
Effect of Bioretention on Pollutant Reduction in Urban Road Runoff
Rubin Jia
*
, Jian Li, Yong Wang, and Di Tang
China Ji Kan Research Institute of Engineering Investigation and Design, Co., Ltd, Xi’an, 710043, China
Keywords: Bioretention, Urban road runoff, Pollutant, Reduction
Abstract: Bioretention is an efficient low impact development to reducing urban non-point source pollution. This paper
studies a bioretention which was settled on one sides of urban roads. In three rainfall events, the content of
TSS (Total Suspended Solids), TN (Total Nitrogen), TP (Total Phosphorus) NH
4+
-N, NO
3—
N, Cu and Zn in
inflow and outflow of the bioretention were analysed, and the bioretention's ability to reduce pollutants was
evaluated. This work provides a reference for the design and construction of bioretention.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, urban non-point source pollution,
especially road runoff pollution under rainfall
conditions, has attracted more and more attention
(Abi Aad et al., 2014). How to effectively control road
rainwater runoff pollution and improve rainwater
utilization rate in the process of rapid urbanization is
a new challenge for urban environment and municipal
management departments (U. S. EPA, 2000). Low
impact development (LID) is an effective measure to
manage rainwater and pollutants in situ through
source and decentralized measures (Ahiablame et al.,
2012). Ecological detention basin, as a typical LID
measure, has strong applicability with design and
construction, and is applied in many cities in China.
Hao (2020) studied the "ecological" and "functional"
aspects of the evaluation and analysis of runoff on the
operation effect of biological retention facilities.
Bioretention can collect road rainwater runoff,
adsorb pollutants in runoff through fillers, and then
supplement groundwater. Many researchers have
systematically studied the effect of Bioretention on
runoff branch reduction, the adsorption capacity of
filler types on pollutants, and the relationship between
layout and runoff reduction. Lu et al. (2021) used LID
facilities to control urban road rain water
significantly, which can effectively reduce runoff,
reduce peak flow and delay peak rain time. But for
different rainfall intensity conditions, bioretention on
road runoff pollutant reduction effect is rarely
reported.
In this study, through the establishment of
bioretention facilities on both sides of urban roads, the
water quality of inflow and outflow of bioretention
facilities under rainfall conditions was monitored, and
the reduction effects of bioretention facilities on
COD, SS, TN and TP in urban road runoff pollutants
were studied, so as to provide reference for exploring
and optimizing the effect of bioretention facilities in
practical application.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of bioretention (Unit: m).
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1 Experimental Installation
As shown in Figure 1, the design size of bioretention
is 10 m × 1 m × 1 m, and the inlet is close to the road
edge. At the bottom of the bioretention, 5cm thick
gravel layer is easy to disperse water. The substrate of
bioretention is sand and fly ash, and the bottom layer
is fly ash (30 cm). The last time is coarse sand (30
cm). The substrate covered the planting soil layer
(30cm). The bioretention has a concave depth of 5 cm,
which is convenient for water collection and
infiltration. A perforated pipe with a diameter of 1 cm
Jia, R., Li, J., Wang, Y. and Tang, D.
Effect of Bioretention on Pollutant Reduction in Urban Road Runoff.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Water Resource and Environment (WRE 2021), pages 449-452
ISBN: 978-989-758-560-9; ISSN: 1755-1315
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
449
is installed at the bottom of the bioretention to collect
rainwater from infiltration into the sampling pit.
The plants planted in the bioretention were
boxtree and ryegrass (1: 1). Boxwood (Buxus sinica
(Rehd. et Wils.) Cheng) which is shade-tolerant and
light-happy can maintain good growth in general
indoor and outdoor conditions. And soil requirements
are not strict while it is better to use loose and fertile
sandy loam. Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) is a
perennial plant with a stalk height of 30 – 90 cm.
Excellent forages are widely introduced and
cultivated in various regions. Ryegrass likes a cool
and moist climate. Better moisture resistance, but
poor drainage or high groundwater level is also
adverse to ryegrass growth. Intolerance to drought,
especially high heat and drought in summer, is more
unfavorable.
