
Research Situation Analysis of Global 3D Printing based on
Bibliometrics
Duanwu Yan
1a
, Yue Chen
1b
, Shuang Lv
1c
and Biao Ma
1,2 d
1
School of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
2
Internet Network Information Center, Jiangsu Provincial Education Examination Authority, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Keywords: 3D Printing; Bibliometrics; Development Trend; Visual Analysis.
Abstract: The research on the development trend of 3D printing technology is helpful to provide useful competitive
intelligence for the practical application and industrial development of 3D printing. Based on the web of
Sciences core database, this paper uses the visual analysis software CiteSpace to analysis the annual number
of papers, core authors, discipline layout, institutions, countries and keywords, and comprehensively reveals
the research trend, research capacity and research hotspots in the field of global 3D printing from 2011 to
2020. The results show that the overall development trend of global 3D printing shows an increasing trend.
The United States, China, Britain and other countries are at the leading level of technological development,
and most of countries have close international cooperation relations, advanced countries are at the centre of
cooperation network, bioengineering and printing materials will continue to become research hotspots.
1 INTRODUCTION
3D printing technology (3D printing), also known as
additive manufacturing technology, is a technology
based on the principle of layering / accumulation,
using computer-aided technology, selecting
appropriate materials based on digital model files,
printing layer by layer according to the two-
dimensional digital path of each layer, and finally
superimposing to form a three-dimensional solid
(Shahrubudin, Lee, Ramlan, 2019).
Compared with traditional processing and
manufacturing technology, 3D printing technology is
a revolutionary innovation technology in the
production and manufacturing industry. It can not
only save materials and improve material utilization,
but also reduce time cost and meet consumer needs to
a greater extent. With the rapid development of 3D
printing technology, more and more kinds of
materials are involved in this technology, the 3D solid
structure is more complex, the accuracy is also
improving. Therefore, the application scope of 3D
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9893-2302
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4316-4868
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3613-9990
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0937-5602
printing technology has been further expanded. At
present, the research on 3D printing technology in
Europe, America and other countries is relatively
mature, which is applied to aerospace, automobile
manufacturing, medical treatment, industry,
construction, biotechnology and other fields, and
large-scale marketization has formed the
corresponding industrial chain. Although the research
on 3D printing technology in China started late, the
great potential of 3D printing technology has been
valued by a large number of researchers, and China's
3D printing technology has developed rapidly. There
are many researches on the key technologies and
development status of 3D printing applied in various
fields at home and abroad, but there are few
researches on the analysis of international 3D printing
technology from the perspective of journal papers.
Therefore, based on bibliometrics, this paper studies
and analyzes the journal papers of international 3D
printing technology from different angles, analyzes
the publication of papers, author cooperation,
countries, institutions and discipline distribution,
especially studies the hot spots and trends of 3D
Yan, D., Chen, Y., Lv, S. and Ma, B.
Research Situation Analysis of Global 3D Printing based on Bibliometrics.
DOI: 10.5220/0011342600003437
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2021), pages 269-274
ISBN: 978-989-758-589-0
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
269
printing technology according to the keyword co-
occurrence analysis, so as to provide some basis and
reference for the research work of scientific
researchers.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Data Collection
In this study, we took the Web of Science Sore
Collection as the data source, selected advanced
retrieval. The theme for retrieval was set as"3D print"
or "three dimension print". The retrieval time range
was set from 2011 to 2020, the language was set to
“English”, the document type was set to "article". The
articles retrieved from the database were exported to
the local database in the format of txt. The irrelevant
articles were manually eliminated, and then we
merged these articles and removed duplicates.
Finally, 24082 articles are determined.
2.2 Statistical Methods
Based on bibliometrics, this research made statistical
analysis and visual analysis of all articles on the
theme of "3D printing" from 2011 to 2020, so as to
reveal the research theme, development trend and
frontier in the research of 3D printing technology.
