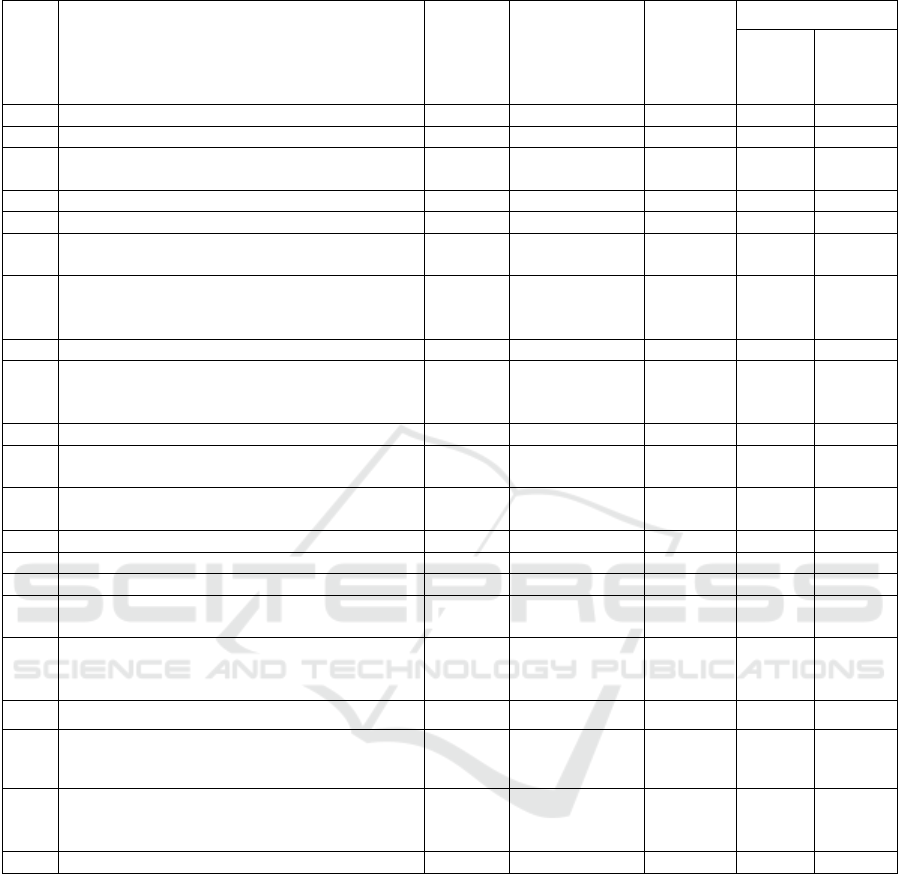
Table 3: Statistical data on the distribution of individual entrepreneurs by type of economic activity
No.
Type of activity
as of
January
1
2018
as of January
1
2019
as of
January
1
2020
in % to
the
bottom
line
1
January
2019
Total
37669 36408 35653
100.0
97.9
1
of which by type of economic activity:
2
agriculture, forestry, hunting, fishing and
fish farming
4487
4003
3642
10.2
91.0
3
mineral extraction
41 33 35
0.10
106.1
4
p
rocessing
2855 2769 2669
7.5
96.4
5
provision of electricity, gas and steam;
air conditioning
68
60
60
0.2
100.0
6
water supply; water disposal, organization of
waste collection and disposal, liquidation of
p
ollution
126
121
125
0.4
103.3
7
construction
3743 3685 3770
10.6
102.3
8
wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor
vehicles
vehicles and motorc
y
cles
10 974
10 659
10 299
28.9
96.6
9
trans
p
ortation and stora
g
e
6228 6046 5902
16.6
97.6
10
activities of hotels and enterprises of public
caterin
g
1124
1139
1199
3.4
105.3
11
activities in the field of information and
communication
704
663
710
2.0
107.1
12
financial and insurance activities
178 168 157
0.4
93.5
13
real estate activities
713 768 794
2.2
103.4
14
p
rofessional, scientific and technical activities
2411 2348 2350
6.6
100.1
15
administrative activities and related
additional services
838
798
788
2.2
98.7
16
government management and support of
military
securit
y
; social securit
y
5
3
3
0.008
100.0
17
district
348
376
388
1.1
103.2
18
activities in the field of health and social
services
342
315
272
0.8
86.3
19
activities in the field of culture, sports,
organization of
leisure and entertainment
425
427
439
1.2
102.8
20
p
rovision of other types of services
2036 2005 2026
5.7
101.0
Source: the data in the table are compiled from the reporting data of the administrations of municipalities (municipal districts)
of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) as of 16.10.2020.
July 2020. The statistical picture is interesting in that
the trend is upward, which is confirmed by a 4-fold
increase in unemployed citizens expiring since the
beginning of 2020 (Table 4).
