
Research on Evolution Process and Countermeasures of
E-Government based on Supply Chain Theory
Dandan Shi
a
and Xiao Wu
b
Harbin University of Commerce, Department of Finance and Public Administration, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
Keywords: E-Government, Internet Technology, Supply Chain Theory, Public Services.
Abstract: With the rapid development of Internet technology, many traditional industries and departments are
experiencing an information revolution, and e-government based on the Internet has gradually grown up with
the development of the Internet. Originally, the supply chain was designed to solve the problems in the
production process of enterprises. E-commerce was produced based on the supply chain technology, which
greatly improved the production efficiency of enterprises and created considerable social wealth. When the
supply chain technology is applied to other fields, it also shows great vitality, which provides new ideas for
solving problems in other fields. On the basis of reviewing the evolution of e-government, and analyzing the
characteristics and functions of e-government in each stage, this paper concludes the development process of
e-government from "digital government" to "intelligent government" and finally to "intelligent government",
and finds out the existing problems in e-government. The theory of supply chain is introduced into the field
of public management, and the enlightenment to solve the problem is obtained. Finally, the corresponding
suggestions are put forward. Thus, e-government can be continuously optimized in the era of rapid
development of Internet technology, and relevant departments can also provide more perfect public services.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the exquisite application of computers and the
rapid development of information technology, the
traditional departments and industries that have
undergone a long evolution process are hard to resist,
and they are forced to make digital changes in order
to adapt to the new social ecological environment.
The same is true of government departments and
operation modes based on bureaucratic organization
theory, which has been confirmed in the change of
"traditional government affairs-office automation-e-
government affairs". As early as 1980s, the
phenomenon of using computers to process
documents and manage archives has appeared in
Chinese government departments, that is, the
embryonic form of the concept of "office
automation". Although it is not really e-government
in essence, the transformation of its way of realizing
government affairs from "paper age" to "electronic
age" should belong to the category of e-government
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9517-6356
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6690-2213
and start the journey of development and research of
e-government in China.
After more than 30 years' efforts, especially the
comprehensive and rapid development in recent
fifteen years, China's e-government has achieved
remarkable results in information disclosure, mobile
government affairs, online service, electronic
participation, new technology application ability,
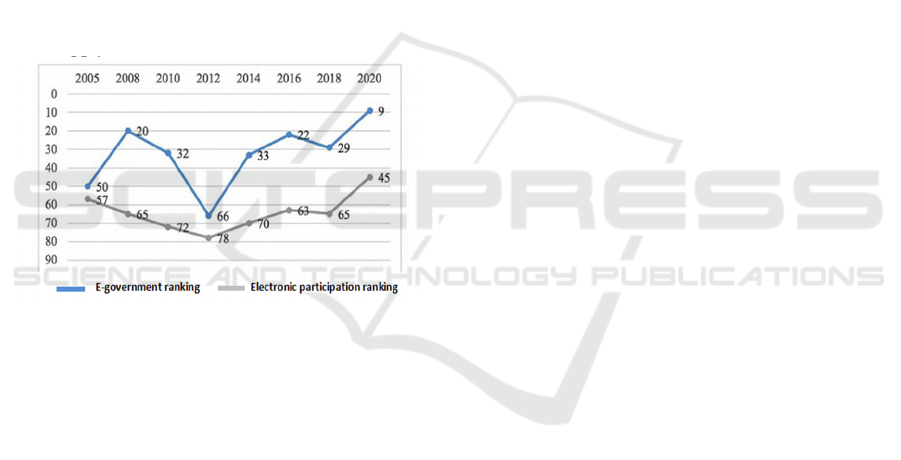
business and regional coverage. As shown in Figure 1
(
Bertot 2010).
In the development process of China's e-
government, both Max. Weber's bureaucracy, what
Hu De called "new public management", Robert B.
Denhardt and Janet V. Denhardt's new public service,
and Goldsmith and Egers' network governance, all
provide guidance for its development in a certain
period of time. E-government in the digital age is no
longer a problem at the level of information
technology, or simply a problem of system
management and information management. It is
necessary to study it with reference to the theoretical
system of public management, and explore how the
306
Shi, D. and Wu, X.
Research on Evolution Process and Countermeasures of E-Government based on Supply Chain Theory.