2.2 Experimental Method
In this experiment, two typical rainfall events were
monitored, and rainfall intensity, rainfall and rainfall
duration were recorded respectively. Rainfall
characteristics are shown in table 1. The analysis and
determination of water quality indexes of influent and
effluent of Bioretention mainly refer to the national
standard determination method.
Table 1: Rainfall characteristics.
Rainfall events rainfall duration /h rainfall /m
m
rainfall intensit
y
/mmꞏh clea
r
-da
y
b
efore Rain/da
y
Events 1 3.5 12 3.12 20
Events 2 2.5 9.2 3.5 10
Events 2 4 30 8.3 6
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Removal Effect of Bioretention on
TSS In Urban Road Runoff
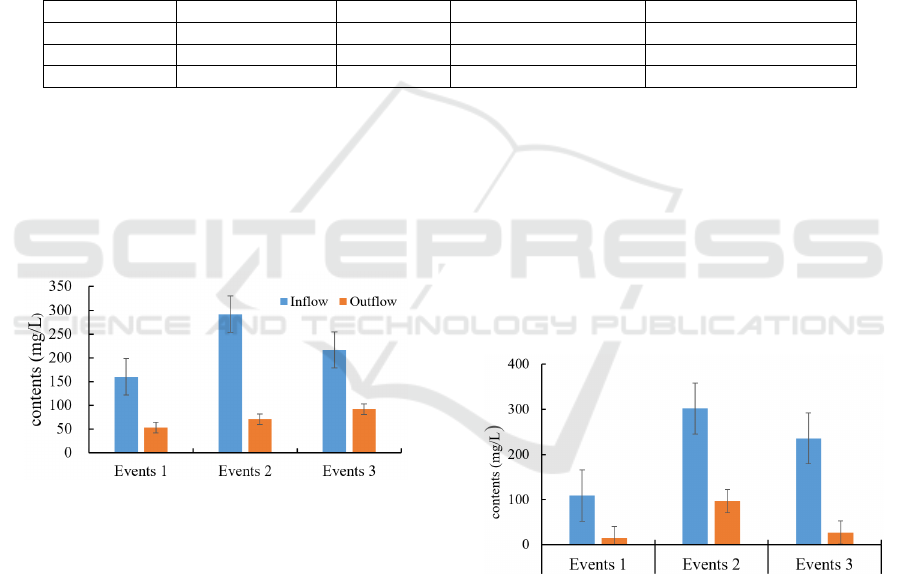
Figure 2: Removal effect of bioretention on TSS.
By analyzing the removal effect of bioretention on
TSS in road rainwater runoff, it can be seen from
Figure 2 that in the first rainfall, the influent TSS was
160 mg / L, and after the treatment of bioretention, the
effluent TSS was 53.4 mg / L, with a removal rate of
67%. In the second rainfall process, the TSS content
in the influent and effluent of the biological detention
facility was higher than that of the first rainfall period.
The TSS removal rate of the detention facility also
increased to 76%, which was the highest in the three
rainfall processes. During the third precipitation
period, the removal rate of TSS by bioretention was
the lowest, only 58 %. There are many factors
affecting the removal rate of TSS in bioretention, and
rainfall intensity is an important factor. When the
rainfall intensity is large, the hydraulic load is strong,
and the impact on the bioretention is enhanced, which
is easy to cause the increase of TSS content in the
effluent.
3.2 Removal Effect of Bioretention on
COD in Urban Road Runoff
Figure 3: Removal effect of bioretention on COD.
