
Study on the Reduction Effect of Bioretention Facility on Typical
Heavy Metal Pollutants in Rainfall Runoff
Rubin Jia*, Jian Li, Yong Wang, and Di Tang
China Ji Kan Research Institute of Engineering Investigation and Design, Co., Ltd, Xi’an, 710043, China
Keywords: Bioretention facility, Urban runoff, Heavy metals, Reduction effect
Abstract: This paper studied the effect of different inflow water, heavy metal (Cu, Zn, Cd) concentration and rainfall
interval on heavy metal reduction in bioretention facility. The results showed that the removal ability of
heavy metals was different among the three bioretention facilities, and the removal effect of Cu was the best,
while the removal effect of Cd was not stable. High inflows reduce the reducton efficiency of heavy metals
in bioretention facilities. The concentration changes of heavy metals in influent did not significantly change
the reduction efficiency. After comprehensive comparison, it was found that the bioretention facility with
(sand + fly ash) as filler had the best reduction effect on heavy metals, and the removal rate reached 88%.
The research results can provide basic data support for the design and application of bioretention facility.
1 INTRODUCTION
Bioretention facility is an efficient and low-impact
development technology (LID) (Wu, 2006) that
integrates landscape, water quality purification and
rainfall runoff control. Some researchers have
carried out relevant research on the reduction effect
of bioretention facility (Zhang et al., 2021; Zhou,
2021), structural improvement (Pan et al., 2020),
matrix combination (Chen, 2020), filler type (Zhang
et al., 2020; Ellis et al., 1987) and some research
results have been achieved on the reduction effect of
nitrogen and phosphorus pollutants. However, there
are still problems about the stability and efficiency
of the technology, resulting in the reduction effect of
the technology in the application is often not high.
Especially, there are few studies on the mechanism
of heavy metal reduction. In the actual rainfall runoff
process, rainfall intensity, influent heavy metal
concentration and rainfall interval are also the key
factors determining the bioretention facility, which
directly affect the reduction effect of heavy metal
ions by bioretention facility. Based on the above
background, this paper uses simulated rainwater
pollution to study the removal effect of different
bioretention facility fillers on heavy metals in runoff
and its influencing factors, in order to provide
reference for the design and optimization of
bioretention facility.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
2.1 Bioretention Facility System
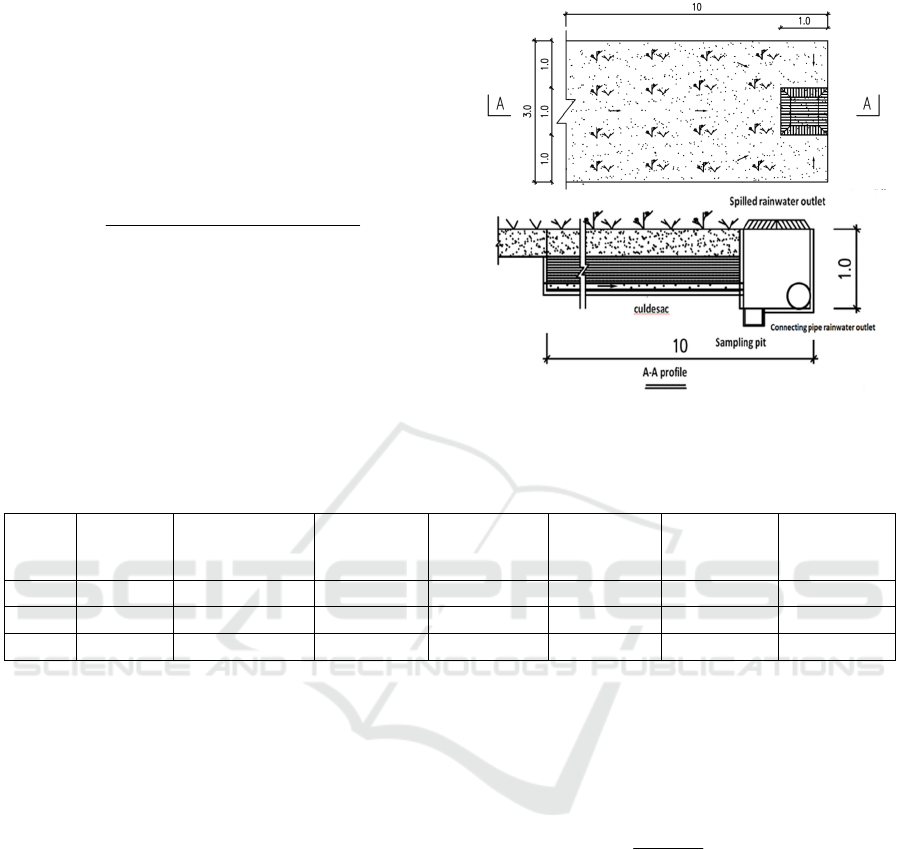
The biological retention facility is shown in Figure 1,
the size of the bioretention facility in this experiment
was 2.0m in length × 0.5m in width × 1.0m in depth,
and poplar and ryegrass were planted in the facility.
