
Indicators of Personnel Threats to the Information Potential of an
Enterprise
Elena Karanina
Vyatka State University, Kirov, Russian Federation
Keywords: Company, information potential, information, personnel, threats, indicator.
Abstract: The article substantiates the possibility of assessing the level of the information potential of a company, taking
into account indicators of personnel threats. The analysis of methods for assessing the information potential
of companies proposed by Russian scientists is carried out. Conclusions about the need to increase the role of
the personnel block in the integral indicator of the information potential are made. The authors summarized
and systematized threats to the information security and, consequently, the information potential. A proposal
to systematize personnel threats into three groups in accordance with the classification criterion by subject
(source of threats) – a company employee, company management and third parties – was made. Personnel
threats correspond to information security threats. The authors concluded that it is necessary to form indicators
for personnel threats, based on principles of their construction: validity, measurability, simplicity. The article
presents a system of indicators offered by the authors for each personnel threat. The developed indicators
correspond to the stated principles.
1 INTRODUCTION
The role of information in the economy as a field of
activity, along with other areas of human activities, is
difficult to overestimate. Assessment of the economic
potential of a company cannot be complete without
including assessment of the information potential as
the basis for making management decisions at any
level of the organizational structure of an enterprise.
This is noted by many scientists and specialists, in
particular, Y.B. Bashin, K.B. Borisova, E.O.
Dmitrieva, N.A. Mansurova, P.V. Ovechkina, K.V.
Orlova, E.A. Sintsova, I. G. Chernyshov. When
revealing the content of the information potential of
an enterprise, almost all scientists include the
personnel block in its structure. The importance of the
personnel in the activity of both information
processing, including its collection, reception,
transformation, storage and transmission, and the
software and hardware of these processes, is not
underestimated by any of the authors. Indicators for
assessing the information potential, offered by
scientists and specialists, reflect the state of this area
of the company activity. However, for successful
development of any type of activity it is necessary to
understand not only the achieved level, but also the
potential various threats of violations and failures.
Information security is an area of activity, the
purpose of which is to identify and prevent threats in
the information sphere of a company. However,
specialists in the field of information security mainly
focuse on its software and hardware unit (V.V.
Gafner, O.A. Grunin, L.I. Zabara, V.M. Zaplatinsky,
S.V. Petrov, A. S. Trifanova). Personnel and threats
from people, including employees of an enterprise,
are considered only from the point of view of sources
of their formation.
Due to the lack of published works on the
assessment of personnel threats to information
activities, the study was carried out to test the
hypothesis: the level of assessment of the company
information potential depends on the presence and on
the level of personnel threats reflected in
corresponding indicators.
The purpose of the study is to develop indicators
of personnel threats to the information potential. In
accordance with this purpose, the study solved two
tasks:
- to form personnel threats to the information
potential of a company;
- to build indicators of personnel threats to the
information potential of a company.
376
Karanina, E.
Indicators of Personnel Threats to the Information Potential of an Enterprise.
DOI: 10.5220/0010705700003169
In Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference "Ensuring the Stability and Security of Socio-Economic Systems: Overcoming the Threats of the Crisis Space" (SES 2021),
pages 376-381
ISBN: 978-989-758-546-3
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The research methodology is based on the
fundamental provisions of the theory of information
and economic security. When building indicators of
personnel threats to the information potential,
methods of logical and mathematical modeling were
used.
The study is based on the logical analysis of
scientific papers on assessing the information
potential of a company and indicative assessment of
the company personnel and information security. The
works of such scientists as Y.B. Bashin, K.B.
Borisova, E.O. Dmitrieva, N.A. Mansurova, P.V.
Ovechkina, K.V. Orlova, E.A. Sintsova, I. G.
Chernyshova and others influenced significantly on
substantiation of the conceptual approach to assessing
the impact of personnel threats on the level of the
information potential of a company
The work used materials carried out researched in
the field of the theory of personnel security of
companies by I. Bogatyreva, N.V. Borovskikh, R.S.