By analyzing the removal effect of bioretention on
COD in road rainwater runoff, it can be seen from
Figure 3 that in the three rainfall processes, the
removal rate of COD by bioretention was 68 % – 89
%, and the removal rate in the third rainfall process
was the highest. In addition to the removal of COD by
substrate adsorption in bioretention, the growth and
reproduction of a large number of microorganisms
living in fillers also play an important role in COD
degradation.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
450
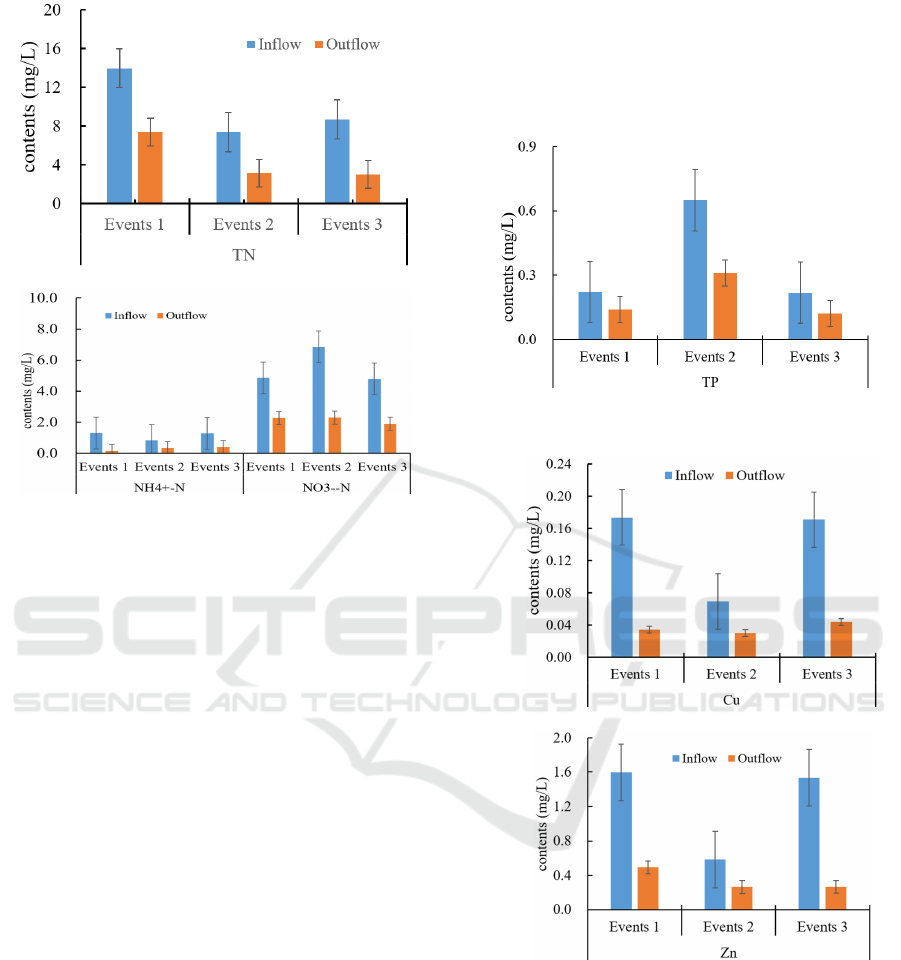
Figure 4: Removal effect of bioretention on Nitrogen.
3.3 Removal Effect of Bioretention on
Nitrogen in Urban Road Runoff
By analyzing the removal efficiency of various forms
of nitrogen (TN, NH
4+
-N and NO
3-
-N) by
bioretention, it was found from Figure 4 that the
removal rate of TN was 47 % -65 %, and the average
removal rate was 56 %. The removal rate of NH
4+
-N
was 61% ~ 88%, and the average removal rate was
73%. The removal rate of NO
3-
-N was 53 % ~ 66 %,
and the average removal rate was 60 %. It can be seen
that the bioretention has the best removal effect on
ammonia nitrogen, and the removal effect of the most
total nitrogen is relatively poor. In the later practical
application, if the TN content in the effluent needs to
be controlled, the substrate and filler need to be
adjusted and optimized to achieve better total nitrogen
removal.
3.4 Removal Effect of Bioretention on
TP In Urban Road Runoff
As shown in Figure 5, analysis of the removal effect
of total phosphorus by bioretention showed that the
removal rate was the highest in the first rainfall
process, reaching 66%. The removal rate of the
second rainfall was 52 %, and that of the third rainfall
was low, only 44 %. This may be related to the large
intensity of the third rainfall. Under the condition of
strong hydraulic load, the total phosphorus in the
rainwater runoff is less adsorbed by the filler of the
biological retention facility and is discharged with the
secondary effluent of the retention facility, resulting
in low yield efficiency.