Each device from top to bottom are water storage
layer (10cm), planting soil layer (30cm), artificial
filler layer (60cm). Permeable geotextile is laid
between each filler medium. Perforated drainage
pipe is located at the bottom of the filler layer, and
the drainage pipe is wrapped by geotextile. Three
bioretention facilities (1#, 2# and 3#) were set up in
the experiment. There were only differences in the
artificial filler layer. The artificial filler layer was
sand + fly ash (volume ratio of 1:1), sand + green
zeolite (volume ratio of 1:1) and planting soil (Lin &
He, 2019).
2.2 Condition Setting of Test
Parameters
The effects of inflow rate, heavy metal (Cu, Zn, Cd)
concentration and rainfall interval on the reduction
of heavy metals in the system were investigated. The
inflow flow is reflected by the difference of rainfall
intensity, and other parameters (pollution
Jia, R., Li, J., Wang, Y. and Tang, D.
Study on the Reduction Effect of Bioretention Facility on Typical Heavy Metal Pollutants in Rainfall Runoff.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Water Resource and Environment (WRE 2021), pages 37-42
ISBN: 978-989-758-560-9; ISSN: 1755-1315
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
37
concentration is low, rainfall interval is 7days) are
consistent. The rainfall intensity is determined by the
rainstorm intensity formula (1) and the catchment
area of bioretention facilities in Xi’an. The designed
bioretention facility consumes 3 times of its own
surface area. The water calculation results are shown
in Table 1, and the rainfall intensity is determined
according to the road runoff monitoring results and
existing research (Chen et al., 2012; Dong, 2013).
9302.0
)813.16(
)lg1658.11(833.2785
t
P
q
FqQ
s
Formula:
q is the design rainstorm intensity [ L / (sꞏhm
2
) ].
P is the design recurrence period. T is rainfall
duration.
Qs is designed for rainwater flow (L/s).
ø is the runoff coefficient.
F is catchment area (hm
2
).
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of bioretention facilities.
Table 1: Water Quantity Calculation Table.
return
period
P/a
duration of
rainfall
t/min
rainfall intensity
q/(L/s.ha)
runoff
coefficientφ
catchment area
F/ha
designed
discharge
Qs/
(
L/s
)
design flow
V/L
Rainfall
mm
5 120 52.0922 0.9 0.0017 0.0798 573.7561 33.67
2 120 38.7762 0.9 0.0017 0.0594 427.2015 25.08
0.5 120 18.6300 0.9 0.0017 0.0287 205.3210 12.11
The concentration of heavy metals remained
constant during simulated rainfall. Cu, Zn and Cb
were selected as typical heavy metals with the
highest detection frequency and concentration in
Xi’an rainfall runoff process. The concentration of
heavy metals was set according to the monitoring of
pollutants in Xi’an rainfall (Guo, 2015; Davis et al.,
2009
)
. The concentration of heavy metals included
high and low concentrations. When the rainfall
interval is 7 days and the monitoring period is 5
years, the concentrations of three heavy metals were
Cu (CuCl
2
ꞏ2H
2
O), 0.1mg/L and 0.05mg/L. Zn
(ZnSO
4
ꞏ7H
2
O), 1.5mg/L and 0.8mg/L. Cd
(CdCl
2
ꞏ2.5H
2
O), respectively.0.05 mg/L and 0.03
mg/L. The rainfall interval was set to 3d, 5d and 7d,
the concentration of heavy metals was set at low
concentration, and the rainfall intensity was 2a.
2.3 Analysis Methods and Evaluation
Criteria of Heavy Metals
The concentration of heavy metal ions was
determined by flame atomic absorption spectrometry
(AAS), and the instrument was AAS Zeenit 700
atomic absorption spectrometer. The purification
effect of bioretention facilities is quantitatively
analyzed, and Ri represents the removal rate. The
calculation formula is as follows:
0
0
100
i
CC
R%
C
Formula:
C
0
is influent pollutant concentration, mg/L.
