
Effect of Chemical Conditioning of Sewage Sludge on Dewatering
Performance and Structural Components
Tian Wan
1,*
, Chuanrui Li
1
, Xiaokang Ju
2
, Xingxing Yan
1
, Min Wang
1
, Jiehui Ren
1
, and Wen Cheng
1
1
State Key Laboratory of Eco-hydraulics in Northwest Arid Region of China, Xi’an University of Technology, No.5, South
Jinhua Road, Xian, Shaanxi, 710048, P.R. China
2
The third reclaimed water plant of Xi'an water purification Co., Ltd, Xi 'an, China
Keywords:
Excess sludge, dewatering performance, Extracellular polymer, fractal dimension
Abstract: Chemical conditioning is a commonly used sewage sludge pretreatment method of dewatering in wastewater
treatment plants. As a result of a large number of chemicals used, the cost of sewage treatment plants increased,
and negative environmental impact might be happened. Therefore, it is necessary to illustrate the dewatering
performance and structural components during chemical conditioning, in order to control the dosage of
chemicals. In this paper, the excess sludge was treated by cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM). The physical and
chemical properties of excess sludge were analyzed. The moisture content of sludge filter cake, the change of
moisture distribution, the specific resistance of filtration, and capillary suction time (CST) of sludge were
used as dewaterability parameters. The Zeta potential and particle size of sludge were measured, and the
change of fractal dimension was analyzed. The changes of protein and polysaccharide content in extracellular
polymeric substances (EPS) during conditioning were explored. Results showed that with the optimal CPAM
dosage of 0.225 g/L, the moisture content of sludge cake reached 70.19 %, the specific resistance of sludge
was 0.15×1012 m/kg, and CST was 6.45s. After conditioning, the Zeta negative electricity decreased, the
particle size increased, the fractal dimension increased, and the contents of protein and polysaccharide in EPS
increased. Tight EPS (TB-EPS) was released to loosen EPS (LB-EPS) and dissolved EPS (S-EPS), indicating
that cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) can effectively improve the dewatering performance of sludge.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid development of urbanization and
industrialization, the total amount of sewage
discharge and the output of municipal sludge in China
have increased significantly. The disposal and
management of sewage sludge is urgent. High
moisture content in excess sludge causes a huge
volume, which is the mainbottleneck problem for
effective disposal (Zhou et al., 2014). Dewatering
was known as the most useful approach to improve
the treatment and reuse of excess sludge.
Conditioning is commonly used as pretreatment
method to increase the sludge cake volume (Zhen et
al., 2018). Among various conditioning methods,
chemical coagulants such as ferric and aluminum
salts and bioflocculant are the most commonly
method to improve sludge dewatering performance in
wastewater treatment plant, due to the easy operation
(Guo et al., 2021). However, large number of
chemical coagulants have great negative impact on
disposal equipment, and huge adding dosage also
increases the operation cost of WWTP.
Compared with inorganic coagulants, organic
polymer coagulants have the advantages of small
consumption, safe treatment, simple operation, weak
acidity or weak alkalinity in water and small
corrosiveness in sludge conditioning. Cationic
polyacrylamide (CPAM) is a typical and common
organic polymer coagulant. CPAM conditioning
greatly improved the dewatering performance of
sludge (Wu et al., 2021). Guo et al (2020). found that
CPAM was a chain polymer with a large number of
positive charge groups, which is opposite to the
charged property of surplus sludge and can play its
electric neutralization role. Moreover, CPAM has
high characteristic viscosity and strong adsorption
and bridging effect on sludge particles.
EPS plays an important role in the water capacity
of sludge, and a large amount of combined water in
sludge is in EPS. (Guo et al., 2021). CPAM had a good
promoting effect on proteins in EPS (Bi et al., 2015).
440
Wan, T., Li, C., Ju, X., Yan, X., Wang, M., Ren, J. and Cheng, W.
Effect of Chemical Conditioning of Sewage Sludge on Dewatering Performance and Structural Components.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Water Resource and Environment (WRE 2021), pages 440-448
ISBN: 978-989-758-560-9; ISSN: 1755-1315
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

As an organic colloidal substance, CPAM was
adsorbed on the outside of cells. The surface of
activated sludge EPS was negatively charged, and
CPAM combined with the negative functional groups
on proteins to promote the secretion of proteins by
cells.
Although a lot of research has been done on
sludge dewatering and conditioning, it is difficult to
further improve the sludge dewatering performance
due to the lack of understanding of the structural
component changes in sludge conditioning process.
Therefore, it is necessary to illustrate the changes
mechanisms of components and properties of sludge
flocs, such as surface charge, particle size distribution
fractal division.
Based on this, CAPM is used as conditioner to
adjust the excess sludge to improve the sludge
dewatering performance. The relationship between
sludge structure and dewatering performance was
studied by measuring the specific resistance of
sludge, moisture content of sludge cake, capillary
suction time and the change of sludge water transfer
law and fractal dimension during conditioning. At the
same time, in order to further explore the mechanism
of CPAM on improving the dewatering performance
of excess sludge, Zeta potential and EPS component
changes in excess sludge were measured and
analyzed. The implementation of this study will
contribute to the improvement of sludge dewatering
and thus the management of wastewater treatment
plants.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Sources and Basic Properties of
Experimental Sludge Samples
The sludge used in the experiment was taken from the
surplus sludge of the second sedimentation tank of
Xi'an No. 4 sewage treatment plant and stored in a
refrigerator at 4℃after being retrieved. Table 1 shows
the basic physical and chemical properties of the raw
sludge in this experiment. At least three parallel
samples were taken for each characteristic index, and
it was found that there was no significant change in
the characteristics of sludge sampled three times
during the experiment.