Statistical analysis mainly presented the number of
articles published, authors and countries. Visual
analysis used the software “CiteSpace” to analysis the
author cooperation, institutional cooperation,
national cooperation, keyword co-occurrence and
other analysis and finally formed visual maps.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
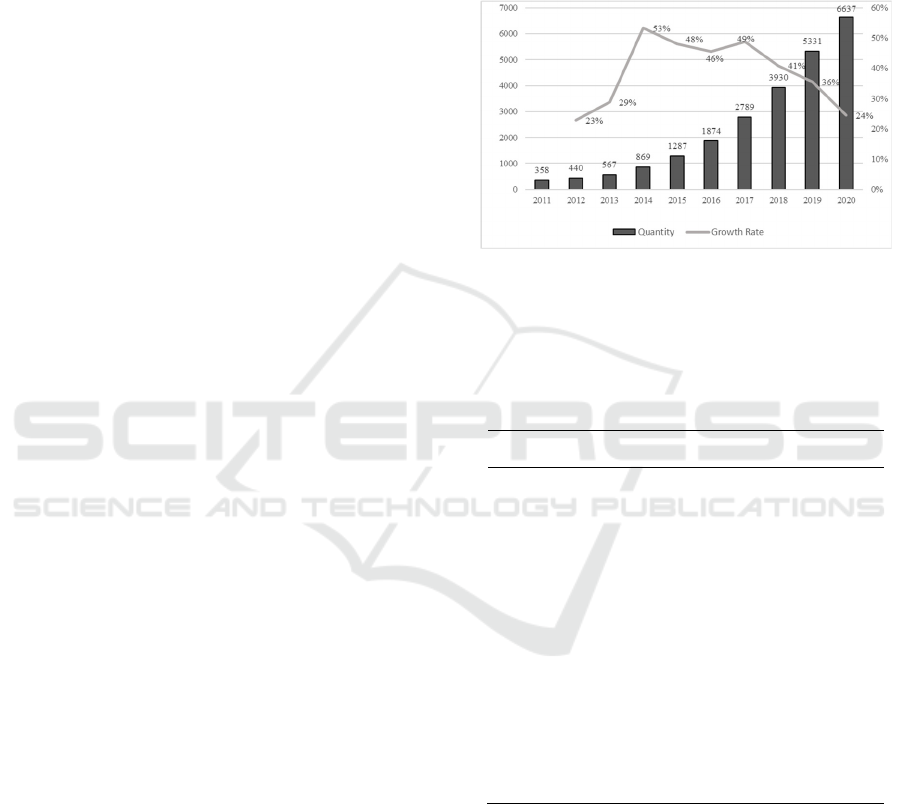
3.1 Analysis of Papers’ Annual Amount
The number of published papers within a certain time
range can be used as a measure of the development
trend of a field, and intuitively show the development
level, development speed and activity of research in
this field. Figure 1 shows the output of global 3D
printing core papers from 2011 to 2020, with a total
number of 24082, showing a continuous upward
trend as a whole. From 2011 to 2014, the average
development level of global 3D printing technology
was in the embryonic stage. Although the number of
papers was small, the technology received attention
and developed rapidly. From 2015 to 2020, with the
upsurge of research enthusiasm, global 3D printing
research developed rapidly. Although the annual
amount of papers growth rate decreased slightly since
2017, the number of published papers was still
growing steadily. It can be seen that in the future, the
steady development trend of 3D printing technology
research will continue, and the technology is
becoming more and more mature.
Figure 1: Number and types of papers published from 2011
to 2020.
3.2 Analysis of Discipline Layout
Table 1: WoS Categories of “3D print” research papers
from 2011 to 2020.
