
The Study on Tomato with Different Planting Patterns in Coastal
Saline-Alkali Land
Songgan Weng
*1
, Jun Wang, Yihong Wang, Wang Wu and Xinyuan Zhang
Jiangsu Hydraulic Research Institute, 97 Nanhu Road, Nanjing 210017, China
Keywords: Coastal saline-alkali land, Greenhouse, Planting patterns, Ridge planting, Root-limiter
Abstract: In this paper, the plants’ height, yield of tomato and soil surface conductivity were studied under drip
irrigation conditions in greenhouses, with three planting patterns: root-limiter planting, ridge planting
without film, and ridge planting with film-mulching. The result showed that the planting pattern had a
significant impact on the height and yield of tomato. Comparing to the ridge with non-film planting,the
plants of ridge with film-mulching were 6.5 cm taller. The average yield per plant with root-limiter was
1018.0g, and the ridge without film was 650.0g barely. The root-limiter was better than the ridge-planting as
a whole. Compared with the soil surface conductivity before planting, the root-limiter, ridge with
film-mulching, as well as ridge without film increased the conductivity of the soil by 2.0%, 5.2%, and
22.0%, respectively. In summary, ridge with film-mulching could achieve higher yields with the use of drip
irrigation for greenhouses with mild salinization. Root-limiter with off-soil could maximize the overall
benefits for greenhouses with more severe salinization.
1
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2122-8576
1 INTRODUCTION
Saline-alkali land is widely distributed in China, and
it has weak environmental carrying capacity. These
factors limit the sustainable development of
economic, social, and ecological environment. At the
same time, saline-alkaline soil is an important
reserve resource of arable land in China.
Saline-alkaline soil management and agricultural
utilization play an important role in ensuring the
absolute safety of rations, maintaining the stability of
existing arable land, and adhering to the safety
bottom line of basic food self-sufficiency (Liu et al.,
2021; Liu, 2021).
In recent years, facility agriculture has been
greatly developed, among which facility vegetables
represented by greenhouses have developed the
fastest (Qiao & Wang, 2021;
Gao & Lu, 2021;
Zhang, 2011). However, it has brought increasingly
serious soil problems with the long-term relatively
closed production environment. The soil salinization
has become most apparent with the using of
greenhouses. It was mainly composed of coastal
saline soil, tidal saline soil, and fluvo-aquic soil in
coastal saline-alkali land.
With the high groundwater level and high salt
content, it has led to the salinization of greenhouse
soil, and appeared massive, quick and harmful. Some
greenhouses have been invalid and unsuited to
planting only 1 to 2 years (Lu et al., 2009). There
was little effect to inhibition the raise of the
groundwater level and salt-accumulation, with the
traditional fresh-water irrigation (Li & Wang, 2007).
Therefore, the appropriate planting method was of
great significance to alleviate the salinization of
greenhouses planting areas in the coastal area.
The drip irrigation has the characteristics of high
frequency, small flow and long time, among many
planting methods. It could leach soil salinity, and
then enhance the absorption of water by plant roots,
which effectively preserves moisture, and improve
saline-alkali land (Dou & Kang, 2010). The
film-mulching planting could effectively reduce soil
surface evaporation, maintain soil moisture and
inhibit the accumulation of salt to the soil surface
(Jiao et al., 2008). The root-limiting cultivation has
been a trial to introduce in the saline-alkali
cultivation. The ridge cultivation with root-zone
414
Weng, S., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Wu, W. and Zhang, X.
The Study on Tomato with Different Planting Patterns in Coastal Saline-Alkali Land.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Water Resource and Environment (WRE 2021), pages 414-418
ISBN: 978-989-758-560-9; ISSN: 1755-1315
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

restriction cultivation could effectively improve the
survival rate of seedlings of Chinese wolfberry in
medium-to-severe saline-alkali soils (Jin et al., 2021).
In the light of the soil salinization, it has a great
significance in the choice of suitable planting
method in the coastal soil salinization areas.
In this paper, we have studied the effect on
tomato growth and soil surface conductivity with
three planting method under drip irrigation
conditions. The structure of the paper is as follows.
