
Research on Emotional Labor and Influencing Factors based on
Visual Analysis
Jun Liu
a
, Lijuan Gao
b
and Xianxin Tan
c
School of Business Administration, Guangdong University of Finance & Economics, Guangzhou, China
Keywords: Emotional Labor, Citespace, Visual Analysis, Conservation of Resources Theory, Emotional Contagion
Theory, Social Exchange Theory, Different Perspectives, Theoretical Review.
Abstract: Information visualization is one of the data mining methods that have emerged in recent years. It can use the
ability of humans to obtain models and structures in the form of visualization to solve the problem of excessive
literature and cannot be processed quickly. It can filter and process data, and find information hidden behind
the data. Therefore, this article uses the citespace software developed by Jie Li and Chaomei Chen, With the
theme of “emotional labor”, all the documents from 2000 to 2021 were downloaded from the web of science
database, and the keywords of this topic were visually analyzed to obtain a keyword co-occurrence map. The
result shows that the analysis of antecedent variables is the focus of the research on this topic. At the same
time, this article reviews the influencing factors and formation mechanism of emotional labor from the
perspectives of conservation of resources theory, emotional contagion theory, and social exchange theory, and
sorts out representative empirical research to provide new directions and ideas for future related researches.
1 INTRODUCTION
Emotional labor refers to that employees adjust their
emotional feelings and expressions in accordance
with the requirements of the organization at work
(Fang, Wei, Luo, Liu, Shi & Zhan, 2019). In 1983,
Hochschild first proposed the concept of emotional
labor, but it did not attract too much attention from
service managers at that time. It was not until 1993
that Ashforth systematically expounded the impact of
emotional labor on service organizations and
individual employees that researchers invested a lot
of research interest in emotional labor phenomena.
Since the development of emotional labor,
relevant research results have been quite rich. The
influencing factors of emotional labor are very
complex. Due to the differences in research
paradigms, different theories often focus on specific
influencing factors for research, and they rarely study
from the perspective of comprehensive theory.
Therefore, this article sorts out a large number of
representative empirical studies on emotional labor at
home and abroad, and analyzes the influencing
factors and generation mechanism of emotional labor
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0384-1599
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1770-3031
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6905-9172
from the multi-dimensional perspectives of resource
preservation theory, emotional infection theory,
1
and
social exchange theory, and then gives emotional
labor The influencing factor model and the future
research framework are expected to provide
suggestions for future research on emotional labor.
2 CO-OCCURRENCE ANALYSIS
OF KEYWORDS IN
EMOTIONAL LABOR
RESEARCH
In order to understand the hot topics of emotional
labor research, download all the documents from
2000 to 2021 in the web of science data. After data
cleaning, duplicate and invalid data were deleted, and
finally 3913 documents were obtained. Based on the
bibliometric method, the keywords of emotional
labor research are visualized and analyzed through
the citespace software, and the keyword map is
finally derived. In the keyword graph, the size of
nodes and fonts reflects the frequency of keywords.
314
Liu, J., Gao, L. and Tan, X.