The dynamics of the indicators presented in Table
4 reflects a favorable climate, since the number of
officially registered citizens decreased by 20% in
July-October 2020. The number of people employed
in the economy of the republic in July-September
2020 increases by 2%. However, there is a
discrepancy between the indicators of the number of
unemployed citizens and the number recognized as
unemployed, recorded in the register of the
employment service of citizens, due to the fact that
53% of unemployed citizens have the status of
pensioners, disabled persons of group 3 and other
social strata of the population.
The growth in the number of SMEs for the period
from January 1, 2019 to September 1, 2020 is
observed in 7 districts (uluses) of the republic, which
belong to the Arctic group of districts (uluses) -
Anabarsky, Verkhnekolymsky, Zhigansky,
Nizhnekolymsky, Oleneksky, Ust-Yansky, Eveno -
Bytantaysky (Table 5).
Regional Dynamics of Self-employment Development in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
369
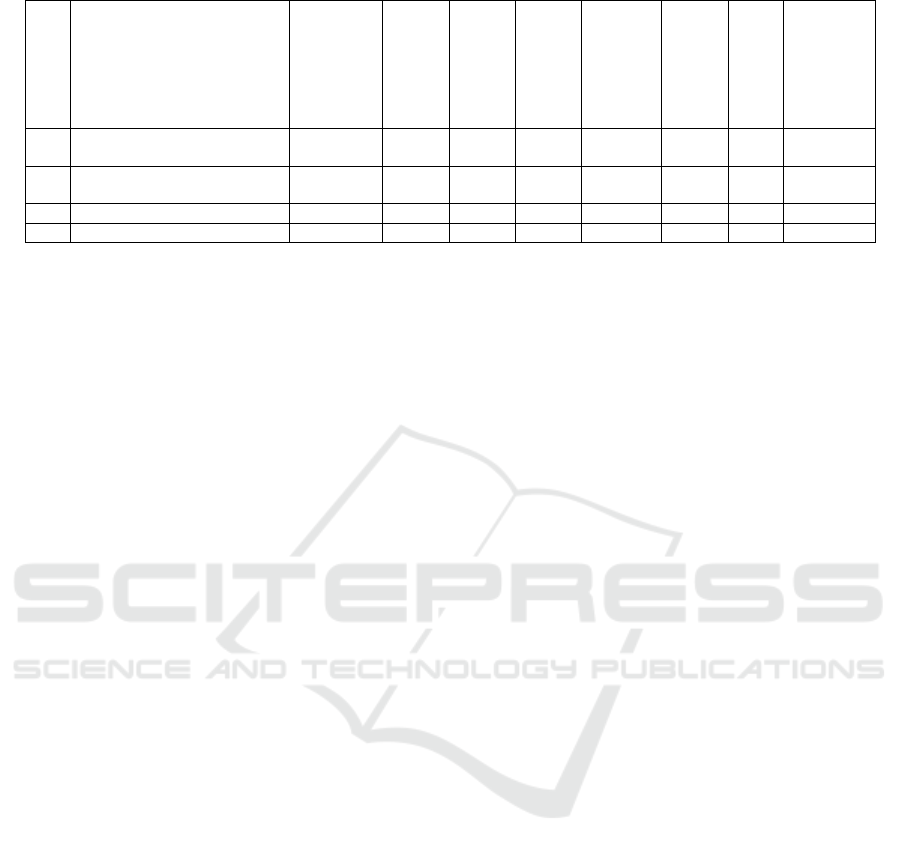
Table 4: Dynamics of the unemployed, employed and self-employed in July-October 2020
No. Indicator UOM
December
2019
June
2020
July
2020
August 2020
September 2020
October 2020
Growth
rate, %
1 Number of unemployed
citizens
th. persons 8.3 24.6 29.0 32.6 32.3 33.3 133
2 Number of citizens recognized
as unemploye
d
th. persons 1.5 5.3 5.9 5.6 4.2 4.3 80
3 Employed th. persons 465.8 456.7 451 456.1 464.1 0 102.0
4 Number of self-employe
d
th. persons n/a n/a 0.4 0.9 1.5 2.2 591
Source: the data in the table were compiled by the authors from the reporting data of the administrations of municipalities
(municipal districts) of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) as of 16.10.2020.
The group dynamics of the number of SMEs in
Yakutia, grouped in Table 5, reflects the indisputable
leadership of the Olekminsky, Anabarsky and Eveno-
Bytantaysky districts (uluses). The growth in the
number of SMEs in the Olekminsky and Anabar
districts (ulus) is explained by the growing demand
for goods and services related to the maintenance and
provision of extractive industries, as well as
population growth due to the emergence of new jobs
and a relative increase in the population’s income,
which form effective demand.
According to the summary data of the tax
authority, the number of liquidated SMEs was
certified in relation to the number of registered
entities in March - August 2020 with an excess of 1.4
times in favor of the first, and the ratio of liquidated
SMEs to those registered for the noted period
pursuant to the LE criterion was 1 , 9, IE - 1.3 (Table
6).