DOI: 10.5220/0011343700003437
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2021), pages 306-313
ISBN: 978-989-758-589-0
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
public departments and institutions with the
government as the core can use modern information
technology and governance theory in the digital age
to improve the way of handling government affairs
and improve the efficiency of public services. This is
not only a realistic task for government governance,
but also a necessary way to achieve a higher level of
public services, and it is also a forward-looking move
to scientifically develop China's e-government.
At present, the understanding of e-government is
not sufficient, and there is no specific means to solve
the problems. On the basis of reviewing the world's e-
government research literature, this paper analyzes
the characteristics and functional characteristics of e-
government in each stage, summarizes the
development process from "digital government" to
"intelligent government" and then to "intelligent
government", finds out the existing problems of e-
government, and focuses on how e-government
obtains enlightenment and solves problems with the
aid of supply chain.
Figure 1: China's Ranking in UN E-government Survey.
2 EVOLUTION AND EXISTING
PROBLEMS OF
E-GOVERNMENT
2.1 E-Government Development
Process
In the process of e-government development,
technology will become more and more complex, so
the difficulty of integration will also increase. It can
be roughly divided into four stages: the first stage is
the document cataloguing stage, in which the
government releases information to the outside by
establishing a website. The second stage is the
transaction stage, in which the government can
conduct online transactions through the Internet. The
third stage is the stage of vertical integration of
government functions. The fourth stage is the
horizontal integration stage. The first two stages
focus on the development and establishment of an
electronic interface for government information,
which belongs to the digital government stage. The
latter two stages are the integration of e-government
under the existing government structure, so they
belong to the intelligent government stage and the
intelligent government stage respectively.
2.2 E-Government Problems in the
Development Process
2.2.1 The Service Capability of Government
Websites Needs to Be Strengthened
The construction of government websites has not
received sufficient attention. In November 2003, the
United Nations Bureau of Economic and Social
Affairs inreleased the survey report Global Public
Sector Report 2003: E-government at Crossroads.
The report assesses the e-government level of the 173
UN member states that have launched government
websites from key indicators such as the accessibility
of government websites, the construction of network
infrastructure and the level of e-government. It
released the ranking by way of "digital government
completeness index", ranking China at 74th. The
report also evaluated the residents' convenience in
obtaining government information and their
enthusiasm in participating in government decision-
making by measuring "electronic participation
index", ranking China at 86th. As can be seen from
the comparison of the average value of the first-level
government service capability index of the provincial
government websites in China from 2017 to 2020, as
shown in Figure 2, the online service maturity index
and online processing maturity are relatively low,
which further illustrates the problem that the
government website service capability needs to be
strengthened.
Research on Evolution Process and Countermeasures of E-Government based on Supply Chain Theory