Materials and Methods are described in Section 2.
Results are discussed in Section 3. Section 4
contains concluding remarks.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Experimental Site
The experiments were conducted in the greenhouse
of the coastal experiment base of Jiangsu hydraulic
research Institute in 2020, Jiangsu. The annual
average temperature was 14.5℃, wind-speed was
3.3 m/s, and the annual average sunshine-hour was
2231.9 h. There was a large disparity in rainfall
during the flood season and non-flood season, 733.4
mm in the flood season and 331.8 mm in the
non-flood season. It was prone to drought and flood
disasters. The soil in the experiment area belonged to
coastal siltation sandy soil with light saline-alkaline
and strong water permeability, which was easy to
reach saturation during precipitation.
2.2 Experimental Material
The tested crop was tomato, and the variety was
Cooperative 903 Royal Scarlet. It was planted on
April 8, 2020, harvested began in mid-June, and
pulled up straw in late August.
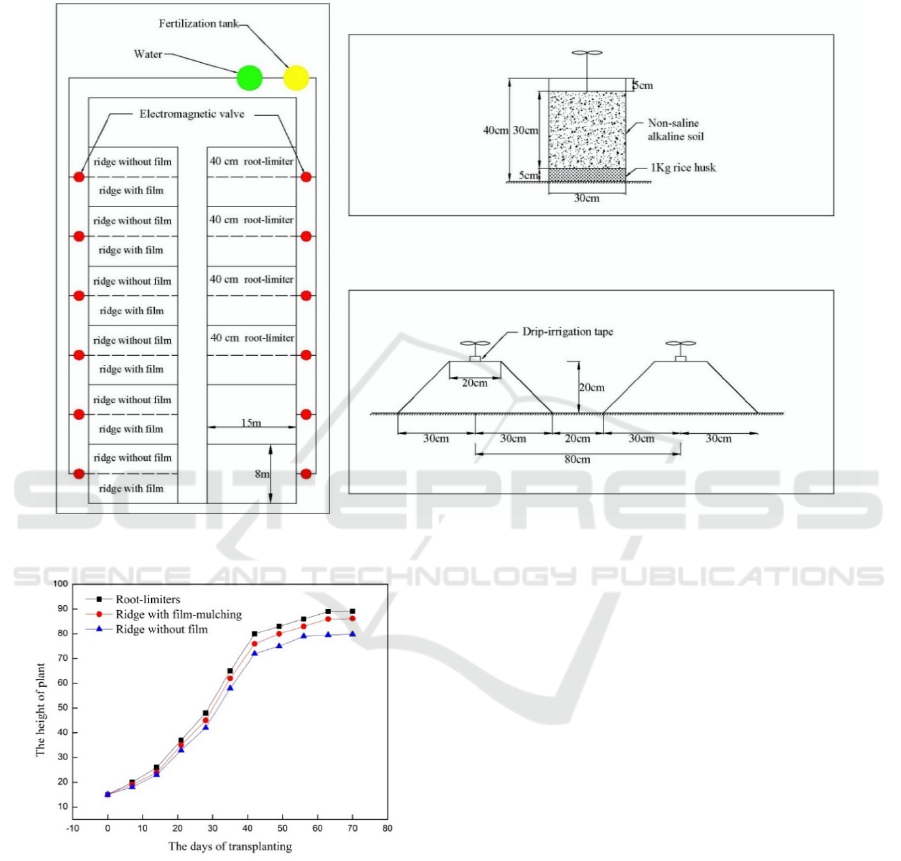
2.3 Experimental Setup
The experiment was carried out in a glass
greenhouse, and the temperature was strictly
controlled to reduce the influence of uneven
temperature. There were three planting methods
(Figure 1), including root-limiter, ridge with
film-mulching, and ridge without film. The
fertilization and irrigation conditions were the same
in the three planting methods. The isolation belts and
protection lines were set up between the plots.
Root-limiter planting: The high of root-limiter
was 40 cm and the diameter was 30 cm. The
root-limiter was filled with 1 kg rice husk at the
bottom, and non-saline alkaline soil was loaded on
the rice husk. The spacing between rows of plants
was 80 cm, and the spacing between plants was 50
cm.