The explanation for the negative ratio reflected in
Table 6, in which a sharp increase in the number of
liquidated SMEs is noticeable, is the situation
associated with the implementation of restrictive
measures due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Further,
before the 2nd wave of the COVID-19 pandemic,
there is a positive trend, which is characterized by a
narrowing gap between the indicators of liquidated
and registered SMEs. More detailed information on
the dynamics of liquidated and registered SMEs is
presented in Table 7.
A clear demonstration of the negative dynamics
presented in Table 7 in the summary indicates that it
is difficult for SMEs to compete in the market space
of Yakutia, including the conditions for the impact of
the pandemic on business results. Considering that
the pandemic was announced only at the end of
March, the totality of relations, liquidated and
registered SMEs is catastrophic as of March 2020,
compared to the following months through August
2020, that is, the reason for this difference cannot be
directly attributed to the pandemic. Of course, the rate
of reduction of the difference for the period of the
declared pandemic, in the final value with an
impressively negative indicator and in comparison
with the difference in March 2020, which reaches
⁓35%.
A qualitative picture of the growth rate of SMEs
by comparing equal periodizations makes it possible
to assess the real changes taking place in the region’s
economy.
Table 8 provides exhaustive information about the
natural course of events in the region’s economy,
associated with the fact that the existing economic
model is entering the stage of decline. This is due to
the fact that the growth rate for 9 months 2019 is 79%,
and the difference between the September and
December intervals is also decreasing, although in
comparison with 9 months. 2020, the growth rate
accelerates sharply.
However, in quantitative terms of the comparative
analysis, the average number of SMEs in 2019
significantly exceeds the indicators of 2020, which
means that the problem of reducing the number of
SMEs in 2019 is natural. And the growth rate in terms
of indicators for 2020 may be conditionally attributed
to the effect of the introduction of a tax on
professional activities.
The dynamics of the number and average number
of SMEs in the regions of the Republic of Sakha
(Yakutia) characterizes the quantitative and
qualitative indicators of the development of SMEs in
the regional economy. However, there is a trend that
should be analyzed as newly created SMEs.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
370
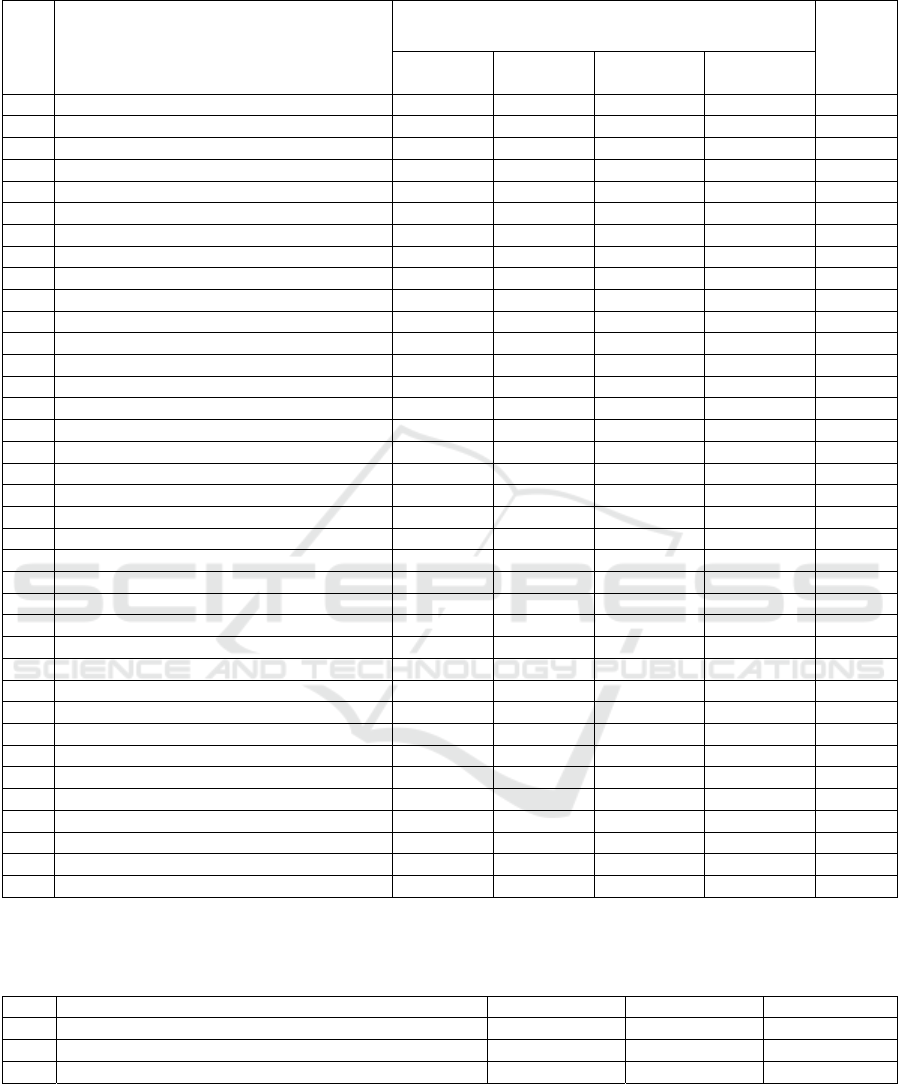
Table 5: Dynamics of the number of SMEs by districts of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
No.