307
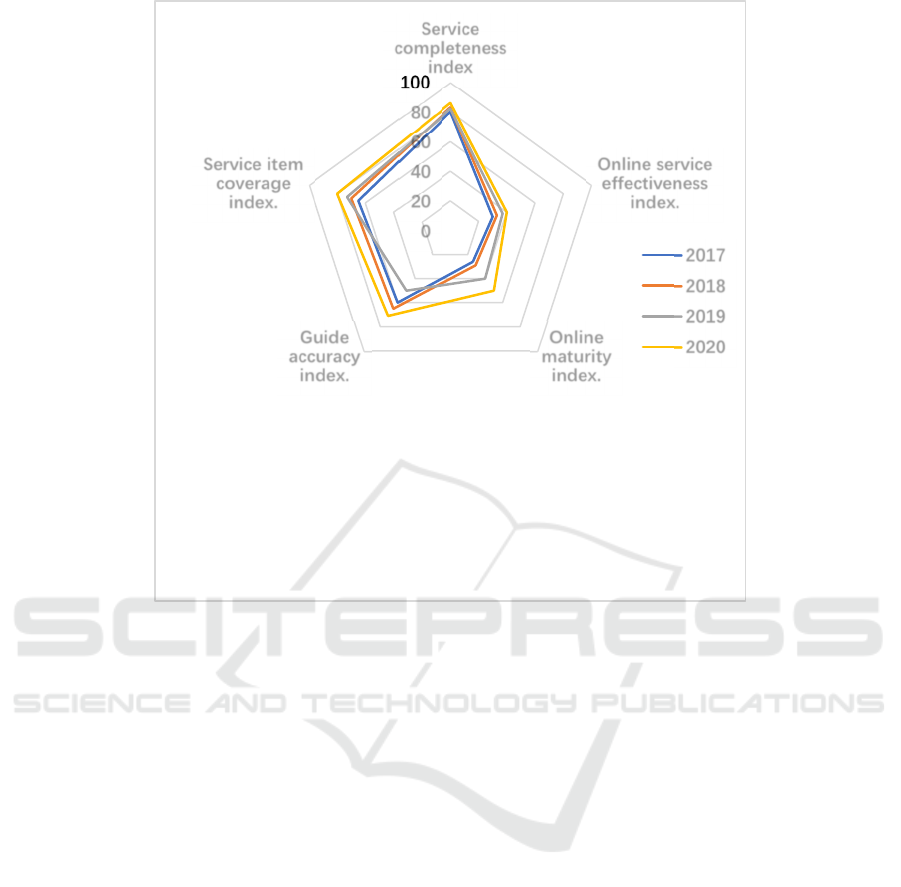
Figure 2: 2017-2020 comparison of the average value of the first level index of government service capacity of provincial
government websites in China, Data source: https://publicadministration.un.org/egovkb/en-us/data-center.
2.2.2 The Low Efficiency of Electronization
Many government websites show that they have the
function of handling affairs online, but when users
click on it, the system is usually being maintained, or
there is only one flow chart, which does not really
have this function. This is the typical low efficiency
of electronization. We can see that many government
websites only hang the names of the businesses they
handle on the front page, but they do not have this
practical function and can only be regarded as a
simple open process. This cannot be done by
electronic means to improve administrative
efficiency. This reflects the current form of electronic
government affairs in China.
2.2.3 E-Government Projects Lack Uniform
Standards
At present, China's e-government is developing
rapidly. Most of the provincial, municipal and county
government departments have their own websites.
However, problems such as repeated construction,
unreasonable website design, unclear website
objectives, poor operability and nonstandard security
management have become obstacles that hinder
China's e-government to move to a higher level. For
example: < font > tags have been listed as deprecated
tags by the W3C as early as April 1998 in the
HTML4.0 standard, but many websites have little
code like < font color=blue > on their home pages. In
fact, most of the large-scale websites fail to pass the
W3C's strict correctness verification. There are many
reasons for this situation, such as the adoption of the
old information release system, and the lack of skills
and awareness of web designers. However, the root
cause of this problem is the lack of standardization
and standardization of our government websites. "In
the average score table for website monitoring of the
third and fourth level cities in the Research Report on
China's Prefecture-level Cities' E-government, the
highest score is 7.1819 and the lowest score is 0.52
(there are 27 cities with zero scores), which shows the
large gap.
0
20
40
60
80
100
Service
completeness
index
Online service
effectiveness
index.
Online
maturity
index.
Guide
accuracy
index.
Service item
coverage
index.
2017
2018
2019
2020
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
308
2.2.4 Lack of Integrated Government
Supply Chain
In the traditional sense, the government business
process usually starts from the actual operation of the
department, and lacks of unified coordination and
overall planning between departments. This directly
results in the actual operation of each department and
the formation of a government supply chain with the
department itself as the center. In the final analysis,
the formation of this supply chain is due to the
specific business processes between departments.
The motive force for the development of e-
government in China came from all levels of
government departments at the earliest. While
carrying out e-government activities, all levels of
government departments often have a fragmented
situation and lack of macro-control and unified
planning, which results in the lack of large-scale
unified integration of all e-government supply chains.
In solving the above problems, many scholars
have found that in the actual operation process of e-
government, there are many characteristics similar to
supply chain, and they have the idea of obtaining
inspiration from supply chain theory and looking for
countermeasures.