Research on Emotional Labor and Influencing Factors based on Visual Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0011343800003437
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2021), pages 314-320
ISBN: 978-989-758-589-0
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
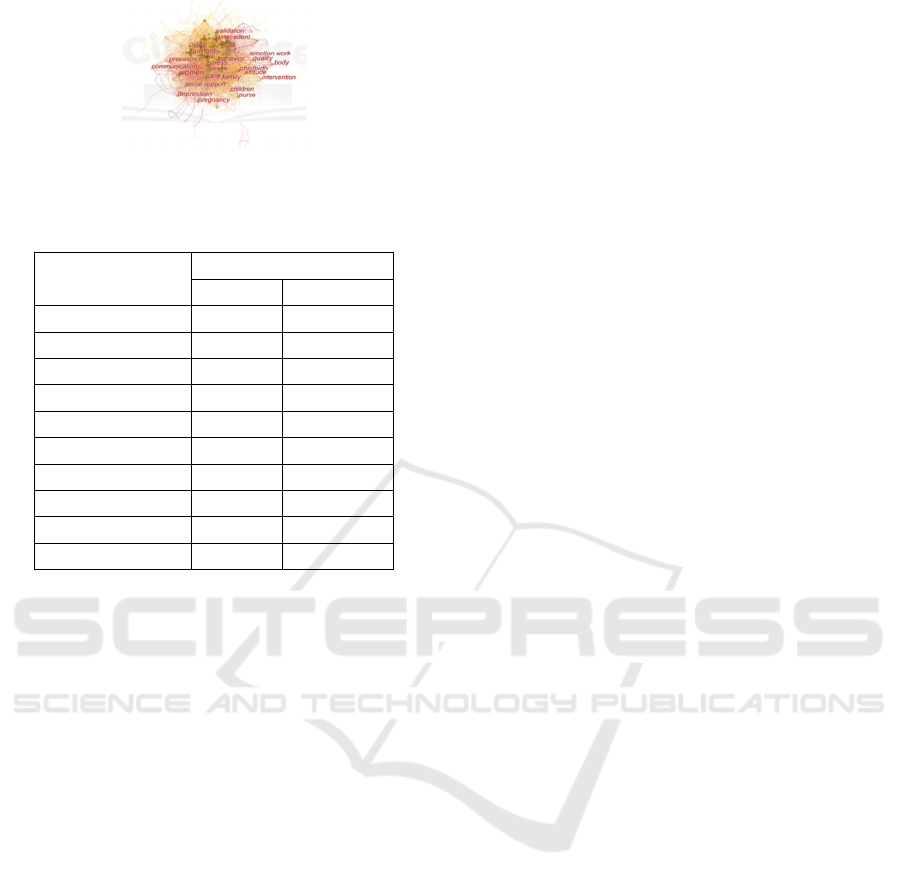
Figure 1: Keyword co-occurrence map.
Table 1: Keyword frequency statistics.
Key Words
Relevant information
Number Frequency
emotional labor 1 986
work 2 737
labor 3 694
burnout 4 514
consequence 5 444
emotional labour 6 383
gender 7 380
performance 8 363
antecedent 9 341
stress 10 337
The larger the node, the more the keywords have been
studied. The number of connections indicates the
closeness of the relationship with other keywords.
Combining Figure 1 and Table 1, it can be seen that
the node corresponding to the term "emotional labor"
is the largest, with 986 occurrences, and the densest
connection with other nodes, which is the core
research theme of the field; Secondly, the nodes and
labels of words such as work (737 times), labor (694
times), burnout (514 times), and consequence (444)
are also relatively large, indicating that the research
in the past 20 years has mainly focused on these
fields. Among the top 10 keywords in the frequency
ranking, keywords related to the pre-dependent
variable of emotional labor accounted for 41.55%,
keywords related to the outcome variable accounted
for 32.01%, and focused on the topic of "emotional
labor" itself accounted for 26.05%. The analysis of
dependent variables is the focus of this topic research.
3 EMOTIONAL LABOR FROM
THE PERSPECTIVE OF
CONSERVATION OF
RESOURCRS THEORY
In 1989, Hobfoll first systematically proposed the
conservation of resources theory (COR). The theory
believes that individuals have the tendency to
preserve, protect, and obtain resources. Therefore,
whether it is a potential threat of resource loss or
actual resource loss, it will cause individual tension
and pressure (Hobfoll, 1989. Hobfoll, Halbesleben,
Neveu & Westman, 2018). Therefore, employees
always try to maintain the existing resources and
reduce the loss caused by resource consumption in
order to achieve a balance between resource
acquisition and consumption. The efforts of
employees at work will result in resource loss, and
getting paid can supplement resources.