Esikova, L. Ilyukhina, O. A. Klindukhova, A. Ya.
Kibanov, E.A. Kippervar, K.V. Lysak, A.O. Lysenko,
I.N. Makhmudov, A.M. Morozova, E.I. Mustafieva,
I.I. Salnikov, L.T. Snitko, T.O. Solomandina, V.G.
Solomandin, T.F. Tarasova, Redman, T., Wilkinson,
A. Kontemporary, F.M Roka, Z. Guan, S. Urošević,
B. Pejčić and others.
When developing indicators of the personnel
security, the results of researches of N.V. Borovskikh,
M.V. Varlamova, O.K. Denisova, V.N. Druzhkova,
A.V. Glushchenko, N.L. Gryaznova, I.E. Ilyakova,
E.A. Kipervar, N.I. Klevets, A.S. Kobenko, E.P.
Kucherova, I.N. Sannikova, O.S. Sausheva, T.O.
Solomandina, V.G. Solomandina, I.I. Tsvetkova and
others were taken into consideration.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The economic potential of a company is directly
dependent on its information potential, which
determines the validity and timeliness of the taken
management decisions. E.O. Dmitrieva understands
the information potential as “a set of information
resources, information support systems and their
maximum ability to provide timely, reliable and
complex (complete) information necessary for
making management decisions” (Dmitrieva, 2010).
N. A. Mansurova and K.V. Orlova clarify the concept
of the information potential, revealing its composition
and procedures: "a set of tools, methods, conditions,
as well as software that allow to receive, store,
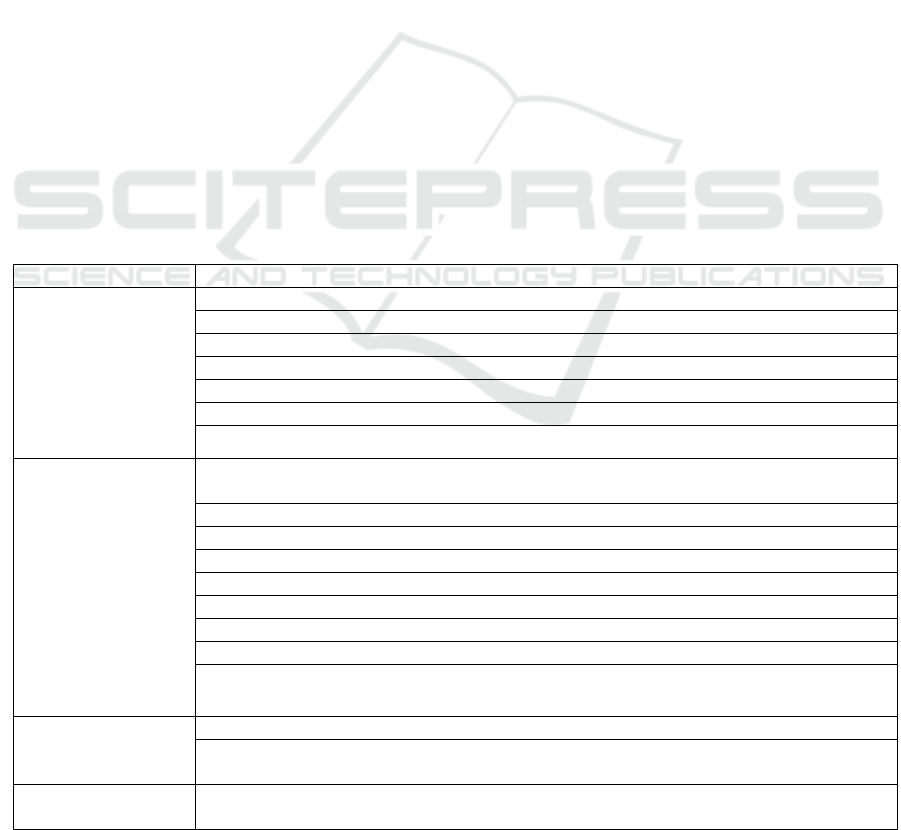
Table 1: Indicators of the personnel block for assessing the information potential of a company
Authors Indicators
Personal data age (Dmitrieva, 2010)
qualifications (Dmitrieva, 2010; Chernyshova, 2012)
employment experience in a speciality (Dmitrieva, 2010)
years of work in a company (Dmitrieva, 2010)
computer literacy (Dmitrieva, 2010)
information literacy, education (Nansurova & Orlova, 2016, Chernyshova, 2012)
ability and readiness of managers to use new information technologies (Dmitrieva, 2010)
Characteristics of the
company personnel
indicators of movement and efficiency of using labor resources in the information system of an
enterprise (Dmitrieva, 2010)
age structure (Dmitrieva, 2010)
qualification structure (Dmitrieva, 2010; Chernyshova, 2012)
skills availability of an enterprise (Nansurova & Orlova, 2016)
average work experience in a specialty (Dmitrieva, 2010)
the number of employees who work with information systems (Dmitrieva, 2010)
the average number of years of work of specialists in a company (Dmitrieva, 2010)
computer literacy (Dmitrieva, 2010)
coefficient of the optimality of the number of personnel of the information department as the
ratio of the actual number of personnel to the number required (Nansurova & Orlova, 2016)
Organization of work
with personnel
existence or organization of refresher courses, (Dmitrieva, 2010; Chernyshova, 2012)
share of costs for personnel training to work with new information resources in the structure of
total personnel training costs (Nansurova & Orlova, 2016)
Performance results
of employees
share and novelty of information products created by company specialists (Dmitrieva, 2010)
Indicators of Personnel Threats to the Information Potential of an Enterprise
377

analyze, generalize and update the information
necessary to adapt an enterprise to market conditions"
(Nansurova & Orlova, 2016, P. 647). Detailed lists of
information resources and systems for their support,
as well as indicators that allow assessing their level,
demonstrate that scientists ignore the information that
employees of an enterprise have, which is necessary