The name of the municipal formation
(municipal district)
Number of SMEs, units
Growth
rate, %
as of
1.01.2019
as of
1.09.2019
as of
01.01.2020
as of
01.09.2020
1 City of Yakuts
k
18905 18687 19073 17834 94
2 Aldansk
y
district 1540 1519 1535 1462 95
3 Zhata
y
342 315 315 301 88
4 Vil
y
u
y
sk ulus 674 613 624 612 91
5 Neryungrinsky district 3025 2925 2973 2802 94
6 Abyysky district 113 98 99 100 88
7 Allaikhovsky district 51 51 52 46 90
8 Bulunsk
y
district 165 151 162 154 93
9 Anabarsk
y
district 71 70 72 82 115
10 Amginsky district 559 523 524 492 88
11 Verkhnevilyuysky district 500 472 483 456 91
12 Verkhnekolymsky district 122 123 125 134 110
13 Verkho
y
ansk
y
district 425 403 415 413 97
14 Mountainous area 406 386 386 373 92
15 Zhi
g
ansk
y
district 129 121 123 136 105
16 Kobyaysky district 360 309 320 272 76
17 Lensky district 1242 1188 1200 1170 94
18 Megino-Kangalassky district 1050 1038 1028 1026 98
19 Mirninsk
y
district 2233 2164 2195 2082 93
20 Momsk
y
district 129 122 129 125 97
21 Namsky district 749 709 717 696 93
22 Nizhnekolymsky district 98 99 103 96 98
23 Nyurbinsky district 635 614 614 567 89
24 O
y
m
y
akonsk
y
district 403 380 386 355 88
25 Olekminsk
y
district 575 541 557 534 93
26 Oleneksk
y
district 98 92 92 119 121
27 Srednekolymsky district 188 177 180 168 89
28 Suntarsky district 653 639 633 591 91
29 Tattinsky district 675 666 661 613 91
30 Tom
p
onsk
y
district 407 396 393 365 90
31 Ust-Aldansk
y
district 601 616 611 544 91
32 Ust-Ma
y
sk
y
district 233 218 216 226 97
33 Ust-Yansky district 272 279 291 276 101
34 Hangalassky district 977 936 934 877 90
35 Chura
p
chinsk
y
district 751 720 717 726 97
36 Eveno-B
y
tanta
y
sk
y
77 74 79 86 112
Total 39435 38432 39017 36911 93.6
Source: the data in the table were compiled by the authors from the reporting data of the administrations of municipalities
(municipal districts) of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) as of 16.10.2020.
Table 6: Ratio of liquidated and registered SMEs, units
No. Indicato
r
Total LE IE
1 Number of liquidated SMEs 3778 1150 2628
2 Number of re
g
istered SMEs 2699 599 2100
3 The ratio of li
q
uidated to re
g
istered SMEs 1.4 1.9 1.3
Source: the data in the table were compiled by the authors from the reporting data of the administrations of municipalities
(municipal districts) of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) as of 16.10.2020.