Table 1: Basic physicochemical properties of raw sludge.
moisture content
%
organic
matter
%
Specific resistance of filtration
×10
12
m/kg
CST
s
Zeta potential of supernatant
mV
Redox potential
mV
L1 96.12 36.34 0.45 23.25 -18.93 -280.0
L2 96.07 36.30 0.49 23.21 -18.71 -280.3
L3 96.15 36.52 0.53 23.74 -19.14 -280.2
The scanning electron microscope was used to
observe the raw sludge, as shown in Figure 1. The
internal structure of the raw sludge is composed of
granular and dense particles, and the surface is
relatively smooth, complete and basically non-
porous.
SEM can qualitatively describe the sludge floc
structure. The effect of CPAM conditioning on the
surface structure of sludge flocs was analyzed.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to
observe the raw sludge and CPAM treated sludge. As
shown in Figure 1, the internal structure of the raw
sludge is composed of dense granular particles with
smooth surface and complete block structure. After
CPAM conditioning, the internal pore structure of
sludge particles is more abundant, and it is easier for
water to flow out, so the filtration performance is the
best.
2.2 Main Instruments and Reagents
Six-axis mixer (JJ-4, Changzhou Zhiborui Instrument
Manufacturing Co, LTD.); Uv-visible
spectrophotometer (DR5000, Hach Company);
Electronic Balance (CP213, Ohaus Instrument Co,
LTD.); Specific resistance of filtration measuring
device (TG-250, Shanghai Tongguang Science and
Education Instrument Co, LTD.); Zeta potential
Analyzer (ZS90, Malvern); Fluorescence
spectrophotometer (F-7000, Hitachi); Laser particle
size analyzer (BT-9300S, Dandong Baxter
Instrument Co, LTD.).
Cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM), sodium
hydroxide (NaOH), anthrone (C14H10O),
concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4), Folin-phenol
reagent, glucose and potassium dichromate
(K2Cr2O7) were analytically pure.
Effect of Chemical Conditioning of Sewage Sludge on Dewatering Performance and Structural Components
441
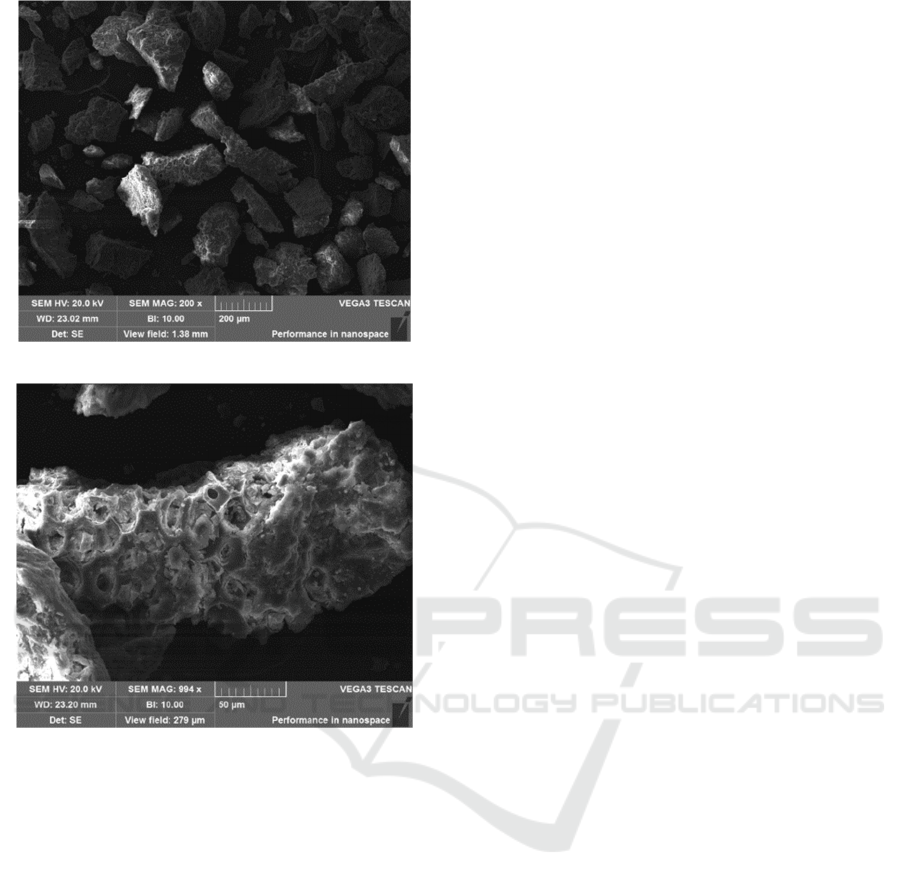
(a) Raw sludge 200 μm
(b) CPAM treated sludge 50μm
Figure 1: Caption to Scanning electron microscope (SEM)
images of raw sludge.
2.3 Experimental Methods
Six 250 mL conical bottles were added to 100 mL of
surplus sludge, and 0.0375, 0.075, 0.15, 0.225, 0.3,
0.375 g/L of 0.3% CPAM solution were added,
respectively, stirring at 300 r/min for 5 min. After
conditioning, the sludge dewatering index was
determined; The composition and distribution of
sludge EPS were analyzed. At least three groups of
parallel samples were set up in each experiment.