Ridge planting: There were 20 tomatoes in each
row, with single ridge and single row. The height of
ridge was 20 cm, the top width of ridge was 20 cm,
the bottom width of ridge was 60 cm. There was
80cm between the spacing of ridge. There was a drip
irrigation tape arranged for each row of crops. The
distance between the emitters was 50 cm, and the
flow rate of emitter was 1.5 L/h.
2.4 Experimental Parameters and
Methods
The conductivity of the lower layer soil under
different planting methods was measured by a
portable conductivity meter. The samples were
prepared with a ring knife. The plant height of
tomato was measured every 7 days with a tape
measure, after tomato transplanting. The yield of
plant was weighed independently at the harvest time.
There were 30 plants randomly measured with each
planting method.
2.5 Experimental Data Processing
The SPSS Statistics software was used to calculate
the standard error and variance analysis of the
experimental data. Therefore, the Origin software
was used for drawing.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 The Effect of Plant Height with
Different Planting Methods
3.1.1 The Effect on the Growth Rate of Plant
Height
The growth regularity of tomato planted with
root-limiters showed a trend of slow growth first,
then rapid growth, and finally stable, in Figure 2.
Within 21 days, the plant height increased rapidly,
with an average increase of 22 cm and a growth rate
of 0.79 cm/d. From 21 to 42 days, it was a rapid
growth stage, with an average increase of 43 cm and
a growth rate of 2.05 cm/d. From 42 to 70 days, the
growth rate of plants tended to be stable, with an
average increase of 9.1 cm, and the growth rate was
0.33 cm/d.
The Study on Tomato with Different Planting Patterns in Coastal Saline-Alkali Land
415
The growth trend of ridge-planting was basically
the same as root-limiter planting. In the first 21 days,
the height of tomato increased by an average of 20
cm, and the growth rate was 0.54 cm/d. From 21 to
42 days, it grew with an average increase of 42 cm
and the growth rate was 2.00 cm/d. From 42 to 70
days, the growth rate of crops represented an average
increase of 10.2 cm, and the growth rate was 0.36
cm/d.
Figure 1: The layout of experimental area with different planting methods.
Figure 2: The influence of plant height on tomato with
different planting methods.
In summary, the plant height raised the fastest
with the root-limiter planting method. During
full-growth period, the law of the plant height and
the growth rate with three planting methods
expressed as root-limiter > ridge-planting with film >
ridge-planting without film.
3.1.2 The Effect on the Final Plant Height
The growth rate of plant height with different growth
stages and different planting methods was different,
which resulted in different final plant heights.
Comparing to ridge planting and ridge planting
without film, the final plant height of tomatoes
planted with root-restrictor planting during the whole
growth period was the highest. The tomato with
root-limiter was 4.0 cm and 9.5 cm taller than the
ridge-planting with film and ridge-planting without
film, respectively. The reason was that the rice husk
blocked the penetration of salt and the root-limiter
was filled in off-site soil with low salt content. In the
first 21 days, there was little difference in plant
height of tomato planted with two ridge-planting
methods. The temperature was relatively low in the
greenhouse, and the evaporation was small. The soil
salinization was not obvious, and soil salinity has
little effect on plant growth in the early stage of
planting. Furthermore, the tomato plants were small,
with less water required in the early stage of planting.
From 21 to 42 days, the difference in plant height
gradually increased between the two ridge-plantings.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
416

The tomato plants of ridge with film-mulching were
6.5 cm taller, comparing to the ridge with non-film
planting. The plant's water-demand and
transpiration-evaporation were enhanced with the
temperature rising in the greenhouse. Based on the
same irrigation system, the water retention capacity
of ridge with film-mulching was better than that of
ridge without film. In summary, root-limiter planting
and ridge with film-mulching could promote the
growth of tomatoes, and root-restrictor planting was
the more prominent among the three planting
methods.
Figure 3: The influence of tomato yield with different
planting methods.