In 2003, Brotheridge and others introduced the
conservation of resources theory into the field of
emotional labor, and believed that the conservation of
resources theory could better explain why emotional
labor produces different results. The theory believes
that when interpersonal employees perform
emotional labor, they need to consume a certain
amount of resources, which results in resource loss.
If the employee's resource loss is not compensated for
in time, it will lead to resource imbalance, and the
employee will take to reduce the effort at work
measures to maintain the balance of their own
resources.
Many domestic and foreign scholars have
conducted a large number of empirical studies in the
field of emotional labor based on this theory. This
research is classified and sorted according to the
existing literature, and the results are shown in Table
1. The empirical studies of scholars such as Liu Zhe
and scholars such as Wang Zhen have proved that
work input positively affects deep acting and true
expression (Liu, Yang, Tang, Ma & Li, 2018. Wang &
Li, 2013). The empirical studies of Tsung-Yu Wu,
Changya Hu, Dawn Carlson and others have shown
that abusive management is positively correlated with
surface acting (Wu & Hu, 2013. Carlson, Ferguson,
Hunter & Whitten, 2012). The research of Tsung-Yu
Wu and Changya Hu further proves that plays a
negative correlation (Wu & Hu, 2013). It is worth
noting that variables such as job input, job
satisfaction, and organizational commitment are not
only the antecedent variables of emotional labor, but
also the result variables of emotional labor.
It can also be seen from the table 1 that the
outcome variables of emotional labor are mostly
negative variables, which further confirms the
connotation of resource conservation theory, that is,
emotional labor consumes employees' resources. If
the consumed resources are not replenished,
employees will reduce their efforts at work, which
will have a negative impact on customers and the
organization, and employees themselves will also be
Research on Emotional Labor and Influencing Factors based on Visual Analysis
315

caused by resource imbalances. Reactions to
emotional exhaustion and stress.
The application of resource preservation theory in
the field of emotional labor can also give some
suggestions to managers in organizations. First,
managers can organize, encourage and support the
skills training required for employees to participate in
work, and reserve available resources in advance;
The second is to create a comfortable working
environment and reduce the occurrence of damage to
employee resources; The third is that when
employees' resources are lost, they should provide
effective resource support in a timely manner to avoid
further damage to their resources.
4 EMOTIONAL LABOR FROM
THE PERSPECTIVE OF
EMOTIONAL CONTAGION
THEORY
In 1994, Hatfield systematically expounded the
emotional contagion theory in his book "Emotional
Contagion". The theory believes that emotional
infection is a tendency to automatically imitate and
synchronize with others' expressions, voices,
postures, and actions. As a result, the emotions of the
two interacting parties are often aggregated and
unified (Hatfield, Cacioppo & Rapson, 1992. Barger
& Grandey, 2006). Emotional infection theory
provides a good explanation for understanding the
emotional interaction process of people in
organizational contexts. Emotional infection plays an
important role in organizational behavior, leadership,
marketing and other fields. Pugh first used the theory
of emotional infection to explain the phenomenon of
service interaction. Based on the theory of emotional
labor, he proposed that when employees interact with
customers, customers will subconsciously imitate the
emotional expression of employees, and then the
customer's own emotions will change (Pugh, 2001).
By combing the existing empirical research using
the emotional contagion theory, it can be seen that a
large number of existing researches basically discuss
the employee-customer relationship individually.
However, in fact, the emotions of customers will also
affect the emotions of employees, and similarly, the
emotions of employees and leaders will also infect
each other. However, in fact, the emotions of
customers will also affect the emotions of employees,
and similarly, the emotions of employees and leaders
will also infect each other.
It can be seen that there are still research gaps in
the existing empirical research in the field of
emotional labor based on the theory of emotional
contagion, future research can continue to explore
whether the emotions of customers will affect the
emotions of employees and the path of influence.
Similarly, the emotional contagion between leaders
and employees can also be studied.