to achieve the goals of creating an enterprise - the
release of a product in demand by the market. The
authors consider information resources as being
equipped with computers, services, etc. When
assessing the information potential, the ability of
employees of an enterprise to use software and
hardware is taken into account. A rare exception is
E.A. Sintsova and P.V. Ovechkina, who understand
information resources as knowledge, experience,
skills, and skills of company employees (Sintsova &
Ovechkina, 2015). It is this understanding of the
information resource that allows us to define as an
object of both the information system and the security
system of the information activity the holder of these
resources - the person. This circumstance is of
fundamental nature for creation of a system for
assessing both the information potential and its
security. The concept of a system for assessing the
security of the information activity should proceed
from the dualism of subjects (company employees):
employees, on the one hand, are the object of the
information system as holders of knowledge and
skills, and, on the other hand, they are the subject that
ensures functioning of the information system.
The indicators proposed by scientists and
specialists for assessing the information potential of a
company were systematized according to four
unequal blocks: personal data, characteristics of the
company personnel, organization of work with
personnel and performance results of employees
(Table 1).
Most of the indicators (13 out of 19) reflect the
state of human resources, insignificant number of
indicators (3 out of 19) highlight work carried out by
a company to improve qualifications of employees
and results of the intellectual activity of employees.
And only three indicators (ability and readiness of
managers to use new information technologies, skills
availability of an enterprise and coefficient of the
optimality of the number of personnel of the
information department) can reflect personnel threats
Table 2: Classification of information security threats by object
Group according
to the object of
threats
Content of threats
information -unauthorized access to information resources;
- illegal copying of data in information systems;
- theft of information from libraries, archives, banks and databases;
- interception, decryption, substitution and destruction of information in communication channels;
- illegal collection and use of information, including passing to third parties;
- intentional or unintentional destruction of information;
- leakage of confidential information;
- intentional and unintentional distortion of information;
- substitution of information;
- formation of inaccurate data
technologies,
technical means
- violation of the information processing technology;
- damage to technical equipment;
- violation of normal operation of technical means; failures and malfunctions of computer
equipment;
- damage to programs;
- unauthorized covert operation of information and computing resources (for example, when
creating a botnet);
- theft of a server or computer with personal information;
- use of potentially dangerous objects in the external network;
- use of malicious software (trojans, backdoors, blockers, encryptors);
- operation errors in the software;
- failures and malfunctions of computer equipment;
- violation of targeting and timeliness of information exchange;
- unauthorized access to confidential and other information;
- software infection with viruses or malware.