2.4 Analysis Method of Experimental
Indexes
In this experiment, 12 million CPAM was configured
into 0.3% solution for determination, and the brinell
funnel method was used to determine specific
resistance of filtration. The moisture content of
sludge was determined by gravimetric method
(Klomklao et al., 2017); The particle size distribution
of sludge was determined by laser particle size
analyzer (Zeng et al., 2019).
Modified Folin-Lowry method and anthrone-
sulfuric acid method were used to determine the
concentration changes of proteins and
polysaccharides in EPS before and after sludge
conditioning. Extraction of EPS from Sludge by
NaOH method (Sun et al., 2017), and the residual
cells and other substances in the extract were
removed by 0.45μm filter membrane.
A fluorescence spectrophotometer (F-7000,
Hitachi) was used to determine the three-dimensional
fluorescence spectrum. The parameters were set as
the excitation wavelength (Ex) was 240 ~ 550 nm, the
emission wavelength (Em) was 260 ~ 600 nm, the
step length was 4 nm, and the slit width was 3 nm.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Effect of Cationic Polyacrylamide
Conditioning on Sludge Dewatering
Performance
The influence results of moisture content and
moisture distribution of sludge cake under different
dosage of CPAM are shown in Figure 2. As can be
seen from Figure 2, with the increase of CPAM
dosage, the moisture content of mud cake decreased
first and then increased. When the dosage of CPAM
was 0.225 g/L, the moisture content of mud cake
reached the lowest value of 70.19%, and the reduction
rate was 26.99%. With the increase of CPAM dosage,
the proportion of free water in sludge firstly increased
and then decreased, and reached the maximum value
of 80.08% when CPAM dosage was 0.225 g/L. The
change trend of bound water was just opposite to the
change of free moisture content, which reached the
minimum value of 19.92% when CPAM dosage was
0.225 g/L. The reason for this phenomenon may be
that sludge particles become unstable under the action
of electrical neutralization and aggregate into flocs,
which gradually form larger flocs through the action
of long chain bridge and net capture of flocculant, and
then settle under the drive of gravity and external
force(Wang et al., 2014).The low dosage of
flocculant leads to the weak effect of electric
neutralization, which is insufficient to make most of
the suspended sludge particles accumulate and settle.
Excessive flocculant will lead to electrostatic effect
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
442
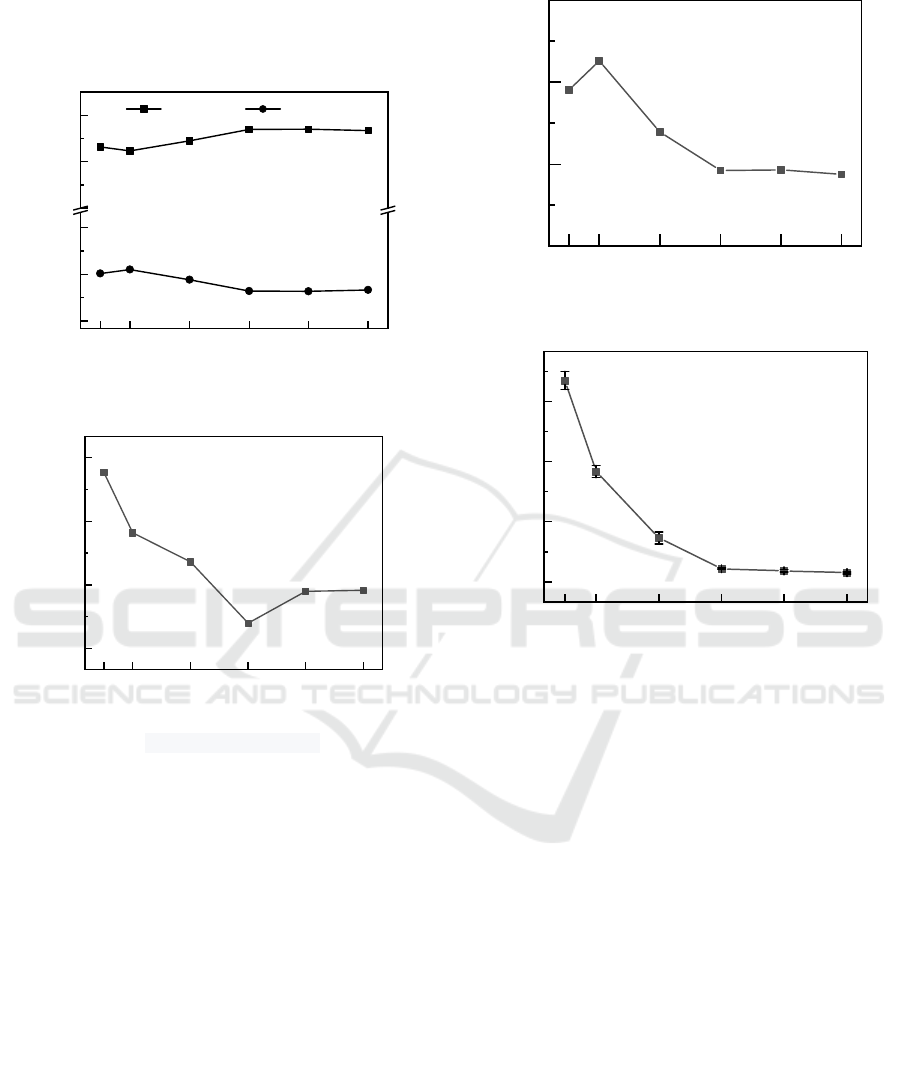
and certain space between particles, which can restore
the stability of sludge particles and fail to achieve the
effect of flocculation and dehydration.