SN WoS Categories Quantity Proportion
1
Engineering 8426 34.99%
2 Materials
Science
8100 33.64%
3
Chemistry 3911 16.24%
4 Science &
Technolo
gy
3631 15.08%
5
Physics 3281 13.62%
6 Electrical &
Electronic
3084 12.81%
7
Physics Applied 2857 11.86%
8 Compute
r
Science
2468 10.25%
9 Nanoscience &
Nanotechnolo
gy
2437 10.12%
10
Biomedical 1714 7.12%
Based on the classification of web of science, the
scientific layout of papers on the research theme of
"3D printing" is analyzed. Table 1 shows the top 10
disciplines in the global paper category in the field of
3D printing technology from 2011 to 2020. The two
disciplines with the largest proportion are
engineering and materials science, with 8426 and
8100 relevant literatures respectively, covering
34.99% and 33.64% of the papers issued in the field
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
270

of 3D printing technology, followed by Chemistry
(16.24%) and science and Technology (15.08%).
3.3 Core Authors Analysis
The research on the structural network between high-
yield authors in a field is helpful to understand the
cooperative relationship between core authors and
provide reference basis for academic exchange,
international cooperation and talent introduction
(White H D 2003). Figure 2 display the network map
with the author as the node. The larger the node, the
higher the frequency of the authors in the research
field. The thicker the line, the higher the frequency of
cooperation. As shown in Fig. 2 and table 2, there are
15 high-frequency authors in the field of 3D printing
technology (frequency ≥ 35), including Ianzhong Fu
(64) published the research on 3D bioprinting
methods for the first time in 2015 (Gao, He, Fu,
2015), and the formed a strong cooperative research
team with Yong He (46) and others. Dongwoo CHO
(62) has been cited 902 times at most, and his team is
good at physics, chemistry, bioengineering and other
fields; Dichen Li (60) the paper was first published in
2013, and the highest number of citations reached
402. These high-frequency authors are basically in
the center of the network, and the cooperative
relationship between high-frequency authors is
closer.
Figure 2: Author Cooperation Network Map.
Table 2: TOP 5 Key Authors.
F Centrality Author Year
Highest
Citations
64 0.02
IANZHONG
FU
2015 285
62 0.03 DONGWOO CHO 2014 902
60 0.01 DICHEN LI 2013 402
46 0.02 YONG HE 2015 285
46 0.01
JACQUES
LALEVEE
2017 75
3.4 Research Institutions Analysis
This paper took the research institution of the first
author as the object to make statistics on the top 20
research institutions in the field of 3D printing
technology (Table 3). In terms of the number of
papers published, China's research institutions
account for a large proportion. The Chinese Academy
of Sciences accounts for 2.3% of the world's total
number of papers. Institutions with a large number of
papers published in other countries mainly include
Nanyang Technological University, Massachusetts
Institute of technology, Georgia Institute of
technology, etc. We used CiteSpace to processes all
data to form a cooperative relationship network
between research institutions, as shown in Figure 3.
There is less cooperation between research
institutions in China, and more tend to inter agency
internal cooperation or small group cooperation. The
relationship between research institutions in other
countries is relatively close, with more partners and a
wider range of cooperation. The cooperation centers
of the research institute network mainly include
Harvard University, North Polytech University,
Chinese Academy of Sciences, University Western
Australia, King Abdulaziz University, etc.
Figure 3: Institution Cooperation Network Map.
Research Situation Analysis of Global 3D Printing based on Bibliometrics
271

Table 3: Top 20 Research Institutions.