The enlightenment that this brings to managers is:
For the selection of positions that need to deal with
customers frequently, managers should select
employees with positive emotional expression and
high emotional intelligence, so as to bring positive
emotional experience to customers and improve
customer satisfaction degree.
5 EMOTIONAL LABOR FROM
THE PERSPECTIVE OF
SOCIAL EXCHANGE THEORY
Social exchange theory was jointly proposed by
George Casper Homans, Peter Blau and Richard
Emerson. The theory believes that all parties will
have valuable things that others want, and the
exchanged objects and their quantity are jointly
decided by both parties. In the research of social
exchange theory in the field of organization, there are
mainly two kinds of exchange relationships, namely,
the exchange relationship between employees and the
organization and the exchange relationship between
superiors and subordinates.
According to the review of existing empirical
research (it can be seen from the table 2), social
exchange theory is mainly applied to the exchange
relationship between employees and the organization
in the field of emotional labor, and there are few
researches on the relationship exchange between
superiors and subordinates in the organization. When
an organization provides employees with more
economic and social emotional resources, employees
will feel that they have more obligations to repay the
organization, and thus devote more energy to work,
in return for the organization's feedback to
employees.
Based on this, the managers in the organization
should cultivate a view of the mutually beneficial
relationship between employees and the organization,
so that employees believe that when they devote
themselves to the construction of the organization,
the organization will also give them back.
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
316

6 EMOTIONAL LABOR FROM
OTHER THEORETICAL
This part combs the empirical research of emotional
labor and its influencing factors from other
theoretical perspectives, such as Self-depletion
Theory, Relationship Marketing Theory, Optimal
Differentiation Theory, Job Demands-resources
Model, Emotions as Social Information Theory. The
specific results are shown in Table 3.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND
RECOMMENDATIONS
In summary, different theoretical perspectives have
enriched the research content in the field of emotional
labor, and brought many lessons for companies in the
service industry. Conservation of resources theory
tells leaders to pay attention to protecting employees'
resources, and to compensate employees in time
when their resources are damaged. The emotional
infection theory tells leaders to select employees who
express positive emotions and high emotional
intelligence when recruiting, and managers
themselves must strengthen the expression of positive
emotions. Social exchange theory emphasizes the
establishment of long-term and rewarding exchange
relationships between organizations and employees,
as well as between superiors and subordinates. Other
theoretical perspectives have also brought us many
useful suggestions.
The research on emotional labor has the following
suggestions, we must realize that the breadth and
depth of empirical research in the field of emotional
labor needs to be improved. The first is that empirical
research uses less research on theories, and most
empirical research involves multiple theories
throughout and cannot integrate a certain theory with
empirical research. Secondly, empirical research is
mostly concentrated in the service and nursing
industries. Others, such as the judge industry that
needs to maintain objectivity and fairness at work,
and the police industry that maintains serious or even
negative sentiments, have less empirical research in
such industries. Future research can go to these
industries to development correlative research. Third,
most of the current empirical researches study the
impact of employees' emotional labor on employees,
organizations, and customers. Few studies involve
the emotional labor of leaders in organizations that
affect employees. Every researcher still has a long
way to go, and more in-depth work needs to be
continued.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to thank the teachers of the PMBDA
meeting group for their valuable comments and
suggestions on my thesis.
Table 2: List of relevant variables of empirical research on conservation of resources theory.
