Affecting Variables Breastfeeding in Indonesian Urban Areas:
2017 IDHS Data Analysis
Onny Fatimah and Risni Julaeni Yuhan
Politeknik Statistika STIS, Indonesia
Keywords: Breast Milk, Breastfeeding, Urban, Binary Logistic Regression.
Abstract: Breast milk is an important source of nutrients for child growth and development. The data of BPS 201,
achievement of breastfeeding in urban areas of Indonesia (81.72 percent) is more critical than rural areas
(73.82 percent). This is exacerbated by the infant mortality rate (IMR) in urban areas which is higher than in
rural areas. Therefore, in this study, we examine the variables that affect breastfeeding in Indonesian urban
areas using the 2017 IDHS data using the binary logistic regression method. The variables studied included
mother's education, mother's working status, birth attendant, place of delivery, early initiation of
breastfeeding, pregnancy visits, and household economic status. The data showed that 94.7 percent of mothers
gave breast milk and 5.3 percent of mothers did not breastfeed their children. The result showed that several
variables that had a significant effect on breastfeeding for children under two years of age were the mother’s
working status, pregnancy visits, and early initiation of breastfeeding. Mothers tend to breastfeed is the mother
who does not work, carry out the IMD and women who undergo pregnancy visit of more than equal to four
times.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to Law Number 35 of 2014, a child is
someone who is not yet 18 years old, including
children who are still in the womb. Children are an
asset for a nation in the future. For this reason, the
government through Law Number 36 Year 2009
states that efforts to maintain infant and child health
must be aimed at preparing future generations who
are healthy, intelligent, and qualified and to reduce
infant and child mortality. In order to maintain the
health of infants and children, it is important to meet
the nutritional intake for children.
Breast milk is the main source of nutrition for
children. Breast milk contains white blood cells,
immunoglobulins, enzymes, hormones, specific
proteins, and other nutrients needed for the growth
and development of children (Law Number 3, 2010).
Breastfeeding is recommended for the first six
months without complementary foods. Then
breastfeeding is continued until the child is two years
old.
Based on the 2030 Sustainable Development
Goals (SDGs), there are several goals that are closely
related to breastfeeding. This goal is contained in the
second goal of ending hunger and the third goal of
good health and well-being. This goal can be
achieved by ending all forms of malnutrition and
reducing neonatal mortality. Every year, there are
more than 25,000 babies in Indonesia and 1.3 million
babies in the world can be saved from death by
breastfeeding.
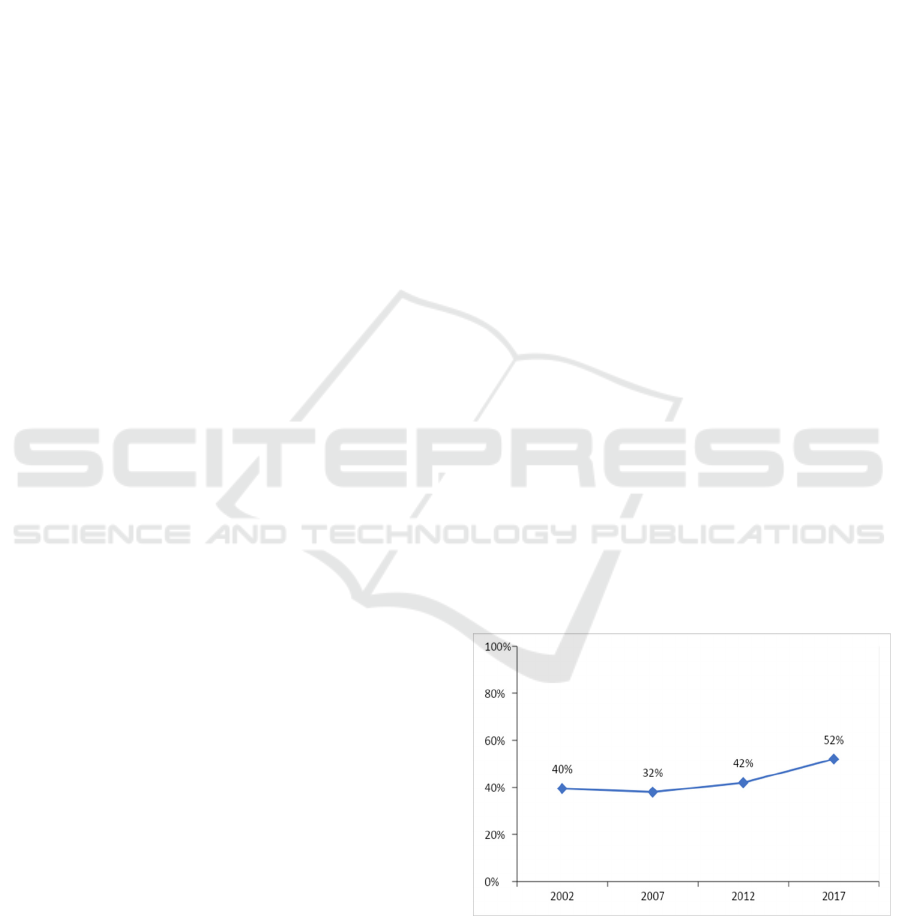
Source: IDHS 2002-2017
Figure 1. Percentage of coverage of exclusive breastfeeding
in Indonesia in 2002-2017.