Figure 5: Removal effect of bioretention on TP.
Figure 6: Removal effect of bioretention on heavy metals
(Cu, Zn).
3.5 Removal Effect of Bioretention on
Heavy Metals in Urban Road
Runoff
As shown in Figure 6, the removal rate of Cu by
bioretention was 57 % – 80 %, with an average of 70
%. The removal rate of Zn by bioretention was 69 %
– 83 %, and the average removal rate was 69 %. It can
be seen that the bioretention has a good removal rate
Effect of Bioretention on Pollutant Reduction in Urban Road Runoff
451

of two typical heavy metals in road rainwater runoff,
which may be due to the small particle size of fly ash
and strong adsorption capacity, which can quickly
combine with metal cations to remove heavy metal
pollutants in water
(Li et al., 2016).
4 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
Bioretention have certain purification capacity for
various pollutants in road rainwater runoff (Cheng et
al., 2009)
. By analyzing the concentrations of TSS,
TN, TP and heavy metal pollutants in the influent /
effluent of the bioretention, it was found that the
concentrations of various pollutants in the effluent
decreased, indicating that the bioretention facility is
an effective rainwater treatment facility for road
runoff.
Rainfall characteristics (rainfall, rainfall intensity,
rainfall duration, etc.) have a certain impact on the
treatment efficiency of bioretention, especially
rainfall intensity (
Wang et al., 2014). Under the
condition of high rainfall intensity, the inflow of
biological detention facilities is large, the turbulent
kinetic energy of water body is strong, and the
hydraulic load is large, which may reduce the
purification effect of bioretention (
Wang et al., 2015).
Therefore, in the design process of bioretention, the
local rainfall characteristics and the hydraulic
characteristics of road rainwater runoff should be
fully considered in order to design reasonable
bioretention.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the Key Research and
Development Program of Shaanxi
Province(2017ZDXM-SF-081).
REFERENCES
Abi Aad, M. P., Suidan, M. T., Shuster, W. D. (2014).
Modeling Techniques of Best Management Practices,
Rain Barrels and Rain Gardens Using EPA SWMM-5.
Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 15(6), 434-443.
Ahiablame, L. M., Engel, B. A., & Chaubey, I. (2012).
Effectiveness of Low Impact Development Practices,
Literature Review and Suggestions for Future Research.
Water Air & Soil Pollution, 223(7), 4253-4273.
Cheng, J., Yang, K., Lv, Y. P., Li, B., & Lv, S. H. (2009).
Experimental study on rainfall - runoff pollutant
reduction by urban greenspace. Environmental Science,
30(11), 3236-3242.
Hao, Y. (2020). Functional study of plant physiology and
substrate clogging rule based on biological retention
facility. Beijing University of Civil Engineering and
Architecture.
Li, S. Y., Cooke, R. A., Wang, L., Ma, F., Bhattarai, R.
(2016). Characterization of fly ash ceramic pellet for
phosphorus removal. Journal of Environmental
Management, 189, 67-74.
Lu, M. M., Jiang, S. H., & Qiu, H. F. (2021). Study on
rainwater control effect of URBAN Road LID Facilities
based on SWMM, A case study of Wuhan Industrial
Road. Huazhong Architecture, 39(06), 58-64.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (2000).
Low impact development, A Literature Review. USA:
Washington, DC.
Wang, Y., Wang, Y., & Wang, Y., (2014). A review of the
current situation and development trend of municipal
wastewater treatment and reuse in China. Journal of
Environmental Science and Technology, 32(4), 63-75.
Wang, S. & Zhang, L. Q. (2015). The cutting effect of
phosphorus in simulated road runoff by concave
herbaceous field. Environmental Science &
Technology, 38(9), 119-122.
WRE 2021 - The International Conference on Water Resource and Environment
452