Distal anterior dependent
variables of emotional
labor
Individual variables Autonomous motivation,
j
ob satisfaction
Organizational variables
Service-oriented leadership, transformational
leadershi
p
Situational variables Dis
p
la
y
rules, customer irrational behavio
r
The proximal antecedent
variables of emotional
labor
Individual variables
Emotional intelligence, work insecurity, work
engagement, role characteristics, negative emotions,
psychological capital, job satisfaction, workplace
mental
p
owe
r
Or
g
anizational variables Abusive mana
g
ement, or
g
anizational commitment
Situational variables Emotional dis
p
la
y
rules, customer im
p
olite behavio
r
The output of emotional
labor
Impacts on individuals
Emotional exhaustion, decreased sense of
accomplishment, job satisfaction, absenteeism, work-
family conflict, work engagement, salary rate,
emotional disorders, psychological disengagement,
job performance, stress, employee creativity,
employee perception of internal identity, active
sabotage behavior, organization Citizenship,
turnover intention
Im
p
acts on customers Customer service
q
ualit
y
, customer satisfaction
Impacts on the organization Employee turnover rate, organizational commitment
Research on Emotional Labor and Influencing Factors based on Visual Analysis
317
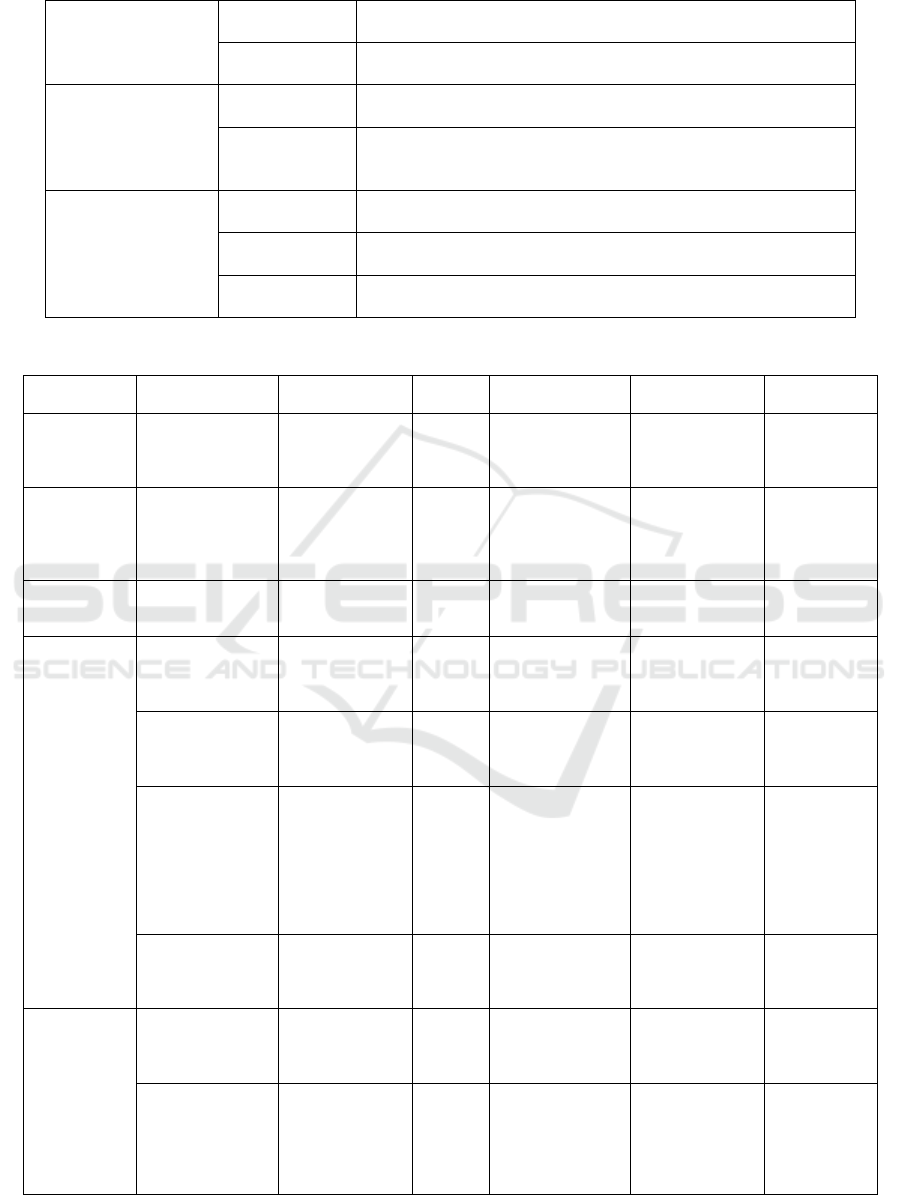
Table 3: List of relevant variables of empirical research on social exchange theory.