Figure 1 shows that the coverage of exclusive
breastfeeding from 2002 to 2017 has fluctuated. The
coverage of exclusive breastfeeding in Indonesia has
Fatimah, O. and Yuhan, R.
Affecting Variables Breastfeeding in Indonesian Urban Areas: 2017 IDHS Data Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0010759800003235
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Social Determinants of Health (ICSDH 2021), pages 189-194
ISBN: 978-989-758-542-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
189

not met the target set by the government, which is 80
percent. Meanwhile, the percentage of children aged
0-23 months who were still breastfed in 2017 was
77.4 percent. This figure has decreased from 2016 of
78.49 percent. The practice of breastfeeding that has
not met the target will cause problems in achieving
optimal growth and development as well as
malnutrition in children. Septikasari (2018) states that
the success of exclusive breastfeeding has an
influence on the incidence of malnutrition in children
aged 6-12 months.
Based on 2017 BPS data, the achievement of
exclusive breastfeeding in urban areas in Indonesia in
2017 was 54.77 percent. Meanwhile, the coverage of
exclusive breastfeeding in rural areas of Indonesia in
the same year was 57.22 percent. The same condition
also occurs in children aged 0-23 months who are still
breastfed in rural areas by 81.72 percent. This figure
is higher than urban areas with a percentage of 73.82
percent. The condition of breastfeeding in urban areas
in Indonesia is more critical than in rural areas. This
is also exacerbated by the infant mortality rate (IMR)
in urban areas which is higher than in rural areas
.
IMR in urban areas is 24 deaths per 1000 live
births. In rural areas, this figure is lower at 23 deaths
per 1000 live births. It is interesting to study further
with regard to the characteristics of urban areas that
affect breastfeeding.
In order to optimize breastfeeding for children, it
is necessary to know what factors are related to a
person's behavior related to health. According to
Lawrence Green (1980), human behavior related to
health is formed through several factors including the
following:
1. Predisposing factors which include
knowledge, attitudes, beliefs, beliefs, socio-
cultural values, and so on,
2. Enabling factors which include the physical
environment, available or the unavailability
of health facilities or facilities, such as health
centers, medicines, sterile tools and so on.
3. The driving factor which includes the
attitudes and behavior of health or other
staff, which is a reference group for
community behavior.
Predisposing factors are factors that become the
basis of a person's motivation or intention to do
something. Variables that are included in the
predisposing factors include education level and work
status. Enabling factors are factors that make it
possible to perform a behavior or action. Enabling
factors in this study used variables of economic
status, place of delivery, pregnancy visits and BMI
status. While the driving factor is a factor that
strengthens a person's behavior. The driving factor in
this study was a delivery assistant variable.
Research conducted by Astuti (2013) concluded
that mother's education, mother's occupation,
mother's knowledge, mother's attitude, role of
officers, media exposure, husband's role, parental role
had a significant effect on exclusive breastfeeding.
Hasiana (2016) in his research stated that there was a
significant effect between the implementation of IMD
and the success of exclusive breastfeeding.