Regional Dynamics of Self-employment Development in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
371
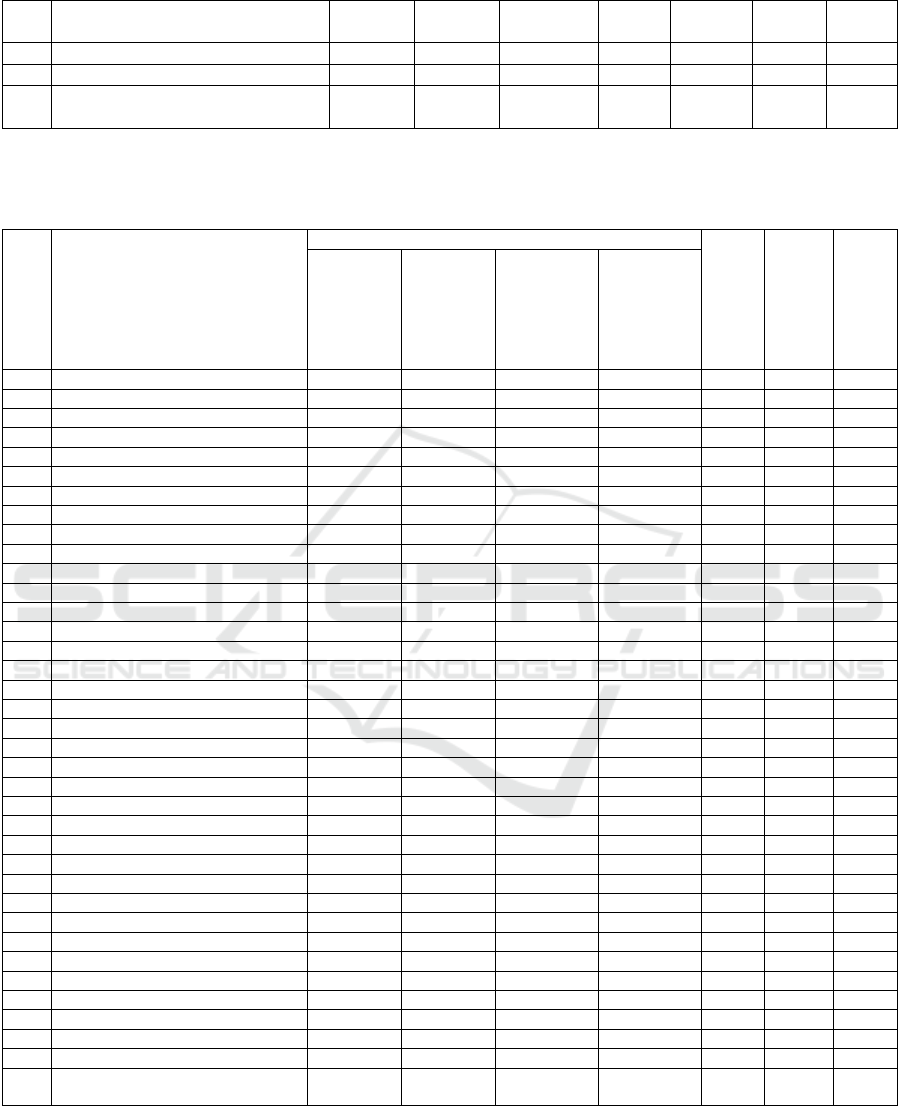
Table 7: Dynamics of liquidated and registered SMEs in March-August 2020, units
No. All SMEs
March
2020
April
2020
May 2020
June
2020
July
2020
August
2020
Total
1 Liquidate
d
1072 460 364 576 763 543 3778
2 Registered 695 190 259 433 599 523 2699
3 Difference between registered and
liquidated SMEs
-377 -270 -105 -143 -164 -20 -1079
Source: the data in the table were compiled by the authors from the reporting data of the administrations of municipalities
(municipal districts) of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) as of 16.10.2020.
Table 8: Dynamics of the average number of SMEs by regions of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
No.
The name of the municipal
formation (municipal district)
Average number of SMEs, people
Growth rate in 9
months 2019, %
Growth rate in
9 months of 2020, %
Growth rate for
2020/2019, %
as of
1.01.2019
as of
1.09.2019
as of
01.01.2020
as of
01.09.2020
1 City of Yakuts
k
32768 31305 22926 23171 70 101 71
2 Aldansky distric
t
3557 2885 2766 2942 78 106 83
3 Zhatay 209 170 170 181 81 106 87
4 Vilyuysk ulus 1075 998 998 942 93 94 88
5 Neryungrinsky district 6338 5753 5639 5529 89 98 87
6 Abyysky distric
t
6554554883 90 78
7 Allaikhovsky distric
t
61 92 92 85 151 92 139
8 Bulunsky distric
t
162 242 248 543 153 219 335
9 Anabarsky distric
t
42 41 42 65 100 155 155
10 Amginsky distric
t
711 646 646 619 91 96 87
11 Verkhnevilyuysky distric
t
435 288 293 259 67 88 60
12 Verkhnekolymsky distric
t
165 174 176 177 107 101 107
13 Verkhoyansky district 299 272 273 266 91 97 89
14 Mountainous area 247 293 300 315 121 105 128
15 Zhigansky distric
t
186 152 152 160 82 105 86
16 Kobyaysky distric
t
319 227 246 235 77 96 74
17 Lensky distric
t
1938 1856 1874 1821 96 97 95
18 Megino-Kangalassky distric
t
1011 1024 1019 1051 101 103 104
19 Mirninsky distric
t
3154 3014 2915 3004 92 103 95
20 Momsky district 128 140 140 146 109 104 114
21 Namsky district 624 537 533 484 84 92 77
22 Nizhnekolymsky district 261 228 229 178 88 78 68
23 Nyurbinsky distric
t
909 888 865 752 95 87 83
24 Oymyakonsky district 841 748 755 930 90 123 111
25 Olekminsky distric
t
932 820 817 768 88 94 82
26 Olenyoksky distric
t
78 91 91 111 118 121 144
27 Srednekolymsky district 103 86 86 101 83 117 98
28 Suntarsky distric
t
1095 1005 1000 886 91 89 81
29 Tattinsky distric
t
856 788 550 654 64 119 76
30 Tomponsky distric
t
538 547 540 548 100 101 102
31 Us
t
-Aldansky distric
t
357 321 319 299 89 94 84
32 Us
t
-Maysky distric
t
506 488 666 500 132 75 99
33 Us
t
-Yansky distric
t
431 395 409 318 95 78 74
34 Hangalassky distric
t
1121 853 852 884 78 103 80
35 Churapchinsky district 871 787 789 737 91 93 85
36 Eveno-Bytantaysky 110 108 108 81 98 75 74
Total
62493 58317 49578 49793 79
100.