(a) Sludge moisture distribution
(b) Sludge moisture content
Figure 2: Caption to Effect of different CPAM dosage.
The changes of specific resistance and CST under
different CPAM dosage were shown in Figure 3. With
the increase of CPAM dosage, the specific resistance
of sludge first increased, then gradually decreased to
the minimum value and remained basically
unchanged. When the CPAM dosage was 0.225 g/L,
the specific resistance reached the minimum value of
0.15×10
12
m/kg, and the reduction rate was 66.67 %.
With the increase of CPAM dosage, CST gradually
decreased to the minimum value and remained
basically unchanged. When the CPAM dosage was
0.225 g/L, CST reached the minimum value of 6.45 s,
and the reduction rate was 72.26 %. The sludge
dewatering performance was significantly improved.
(a) Specific resistance of filtration
(b) Capillary suction time
Figure 3: Caption to Effect of different CPAM dosage.
3.2 Analysis of Sludge Zeta Potential,
Particle Size and Fractal Dimension
The change of Zeta potential of sludge after CPAM
conditioning was shown in Figure 4(a). With the
increase of CPAM dosage, the Zeta potential
increased first and then decreased, and reached the
maximum value of -12.07 mV when CPAM dosage
was 0.225 g/L. The Zeta potential determines the
flocculation and sedimentation performance of
colloidal particles, and the decrease Zeta potential
negative electricity indicates that the dewatering
performance of sludge has been improved (Hiroyuki,
2019).
It can be seen from Figure 4(b) that with the
increase of CPAM dosage, the repulsion between
sludge flocs decreases, and the particle size of sludge
particles increases, which strengthens the adsorption
bridging effect of sludge flocs (Dai et al., 2018) .The
fine sludge particles after conditioning firstly
destabilise and aggregate through the effective
0
.
0
3
7
5
0
.
0
7
5
0
.
1
5
0
.
2
2
5
0
.
3
0
.
3
7
5
18
21
24
75
78
81
Proportion of water distribution/
%
()
Polyacrylamide dosage/ g/L
Free water Bound water
0
.
0
3
7
5
0
.
0
7
5
0
.
1
5
0
.
2
2
5
0
.
3
0
.
3
7
5
69
72
75
78
Moisture content of mud cake/
%
()Polyacrylamide dosage/ g/L
0.
03
75
0
.
07
5
0
.
1
5
0
.
22
5
0
.
3
0
.
3
7
5
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
(
SRF/ ×10
12
m
.
kg
-1
)
(
Polyacrylamide dosage/ g/L)
0
.
0
3
7
5
0
.
0
7
5
0
.
1
5
0
.
2
2
5
0
.
3
0
.
3
7
5
6
9
12
15
CST/s
()
Pol
y
acr
y
lamide dosa
g
e/
g
/L
Effect of Chemical Conditioning of Sewage Sludge on Dewatering Performance and Structural Components
443
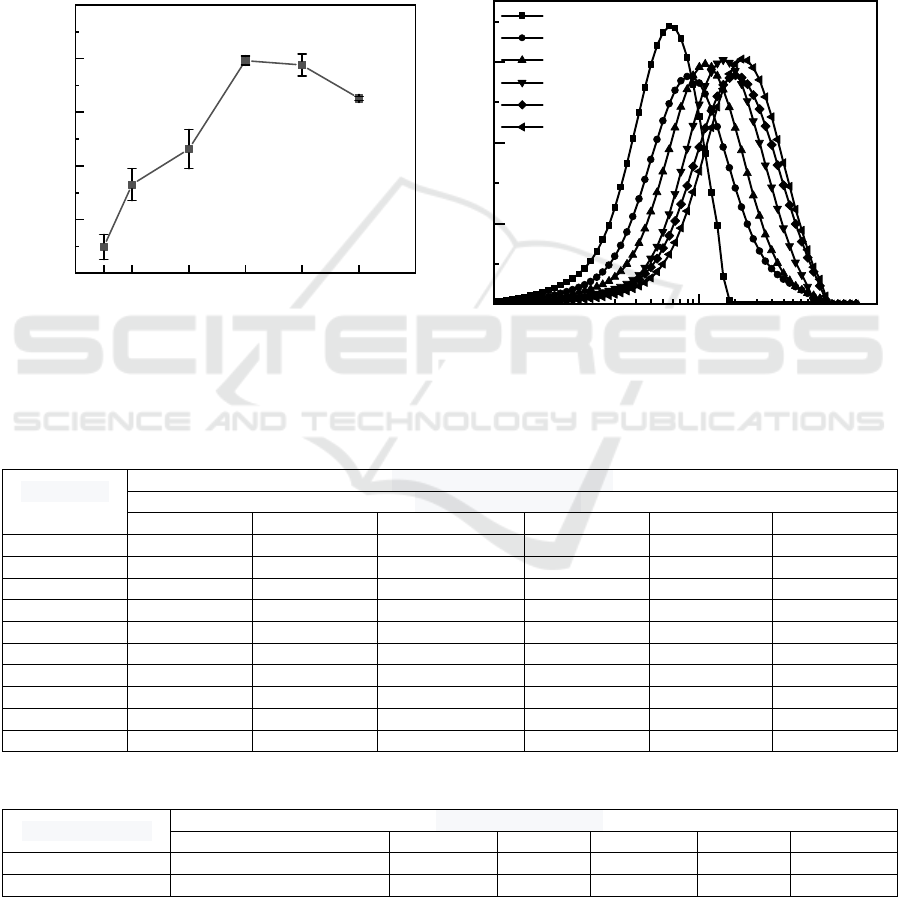
electroneutralization of CPAM, and then form large
and dense sludge flocs under the action of net capture
and sweep between long-chain polymer molecules
with large specific surface area. The large and dense
floc structure determines its excellent settlement
performance.