C is effluent pollutant concentration, mg/L.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Influence of Inflow Water on Heavy
Metal Reduction Rate of Biological
Retention Facilities
The influence of biological retention facilities on
heavy metal reduction under different influent
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
38
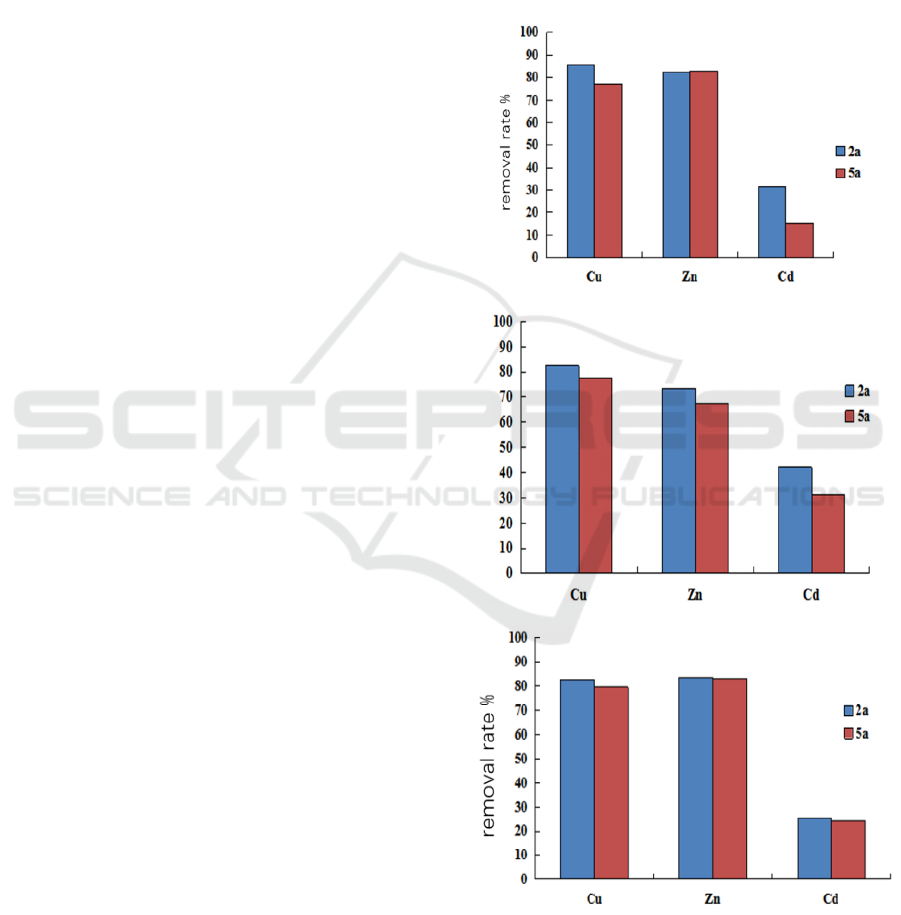
conditions is shown in Figure 2, under the rainfall
conditions corresponding to the 2a and 5a return
periods, the increase of inflow flow reduced the
reduction efficiency of heavy metals in the three
types of bioretention facilities, and the reduction
efficiency of the three heavy metals under different
inflow flow conditions showed Cu>Zn>Cd. Under
the two inflow conditions, the reduction efficiency of
Zn changed little, while the reduction efficiency of
Cu and Cd changed significantly, and the reduction
efficiency of the system decreased under large flow
conditions. This may be due to the increase of inflow
water, the hydraulic retention time in the
bioretention facilities, becomes shorter, and large
water will wash out the heavy metals adsorbed by
the biological retention matrix filler, resulting in the
increase of the concentration of heavy metal
pollutants measured in the effluent.
In the two-year return period, the removal rates
of Cu (>80%) in the three bioretention facilities were
higher than those in the other two heavy metals. The
Cu and Zn reduction efficiency of 1 # bioretention
device is higher. The removal rate of Cd was
obviously low. Davis proved through a series of
experimental studies that the type of matrix filler in
bioretention facilities had a great impact on the
removal effect of heavy metals, mainly because the
physical and chemical properties of matrix fillers
were different, and the removal effect and
mechanism of heavy metals were also different.