Sources (
Bokovnya & Begishev, ets 2020; Gray, 2003; Rossouw von Solms, 1998)
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
378
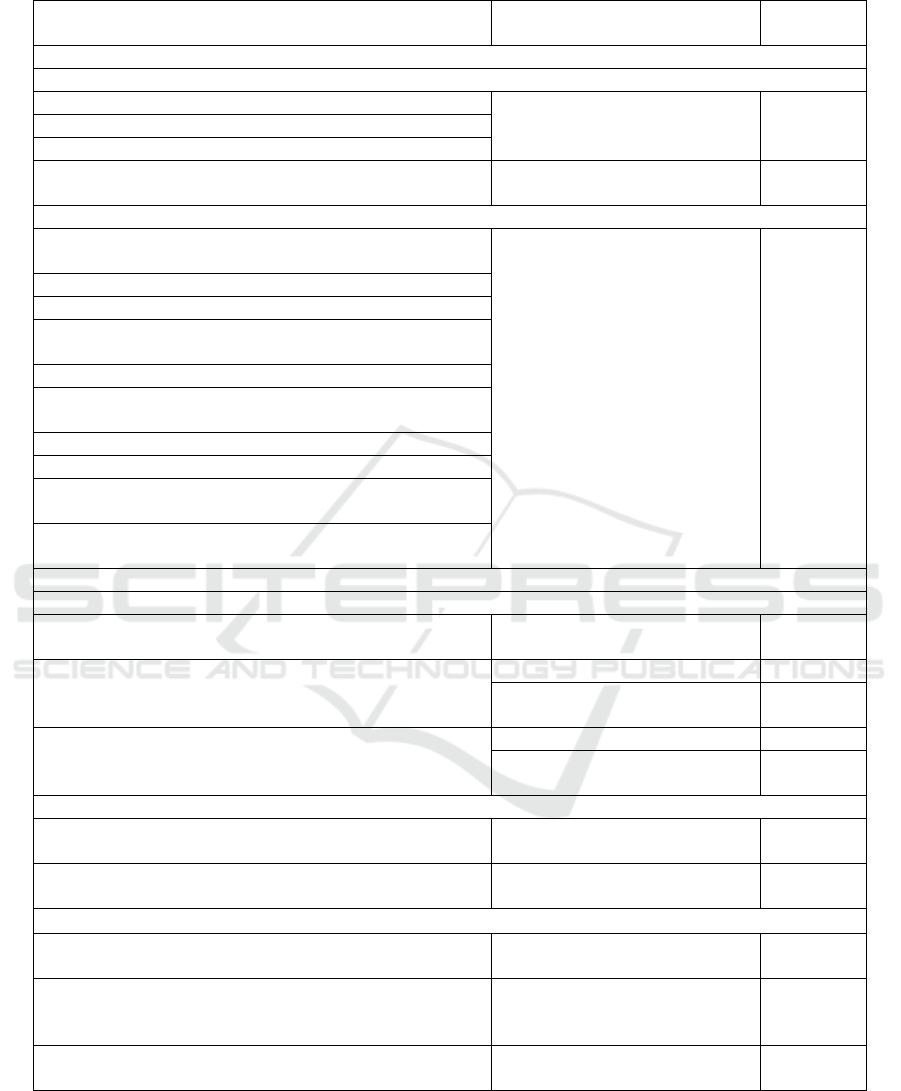
Table 3: Indicators of personnel threats to the information potential of a company
Threats Indicator Calculation
formula
Source: 1. Employee
1.1. Personal qualities of an employee
the presence of addictions (gambling, drug, alcohol, etc.)