3 E-GOVERNMENT BASED ON
SUPPLY CHAIN THEORY
3.1 The Introduction of Relevant
Concepts
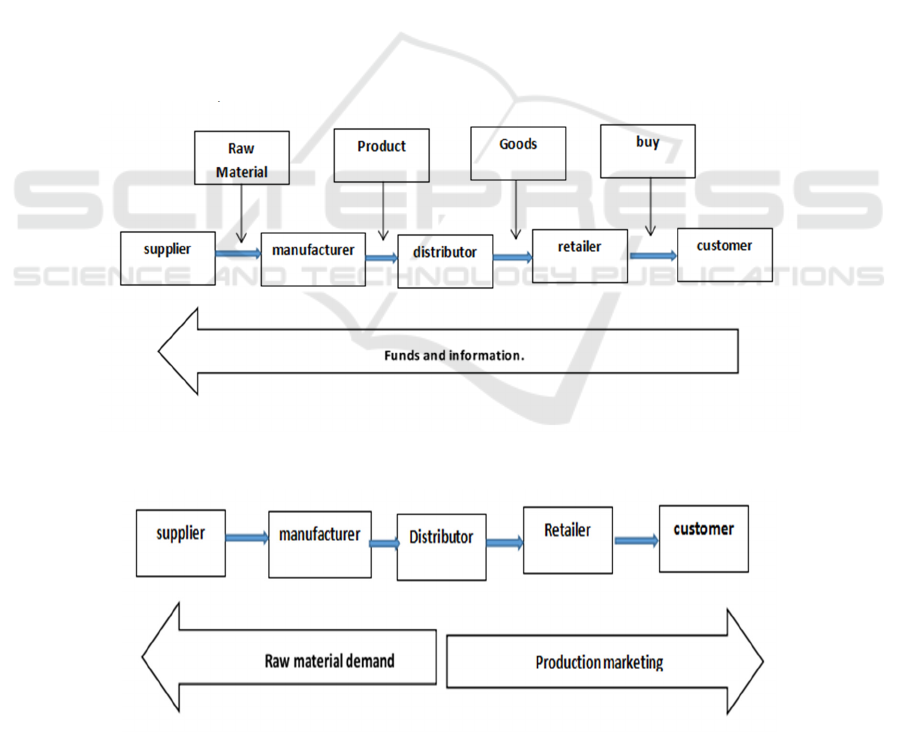
Supply Chain (SCM) refers to an enterprise that
considers the upstream suppliers and downstream
distributors of the core enterprise as a whole in order
to maximize the enterprise's revenue. It runs through
the whole process of raw material procurement,
product processing, distribution and distribution,
terminal sales and customer service, as shown in
Figure 3. It pursues the minimum circulation cost
among the processes and seeks the maximum
circulation benefit.
Figure 3: Circulation in supply chain.
Figure 4: Push Supply Chain Model.
Research on Evolution Process and Countermeasures of E-Government based on Supply Chain Theory
309
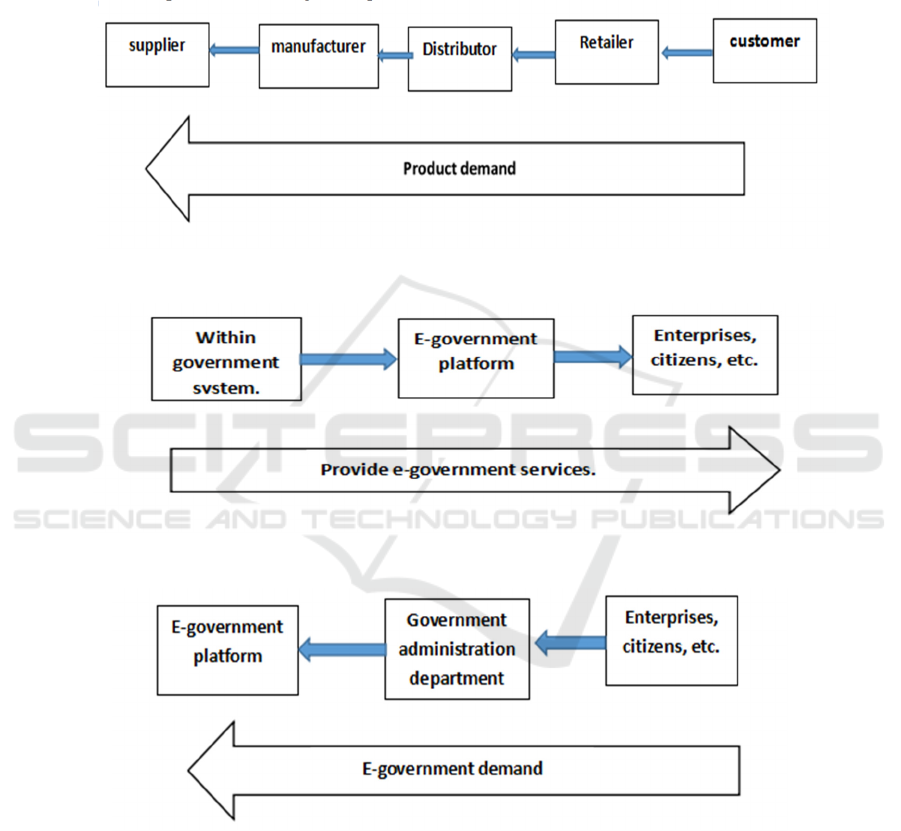
According to the different leading direction, the
supply chain can be divided into push supply chain
and pull supply chain. The push-type supply chain is
production-oriented and is suitable for the
"production-fixed-sales" production model. The pull-
type supply chain is customer-oriented and suitable
for the production model of "fixing production by
sales". In the actual production management process
of push-type supply chain, the enterprise will first
make the necessary forecast and planning for the
market to determine the quantity and type of products
produced by the enterprise, and then determine the
production planning on this basis, and then promote
the optimization of the entire supply chain. The push
supply chain model is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 5: Pull Supply Chain Model.
Figure 6: Push e-government SCM model.
Figure 7: Pull e-government SCM model.
The entire process of the pull-type supply chain is
driven by the customers, the customers generate
demands, information is transmitted to the