3.2 The Effect on Plant Yield with
Different Planting Methods
It showed that the planting method had a greater
impact on yield of tomato in Figure 3. Root-limiter
and ridge-mulching planting performed better than
ridge without film. The average yield per plant with
root-limiter was 1018.0g, which performed the
highest. The average yield per plant with
ridge-mulching was 976.1g, and the ridge without
film was 650.0g barely.
According to one-way ANOVA(Analysis of
variance) of planting method and tomato yield, the
planting method had a significant impact on tomato
yield(P < 0.001, The P value is the probability,
which reflects the probability of occurrence of an
event). The result of analysis of variance showed
that there was no significant difference between
root-limiter and ridge-mulching, and it was
significantly different compared to the ridge without
film. The yield of plant was mainly determined by
the input of water and assimilation substances.
Furthermore, the accumulation of salt in the surface
lowered the yield of tomato with ridge without film.
3.3 The Effect on Soil Conductivity
with Different Planting Methods
The conductivity of surface soil was 315.6μs/cm
with the root-limiter at the end of the growth period,
and increase range was 2.0% according to
non-planting (Figure 4). At the same time, the ridge
with film-mulching appeared 803μs/cm and 5.2%, as
well as the ridge without film appeared 803μs/cm
and 22.0%. The conductivity of the surface soil had
small increases during the tomato growth period
with root-limiter and ridge with film-mulching. In
contrast, the conductivity increased greatly with
ridge without film. It showed that the difference
between planting and non-planting was significant,
and the salinification of soil was obvious.
Figure 4: The effect on soil conductivity with different
planting methods.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The plant’s height and yield of tomato with different
planting methods in coastal saline-alkali land were
studied in the paper. It was concluded that the plant’s
height and yield with root-limiter performed the best
among three planting methods, and the ridge with
film-mulching was better than the ridge without film.
According to the conductivity, the planting with
root-limiter and ridge with film-mulching could
inhibition the salinification of soil.
In conclusion, the ridge with film-mulching
planting could be adopted in the greenhouse of
low-salinization with drip irrigation. The root-limiter
planting with external-soil could be applied in the
greenhouse of heavy-salinization.
The Study on Tomato with Different Planting Patterns in Coastal Saline-Alkali Land
417

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The paper is funded by the Water Resources Science
and Technology Project of Jiangsu Province (Grant
No. 2019040).
REFERENCES
Dou, C. Y., & Kang, Y. H. (2010). Characteristics of soil
salinity distribution in saline-sodic soil with shallow
water table under mulch-drip irrigation in different
planting years. Soils, 42, 630-638.
Gao, Q., & Lu, N. (2021). Current status and prospect of
research on comprehensive management and
development of saline-alkali land. Application of New
Technology, 52(16), 153-155.
Jiao, Y. P., Kang, Y. H., Wan, S. Q., Sun, Z. Q., Liu, W.,
& Dong, F. (2008). Effect of soil matric potential on
the distribution of soil salt under drip irrigation on
saline and alkaline land in arid regions. Transactions
of the CSAE, 24(6), 53-58.
Jin, W., & Wang, H., et al. (2021). Movement of soil water
and salt of drip irrigation under different ridge
cultivation methods with root domain restrictions.
Northern Horticulture, 9, 93-103.
Li, C. M., & Wang, Y. B. (2007). Research on status and
influencing factors of soil salinization in Ningxia
Yellow-River irrigation area. Ground Water, 29,
41-44.
Liu, M., & Wang, Z. C., et al. (2021). Application progress
of biochar in amelioration of saline-alkaline soil.
Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 35, 1-8.
Liu, L. N. (2021). Improvement effects of several control
measures on saline-alkali soil in Northern Shanxi
Province. Shanxi Forestry Scinence and Technology,
50, 36-38.
Lu, J. Y., Cao, Y., & Sun, X. M. (2009). The prevention
and control of salt damage in greenhouse soil.
Northwest Gardening of China, 1, 44.
Qiao, Y. H., & Wang, Y. H. (2021). The effect of NyPa
forage on soil improvement of coastal saline-alkali
land. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 37, 67-72.
Zhang, M. (2011). Reasons and solutions for rapid
salinization of soil in greenhouses in Yancheng.
Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 6,
261-264.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
418