number of cases per 100 (1 000)
people
n х 100 / N
deviant behavior (aggressive, irresponsible, etc.)
mental (psychological) disorder/illness
low qualification level, professional incompetence
number of professional mistakes 100
(1 000) people
n х100 / N
1.2. Employee actions (conscious and unconscious)
transfer, disclosure by an employee of an organization of confidential
information to third parties, including distorted
number of cases per 100 (1 000)
people
n х 100 / N
violation of order, regulations, instructions
abuse of power or authority for personal advantage
financial and property scams of managers, including the conclusion
of unprofitable deals for personal gain
distortion, damage, destruction, theft of information
deliberate damage to property, violation of its qualities and
properties
use of malicious software
theft, seizure of tangible and intangible assets and information
non-purpose use of information, software and hardware for personal
advantage
unprofessional and dishonest performance by an employee of his/her
official duties
2. Enterprise management
2.1. Ineffective personnel management
performance of work by employees who do not have a sufficient
level of competence
number of cases per 100 (1 000)
people
n х 100 / N
presence of less than 50% of young specialists in the personnel and
an increase in the average age of employees
personnel level Sf / Sn,
personnel turnover rate
(Sd / San) х
100
no candidates pool in the organization
personnel level Sf / Sn,
personnel turnover rate
(Sd / San) х
100
2.2. Conditions of work
violation of work and rest regimes
share of personnel with no violations
of labor discipline
(Sv / S) х
100
unfavorable socio-psychological climate in workforce
dynamics of labor conflicts for a
certain period (year, month)
n
i+1
/ n
i
3. External sources
drain of qualified and experienced employees personnel turnover rate
(Sd / San) х
100
persuading employees to engage in illegal actions and violation of
obligations towards the employer (transfer of confidential
information, forgery, etc.)
percentage of personnel who have
created a threat through destructive
actions
(Sw / San) х
100
depletion of labor resources
number of occupational diseases per
100 (1 000) people
n х 100 / N
Indicators of Personnel Threats to the Information Potential of an Enterprise
379

to the information security, since they characterize
the ability to protect information and the
infrastructure that supports it. We took a number of
conceptual provisions developed and presented
earlier as a basis for formation of the structure of
personnel threats to the security of the company
information potential (Karzaeva, 2021):
- the structure of threats is formed based on the
goal of organizing security activities – preventing
threats and minimizing risks;
- a threat is understood as a negative process,
event, action that is probabilistic in nature and can be
prevented by a person;
- a personnel threat is understood as a process,
event, action, as a result of which objects
(information) or interests of both an individual person
– a holder of information and a company are done
harm;
- the specificity of personnel threats is determined
by the dualistic nature of company employees. On the
one hand, he/she is the holder of information, and on
the other hand, he/she, when fulfilling official duties,
deals with information, including negatively.
The construction of the system of personnel
threats to the information potential should be based
on the list of threats to the company information
security (Table 2).
The analysis of this list allows us to conclude that
the source of threats is a person, including an
employee of a company. His/her deliberate
(malicious) or unconscious (unprofessional actions,
inadvertent mistakes) actions can lead to
implementation of these threats. Therefore, we
previously proposed to systematize an entire set of
personnel threats into three groups according to their
source: an employee of an enterprise, the company
management, and third parties in the event that their
unfriendly actions can be prevented by company
employees (Karzaeva, 2021).