manufacturers through intermediate channels, the
manufacturers transmit to the material suppliers, and
the material suppliers determine the material supply
plan. The pull-type supply chain can make production
planning based on customers' demands, and can better
respond to changes in customers' demands. However,
this model greatly increases the response cost in the
back office and reduces the profit of the enterprise to
a certain extent. The production model of the pull
supply chain is shown in Figure 5.
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
310
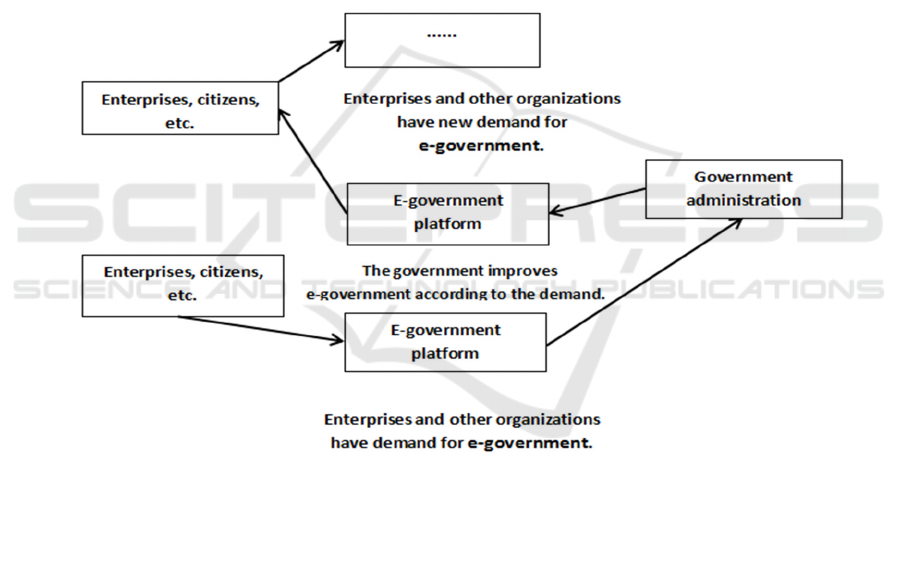
3.2 The Enlightenment of Supply
Chain Theory to E-government
Based on the explanation of enterprise supply chain
theory above, we divide the e-government SCM
model into push e-government SCM model (Fig. 6)
and pull e-government SCM model (Fig. 7).
The push-type e-government SCM model and the
pull-type e-government SCM model have their own
advantages and disadvantages. However, careful
study shows that with the continuous development of
society and economy, both the push-type e-
government SCM model and the pull-type e-
government SCM model will increasingly expose
problems. In the push-type e-government SCM
model, the government's long-term planning is not
compatible with the changing needs of enterprises
and citizens. In the pull-type e-government SCM
model, the government can better take into account
the changing needs of citizens and enterprises, but it
will affect the government's long-term development
planning. It is necessary to establish a comprehensive
e-government SCM model, which can not only ensure
the government to establish a long-term development
plan, but also allow the government to take into
account the changing material and cultural needs of
enterprises and citizens.