Distal anterior
dependent variables
of emotional labor
Individual
variables
Autonomous motivation, job satisfaction
Organizational
variables
Service-oriented leadership, perceived organizational support,
or
g
anizational identit
y
The proximal
antecedent variables
of emotional labor
Individual
variables
Work engagement, psychological empowerment, job satisfaction
Organizational
variables
Leadership style (laissez-faire, transactional, transformational),
organizational identity, perceived organizational support,
or
g
anizational commitment
The output of
emotional labor
Impacts on
individuals
Organizational citizenship behavior, emotional exhaustion,
turnover tendency
Impacts on
customers
Customer orientation, customer satisfaction
Impacts on the
or
g
anization
Organizational commitment, employee innovation behavior,
or
g
anizational reco
g
nition
Table 4: Representative empirical studies from different theoretical perspectives.
Theory Author, year Object of study
Sample
size
Independent
variable
Mediating
variable
Dependent
variable
Self-depletion
theory
Liping Yin &
Xiangqian
Zhang,2019
Service
personnel
990
Surface acting,
deep acting
Self-depletion,
moral license
Pro-
organizational
unethical
b
ehavio
r
Relationship
Marketing
Theory
Yong Yang,
Qinhai Ma,
Guowei Tan, &
Chunjiang Yang,
2015
Customers of
enterprises
321
Deep acting, true
expression
Customer
identification,
emotional value
Customer
loyalty
Optimal
differentiation
theory
Fei Zhou, Qinlan
Chen & Meixian
He, 2018
Colleagemate 150
Inclusive
leadership
Deep acting
Employee
innovation
b
ehavio
r
Job demands-
resources
model
Xiaoyan Li &
ErHua Zhou, 2012
Call center
customer
representative of
mobile company
800
Psychological
capital
Surface acting,