SN Quantity Institution SN Quantity Institution
1 559 Chinese Academy of Sciences 11 173 University of Illinois
2 325 Tsinghua University 12 172
Huazhong University of
Science an
d
Technolo
gy
3 306
Nanyang Technological
Universit
y
13 172 Harvard University
4 303 Zhejiang University 14 167 Sichuan University
5 274 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 15 163 University College London
6 243 Xi An Jiao Tong University 16 159 University of Maryland
7 240
Massachusetts Institute of
Technolo
gy
17 147 Seoul National University
8 239 Georgia Institute of Technology 18 145 Beihang University
9 187 Peking University 19 145 Swiss Fed Inst Technol
10 183 National University of Singapore 20 135 Imperial College London
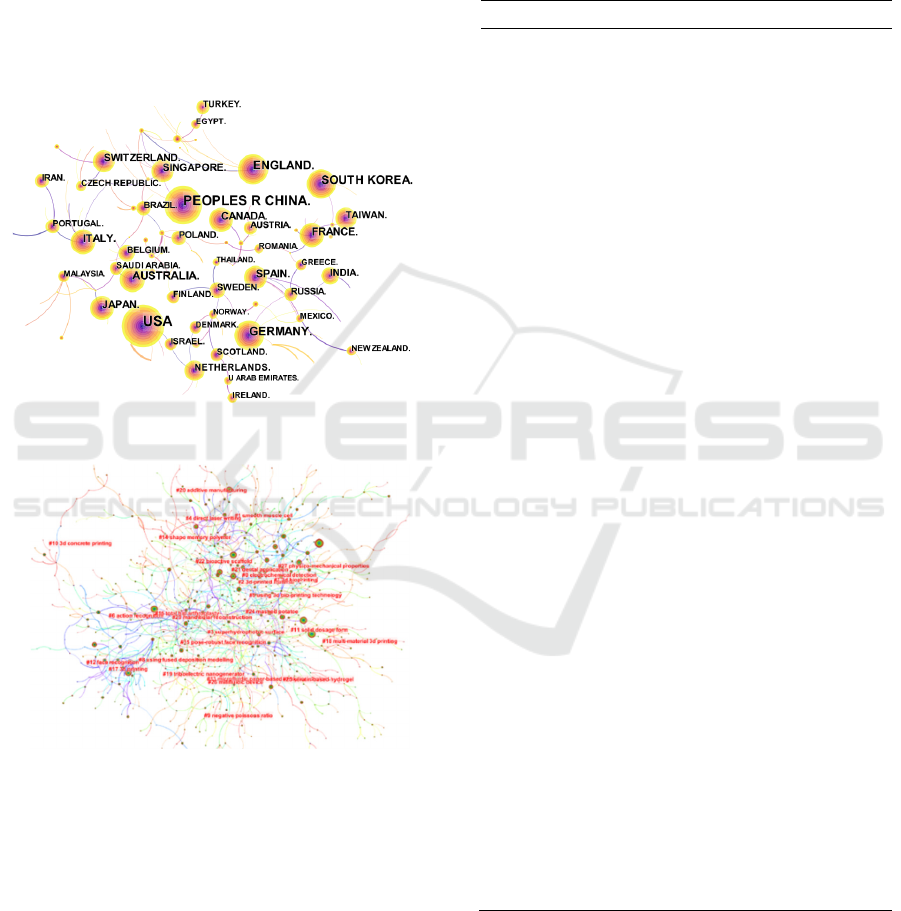
3.5 National Layout Analysis
Use quantitative analysis to explore the productivity
and influence of relevant countries in the field of 3D
printing technology. After searching and processing,
24082 papers come from 153 countries, and there are
461 cooperative relationships. Table 4 shows the top
ten countries in the total number of papers issued in
the field of 3D printing technology in the world, and
Figure 4 shows the national cooperation network. In
terms of productivity, the top three in the total number
of papers issued are the United States, China and the
United Kingdom. The number of papers issued by the
United States and China far exceeds that of other
countries, accounting for 26.82% and 23.94% of the
world respectively, more than three times that of the
United Kingdom and Germany. They are the main
force of research in this field. In terms of influence
(centrality and total number of other citations). The
centrality and total number of other citations in the
United States, Britain and Germany are high, which
obviously has a great influence and plays a central
role in the national cooperation network. China's total
number of other citations is high, but its centrality is
low, reflecting that
China has a low global influence
in the research field of 3D printing technology, tends
to domestic cooperation or small group cooperation,
which needs to be improved Further deepen
cooperation.
Table 4: Top 10 Countries.