Rahmawati (2012) concluded that maternal age,
employment status, baby birth order and support from
health workers had a significant effect on exclusive
breastfeeding. In a study conducted by Elsera (2015)
it was found that there was an effect between neonatal
visits and work with exclusive breastfeeding. In a
study conducted by Tampah-Naah and Kumi-
Kyereme (2013) stated that there is a relationship
between marital status, area and place of delivery
with the practice of exclusive breastfeeding.
Based on the description of the problem, this
study has the following objectives to examine the
description of the characteristics of breastfeeding in
urban areas of Indonesia, analyze the variables that
have a significant effect on breastfeeding in urban
areas of Indonesia, and determine the tendency of
each variable that has a significant effect on
breastfeeding. in children under two years in urban
areas of Indonesia.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Data Collection Methods
This study used secondary data sourced
frommaterials raw data 2017 IDHS. Women of
childbearing age (15-49 years) living in urban areas
who have their last child under two years old are the
unit of analysis in this study. The implementation of
the 2017 IDHS covers 49,250 households with a total
of 1970 census blocks in urban and rural areas.
From the 2017 IDHS data, there are 49,627 WUS
respondents from all over Indonesia. For research
purposes, respondents who lived in rural areas were
excluded, leaving 26,425 WUS respondents. Then
another selection was made to select WUS who had
the last child under two years of age and clean up the
missing value on the dependent variable so that there
were 3467 WUS respondents left. Of the 3467
respondents who were selected, then re-
categorization was carried out.
The dependent variable used in this research is the
status of breastfeeding for children under two years
ICSDH 2021 - International Conference on Social Determinants of Health
190
old, namely breastfeeding and not breastfeeding.
While the independent variables include: education
level, work status, birth attendant, place of delivery,
pregnancy visits, early initiation of breastfeeding, and
economic status.
2.2 Analysis Method
The analytical method used in this research is
descriptive analysis and inferential analysis.
Descriptive analysis used in the form of graphs and
tables to see the general picture of breastfeeding in
urban areas. Meanwhile, inferential analysis uses
binary logistic regression analysis with the aim of
seeing the effect of the independent variable on the
dependent variable. The significance level used in
this study is 5 percent. The binary logistic regression
model used in this study is as follows:
𝑔
𝐷
𝛽
𝛽
𝐷
𝛽
𝐷
𝛽
𝐷
𝛽
𝐷
𝛽
𝐷
𝛽
𝐷
𝛽
𝐷
𝛽
𝐷
𝛽
𝐷
𝛽
𝐷
(1)
Model suitability test was conducted to see if the
model used was suitable to explain breastfeeding
status. Testing using Hosmer and Lemeshow
Goodness of fit test.
Simultaneous test was used to see the effect of the
independent variables together on the variable of
breastfeeding status. Simultaneous test using G.
Partial test is used to determine the significance of
each independent variable on the dependent variable.
This test is carried out using thetest Wald.
The accuracy of the model in classifying the