Comprehensive e-government SCM model: refers
to the alternative use of pull-type e-government SCM
model and push-type e-government SCM model in
the process of e-government construction. In different
stages, push-type and pull-type respectively play a
leading role, and the government can make choices
according to specific conditions, as shown in Figure
8.
Figure 8: Integrated e-government SCM model.
4 COUNTERMEASURES AND
SUGGESTIONS BASED ON
SUPPLY CHAIN THEORY
4.1 The Government Portal Website
Group Technology Implementation
Enterprise supply chain is often built around a large
enterprise. E-government supply chain has
increasingly manifested this development trend, in
which the concept of government portal website
group is a concrete expression of this theory in e-
government. Therefore, how to effectively provide
public services through government websites and
how to improve the public's awareness and
satisfaction of the construction of government
websites have increasingly become hot issues in the
new stage of e-government construction. The
establishment of the government portal website group
system is supported by the content management
system. Through the distributed information
maintenance mode and audit mechanism, the
hierarchical management of information and resource
sharing are achieved. Technically, the implementation
Research on Evolution Process and Countermeasures of E-Government based on Supply Chain Theory
311

of content management of government portal
websites is divided into the following six parts:
The first is the data layer, which schedules and
stores structured data and unstructured data, including
XML and DBMS. Unstructured data includes: text
files, audio and video files, graphics and image files
and files in other formats such as PDF. Web Service
modular components are supported on the data
interface. At the same time, the data service also
provides its upper layer with an application
programming interface API for a large number of data
operations. The second is the support layer, which
provides strong support to the system application
layer through the application server, including:
information capture, data conversion, search engine,
unified users, workload and access statistics, WAP
management, process definition, data submission and
sharing. And through API, PORTLET,
WEBSERVICE, JMS, MQ, DI, URL, DBMS and
other interface services, external resources are
supported to integrate the basic data of content
management and the application data of content
management to external data resources (Shen 2008).
The third is the application layer, which is a very
important part of the government portal website
group and an important part of information
processing. According to different functions, it can be
divided into: information release management,
website group management, system management,
plug-in component management, single sign-on,
personalized customization, content aggregation
RSS. The fourth is the performance level. The final
performance of the government portal website group
is a group of website group systems with the same
standards and the same standard system. It covers the
government master station, all levels of government
sub-websites and all kinds of special sub-websites. At
the same time, the system provides information
resources support for different applications of the
application layer. For example: web, wap, portlet, rss,
E-mail, SMS. Fifth, the access layer. Customers
access the performance layer through devices (such
as mobile phones, PDA's, browsers.) to obtain
information resources. Finally, external public
interfaces provide a large number of application
interfaces for the management layer, application layer
and presentation layer of information resources,
including API, PORTLET, WEBSERVICE, JMS,
MQ, URL, DBMS (
Carter, 2015).
4.2 Clear Management Objectives and
Principles
The goal of e-government supply chain management
is to take the government website as a platform, to
achieve perfect government services and resource
integration, to provide perfect services for the public,
to continuously enhance the innovative services of the
government website while meeting the increasing
trend of public personalized demand, and to make
timely and effective anti-fast response to the trend of
users' personalized demand. In order to reduce the
operation cost of the whole e-government supply
chain, the construction cycle of the supply chain for
e-government is shortened while the service is
realized (
Liu 2014).
4.3 The Establishment of Standardized
E-Government
"E-government Standard System" and "E-
government Standardization Guide" mark the official
start of China's e-government standardization. The e-
government standard system consists of general
standards, application standards, application support
standards, information security standards, network
infrastructure standards, management standards, etc.
Under the basic framework of the "E-government
Standardization Guide", the E-government
Standardization Group commissioned different
agencies to carry out and complete the work of
formulating six e-government standards. The six
specific tasks include: format specification of
electronic official documents based on XML. XML
Application Guide in E-government. General
specification for design method of e-government
business process. Code for information engineering
supervision. E-government data element. E-
government thesaurus. From the overall framework,
the standard system has covered all aspects of the
whole e-government construction. This has pointed
out a basic way for the development of e-government
standards, or basically completed the "meta-standard"
for each item in the e-government application
standards (
Snyder 2011).