SN Quantity Centrality Country Year All Citations
1 6458 0.13 USA 2011 245949
2 5765 0.02 CHINA. 2011 135517
3 1692 0.09 ENGLAND 2011 46521
4 1687 0.12 GERMANY 2011 51765
5 1581 0.04 SOUTH KOREA 2011 36287
6 1007 0.02 AUSTRALIA 2011 37510
7 951 0.12 ITALY 2011 26192
8 906 0.10 FRANCE 2011 21818
9 860 0.05 CANADA 2011 21362
10 752 0.07 JAPAN 2011 13078
3.6 Keywords Analysis
Keywords are the author's highly concentrated and
summarized research content and core ideas of the
article, reflecting the research direction and value of
the article. High frequency keywords are often used
to explore hot issues in a research field. In this paper,
the word frequency statistics of keywords in the
research field of 3D printing technology are carried
out, and the keyword co-occurrence analysis is
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
272
carried out through CiteSpace software to generate
the keyword co-occurrence map of 3D printing
technology research. Keywords with high frequency
at home and abroad include "3D printing", "fabric",
"additional manufacturing", "design", "mechanical
property", "model", "scaffold", "behavior",
"composite", "system", etc. it can be seen that 3D
printing technology has been widely used in
manufacturing engineering, especially in aerospace
(Tan, Fang 2016), biotechnology (Mao, Gu, 2018)
and other fields with high requirements for
mechanical properties.
Figure 4: Country Cooperation Network Map.
Figure 5: Keywords Clustering Map.
The keyword clustering map shows the main
research hotspot in the research field of global 3D
printing technology. As shown in Figure 5, at this
stage, the research in the field of 3D printing
technology is roughly summarized into 26 clustering
labels. It can be seen that the research categories
involved in 3D printing technology are rich and cover
a wide range of fields. This paper can be roughly
summarized into 3D printing technology (such as
melt deposition modeling, selective laser, accuracy),
3D bioprinting (such as bone tissue engineering,
cardiovascular tissue, biological cells, etc.), 3D
printing materials (such as graphene, polylactic acid,
carbon nanotubes), 3D printing performance (such as
mechanical properties, mechanical properties,
process parameters).
Table 5: Distribution of Research Hotspots in Each Stage.
Keywords Strength Begin-End 2011 - 2020
face
reco
g
nition
43.17 2011-2015 ▃▃▃▂▂▂
rapi
d
p
rotot
yp
in
g
41.84 2011-2016
▃▃▃▂▂▂
image 25.52 2011-2014
▃▃▃▂▂▂
lithography 20.28 2011-2017 ▃▃▃▃▃▂
fabrication 19.13 2011-2013
▃▃▂▂▂▂
cell 14.30 2011-2015
▃▃▃▂▂▂
nanostructure 8.82 2011-2015 ▃▃▃▂▂▂
b
iological
p
ro
p
ert
y
6.15 2013-2015
▂▃▃▂▂▂
tissue 14.24 2014-2016
▂▃▃▂▂▂
chemical
s
y
nthesis
11.77 2014-2017 ▂▃▃▃▂▂
tissue
en
g
ineerin
g
8.37 2014-2016 ▂▃▃▂▂▂
biology 7.29 2014-2016
▂▃▃▂▂▂
extracellula
r
matrix
7.45 2015-2016 ▂▂▂▃▂▂
electrochemica
l detection
6.10 2016-2017 ▂▂▂▃▂▂
fuse
d
de
p
osition
6.02 2016-2018
▂▂▂▃▃▂
fluid 4.90 2016-2018
▂▂▂▃▃▂
marrow
stromal cell
4.61 2016-2018 ▂▂▂▃▃▂
transistor 5.56 2017-2018 ▂▂▂▂▃▂
ultrasound 5.56 2017-2018
▂▂▂▂▃▂
gelation 3.49 2017-2018 ▂▂▂▂▃▂
porous material3.30 2017-2018 ▂▂▂▂▃▂
aerogel 6.07 2018-2020
▂▂▂▂▃▃
energy
harvestin
g
4.69 2018-2020 ▂▂▂▂▃▃
p
olyme
r
-matrix
composites
(p
mcs
)
4.41 2018-2020 ▂▂▂▂▃▃
architecte
d
material
4.14 2018-2020
▂▂▂▂▃▃
nanomaterial 3.01 2018-2020 ▂▂▂▂▃▃
Keyword emergence analysis refers to the
analysis of words with high frequency of change or
more times in the published literature in a research
field in a certain period of time. It is often used to
identify the research frontier or predict the
development trend. In this paper, 26 emergent words