observed values can be obtained from looking at the
classification table. The last step is to calculate the
odds ratio of each significant independent variable to
see the trend of breastfeeding between a category and
the reference category.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Descriptive Analysis
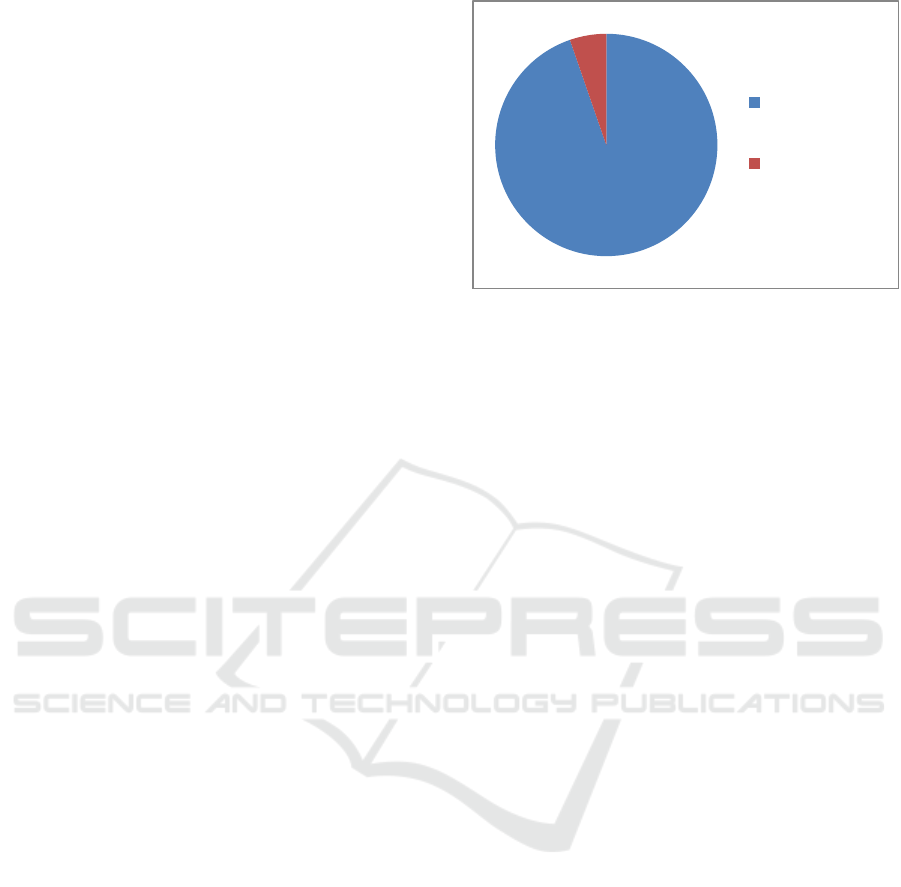
Based on the results of the study, it was found that
94.7 percent of mothers living in urban areas with
children under two years of age gave breast milk and
5.3 percent did not. This indicates that there are still
mothers in urban areas who do not breastfeed their
children.
Source: IDHS data (processed)
Figure 2. Percentage of women of childbearing age based
on breastfeeding status in urban Indonesia.
Based on table 1. Mothers with junior high-high
school education are more dominant than mothers
who do not attend school, elementary/equivalent
education, and education above high school. The
distribution of mothers who do not work is much
greater than that of working mothers. The percentage
of mothers is dominated by mothers with birth
attendants by health workers. Likewise with the
characteristics of the mother's place of delivery. The
percentage of mothers was dominated by mothers
who gave birth in health facilities, which was 93.6
percent. The distribution of mothers was dominated
by mothers who had four or more pregnancy visits
than mothers with less than four pregnancy visits. The
percentage of mothers was dominated by mothers
who did early initiation of breastfeeding than mothers
who did not do early initiation of breastfeeding.
Meanwhile, the percentage of mothers whose
economic status is rich is 58.6 percent, middle
economic status is 21.6 percent, and the economic
status is poor is 19.7 percent. These results indicate
that the number of mothers whose economic status is
rich is more than that of mothers with middle and poor
economic status.
94,7%
5,3%
Breastfeeding
Not
breastfeeding
Affecting Variables Breastfeeding in Indonesian Urban Areas: 2017 IDHS Data Analysis
191

Table 1. Percentage of women of childbearing age in urban
Indonesia based on their characteristics.
Characteristics Percentage
(1) (2)
Mother's education 100.0
No school 0.3
Elementary school 14.8
Middle school 63.1
High school 21.9
Status Workin
g
Mothe
r
100.0
Working 39.1
Not workin
g
60.9
Birth attendant 100.0
Assisted by health workers 97.4
Not assisted b
y
health workers 2.6
Place of deliver
y
100.0
Not in health facilities 6.4
At health facilities 93.6
Pregnancy visit 100.0
≥4 93.9
<4 6.1
Earl
y
initiation of breastfeedin
g
status 100.0
Early initiation of breastfeeding 65.4
No earl
y
initiation of breastfeedin
g
34.6
Economic status 100.0
Rich 58.6
Middle 21.6
Poo
r
19.7
Source: IDHS 2017 (processed)
3.2 Binary Logistics Regression
Analysis
3.2.1 Model Fit Testmodel Fit
Based on the results of thetest , the table shows the C
statistic value of 6.917 with a p-value of 0.546. P-
value is more than = 0.05 so the decision is to accept
H
0
which means that the model is fit. Thus, it can be
concluded that with a 95 percent confidence level the
model used is appropriate in explaining the status of
breastfeeding in children.
Table 2 The value of thetest statistic Hosmer and
Lemeshow.
Chi-s
q
ua
r
e df Si
g
.