43
80
Source: the data in the table were compiled by the authors from the reporting data of the administrations of municipalities
(municipal districts) of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) as of 16.10.2020.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
372
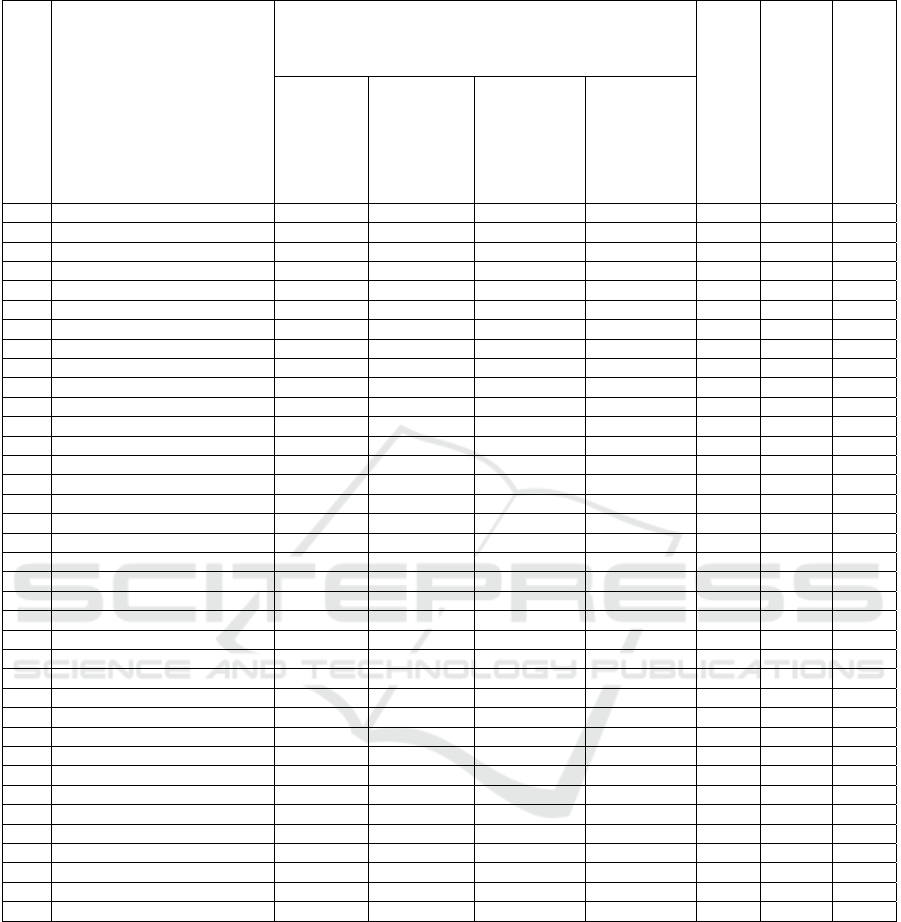
Table 9: Dynamics of newly created SMEs by districts of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
No.
The name of the municipal
formation (municipal district)
Newly created SMEs, pcs.