Almost all scientists who study personnel security
issues compile both lists of threats and their
indicators. These lists are characterized by a variety
that can be explained by not applying the principles
of their formation. Based on our previous studies of
the methodology of indicative safety assessment
(Karanina & Loginov, 2017; Karanina & Ryazanova
ets 2018) and the principles of constructing their
system (Karzaeva & Davydova, 2020), we developed
models for calculating indicators (Table 3). To
achieve objectivity in determining the level of the
indicator, it is necessary to build a calculation model
in which natural units of measurement are used
(Table 3).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The article was prepared with the support of the grant
of the President of the Russian Federation NSh-
5187.2022.2 for state support of the leading scientific
schools of the Russian Federation within the
framework of the research topic «Development
andjustification of the concept, an integrated model
of resilience diagnostics of risks and threats to the
security of regional ecosystems and the technology of
its application based on a digital twin».
4 CONCLUSIONS
As a result of the study, the following main
conclusions were formulated:
- the role of company employees in the
information potential is of a dualistic nature: on the
one hand, the employee is a holder of information
and, on the other hand, the employee influences the
state of both information and software/hardware that
carry out operations with it;
- threats employment information have an impact
on almost all threats to information security;
- assessment of the level of threats to personnel
security by means of indicators will increase the level
of reliability in assessing the information potential of
a company;
- indicators of personnel security should be
objectively measured, therefore it is better to use
natural indicators, as a rule, this is the number of
registered cases.
The findings confirm the hypothesis tested in this
study about the dependence of the level of assessment
of the company information potential on the presence
and level of personnel threats reflected in the
corresponding indicators.
REFERENCES
Bokovnya, A. Yu., Begishev, I. R., Shutova, A. A., Bersei,
D. D., Perchina E. A., Potudinsky V. P. 2020. Motives
and Objektives of Crime Commission Against
Information Security. In AD ALTA: Journal of
Interdisciplinary Research. 10(2). pp. 7-9.
Chernyshova, I. G., 2012. Methodology for assessing the
organizational and informational potential of an
enterprise. In Bulletin of the Bryansk State University.
3-1. pp. 166-170.
Gray, C., 2003. Review: information Security Policies,
Procedures and Standards. In Guidelines for effective
SES 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC-PRACTICAL CONFERENCE "ENSURING THE STABILITY AND SECURITY OF
SOCIO - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS: OVERCOMING THE THREATS OF THE CRISIS SPACE"
380

information Security Management ITNOW. 45(2). p.
30.
Dmitrieva, E. O., 2010. Methods for assessing the
information potential of an industrial enterprise
Problems of improving the organization of production
and management of industrial enterprises. In
Interuniversity collection of scientific papers. 2. pp. 36-
45.
Karanina, E. V., Loginov, D., 2017. Indicators of Economic
Security of the Region: a Risk-Based Approach to
Assessing and Rating. In IOP Conference. Series:
Materials Science and Engineering. 90(1). p. 012087.
Karanina, E. V., Ryazanova, O. A., Timin, A. N.,
Domracheva, L. P., 2018. Diagnostigs and Monitoring
of Economic entities Security. In E3S Web of
Conferences. 2018 Topical Problems of Architecture,
Civil Engineering and Environmental Economics,
TPACEE 2018. p. 08002.
Karzaeva, N. N., 2021. Information Support for Evaluating
Personnel Security in a Company. In The Challenge of
Sustainability in Agricultural Systems. 2. pp. 174-182.
Karzaeva, N. N., Davydova, L. V., 2020. Methodological
methods for creating a system of safety indicators for
the company's utopia and Praxis Latinoamericana.
25(6). pp. 219-228.
Nansurova, N. A., Orlova, K. V., 2016. Assessment of the
intensity of development of the information potential of
an enterprise. In Economic research. 1. p. 1.
Rossouw von Solms, 1998. Information Security
Management. In Guidelines to the Management of
information technology Security (GMITS) Information
Management & Computer Security. 6(5). pp. 221-223.
Sintsova, E. A., Ovechkina, P. V., 2015. Development of
the information potential at industrial enterprises. In
Problems of innovative development of an industrial
enterprise. ST. PETERSBURG. pp. 114-121.
Indicators of Personnel Threats to the Information Potential of an Enterprise
381