(
1
)
(
2
)
(
3
)
6.917 8 0.546
Source: IDHS 2017 (processed)
3.2.2 Simultaneous Test
Based on the results of the simultaneous test, the G
statistic value is 51,742 with a p-value of 0.000. As in
table 3, it can be seen that the P-value <α=0.05 so that
the decision obtained is to reject H
0
. Thus, the results
of the study indicate that there is at least one
independent variable that has a significant effect on
breastfeeding children in urban Indonesia.
Table 3. Omnibus test of model coefficient.
Omnibus
test
Chi-square df Sig.
(1) (2) (3)
51.742 10 0.000
Source: IDHS 2017 (processed)
3.2.3 Partial Test
The next stage is to test the significance of the
independent variable partially on the dependent
variable. Table 5 shows that the variables of
employment status, pregnancy visits and BMI status
were significant at the 5 percent level of significance.
This means that these variables partially affect
breastfeeding for children in urban Indonesia. Based
on the results of the partial test, the equation of the
binary logistic regression model is obtained as
follows:
𝑔
𝐷
0,057 1,067𝐷
0,964𝐷
1,488𝐷
0,544𝐷
0,221𝐷
0,035𝐷
0,916𝐷
0,645𝐷
0,148𝐷
0,169𝐷
(1)
There are four variables no significant effect on
breastfeeding in children. Mother's education level
has no effect on breastfeeding children. Fakhidah and
Palupi (2018) state that mothers with basic education
are no less advanced than mothers with higher
education in accessing information about
breastfeeding because they can use electronic media
or from health workers. The birth attendant had no
significant effect on breastfeeding the child. This
result is in line with Paschalia (2017) in her research,
which revealed that because birth attendants lacked
information about the practice of exclusive
breastfeeding, breastfeeding mothers did not
understand the benefits and advantages of exclusive
breastfeeding. In a study conducted by Sembiring
(2018), it was stated that after the delivery process,
the mother and baby were separated in different
rooms, the mother was in the patient room while the
baby was in the baby room so that the mother could
not give breast milk to her baby.
The ROC curve is used to obtain the cut value
which is then used to form a classification table.
Overall percentage value obtained by 83.1 percent.
This means that the model obtained as a whole is able
ICSDH 2021 - International Conference on Social Determinants of Health
192

to predict the breastfeeding status of children well by
83.1 percent. In addition, the model can classify 36.1
percent of mothers who do not give breast milk
properly and 85.6 percent of mothers who give breast
milk appropriately. The classification table is used as
a support for thetest Goodness of fit.
Comparison the value of the breastfeeding
variable for each change in the value or category of
the independent variable is seen using the odds ratio.
The trend ratio is calculated using the exponential
value of the regression coefficient.
1. Working
Status Mother's working status has a significant
effect on breastfeeding children. Mothers who do not
work have a positive effect on breastfeeding with a
coefficient of 0.544. This means that mothers who do
not work have a tendency to give breast milk by 1.723
times compared to mothers who work. This result is
in line with research conducted by Rahmawati (2010)
which states that mothers who do not work have the
opportunity to breastfeed their babies four times
compared to working mothers. Working mothers face
their own problems in providing breast milk for their
children. In short, the period of maternity or maternity
leave certainly disrupts breastfeeding efforts.
2. Early Initiation of Breastfeeding Status
Early initiation of breasfeeding status has a
significant effect on breastfeeding children. Mothers
who do IMD have a positive effect on breastfeeding
with a coefficient of 0.645. This means that mothers
who do IMD tend to give breast milk to their children
by 1.906 times compared to mothers who do not do
early initiation of breastfeeding. Babies who are
given the opportunity to breastfeed early by putting
the baby in skin-to-skin contact for at least one hour,
the result is twice as long as breastfeeding (Luluk and
Fitria, 20120). This result is also in accordance with
the descriptive which describes the percentage of
mothers who carry out early initiation of
breastfeeding giving more milk than mothers who do
not carry out early initiation of breasfeeding.