Growth rate in 9 months 2019,
%
Growth rate in
9 months of 2020, %
Growth rate for 2020/2019, %
as of
1.01.2019
as of
1.09.2019
as of
01.01.2020
as of
01.09.2020
1 City of Yakuts
k
3404 2837 3770 1436 111 38 42
2 Aldansky distric
t
267 213 295 116 110 39 43
3 Zhatay 82 58 66 30 80 45 37
4 Vilyuysk ulus 120 79 13 56 11 431 47
5 Neryungrinsky district 525 346 473 194 90 41 37
6 Abyysky distric
t
18 11 14 12 78 74 59
7 Allaykhovsky distric
t
10 13 16 8 160 50 80
8 Bulunsky distric
t
34 16 26 12 76 46 35
9 Anabarsky distric
t
17 13 18 13 106 72 76
10 Amginsky distric
t
102 66 89 45 87 51 44
11 Verkhnevilyuysky distric
t
94 68 96 51 102 53 54
12 Verkhnekolymsky distric
t
25 21 26 10 104 38 40
13 Verkhoyansky district 99 66 91 45 92 49 45
14 Mountainous area 64 49 64 40 100 63 63
15 Zhigansky distric
t
24 14 24 18 100 75 75
16 Kobyaysky distric
t
84 29 55 17 65 31 20
17 Lensky distric
t
187 147 186 115 99 62 63
18 Megino-Kangalassky distric
t
218 172 209 135 96 65 62
19 Mirninsky distric
t
478 326 435 169 91 39 35
20 Momsky district 19 23 32 13 168 41 68
21 Namsky district 155 108 145 85 94 59 55
22 Nizhnekolymsky district 13 15 24 10 185 42 77
23 Nyurbinsky distric
t
97 87 119 58 123 49 60
24 Oymyakonsky district 84 54 68 42 81 62 50
25 Olekminsky distric
t
79 70 104 65 132 63 82
26 Oleneksky distric
t
18 11 12 12 67 100 67
27 Srednekolymsky district 40 36 46 22 115 48 55
28 Suntarsky distric
t
102 94 106 54 104 51 53
29 Tattinsky distric
t
107 88 109 57 102 52 53
30 Tomponsky distric
t
70 66 75 29 107 39 41
31 Us
t
-Aldansky distric
t
103 90 120 50 117 42 49
32 Us
t
-Maysky distric
t
41 37 40 24 98 60 59
33 Us
t
-Yansky distric
t
38 36 48 18 126 38 47
34 Hangalassky distric
t
186 149 188 104 101 55 56
35 Churapchinsky district 111 94 126 87 114 69 78
36 Eveno-Bytantaysky 10 9 13 7 130 54 70
Total 7127 5609 7341 3259 103 44.39 46
Source: the data in the table were compiled by the authors from the reporting data of the administrations of municipalities
(municipal districts) of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) as of 16.10.2020.
In accordance with Table 9, the dynamics are
high, since in these regions of the republic in 2019
there is a rapid increase in the number of newly
created SMEs in the context of between 114% and
185%, which served as a good start for maintaining
"inertia" for 2020. This positive phenomenon may be
justified by the existing three factors affecting the
reduction in the number of newly created SMEs on
the example of the Olekminsky district (ulus), which
are due to:
1) preparation starting from 2016 for the national
holiday Ysyakh Olonkho 2020, the event on which
was postponed by the order of the Head of the
Republic to 2023;
2) in 2019, a Business Incubator was created
pursuant to the state program of the Republic of
Sakha (Yakutia);
3) implementation of a megaproject on the
territory of the Olekminsky district: construction of
the VSTO oil pipeline.
Regional Dynamics of Self-employment Development in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
373

It is also worth highlighting 3 municipalities with
low indicators, which recorded a rapid decline in the
number of newly created SMEs. In Mirny, Bulunsky
and Kobyaysky districts (ulus), the share of newly
created SMEs at the level of 2019 and 2020 does not
reach 35%.
Accordingly, the natural economic processes in
the region do not allow assessing the degree of
influence of the tax on professional activities using
the standard analytical approach of the study.
Changes in the growth rate of the number of SMEs in
the republic in comparison with two-year parameters,
which turn out to be incompatible with the
introduction of a tax on professional activities, but are
more characteristic of the state of development with
global trends that negatively affect the activities of
SMEs.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The relevance and expediency of establishment of a
tax on professional income does not raise doubts.
Civil duties and social responsibility should be in the
first place for each citizen of Russia. That is why the
initiative to apply the tax on professional income on
the territory of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) from
July 1, 2020 should be justified by the fact that a
significant part of socially vulnerable and unprotected
categories of the population may legally engage in
professional activities. Herewith, such activity which
is not burdened by excessive document flow and
additional expenses. In addition, such form of
employment promotes the free choice of the citizen
on time and due dates of the professional obligations.
The prospect of the development of self-
employment in the conditions remote from the center
of the territory may allow to enhance the technology
of rendering services to the population and legal
entities in order to be able to accumulate retirement
services. However, there is uncertainty due to the
changes expected in the field of state pension policy,
due to which the self-employed category of the
population may deliberately hide income from
taxation. Obviously, in this situation, the tax
innovation should provide for a special regime of
control over the income of the self-employed. After
all, only those contracts that will be concluded by the
self-employed with legal entities will fall under
control, and those contracts that oblige the self-
employed to perform professional work for
individuals will be impossible to control.
By the fact of the current legislation, self-
employment within the limits of their activities is
already surrounded by tax restrictions. The Law on
Tax on Professional Income determines the
maximum amount in the amount not exceeding 2.4
RUR mln income in the current calendar year.
However, a self-employed citizen will not be able to
refuse the opportunity to earn an amount in excess of
the amount of income specified in the law. The
legislator in this situation does not model the social
and legal behavior of a self-employed citizen.