active/passive
deep acting
Job burnout
Michal Biron &
Marc van
Veldhoven, 2012
Family and
friends of
research
assistants
254 Mental flexibility Surface acting
Emotional
exhaustion
Brenda, L S &
Elizabeth, A C,
2009
Nurse aides and
childcare
workers
363
Surface acting,
emotional
enhancement
/
Job
satisfaction,
emotional
commitment,
emotional
exhaustion,
turnover
intention
Seery, B L,
Corrigall, E A &
Harpel T, 2008
Nurse aides,
childcare
workers
347
Surface acting,
emotional
enhancement
/
Work-family
conflict,
work-family
promotion
Emotions as
social
information
theory
Chen Yang &
Jianbiao Li, 2017
College
undergraduate
144
Emotional
harmony,
emotional
disorders
Emotional
response,
performance
inference
Work
performance
Tae Won Moon,
Won-Moo Hur &
Yong Jun Choi,
2018
Hospital staff 268
Perceived leader’s
true behavior
Subordinates'
perception of
true leadership,
subordinates'
recognition and
trust in the leade
r
Work
performance
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
318
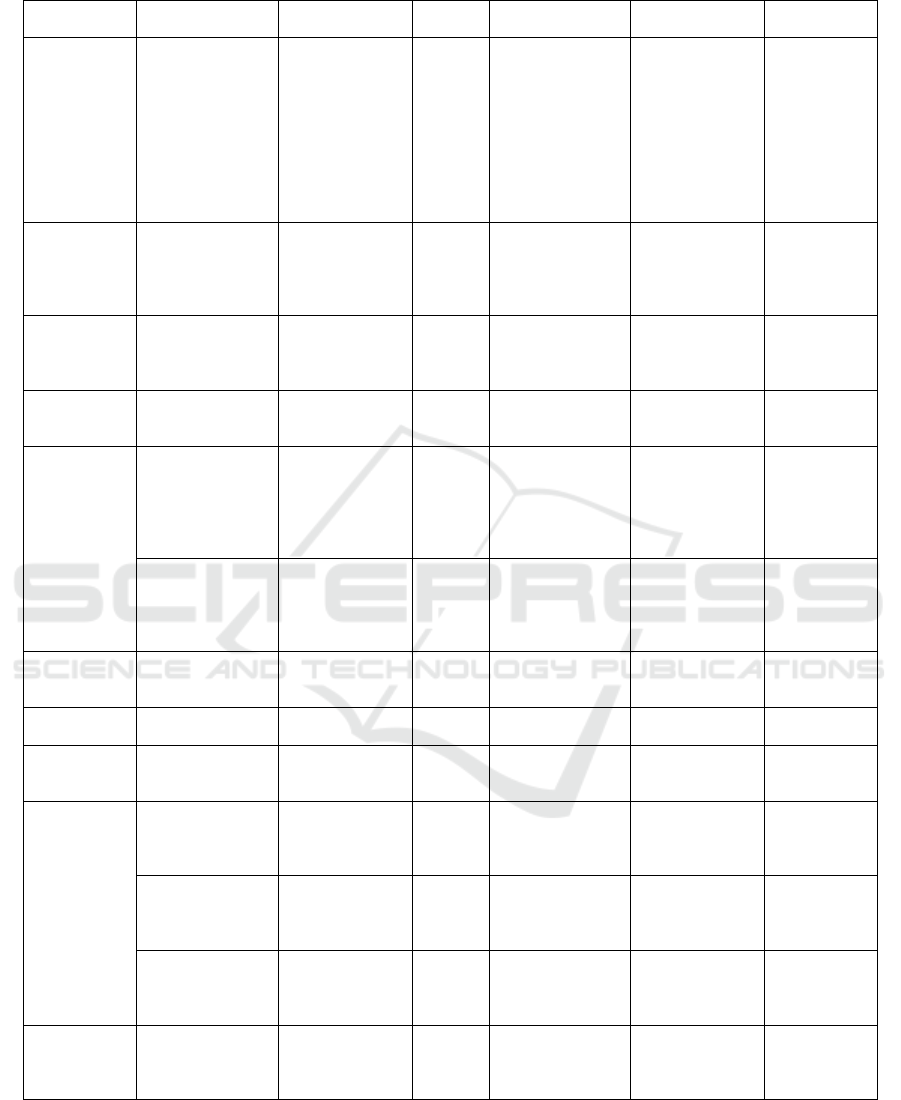
Table 4: Representative empirical studies from different theoretical perspectives (cont.).
Theory Author, year Object of study
Sample
size
Independent
variable
Mediating
variable
Dependent
variable
Customer
identity
theory
Yong Yang,
Qinhai Ma, Chen
Pan Chen & Man
Li, 2017
Employees and
customers of
companies in the
beauty,
insurance,
catering and
other industries
352
Deep acting, true
expression
Emotional value
Customer
value co-
creation
behavior
(customer
participation
behavior,
customer
citizenship
b
ehavior)
Self-control
theory
Brent, A S, et al.
2012
The employees
of bus company
522 Surface acting /
Job
satisfaction,
turnover rate,
self-
monitoring
Social
support
theory
Duke, A B, et al.