The cumulative yield under the sieve under
different CPAM dosages is shown in Table 2. The
grain size-cumulative yield under the sieve is drawn
in the log-log coordinate system, and its slope value
B is obtained after fitting. The fractal dimension D of
sludge can be calculated according to the formula D
= 3-b, as shown in Table 3. Fractal dimension is a
measure of fractal irregularity (Li et al., 2020). The
higher the value of D, the more compact the flocs
(Tang et al., 2020). As can be seen from Table 3, with
the increase of CPAM dosage, the fractal dimension
D also gradually increases, indicating that the sludge
dewatering performance becomes better after CPAM
conditioning
.
(a) zeta potential (
b
)
p
article size of sludge
Figure 4: Caption to Effect of different CPAM dosage.
Table 2: Distribution of cumulative yield under screen at different CPAM dosages.
Particle size
/μm
Cumulative yield under screen/%
CPAM dosin
g
q
uantit
y
g
/L
0.0375 0.075 0.15 0.225 0.3 0.375
5 0 0.09 0.13 0.34 0.55 1.96
10 0.28 0.68 0.76 1.39 2.09 4.69
30 1.96 4.77 4.24 7.56 12.57 25.13
50 4.57 8.16 8.44 15.99 25.91 47.57
70 8.33 15.33 15.07 27.13 40.15 66.06
100 15.66 20.76 26.64 42.99 56.93 84.18
300 71.22 71.87 81.54 90.58 92.97 98.04
500 88.33 88.49 94.24 96.83 96.95 98.04
1000 100 99.96 99.87 99.66 99.45 98.04
2000 100 100 100 100 100 100
Table 3: Fractal dimension of sludge after CPAM conditioning.
Fractal dimension
CPAM dosin
g
q
uantit
y
g
/L
0.0375 0.075 0.15 0.225 0.3 0.375
b
1.14 1.13 1.11 0.94 0.84 0.63
D 1.86 1.87 1.89 2.06 2.16 2.37
0
.
0
3
7
5
0
.
0
7
5
0
.
1
5
0
.
2
2
5
0
.
3
0
.
3
7
5
-20
-18
-16
-14
-12
-10
()Pol
y
acr
y
lamide dosa
g
e/
g
/
L
Zeta potential/mV
10 100 1000
0
2
4
6
T
h
e percentage
/%
Particle size/
μ
m
0.0375 g/L
0.0750 g/L
0.1500 g/L
0.2250 g/L
0.3000 g/L
0.3750 g/L
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
444
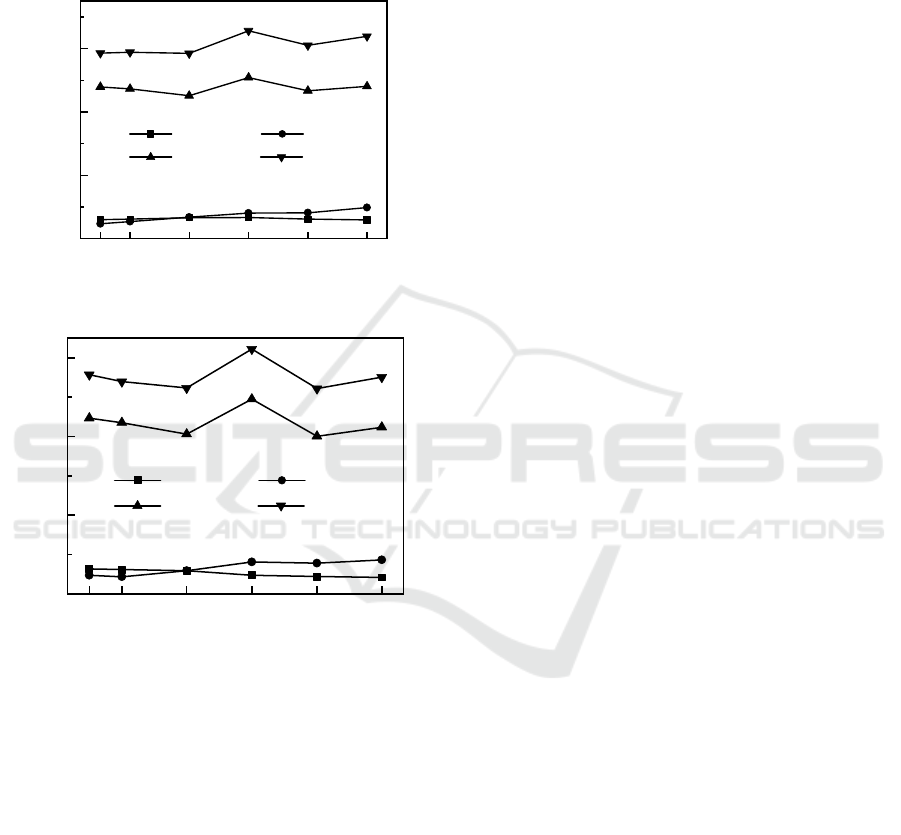
3.3 Effect of Cationic Polyacrylamide
Conditioning on the Structure
Characterization of EPS
3.3.1 Effect of Conditioning Process on EPS
Component and Content Change
(a) Distribution of protein when adding CPAM
(b) Distribution of polysaccharide when adding CPAM
Figure 5: Caption to effect of different CPAM dosage.