Although, if the maximum amount of income was
exceeded, it should have been mentioned in the Law
on the standard tax rate of 13% of personal income
tax, if the amount of income is in the range of 2.4-5.0
RUR mln and on the tax rate of 15% of personal
income tax, if the amount of income is 5.0-8.0 RUR
mln, while maintaining the status of a self-employed
citizen.
However, the excess of income from 8.0 RUR
mln, then in this situation it is the duty of a self-
employed citizen to formalize individual
entrepreneurship or to choose another organizational
and legal form.
Thus, it is possible to achieve specific social and
legal behavior of self-employed citizens, whose
organizational and legal status will be detailed and
defined so that the self-employed citizen does not
even think that he should solve problems that do not
fit into the legislative framework.
The likelihood of a group dynamics of an increase
in self-employed citizens is alarming, the number of
which may provoke a personnel shortage for the
business environment. According to statistical data on
the distribution of individual entrepreneurs by type of
economic activity in the republic, there is already
activity in such areas as health care and the provision
of social services, but they have catastrophically low
indicators (86.3%), agriculture, forestry, hunting,
fishing and fish farming (91%), and activity in the
field of information and communication leads
(107.1%) among individual entrepreneurship in the
republic.
Therefore, there is a need for legislative
enhancement of the norms governing the behavior of
the self-employed pursuant to the levels of income
derived from professional activity, taking into
account socio-economic differences and the degree of
development of territories.
REFERENCES
Ageeva, A. K., 2019. Introduction of the self-employed
citizens. In International Journal of Humanities and
Natural Sciences. 12-4(39). pp. 10-12.
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
374

Apresova, N. G., 2020. The legal status of self-employed as
a taxpayer. In Courier of Kutafin Moscow State
University (MSAL). 7. pp. 130-137.
Bakirova, R.R., Khaziakhmetov, R.A., Gubaydullin, B.F.,
Sheina, A.Yu., 2020. Modern trends in tax
administration in the Russian Federation. In Journal of
Economics, Entrepreneurship and Law. 2. pp. 459-470.
Berdnikova, G.I., 2019. Theoretical and methodological
bases of research of employment and self-employment
of the population in Russia. In Corporate Economics.
4(20). pp. 45-51.
Voronina, L. I., Kasyanova, T. I., 2018. Mechanisms for
promotion and development of selfemployment of
unemployed citizens: a comparative analysis of foreign
and Russian experience. In Tomsk State University
Journal. Economy. 44. pp. 264-282.
Konkin, A. N., Chudaykina, T.N., 2020. Features of the
application of professional income tax in construction.
In Moscow economic journal. 12. pp. 615-621.
Krivin, D. V., 2020. Professional income tax in
Entrepreneurship: problem and prospects of
Experiment in science and practice. In University
proceedings. Volga region. Social sciences. Economics.
3(55). pp. 113-126.
Kurnosova, A.V., Chernousova, K. S., 2020. Analysis of
the introduction of a new tax regime for self-employed
citizens of the Russian Federation. In International
Journal of Humanities and Natural Sciences. 4-2(43).
pp. 99-102.
Lavrova, D. P., Ivanov, N. Yu., 2013. Mojor Errors and
mistakes of marketing position agrarian of small and
medium sized business. In Scientific Works of the Free
Economic Society of Russia. 179. pp. 281-286.
Lavrova, D. P., Ivanov, N. Yu., 2014. The state of
development of the small and medium-sized business
market in Yakutia. In Scientific Works of the Free
Economic Society of Russia. 189. pp. 368-372.
Mashrapov, N. K., 2015. On the issue of problems of small
and medium-sized businesses. In Problemy
sovremennoy ekonomiki (Novosibirsk). 24. pp. 72-74.
Nesterenko, Yu. N., Protasova, E. A., 2019. Self-
employment in Russia: State abd Potential for
development. In Population. 22(4). pp. 78-89.
Pavlovskaya, O. Yu., 2015. Material Support of Self-
employment for the Unemployed: Algorithm and
Aspects of Law Enforcement. In Pravo. Zhurnal
Vysshey shkoly ekonomiki. 1. pp. 67–80.
Samitov, R. M., 2020. Self-employed. In Economic
Scientific Journal «Investment Assessment». 1(15). pp.
46-55.
Safonov, A. Y., 2020. Prospects of self-employment in
agricultural complex. In Moscow economic journal. 6.
pp. 265-272.
Tereshkina, M. A., 2014. Problems of small and medium
business in Russia. In International Research Journal.
2-2 (21). pp. 79-80.
Chernysheva, Y. G., Shepelenko, G. I., 2010.
Differentiation status of the entrepreneur. In Vestnic of
Rostov-on-Don State Economic University (RINH). 3.
pp. 12-18.
Chistyakova, M. K., 2018. Development of small business
in the agroindustrial complex. In Bulletin of Agrarian
Science. 4 (73). pp.115-119.
Regional Dynamics of Self-employment Development in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
375