2009
Retail company 338 Emotional labor /
Job
satisfaction,
job
performance
Social
identity
theory
Qin Zhang &
Weihong Zhu,
2008
College English
Teacher
164
Surface acting,
deep acting, true
expression
/
Job
satisfaction,
job burnou
t
Affective
event theory
Deborah, E R &
Sharmin Spencer,
2006
College Students 123
Customer
experience
(fair/unfair),
customer
interaction is
fair/unfai
r
Emotions: anger,
happiness
Emotional
labor
Wing Lam &
Ziguang Chen,
2012
Hotel staff and
supervisors
424
Supervisor
support,
organizational
fairness, negative
emotions
Surface acting,
deep acting
Job
satisfaction,
service
quality,
turnover rate
Cognitive
dissonance
theory
Ziguang Chen, et
al. 2012
Hotel staff 317
Surface acting,
deep acting
Job satisfaction,
job burnout
work
performance
Person-work
fit theory
JungHoon (Jay)
Lee, et al. 2016
Hotel staff 309
Customer
orientation
Surface acting,
deep acting
Job
satisfaction
Contingency
leadership
theory
Jun Liu, et al.
2013
8 organizations
in China
450
Transactional
leadership
Team
effectiveness
Team
innovation
Social
emotional
choice theory
Francis Yue-lok
Cheung &
Catherine So-kum
Tang, 2010
Hong Kong
Organization
386 Age
Surface acting,
deep acting, true
expression
Job
satisfaction,
psychological
distress
Michael Sliter, et
al. 2013
The employees
of service
industry
519
Age, emotional
intelligence,
positive emotional
expression
Surface acting,
deep acting
Employee
happiness
Jason, J D & Luis,
A P, 2010
The employees
of service
industry
186 Age
Positive
emotions
Surface
acting, deep
acting, true
expression
Regulatory
matching
theory
Nai-Wen Chi, et
al. 2016
Bank teller 397
Surface acting,
deep acting
/
Emotional
delivery,
service
destruction
Note: The table only lists representative empirical studies.
Data source: sorted according to existing literature
Research on Emotional Labor and Influencing Factors based on Visual Analysis
319

REFERENCES
Barger, P B & Grandey, A A. Service with a smile and
encounter satisfaction: emotional contagion and
appraisal mechanisms[J]. Academy of Management
Journal, 2006, 49(6): 1229-1238.
Carlson, D., Ferguson, M., Hunter, E., & Whitten, D.
Abusive supervision and work–family conflict: The
path through emotional labor and burnout[J].
Leadership Quarterly, 2012, 23(5): 849-859.
Hatfield, E, Cacioppo, J T, Rapson, R L. Primitive
emotional contagion[J]. Personality and Social
Psychology Review, 1992, 14(3):151-177.
Hobfoll, S E. Conservation of resources: A new attempt at
conceptualizing stress[J]. Am Psychol, 1989, 44(3):
513-524.
Hobfoll, S. E., Halbesleben, J., Neveu, J. P., & Westman,
M. Conservation of resources in the organizational
context: The reality of resources and their
consequences[J]. Annual Review of Organizational
Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 2018, 5: 103-
128.
Pugh, S D. Service with a Smile: Emotional Contagion in
the Service Encounter[J]. Academy of Management
Journal, 2001, 44(5): 1018-1027.
Wu, T Y, Hu, C. Abusive supervision and subordinate
emotional labor: The moderating role of openness
personality[J]. Journal of Applied Social Psychology,
2013, 43(5): 956-970.
Yanran Fang, Wei Wei, Ping Luo, Xiaodong Liu, Junqi Shi
& Yujie Zhan. The influence of employees' negative
emotions on emotional labor strategies[J]. Acta
Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(03): 353-365.
Zhe Liu, Yong Yang, Jiafu Tang, Qinhai Ma, Zhe Li. The
multi-level mechanism of autonomous motivation and
service-oriented leadership on emotional labor: an
intermediary moderating model[J]. Journal of
Industrial Engineering and Engineering Man, 2018, 32
(03): 52-62.
Zhen Wang, Xupei Li. Transformational leadership and
emotional labor strategies: the mediating role of work
engagement[J]. Management Scientists (Academic
Edition), 2013(09): 21-30.
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
320