EPS is a highly hydrated biopolymer, which plays an
important role in the stability of biological
flocculation and the separation of solid and water
(Salama et al., 2016). Proteins and polysaccharides
account for about 70% ~ 80% of the total EPS (Zhang
et al., 2021) .The analysis of the changes in protein
and polysaccharide contents of EPS layers in sludge
helps to clarify the mechanism of sludge dewatering
performance. The changes of protein and
polysaccharide contents in different sludge
components under different CPAM dosages are
shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5(a) shows the changes of protein content
in different components of EPS. With the addition of
CPAM, protein content concentration in total EPS
increases. When the dosage of CPAM was increased
from 0.0375 g/L to 0.15 g/L, the protein content in
total EPS decreased gradually. When the dosage of
CPAM was 0.15 g/L to 0.3 g/L, the protein content in
total EPS increased first and then decreased, and
reached the maximum value at 0.225 g/L. The change
trend of protein content in TB-EPS was consistent
with that in total EPS, and reached the maximum
when CPAM dosage was 0.225 g/L. The protein
content of S-EPS decreased slightly with the increase
of CPAM dosage. The change trend of protein in LB-
EPS was just opposite to that in S-EPS, which
gradually increased with the increase of CPAM
dosage. This indicates that the addition of CPAM
transfers proteins in S-EPS layer to LB-EPS layer and
TB-EPS layer, which changes the distribution pattern
of proteins in sludge stratification, thus achieving the
purpose of sludge particle flocculation and improving
the dewatering performance of sludge (Tripathy et al.,
2001).
It can be found from Figure 5(b) that when the
dosage of CPAM increased from 0.0375 g/L to 0.15
g/L, the polysaccharide content in total EPS
decreased slowly. When the dosage of CPAM was
0.15 g/L to 0.3 g/L, the polysaccharide content in total
EPS increased first and then decreased, and the
polysaccharide content reached the maximum at
0.225 g/L. The change trend of polysaccharides in
LB-EPS was exactly opposite to that in S-EPS, and
gradually increased with the increase of CPAM
dosage. The change trend of polysaccharide content
in TB-EPS was consistent with that in total EPS, and
reached the maximum when the dosage of CPAM was
0.225 g/L. The results showed that after CPAM was
added, the distribution pattern of polysaccharides in
sludge stratification was changed by compressing the
double layer and the principle of electrical
neutralization. The polysaccharides in S-EPS were
transferred to LB-EPS and TB-EPS, so that the sludge
particles were flocculated (Zhang et al., 2017).
0
.
0
3
7
5
0
.
0
7
5
0
.
1
5
0
.
2
2
5
0
.
3
0
.
3
7
5
0
100
200
300
Protein content/
(
)
mg/L
Pol
y
acr
y
lamide dosa
g
e
()/
g
/L
S-EPS LB-EPS
TB-EPS Total EPS
0
.
0
3
7
5
0
.
0
7
5
0
.
1
5
0
.
2
2
5
0
.
3
0
.
3
7
5
0
40
80
120
The polysaccharide content/
()
mg/L
Polyacrylamide dosage
()
/g/L
S-EPS LB-EPS
TB-EPS Total EPS
Effect of Chemical Conditioning of Sewage Sludge on Dewatering Performance and Structural Components
445
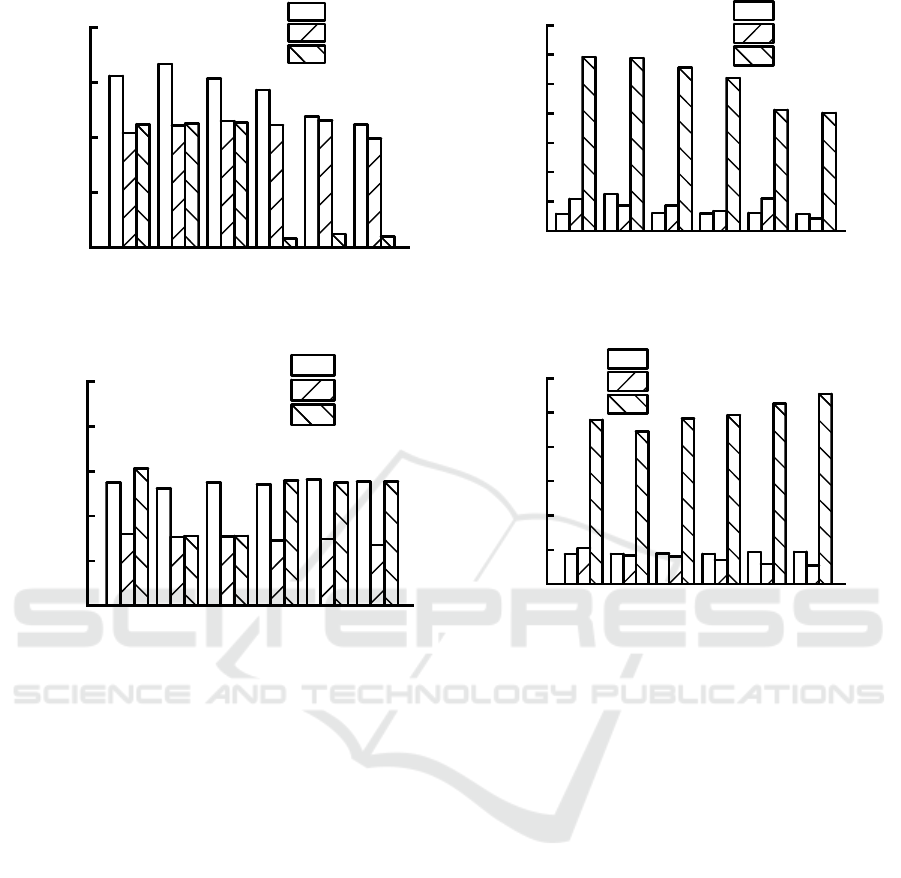
(a) Protein-like substance (b) Humic acid-like
(c) Fulvic-like acid (d) Humic acid-like
Figure 6: Effect of cationic polyacrylamide dosage on the distribution of maximum fluorescence intensity of different
components: (a) Soluble microbial by-product-like; (b) Tyrosine protein; (c) Humic acid-like; (d)Humic acid-like.