3.2 Effect of Influent Heavy Metal
Concentration on Heavy Metal
Reduction in Three Bioretention
Facilities
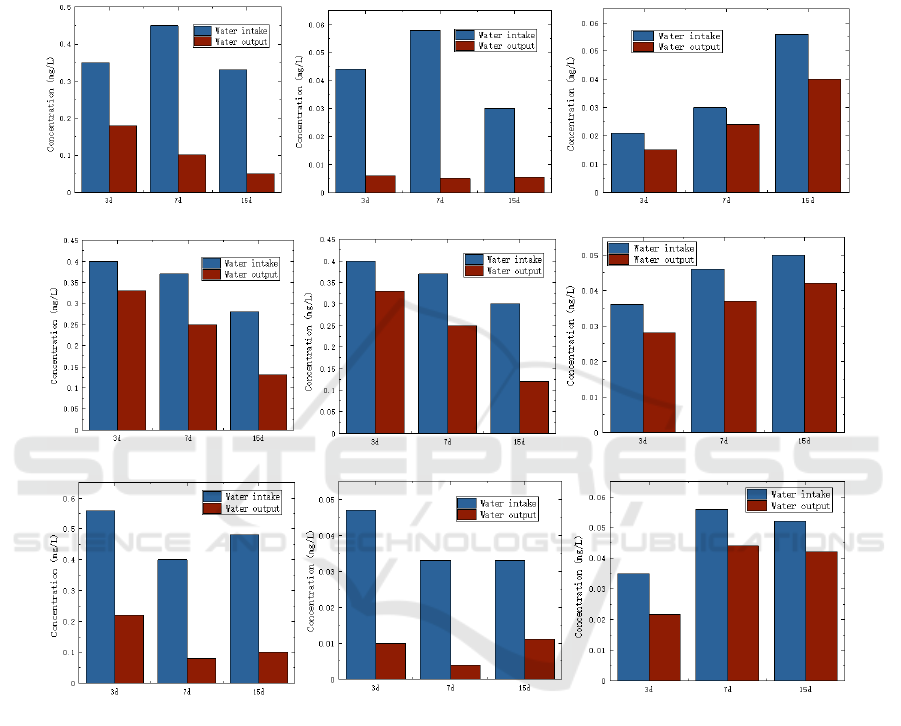
Under different concentrations of heavy metals, the
removal efficiency of heavy metals by bioretention
facilities with three kinds of fillers is shown in figure
3. In the 1 # bioretention facility, the reduction
efficiency of Cu and Zn was more than 70%, while
the reduction efficiency of Cd was significantly
lower (about 15%). The reduction efficiencies of Cu,
Zn and Cd in device 2# were significantly different
from those in device 1#, and the reduction rates from
high to low were Cu> Zn>Cd. The distribution of
heavy metal reduction efficiency in 3# plant is
similar to that in 1# plant. The reduction efficiency
of Cu and Zn is significantly higher, while the
reduction efficiency of Cd is 17-25%. Under the
condition of high concentration influent, the
reduction efficiency of heavy metals by bioretention
facilities was slightly lower than that under low
concentration influent, which may be mainly related
to the adsorption rate of fillers. When the
concentration of heavy metal ions in the influent is
high, the filler cannot adsorb all metal ions, so there
will be a large number of unabsorbed metal ions
discharged from the detention facilities with the
effluent. Comprehensive three types of bioretention
facilities can be concluded that the reduction
efficiency of 1# and 3# devices is higher, and the
reduction effect of 3# on Cd is obvious.
(a) 1#
(b) 2#
(c) 3#
Figure 2: Effects of three bioretention facilities on heavy
metal reduction under different inflow conditions.
Study on the Reduction Effect of Bioretention Facility on Typical Heavy Metal Pollutants in Rainfall Runoff
39

3.3 Effect of Rainfall Interval on Heavy
Metal
Reduction by Three
Bioretention Facilities
The reduction efficiency of heavy metals in
bioretention facilities with three fillers is
significantly different under different rainfall
intervals, as shown in Figure 4. The removal rate of
Cd in the three bioretention facilities had no
significant change with the increase of rainfall
interval time, and the reduction effect was
maintained at 15-25%, indicating that the length of
rainfall interval had little effect on the purification
effect of heavy metal Cd. The difference is that the
removal rates of Cu and Zn in the three bioretention
facilities have a relatively obvious change trend with
the rainfall interval. The reduction efficiency of Cu
in 1# device increases with the increase of the
interval, and the reduction efficiency can reach 88%
at the interval of 15 days, while the reduction
efficiency of Zn in different rainfall intervals is not
obvious, reaching the highest at 7 days. Cu and Zn
reduction efficiency of 2# device increased with the
increase of rainfall interval, and reached the
maximum reduction efficiency at 15d. The reduction
efficiencies of Cu and Zn in device 3# were like
those in device 1#, and the maximum reduction rate
of Zn (about 90%) appeared in the rainfall interval of
7d, while the reduction rate of Cu did not change
basically in the rainfall interval > 7d, and the optimal
reduction rate could reach 80%. Based on the results
of three types of bioretention facilities in different
inflow rates, influent concentrations, and rainfall
intervals, it can be concluded that the bioretention
facilities of 1# (sand + fly ash) artificial substrate
have better reduction efficiency and stability for
heavy metals.