4.4 Establish an "E-Government
Supply Chain" based on Internet
Technology
While pay attention to that technical standards,
special attention is now bee paid to the quantitative
research and management of government affairs, and
on this basis, the construction of most government
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
312

management projects and link is standardized, the
local and national standards of government process
links are formulated, and the non-arbitrariness of
government management and the transparency of
government processes are realized. In the practical
work involving the management of e-government
supply chain, manual and traditional information
exchange methods have failed to meet the
requirements of efficient management. Developing
various related systems and software based on
Internet technology is the only way to build an e-
supply chain (
Nations 2008).
5 CONCLUSION
After more than 30 years' construction and
development, the overall situation of China's e-
government can be summarized as a late start and
rapid progress, which has achieved remarkable results
in many fields and faced bottlenecks in various
aspects. Now, it has entered a rising period of rapid
take-off and a critical period of deep application. E-
government is an "imported product", from hardware
to software, without exception, it comes from abroad,
but it can quickly integrate with China's reality and
make continuous breakthroughs and innovations in
theory and practice. In 1980s, Chinese traditional
government departments introduced computers to
assist in simple government affairs, such as text
editing, file storage, data statistics. which started the
process of reforming the way of realizing government
affairs. In the true sense, it marked the germination of
Chinese e-government. Due to the restriction of
technical equipment, administrative environment and
other factors, it mainly served the government rather
than the public, resulting in weak public service
capacity of e-government in this period. In 1990s,
with the popularization and application of
information technology and Internet in China,
government departments actively provided favorable
conditions in terms of capital, science and technology,
policies and ideas, focused on guiding and promoting
the leap-forward development of e-government,
initially explored the great potential of e-government,
and showed its convenience and efficiency in
government affairs processing, making e-government
an indispensable tool for government departments. At
the beginning of the 21st century, the emerging
information technologies such as "internet plus",
cloud computing, big data, all-media and intelligent
mobile, on the one hand, create a broader
development space for e-government, on the other
hand, make great changes in the administrative
ecology of the government, and the existing
governance theories encounter difficulties in practice.
The e-government based on the operating mechanism
of government organizations and information
technology is also placed at the crossroads of where
to go.
By analyzing the evolution of e-government, this
paper finds that the service capacity of e-government
government website needs to be strengthened, and by
studying the supply chain model, it gets
enlightenment and finds out the corresponding
solutions (
Layne 2002).
However, there are some shortcomings in this
research. The development plan that relies on the
digital age and combines with the supply chain tends
to the theoretical level and needs to be further refined
and deepened in practice. In addition, as a new theory,
like other theories, it will be criticized in the process
of development, in order to improve and surpass the
follow-up research (
Ding 2004).
REFERENCES
Bertot, J. C., Jaeger, R. T., & Grimes, R. M. (2010). Using
icts to create a culture of transparency: e-government
and social media as openness and anti-corruption tools
for societies. Government Information Quarterly, 27(3),
264-271.
Carter, C. R., Rogers, D. S., & Choi, T. Y. (2015). Toward
the theory of the supply chain. Journal of Supply Chain
Management, 51.
Ding, H. (2004). On the application of supply chain theory
in enterprises distributing farm produce. China
Business and Market.
Layne, K., &Lee, J. (2002). Developing fully functional e-
government: a four stage model. Government
Information Quarterly, 18(2), 122-136.
Liu, G., Liu, X., Yang, Z., Chen, B., Su, M., &Zhang, Y.
(2014). A predictive analysis of china's energy security
based on supply chain theory. Energy Procedia, 61, 184-
189.
Nations, U. (2008). United nations e-government survey
2008 from e-government to connected governance.
Snyder, L. V., &Shen, Z. (2011). Fundamentals of Supply
Chain Theory. Wiley.
United Nations. Dept. of Economic and Social Affairs.
Division of Public Administration and Development
Management. (2008). United Nations e-government
survey.: from e-government to connected governance.
United Nations.
Research on Evolution Process and Countermeasures of E-Government based on Supply Chain Theory
313