3.3.2 Analysis of EPS Fluorescence
Characteristics
Fluorescence spectroscopy is a sensitive method for
the analysis of organic matter, which has been widely
used in the analysis of organic matter in sludge EPS.
To study the changes of fluorescent organic matter in
sludge dewatering process treated by CPAM
conditioning, three-dimensional fluorescence
spectroscopy analysis of raw sludge and sludge after
conditioning was carried out (Zhu et al., 2012).
Figure 6 is the distribution map of the maximum
fluorescence intensity of EPS components under
different CPAM dosage. From Figure 6(a), with the
addition of CPAM, the protein-like substances in EPS
gradually decreased, Zhang et al (2016) pointed out
that the decrease of protein-like content is helpful for
sludge dewatering. It can be seen from Figure 6(b)
that with the addition of CPAM, the content of marine
humic substances in LB-EPS and S-EPS changed
little, and the content in TB-EPS decreased gradually.
It can be seen from Figure 6 (c) that the addition of
CPAM had little effect on the fulvic-like acid content,
and the fulvic-like acid content in EPS was basically
unchanged. It can be seen from Figure 6(d) that the
total amount of humic acids in sludge after CPAM
conditioning increased, and the content of TB-EPS
increased significantly. The content of LB-EPS
decreased slightly, while the content of S-EPS
remained basically unchanged. The increase in
humic-like substance content indicates that organic
substances in sludge form humic acid through
polymerization, and charged substances are
condensed into polymers, so that the charge on the
surface of sludge is low, which is conducive to sludge
dewatering. The increase in humic-like substance
content in TB-EPS may be due to the release of
substances wrapped by EPS in cell phase into EPS.
0.0375 0.075 0.15 0.225 0.3 0.375
0
10
20
30
40
Maximum fluorescence intensity/ (×10
4
)
Polyacrylamide dosage/(g/L)
S-EPS
LB-EPS
TB-EPS
0.0375 0.075 0.15 0.225 0.3 0.375
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Maximum fluorescence intensity/ (×10
4
)
Polyacrylamide dosage/(g/L)
S-EPS
LB-EPS
TB-EPS
0.0375 0.075 0.15 0.225 0.3 0.375
0
5
10
15
20
25
Maximum fluorescence intensity/ (×10
4
)
Polyacrylamide dosage/(g/L)
S-EPS
LB-EPS
TB-EPS
0.0375 0.075 0.15 0.225 0.3 0.375
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Maximum fluorescence intensity/
(
×10
4
)
Polyacrylamide dosage/(g/L)
S-EPS
LB-EPS
TB-EPS
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
446

4 CONCLUSION
(1) The optimal dosage of CPAM was 0.225 g/L for
the dewatering performance of excess sludge. Under
these conditions, the moisture content of sludge filter
cake was 70.19%, the specific resistance of sludge
was 0.15×10
12
m/kg, and the CST was 6.45s.
(2) After the conditioning of cationic
polyacrylamide (CPAM), the sludge particle size
increased, the fractal dimension increased, the sludge
Zeta potential increased from -18.93 mV to -
12.07mV, the electronegativity decreased.
(3) After CPAM conditioning of the surplus
sludge, through the action of electrical neutralization
and dehydration, colloidal particles are destabilized to
form large flocs, which changes the distribution of
proteins and polysaccharides in each layer of sludge,
so that intracellular substances and TB-EPS are
released into LB-EPS and S-EPS, so as to improve the
performance of sludge dehydration.
(4) After conditioning, the protein-like
concentration of S-EPS in surplus sludge EPS
decreased, while the humic acid-like concentration of
TB-EPS increased.
REFERENCES
Bi, D., Guo, X., Cai, Z. (2015). Enhanced dewaterability of
waste-activated sludge by combined cationic
polyacrylamide and magnetic field pretreatment.
Environmental Technology, 36(1-4), 455-462.