Research Situation Analysis of Global 3D Printing based on Bibliometrics
273

with high emergent value are obtained by CiteSpace
software. Combined with the further analysis of
emergent intensity and duration, this paper explored
the frontier problems and evolution trend of 3D
printing technology research. According to table 5,
the development of 3D printing from 2011 to 2020 is
divided into three stages. From 2011 to 2013, the
research of this stage mainly focuses on 3D printing
technology, including stereo lithography, rapid
prototyping, image processing. From 2013 to 2018,
the research focusing on bioscience, tissue
engineering and other hot spots began to appear;
Since 2018, 3D printing materials such as hydrogels,
carbon nanotubes and polymers have become the
mainstream of research.
4 CONCLUSIONS
With the help of the bibliometric analysis software
CiteSpaces, this paper analyzed the articles related to
3D printing included in the web of science core
collection from 2011 to 2020. This paper
systematically and comprehensively expounded from
the six perspectives of annual document volume,
discipline layout, core authors, research institutions,
national distribution and keywords, explored the hot
spots and overall situation in the field of 3D printing
through keyword cluster analysis and keyword
emergence analysis. To sum up, in the past decade,
3D printing technology has been booming at an
amazing speed, mainly used in engineering, materials
and chemistry. The research countries are widely
distributed and the overall international cooperation
relationship is close.
The visual situation analysis of 3D printing
technology research can provide reference for the
development of 3D printing in China in the aspects of
introducing talents, carrying out international
cooperation and focusing on research hotspots.
Compared with other advanced countries, the overall
level of 3D printing research in China needs to be
improved, which is mainly reflected in the large
number of articles published in China but few highly
cited articles, the degree of international cooperation
is low and China is not at the center of the national
cooperation network. Therefore, China needs to
enhance the national strategic position of innovative
technologies such as 3D printing, strengthen the R &
D of key technologies, deepen international
cooperation, grasp research hotspots and future
trends, optimize the industrial chain, provide
assistance for talent training and rapid and high-
quality development of 3D printing technology, and
move forward to deeper research.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
*This research was financially supported by
Humanity Social Sciences Fund Project of the
Ministry of Education (Grant NO. 19YJA870015)
and Jiangsu Province Social Science Fund Project
(Grant NO. 17TQB009).
REFERENCES
Gao Q, He Y, Fu J. (2015). Coaxial nozzle-assisted 3D
bioprinting with built-in microchannels for nutrients
delivery. J. Biomaterials. 61: 203-215.
Mao Hongli, Gu Zhongwei. (2018). Polymers in 3D
Bioprinting: Prgress and Challenges. J. Materials
China. 37(12): 949-969. (in Chinese).
Shahrubudin N, Lee T C, Ramlan R. (2019). An Overview
on 3D Printing Technology: Technological, Materials,
and Applications. Z. 35: 1286-1296.
Tan Lizhong, Fang Fang. (2016). 3D Printing Technology
and it’s Application in Aerospace Industry. J. Tactical
Missile Technology. (04): 1-7. (in Chinese).
White H D. (2003). Pathfinder networks and author
cocitation analysis: A remapping of paradigmatic
information scientists. J. Journal of the American
Society for Information Science & Technology. 54(5):
423-434.
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
274