3. Pregnancy visits
Pregnancy visits have a significant effect on
breastfeeding children. Mothers who made pregnancy
visits four times or more had a positive effect on
breastfeeding with a coefficient of 0.916. This means
that mothers with four pregnancy visits or more tend
to breastfeed their children by 2,498 compared to
mothers with less than four pregnancy visits. These
results are in accordance with the research conducted
by Ogbo et al. (2019) stated that pregnancy visits
have a relationship with breastfeeding. In Chipo
(2019) explained that the knowledge and skills gained
during pregnancy visits can increase the mother's
confidence and intention to breastfeed her child. This
result is in accordance with the descriptive which
illustrates that the percentage of mothers who visited
pregnancy check-ups more than four times more gave
breast milk than mothers who checked their
pregnancy less than four times.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND
RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the results and discussions that have been
described, the following conclusions can be drawn:
1. The status of breastfeeding for children under two
years old in urban areas in Indonesia has not yet
reached 100 percent. Mothers who breastfeed
their children the most with the characteristics:
high school education, not working, delivery
assisted by health workers, giving birth in health
facilities, having pregnancy visits four or more
times, carrying out early initiation of
breastfeeding, and rich economic status.
2. Variables that significantly affect breastfeeding
for children under two years old are: working
status of the mother, pregnancy visits, and early
initiation of breastfeeding.
3. The tendency of mothers who give breast milk to
children under two years old are mothers who do
not work, make pregnancy visits four or more
times, and mothers who carry out early initiation
of breastfeeding.
Suggestions that can be given by the author in
relation to the results of this study are:
1. For government or private agencies that have
female employees in breastfeeding conditions,
they are expected to provide adequate facilities for
breastfeeding such as providing lactation rooms
and so on.
2. The government and all parties can increase
educational activities in the form of counseling
and socialization about the importance of
maternal health during pregnancy so that at the
time of delivery they are ready to carry out IMD
and provide breast milk.
3. In this study, the variables used only looked at
aspects of the mother and household conditions.
In future research, it is possible to use variables
related to gender equality and variables from the
husband's aspect.
Affecting Variables Breastfeeding in Indonesian Urban Areas: 2017 IDHS Data Analysis
193

REFERENCES
Astuti, Isroni. (2013). Determinants of Exclusive
Breastfeeding in Breastfeeding Mothers. Journal of
Health Quality. Accessed on September 10, 2020 via
https://www.poltekkesjakarta1.ac.id/wp-
content/uploads/legacy/jurnal/document/41Jurnal_ISR
ONI.pdf
Central Bureau of Statistics. (2018). Maternal and Child
Health Profile. Jakarta: BPS.
BKKBN, BPS, Ministry of Health. (2018). Indonesia
Demographic and Health Survey 2017. Jakarta:
BKKBN, BPS, and Ministry of Health.
Hasiana, S., Ivone, J., & Wiharja, W. (2014). Effect of Early
Initiation of Breastfeeding on the Success of Exclusive
Breastfeeding. Accessed on 15 February 2021 via
https://repository.maranatha.edu/12604/
Hosmer, DW, & Lemeshow, S. (2000). Applied Logistic
Regression (2nd ed.). New York: John Wiley and Son.
Ministry of Health. (2014). Exclusive Breastfeeding
Situation and Analysis. Jakarta: Ministry of Health.
Ogbo. (2019). Regional prevalence and determinants of
exclusive breastfeeding in India. International
Breastfeeding Journal. Accessed on November 20,
2020 via https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-019-0214-0
Government of Indonesia. (2009). Law of the Republic of
Indonesia Number 36 Year 2009 concerning Health.
Jakarta: Government of the Republic of Indonesia.
Indonesian government. (2014). Republic Law Number 35
of 2014 concerning Amendments to Law Number 23 of
2000 concerning Child Protection. Jakarta:
Government of the Republic of Indonesia.
Rahmawati, M. (2010). Factors influencing exclusive
breastfeeding for breastfeeding mothers in Pedalangan
Village, Banyumanik District, Semarang City. Kusuma
Husada Health Journal. Accessed on November 20,
2020 via
https://internationalbreastfeedingjournal.biomedcentral
.com/articles/10.1186/1746-4358-8-13?optIn=true
Tampah-Naah, A., & Kumi-Kyereme, A. (2013).
Determinants of exclusive breastfeeding among
mothers in Ghana: a cross-sectional study. Accessed
on November 20, 2020 via
https://internationalbreastfeedingjournal.biomedcentral
.com/articles/10.1186/1746-4358-8-13?optIn=true
ICSDH 2021 - International Conference on Social Determinants of Health
194