Dai, Q. X., Ma, L. P., Ren, N. Q., Ning, P., Guo, Z. Y., Xie.,
L. G. and Gao, H. J. (2018). Investigation on
extracellular polymeric substances, sludge flocs
morphology, bound water release and dewatering
performance of sewage sludge under pretreatment with
modified phosphogypsum. Water Research, 142, 337-
346.
Guo, J. Y., Gao, Q. F., Chen, Y. H., He, Q. L., Zhou, H. B.,
Liu, J. B., Zou, C. W. and Chen, W. J. (2021). Insight
into sludge dewatering by advanced oxidation using
persulfate as oxidant and Fe
2+
as activator:
Performance, mechanism and extracellular polymers
and heavy metals behaviors. Journal of Environmental
Management, 288, 112476.
Guo, K., Gao, Y. and Gao, B. (2019). Structure-activity
relationships of the papermill sludge-based flocculants
in different dye wastewater treatment. Journal of
Cleaner Production, 266, 121944.
Hiroyuki, O. (2019). Electrophoretic mobility of a charged
spherical colloidal particle in an uncharged or charged
polymer gel medium. Colloid and Polymer Science,
297(5), 719–728.
Klomklao, P., Kuntinugunetanon, S. and Wongkokua. W.
(2017). Moisture content measurement in paddy.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 901(1), 012068.
Li, Z. H., Guo, Y., Hang, Z. Y., Zhang, T. Y. and Yu, H. Q.
(2020). Simultaneous evaluation of bioactivity and
settleability of activated sludge using fractal dimension
as an intermediate variable. Water Research, 178,
115834.
Salama, Y., Chennaoui, M., Sylla, A., Mountadar, M.,
Rihani, M. and Assobhei. O. (2016). Characterization,
structure, and function of extracellular polymeric
substances (EPS) of microbial biofilm in biological
wastewater treatment systems: a review. Desalination
and Water Treatment, 57(35), 16220-16237.
Sun, X. Y., Tang, Z. and Yang, X. P. (2017). Comparison
of Extraction Methods of Extracellular Polymeric
Substances from Activated Sludge. Huanjing Kexue,
39(7), 3306-3313.
Tang, P., Greenwood, J., Raper, J. A. (2002). A Model to
Describe the Settling Behavior of Fractal Aggregates.
Journal of Colloid And Interface Science, 247(1), 210-
219.
Tripathy, T., Karmakar, N. C., Singh, R. P. (2001).
Development of novel polymeric flocculant based on
grafted sodium alginate for the treatment of coal mine
wastewater. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 82(2),
375-382.
Wang, L. F., He, D. Q., Tong, Z. H,m Li, W. W. and Yu, H.
Q. (2014). Characterization of dewatering process of
activated sludge assisted by cationic surfactants.
Biochemical Engineering Journal, 91, 174-178.
Wu, W., Ma, J. X., Xun, J. and Wang, Z. W. (2021).
Mechanistic insights into chemical conditioning by
polyacrylamide with different charge densities and its
impacts on sludge dewaterability. Chemical
Engineering Journal, 410, 128425.
Zeng, Q., Zan, F. X., Hao, T. W., Biswal, B. K., Lin, S., van
Loosdrecht, M. C. M.and Chen, G. H. (2019).
Electrochemical pre-treatment for stabilization of waste
activated sludge: Simultaneously enhancing
dewaterability, inactivating pathogens and mitigating
hydrogen sulfide. Water Research, 166, 115035.
Zhang, J., Zhang, J., Tian, Y. (2016). Changes of
physicochemical properties of sewage sludge during
ozonation treatment: Correlation to sludge
dewaterability. Chemical Engineering Journal, 301,
238-248.
Zhang, W. J., Chen, Z., Cao, B. D., Du, Y. J., Wang, C. X.,
Wang, D. S., Ma. T. and Xia, H. (2017). Improvement
of wastewater sludge dewatering performance using
titanium salt coagulants (TSCs) in combination with
magnetic nano-particles: Significance of titanium
speciation. Water Research, 110, 102-111.
Zhang, Y. P., Li, T. T., Tian, J. Y., Zhang, H. C., Li, F. and
Pei, J. H. (2021). Enhanced dewaterability of waste
activated sludge by UV assisted ZVI-PDS oxidation.
Journal of Environmental Sciences, 113, 152-164.
Zhen, G., Lu, X., Su, L., Kobayashi, T., Kumar, G., Zhou,
T., Xu, K., Li, Y. Y., Zhu, X. and Zhao, Y. (2018).
Unraveling the catalyzing behaviors of different iron
Effect of Chemical Conditioning of Sewage Sludge on Dewatering Performance and Structural Components
447

species (Fe
2+
vs. Fe
0
) in activating persulfate-based
oxidation process with implications to waste activated
sludge dewaterability. Water Research, 134, 101–114.
Zhou, X., Jiang, G. M., Wang, Q. L. and Yuan, Z.G. (2014).
A review on sludge conditioning by sludge pre-
treatment with a focus on advanced oxidation. RSC
Advances, 4, 50644–50652.
Zhu, L., Qi, H. Y., Lv, M. L., Kong, Y., Yu, Y. W. and Xu,
X. Y. (2012). Component analysis of extracellular
polymeric substances (EPS) during aerobic sludge
granulation using FTIR and 3D-EEM technologies.
Bioresource Technology, 124, 455-459.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
448