(a) 1#
(b) 2#
(c) 3#
Figure 3: Effects of three bioretention facilities on heavy
metal reduction under different heavy metal
concentrations.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
(1) Bioretention facilities with different fillers have
different reduction effects on three typical heavy
metals. In the three types of systems, the reduction
effect of heavy metals from high to low is
Cu>Zn>Cd, and the reduction efficiency of Cu and
Zn is more than 70%, while the reduction efficiency
of Cd is significantly lower, and the efficiency is less
than 30%.
(2) Inflow rate, influent heavy metal
concentration and rainfall interval affected the
reduction effect of bioretention facilities on heavy
metals. Compared with the case when the rainfall
return period was 5a, the bioretention facilities had
higher purification efficiency for heavy metals when
the rainfall return period was 2a. The increase in the
concentration of heavy metals entering the
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
40
bioretention facilities will increase the metal content
in the effluent of the system, but the overall
reduction efficiency of the system is not significantly
affected. Higher rainfall intervals contribute to more
Cu and Zn reductions, while the reduction efficiency
of Cd fluctuates less in different intervals.
(3) The reduction effect of three types of filler
bioretention facilities on heavy metals from high to
low was 1#>3#>2#, indicating that sand + fly ash as
artificial matrix has better stability for heavy metal
reduction in bioretention facilities.
(a) 1#
(b) 2#
(c) 3#
Figure 4: Effects of three bioretention facilities on heavy metal reduction under different rainfall intervals.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the Key Research
and Development Program of Shaanxi Province
(2017ZDXM-SF-081).
REFERENCES
Chahal, M. K., Shi, Z., & Flury, M. (2016). Nutrient
Leaching and Copper Speciation in Compost
-Amended Bioretention Systems. Science of the Total
Environment, 556, 302-309.
Chen, H. J. (2020). The effects of different fillers on the
effects of biological retention facilities are described.
Jiangxi Chemical Industry, 6, 6-8.
Chen, Y., Zhao, J. Q., Hu, B., Liu, J., & Mao, H. Q. (2012).
First flush effect of urban trunk road runoff in Xi’an.
Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 6(3),
929-935.
Dong, W. (2013). Characteristics and control of non-point
source pollution in northwest China -- a case study of
Xi’an city. Xi 'an, Xi’an University of Technology.
Study on the Reduction Effect of Bioretention Facility on Typical Heavy Metal Pollutants in Rainfall Runoff
41

Davis, A. P., Hunt, W. F., & Traver, R. G. (2009).
Bioretention Technology, Overview of Current
Practice and Future Needs. Journal of Environmental
Engineering, 135(3),109-117.
Ellis, J. B., Revitt, D. M., Harrop, D. O. (1987). The
contribution of highway surfaces to urban stormwater
sediments and metal loadings. Science Total
Environment, 59, 339-349.
Guo, W. J. (2015). Research on Urban Rainfall-runoff
Pollution Characteristics and Load Estimation in Xi`an.
Xi 'an, Xi’an University of Technology.
Lin, Z. Z., & He, Q. M. (2019). Composition of
Bioretention System and Optimization of Engineering
Design Parameters. Water Purification Technology,
38(12), 116-121.
Pan, J. K., Liu, Y., Qu, Y., & Gao, J P. (2020). Removal
effect of compound packing biological retention
facility on runoff pollutants. The people of the Yellow
River, 42(08), 93-99.
Wu, R. F. (2006). Urban stormwater runoff pollution
control technology. Industrialsafety and environmental
protection, 32(02), 41-42.
Zhang, T., Feng, Y., He, M. Z., Gu, Z. G., & Bai, X.
(2020). Filling Layer’s Optimal Ratio of Bioretention
Facilities Based on Removal Effect of Nitrogen and
Phosphorus in Initial Rainwater Runoff. China Rural
Water and Hydropower, 6, 82-86.
Zhang, S., Li, J. Q., Li, X. J., & Sun, Y. (2021) Reduction
Effect of Bioretention on Urban Stormwater Runoff
Thermal Pollution. China Water & Wastewater,
37(03), 116-120.
Zhou, S. Y. (2021). Review on Rainwater Runoff Control
by Bioretention Facilities. Tianjin Construction
Science and Technology, 31(06), 7-11.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
42
